Loxolophodon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Eobasileus cornutus'' ("horned dawn-king") was a prehistoric

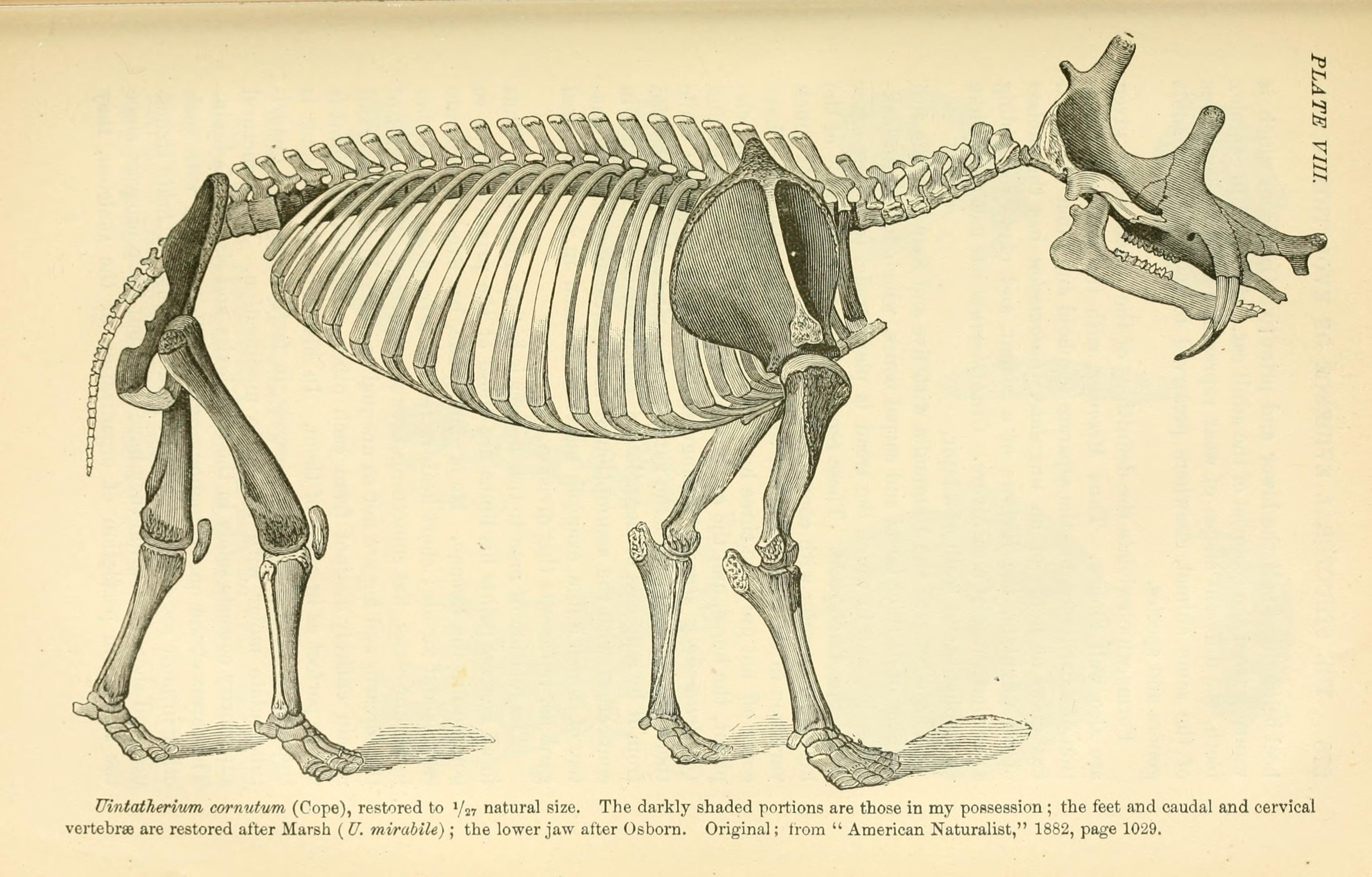
 About long, and standing some tall at the shoulder, with a weight estimated to be around , ''Eobasilius'' was the largest
About long, and standing some tall at the shoulder, with a weight estimated to be around , ''Eobasilius'' was the largest
Dinoceratans Eocene mammals of North America Fossil taxa described in 1872 Eocene United States Prehistoric placental genera {{paleo-mammal-stub
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of dinocerate mammal.
Description


 About long, and standing some tall at the shoulder, with a weight estimated to be around , ''Eobasilius'' was the largest
About long, and standing some tall at the shoulder, with a weight estimated to be around , ''Eobasilius'' was the largest uintathere
Uintatheriidae is a family of extinct ungulate mammals that includes ''Uintatherium''. Uintatheres belong to the order Dinocerata, one of several extinct orders of primitive hoofed mammals that are sometimes united in the Condylarthra.
Uintathe ...
. It looked much like the related ''Uintatherium
''Uintatherium'' ("Beast of the Uinta Mountains") is an extinct genus of herbivorous mammal that lived during the Eocene epoch. Two species are currently recognized: ''U. anceps'' from the United States during the Early to Middle Eocene (56–38 ...
''. Like ''Uintatherium'', it had three pairs of blunt horns Horns or The Horns may refer to:
* Plural of Horn (instrument), a group of musical instruments all with a horn-shaped bells
* The Horns (Colorado), a summit on Cheyenne Mountain
* ''Horns'' (novel), a dark fantasy novel written in 2010 by Joe Hill ...
on its skull, possibly covered with skin like the ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of horns and antlers by their unique ...
s of a giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
. The frontal pair may have been composed of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
, like the horn(s) of a rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species o ...
. ''Eobasileus'' also had a pair of tusks
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. Tusks share co ...
shielded by bony protrusions of the lower jaw.
A dispute over ''Eobasilius'' specifically and the uintatheres more generally helped to spark the Bone Wars
The Bone Wars, also known as the Great Dinosaur Rush, was a period of intense and ruthlessly competitive fossil hunting and discovery during the Gilded Age of American history, marked by a heated rivalry between Edward Drinker Cope (of the Acade ...
between Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested ...
and Othniel Charles Marsh
Othniel Charles Marsh (October 29, 1831 – March 18, 1899) was an American professor of Paleontology in Yale College and President of the National Academy of Sciences. He was one of the preeminent scientists in the field of paleontology. Among h ...
. Cope, Marsh, and Joseph Leidy independently discovered specimens from related species—though Cope and Marsh believed they had each discovered the same species—in the Fort Bridger area, leading to disputes over naming rights for the animals and a series of increasingly hostile letters to various scientific journals. In 1873, for example, Marsh wrote "Cope has endeavored to secure priority by sharp practice, and failed…Prof. Cope's errors will continue to invite correction, but these, like his blunders, are hydra-headed, and life is really too short to spend valuable time in such an ungracious task, especially as in the present case Prof. Cope has not even returned thanks for the correction of nearly half a hundred errors…" The '' American Naturalist'' declined to print this letter as a scientific article, but did publish it as an appendix; Marsh paid for its inclusion in the journal.
References
Dinoceratans Eocene mammals of North America Fossil taxa described in 1872 Eocene United States Prehistoric placental genera {{paleo-mammal-stub