Logico-linguistic Modeling on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Logico-linguistic modeling is a method for building knowledge-based systems with a learning capability using
Logical Soft Systems Modelling for Information Source Analysis - The Case of Hong Kong Telecom
Journal of the Operational Research Society, vol. 50 (2). Information
 The logico-linguistic modeling method comprises six stages.
The logico-linguistic modeling method comprises six stages.
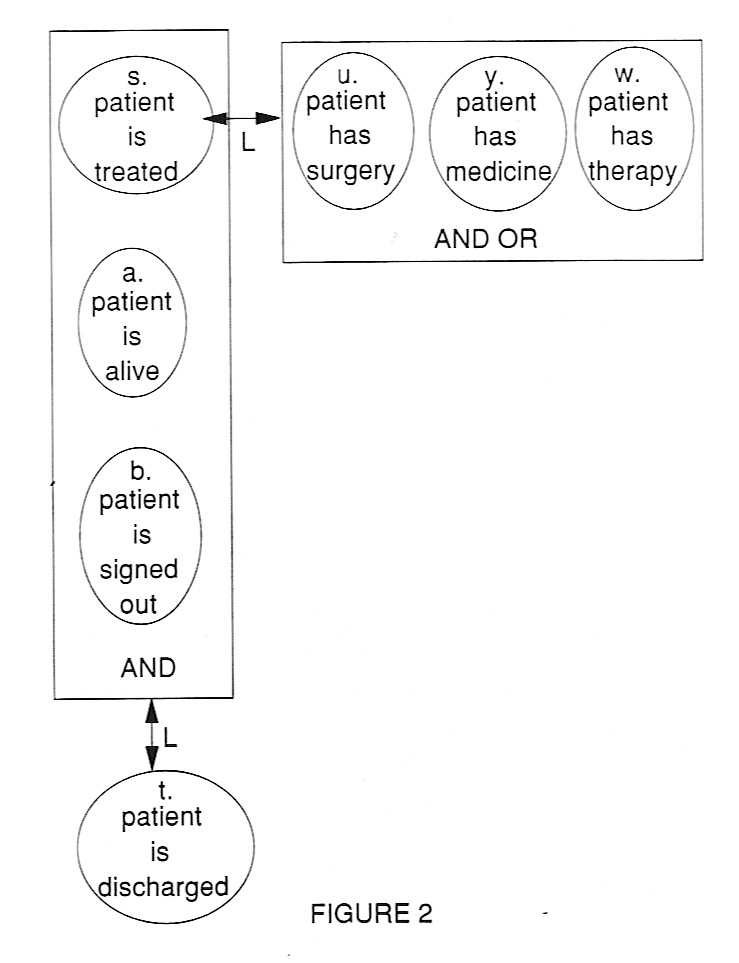 According to the theory behind logico-linguistic modeling the SSM conceptual model building process is a Wittgensteinian language-game in which the stakeholders build a language to describe the problem situation. The logico-linguistic model expresses this language as a set of definitions, see figure 2.
According to the theory behind logico-linguistic modeling the SSM conceptual model building process is a Wittgensteinian language-game in which the stakeholders build a language to describe the problem situation. The logico-linguistic model expresses this language as a set of definitions, see figure 2.
 Modal predicate logic (a combination of modal logic and
Modal predicate logic (a combination of modal logic and
Logical Soft Systems for Modeling Industrial Machinery Buying Decisions in Thailand
Doctor of Business Administration thesis, University of South Australia.
A logical analysis of soft systems modelling: implications for information system design and knowledge based system design
'. PhD thesis, University of Warwick. Knowledge representation Systems analysis Modal logic
conceptual model
A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, physical models are physical object such as a toy model that may be assem ...
s from soft systems methodology, modal predicate logic, and logic programming
Logic programming is a programming paradigm which is largely based on formal logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of log ...
languages such as Prolog
Prolog is a logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily a ...
.
Overview
Logico-linguistic modeling is a six-stage method developed primarily for building knowledge-based systems (KBS), but it also has application in manual decision support systems and information source analysis. Logico-linguistic models have a superficial similarity to John F. Sowa'sconceptual graphs
A conceptual graph (CG) is a formalism for knowledge representation. In the first published paper on CGs, John F. Sowa used them to represent the conceptual schemas used in database systems. The first book on CGs applied them to a wide range of t ...
; both use bubble style diagrams, both are concerned with concepts, both can be expressed in logic and both can be used in artificial intelligence. However, logico-linguistic models are very different in both logical form and in their method of construction.
Logico-linguistic modeling was developed in order to solve theoretical problems found in the soft systems method for information system design. The main thrust of the research into has been to show how soft systems methodology (SSM), a method of systems analysis, can be extended into artificial intelligence.
Background
SSM employs three modeling devices i.e. rich pictures, root definitions, and conceptual models of human activity systems. The root definitions and conceptual models are built by stakeholders themselves in an iterative debate organized by a facilitator. The strengths of this method lie, firstly, in its flexibility, the fact that it can address any problem situation, and, secondly, in the fact that the solution belongs to the people in the organization and is not imposed by an outside analyst.Gregory, Frank Hutson and Lau, Sui Pong (1999Logical Soft Systems Modelling for Information Source Analysis - The Case of Hong Kong Telecom
Journal of the Operational Research Society, vol. 50 (2). Information
requirements analysis
In systems engineering and software engineering, requirements analysis focuses on the tasks that determine the needs or conditions to meet the new or altered product or project, taking account of the possibly conflicting requirements of the ...
(IRA) took the basic SSM method a stage further and showed how the conceptual models could be developed into a detailed information system design.Wilson, Brian ''Systems: Concepts, Methodologies and Applications'', John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 1984, 1990. IRA calls for the addition of two modeling devices: "Information Categories", which show the required information inputs and outputs from the activities identified in an expanded conceptual model; and the "Maltese Cross", a matrix which shows the inputs and outputs from the information categories and shows where new information processing procedures are required. A completed Maltese Cross is sufficient for the detailed design of a transaction processing system.
The initial impetus to the development of logico-linguistic modeling was a concern with the theoretical problem of how an information system can have a connection to the physical world. This is a problem in both IRA and more established methods (such as SSADM) because none base their information system design on models of the physical world. IRA designs are based on a notional conceptual model and SSADM is based on models of the movement of documents.
The solution to these problems provided a formula that was not limited to the design of transaction processing systems but could be used for the design of KBS with learning capability.Gregory, Frank Hutson (1993) SSM for Knowledge Elicitation & Representation, Warwick Business School Research Paper No. 98. Later published in the ''Journal of the Operational Research Society'' (1995) 46, 562-578.
The six stages of logico-linguistic modeling
 The logico-linguistic modeling method comprises six stages.
The logico-linguistic modeling method comprises six stages.
1. Systems analysis
In the first stage logico-linguistic modeling uses SSM forsystems analysis
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees system analysis as a problem-solving technique tha ...
. This stage seeks to structure the problem in the client organization by identifying stakeholders, modelling organizational objectives and discussing possible solutions. At this stage it not assumed that a KBS will be a solution and logico-linguistic modeling often produces solutions that do not require a computerized KBS.
Expert systems
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if� ...
tend to capture the expertise, of individuals in different organizations, on the same topic. By contrast a KBS, produced by logico-linguistic modeling, seeks to capture the expertise of individuals in the same organization on different topics. The emphasis is on the elicitation of organizational or group knowledge rather than individual experts. In logico-linguistic modeling the stakeholders become the experts.
The end point of this stage is an SSM style conceptual models such as figure 1.
2. Language creation
 According to the theory behind logico-linguistic modeling the SSM conceptual model building process is a Wittgensteinian language-game in which the stakeholders build a language to describe the problem situation. The logico-linguistic model expresses this language as a set of definitions, see figure 2.
According to the theory behind logico-linguistic modeling the SSM conceptual model building process is a Wittgensteinian language-game in which the stakeholders build a language to describe the problem situation. The logico-linguistic model expresses this language as a set of definitions, see figure 2.
3. Knowledge elicitation
After the model of the language has been built putative knowledge about the real world can be added by the stakeholders. Traditional SSM conceptual models contain only one logical connective (a necessary condition). In order to represent causal sequences, "sufficient condition
In logic and mathematics, necessity and sufficiency are terms used to describe a conditional or implicational relationship between two statements. For example, in the conditional statement: "If then ", is necessary for , because the truth of ...
s" and "necessary and sufficient condition
In logic and mathematics, necessity and sufficiency are terms used to describe a conditional or implicational relationship between two statements. For example, in the conditional statement: "If then ", is necessary for , because the truth of ...
s" are also required.Gregory, Frank Hutson (1992) Cause, Effect, Efficiency & Soft Systems Models. Warwick Business School Research Paper No. 42. Later published in Journal of the Operational Research Society (1993) 44 (4), pp 149-168 In logico-linguistic modeling this deficiency is remedied by two addition types of connective. The outcome of stage three is an empirical model, see figure 3.
4. Knowledge representation
 Modal predicate logic (a combination of modal logic and
Modal predicate logic (a combination of modal logic and predicate logic
First-order logic—also known as predicate logic, quantificational logic, and first-order predicate calculus—is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quanti ...
) is used as the formal method of knowledge representation. The connectives from the language model are logically true (indicated by the "''L''" modal operator) and connective added at the knowledge elicitation stage are possibility true (indicated by the "''M''" modal operator). Before proceeding to stage 5, the models are expressed in logical formulae.
5. Computer code
Formulae in predicate logic translate easily into theProlog
Prolog is a logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily a ...
artificial intelligence language. The modality is expressed by two different types of Prolog rules. Rules taken from the language creation stage of model building process are treated as incorrigible. While rules from the knowledge elicitation stage are marked as hypothetical rules. The system is not confined to decision support but has a built in learning capability.
6. Verification
A knowledge based system built using this method verifies itself. Verification takes place when the KBS is used by the clients. It is an ongoing process that continues throughout the life of the system. If the stakeholder beliefs about the real world are mistaken this will be brought out by the addition of Prolog facts that conflict with the hypothetical rules. It operates in accordance to the classic principle offalsifiability
Falsifiability is a standard of evaluation of scientific theories and hypotheses that was introduced by the Philosophy of science, philosopher of science Karl Popper in his book ''The Logic of Scientific Discovery'' (1934). He proposed it as t ...
found in the philosophy of science
Applications
Knowledge-based computer systems
Logico-linguistic modeling has been used to produce fully operational computerized knowledge based systems, such as one for the management of diabetes patients in a hospital out-patients department.Manual decision support
In other projects the need to move into Prolog was considered unnecessary because the printed logico-linguistic models provided an easy to use guide to decision making. For example, a system for mortgage loan approvalInformation source analysis
In some cases a KBS could not be built because the organization did not have all the knowledge needed to support all their activities. In these cases logico-linguistic modeling showed shortcomings in the supply of information and where more was needed. For example, a planning department in a telecoms companyCriticism
While logico-linguistic modeling overcomes the problems found in SSM's transition from conceptual model to computer code, it does so at the expense of increased stakeholder constructed model complexity. The benefits of this complexity are questionable and this modeling method may be much harder to use than other methods. This contention has been exemplified by subsequent research. An attempt by researchers to model buying decisions across twelve companies using logico-linguistic modeling required simplification of the models and removal of the modal elements.Nakswasdi, Suravut (2004Logical Soft Systems for Modeling Industrial Machinery Buying Decisions in Thailand
Doctor of Business Administration thesis, University of South Australia.
See also
* Argumented map *Cognitive map
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. ...
* Concept map
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge.
A conc ...
* Fuzzy cognitive map
* Knowledge representation and reasoning
Knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR, KR&R, KR²) is the field of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex tasks such as diagnosing a medic ...
* Semantic network
A semantic network, or frame network is a knowledge base that represents semantic relations between concepts in a network. This is often used as a form of knowledge representation. It is a directed or undirected graph consisting of vertices ...
References
Further reading
{{commons category * Gregory, Frank Hutson (1993)A logical analysis of soft systems modelling: implications for information system design and knowledge based system design
'. PhD thesis, University of Warwick. Knowledge representation Systems analysis Modal logic