lithograph on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Lithography () is a
Lithography () is a
Lithography
section of "Printmaking" article. ''Encyclopedia Britannica'' online. Accessed 23 November 2021. In modern commercial lithography, the image is transferred or created as a patterned
 Lithography works because of the mutual repulsion of oil and water. The image is drawn on the surface of the print plate with a fat or oil-based medium (hydrophobic) such as a
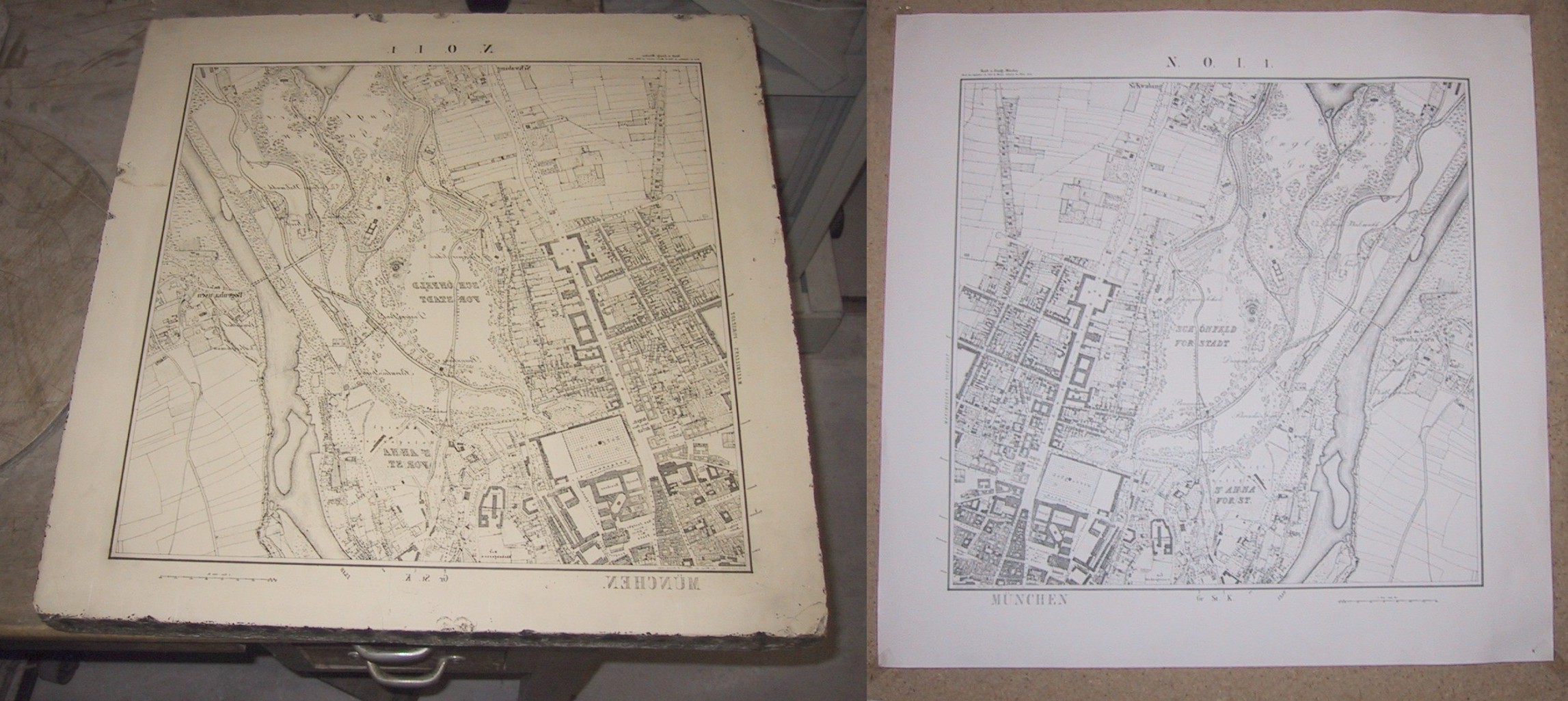
Lithography works because of the mutual repulsion of oil and water. The image is drawn on the surface of the print plate with a fat or oil-based medium (hydrophobic) such as a  "Lithography, or printing from soft stone, largely took the place of engraving in the production of English commercial maps after about 1852. It was a quick, cheap process and had been used to print British army maps during the
"Lithography, or printing from soft stone, largely took the place of engraving in the production of English commercial maps after about 1852. It was a quick, cheap process and had been used to print British army maps during the
 High-volume lithography is currently used to produce posters, maps, books, newspapers, and packaging—just about any smooth, mass-produced item with print and graphics on it. Most books, indeed all types of high-volume text, are now printed using offset lithography.
For offset lithography, which depends on photographic processes, flexible
High-volume lithography is currently used to produce posters, maps, books, newspapers, and packaging—just about any smooth, mass-produced item with print and graphics on it. Most books, indeed all types of high-volume text, are now printed using offset lithography.
For offset lithography, which depends on photographic processes, flexible 
 The plate is affixed to a cylinder on a printing press. Dampening rollers apply water, which covers the blank portions of the plate but is repelled by the emulsion of the image area. Hydrophobic ink, which is repelled by the water and only adheres to the emulsion of the image area, is then applied by the inking rollers.
If this image were transferred directly to paper, it would create a mirror-type image and the paper would become too wet. Instead, the plate rolls against a cylinder covered with a rubber ''blanket'', which squeezes away the water, picks up the ink and transfers it to the paper with uniform pressure. The paper passes between the blanket cylinder and a counter-pressure or impression cylinder and the image is transferred to the paper. Because the image is first transferred, or ''offset'' to the rubber blanket cylinder, this reproduction method is known as ''offset lithography'' or ''
The plate is affixed to a cylinder on a printing press. Dampening rollers apply water, which covers the blank portions of the plate but is repelled by the emulsion of the image area. Hydrophobic ink, which is repelled by the water and only adheres to the emulsion of the image area, is then applied by the inking rollers.
If this image were transferred directly to paper, it would create a mirror-type image and the paper would become too wet. Instead, the plate rolls against a cylinder covered with a rubber ''blanket'', which squeezes away the water, picks up the ink and transfers it to the paper with uniform pressure. The paper passes between the blanket cylinder and a counter-pressure or impression cylinder and the image is transferred to the paper. Because the image is first transferred, or ''offset'' to the rubber blanket cylinder, this reproduction method is known as ''offset lithography'' or '' This press is also called an ink pyramid because the ink is transferred through several layers of rollers with different purposes. Fast lithographic 'web' printing presses are commonly used in newspaper production.
The advent of
This press is also called an ink pyramid because the ink is transferred through several layers of rollers with different purposes. Fast lithographic 'web' printing presses are commonly used in newspaper production.
The advent of
 During the first years of the 19th century, lithography had only a limited effect on
During the first years of the 19th century, lithography had only a limited effect on
File:PhiladelphiaPresidentsHouse.jpg, ''Washington's Residence, High Street, Philadelphia'', 1830 lithograph by William L. Breton
File:Honoré Daumier, Hé! La chian..... li....li....li.....jpg, Hé! La chian..... li....li....li..... t's a blood...dy...dy...dy... mess lithograph of
About Lithography
* Twyman, Michael. ''Early Lithographed Books''. Pinner, Middlesex:
Museum of Modern Art information on printing techniques and examples of prints
The Invention of Lithography
Aloys Senefelder, (Eng. trans. 1911) (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
layered PDF
format)
Theo De Smedt's website, author of ''"What's lithography"''
Extensive information on Honoré Daumier and his life and work, including his entire output of lithographs
Digital work catalog to 4000 lithographs and 1000 wood engravings
* ttp://www.steendrukmuseum.nl Nederlands Steendrukmuseum* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100618221600/http://www.wesleyan.edu/dac/coll/grps/dela/faust_01-10.html Delacroix's ''Faust'' lithographs at the Davison Art Center, Wesleyan University
A brief historic overview of Lithography
University of Delaware Library. Includes citations for 19th century books using early lithographic illustrations.
Library Company of Philadelphia. Provides an historic overview of the commercial trade in Philadelphia and links to a biographical dictionary of over 500 Philadelphia lithographers and catalog of more than 1300 lithographs documenting Philadelphia.
Prints & People: A Social History of Printed Pictures
an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on lithography * Czech author o
lithography
{{Authority control 1796 introductions Communication design Graphic design Planographic printing Printmaking Visual arts media
 Lithography () is a
Lithography () is a planographic
Planographic printing means printing from a flat surface, as opposed to a raised surface (as with relief printing) or incised surface (as with intaglio printing). Lithography and offset lithography are planographic processes that rely on the p ...
method of printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ea ...
originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone
Lithographic limestone is hard limestone that is sufficiently fine-grained, homogeneous and defect free to be used for lithography.
Geologists use the term "lithographic texture" to refer to a grain size under 1/250 mm.
The term "sublithog ...
) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder
Johann Alois Senefelder (6 November 177126 February 1834) was a German actor and playwright who invented the printing technique of lithography in the 1790s.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. p 146
Acto ...
and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146 Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 11 Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography.
Originally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
plate. The stone was then treated with a mixture of weak acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a hydron (chemistry), proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The Dissociation (chemistry), dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively comple ...
and gum arabic
Gum arabic, also known as gum sudani, acacia gum, Arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum, Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum originally consisting of the hardened sap of two species of the ''Acacia'' tree, '' Senegalia se ...
("etch") that made the parts of the stone's surface that were not protected by the grease more hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are ...
(water attracting). For printing, the stone was first moistened. The water only adhered to the gum-treated parts, making them even more oil-repellant. An oil-based ink was then applied, and would stick only to the original drawing. The ink would finally be transferred to a blank paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed ...
sheet, producing a printed page. This traditional technique is still used for fine art
In European academic traditions, fine art is developed primarily for aesthetics or creative expression, distinguishing it from decorative art or applied art, which also has to serve some practical function, such as pottery or most metalwork ...
printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed techniq ...
.Peterdi, Gabor F. (2021):Lithography
section of "Printmaking" article. ''Encyclopedia Britannica'' online. Accessed 23 November 2021. In modern commercial lithography, the image is transferred or created as a patterned
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
coating applied to a flexible plastic or metal plate. The printing plates, whether stone or metal, can be created by a photographic
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed ...
process, a method that may be referred to as "photolithography" (although the term usually refers to a vaguely similar microelectronics manufacturing process). Offset printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on t ...
or "offset lithography" is an elaboration of lithography in which the ink is transferred from the plate to the paper by means of a rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
plate or cylinder, rather than by direct contact of the two. This technique keeps the paper dry and allows high speed fully automated operation. It has mostly replaced traditional lithography for medium- and high-volume printing: since the 1960s, most books and magazines, especially when illustrated in colour, are printed with offset lithography from photographically created metal plates.
As a printing technology, lithography is different from intaglio printing
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that ...
(gravure), wherein a plate is engraved
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an in ...
, etched, or stippled to score cavities to contain the printing ink; and woodblock printing
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, images or patterns used widely throughout East Asia and originating in China in antiquity as a method of printing on textiles and later paper. Each page or image is create ...
or letterpress
Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing. Using a printing press, the process allows many copies to be produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. A worker comp ...
printing, wherein ink is applied to the raised surfaces of letters or images.
The principle of lithography
Lithography uses simple chemical processes to create an image. For instance, the positive part of an image is a water-repelling ("hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ...
") substance, while the negative image would be water-retaining ("hydrophilic"). Thus, when the plate is introduced to a compatible printing ink and water mixture, the ink will adhere to the positive image and the water will clean the negative image. This allows a flat print plate to be used, enabling much longer and more detailed print runs than the older physical methods of printing (e.g., intaglio printing, letterpress printing).
Lithography was invented by Alois Senefelder in the Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German E ...
in 1796. In the early days of lithography, a smooth piece of limestone was used (hence the name "lithography": "lithos" () is the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
word for "stone"). After the oil-based image was put on the surface, a solution of gum arabic in water was applied, the gum sticking only to the non-oily surface. During printing, water adhered to the gum arabic surfaces and was repelled by the oily parts, while the oily ink used for printing did the opposite.
Lithography on limestone
 Lithography works because of the mutual repulsion of oil and water. The image is drawn on the surface of the print plate with a fat or oil-based medium (hydrophobic) such as a
Lithography works because of the mutual repulsion of oil and water. The image is drawn on the surface of the print plate with a fat or oil-based medium (hydrophobic) such as a wax crayon
A crayon (or wax pastel) is a stick of pigmented wax used for writing or drawing. Wax crayons differ from pastels, in which the pigment is mixed with a dry binder such as gum arabic, and from oil pastels, where the binder is a mixture of wax a ...
, which may be pigmented to make the drawing visible. A wide range of oil-based media is available, but the durability of the image on the stone depends on the lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
content of the material being used, and its ability to withstand water and acid. After the drawing of the image, an aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
of gum arabic
Gum arabic, also known as gum sudani, acacia gum, Arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum, Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum originally consisting of the hardened sap of two species of the ''Acacia'' tree, '' Senegalia se ...
, weakly acidified with nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
() is applied to the stone. The function of this solution is to create a hydrophilic layer of calcium nitrate
Calcium nitrate, also called ''Norgessalpeter'' (Norwegian salpeter), is an inorganic compound with the formula Ca(NO3)2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound, which is rarely encountered, absorbs moisture from the air to give the tetrahydrate. Both anhyd ...
salt, , and gum arabic on all non-image surfaces. The gum solution penetrates into the pores of the stone, completely surrounding the original image with a hydrophilic layer that will not accept the printing ink. Using lithographic turpentine
Turpentine (which is also called spirit of turpentine, oil of turpentine, terebenthene, terebinthine and (colloquially) turps) is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin harvested from living trees, mainly pines. Mainly used as a special ...
, the printer then removes any excess of the greasy drawing material, but a hydrophobic molecular film of it remains tightly bonded to the surface of the stone, rejecting the gum arabic and water, but ready to accept the oily ink.
When printing, the stone is kept wet with water. The water is naturally attracted to the layer of gum and salt created by the acid wash. Printing ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker ...
based on drying oils
A drying oil is an oil that hardens to a tough, solid film after a period of exposure to air, at room temperature. The oil hardens through a chemical reaction in which the components crosslink (and hence, polymerize) by the action of oxygen (not ...
such as linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colourless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
and varnish loaded with pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compo ...
is then rolled over the surface. The water repels the greasy ink but the hydrophobic areas left by the original drawing material accept it. When the hydrophobic image is loaded with ink, the stone and paper are run through a press that applies even pressure over the surface, transferring the ink to the paper and off the stone.
Senefelder had experimented during the early 19th century with multicolor lithography; in his 1819 book, he predicted that the process would eventually be perfected and used to reproduce paintings. Multi-color printing was introduced by a new process developed by Godefroy Engelmann
Godefroy Engelmann (August 17, 1788 – April 25, 1839) was a Franco-German lithographer and chromolithographer.
Biography
Godefroy Engelmann was born in 1788 in Mulhouse, Mühlhausen, a small town near the France/Switzerland/Germany border. At ...
(France) in 1837 known as chromolithography
Chromolithography is a method for making multi-colour prints. This type of colour printing stemmed from the process of lithography, and includes all types of lithography that are printed in colour. When chromolithography is used to reproduce ph ...
. A separate stone was used for each color, and a print went through the press separately for each stone. The main challenge was to keep the images aligned ('' in register''). This method lent itself to images consisting of large areas of flat color, and resulted in the characteristic poster designs of this period.
 "Lithography, or printing from soft stone, largely took the place of engraving in the production of English commercial maps after about 1852. It was a quick, cheap process and had been used to print British army maps during the
"Lithography, or printing from soft stone, largely took the place of engraving in the production of English commercial maps after about 1852. It was a quick, cheap process and had been used to print British army maps during the Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain ...
. Most of the commercial maps of the second half of the 19th century were lithographed and unattractive, though accurate enough."
Modern lithographic process
 High-volume lithography is currently used to produce posters, maps, books, newspapers, and packaging—just about any smooth, mass-produced item with print and graphics on it. Most books, indeed all types of high-volume text, are now printed using offset lithography.
For offset lithography, which depends on photographic processes, flexible
High-volume lithography is currently used to produce posters, maps, books, newspapers, and packaging—just about any smooth, mass-produced item with print and graphics on it. Most books, indeed all types of high-volume text, are now printed using offset lithography.
For offset lithography, which depends on photographic processes, flexible aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
, polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
, mylar
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aro ...
or paper printing plates are used instead of stone tablets. Modern printing plates have a brushed or roughened texture and are covered with a photosensitive emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Althoug ...
. A photographic negative
In photography, a negative is an image, usually on a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film, in which the lightest areas of the photographed subject appear darkest and the darkest areas appear lightest. This reversed order occurs because th ...
of the desired image is placed in contact with the emulsion and the plate is exposed to ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
. After development, the emulsion shows a reverse of the negative image, which is thus a duplicate of the original (positive) image. The image on the plate emulsion can also be created by direct laser imaging in a CTP (computer-to-plate Computer-to-plate (CTP) is an imaging technology used in modern printing processes. In this technology, an image created in a Desktop Publishing (DTP) application is output directly to a printing plate.
This compares with the older technology, co ...
) device known as a platesetter. The positive image is the emulsion that remains after imaging. Non-image portions of the emulsion have traditionally been removed by a chemical process, though in recent times, plates have become available that do not require such processing.

 The plate is affixed to a cylinder on a printing press. Dampening rollers apply water, which covers the blank portions of the plate but is repelled by the emulsion of the image area. Hydrophobic ink, which is repelled by the water and only adheres to the emulsion of the image area, is then applied by the inking rollers.
If this image were transferred directly to paper, it would create a mirror-type image and the paper would become too wet. Instead, the plate rolls against a cylinder covered with a rubber ''blanket'', which squeezes away the water, picks up the ink and transfers it to the paper with uniform pressure. The paper passes between the blanket cylinder and a counter-pressure or impression cylinder and the image is transferred to the paper. Because the image is first transferred, or ''offset'' to the rubber blanket cylinder, this reproduction method is known as ''offset lithography'' or ''
The plate is affixed to a cylinder on a printing press. Dampening rollers apply water, which covers the blank portions of the plate but is repelled by the emulsion of the image area. Hydrophobic ink, which is repelled by the water and only adheres to the emulsion of the image area, is then applied by the inking rollers.
If this image were transferred directly to paper, it would create a mirror-type image and the paper would become too wet. Instead, the plate rolls against a cylinder covered with a rubber ''blanket'', which squeezes away the water, picks up the ink and transfers it to the paper with uniform pressure. The paper passes between the blanket cylinder and a counter-pressure or impression cylinder and the image is transferred to the paper. Because the image is first transferred, or ''offset'' to the rubber blanket cylinder, this reproduction method is known as ''offset lithography'' or ''offset printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on t ...
''.
Many innovations and technical refinements have been made in printing processes and presses over the years, including the development of presses with multiple units (each containing one printing plate) that can print multi-color images in one pass on both sides of the sheet, and presses that accommodate continuous rolls (''webs'') of paper, known as web presses. Another innovation was the continuous dampening system first introduced by Dahlgren, instead of the old method (conventional dampening) which is still used on older presses, using rollers covered with molleton (cloth) that absorbs the water. This increased control of the water flow to the plate and allowed for better ink and water balance. Current dampening systems include a "delta effect or vario", which slows the roller in contact with the plate, thus creating a sweeping movement over the ink image to clean impurities known as "hickies".
 This press is also called an ink pyramid because the ink is transferred through several layers of rollers with different purposes. Fast lithographic 'web' printing presses are commonly used in newspaper production.
The advent of
This press is also called an ink pyramid because the ink is transferred through several layers of rollers with different purposes. Fast lithographic 'web' printing presses are commonly used in newspaper production.
The advent of desktop publishing
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using page layout software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online c ...
made it possible for type and images to be modified easily on personal computers for eventual printing by desktop or commercial presses. The development of digital imagesetters enabled print shops to produce negatives for platemaking directly from digital input, skipping the intermediate step of photographing an actual page layout. The development of the digital platesetter Computer-to-plate (CTP) is an imaging technology used in modern printing processes. In this technology, an image created in a Desktop Publishing (DTP) application is output directly to a printing plate.
This compares with the older technology, co ...
during the late 20th century eliminated film negatives altogether by exposing printing plates directly from digital input, a process known as computer-to-plate printing.
Lithography as an artistic medium
 During the first years of the 19th century, lithography had only a limited effect on
During the first years of the 19th century, lithography had only a limited effect on printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed techniq ...
, mainly because technical difficulties remained to be overcome. Germany was the main center of production in this period. Godefroy Engelmann
Godefroy Engelmann (August 17, 1788 – April 25, 1839) was a Franco-German lithographer and chromolithographer.
Biography
Godefroy Engelmann was born in 1788 in Mulhouse, Mühlhausen, a small town near the France/Switzerland/Germany border. At ...
, who moved his press from Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning ''Mill (grinding), mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin Departments of France, department, in the Grand Est Regions of France, region, eastern France, close to the France–Switzerl ...
to Paris in 1816, largely succeeded in resolving the technical problems, and during the 1820s lithography was adopted by artists such as Delacroix Delacroix is a French surname that derives from ''de la Croix'' ("of the Cross").
It may refer to:
People
* Caroline Delacroix (1883–1945), French-Romanian mistress of Leopold II of Belgium
* Charles-François Delacroix (1741–1805), ...
and Géricault. After early experiments such as ''Specimens of Polyautography'' (1803), which had experimental works by a number of British artists including Benjamin West
Benjamin West, (October 10, 1738 – March 11, 1820) was a British-American artist who painted famous historical scenes such as '' The Death of Nelson'', ''The Death of General Wolfe'', the '' Treaty of Paris'', and '' Benjamin Franklin Drawin ...
, Henry Fuseli
Henry Fuseli ( ; German: Johann Heinrich Füssli ; 7 February 1741 – 17 April 1825) was a Swiss painter, draughtsman and writer on art who spent much of his life in Britain. Many of his works, such as '' The Nightmare'', deal with supernatu ...
, James Barry, Thomas Barker of Bath
Thomas Barker or Barker of Bath (1769 – 11 December 1847), was a British painter of landscape and rural life.
Early life
Barker was born in 1769, at Trosnant near the village of Pontypool, in Monmouthshire. His father, Benjamin Barker, was the ...
, Thomas Stothard
Thomas Stothard (17 August 1755 – 27 April 1834) was an English painter, illustrator and engraver.
His son, Robert T. Stothard was a painter ( fl. 1810): he painted the proclamation outside York Minster of Queen Victoria's accession to the t ...
, Henry Richard Greville, Richard Cooper, Henry Singleton, and William Henry Pyne
William Henry Pyne (1769 in London – 29 May 1843 in London) was an English writer, illustrator and painter, who also wrote under the name of Ephraim Hardcastle. He trained at the drawing academy of Henry Pars in London. He first exhibited ...
, London also became a center, and some of Géricault's prints were in fact produced there. Goya
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and ...
in Bordeaux produced his last series of prints by lithography—''The Bulls of Bordeaux'' of 1828. By the mid-century the initial enthusiasm had somewhat diminished in both countries, although the use of lithography was increasingly favored for commercial applications, which included the prints of Daumier, published in newspapers. Rodolphe Bresdin
Rodolphe Bresdin was a French draughtsman and engraver, born in Le Fresne-sur-Loire on 12 August 1822, who died in Sèvres on 11 January 1885.
His fantastic works, full of strange details, particularly attracted Charles Baudelaire, Théophile G ...
and Jean-François Millet
Jean-François Millet (; 4 October 1814 – 20 January 1875) was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the Realism ...
also continued to practice the medium in France, and Adolph Menzel
Adolph Friedrich Erdmann von Menzel (8 December 18159 February 1905) was a German Realist artist noted for drawings, etchings, and paintings. Along with Caspar David Friedrich, he is considered one of the two most prominent German painters of t ...
in Germany. In 1862 the publisher Cadart tried to initiate a portfolio of lithographs by various artists, which was not successful but included several prints by Manet
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points ...
. The revival began during the 1870s, especially in France with artists such as Odilon Redon, Henri Fantin-Latour
Henri Fantin-Latour (14 January 1836 – 25 August 1904) was a French painter and lithographer best known for his flower paintings and group portraits of Parisian artists and writers.
Biography
He was born Ignace Henri Jean Théodore Fantin-La ...
and Degas
Edgar Degas (, ; born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, ; 19 July 183427 September 1917) was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Degas also produced bronze sculptures, prints and drawings. Degas is espec ...
producing much of their work in this manner. The need for strictly limited edition
Edition may refer to:
* Edition (book), a bibliographical term for a substantially similar set of copies
* Edition (printmaking), a publishing term for a set print run
* Edition (textual criticism), a particular version of a text
* Edition Recor ...
s to maintain the price had now been realized, and the medium became more accepted.
In the 1890s, color lithography gained success in part by the emergence of Jules Chéret
Jules Chéret (31 May 1836 – 23 September 1932) was a French painter and lithographer who became a master of ''Belle Époque'' poster art. He has been called the father of the modern poster.
Early life and career
Born in Paris to a poor but ...
, known as the ''father of the modern poster'', whose work went on to inspire a new generation of poster designers and painters, most notably Toulouse-Lautrec
Comte Henri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa (24 November 1864 – 9 September 1901) was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, caricaturist and illustrator whose immersion in the colourful and theatrical life of Paris in the l ...
, and former student of Chéret, Georges de Feure
Georges de Feure (real name Georges Joseph van Sluijters, 6 September 1868 – 26 November 1943) was a French painter, theatrical designer, and industrial art designer in the symbolism and Art Nouveau styles.
De Feure was born in Paris. His f ...
. By 1900 the medium in both color and monotone was an accepted part of printmaking.
During the 20th century, a group of artists, including Braque
Georges Braque ( , ; 13 May 1882 – 31 August 1963) was a major 20th-century List of French artists, French painter, Collage, collagist, Drawing, draughtsman, printmaker and sculpture, sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his all ...
, Calder, Chagall
Marc Chagall; russian: link=no, Марк Заха́рович Шага́л ; be, Марк Захаравіч Шагал . (born Moishe Shagal; 28 March 1985) was a Russian-French artist. An early modernism, modernist, he was associated with se ...
, Dufy, Léger, Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known prima ...
, Miró, and Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
, rediscovered the largely undeveloped artform of lithography thanks to the Mourlot Studios Mourlot Studios was a commercial print shop founded in 1852 by the Mourlot family and located in Paris, France. It was also known as Imprimerie Mourlot, Mourlot Freres and Atelier Mourlot. Founded by Francois Mourlot, it started off producing wallp ...
, also known as ''Atelier Mourlot'', a Parisian printshop founded in 1852 by the Mourlot family. The Atelier Mourlot originally specialized in the printing of wallpaper; but it was transformed when the founder's grandson, Fernand Mourlot
Fernand Mourlot (; 5 April 1895 – 4 December 1988), son of Jules Mourlot, was the director of Mourlot Studios and founder of Editions Mourlot.
Early life and career
Fernand Mourlot was born on 5 April 1895 in Paris, France. He was the si ...
, invited a number of 20th-century artists to explore the complexities of fine art printing. Mourlot encouraged the painters to work directly on lithographic stones in order to create original artworks that could then be executed under the direction of master printers in small editions. The combination of modern artist and master printer resulted in lithographs that were used as posters to promote the artists' work.
Grant Wood, George Bellows
George Wesley Bellows (August 12 or August 19, 1882 – January 8, 1925) was an American realism, American realist painting, painter, known for his bold depictions of urban life in New York City. He became, according to the Columbus Museum of Art ...
, Alphonse Mucha
Alfons Maria Mucha (; 24 July 1860 – 14 July 1939), known internationally as Alphonse Mucha, was a Czech painter, illustrator and graphic artist, living in Paris during the Art Nouveau period, best known for his distinctly stylized and decorat ...
, Max Kahn, Pablo Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
, Eleanor Coen
Eleanor Coen (October 21, 1916 – July 9, 2010) was an American painter.
Biography
Eleanor Coen was born October 21, 1916 in Normal, Illinois. Both a student (and later teacher) at the Art Institute of Chicago, Coen studied there with Bo ...
, Jasper Johns
Jasper Johns (born May 15, 1930) is an American painter, sculptor, and printmaker whose work is associated with abstract expressionism, Neo-Dada, and pop art. He is well known for his depictions of the American flag and other US-related top ...
, David Hockney
David Hockney (born 9 July 1937) is an English painter, draftsman, printmaker, stage designer, and photographer. As an important contributor to the pop art movement of the 1960s, he is considered one of the most influential British artists o ...
, Susan Dorothea White, and Robert Rauschenberg are a few of the artists who have produced most of their prints in the medium. M. C. Escher
Maurits Cornelis Escher (; 17 June 1898 – 27 March 1972) was a Dutch graphic artist who made mathematically inspired woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints.
Despite wide popular interest, Escher was for most of his life neglected in t ...
is considered a master of lithography, and many of his prints were created using this process. More than other printmaking techniques, printmakers in lithography still largely depend on access to good printer
Printer may refer to:
Technology
* Printer (publishing), a person or a company
* Printer (computing), a hardware device
* Optical printer for motion picture films
People
* Nariman Printer (fl. c. 1940), Indian journalist and activist
* James ...
s, and the development of the medium has been greatly influenced by when and where these have been established.
An American scene for lithography was founded by Robert Blackburn in New York City.
As a special form of lithography, the serilith or seriolithograph process is sometimes used. Seriliths are mixed-media original prints created in a process in which an artist uses the lithograph and serigraph
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink (or dye) onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh ...
(screen printing) Fine art prints of this type are published by numerous artists and publishers worldwide, and are widely accepted and collected. The separations for both processes are hand-drawn by the artist. The serilith technique is used primarily to create fine art limited print editions.
Gallery
Louis-Philippe of France
Louis Philippe (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850) was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France.
As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding troops during the Revolutionary War ...
by Honoré Daumier
Honoré-Victorin Daumier (; February 26, 1808February 10, 1879) was a French painter, sculptor, and printmaker, whose many works offer commentary on the social and political life in France, from the Revolution of 1830 to the fall of the second N ...
, 1834
File:Macrolepidoptera15seit 0215.jpg, Butterflies from Adalbert Seitz
Friedrich Joseph Adalbert Seitz, (24 February 1860 in Mainz – 5 March 1938 in Darmstadt) was a German physician and entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera. He was a director of the Frankfurt zoo from 1893 to 1908 and is best known for e ...
's ''Macrolepidoptera of the World'' (1923)
File:Tortilleras Nebel.jpg, An 1836 lithograph of Mexican women making tortilla
A tortilla (, ) is a thin, circular unleavened flatbread originally made from maize hominy meal, and now also from wheat flour. The Aztecs and other Nahuatl speakers called tortillas ''tlaxcalli'' (). First made by the indigenous peoples of Me ...
s by Carl Nebel
Carl Nebel (18 March 1805 – 4 June 1855) was a German engineer, architect and draughtsman,Thieme-Becker, entry "Nebel, Carl" best known for his detailed paintings and lithographic prints made from them of the Mexican landscape and people durin ...
File:Afghan royal soldiers of the Durrani Empire.jpg, Dourraunee chieftains in full armour, 1847
File:William Simpson - George Zobel - England and America. The visit of her majesty Queen Victoria to the Arctic ship Resolute - December 16th, 1856.jpg, Queen Victoria visits HMS ''Resolute'' - George Zobel after William Simpson (1859).
File:GeorgeLeybourne2.jpg, Alfred Concanen's 1867 design for '' Champagne Charlie''
File:Old Man with his Head in his Hands (At Eternity's Gate).jpg, '' At Eternity's Gate'', 1882 lithograph by Vincent van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter who posthumously became one of the most famous and influential figures in Western art history. In a decade, he created about 2 ...
File:Alexandre de Riquer - 3ra. Exposición de Bellas Artes é Industrias Artísticas - Google Art Project.jpg, 3ra. Exposición de Bellas Artes é Industrias Artísticas, 1896 lithograph by Alexandre de Riquer
File:Haeckel Actiniae.jpg, Sea anemones from Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new sp ...
's ''Kunstformen der Natur
(known in English as ''Art Forms in Nature'') is a book of lithographic and halftone prints by German biologist Ernst Haeckel.
...
'' (''Artforms of Nature''), 1904
File:Brooklyn Museum - In the Park, Light - George Wesley Bellows - overall.jpg, ''In the Park, Light'' – George Bellows
George Wesley Bellows (August 12 or August 19, 1882 – January 8, 1925) was an American realism, American realist painting, painter, known for his bold depictions of urban life in New York City. He became, according to the Columbus Museum of Art ...
1916
File:Jean-Baptiste Debret - Vista do Paço de São Cristovão.jpg, Palace of São Cristóvão, the former residence of the Emperors of Brazil, 19th-century lithograph by Jean-Baptiste Debret
Jean-Baptiste Debret (; 18 April 1768 – 28 June 1848) was a French painter, who produced many valuable lithographs depicting the people of Brazil. Debret won the second prize at the 1798 Salon des Beaux Arts.
Biography
Debret studied at th ...
See also
References
External links
About Lithography
* Twyman, Michael. ''Early Lithographed Books''. Pinner, Middlesex:
Private Libraries Association The Private Libraries Association (PLA) came into being in 1956 when 18-year-old Philip Ward wrote a letter to the ''Observer'' inviting booklovers and book collectors to attend a meeting to discuss the setting up of an association whose aims would ...
, 1990
Museum of Modern Art information on printing techniques and examples of prints
The Invention of Lithography
Aloys Senefelder, (Eng. trans. 1911) (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
DjVu
DjVu ( , like French "déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as ima ...
anlayered PDF
format)
Theo De Smedt's website, author of ''"What's lithography"''
Extensive information on Honoré Daumier and his life and work, including his entire output of lithographs
Digital work catalog to 4000 lithographs and 1000 wood engravings
* ttp://www.steendrukmuseum.nl Nederlands Steendrukmuseum* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100618221600/http://www.wesleyan.edu/dac/coll/grps/dela/faust_01-10.html Delacroix's ''Faust'' lithographs at the Davison Art Center, Wesleyan University
A brief historic overview of Lithography
University of Delaware Library. Includes citations for 19th century books using early lithographic illustrations.
Library Company of Philadelphia. Provides an historic overview of the commercial trade in Philadelphia and links to a biographical dictionary of over 500 Philadelphia lithographers and catalog of more than 1300 lithographs documenting Philadelphia.
Prints & People: A Social History of Printed Pictures
an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on lithography * Czech author o
lithography
{{Authority control 1796 introductions Communication design Graphic design Planographic printing Printmaking Visual arts media