List of states during the Middle Ages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
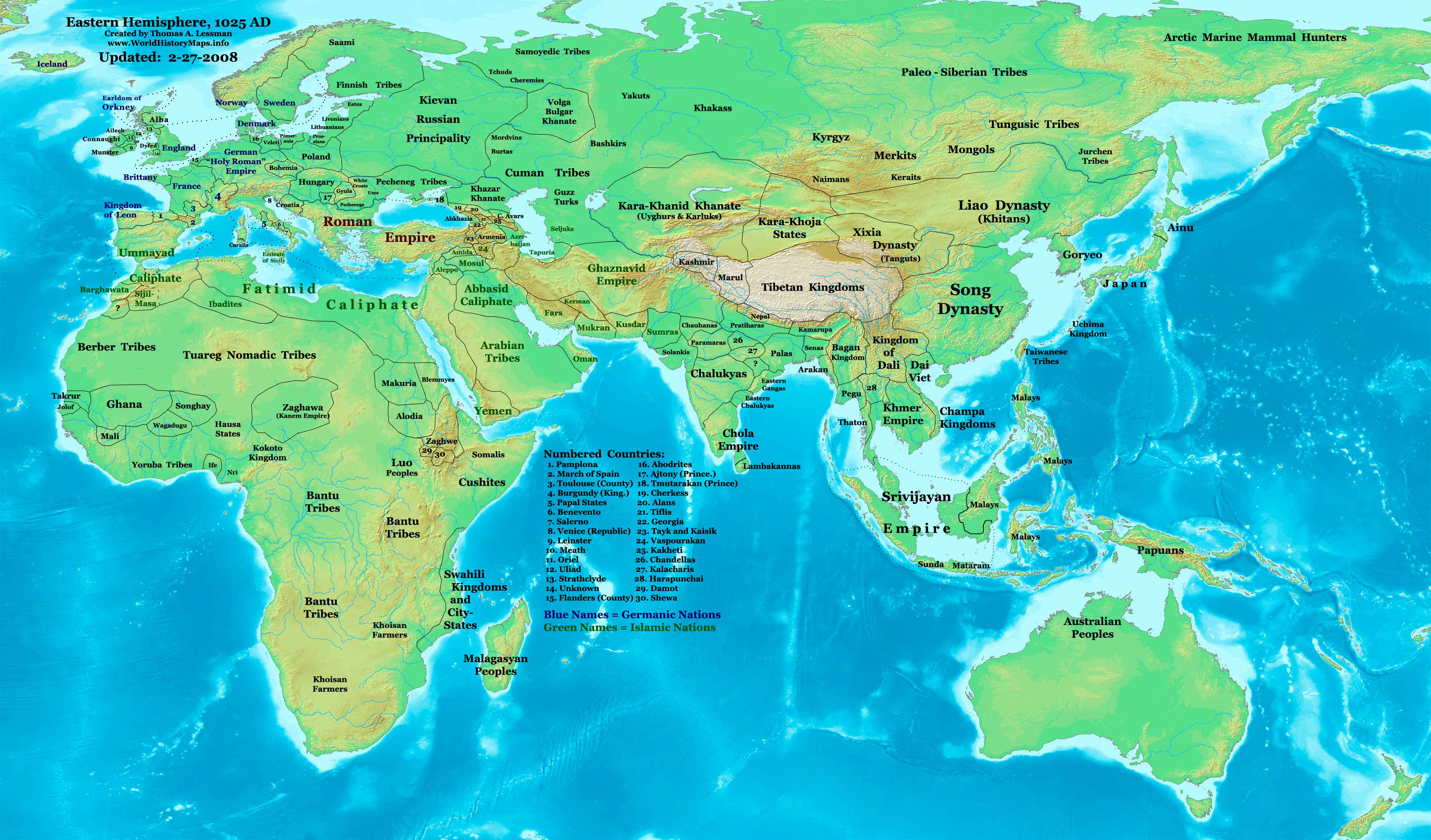


Post-classical history
In world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 AD to 1500, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and development of trade ...
(also called the post-classical era) is the period of time that immediately followed the end of ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200–600 and AD 1200–1500. The name of this era of history derives from classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
(or the Greco-Roman era) of Europe. Though, the everyday context in use is reverse (such as historians reference to Medieval China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
). In European history, "post-classical" is synonymous with the medieval time or Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the period of history from around the 5th century to the 15th century. It began with the collapse
Collapse or its variants may refer to:
Concepts
* Collapse (structural)
* Collapse (topology), a mathematical concept
* Collapsing manifold
* Collapse, the action of collapsing or telescoping objects
* Collapsing user interface elements
** ...
of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
and merged into the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
and the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: Antiquity, Medieval period, and Modern period. The Medieval period is itself subdivided into the early, high, and late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
.
Europe
North and West

South and East
Middle East and North Africa
Eurasian Steppe and Central Asia
East Asia

South and Southeast Asia
Sub-Saharan Africa

Pre-Columbian Americas
These are prehistoric states, listed either based on archaeological evidence or based on their existence at the time of European contact.See also
*List of Bronze Age states
The Bronze Age (c. 3300–1200 BC) marks the emergence of the first complex state societies, and by the Middle Bronze Age (mid-3rd millennium BC) the first empires.
This is a list of Bronze Age polities.
By the end of the Bronze Age, complex ...
(c. 3300–1200 BC)
* List of Iron Age states
The Iron Age is an archaeological age, the last of the three-age system of Old World prehistory.
It follows the Bronze Age, in the Ancient Near East beginning c. 1200 BC, and in Europe beginning
after c. 800 BC.
It is taken to end with the be ...
(c. 1200–600 BC)
* List of Classical Age states (c. 600 BC–200 AD)
* List of states during Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity is a historiographical term for the historical period from c. 200 AD to c. 700 AD, which marks the transition from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages. Precise boundaries for the period are a matter of debate, but historian ...
(c. 200–700)
* List of former sovereign states
A historical sovereign state is a Sovereign state, state that once existed, but has since been dissolved due to conflict, war, rebellion, annexation, or uprising. This page lists sovereign states, country, countries, nations, or empires that have c ...
* Timeline of the Middle Ages
The following is a timeline of major events in post-classical history from the 5th to 15th centuries, loosely corresponding to the Old World Middle Ages, intermediate between Late Antiquity and the early modern period.
Overview
This timet ...
* List of pre-modern great powers
The term "great power" has only been used in historiography and political science since the Congress of Vienna in 1815. Lord Castlereagh, the British Foreign Secretary, first used the term in its diplomatic context in 1814 in reference to the Trea ...
* List of pre-modern states
References
{{Types of state Lists of former countries States and territories established in the 1st millennium States and territories established in the 2nd millennium