longshoremen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
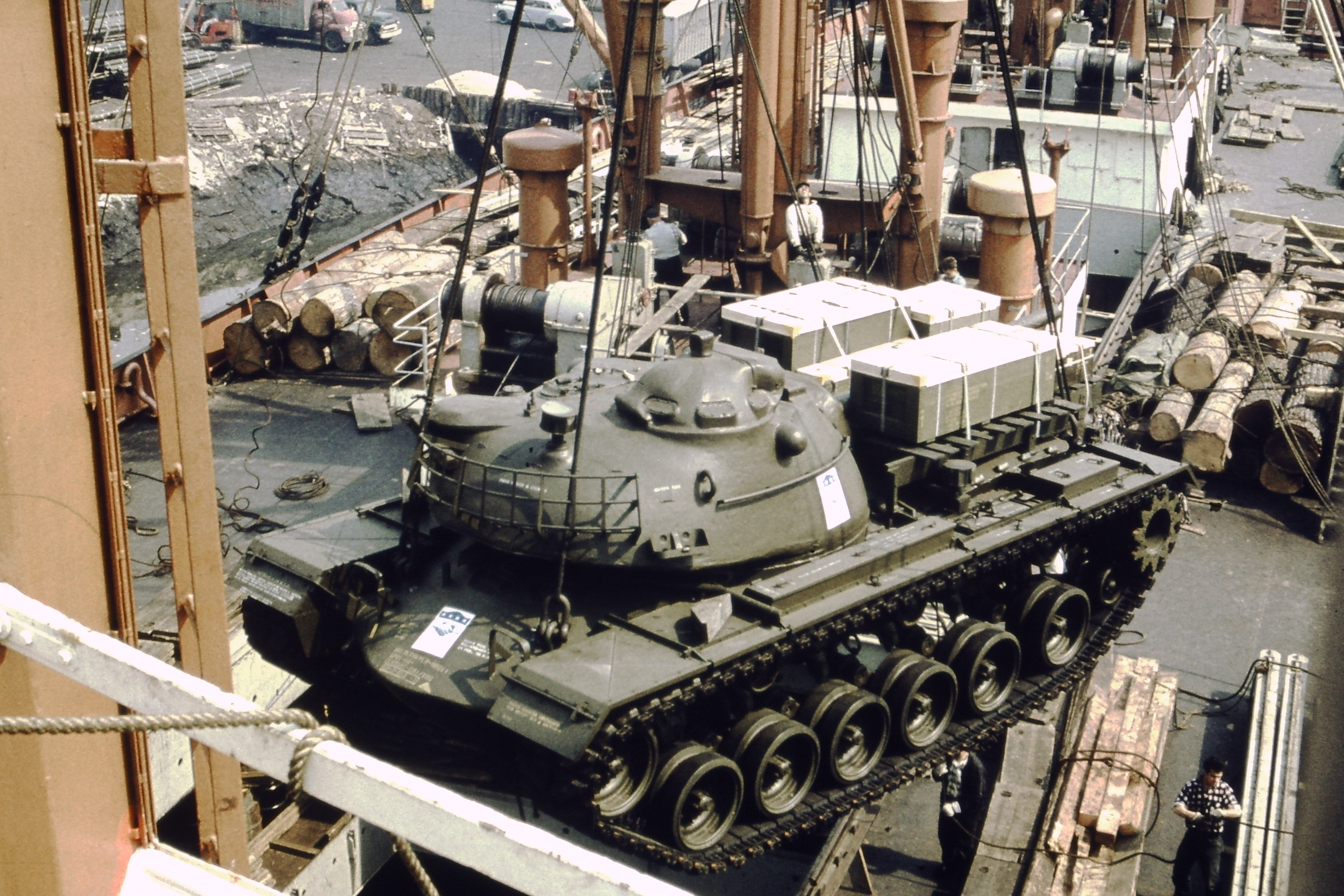 In present-day American waterfront usage, a stevedore is usually a person or a company who manages the operation of loading or unloading a ship. In the early 19th century, the word was usually applied to black laborers or slaves who loaded and unloaded bales of cotton and other freight on and off riverboats. In ''
In present-day American waterfront usage, a stevedore is usually a person or a company who manages the operation of loading or unloading a ship. In the early 19th century, the word was usually applied to black laborers or slaves who loaded and unloaded bales of cotton and other freight on and off riverboats. In ''
"The Irish on the Docks of Portland" by Michael Connolly
{{Authority control Marine occupations Spanish words and phrases Polish-American culture in Baltimore Portuguese words and phrases
A stevedore (), also called a longshoreman, a docker or a dockworker, is a waterfront manual laborer who is involved in loading and unloading
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
– 2005">
File:Hong Kong 2005 auf Reede, zwei Bargen mit Kränen an Backbord fest.jpg, At anchor, two ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
s, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
s, trains
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often know ...
or airplanes
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectr ...
.
After the shipping container
A shipping container is a container with strength suitable to withstand shipment, storage, and handling. Shipping containers range from large reusable steel boxes used for intermodal shipments to the ubiquitous corrugated boxes. In the context of ...
revolution of the 1960s, the number of dockworkers required declined by over 90%.
Etymology
The word ''stevedore'' originated inPortugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
or Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, and entered the English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the is ...
through its use by sailor
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship.
The profession of the s ...
s. It started as a phonetic spelling
A phonemic orthography is an orthography (system for writing a language) in which the graphemes (written symbols) correspond to the phonemes (significant spoken sounds) of the language. Natural languages rarely have perfectly phonemic orthographi ...
of ''estivador'' (Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
) or ''estibador'' (Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
), meaning ''a man who loads ships and stows cargo'', which was the original meaning of ''stevedore'' (though there is a secondary meaning of "a man who stuffs" in Spanish); compare Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''stīpāre'' meaning ''to stuff'', as in ''to fill with stuffing''. In Ancient and modern Greek, the verb στοιβάζω (stevazo) means pile up. In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, people who load and unload ships are usually called ''dockers''; in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, they are called ''dockers'' or ''wharfies''; and, in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the term ''longshoreman'', derived from ''man-along-the-shore'', is used. Before the extensive use of container ships and shore-based handling machinery in the United States, ''longshoremen'' referred exclusively to the dockworkers, while ''stevedores'', in a separate trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
, worked on the ships, operating ship's cranes and moving cargo. In Canada, the term ''stevedore'' has also been used, for example, in the name of the Western Stevedoring Company, Ltd., based in Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, B.C., in the 1950s.
Loading and unloading ships
Loading and unloading ships requires knowledge of the operation of loading equipment, the proper techniques for lifting and stowingcargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
, and correct handling of hazardous material
Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials ( syllabi ...
s. In addition, workers must be physically strong and able to follow orders attentively. To unload a ship successfully, many longshoremen are needed. There is only a limited amount of time that a ship can be at a port, so their work must be completed quickly.
In earlier days before the introduction of containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers and ISO containers). Containerization is also referred as "Container Stuffing" or "Container Loading", which is the pro ...
, men who loaded and unloaded ships had to tie down cargoes with rope. A type of stopper knot
Stopper may refer to:
* Bung, a plug used to stop the opening of a container
** Laboratory rubber stopper, a specific type of bung
* Plug (sanitation), used to stop a drainage outlet
* Defender (association football), in soccer (association footba ...
is called the stevedore knot
The stevedore knot is a stopper knot, often tied near the end of a rope. It is more bulky and less prone to jamming than the closely related figure-eight knot.
Naming
There is a lack of consensus among knot experts regarding the origin of t ...
. The method of securely tying up parcels of goods is called ''stevedore lashing'' or ''stevedore knotting''. While loading a general cargo vessel, they use dunnage
Dunnage is inexpensive or waste material used to load and secure cargo during transportation; more loosely, it refers to miscellaneous baggage, brought along during travel. The term can also refer to low-priority cargo used to fill out transport ca ...
, which are pieces of wood (or nowadays sometimes strong inflatable dunnage bag
Dunnage bags, also known as airbags, and inflatable bags, are used to secure and stabilize cargo.
Introduced around 1970, dunnage bags provide convenient and cost-effective cargo stabilization in ISO sea containers, closed railcars, trucks, and ...
s) set down to keep the cargo out of any water that might be lying in the hold or are placed as shims between cargo crates for load securing
Load securing, also known as cargo securing, is the securing of cargo for transportation. According to the European Commission Transportation Department “it has been estimated that up to 25% of accidents involving trucks can be attributable to i ...
.
Today, the vast majority of non-bulk cargo
Bulk cargo is commodity cargo that is transported unpackaged in large quantities.
Description
Bulk cargo refers to material in either liquid or granular, particulate form, as a mass of relatively small solids, such as petroleum/ crude oi ...
is transported in intermodal container
An intermodal container, often called a shipping container, is a large standardized shipping container, designed and built for intermodal freight transport, meaning these containers can be used across different Mode of transport, modes of trans ...
s. The containers arrive at a port by truck, rail, or another ship and are stacked in the port's storage area. When the ship that will be transporting them arrives, the containers that it is offloading are unloaded by a crane. The containers either leave the port by truck or rail or are put in the storage area until they are put on another ship. Once the ship is offloaded, the containers it is leaving with are brought to the dock by truck. A crane lifts the containers from the trucks onto the ship. As the containers pile up on the ship, the workers connect them to the ship and to the other already-placed containers. The jobs involved include the crane operators, the workers who connect the containers to the ship and each other, the truck drivers that transport the containers from the dock and storage area, the workers who track the containers in the storage area as they are loaded and unloaded, as well as various supervisors. Those workers at the port who handle and move the containers are likely to be considered stevedores or longshoremen.
Before containerization, freight was often handled with a longshoreman’s hook
A hook is a hand tool used for securing and moving loads. It consists of a round wooden handle with a strong metal hook about 8" long projecting at a right angle from the center of the handle. The appliance is held in a closed fist with the hook ...
, a tool which became emblematic of the profession (mostly on the west coast of the United States and Canada).
Traditionally, stevedores had no fixed job, but would arrive at the docks in the morning seeking employment for the day. London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
dockers called this practice ''standing on the stones'', while in the United States it was referred to as ''shaping up'' or assembling for the ''shape-up'', or "catching the breaks". In Britain, due to changes in employment law
Labour laws (also known as labor laws or employment laws) are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, ...
s, such jobs have either become permanent or have been converted to temporary jobs.
Dock workers have been a prominent part of the modern labor movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
.
barges
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by Pusher (boat) ...
with cranes (floating derricks) at port
File:Ein Container wird von Deck gehievt.jpg, A container is lifted from the deck.
File:Hafenarbeiter bei ihrer gefährlichen Arbeit auf den Containern in der Luke.jpg, Dockworkers on the containers in the ship's hatch
File:Starker Gezeitenstrom, Ladungsarbeiten bei schwierigen Arbeitsbedingungen.jpg, Strong tidal current, loading work in adverse conditions
By country
Australia
InAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, the informal term "wharfie" (from wharf labourer) and the formal "waterside worker" include the variety of occupations covered in other countries by words like stevedore. The term "stevedore" is also sometimes used, as in the company name Patrick Stevedores. The term "docker" is also used, as in the Federated Ship Painters and Dockers Union
The Federated Ship Painters and Dockers Union (FSPDU) was an Australian trade union which existed between 1900 and 1993. It represented labourers in the shipbuilding industry, covering "mostly work associated with chipping, painting, scrubbing ...
; and is the mascot of the Fremantle Dockers
The Fremantle Football Club, nicknamed the Dockers, is a professional Australian rules football club competing in the Australian Football League (AFL), the sport's elite competition. The team was founded in 1994 to represent the port city of Fr ...
in the Australian Football League
The Australian Football League (AFL) is the only fully professional competition of Australian rules football. Through the AFL Commission, the AFL also serves as the sport's governing body and is responsible for controlling the laws of the gam ...
.
The Maritime Union of Australia
The Maritime Union of Australia (MUA) was a union which covered waterside workers, seafarers, port workers, professional divers, and office workers associated with Australian ports. The MUA was formed in 1993 with merger of the Seamen's Union ...
has coverage of these workers and fought a substantial industrial battle in the 1998 Australian waterfront dispute to prevent the contracting out of work to non-union workers.
In 1943, stevedores in Melbourne and Sydney were deliberately exposed to mustard gas while unloading the ship ''Idomeneus''. The result was death and permanent disability—all as a result of military secrecy.
New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
usage is very similar to the Australian version; "waterside workers" are also known as "wharfies." The 1951 New Zealand waterfront dispute, involving New Zealand stevedores, was the largest and most bitter industrial dispute in the country's history.
United Kingdom
In theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, the definition of a stevedore varies from port to port. In some ports, only the highly skilled master of a loading gang is referred to as a "stevedore". "Docker" is the usual general term used in the UK for a worker who loads or unloads ships and performs various other jobs required at a seaport.
In some ports, a stevedore is a person who decides where cargo is stowed on a ship, for safe stowage and even balance of a ship. It is not a hands-on role.
It was once known to refer those working on a ship—loading or unloading the cargo—as stevedores, while those working on the quayside were called dockers.
In the ports along the Thames, stevedores load, whilst dockers unload (according to Michael Budge, ex docker, Tilbury and Dave Penn, ex docker, Tilbury, 1978–2018).
United States
 In present-day American waterfront usage, a stevedore is usually a person or a company who manages the operation of loading or unloading a ship. In the early 19th century, the word was usually applied to black laborers or slaves who loaded and unloaded bales of cotton and other freight on and off riverboats. In ''
In present-day American waterfront usage, a stevedore is usually a person or a company who manages the operation of loading or unloading a ship. In the early 19th century, the word was usually applied to black laborers or slaves who loaded and unloaded bales of cotton and other freight on and off riverboats. In ''Two Years Before the Mast
''Two Years Before the Mast'' is a memoir by the American author Richard Henry Dana Jr., published in 1840, having been written after a two-year sea voyage from Boston to California on a merchant ship starting in 1834. A film adaptation under the ...
'' (1840), the author Richard Henry Dana Jr.
Richard Henry Dana Jr. (August 1, 1815 – January 6, 1882) was an American lawyer and politician from Massachusetts, a descendant of a colonial family, who gained renown as the author of the classic American memoir ''Two Years Before the Mast''. ...
describes the steeving of a merchant sailing ship in 1834. This was the process of taking a mostly-full hold and cramming in more material. In this case, the hold was filled with hides from the California hide trade
The California hide trade was a trading system of various products based in cities along the California coastline, operating from the early 1820s to the mid-1840s.
In exchange for hides and tallow from cattle owned by California ranchers, sailors ...
up to four feet below the deckhead (equivalent of 'ceiling'). "Books" composed of 25–50 cattle skins folded into a bundle were prepared, and a small opening created in the middle of one of the existing stacks. Then the book was shoved in by use of a pair of thick strong pieces of wood called steeves. The steeves had one end shaped as a wedge which was placed into the middle of a book to shove it into the stack. The other ends were pushed on through block and tackle
A block and tackle or only tackle is a system of two or more pulleys with a rope or cable threaded between them, usually used to lift heavy loads.
The pulleys are assembled to form blocks and then blocks are paired so that one is fixed and on ...
attached to the hull and overhead beams and hauled on by sailors.
Typically one ethnic group dominated the stevedore market in a port, usually the Irish Catholics, as seen in the 1954 film about New York ''On the Waterfront
''On the Waterfront'' is a 1954 American crime drama film, directed by Elia Kazan and written by Budd Schulberg. It stars Marlon Brando and features Karl Malden, Lee J. Cobb, Rod Steiger, Pat Henning, and Eva Marie Saint in her film debut. ...
''. In New Orleans there was competition between the Irish and the blacks.
In the Port of Baltimore
Helen Delich Bentley Port of Baltimore is a shipping port along the tidal basins of the three branches of the Patapsco River in Baltimore, Maryland on the upper northwest shore of the Chesapeake Bay. It is the nation's largest port facilities f ...
, Polish Americans
Polish Americans ( pl, Polonia amerykańska) are Americans who either have total or partial Poles, Polish ancestry, or are citizens of the Republic of Poland. There are an estimated 9.15 million self-identified Polish Americans, representing abou ...
dominated. In the 1930s, about 80% of Baltimore's longshoremen were Polish or of Polish descent. The port of Baltimore had an international reputation of fast cargo handling credited to the well-organized gang system that was nearly free of corruption, wildcat strikes, and repeated work stoppages of its other East coast counterparts. The New York Anti-Crime Commission and the Waterfront Commission looked upon the Baltimore system as the ideal one for all ports. The hiring of longshoremen in Baltimore by the gang system dates back to 1913 when the ILA was first formed. The Polish longshoremen began setting up the system by selecting the most skilled men to lead them. This newly formed gang would usually work for the same company, which would give priority to the gang. During the times where there was no work within the particular company, the gang would work elsewhere, or even divide to aid other groups in their work, which would speed up the work and make it more efficient.Delich, Helen. "Noted for Fast, Efficient Work Baltimore System of Operating is Termed Ideal for All Ports." ''Baltimore Sun'', 1955. In an environment as dangerous as a busy waterfront, Baltimore's gangs always operated together as a unit, because the experience let them know what each member would be doing at any given time, making a waterfront a much safer place. At the beginning of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Polish predominance in the Port of Baltimore significantly diminished, as many Poles were drafted.
It is common to use the terms "stevedore" and "longshoreman" interchangeably. The U.S. Congress has done so in the Ship Mortgage Act, 46 app. U.S.C. section 31301(5)(C) which designates both "crew wages" and "stevedore wages" as preferred maritime liens. The statute intended to give the wages of the seamen and longshoremen the same level of protection. Sometimes the word "stevedore" is used to mean "the man who loads and unloads a ship" as the British "docker".
Today, a stevedore typically owns the equipment used in the loading or discharge operation and hires longshoremen who load and unload cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
under the direction of a stevedore superintendent. This type of work along the East Coast
East Coast may refer to:
Entertainment
* East Coast hip hop, a subgenre of hip hop
* East Coast (ASAP Ferg song), "East Coast" (ASAP Ferg song), 2017
* East Coast (Saves the Day song), "East Coast" (Saves the Day song), 2004
* East Coast FM, a ra ...
waterfront was characteristic of ports like New York, Boston, and Philadelphia.
Today, a commercial stevedoring company also may contract with a terminal
Terminal may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Terminal (electronics), a device for joining electrical circuits together
* Terminal (telecommunication), a device communicating over a line
* Computer terminal, a set of primary input and output dev ...
owner to manage all terminal operations. Many large container ship
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal ...
operators have established in-house stevedoring operations to handle cargo at their own terminals and to provide stevedoring services to other container carriers.
One union within the AFL–CIO
The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL–CIO) is the largest federation of unions in the United States. It is made up of 56 national and international unions, together representing more than 12 million ac ...
represent longshoremen: the International Longshoremen's Association
The International Longshoremen's Association (ILA) is a North American labor union representing longshore workers along the East Coast of the United States and Canada, the Gulf Coast, the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, and inland waterways. The ILA h ...
, which represents longshoremen on the East Coast, on the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and connected waterways and along the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
. The International Longshore and Warehouse Union
The International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU) is a labor union which primarily represents dock workers on the West Coast of the United States, Hawaii, and in British Columbia, Canada. The union was established in 1937 after the 1934 Wes ...
, which represents longshoremen along the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
, Hawaii and Alaska, was formerly affiliated with the AFL–CIO but disaffiliated in 2013.

Famous former stevedores
Former stevedores and longshoremen include: *Crispus Attucks
Crispus Attucks ( – March 5, 1770) was an American whaler, sailor, and stevedore of African and Native American descent, commonly regarded as the first person killed in the Boston Massacre and thus the first American killed in the Amer ...
– American Patriot
* Frithjof Bergmann
Frithjof Harold Bergmann (24 December 1930 – 23 May 2021) was a German professor of philosophy at the University of Michigan, where he taught courses on existentialism, continental philosophy, Hegel, and Marx. He was known for the concept o ...
– philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
* Jaguaré Bezerra de Vasconcelos
Jaguaré is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Espírito Santo. Its population was 31,039 (2020) and its area is 660 km².
The municipality contains part of the Sooretama Biological Reserve
Sooretama Biological Reserve ( pt, Rese ...
– Brazilian football goalkeeper
* Mestre Bimba
Manuel dos Reis Machado, commonly called Mestre Bimba (; November 23, 1899 – February 5, 1974), was a Brazilian capoeira ''mestre'' (a master practitioner). He founded the '' capoeira regional'' school, one of the art's two main branches.
E ...
– founder of the Regional style of Capoeira
Capoeira () is an Afro-Brazilian martial art that combines elements of dance, acrobatics, music and spirituality. Born of the melting pot of enslaved Africans, Indigenous Brazilians and Portuguese influences at the beginning of the 16th century ...
* Ronald Bird
Ronald Ernest Bird
(4 April 1915 – 20 February 1985) was an English cricketer who played 195 first-class matches in the years after the Second World War. 190 of these were for Worcestershire, while the other five were for Marylebone Cricket ...
– English cricketer
* Jerry Colonna – Movie actor/comedian*
* Terry Bollea – Better known as professional wrestler
Professional wrestling is a form of theater that revolves around staged wrestling matches. The mock combat is performed in a ring similar to the kind used in boxing, and the dramatic aspects of pro wrestling may be performed both in the ring or ...
Hulk Hogan
* Murray Bookchin
Murray Bookchin (January 14, 1921 – July 30, 2006) was an American social theorist, author, orator, historian, and political philosopher. A pioneer in the environmental movement, Bookchin formulated and developed the theory of social ec ...
– American libertarian socialist
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (201 ...
, founder of social ecology Social ecology may refer to:
* Social ecology (academic field), the study of relationships between people and their environment, often the interdependence of people, collectives and institutions
* Social ecology (Bookchin), a theory about the relat ...
* Harry Bridges – founder of the International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU)
* James Braddock – heavyweight boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
champion from 1935 to 1937
* Joey Coyle
Joseph William Coyle (February 26, 1953 – August 15, 1993) was an unemployed longshoreman in Philadelphia who, in February 1981, found $1.2 million in the street, after it had fallen out of the back of an armored car, and kept it. His story was ...
– basis for the movie '' Money for Nothing''
* Jack Dash – British dock workers trade union leader
* Francois Faber – road racing cyclist
Road bicycle racing is the cycle sport discipline of road cycling, held primarily on paved roads. Road racing is the most popular professional form of bicycle racing, in terms of numbers of competitors, events and spectators. The two most common ...
, Tour de France
The Tour de France () is an annual men's multiple-stage bicycle race primarily held in France, while also occasionally passing through nearby countries. Like the other Grand Tours (the Giro d'Italia and the Vuelta a España), it consists ...
winner
* Chief Dan George – Native American actor
* Danny Greene
Daniel John Patrick Greene (November 14, 1933 – October 6, 1977) was an Irish-American organized crime figure based in Cleveland, Ohio. Greene gained power first in the local chapter of the International Longshoremen's Association, where h ...
– American mobster
* Eric Hoffer
Eric Hoffer (July 25, 1902 – May 21, 1983) was an American moral and social philosopher. He was the author of ten books and was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in February 1983. His first book, '' The True Believer'' (1951), was wide ...
– author and philosopher
* James J. Hill
James Jerome Hill (September 16, 1838 – May 29, 1916) was a Canadian-American railroad director. He was the chief executive officer of a family of lines headed by the Great Northern Railway, which served a substantial area of the Upper Midwes ...
– railroad industrialist and financier
* Brian Jacques
James Brian Jacques (, as in "Jakes"; 15 June 1939 – 5 February 2011) was an English novelist known for his ''Redwall'' series of novels and ''Castaways of the Flying Dutchman'' series. He also completed two collections of short stories entit ...
– author of the ''Redwall
''Redwall'' is a series of children's fantasy novels by British writer Brian Jacques, published from 1986 to 2011. It is also the title of the first book of the series, published in 1986, as well as the name of the abbey featured in the book, ...
'' book series
* Vladimir Kokkinaki
Vladimir Konstantinovich Kokkinaki (russian: Владимир Константинович Коккинаки; – 6 January 1985) was a test pilot in the Soviet Union, notable for setting twenty-two world records and serving as president of the ...
– the most famous test pilot in the Soviet Union
* Mauno Koivisto
Mauno Henrik Koivisto (; 25 November 1923 – 12 May 2017) was a Finnish politician who served as the ninth president of Finland from 1982 to 1994. He also served as the country's prime minister twice, from 1968 to 1970 and again from 1979 to 19 ...
– President of Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
from 1982 to 1994
* Artie Lange
Artie is a masculine given name, usually a diminutive of Arthur. Notable people with the given name include:
People
* Artie Bettles (1891–1971), Australian rules footballer
* Artie Butler (born 1942), American popular music arranger, songwrite ...
– comedian/radio personality, ''The Howard Stern Show
''The Howard Stern Show'' is an American radio show hosted by Howard Stern that gained wide recognition when it was nationally syndicated on terrestrial radio from WXRK in New York City, between 1986 and 2005. The show has aired on Howard 100 a ...
''
* Tom Mann
Thomas Mann (15 April 1856 – 13 March 1941), was an English trade unionist and is widely recognised as a leading, pioneering figure for the early labour movement in Britain. Largely self-educated, Mann became a successful organiser and a ...
– British trade unionist and organizer of the London Dock Strike of 1889
The London dock strike was an industrial dispute involving dock workers in the Port of London. It broke out on 14 August 1889, and resulted in victory for the 100,000 strikers and established strong trade unions amongst London dockers, one of whi ...
* Charles Manson
Charles Milles Manson (; November 12, 1934November 19, 2017) was an American criminal and musician who led the Manson Family, a cult based in California, in the late 1960s. Some of the members committed a series of nine murders at four loca ...
– convicted murderer, worked as a longshoreman from 1954 to 1956.
* Peter MacKay
Peter Gordon MacKay (born September 27, 1965) is a Canadian lawyer and politician. He was a Member of Parliament from 1997 to 2015 and has served as Minister of Justice and Attorney General (2013–2015), Minister of National Defence (2007� ...
– Minister of National Defense of Canada
* Frank McCourt
Francis McCourt (August 19, 1930July 19, 2009) was an Irish-American teacher and writer. He won a Pulitzer Prize for his book ''Angela's Ashes'', a tragicomic memoir of the misery and squalor of his childhood.
Early life and education
Frank McC ...
– Irish-American author
* Daniel Patrick Moynihan
Daniel Patrick Moynihan (March 16, 1927 – March 26, 2003) was an American politician, diplomat and sociologist. A member of the Democratic Party, he represented New York in the United States Senate from 1977 until 2001 and served as an ...
– sociologist, ambassador to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
and to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, U.S. Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
* Don Muraco
Don Muraco (born September 10, 1949) is an American retired professional wrestler and podcaster. He is best known for his appearances with the World Wrestling Federation from 1981 to 1988, where he held the WWF Intercontinental Heavyweight Cha ...
– former professional wrestler, most famous as "Magnificent Muraco"
* Michael "Ozzie" Myers – U.S. Representative
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they c ...
from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
* Bruce Nelson – labor historian, author of '' Workers on the Waterfront''
* Bartolomeo Pagano
Bartolomeo Pagano (27 September 1878 – 24 June 1947) was an Italian motion picture actor.
Before his cinema career, Pagano was a stevedore who worked at the port of Genoa. There, he was discovered and selected to play the role of Maciste, a m ...
– Italian actor
* Charles Plymell
Charles Plymell (born April 26, 1935, in Holcomb, Kansas) is a poet, novelist, and small press publisher. Plymell has been published widely, collaborated with, and published many poets, writers, and artists, including principals of the Beat Gene ...
– poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or writte ...
* Benito Quinquela Martín
Benito Quinquela Martín (March 1, 1890 – January 28, 1977) was an Argentine painter. Quinquela Martín is considered the port painter-par-excellence and one of the most popular Argentine painters. His paintings of port scenes show the activ ...
– painter
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
from Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, Argentina. His works reflect the work at the docks in La Boca, a portuary district of Buenos Aires.
* Joe Rollino
Joseph Rollino (March 19, 1905 – January 11, 2010) was a decorated World War II veteran, weightlifter, and strongman. The son of Italian immigrants, Rollino dubbed himself the world's strongest man in the 1920s, moving with his back during ...
– boxer and strongman
* Glenn Theodore Seaborg
Glenn Theodore Seaborg (; April 19, 1912February 25, 1999) was an American chemist whose involvement in the Synthetic element, synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Che ...
– 1951 Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
winner, member of The Manhattan Project
* Hubert Selby Jr.
Hubert "Cubby" Selby Jr. (July 23, 1928 – April 26, 2004) was an American writer. Two of his novels, ''Last Exit to Brooklyn'' (1964) and ''Requiem for a Dream'' (1978) explore worlds in the New York area and were adapted as films, both of whi ...
– Writer, ''Last Exit To Brooklyn
''Last Exit to Brooklyn'' is a 1964 novel by American author Hubert Selby Jr. The novel takes a harsh, uncompromising look at lower class Brooklyn in the 1950s written in a brusque, everyman style of prose.
Critics and fellow writers praised ...
''
* Mark E. Smith
Mark Edward Smith (5 March 1957 – 24 January 2018) was an English singer, who was the lead singer, lyricist and only constant member of the post-punk group the Fall. Smith formed the band after attending the June 1976 Sex Pistols gig at the ...
– singer/songwriter of the British band The Fall
* Stan Weir – blue-collar intellectual and sociologist, founder of Singlejack Press
* Isaac Woodard
Isaac Woodard Jr. (March 18, 1919 – September 23, 1992) was an American soldier and victim of racial violence. An African-American World War II veteran, on February 12, 1946, hours after being honorably discharged from the United States Army, ...
– African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
victim of a notorious racist
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
attack
* J. S. Woodsworth
James Shaver Woodsworth (July 29, 1874 – March 21, 1942) was a pre–First World War pioneer of the Canadian Social Gospel, a Christian religious movement with social democratic values and links to organized labour. He was a long-time leader ...
– a founder of the Cooperative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF; french: Fédération du Commonwealth Coopératif, FCC); from 1955 the Social Democratic Party of Canada (''french: Parti social démocratique du Canada''), was a federal democratic socialistThe follo ...
, the forerunner of the New Democratic Party of Canada
The New Democratic Party (NDP; french: Nouveau Parti démocratique, NPD) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* th ...
* Howard Zinn
Howard Zinn (August 24, 1922January 27, 2010) was an American historian, playwright, philosopher, socialist thinker and World War II veteran. He was chair of the history and social sciences department at Spelman College, and a political scien ...
– historian, playwright, and activist
In popular culture
* PoetElla Wheeler Wilcox
Ella Wheeler Wilcox (November 5, 1850October 30, 1919) was an American author and poet. Her works include the collection '' Poems of Passion'' and the poem "Solitude", which contains the lines "Laugh, and the world laughs with you; weep, and you ...
recited her poem "The Stevedores" (which includes the lyric: "Here's to the Army stevedores, lusty and virile and strong ... ") while visiting a camp of 9,000 stevedores in France during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
*In 1949, reporter Malcolm Johnson was awarded a Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made h ...
for a 24-part investigative series titled ''Crime on the Waterfront'', published in the ''New York Sun
''The New York Sun'' is an American online newspaper published in Manhattan; from 2002 to 2008 it was a daily newspaper distributed in New York City. It debuted on April 16, 2002, adopting the name, motto, and masthead of the earlier New York ...
''.
*The material from Malcolm Johnson's investigative series was fictionalized and used as a basis for the influential film ''On the Waterfront
''On the Waterfront'' is a 1954 American crime drama film, directed by Elia Kazan and written by Budd Schulberg. It stars Marlon Brando and features Karl Malden, Lee J. Cobb, Rod Steiger, Pat Henning, and Eva Marie Saint in her film debut. ...
'' (1954), starring Marlon Brando
Marlon Brando Jr. (April 3, 1924 – July 1, 2004) was an American actor. Considered one of the most influential actors of the 20th century, he received numerous accolades throughout his career, which spanned six decades, including two Academ ...
as a longshoreman, and the working conditions on the docks figure significantly in the film's plot. ''On the Waterfront'' was a critical and commercial success that received twelve Academy Award
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
nominations, and won eight including Best Picture, Best Actor for Brando, Best Supporting Actress for Eva Marie Saint
Eva Marie Saint (born July 4, 1924) is an American actress of film, theatre and television. In a career spanning over 70 years, she has won an Academy Award and a Primetime Emmy Award, alongside nominations for a Golden Globe Award and two Brit ...
, and Best Director for Elia Kazan
Elia Kazan (; born Elias Kazantzoglou ( el, Ηλίας Καζαντζόγλου); September 7, 1909 – September 28, 2003) was an American film and theatre director, producer, screenwriter and actor, described by ''The New York Times'' as "one o ...
. The American Film Institute
The American Film Institute (AFI) is an American nonprofit film organization that educates filmmakers and honors the heritage of the motion picture arts in the United States. AFI is supported by private funding and public membership fees.
Leade ...
ranked it the 8th-greatest American movie of all time in 1997 and 19th in 2007.
*Playwright Arthur Miller
Arthur Asher Miller (October 17, 1915 – February 10, 2005) was an American playwright, essayist and screenwriter in the 20th-century American theater. Among his most popular plays are '' All My Sons'' (1947), ''Death of a Salesman'' ( ...
was involved in the early stages of the development of ''On the Waterfront''; his play ''A View from the Bridge
''A View from the Bridge'' is a play by American playwright Arthur Miller. It was first staged on September 29, 1955, as a one-act verse drama with ''A Memory of Two Mondays'' at the Coronet Theatre on Broadway. The run was unsuccessful, and M ...
'' (1955) also deals with the troubled life of a longshoreman.
*In season 2 Season 2 may refer to:
* ''Season 2'' (Infinite album)
* '' 2econd Season''
See also
*
{{disambig ...
of the HBO
Home Box Office (HBO) is an American premium television network, which is the flagship property of namesake parent subsidiary Home Box Office, Inc., itself a unit owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The overall Home Box Office business unit is ba ...
series ''The Wire
''The Wire'' is an American Crime film, crime drama Television show, television series created and primarily written by author and former police reporter David Simon. The series was broadcast by the cable network HBO in the United States. ''The ...
'', which first aired in 2003, the Stevedore Union and its members working in Baltimore, particularly Frank Sobotka
Francis "Frank" Sobotka is a fictional character in of the HBO drama '' The Wire'', played by the actor Chris Bauer.
Plot
Frank is a respected Polish-American treasurer for the International Brotherhood of Stevedores at the Baltimore docks ...
, figure prominently in the second season's story.
* The American film ''Kill the Irishman
''Kill the Irishman'' is a 2011 American biographical crime film directed by Jonathan Hensleigh, and starring Ray Stevenson, Vincent D'Onofrio, Christopher Walken, and Val Kilmer. Written by Hensleigh and Jeremy Walters, it is based on the lif ...
'' (2011) features Ray Stevenson
George Raymond Stevenson (born 25 May 1964) is an actor from Northern Ireland. He is known for playing Dagonet in the film ''King Arthur'' (2004) and Titus Pullo in the BBC/HBO television series ''Rome'' (2005–2007). He has portrayed two Marv ...
as Danny Greene, head of the Longshoreman's Union.
* The tenth book of the webcomic ''Schlock Mercenary
''Schlock Mercenary'' is a comedic webcomic written and drawn by Howard Tayler. It follows the tribulations of a star-travelling mercenary company in a satiric, mildly dystopian 31st-century space opera setting. After its debut on June 12, 2000 ...
'', titled ''The Longshoreman of the Apocalypse'', features a robotic stevedore as a central character.
See also
*1913 Sligo Dock strike
The 1913 Sligo Dock strike in the port of Sligo in northwest Ireland was a labour dispute lasting 56 days from 8 March to 6 May 1913. During the strike, there were numerous clashes on the docks and riots in the town, resulting in one fatality.
Occ ...
*Admiralty law
Admiralty law or maritime law is a body of law that governs nautical issues and private maritime disputes. Admiralty law consists of both domestic law on maritime activities, and private international law governing the relationships between priva ...
*Battle of Ballantyne Pier
The Battle of Ballantyne Pier occurred in Ballantyne Pier during a docker's strike in Vancouver, British Columbia, in June 1935.
The strike can be traced back to 1912 when the International Longshoremen's Association (ILA), began organizing t ...
(Canada)
* Dockers' Union (UK) (disambiguation)
*Dunnage
Dunnage is inexpensive or waste material used to load and secure cargo during transportation; more loosely, it refers to miscellaneous baggage, brought along during travel. The term can also refer to low-priority cargo used to fill out transport ca ...
*Federated Ship Painters and Dockers Union
The Federated Ship Painters and Dockers Union (FSPDU) was an Australian trade union which existed between 1900 and 1993. It represented labourers in the shipbuilding industry, covering "mostly work associated with chipping, painting, scrubbing ...
* History of Squamish and Tsleil-Waututh longshoremen, 1863–1963
*International Longshore and Warehouse Union
The International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU) is a labor union which primarily represents dock workers on the West Coast of the United States, Hawaii, and in British Columbia, Canada. The union was established in 1937 after the 1934 Wes ...
(United States)
*Liverpool dockers' strike (1995–98)
Throughout the history of the Liverpool docks, known as Mersey Docks and Harbour Company, there have been numerous strike actions by dock workers, although some have been part of larger industrial action affecting other trades and union workers. Th ...
(UK)
*Mersey Docks and Harbour Company
The Mersey Docks and Harbour Company (MDHC), formerly the Mersey Docks and Harbour Board (MDHB), owns and administers the dock facilities of the Port of Liverpool, on the River Mersey, England. These include the operation of the enclosed nort ...
*Mudlark
A mudlark is someone who scavenges in river mud for items of value, a term used especially to describe those who scavenged this way in London during the late 18th and 19th centuries. The practice of searching the banks of rivers for items cont ...
*National Union of Dock Labourers
The National Union of Dock Labourers (NUDL) was a trade union in the United Kingdom which existed between 1889 and 1922.
History
It was formed in Glasgow in 1889 but moved its headquarters to Liverpool within a few years and was thereafter ...
*Scottish Union of Dock Labourers
The Scottish Union of Dock Labourers was a Glasgow-based trade union for waterfront workers. It was formed during the seamen's and dockers' strikes of June–July 1911. Locally, it replaced the National Union of Dock Labourers, which had been ...
*Teamster
A teamster is the American term for a truck driver or a person who drives teams of draft animals. Further, the term often refers to a member of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, a labor union in the United States and Canada.
Origi ...
*Weeks Marine
Weeks Marine is a marine construction and dredging contractor based in Cranford, NJ. It was founded by Francis Weeks and his son Richard B. Weeks in 1919 as the Weeks Stevedoring Company.
Company
Weeks has three key divisions—Construction, D ...
References
Further reading
* * * Callebert, Ralph (2017). ''On Durban's Docks: Zulu Workers, Rural Households, Global Labor''. University of Rochester Press. * * * * * * * * * *External links
"The Irish on the Docks of Portland" by Michael Connolly
{{Authority control Marine occupations Spanish words and phrases Polish-American culture in Baltimore Portuguese words and phrases