List Of Solar System Objects Most Distant From The Sun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
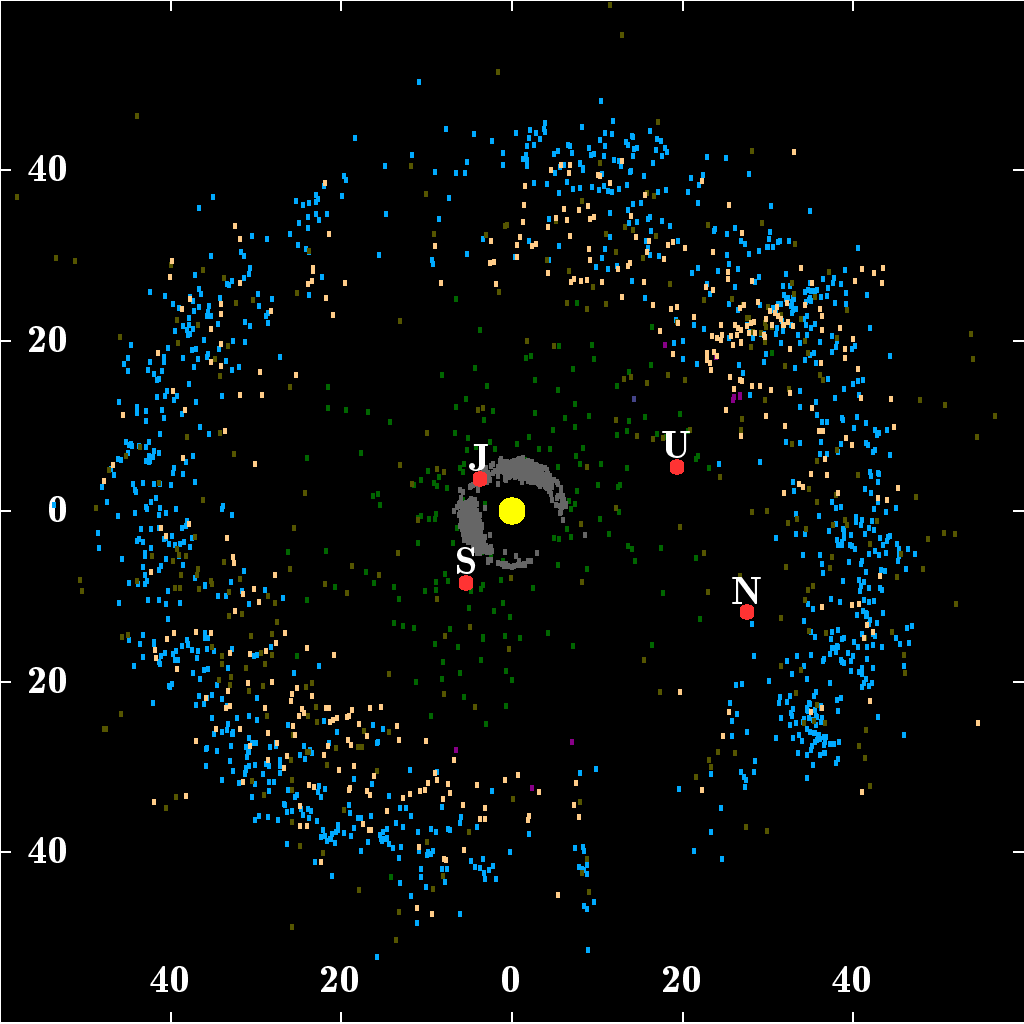 These
These
''Most Distant Object In Solar System Discovered''
NASA.gov; (2004) Sedna is the largest known
File:2018 AG37-orbit.png, Orbit diagram of , the furthest known Solar System object from the Sun as of 2022
File:Sednoid orbits.png, The orbits of the three known sednoids: 90377 Sedna, , and Leleākūhonua
File:Eris and dysnomia2.jpg, Eris and its moon Dysnomia as viewed with the
 These
These Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
minor planets are the furthest from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. The objects have been categorized by their approximate current distance from the Sun, and not by the calculated aphelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
of their orbit. The list changes over time because the objects are moving. Some objects are inbound and some are outbound. It would be difficult to detect long-distance comets if it were not for their comas, which become visible when heated by the Sun. Distances are measured in astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits t ...
s (AU, Sun–Earth distances). The distances are not the minimum (perihelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
) or the maximum (aphelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
) that may be achieved by these objects in the future.
This list does not include near-parabolic comets of which many are known to be currently more than from the Sun, but are currently too far away to be observed by telescope. Trans-Neptunian objects
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has a semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (au).
Typically, ...
are typically announced publicly months or years after their discovery, so as to make sure the orbit is correct before announcing it. Due to their greater distance from the Sun and slow movement across the sky, trans-Neptunian objects with observation arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly use ...
s less than several years often have poorly constrained orbits. Particularly distant objects take several years of observations to establish a crude orbit solution before being announced. For instance, the most distant known trans-Neptunian object was discovered by Scott Sheppard in January 2018 but was announced three years later in February 2021.
Noted objects
One particularly distant body is 90377 Sedna, which was discovered in November 2003. It has an extremely eccentric orbit that takes it to an aphelion of 937 AU. (Solution using the Solar Systembarycenter
In astronomy, the barycenter (or barycentre; ) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that orbit one another and is the point about which the bodies orbit. A barycenter is a dynamical point, not a physical object. It is an important conc ...
. Select Ephemeris Type:Elements and Center:@0) (Saved Horizons output file 2011-Feb-04 ) In the second pane "PR=" can be found, which gives the orbital period in days (4.160E+06, which is 11,390 Julian years).
Although it takes over 10,000 years to orbit, during the next 50 years it will slowly move closer to the Sun as it comes to perihelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
at a distance of 76 AU from the Sun.NASA.gov; (2004) Sedna is the largest known
sednoid
A sednoid is a trans-Neptunian object with a perihelion well beyond the Kuiper cliff at . Only four objects are known from this population: 90377 Sedna, , 541132 Leleākūhonua (), and , but it is suspected that there are many more. All four ha ...
, a class of objects that play an important role in the Planet Nine hypothesis.
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
(30–49 AU, about 34 AU in 2015) was the first Kuiper belt object to be discovered (1930) and is the largest known dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to p ...
.
Gallery
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
, 2007
File:Sedna PRC2004-14d.jpg, Sedna viewed with Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
, 2004
Known distant objects
This is a list of known objects at heliocentric distances of more than 65 AU. In theory, theOort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from 2 ...
could extend over from the Sun.
See also
*List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System
The artificial objects leaving the Solar System are all space probes and the upper stages of their launch vehicles, all launched by NASA. Three of the probes, ''Voyager 1'', ''Voyager 2'', and '' New Horizons'' are still functioning and are reg ...
* Lists of astronomical objects
This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object.
Solar System
* List of Solar System objects
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
* List of So ...
* List of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion
This is a list of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion or the greatest distance from the Sun that the orbit could take it if the Sun and object were the only objects in the universe. It is implied that the object is orbiting the Sun in a t ...
* List of hyperbolic comets
This is a list of parabolic and hyperbolic comets in the Solar System. Many of these comets may come from the Oort cloud, or perhaps even have interstellar origin. The Oort Cloud is not gravitationally attracted enough to the Sun to form into a ...
* List of trans-Neptunian objects
This is a list of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), which are minor planets in the Solar System that orbit the Sun at a greater distance on average than Neptune, that is, their orbit has a semi-major axis greater than 30.1 astronomical units (AU) ...
References
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Science *2021 Trans-Neptunian objects