Locomobile Company of America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Locomobile Company of America was a pioneering American automobile manufacturer founded in 1899, and known for its dedication to precision before the assembly-line era. It was one of the earliest car manufacturers in the advent of the automobile age. For the first two years after its founding, the company was located in

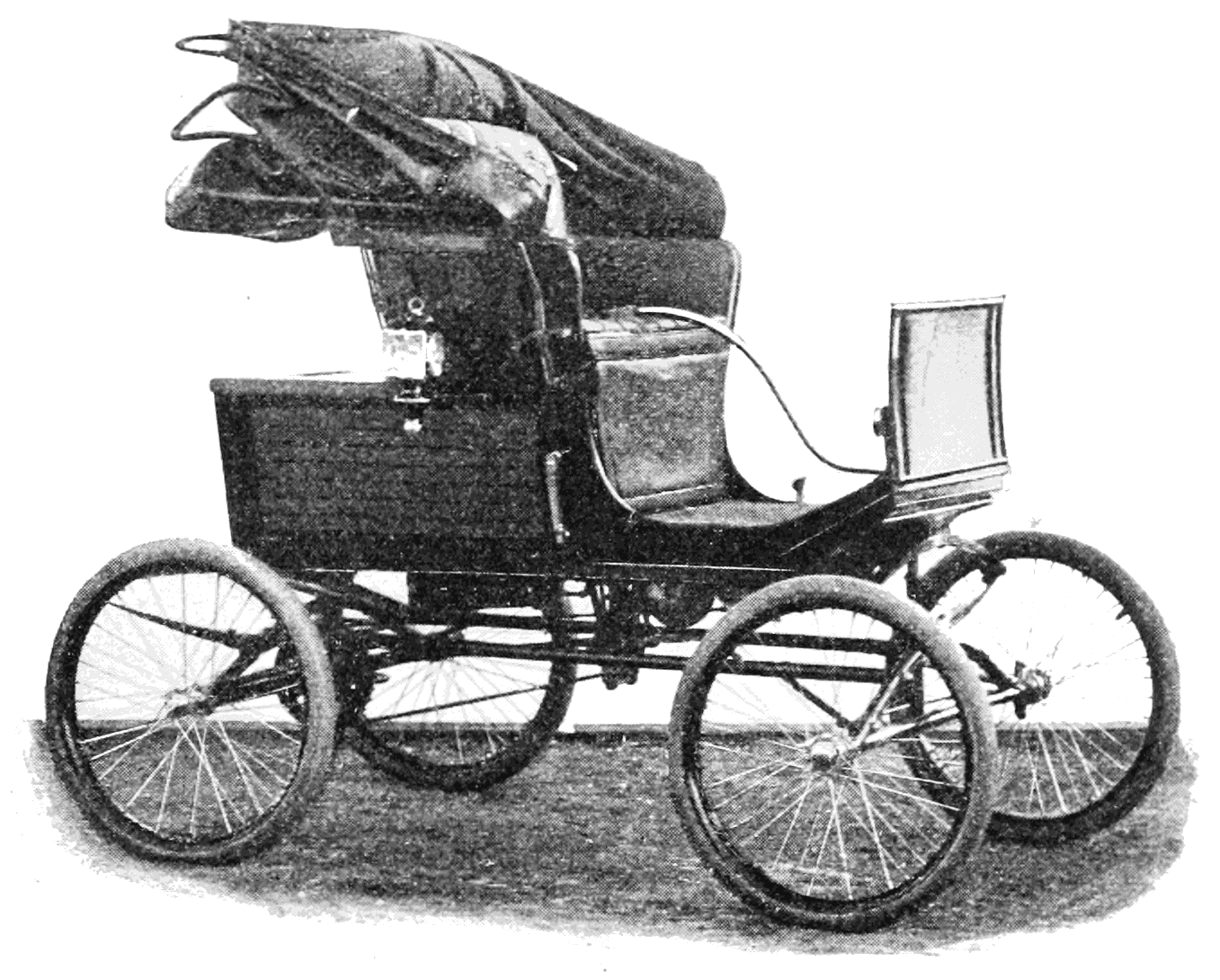
 The Locomobile Company of America was founded in 1899, the name coined from " locomotive" and "automobile". John B. Walker, editor and publisher of '' Cosmopolitan'', bought the plans for an early steam-powered vehicle produced by
The Locomobile Company of America was founded in 1899, the name coined from " locomotive" and "automobile". John B. Walker, editor and publisher of '' Cosmopolitan'', bought the plans for an early steam-powered vehicle produced by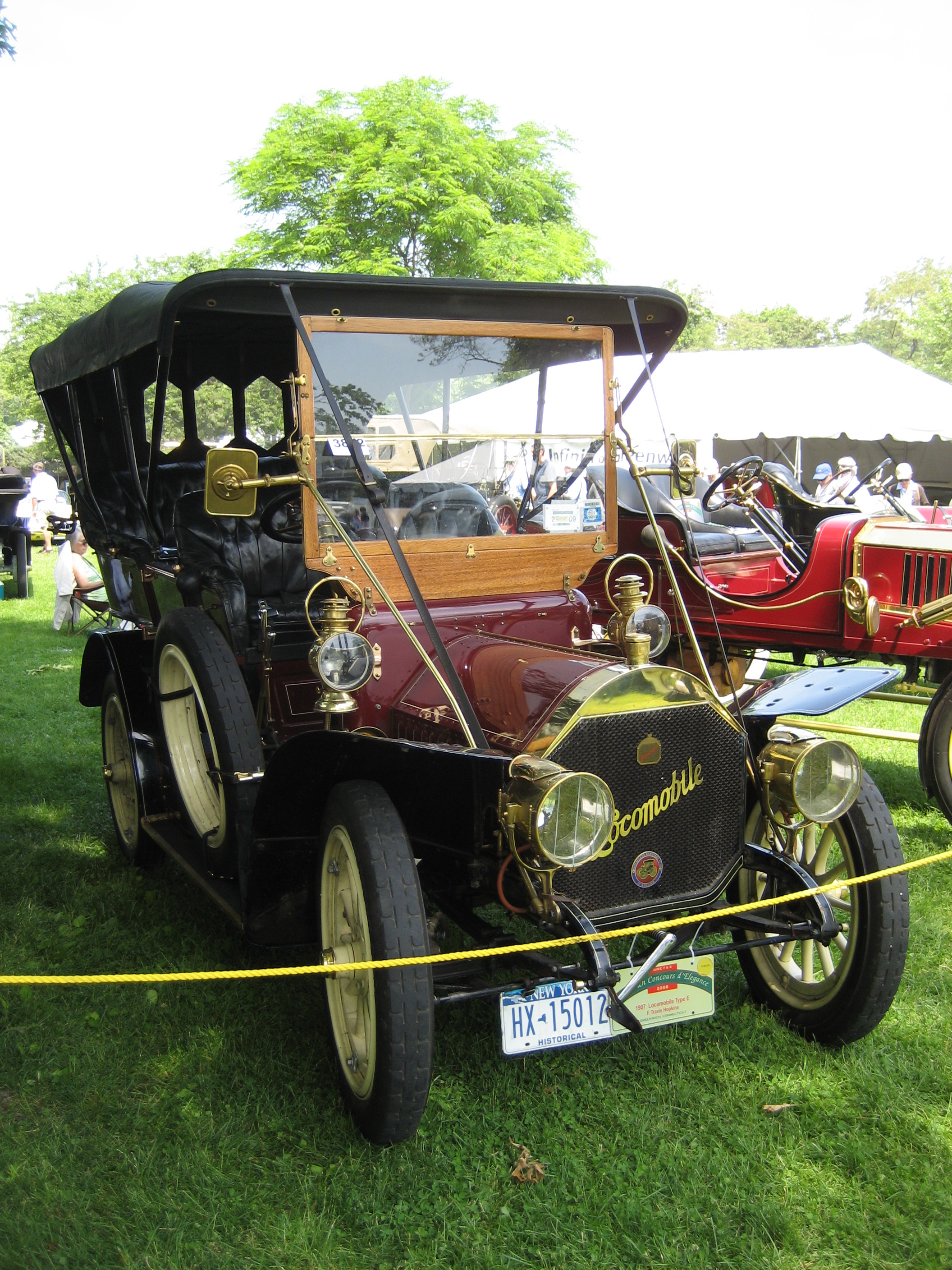  Locomobile began by producing steam cars. The steam Locomobiles were unreliable, finicky to operate, prone to
Locomobile began by producing steam cars. The steam Locomobiles were unreliable, finicky to operate, prone to  During the
During the
Old 16 Locomobile
(VanderbiltCupRaces.com)
The story of the 1908 Vanderbilt Cup win
Locomobile Catalog on DurantCars site
1920s Locomobiles
Locomobile items on Henry Ford Museum site
Locomobile Society Home Page
View the old locomobile ads
{{DEFAULTSORT:Locomobile Company Of America Brass Era vehicles Vintage vehicles Defunct motor vehicle manufacturers of the United States Luxury motor vehicle manufacturers Steam cars Durant Motors Companies based in Bridgeport, Connecticut 1899 establishments in Massachusetts Vehicle manufacturing companies established in 1899 American companies established in 1899 1890s cars 1900s cars 1910s cars 1920s cars Veteran vehicles Vehicle manufacturing companies disestablished in 1929 Cars introduced in 1899 Motor vehicle manufacturers based in Connecticut
Watertown, Massachusetts
Watertown is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, and is part of Greater Boston. The population was 35,329 in the 2020 census. Its neighborhoods include Bemis, Coolidge Square, East Watertown, Watertown Square, and the West End.
Watertow ...
. Production was transferred to Bridgeport, Connecticut, in 1900, where it remained until the company's demise in 1929. The company manufactured affordable, small steam car
A steam car is a car (automobile) propelled by a steam engine. A steam engine is an external combustion engine (ECE) in which the fuel is combusted outside of the engine, unlike an internal combustion engine (ICE) in which fuel is combusted in ...
s until 1903, when production switched entirely to internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
-powered luxury automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s. Locomobile was taken over in 1922 by Durant Motors
Durant Motors Inc. was established in 1921 by former General Motors CEO William "Billy" Durant following his termination by the GM board of directors and the New York bankers who financed GM.
Corporate relationships
Durant Motors attempted t ...
and eventually went out of business in 1929. All cars ever produced by the original company were always sold under the brand name Locomobile.
History


 The Locomobile Company of America was founded in 1899, the name coined from " locomotive" and "automobile". John B. Walker, editor and publisher of '' Cosmopolitan'', bought the plans for an early steam-powered vehicle produced by
The Locomobile Company of America was founded in 1899, the name coined from " locomotive" and "automobile". John B. Walker, editor and publisher of '' Cosmopolitan'', bought the plans for an early steam-powered vehicle produced by Francis
Francis may refer to:
People
*Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome
* Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Francis (surname)
Places
*Rural ...
and Freelan Stanley for a price they could not resist, US$250,000 (). At the time, one car had been built, and 199 more had been ordered. Walker promptly sold half of his interest to paving contractor Amzi L. Barber for the same price as he had purchased the entire company. Walker and Barber's partnership lasted two weeks. Walker went on to found Mobile Company of America
The Mobile Company of America was an American steam automobile manufacturer founded in 1899 by John Brisben Walker with production in Tarrytown, New York.
History
John Brisben Walker arranged the purchase of F. E. Stanley and F. O. Stanley's ...
at the Stanley works in Tarrytown, New York
Tarrytown is a village in the town of Greenburgh in Westchester County, New York. It is located on the eastern bank of the Hudson River, approximately north of Midtown Manhattan in New York City, and is served by a stop on the Metro-Nort ...
, while Barber moved house to Bridgeport, Connecticut, as Locomobile, where the Stanley twins were named general managers. The Stanley twins founded the Stanley Motor Carriage Company
The Stanley Motor Carriage Company was an American manufacturer of steam cars; it operated from 1902 to 1924. The cars made by the company were colloquially called Stanley Steamers, although several different models were produced.
Early history ...
in 1902, becoming the sharpest rival to Locomobile.
kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was reg ...
fires, had small water tanks (getting only per tank), and took time to raise steam; author Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British Raj, British India, which inspired much o ...
described one example as a "nickel-plated fraud". Initially, they were offered with a single body style only, an inexpensive runabout at $600 (). Nevertheless, they were a curiosity and middle-class Americans clamoured for the latest technology. Salesmen, doctors, and people needing quick mobility found them useful. More than 4,000 were built between 1899 and 1902.
In 1901, Locomobile offered seven body styles at prices between $600 () and $1,400 (). Most Locomobiles had simple twin-cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infi ...
engines (3x4 in, 76.2x102 mm; 57 in3, 927 cm3) and a wire-wrapped 300-psi boiler, and burned the liquid fuel naphtha
Naphtha ( or ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture.
Mixtures labelled ''naphtha'' have been produced from natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the distillation of coal tar and peat. In different industries and regions ...
to create steam. Typical of the product was the 1904 Runabout, which seated two passengers and sold for $750 (). The two-cylinder steam engine was situated amidships of the wood-framed car. By now, the car had improved boilers and a new water pump, manufactured by the Overman Wheel Company
Overman Wheel Company was an early bicycle manufacturing company in Chicopee Falls, Massachusetts from 1882 to 1900. It was known for bicycles of higher quality and lower weight than other bicycles of its time. Despite a nationwide bicycle craze ...
in Chicopee Falls, Massachusetts. This company itself built the Victor Steamer.
 During the
During the Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sout ...
, Locomobile did establish a new mark of sorts, becoming the first automobile to be used in war; it was a generator and searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a particular dir ...
tractor used to dismantle the Klein Nek minefield. Chin (1993), p. 49 It also served as a catering vehicle, with the useful ability (in British eyes, at least) of being able to brew a cup of tea by tapping the boiler.
This was, unfortunately, not a sure way to guarantee commercial success, even in Britain, and Locomobile started experimenting with gasoline internal combustion engines in 1902, starting with a four-cylinder, steel-chassis model designed by Andrew L. Riker. This encouraged the firm to drop steam vehicles the following year, selling the Stanley brothers back their rights for $20,000. In 1903, Barber relinquished his position to his son-in-law Samuel Todd Davis, Jr., who became President of the Locomobile Company. Chin (1993), p. 36
Switch to internal combustion engines
The 1904 internal combustion LocomobileTouring car
Touring car and tourer are both terms for open cars (i.e. cars without a fixed roof).
"Touring car" is a style of open car built in the United States which seats four or more people. The style was popular from the early 1900s to the 1930s.
Th ...
had a tonneau and space for five passengers, and sold for $4500, quite a change from the low-priced steam buggies. The front-mounted, vertical, water-cooled straight-four engine produced . A three-speed sliding transmission was used, as on the ''Système Panhard
In automotive design, a FR, or front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is one where the engine is located at the front of the vehicle and driven wheels are located at the rear via a drive shaft. This was the traditional automobile layout for mo ...
'' cars with which it competed. The angle steel-framed car weighed . The 1908 Locomobile 40 Runabout was a two-seater and sold for $4,750 (). On the strength of recent competition successes, Locomobile soon became known for well-built and speedy luxury cars.

In competition
Like other early marques, Locomobile enteredmotor racing
Motorsport, motorsports or motor sport is a global term used to encompass the group of competitive sporting events which primarily involve the use of motorized vehicles. The terminology can also be used to describe forms of competition of tw ...
, contesting the 1905 Gordon Bennett Cup with a racer; after suffering a transmission gear failure, and with no spare available, driver Joe Tracy
Joseph Tracy (March 22, 1873 – March 20, 1959) was an American racing driver.
Life and career
Tracy was born in Waterford, Ireland. A British subject, he emigrated to the United States at age 19, later becoming an American citizen.
Tracy ...
only managed two circuits of Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label= Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auve ...
before the transmission packed up entirely. Tracy did better for the company at the Vanderbilt Cup
The Vanderbilt Cup was the first major trophy in American auto racing.
History
An international event, it was founded by William Kissam Vanderbilt II in 1904 and first held on October 8 on a course set out in Nassau County on Long Island, ...
, placing third. A , F-head was damaged by tire trouble, so Tracy failed again in the 1906 Vanderbilt, but in 1908, George Robertson (wearing number 16) took the win in this car, ahead of fellow Locomobile pilot Joe Florida in third, becoming the first United States-built car to win in international competition. This was the high-water mark for Locomobile racing, and they soon faded from the scene, though Orin Davis did score a win in the Los Angeles– Phoenix rally
Rally or rallye may refer to:
Gatherings
* Demonstration (political), a political rally, a political demonstration of support or protest, march, or parade
* Pep rally, an event held at a United States school or college sporting event
Spor ...
in 1913. A Locomobile was raced by Genevra Delphine Mudge, believed to be the first female driving licence holder and first female racing driver. In 1925, the Locomobile team entered a front-wheel-drive Miller car called the "Junior Eight Special" after their recently introduced smaller car at the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly called the Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at Indianapolis Motor Speedway (IMS) in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of India ...
, but there was nothing Locomobile about it aside from the name.
Model 48 and the Durant years
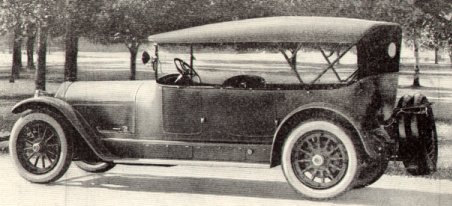
The most important model for the marque became the impressive Model 48. Introduced in 1911 as the "type M," it had a very conservative, perhaps dated, concept. It had a conventional but huge chassis with a wheelbase of . Its engine was a straight six with side valves; cylinders were still cast in pairs and it featured a nonremovable cylinder head. Displacement was , from a bore and stroke, giving it a 48.6-hp tax rating by the North American Chamber of Commerce. Chin (1993), p. 37 While called the "M" internally, this car is usually referred to by its tax hp rating. The brake horsepower rating was somewhere north of 90 for the original model, higher in the later versions. Quality of materials and workmanship were impeccable and among the best in the world. Chin (1993), p. 39 Such was also its pricing: A typical open-body cost about $10,000 when the average Model T Ford Phaeton cost about $300. Locomobile also offered custom designs for the lamps and metal work, carried out by Tiffany Studios. Until 1915, left- or right-hand drive could be specified; afterwards, left-hand drive became standard. Right-hand drive cars were meant for export and sat on a chassis four inches shorter. Around 1919, the engine was updated with a longer stroke, for displacement while retaining the same tax hp rating. A smaller "38 hp" model, very similar to the Model 48, was added in 1913. Chin (1993), p. 40 The model 38 has a , version of the T-head six and sits on a somewhat shorter wheelbase. By 1914, Locomobile had stopped selling all four-cylinder models to concentrate exclusively on sixes. In July 1922, Locomobile was acquired byDurant Motors
Durant Motors Inc. was established in 1921 by former General Motors CEO William "Billy" Durant following his termination by the GM board of directors and the New York bankers who financed GM.
Corporate relationships
Durant Motors attempted t ...
, which not only continued using the Locomobile brand name for their top-of-the-line autos until 1929, but also still produced the Model 48 until its demise in 1929. Until the mid-1920s, this car was Locomobile's only offering. In 1925, the marque brought out their first new model, the 8-66 Junior Eight, with a more contemporary straight-eight engine, and more importantly, a lower price of $1,785.
Introduction of the even smaller Junior Six was in 1926, but this car stayed only for one model year. The larger Model 90 that appeared in the same year was produced until 1929.
With the 8-70 of 1927, Locomobile added one more eight-cylinder car. Using an off the shelf Lycoming engine, this was not accepted as a true Locomobile in the marketplace and served to damage the company's reputation. Chin (1993), p. 45 In the following year, the Junior Eight 8-66 was phased out.
For 1929, a new 8-86 and 8-88 came out, but it was too late to save the company. Locomobile production ended in 1929.
Locomobile model specifications
* Locomobile Model 48 SportifLocomobiles in fiction
A Locomobile is the setting for one of the final scenes of F. Scott Fitzgerald's first novel, ''This Side of Paradise
''This Side of Paradise'' is the debut novel by American writer F. Scott Fitzgerald, published in 1920. It examines the lives and morality of carefree American youth at the dawn of the Jazz Age. Its protagonist, Amory Blaine, is an attractive ...
'', in which the protagonist, Amory Blaine, argues for socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
to the father of a college friend, who staunchly defends the capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, pri ...
ideal.
In the spring and summer of 1946, a seven-passenger 1911 Locomobile touring car was driven from Boston to Los Angeles and back as a promotional tour for the Columbia Pictures film '' Gallant Journey''. While not appearing in the movie, the Locomobile attracted much attention for the picture on the tour.
In Thomas Savage's 1967 novel ''The Power of the Dog'', set in the 1920s, the Locomobile is esteemed by protagonist Peter Gordon as a peer to the Pierce-Arrow: "... Those were the vehicles of the high and mighty, and he knew that only the Locomobile (fancied by old General Pershing, among others) rivaled the Pierce."
Clive Cussler
Clive Eric Cussler (July 15, 1931 – February 24, 2020) was an American adventure novelist and underwater explorer. His thriller novels, many featuring the character Dirk Pitt, have reached ''The New York Times'' fiction best-seller list ...
's 2007 novel, '' The Chase'', as well as his 2010 novel ''The Spy'', featured a 1906 Locomobile.
In Dashiell Hammett's 1925 mystery story "Scorched Face", the rich girls for whom the Continental Op is looking, were driving a Locomobile "with a special cabriolet body" when they disappeared.
Papa LaBas from Ishmael Reed's 1972 novel '' Mumbo Jumbo'' drives a Locomobile.
The Locomobile is central to the 2015 historical novel by Lisa Begin-Kruysman titled ''Around the World in 1909: Harriet White Fisher and Her Locomobile''. The novel is based on Harriet White Fisher
Harriet White Fisher Andrew was an American known for being the first woman to circle the globe in a Locomobile Company of America, Locomobile.
Birth and early life
Harriet White was born in Crawford County, Pennsylvania on March 31, 1861. She ...
's circumnavigation of the globe; the Locomobile is driven, hauled, pushed, and floated in places where no man, let alone woman, had yet explored, certainly not on wheels.
See also
*List of defunct United States automobile manufacturers
This is a list of defunct automobile manufacturers of the United States. They were discontinued for various reasons, such as bankruptcy of the parent company, mergers, or being phased out.
A
* A Automobile Company (1910–1913) 'Blue & Gold' ...
References
Further reading
* ''Frank Leslie's Popular Monthly'' (January 1904) * * * Ball, Donald L. ''The Genealogy of the Locomobile Steam Carriage, 1899–1904'', 1994 *External links
Old 16 Locomobile
(VanderbiltCupRaces.com)
The story of the 1908 Vanderbilt Cup win
Locomobile Catalog on DurantCars site
1920s Locomobiles
Locomobile items on Henry Ford Museum site
Locomobile Society Home Page
View the old locomobile ads
{{DEFAULTSORT:Locomobile Company Of America Brass Era vehicles Vintage vehicles Defunct motor vehicle manufacturers of the United States Luxury motor vehicle manufacturers Steam cars Durant Motors Companies based in Bridgeport, Connecticut 1899 establishments in Massachusetts Vehicle manufacturing companies established in 1899 American companies established in 1899 1890s cars 1900s cars 1910s cars 1920s cars Veteran vehicles Vehicle manufacturing companies disestablished in 1929 Cars introduced in 1899 Motor vehicle manufacturers based in Connecticut