Long Range Reconnaissance Imager on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) is a telescope aboard the ''
Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) is a telescope aboard the ''
 LORRI was used to calculate
LORRI was used to calculate
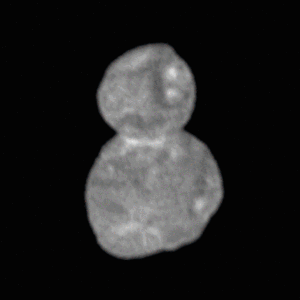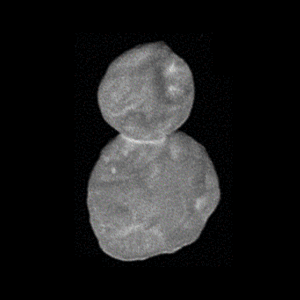
 In August 2018, LORRI was able to detect Arrokoth at distance of around .
A large stack of images of Arrokoth from August to December 2018 was used to confirm a closer flyby, rather than more distant by ruling out moons and rings systems to a certain level of detection.
On the night of December 24, 2018 LORRI was used to take images of Arrokoth at a distance of . Three images were taken each with a half second long exposure, at a 1024x1024 pixel resolution.
In August 2018, LORRI was able to detect Arrokoth at distance of around .
A large stack of images of Arrokoth from August to December 2018 was used to confirm a closer flyby, rather than more distant by ruling out moons and rings systems to a certain level of detection.
On the night of December 24, 2018 LORRI was used to take images of Arrokoth at a distance of . Three images were taken each with a half second long exposure, at a 1024x1024 pixel resolution.
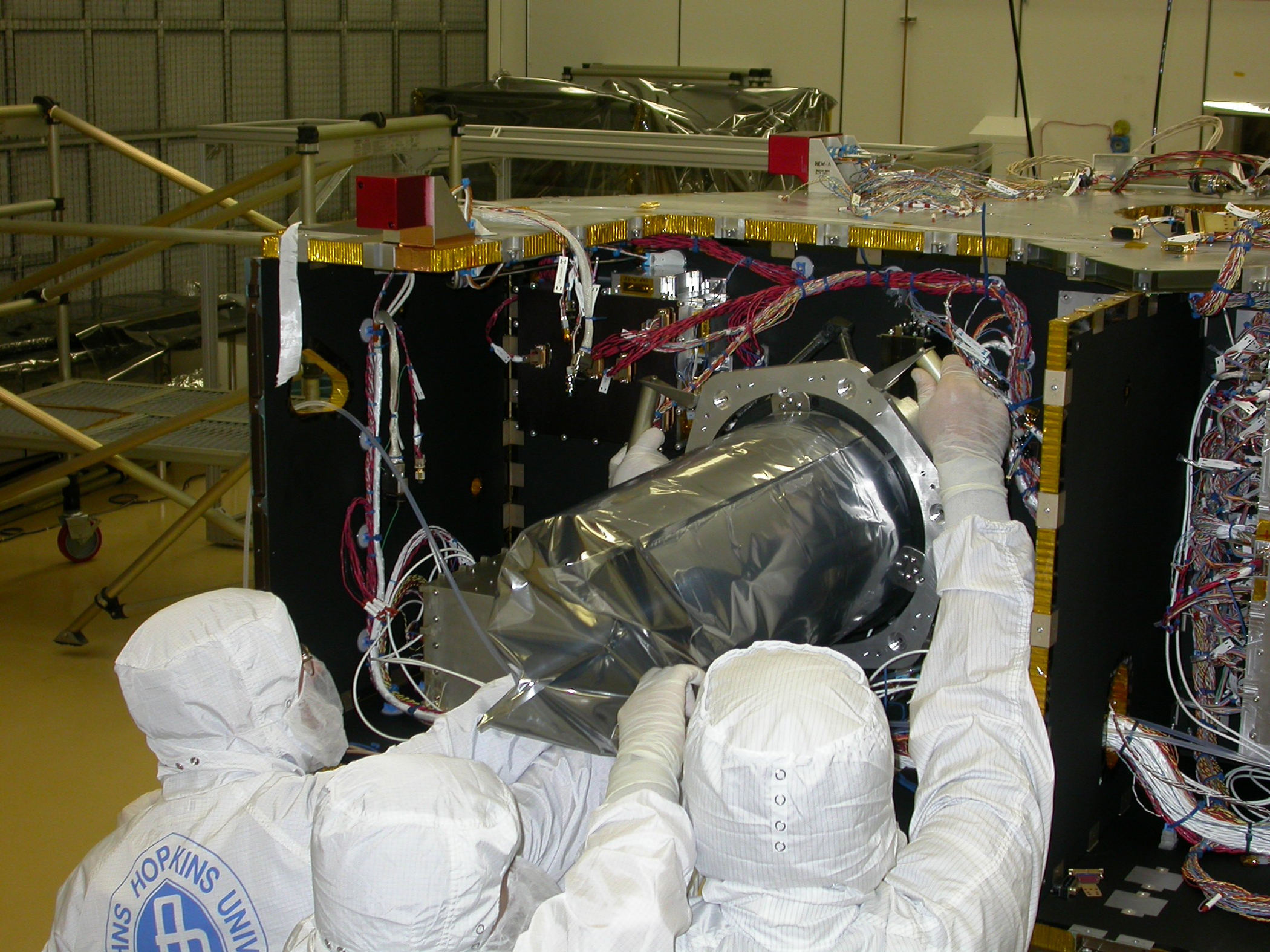 LORRI is a reflective telescope integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft. It can take greyscale images of astronomical targets.
Specifications:
*Telescope style: Ritchey-Chrétien
*Aperture: 208 mm (8.2 inches)
**f/12.6
**Effective
LORRI is a reflective telescope integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft. It can take greyscale images of astronomical targets.
Specifications:
*Telescope style: Ritchey-Chrétien
*Aperture: 208 mm (8.2 inches)
**f/12.6
**Effective







NASA LORRI gallery
* ttp://pluto.jhuapl.edu/soc/UltimaThule-Encounter/ LORRI imagesbr>NASA page showing Arrokoth picture comparing MVIC (lower resolution but color) and LORRI (greyscale but sharper), and a third image product combining the data
(January 2, 2019) {{Satellite and spacecraft instruments New Horizons Space imagers
 Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) is a telescope aboard the ''
Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) is a telescope aboard the ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' spacecraft for imaging. LORRI has been used to image Jupiter, its moons, Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
and its moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
, and Arrokoth since its launch in 2006. LORRI is a reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
of Ritchey-Chrétien design, and it has a main mirror diameter of 208 mm (8.2 inches) across. LORRI has a narrow field of view, less than a third of a degree. Images are taken with a CCD capturing data with 1024 × 1024 pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
s. LORRI is a telescopic panchromatic camera integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft, and it is one of seven major science instruments on the probe. LORRI does not have any moving parts and is pointed by moving the entire ''New Horizons'' spacecraft.
Operations
 LORRI was used to calculate
LORRI was used to calculate albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of sunlight, solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body ...
s for Pluto and Charon. LORRI is also used for navigation, especially to more precisely determine the location of a flyby target. In 2018, ''New Horizons'' spacecraft used navigation data from LORRI for its planned flyby of Arrokoth in a couple months.
During the cruise to Jupiter, LORRI data was also used to determine a value for the cosmic optical background as an alternative to other methods. At Jupiter, LORRI was used for an extensive observation campaign of Jupiter's atmosphere, rings, and moons.
On August 29, 2006, the cover on LORRI was opened and it took an image in space of Messier 7
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. The cluster is easily detectable with the naked eye, close to the "stinger" of Scorpius. With a d ...
(aka Ptolemy’s Cluster) for its first light image. The following year, in 2007 when it flew by Jupiter for its gravity assist, it was used to image Jupiter and its moons. LORRI also imaged the Jovian system in 2010 as part of an annual checkout confirming the operation of LORRI, taking pictures from a distance of about 16 AU.
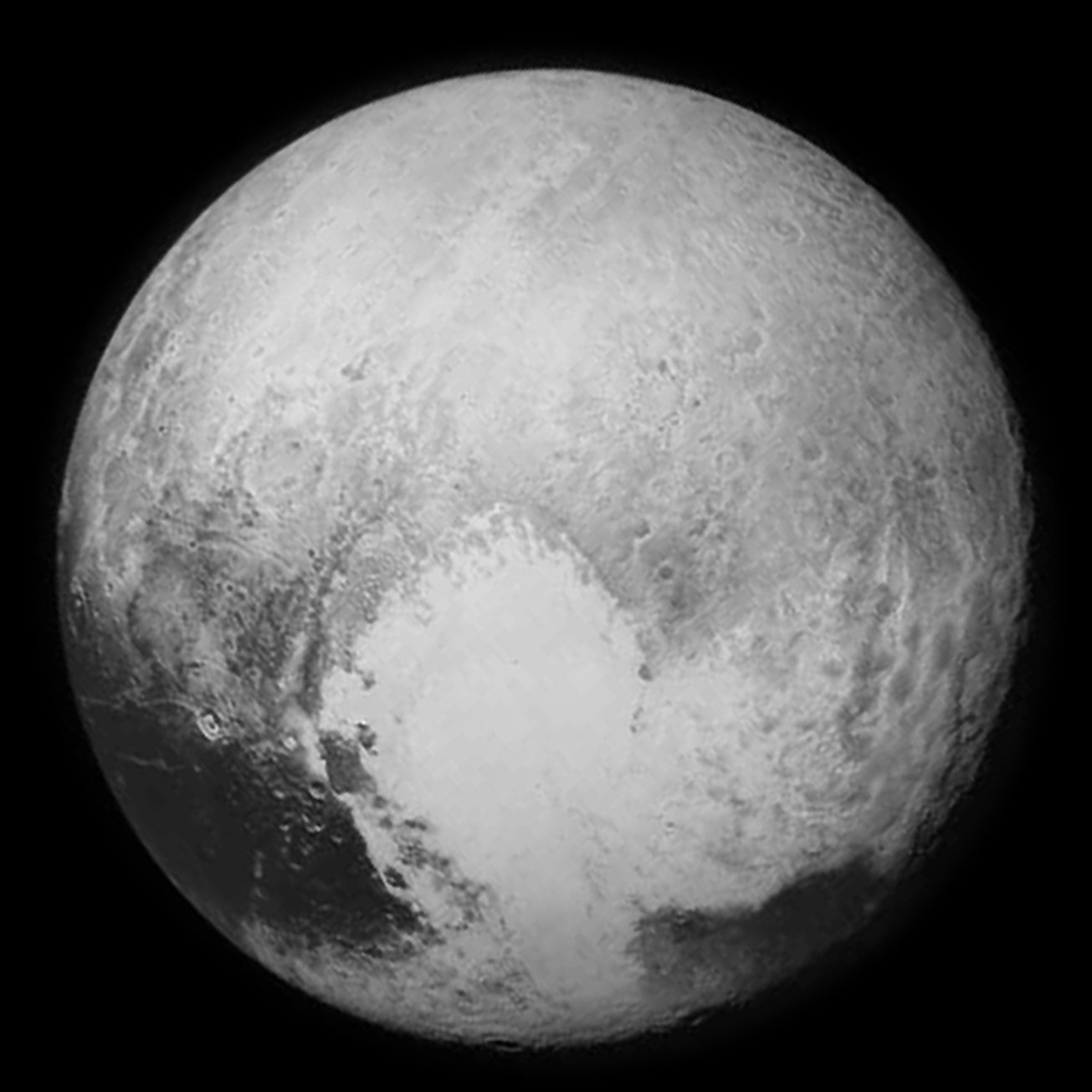
In 2015, LORRI was used to image Pluto before and during the flyby.
In December 2017, LORRI took an image at a greater distance from Earth than ''Pale Blue Dot
''Pale Blue Dot'' is a photograph of planet Earth taken on February 14, 1990, by the ''Voyager 1'' space probe from a record distance of about kilometers ( miles, 40.5 AU), as part of that day's ''Family Portrait'' series of images of the ...
'' by ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'', in this case of the Wishing Well Cluster. This cluster was also the first light image for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera
The Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WFPC) (pronounced as wiffpick (Operators of the WFPC1 were known as "whiff-pickers")) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope launched in April 1990 and operated until December 1993. It was one of ...
of the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
, taken in May 1990.First Image Taken by Hubble's Wide Field Planetary CameraHubblesite.org
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the ...
 In August 2018, LORRI was able to detect Arrokoth at distance of around .
A large stack of images of Arrokoth from August to December 2018 was used to confirm a closer flyby, rather than more distant by ruling out moons and rings systems to a certain level of detection.
On the night of December 24, 2018 LORRI was used to take images of Arrokoth at a distance of . Three images were taken each with a half second long exposure, at a 1024x1024 pixel resolution.
In August 2018, LORRI was able to detect Arrokoth at distance of around .
A large stack of images of Arrokoth from August to December 2018 was used to confirm a closer flyby, rather than more distant by ruling out moons and rings systems to a certain level of detection.
On the night of December 24, 2018 LORRI was used to take images of Arrokoth at a distance of . Three images were taken each with a half second long exposure, at a 1024x1024 pixel resolution.
Specifications
 LORRI is a reflective telescope integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft. It can take greyscale images of astronomical targets.
Specifications:
*Telescope style: Ritchey-Chrétien
*Aperture: 208 mm (8.2 inches)
**f/12.6
**Effective
LORRI is a reflective telescope integrated with the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft. It can take greyscale images of astronomical targets.
Specifications:
*Telescope style: Ritchey-Chrétien
*Aperture: 208 mm (8.2 inches)
**f/12.6
**Effective focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative foca ...
2630 mm (103.5 inches)
**Mirror substance: Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal sin ...
*Mass: 8.8 kilograms (19.4 pounds)
*Average electrical power use: 5.8 watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
s
*Field of View: 0.29 degrees
*Resolution: 4.95 μrad pixels
*Bandpass: from about 350 nm to 850 nm
*Operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
: 148K to 313K
*Sensor: E2V Technologies CCD47-20 and Analog Devices AD9807 ADC
** Frame-Transfer Back-Illuminated CCD
** Size: 13.3×13.3 mm
** Pixel size: 13×13 μm native size with 4×4 pixel on-chip binning possible
** 1024×1024 active pixels
** 12 bits ADC
The mirror is made of silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal sin ...
which helped support meeting the thermal requirements of the design.
The instrument is a thinned backside-illuminated charge-coupled device, and captures images at a resolution of 1024 by 1024 pixels, with a variety of exposure settings. LORRI can take one picture per second and store the picture digitally as a 12-bit image, with either lossless or lossy compression
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size ...
. (See also Data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
)
LORRI incorporates a field-flattening lens with three elements.
The design can take images at very low light levels required for the mission, including light levels 1/900 those of Earth when it is at Pluto. For the Arrokoth encounter the longest exposure time (up to ten seconds for the Pluto flyby) was increased. This was accomplished after the Pluto flyby by the team, to support taking images in even lower light levels.
After the Pluto flyby, exposure times of at least 30 seconds were made possible, which was also useful for taking reconnaissance images and enabling imaging down to a magnitude of 21.
LORRI is pointed by moving the entire spacecraft, which limits the exposure time. The spacecraft does not have reaction wheels and is stabilized by thrusters.
Jovian system
While passing by Jupiter in February 2007, the Jovian system was observed using LORRI and other instruments. LORRI views of theGalilean moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in December 1609 or January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupiter ...
:

Pluto
Due to its telescope power, LORRI was able to capture images of Pluto and its moons, offering the closer views as the spacecraft flew by the dwarf planet.
Charon

15810 Arawn
In 2016 ''New Horizons'' observed the Kuiper belt object,15810 Arawn
15810 Arawn, provisional designation , is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) from the inner regions of the Kuiper belt, approximately in diameter. It belongs to the plutinos, the largest class of resonant TNOs. It was named after Arawn, the ruler of ...
. It is the object that is pointed with an arrow.

486958 Arrokoth
Long-distance views


Approach views


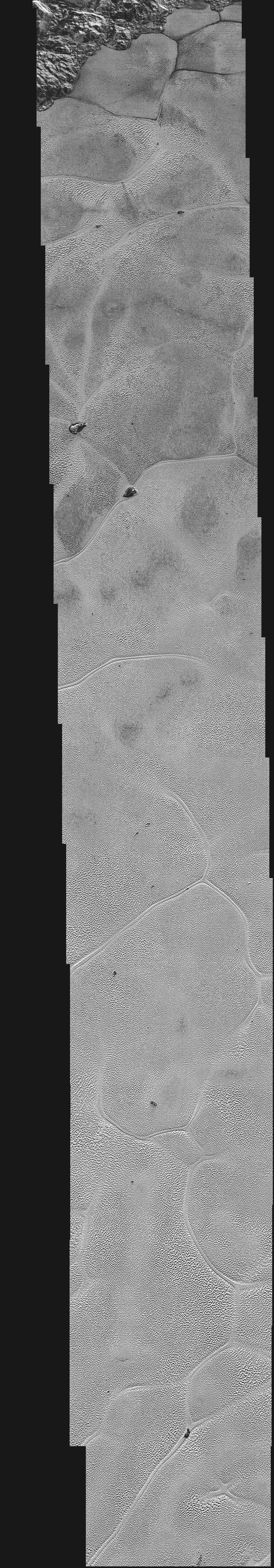
Closest views of Pluto flyby
Since LORRI had the highest magnification of the instruments, it captured the closest views of Pluto's terrain during the flyby. Its smaller field of view was panned across Pluto, capturing a stripe of the dwarf planet's terrain.
See also
*HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction o ...
*Mars Orbiter Camera
The Mars Orbiter Camera and Mars Observer Camera (MOC) were scientific instruments on board the Mars Observer and Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. The camera was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) for NASA and the cost of the whole MOC s ...
* List of ''New Horizons'' topics
* DART Spacecraft, using Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (DRACO) Imager, based on LORRI
*Lucy_(spacecraft)
''Lucy'' is a NASA space probe on a twelve-year journey to eight different asteroids, visiting a main belt asteroid as well as seven Jupiter trojans, asteroids which share Jupiter's orbit around the Sun, orbiting either ahead of or behind the ...
, using L'LORRI, based on LORRI
References
External links
*NASA LORRI gallery
* ttp://pluto.jhuapl.edu/soc/UltimaThule-Encounter/ LORRI imagesbr>NASA page showing Arrokoth picture comparing MVIC (lower resolution but color) and LORRI (greyscale but sharper), and a third image product combining the data
(January 2, 2019) {{Satellite and spacecraft instruments New Horizons Space imagers