List of ancient Daco-Thracian peoples and tribes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This is a list of four ancient peoples and their tribes that were possibly related and formed an extinct
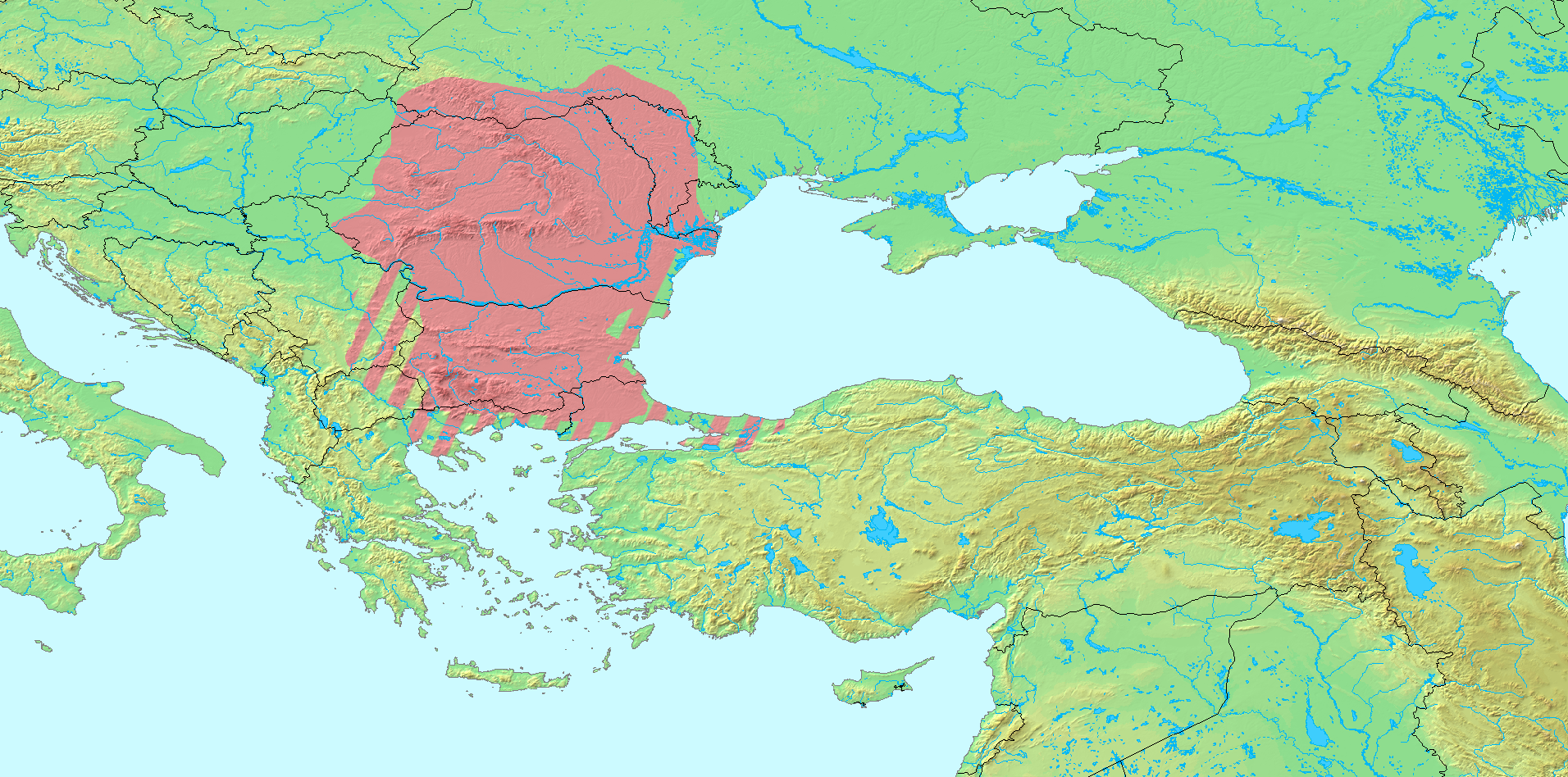
 *
*
"To the Dardaniatae belong also the Galabrii, among whom is an ancient city, and the Thunatae..." **
 *
*
Dacian toponyms, hydronyms and tribe names
- Source texts of ancient Greek and Roman authors.
- Strabo's work ''The Geography'' (
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
branch of peoples and languages in the eastern Balcans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, low Danube basin
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
. These peoples dwelt from west of the Tyras
Tyras ( grc, Τύρας) was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of the Black Sea. It was founded by colonists from Miletus, probably about 600 BC. The city was situated some 10 km from the mouth of the Tyras River, which is no ...
(Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
) river and east of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
in the north, to the north coast of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
in the south, from the west coast of the Pontus Euxinus
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
(Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
) in the east, to roughly the Angrus (modern South Morava
The South Morava ( Macedonian and Serbian: Јужна Морава, ''Južna Morava'', ; sq, Lumi Morava) is a river in eastern Kosovo and in southern Serbia, which represents the shorter headwater of Great Morava. Today, it is 295 km lon ...
) river basin, Tisia (modern Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
) and Danubius
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
(modern Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
) rivers in the west. This list is based in the possible ethnolinguist affiliation of these peoples - Geto-Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, Moesians
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
, Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
(including possibly or partly Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
or Dacian tribes) and not only on a geographical base (that includes other peoples that were not Dacians or Thracians like the Celts that lived in Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
or in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
).
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from t ...
(Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
speakers)
** Proto-Daco-Thracians ( Proto-Daco-Thracian speakers)
Daco
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consi ...
-Moesian
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south o ...
s

Geto-Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
 *
*Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
/ Daci (a closely related people to the Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
, mainly west of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
, roughly matching the Dacia Superior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today ...
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
)
**Albocenses
The Albocenses ( la, Albocenses/Albocensii) were a Dacian tribe that inhabited the area of Banat (Serbia, Romania) with the towns of Kovin (''Contra Margum''), ''Trans Tierna'', ''Ad Medias II'', Kladovo (''Ad Pontes''), ''Apu'', '' Arcidava'', '' ...
** Ansamenses
**Apuli
The Apuli or Biefi were a Dacian tribe centered at the Dacian town ''Apulon'' (Latin '' Apulum'') near what is now Alba Iulia in Transylvania, Romania.
''Apuli'' has clear resemblance to Apulia, the ancient southeastern Italy region, which is b ...
/ Appuli / Apulenses ( Dacian Apuli) with the center at Apulon
Apulon (''Apoulon'', ''Apula'') was a Dacian fortress city close to modern Alba Iulia, Romania. The Latin name of Apulum is derived. The exact location is believed by many archaeologists to be the Dacian fortifications on top of ''Piatra Craivi ...
**Biephi
Biephi was a Dacian tribe.Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
*List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around ...
/ Biephes
** Bures / Buri ( Northwest Buri), they lived in the northwest of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
- South of Slovakian Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
, in the Upper Basin of the Tisia / Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
, although related, they were a different tribe from the one centered in Buridava
Buridava (''Burridava'') was a Dacian town. situated in Dacia, later Dacia Apulensis, now Romania, on the banks of the river Aluta, now Olt.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
The name is Geto- ...
. (not to be confused with the Germanic tribe called Buri)
** Caucoenses or Cauci
The Cauci (Καῦκοι) were a people of early Ireland, uniquely documented in Ptolemy's 2nd-century ''Geography'', which locates them roughly in the region of modern County Dublin and County Wicklow.
Theories
From the early 19th century, comp ...
**Costoboci
The Costoboci (; lat, Costoboci, Costobocae, Castabocae, Coisstoboci, grc, Κοστωβῶκοι, Κοστουβῶκοι or Κοιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains an ...
/ Costoboces / Coertoboci
The Costoboci (; lat, Costoboci, Costobocae, Castabocae, Coisstoboci, grc, Κοστωβῶκοι, Κοστουβῶκοι or Κοιστοβῶκοι) were a Dacian tribe located, during the Roman imperial era, between the Carpathian Mountains an ...
also Koistobokoi and Koistobokoi Montanoi
**Osi
OSI may refer to:
Places
* Osijek Airport (IATA code: OSI), an airport in Croatia
* Ősi, a village in Veszprém county, Hungary
* Oši, an archaeological site in Semigallia, Latvia
* Osi, a village in Ido-Osi, Ekiti State, Nigeria
* Osi, Ekiti ...
/ Osii, they were a Dacian tribe but it is also argued that it was Germanic or Celtic. It was among the enemies of the Romans in the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars (Latin: ''bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum'', "German and Sarmatian War") were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi ...
(166-180 AD), according to Julius Capitolinus
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
"
**Predasenses
The Predasenses were a Dacian tribe.Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
*List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in ...
/ Predavensii
** Ratacenses / Rhadacenses
** Saboci / Sabokoi, they were a Dacian tribe, among the enemies of the Romans in the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars (Latin: ''bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum'', "German and Sarmatian War") were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi ...
(166-180 AD), according to Julius Capitolinus
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
"
** Serri
**Senses
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
/ Sensii
**Suci
The Socialist Unity Centre of India (Communist) or SUCI(C), previously called the Socialist Unity Centre of India and "Socialist Unity Centre", is an anti-revisionist Marxist-Leninist communist party in India. The party was founded by Shibda ...
** Trixae
*Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
(a closely related people to the Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, mainly east of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
, roughly matching the Dacia Inferior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today ...
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
)
** Britolages
** Buridavenses / Burridensii ( Southeast Buri), their capital was Buridava
Buridava (''Burridava'') was a Dacian town. situated in Dacia, later Dacia Apulensis, now Romania, on the banks of the river Aluta, now Olt.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
The name is Geto- ...
, on the southern slope of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
(although related, they were a different tribe from the one that lived in the northwest of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
- South of Slovakian Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
, in the Upper Basin of the Tisia (modern Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
) (not to be confused with the Germanic tribe called Buri)
**Carpi
Carpi may refer to:
Places
* Carpi, Emilia-Romagna, a large town in the province of Modena, central Italy
* Carpi (Africa), a city and former diocese of Roman Africa, now a Latin Catholic titular bishopric
People
* Carpi (people), an ancie ...
/ Carpiani / Carpians
The Carpi or Carpiani were a Dacian tribe that resided in the eastern parts of modern Romania in the historical region of Moldavia from no later than c. AD 140 and until at least AD 318.
The ethnic affiliation of the Carpi remains disputed, as ...
, Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
name is based on this tribe
**Ciaginsi
Ciaginsi was a Dacian tribe.Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
*List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and arou ...
/ Ciagisi
** Cotesii
**Crobyzi
Krobyzoi ( el, "Κρόβυζοι") is a Thracian, Getae or Dacian tribe.''Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization'' by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
* List of Dacian tribes
* List of Thracian tribes
* List of ancient cities i ...
/ Krobyzoi
Krobyzoi ( el, "Κρόβυζοι") is a Thracian, Getae or Dacian tribe.''Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization'' by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
* List of Dacian tribes
* List of Thracian tribes
* List of ancient cities i ...
/ Crobidae
Krobyzoi ( el, "Κρόβυζοι") is a Thracian, Getae or Dacian tribe.''Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization'' by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
See also
* List of Dacian tribes
* List of Thracian tribes
* List of ancient cities ...
, perhaps Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
John Boardman in his History wrote “However, a text of the Hellanicus associates the Crobyzi as well the Terizi (From the Tirizian promontory) with the Getae, who “immortalize” (Hdt IV94) that is “render immortal” by ritual. The Crobizi were a subgroup of the Getae tribes. Already known to Hecataeus they are grouped by Herodotus with Thracians” The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond, , 1992, page 598/
** Getae Proper
***Aedi
The Aedi ( grc, Αἶδοι) were an ancient people living between the Haemus Mountains and the Danube river. They are known from only one passage from Pliny the Elder's ''Naturalis Historia'', where he mentions them alongside the Clariae and ...
***Clariae
The Clariae were an ancient people living between the Haemus Mountains and the Danube river. They are known from only one passage from Pliny the Elder's ''Naturalis Historia'', where he mentions them alongside the Aedi and Scaugdae as the neighb ...
***Scaugdae
The Scaugdae were an ancient people living between the Haemus Mountains and the Danube river. They are known from only one passage from Pliny the Elder's ''Naturalis Historia'', where he mentions them alongside the Aedi and Clariae as the neighb ...
The Cambridge ancient history Volume 3, page 598, by John Boardman, 1991, , "Getic tribes were probably the Aedi, the Scaugdae and the Clariae ... They were known in antiquity as Getae..."
** Harpii
** Obulenses
**Ordes
Ordes is a Municipalities of Spain, municipality of northwestern Spain in the A Coruña (province), province of A Coruña, in the autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia. It belongs to the comarca of Ordes. The population in 2008 was 12,5 ...
** Piephigi
** Potulatenses
**Saldenses
Saldenses was a Dacian tribe.
See also
*List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but s ...
/ Saldensii
** Terici / Terizi
**Tyragetae The Tyrageti, Tyragetae, or Tyrangitae (, Strabo vii.; Ptol. iii. 5. § 25), literally, the Getae of the Tyras, were a sub-tribe of the Getae, situated on the river ''Tyras'' (modern-day Dniester in Moldova and Ukraine). They were regarded as an im ...
/ Tyrageti The Tyrageti, Tyragetae, or Tyrangitae (, Strabo vii.; Ptol. iii. 5. § 25), literally, the Getae of the Tyras, were a sub-tribe of the Getae, situated on the river ''Tyras'' (modern-day Dniester in Moldova and Ukraine). They were regarded as an im ...
**Troglodytae
The Troglodytae ( el, , ''Trōglodytai''), or Troglodyti (literally "cave goers"), were people mentioned in various locations by many Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman geographers and historians, including Herodotus (5th centu ...
( Getian Troglodytae)
Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
mixed with other peoples=
Daco
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consi ...
-Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
=
*Anartes
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacian ...
/ Anarti
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacian ...
(Dacianized Celtic tribe, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
origin tribe later assimilated by the Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
)Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, , 2007, page 46
*Teurisci
Teurisci was a Dacian tribe at the time of Ptolemy (140 AD). They were originally considered a branch of the Celtic Taurisci (Noricum), who moved to Upper Tisza. However, the archaeology shows that Celts have been absorbed by Dacians, at some point ...
=
Daco
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consi ...
-Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
=
* Napae (Dacianized Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
tribe, Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
origin tribe later assimilated by the Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, after whom the city of Napoca is possibly named
Moesians
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
/ Moesi
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south o ...
/ Mysi
* Artacii / Artakioi
Artakioi was a Moesian tribe mentioned in the Roman period. Cassius Dio (155–235) mentioned the tribe. The ethnonym has been connected with the Roman-era toponyms Artiskos (a tributary of the Maritsa) and Artanes (a tributary of the Danube). The ...
* Aureliani
* Picenses - They lived south of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
Iron Gates
The Iron Gates ( ro, Porțile de Fier; sr, / or / ; Hungarian: ''Vaskapu-szoros'') is a gorge on the river Danube. It forms part of the boundary between Serbia (to the south) and Romania (north). In the broad sense it encompasses a rou ...
(see Map 5).
*Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
Certain tribes and subdivisions of tribes were named differently by ancient writers but modern research points out that these were in fact the same tribe. The name ''Thracians'' itself seems to be a Greek exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
and we have no way of knowing what the Thracians called themselves. Also certain tribes mentioned by Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
are not indeed historical.
*Agrianes
The Agrianes (Ancient Greek: Ἀγρίανες, ''Agrianes'' or Ἀγρίαι ''Agriai'') or Agrianians, were a tribe whose country was centered at Upper Strymon, in present-day central Western Bulgaria as well as southeasternmost Serbia, at the ...
(it is also claimed that this tribe was Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
)Early symbolic systems for communication in Southeast Europe, Part 2
by Lolita Nikolova, , 2003, page 529, "eastern Paionians (Agrianians and Laeaeans)"
*Apsynthii Apsinthii ( el, Ἀψίνθιοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe mentioned by Herodotus. The Apsinthii were located east of the Dolonci, another Thracian tribe, and on Chersonesos. It was due to them that Miltiades erected a wall from Cardia to Pa ...
*Astae Asti ( el, Αστοί) is the name of a Thracian tribe which is mentioned by Livy. It is believed that they lived around the old Thracian capital of Bizye.
List of rulers
A possible continuation of the earlier Odrysian monarchy under a line of ki ...
/ Asti
Asti ( , , ; pms, Ast ) is a ''comune'' of 74,348 inhabitants (1-1-2021) located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River. It is the capital of the province of Asti and it is deemed t ...
,The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, , 2001, page 11: "After the battle, 10,000 Thracians drawn from the Asti
Asti ( , , ; pms, Ast ) is a ''comune'' of 74,348 inhabitants (1-1-2021) located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River. It is the capital of the province of Asti and it is deemed t ...
i, Caeni Kainoi ( el, Καινοί) or Caeni is the name of a Thracian tribe, mentioned by the Roman historian Livy.
References
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) includi ...
, Maduateni Ethnicon for the place name Madytus, often erroneously regarded as a small Thracian tribe, mentioned only in Liv. 38,40,7 in connection with the attack by Thracian tribes on Cn. Manlius Vulso in 188 BC.von Bredow, Iris (Bietigheim-Bissingen), “Ma ...
and Coreli occupied each side of a narrow forested pass ..." they appear in the 2nd century BC to 1st century BC
*Beni
is a Japanese R&B singer, who debuted in 2004 under the Avex Trax label. In 2008, Arashiro left Avex Trax and transferred to Universal Music Japan where she started to perform as simply Beni (stylized as BENI).
She was initially best known fo ...
*Bessi
The Bessi (; grc, Βῆσσοι, or , ) were a Thracian tribe that inhabited the upper valley of the Hebros and the lands between the Haemus and Rhodope mountain ranges in historical Thrace.
Geography
The exact geographic location of the Bes ...
/ Biessoi, they were among the enemies of the Romans in the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars (Latin: ''bellum Germanicum et Sarmaticum'', "German and Sarmatian War") were a series of wars lasting from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi ...
(166-180 AD), according to Julius Capitolinus
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, designated heirs and usurpers from 117 to 284. Supposedly modeled on the sim ...
"
*Bisaltae The Bisaltae ( el, Βισάλται) were a Thracian people on the lower Strymon river, who gave their name to Bisaltia, the district between Amphipolis and Heraclea Sintica (the modern village of Rupite, Bulgaria) on the east and Crestonice on th ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen and Thomas Heine Nielsen, 2005, , page 854, "... Various tribes have occupied this part of Thrace: Bisaltians (lower Strymon valley), Odomantes (the plain to the north of the Strymon) ..."
*Bistones
Bistones ( el, "Βίστονες") is the name of a Thracian people who dwelt between Mount Rhodopé and the Aegean Sea, beside Lake Bistonis, near Abdera "extending westward as far as the river Nestus". It was through the land of the Bistones ...
The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubrey de Selincourt, , 2003, page 452: "... I10 The Thracian tribes lying along his route were the Paeti, Cicones, Bistones, Sapaei, Dersaei, Edoni, and Satrae..."
*Bithyni
The Bithyni (; el, Βιθυνοί) were a Thracian tribe who, along with the Thyni, migrated to Anatolia. Herodotus, Xenophon and Strabo all assert that the Bithyni and Thyni settled together in what would be known as Bithynia and Thynia. Accordin ...
or Bythini, migrated to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
or Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
*Brenae
Brenae ( el, Βρέναι) is the name of a Thracian tribeStrabo, Geography, book 7, chapter fragments: "... and a fourth to Pelagonia. Along the Hebrus dwell the Corpili, the Brenæ still higher up, above them..." that was located above the Corpi ...
Strabo, Geography, book 7, chapter fragments: ... and a fourth to Pelagonia. Along the Hebrus dwell the Corpili, the Brenæ still higher up, above them, and lastly
*Caeni Kainoi ( el, Καινοί) or Caeni is the name of a Thracian tribe, mentioned by the Roman historian Livy.
References
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) includi ...
/ Kainoi Kainoi ( el, Καινοί) or Caeni is the name of a Thracian tribe, mentioned by the Roman historian Livy.
References
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) includi ...
*Cebrenii Cebrenii ( el, Κεβρήνιοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe, they are mentioned by PolyaenusPolyaenus: Stratagems - BOOK 7: The generals of the Cebrenii and Sycaeboae, two Thracian tribes, were chosen from among the priests of Hera. Cosingas, ...
Polyaenus: Stratagems - BOOK 7, The generals of the Cebrenii and Sycaeboae, two Thracian tribes, were chosen from among the priests of Hera. Cosingas, according to the tradition of the country, was elected to be their priest and general; but the army took some objection to him, and refused to obey him. To suppress the rebelliousness that had taken hold of the troops, Cosingas built a number of long ladders, and fastened them one to another. He then put out a report, that he had decided to climb up to heaven, in order to inform Hera of the disobedience of the Thracians. The Thracians, who are notoriously stupid and ridiculous, were terrified by the idea of their general's intended journey, and the resulting wrath of heaven. They implored him not to carry out his plan, and they promised with an oath to obey all of his future commands.
*Cicones
The Cicones (; ) or Ciconians were a Homeric ThracianHerodotus, ''The Histories'' (Penguin Classics), edd. John M. Marincola and Aubery de Selincourt, 2003, p. 452 (I10): "The Thracian tribes lying along his route were the Paeti, Cicones, Biston ...
(Kikones
The Cicones (; ) or Ciconians were a Homeric ThracianHerodotus, ''The Histories'' (Penguin Classics), edd. John M. Marincola and Aubery de Selincourt, 2003, p. 452 (I10): "The Thracian tribes lying along his route were the Paeti, Cicones, Biston ...
), mentioned by Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
in Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
*Coelaletae Koilaletoi ( el, Κοιλαλέτοι) or Coilaletae or Coelaletae is the name of a Thracian tribe. Other parts of this tribe were, the Coelaletae Maiores and Coelaletae Minores. They are mentioned by Tacitus.
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
Thi ...
*Coreli Koreli or Coreli is the name of a Thracian tribe. is the name of a Thracian tribe. The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, , 2001, page 11: "... After the battle, 10,000 Thracians drawn from the Astii, Caeni ...
/ Coralli
Coralli is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Claudio Coralli (born 1983), Italian footballer
* Giulio Coralli (born 1641), Italian painter
*Jean Coralli (1779–1854), French dancer and choreographer
See also
*Corallo
Corallo ...
*Corpili Korpiloi ( el, Κορπίλοι) or Corpili is the name of a Thracian tribeStrabo, ''Geography'', book 7, chapter fragments: "... and a fourth to Pelagonia. Along the Hebrus dwell the Corpili, the Brenæ still higher up, above them, and ..." that wa ...
/ Corpillices
*Crousi Crousi ( el, Κρουσαῖοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. ...
The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond, , 1992, page 601-602
*Dersaei
Dersaei ( el, Δερσαῖοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe. They are mentioned by Herodotus. They were allied with the Maedi tribe against the Getae during their campaign with the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capi ...
*Dentheletae
The Dentheletae ( el, Δενθελῆται), also Danthaletae (Δανθαλῆται) or Denseletae, were a Thracian tribe that in antiquity lived near the sources of the River Strymon, and are mentioned in texts by Polybius, Cassius Dio, Tacit ...
*Derrones
The Derrones (or ''Deroni, Derroni'') were a Thracian or a Paionian tribe. Our knowledge of them comes from coins bearing variations of the legend of DERRONIKON (ΔΕΡΡΟΝΙΚΟΝ) - DERR (ΔΕΡΡ). The letters used in the coins are Greek, alt ...
(it is also claimed that this tribe was Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
)
*Digeri
Digeri ( el, "Δίγηροι", la, Digerri) is the name of a Thracian tribe mentioned by Pliny the ElderPlin. Nat. 4.18,"Thrace now follows, divided into fifty strategies1, and to be reckoned among the most powerful nations of Europe. Among its pe ...
*Dii
:''Dii'' ''is also the plural of Latin Deus.''
The Dii (; grc, Δίοι, Díoi) were an independent Thracian tribe, swordsmen, who lived among the foothills of Mount Rhodope in Thrace, and particularly in the east bank of Nestos, from the sp ...
/ DioiThe Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond, , 1992, page 607: "The existence of a tribe called Diobessi (Plin.Loc.Cit.) links together ethnically the Bessi and the Dii..."
* Diobesi
*Dolonci Dolonci or Dolonki ( el, Δόλογκοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe in Thracian Chersonese. They are mentioned by Herodotus.
References
See also
*List of Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴ ...
*Edoni
The Edoni (also ''Edones'', ''Edonians'', ''Edonides'') ( el, Ἠδωνιοί) were a Thracian people who dwelt mostly between the Nestus and the Strymon rivers in southern Thrace, but also once dwelt west of the Strymon at least as far as the Axi ...
/ Edones
The Edoni (also ''Edones'', ''Edonians'', ''Edonides'') ( el, Ἠδωνιοί) were a Thracian people who dwelt mostly between the Nestus and the Strymon rivers in southern Thrace, but also once dwelt west of the Strymon at least as far as the Axi ...
*Maduateni Ethnicon for the place name Madytus, often erroneously regarded as a small Thracian tribe, mentioned only in Liv. 38,40,7 in connection with the attack by Thracian tribes on Cn. Manlius Vulso in 188 BC.von Bredow, Iris (Bietigheim-Bissingen), “Ma ...
*Maedi
The Maedi (also ''Maidans'', ''Maedans'', or ''Medi''; grc, Μαῖδοι or Μαιδοί) were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along th ...
**MaedoBythini
The Maedi (also ''Maidans'', ''Maedans'', or ''Medi''; grc, Μαῖδοι or Μαιδοί) were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along th ...
, Maedi
The Maedi (also ''Maidans'', ''Maedans'', or ''Medi''; grc, Μαῖδοι or Μαιδοί) were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along th ...
that migrated to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
or Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
*Melanditae Melanditae or Melanditai ( gr, Μελανδίται) is the name of a Thracian tribeAnabasis by H. G. Dakyns, 2006, , page 321: "... his sway extended over the Melanditae, the Thynians, and the Tranipsae. Then the affairs of the Odrysians took ..." ...
Anabasis by H. G. Dakyns, 2006, , page 321: "... his sway extended over the Melanditae, the Thynians, and the Tranipsae. Then the affairs of the Odrysians took ..."
* Melinophagi
*Nipsaei Nipsai or Nipsaioi ( el, Νιψαίοι) is the name of a Thracian tribe.The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, , 2003, page 271, "The Thracians of... those who live beyond Apollonia and Mesembria ...
The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, , 2003, page 271, "The Thracians of... those who live beyond Apollonia and Mesembria, known as the Scyrmiadae and Nipsaeans, surrendered without fighting; but the Getae..."
*Odomanti
Odomanti or Odomantes ( grc, Ὀδόμαντες) were an ancient tribe. Some regard it as Paeonian, while others claim, that the tribe was with certainty Thracian. The Odomanti are noted by Herodotus, Thucydides, Stephanus of Byzantium and Pliny ...
/ Odomantes
Odomanti or Odomantes ( grc, Ὀδόμαντες) were an ancient tribe. Some regard it as Paeonian, while others claim, that the tribe was with certainty Thracian. The Odomanti are noted by Herodotus, Thucydides, Stephanus of Byzantium and Pliny ...
(it is also claimed that this tribe was Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
)
*Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
/ Odrysians
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
*Paeti Paiti ( el, Παίτοι) is the name of a Thracians, Thracian tribe.The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, , 2003, page 452: "... I10 The Thracian tribes lying along his route were the Paeti, Cic ...
*Pieres
The Pieres (Ancient Greek: Πίερες) were an ancient tribe that long before the archaic period in Greece occupied the narrow strip of plain land, or low hill, between the mouths of the Peneius and the HaliacmonE.C. Marchant, Commentary on Thuc ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen and Thomas Heine Nielsen, 2005, , page 803: "... a ..decree from Gonnoi. Originally populated by Thracian Pieres, Leibethra and this part of Pieria were conquered by the ..." (They also may have been a Brygian tribe, related to the Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors used ...
and the Mygdones, and not a Thracian tribe)
* Saii / Saioi / Saianes ( Saians) - Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
tribe that inhabited Thassos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
island before Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonization.
* Samothraci / Samothrakoi - Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
tribe that lived in the island of Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
after the Pelasgians
The name Pelasgians ( grc, Πελασγοί, ''Pelasgoí'', singular: Πελασγός, ''Pelasgós'') was used by classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergenc ...
and before the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
that came from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
island.
*Sapaei
Sapaeans, Sapaei or Sapaioi (Ancient Greek, "Σαπαίοι") were a Thracian tribe close to the Greek city of Abdera, Thrace, Abdera. One of their kings was named Abrupolis
and had allied himself with the Ancient Rome, Romans. They Sapaean kingdo ...
, close to Abdera, ruled Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
after the Odrysians
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
*Satrae The Satrae ( el, "Σάτραι") were, in ancient geography, a Thracian people, inhabiting part of Mount Pangaeus between the rivers Nestus (Mesta) and Strymon (Struma).
According to Herodotus, they were independent in his time, and had never be ...
/ Satri The Satrae ( el, "Σάτραι") were, in ancient geography, a Thracians, Thracian people, inhabiting part of Mount Pangaeus between the rivers Nestus (Mesta) and Struma (river), Strymon (Struma).
According to Herodotus, they were Independence, in ...
*Scyrmiadae Scyrmiadae ( el, Σκυρμιάδαι) is the name of a Thracian tribe.The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, , 2003, page 271, "The Thracians of... those who live beyond Apollonia and Mesembria, ...
*Sintians
The Sintians (; grc-gre, Σίντιες), "the Raiders, the Plunderers", from Ancient Greek ''sinteis'', "destructive") were known to the Greeks as pirates and raiders; they are also referred to as a Thracian people who once inhabited the area ...
*Sithones Sithōnes ( el, Σίθωνες) is the name of a Thracian tribe.The central Balkan tribes in pre-Roman times: Triballi, Autariatae,Dardanians, Scordisci and Moesians,, page 69,by Fanula Papazoglu - 1978,"were directed against the Thracian coast. The ...
*Sycaeboae Sycaeboae ( el, "Συκαιβόαι") is the name of a Thracian tribe, which was mentioned by Polyaenus.Polyaenus: Stratagems - BOOK 7 ,The generals of the Cebrenii and Sycaeboae, two Thracian tribes, were chosen from among the priests of Hera. Cosi ...
*Thyni
The Thyni ( el, Θυνοί) were a Thracian tribe that lived in south-eastern Thrace. The Thyni were closely related to the Bithynians, with whom they often exchanged troops and royal marriages, later a section of the Thyni, along with the Bithyni ...
, migrated to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
/Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
*Tilataei
Tilataei ( el, "Τιλαταίοι") is the name of a Thracian tribeThe Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, ...
* Tralles
* Tranipsae
*Trausi
The Trausi ( el, "Τραύσοι" or "Τραυσοί") ( Herod., ''Trausoi'') or Thrausi ( Liv.) were a Thracian tribe who inhabited the southwestern region of the Rhodopes.
Herodotus writes of the Trausi:
:"''The Trausi in all else resemble th ...
*Treres Treri ( grc, Τρηροι, Trēroi, or , romanized: ; Latin: or ) is the name of a Thracian tribe.
In Thrace
The Treri lived in northwest Thrace, in the region of Serdica (now the Bulgarian capital city of Sofia). The Treri of the Serdica region w ...
Thracians mixed with other peoples
Thraco
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
-Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
*Tricornenses The Tricornenses of Tricornum (modern Ritopek
Ritopek (Serbian Cyrillic: Ритопек, ) is a suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Grocka, 20 km east of Belgrade and 19 km west of the municipa ...
/ Tricornesii (Romanized
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
Thraco
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
-Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
community, artificially created by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, that replaced the Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
Celegeri
Celegeri were a CelticJ. J. Wilkes, The Illyrians, 1992, , p. 217. tribe, together with the Dindari a branch of the Scordisci that migrated to Illyria after the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. They inhabited Moesia Superior (mod ...
)
Thraco
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
-Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
Mixed tribes of Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
, Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
seem to have belonged to two ethnolinguistic different branches of Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
peoples.
*Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
**Galabri The Galabri (Ancient Greek: Γαλάβριοι) were a Dardanian tribe, along with the Thunatae, mentioned by Strabo.; .
Name
The tribe is mentioned by Ancient Greek author Strabo in his ''Geographica'' as ''Galabrioi''. The tribal name ''Galabr ...
, subtribe of the Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
.Strabo"To the Dardaniatae belong also the Galabrii, among whom is an ancient city, and the Thunatae..." **
Thunatae The Thunatae (Ancient Greek: Θουνᾶται) were a Dardanian tribe, along with the Galabri, mentioned by Strabo. The Thunatae are mentioned as neighbors of the Maedi, a Thracian tribe.; .
Name
The tribe is mentioned by Ancient Greek author St ...
, subtribe of the Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
.
Thraco
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
-Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors used ...
Mixed tribes of Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors used ...
, however Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors used ...
seem to have been a people ethnolinguistically closer to the Hellenic peoples, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
and ancient Macedonians, and not to the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
.
* Mygdones
*Pieres
The Pieres (Ancient Greek: Πίερες) were an ancient tribe that long before the archaic period in Greece occupied the narrow strip of plain land, or low hill, between the mouths of the Peneius and the HaliacmonE.C. Marchant, Commentary on Thuc ...
(They also may have been a Brygian tribe, related to the Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Ancient Greek authors used ...
and the Mygdones, and not a Thracian tribe)
Possible Daco-Thracian peoples
Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
/ Paeones
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania (Roman province), Dardania, to the west of Thrace a ...
There are different views and still no agreement among scholars about the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
' ethnic and linguistic kinship. Some such as Wilhelm Tomaschek
Wilhelm Tomaschek, or Vilém Tomášek (May 26, 1841, Olomouc – September 9, 1901, Vienna) was a Czech-Austrian geographer and orientalist. He is known for his work in the fields of historical topography and historical ethnography.
and Paul Kretschmer Paul Kretschmer (2 May 1866 – 9 March 1956) was a German linguist who studied the earliest history and interrelations of the Indo-European languages and showed how they were influenced by non-Indo-European languages, such as Etruscan.
Biography ...
claim that the language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
spoken by the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
belonged to the Illyrian family, while Dimitar Dechev claims affinities with Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
. Irwin L. Merker Irwin may refer to:
Places
;United States
* Irwin, California
* Irwin, Idaho
* Irwin, Illinois
* Irwin, Iowa
* Irwin, Nebraska
* Irwin, Ohio
* Irwin, Pennsylvania
* Irwin, South Carolina
* Irwin County, Georgia
* Irwin Township, Venango County, Pe ...
considers that the language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
spoken by the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
was closely related to Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(and ancient Macedonian if it was a distinct language from ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
), a Hellenic language with "a great deal of Illyrian and Thracian influence as a result of this proximity".
Agrianes
The Agrianes (Ancient Greek: Ἀγρίανες, ''Agrianes'' or Ἀγρίαι ''Agriai'') or Agrianians, were a tribe whose country was centered at Upper Strymon, in present-day central Western Bulgaria as well as southeasternmost Serbia, at the ...
(also, ''Agriani'' and ''Agrii'') (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
)
*Almopians
Almopians or Almopes (Ancient Greek: Ἀλμῶπες or Ἀλμωπεῖς) were an ancient Paeonian tribe. They inhabited the region of Almopia in Lower Macedonia, which was named after the tribe. They were expelled after the conquest of the reg ...
(also ''Almopioi'')
*Derrones
The Derrones (or ''Deroni, Derroni'') were a Thracian or a Paionian tribe. Our knowledge of them comes from coins bearing variations of the legend of DERRONIKON (ΔΕΡΡΟΝΙΚΟΝ) - DERR (ΔΕΡΡ). The letters used in the coins are Greek, alt ...
(also ''Derroni'') (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
)
* Doberes
*Laeaeans
The Laeaeans (; grc, Λαιαῖοι) were a Paeonian tribe who in the 4th century BC lived adjacent to the Agrianes, another Paeonian tribe, along the upper course of the Strymon river, at the western edge of Thrace. They were not incorporated ...
(also ''Laeaei'' and ''Laiai'')
*Odomantes
Odomanti or Odomantes ( grc, Ὀδόμαντες) were an ancient tribe. Some regard it as Paeonian, while others claim, that the tribe was with certainty Thracian. The Odomanti are noted by Herodotus, Thucydides, Stephanus of Byzantium and Pliny ...
(also ''Odomanti'') (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
)
*Paeoplae
Paeoplae (Ancient Greek: Παιόπλαι) were an ancient Paeonian tribe in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now spl ...
*Siropaiones
Siro-Paeonians or Siropaiones (Ancient Greek: Σιροπαίονες, gr, Σιριοπαίονες, ή Σιρινοπαίονες) were an ancient Paeonian tribe inhabiting the ancient city of Siris (present day Serres) and the Strymon plain. They ...
The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, , 2003, page 315, "... was that a number of Paeonian tribes – the Siriopaeones, Paeoplae, ..."
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West A ...
*Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West A ...
could have been a people of Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
- Dacian origin with an Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
overlordship, a mixture of Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Iranians or a missing link and a transitional people between Indo-Iranian peoples and Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
.
Sources
Ancient
* * * * * * *Modern
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *See also
*Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
* Getans
*Moesians
In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi ( or ; grc, Μοισοί, ''Moisoí'' or Μυσοί, ''Mysoí''; lat, Moesi or ''Moesae'') appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the River Timok to the south ...
*Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
*Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
*List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ...
References
External links
Dacian toponyms, hydronyms and tribe names
- Source texts of ancient Greek and Roman authors.
- Strabo's work ''The Geography'' (
Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
). Book 7, Chapters 3 and 6, are about Dacia, Thracia, Danube region (Southeastern Europe).
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Thracian Tribes
Lists of ancient Indo-European peoples and tribes
Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ...
Thracian tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ...