List of Lycian place names on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
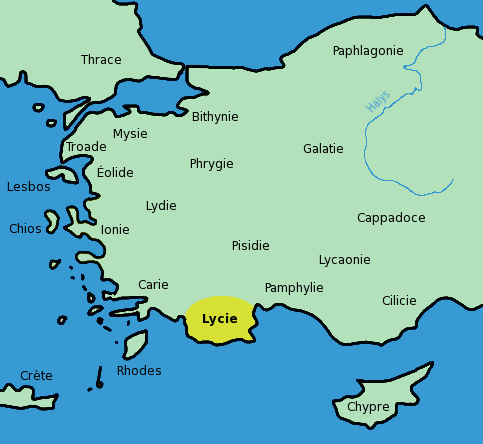



































 This article contains a list of Lycian place names that have survived from ancient
This article contains a list of Lycian place names that have survived from ancient


































 This article contains a list of Lycian place names that have survived from ancient
This article contains a list of Lycian place names that have survived from ancient Lycia
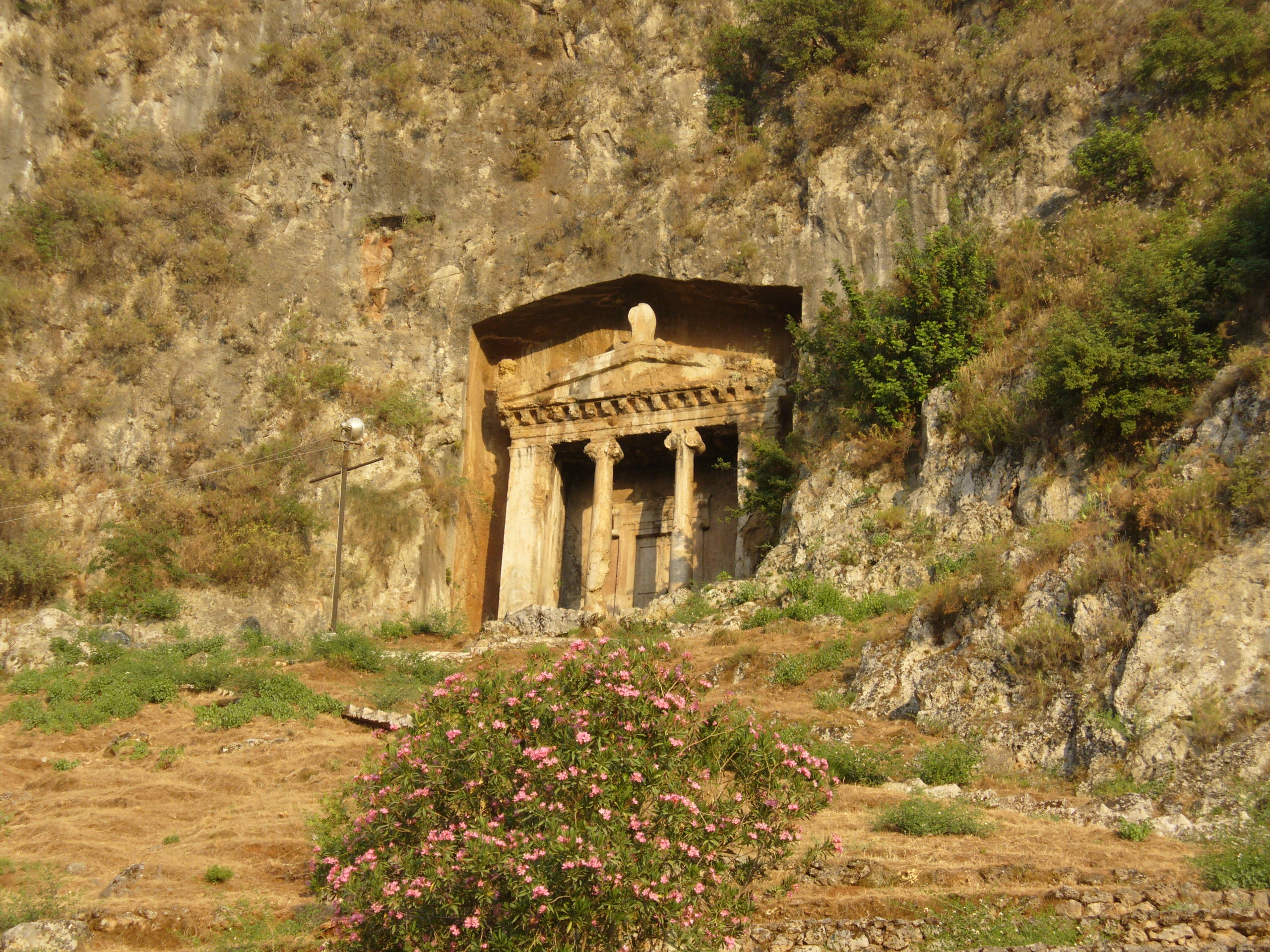
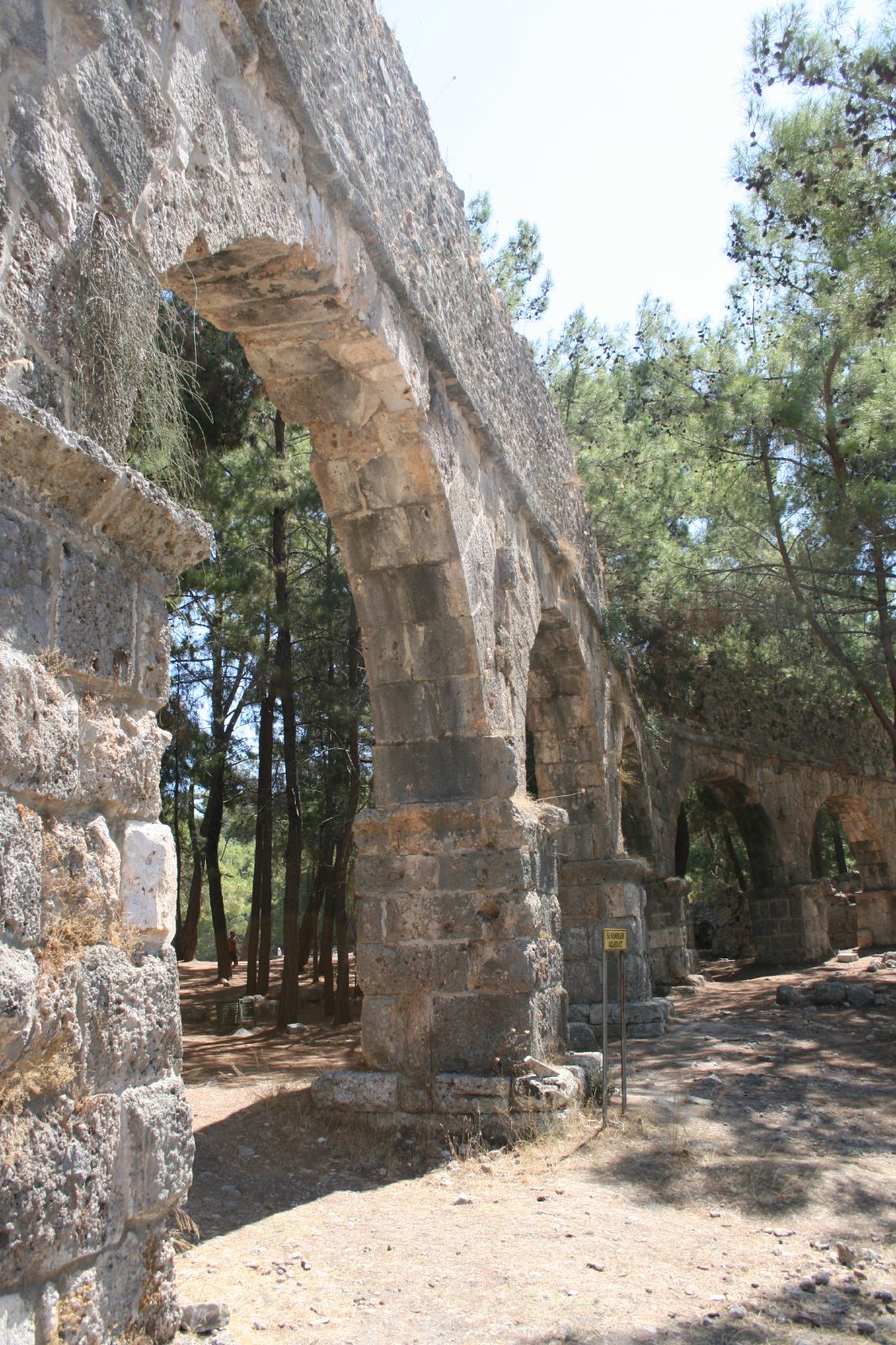
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
. Names of settlements and geomorphic features are known from ancient literary sources. Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
'' lists places in Asia Minor and specifically Lycia. Strabo's ''Geography'' has a section on Lycia as well, as does Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
's ''Natural History''. Stephanus of Byzantium includes a large number of Lycian places in ''Ethnica''. Hierocles in ''Synecdemus'' lists the cities in the eparchy
Eparchy ( gr, ἐπαρχία, la, eparchía / ''overlordship'') is an ecclesiastical unit in Eastern Christianity, that is equivalent to a diocese in Western Christianity. Eparchy is governed by an ''eparch'', who is a bishop. Depending on the ...
of Lycia. William Martin Leake
William Martin Leake (14 January 17776 January 1860) was an English military man, topographer, diplomat, antiquarian, writer, and Fellow of the Royal Society. He served in the British military, spending much of his career in the
Mediterrane ...
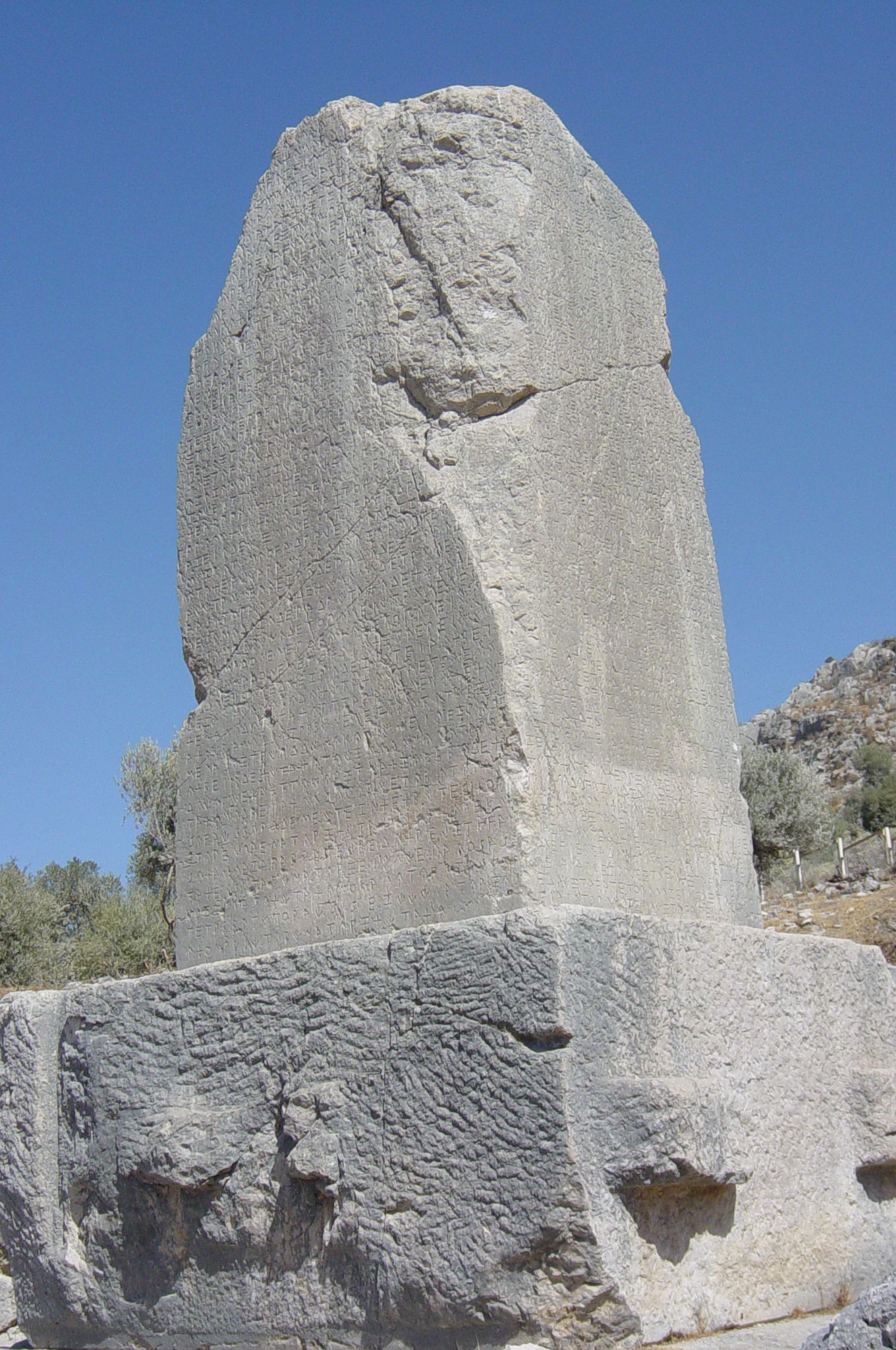
's ''Journal'' of his own trips through Anatolia, as well as of those of many other travellers, with analyses of sources, mainly Ptolemy, is still a valuable source of information on the locations and appearances of the Lycian sites. In addition, numerous inscriptions in the Lycian language
The Lycian language ( )Bryce (1986) page 30. was the language of the ancient Lycians who occupied the Anatolian region known during the Iron Age as Lycia. Most texts date back to the fifth and fourth century BC. Two languages are known as Lyci ...
state some place names in their Lycian forms. The topographical information comes from the Aydin thesis, and was developed from Turkish military maps.
This article does not address the task of defining Lycia. Over a thousand or more years, the borders of the historical territory, called Lycia in English, are not likely to have remained invariant. This list includes places named by some source at some time as "Lycian", and also any settlement with a Lycian language name, even though located in some other city-state. "Lycia" therefore represents a maximum territory, to which any historical Lycia was never exactly identical.
Aydin studied 44 out of 78 known ancient settlements. Many more archaeological sites are not identifiable with ancient settlements. Aydin also collected information on 870 Turkish settlements over the same region.. The moderns, certainly, populate the region much more densely than the ancients.
Some of the modern place names are given in Turkish. For the most part, the equivalent English, French or German pronunciations are good approximations, but Turkish has some letters not present in those languages. Ğ or ğ is not pronounced, but lengthens the preceding vowel. For example, dağ, "mountain", is pronounced daa. Substitution of an English G or g is false. Ç or ç is a ch as in child, Ş or ş is an sh as in shore. What appear to be an English C or c is a J as in John, while the J or j is pronounced as the z in azure. The vowels have a short rather than a long pronunciation. As Turkish is an agglutinative language, the endings do not have the same meanings; e.g., daği is not the plural of dağ, which is daĝlar (daalar).
: Top 0–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z __NOTOC__A
B
C
D
E
G
H
I
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
X
Notes
References
* * * * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Lycian Place Names * Lycian