Low Rhenish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

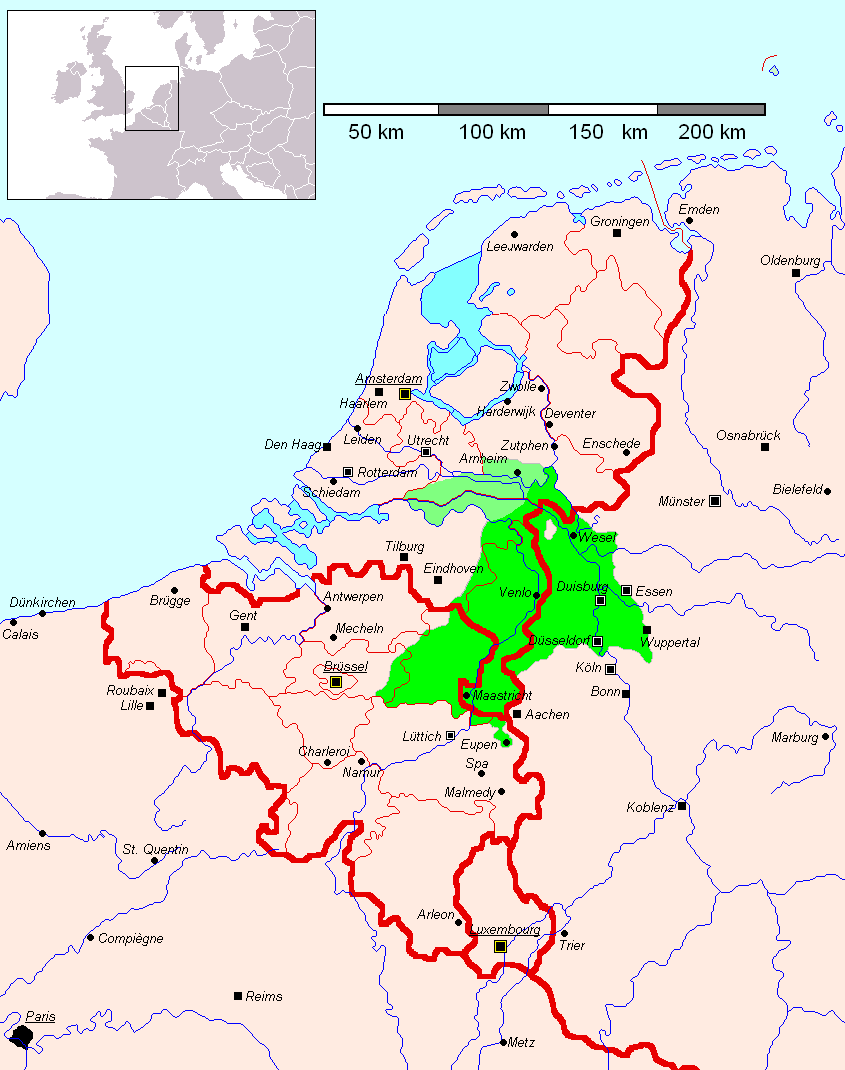
 Meuse-Rhenish (German: ''Rheinmaasländisch'', Dutch: ''Maas-Rijnlands'', and French: ''francique rhéno-mosan'') is the modern term for literature written in the Middle Ages in the greater Meuse-Rhine area, in a literary language that is effectively
Meuse-Rhenish (German: ''Rheinmaasländisch'', Dutch: ''Maas-Rijnlands'', and French: ''francique rhéno-mosan'') is the modern term for literature written in the Middle Ages in the greater Meuse-Rhine area, in a literary language that is effectively
 Today, Low Franconian dialects are spoken mainly in regions to the west of the rivers
Today, Low Franconian dialects are spoken mainly in regions to the west of the rivers
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarch ...
. This area stretches in the northern triangle roughly between the rivers Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
(in Belgium and the Netherlands) and Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
(in Germany).
However it also applies to the Low Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
dialects that have been spoken in that area continuously from medieval times up to now in modern times in a non-literary context. It includes varieties of South Guelderish
South Guelderish ( nl, Zuid-Gelders , german: Südgeldersch, ''Kleverländisch'') refers to the easternmost group of Dutch dialects spoken along the lower Rhine (Dutch Nederrijn and German Niederrhein). In its narrower sense, the term refers str ...
( Zuid-Gelders) and Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
in the Belgian and Dutch provinces of Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
, and their German counterparts Low Rhenish (German: ''Niederrheinisch'') including '' Bergish'' in German Northern Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
. Although some dialects of this group are spoken within the language area where German is the standard, they actually are Low Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
in character, and are more closely related to Dutch than to High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
, and could therefore also be called Dutch (see also Dutch dialects
Dutch dialects are primarily the dialects that are both cognate with the Dutch language and are spoken in the same language area as the Dutch standard language. Dutch dialects are remarkably diverse and are found in the Netherlands and Flanders, ...
). With regard to this German part only, Meuse-Rhenish equals the total of Low Rhenish vernaculars.
Low Rhenish and Limburgish
Low Rhenish (german: Niederrheinisch, nl, Nederrijns) is the collective name in German for the regionalLow Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
language varieties spoken alongside the so-called Lower Rhine
The Lower Rhine (german: Niederrhein; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the river Rhine) flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands (including the Nederrijn or "Nether Rhine" within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta); al ...
in the west of Germany.
Low Franconian is a language or dialect group that has developed in the lower parts of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
, northwest of the Benrath line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs f ...
. From this group both the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and later the Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gra ...
standard languages have arisen. The differences between Low Rhenish and Low Saxon are smaller than between Low Rhenish and High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
. Yet, Low Rhenish does not belong to Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle L ...
, but to Low Franconian. Therefore, it could properly be called ''German Dutch''. Indeed, ''Deutschniederländisch'' was the official term under the Prussian Reign of the 19th century.
 Today, Low Franconian dialects are spoken mainly in regions to the west of the rivers
Today, Low Franconian dialects are spoken mainly in regions to the west of the rivers Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
and IJssel
The IJssel (; nds-nl, Iessel(t) ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, in the Dutch speaking part of Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, but also in Germany in the Lower Rhine
The Lower Rhine (german: Niederrhein; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the river Rhine) flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands (including the Nederrijn or "Nether Rhine" within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta); al ...
area. Only the latter have traditionally been called ''Low Rhenish'', but they can be regarded as the German extension or counterpart of the Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
s in the Netherlands and Belgium, and of Zuid-Gelders (''South Guelderish'') in the Netherlands.
Low Rhenish differs strongly from High German. The more to the north it approaches the Netherlands, the more it sounds like Dutch. As it crosses the Dutch-German as well as the Dutch-Belgian borders, it becomes a part of the language landscape in three neighbouring countries. In two of them Dutch is the standard language. In Germany, important towns on the Lower Rhine and in the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
-Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
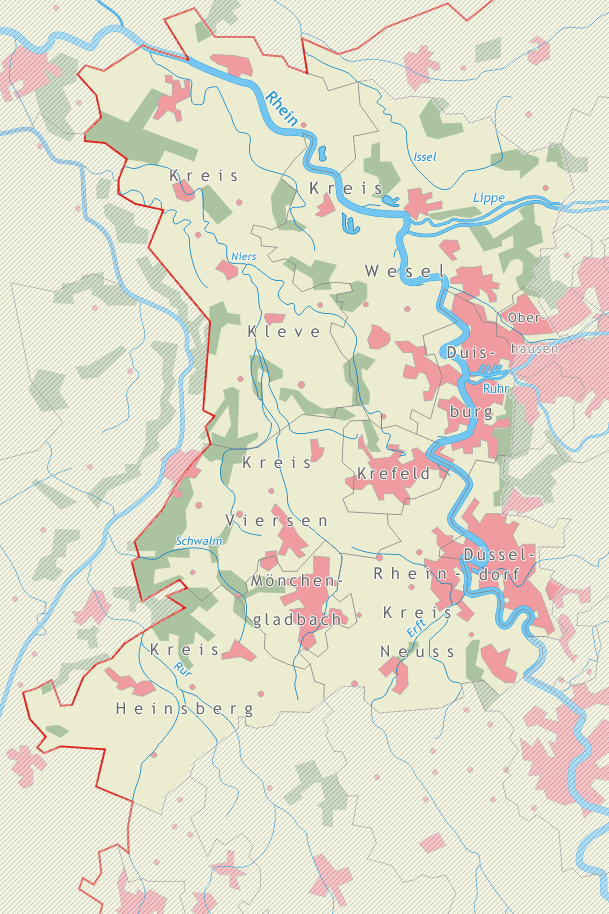
area, including parts of the Düsseldorf Region, are part of it, among them Kleve
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century ...
, Xanten
Xanten (, Low Rhenish: ''Santen'') is a town in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the district of Wesel.
Xanten is known for the Archaeological Park, one of the largest archaeological open air museums in the wor ...
, Wesel
Wesel () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
Geography
Wesel is situated at the confluence of the Lippe River and the Rhine.
Division of the city
Suburbs of Wesel include Lackhausen, Obrighove ...
, Moers
Moers (; older form: ''Mörs''; archaic Dutch language, Dutch: ''Murse'', ''Murs'' or ''Meurs'') is a German List of cities and towns in Germany, city on the western bank of the Rhine, close to Duisburg. Moers belongs to the district of Wesel (d ...
, Essen
Essen (; Latin: ''Assindia'') is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and D ...
, Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in Nor ...
, Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in th ...
, Oberhausen
Oberhausen (, ) is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen ( ). The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Rout ...
and Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; "''Wupper Dale''") is, with a population of approximately 355,000, the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia as well as the 17th-largest city of Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of the cities and to ...
. This language area stretches towards the southwest along cities such as Neuss
Neuss (; spelled ''Neuß'' until 1968; li, Nüss ; la, Novaesium) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the west bank of the Rhine opposite Düsseldorf. Neuss is the largest city within the Rhein-Kreis Neuss district. It ...
, Krefeld
Krefeld ( , ; li, Krieëvel ), also spelled Crefeld until 1925 (though the spelling was still being used in British papers throughout the Second World War), is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, i ...
and Mönchengladbach
Mönchengladbach (, li, Jlabbach ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located west of the Rhine, halfway between Düsseldorf and the Dutch border.
Geography Municipal subdivisions
Since 2009, the territory of Mönchengladbac ...
, and the Heinsberg
Heinsberg (; li, Hinsberg ) is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the seat of the district Heinsberg. It is situated near the border with the Netherlands, on the river Wurm, approx. 20 km north-east of Sittard and 30 km ...
district, where it is called Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
, crosses the German-Dutch border into the Dutch province of Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
, passing cities east of the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
river (in both Dutch and German called ''Maas'') such as Venlo
Venlo () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg (Netherland ...
, Roermond
Roermond (; li, Remunj or ) is a city, municipality, and diocese in the Limburg province of the Netherlands. Roermond is a historically important town on the lower Roer on the east bank of the river Meuse. It received town rights in 1231. Roer ...
and Geleen
Geleen (; li, Gelaen ) is a city in the southern part of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg in the Netherlands. With 31,670 inhabitants in 2020, it is part of the municipality of Sittard-Geleen. Geleen is situated along the river Gele ...
, and then again crosses the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
between the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg, encompassing the cities of Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
(NL) and Hasselt
Hasselt (, , ; la, Hasseletum, Hasselatum) is a Belgian city and municipality, and capital and largest city of the province of Limburg in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is known for its former branding as "the city of taste", as well as its ...
(B). Thus a mainly political-geographic (not linguistic) division can be made into western (Dutch) South Guelderish and Limburgish at the west side, and eastern (German) Low Rhenish and South East Low Franconian at the east side of the border. The eastmost varieties of the latter, east of the Rhine from Düsseldorf to Wuppertal, are referred to as Bergish.
Limburgish is recognised as a regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
in the Netherlands. As such, it receives moderate protection under chapter 2 of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. The area in which Limburgish is spoken roughly fits within a wide circle from Venlo
Venlo () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg (Netherland ...
(NL) to Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in th ...
(D) to Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
(D) to Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
(NL) to Hasselt
Hasselt (, , ; la, Hasseletum, Hasselatum) is a Belgian city and municipality, and capital and largest city of the province of Limburg in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is known for its former branding as "the city of taste", as well as its ...
(B) and back to Venlo. In Germany, it is common to consider the Limburgish varieties as belonging to the Low Franconian language varieties; in the Netherlands and Belgium, however, all these varieties are traditionally considered to be West Central German
West Central German (german: Westmitteldeutsch) belongs to the Central, High German dialect family of German. Its dialects are Franconian and comprise the parts of the Rhinelandic continuum located south of the Benrath line isogloss, including ...
, part of High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
. This difference is caused by a difference in definition: linguists of the Low Countries define a High German variety as one that has taken part in any of the first three phases of the High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probably ...
.
In German sources, the dialects linguistically counting as Limburgish spoken east of the river Rhine are often called " Bergish" (after the former Duchy of Berg
Berg was a state—originally a county, later a duchy—in the Rhineland of Germany. Its capital was Düsseldorf. It existed as a distinct political entity from the early 12th to the 19th centuries.
The name of the county lives on in the modern ...
). West of the river Rhine they are called "Low Rhenish", "Limburgish" or "Ripuarian". Limburgish is not recognised by the German government as an official language. Low Rhenish is considered as a group of dialects in Germany. Together all these varieties belong to a greater continuum; this superordinating group is called Meuse-Rhenish. These insights are rather new among dialectologists on both sides of the national Dutch-German border.
German population in the Meuse-Rhine area are used to let the geographic 'Lower Rhine' area begin approximately with the Benrath line, coincidentally. They do mostly not think of the Ripuarian-speaking area as Low Rhenish, which includes the South Bergish or Upper Bergish area east of the Rhine, south of the Wupper
The Wupper is a right tributary of the Rhine in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Rising near Marienheide in western Sauerland it runs through the mountainous region of the Bergisches Land in Berg County and enters the Rhine at Lever ...
, north of the Sieg
The Sieg is a river in North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a right tributary of the Rhine.
The river is named after the Sicambri. It is in length.
The source is located in the Rothaargebirge mountains. From here t ...
.
The Meuse-Rhine triangle
This whole region between the Meuse and the Rhine was linguistically and culturally quite coherent during the so-called Early modern period (1543–1789), though politically more fragmented. The former predominantly Dutch speaking duchies ofGuelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in pr ...
and Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
lay in the heart of this linguistic landscape, but eastward the former duchies of Cleves
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century ...
(entirely), Jülich
Jülich (; in old spellings also known as ''Guelich'' or ''Gülich'', nl, Gulik, french: Juliers, Ripuarian: ''Jöllesch'') is a town in the district of Düren, in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. As a border region betwe ...
, and Berg Berg may refer to:
People
*Berg (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
*Berg Ng (born 1960), Hong Kong actor
* Berg (footballer) (born 1989), Brazilian footballer
Former states
*Berg (state), county and duchy of the Holy ...
partially, also fit in.
The northwestern part of this triangular
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- collinea ...
area came under the influence of the Dutch standard language, especially since the founding of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
in 1815. The southeastern part became a part of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Re ...
at the same time, and from then it was subject to High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
language domination. At the dialectal level however, mutual understanding is still possible far beyond both sides of the national borders.
The close relation between Limburgish of Belgium and the Netherlands and Bergish is paralleled with that between Zuid-Gelders and Kleverlandish
South Guelderish ( nl, Zuid-Gelders , german: Südgeldersch, ''Kleverländisch'') refers to the easternmost group of Dutch dialects spoken along the lower Rhine (Dutch Nederrijn and German Niederrhein). In its narrower sense, the term refers str ...
, which are even more clearly belonging to Low Franconian. By including Zuid-Gelders-Kleverlandish-East Bergish in this continuum, we are enlarging the territory and turn the wide circle of Limburgish into a triangle with its top along the line Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both banks of ...
– Kleve
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century ...
– Wesel
Wesel () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
Geography
Wesel is situated at the confluence of the Lippe River and the Rhine.
Division of the city
Suburbs of Wesel include Lackhausen, Obrighove ...
– Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in Nor ...
– Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; "''Wupper Dale''") is, with a population of approximately 355,000, the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia as well as the 17th-largest city of Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of the cities and to ...
(along the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
-IJssel
The IJssel (; nds-nl, Iessel(t) ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour ...
Line). The Diest
Diest () is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. Situated in the northeast of the Hageland region, Diest neighbours the provinces of Antwerp to its North, and Limburg to the East and is situated around 60 ...
- Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 6 ...
Line is its western border, the Benrath line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs f ...
(from Eupen
Eupen (, ; ; formerly ) is the capital of German-speaking Community of Belgium and is a city and municipality in the Belgian province of Liège, from the German border (Aachen), from the Dutch border (Maastricht) and from the "High Fens" na ...
to Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; "''Wupper Dale''") is, with a population of approximately 355,000, the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia as well as the 17th-largest city of Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of the cities and to ...
) is a major part of the southeastern one.
Within the Dutch speaking area, the Western continuance of Low Rhenish is divided into Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
and Zuid-Gelders. Together they belong to the greater triangle-shaped Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
-Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
area, a large group of southeastern Low Franconian dialects, including areas in Belgium, the Netherlands and the German Northern Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
.
Southeast Limburgish around Aachen
''Southeast Limburgish
Southeast Limburgish (Dutch: ''Zuidoost-Limburgs'', Ripuarian: ''Süüdoß-Limburjesch''), also referred to as Southern Meuse-Rhenish, is a subdivision of what recently has been named Meuse-Rhenish. Both terms denote a rather compact grouping of ...
'' is spoken around Kerkrade
Kerkrade ( Ripuarian: ; li, Kirkraoj; german: Kerkrade or ''Kirchrath'') is a town and a municipality in the southeast of Limburg; the southernmost province of the Netherlands. It forms part of the Parkstad Limburg agglomeration.
Kerkrade is the ...
, Bocholtz
Bocholtz (; Ripuarian: is a town in the Dutch province of Limburg. It is a part of the municipality of Simpelveld, and lies about 7 km southwest of Kerkrade. Until 1982, it was a separate municipality.
History
Bocholtz dates back to th ...
and Vaals
Vaals (; Ripuarian: ) is a town in the extreme southeastern part of the Dutch province of Limburg, which is in the southeastern part of the Netherlands.
The municipality covers an area of in the foothills of the Ardennes–Eifelrange a ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Raeren
Raeren () is a municipality of east Belgium located in the Walloon province of Liège. It was part of Germany until the First World War, after which it became part of Belgium. It is one of several towns in eastern Belgium which predominantly spe ...
and Eynatten
Eynatten is a village in the Belgian municipality of Raeren, part of the German-speaking Community of Belgium. Eynatten is on the border to Germany, south from Aachen. Around half of the population are non-Belgians, most of them Germans.
Eynatte ...
in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
. In Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
it is mostly considered as a form of Ripuarian, instead of Limburgish. According to a contemporary vision, all varieties in a wider half circle some 20 km around Aachen and also the so-called Low Dietsch
Low Dietsch ( nl, Platdiets, li, Platduutsj, french: francique rhéno-mosan or ) refers to a handful of transitional Limburgish– Ripuarian dialects spoken in a number of towns and villages (e.g., Gemmenich, Hombourg, Montzen, Welkenraedt).
T ...
area between Voeren
Voeren (; ) is a Flanders, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking Municipalities of Belgium, municipality with Municipalities with language facilities, facilities for the Walloons, French-speaking minority, located in the Belgium, Belgian provi ...
and Eupen
Eupen (, ; ; formerly ) is the capital of German-speaking Community of Belgium and is a city and municipality in the Belgian province of Liège, from the German border (Aachen), from the Dutch border (Maastricht) and from the "High Fens" na ...
in Belgium, can be taken as a group of its own, which recently has been named ''Limburgish of the Three Countries Area'' (Dutch: ''Drielandenlimburgs'', German: ''Dreiländerplatt''), referring to the place where the Netherlands, Belgium and Germany meet. This variety still possesses interesting syntactic idiosyncrasies, probably dating from the period in which the old Duchy of Limburg
The Duchy of Limburg or Limbourg was an imperial estate of the Holy Roman Empire. Much of the area of the duchy is today located within Liège Province of Belgium, with a small portion in the municipality of Voeren, an Enclave and exclave, excla ...
existed. In Belgium, the south-eastern boundary between Meuse-Rhenish or (French) ''francique rhéno-mosan'' and Ripuarian is formed by the Low Dietsch
Low Dietsch ( nl, Platdiets, li, Platduutsj, french: francique rhéno-mosan or ) refers to a handful of transitional Limburgish– Ripuarian dialects spoken in a number of towns and villages (e.g., Gemmenich, Hombourg, Montzen, Welkenraedt).
T ...
language area.
If only tonality is to be taken as to define this variety, it stretches several dozen kilometers into Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. In Germany, the consensus is to class it as belonging to High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
varieties. But this is a little over-simplified. In order to include them properly, a more encompassing concept is needed. The combination of Meuse-Rhenish and Ripuarian, including their overlapping transitional zones of Southeast Limburgish
Southeast Limburgish (Dutch: ''Zuidoost-Limburgs'', Ripuarian: ''Süüdoß-Limburjesch''), also referred to as Southern Meuse-Rhenish, is a subdivision of what recently has been named Meuse-Rhenish. Both terms denote a rather compact grouping of ...
and Low Dietsch
Low Dietsch ( nl, Platdiets, li, Platduutsj, french: francique rhéno-mosan or ) refers to a handful of transitional Limburgish– Ripuarian dialects spoken in a number of towns and villages (e.g., Gemmenich, Hombourg, Montzen, Welkenraedt).
T ...
, will do.
Classification
*Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
** Germanic
*** West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into t ...
**** Low Franconian
Low Franconian, Low Frankish, NetherlandicSarah Grey Thomason, Terrence Kaufman: ''Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics'', University of California Press, 1991, p. 321. (Calling it "Low Frankish (or Netherlandish)".)Scott Shay ...
***** Meuse-Rhenish
****** Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
and Zuid-Gelders / Low Rhenish
Sources
*Ad Welschen 2000–2005: Course ''Dutch Society and Culture'', International School for Humanities and Social Studies ISHSS, Universiteit van Amsterdam *Georg Cornelissen 2003: ''Kleine niederrheinische Sprachgeschichte (1300–1900) : eine regionale Sprachgeschichte für das deutsch-niederländische Grenzgebiet zwischen Arnheim und Krefeld'' ith an introduction in Dutch. Geldern / Venray: Stichting Historie Peel-Maas-Niersgebied, *Michael Elmentaler, Die Schreibsprachgeschichte des Niederrheins. Forschungsprojekt der Uni Duisburg, in: ''Sprache und Literatur am Niederrhein'', Schriftenreihe der Niederrhein-Akademie Bd. 3, 15–34. *Theodor Frings 1916: ''Mittelfränkisch-niederfränkische studien I. Das ripuarisch-niederfränkische Übergangsgebiet. II. Zur Geschichte des Niederfränkischenn'' in: ''Beiträge zur Geschichte und Sprache der deutschen Literatur'' 41 (1916), 193–271 en 42, 177–248. *Irmgard Hantsche 2004: ''Atlas zur Geschichte des Niederrheins'' (= Schriftenreihe der Niederrhein-Akademie 4). Bottrop/Essen: Peter Pomp (5e druk). *Uwe Ludwig, Thomas Schilp (red.) 2004: ''Mittelalter an Rhein und Maas. Beiträge zur Geschichte des Niederrheins. Dieter Geuenich zum 60. Geburtstag'' (= Studien zur Geschichte und Kultur Nordwesteuropas 8). Münster/New York/München/Berlin: Waxmann. *Arend Mihm 1992: Sprache und Geschichte am unteren Niederrhein, in: ''Jahrbuch des Vereins für niederdeutsche Sprachforschung'', 88–122. *Arend Mihm 2000: Rheinmaasländische Sprachgeschichte von 1500 bis 1650, in: Jürgen Macha, Elmar Neuss, Robert Peters (red.): ''Rheinisch-Westfälische Sprachgeschichte''. Köln enz. (= Niederdeutsche Studien 46), 139–164. *Helmut Tervooren 2005: ''Van der Masen tot op den Rijn. Ein Handbuch zur Geschichte der volkssprachlichen mittelalterlichen Literatur im Raum von Rhein und Maas''. Geldern: Erich Schmidt.See also
*Moselle Franconian
__NOTOC__
Moselle Franconian (german: Moselfränkisch, lb, Muselfränkesch) is a West Central German language, part of the Central Franconian dialects, Central Franconian languages area, that includes Luxembourgish.
It is spoken in the southe ...
*Low Dietsch
Low Dietsch ( nl, Platdiets, li, Platduutsj, french: francique rhéno-mosan or ) refers to a handful of transitional Limburgish– Ripuarian dialects spoken in a number of towns and villages (e.g., Gemmenich, Hombourg, Montzen, Welkenraedt).
T ...
{{Languages of Germany
West Germanic languages
Languages of Germany
German dialects
Dutch language
Dutch dialects
Languages of the Netherlands
Languages of Belgium
North Rhine-Westphalia
Rhineland