List of acupuncture points on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article provides a comprehensive list of
This article provides a comprehensive list of
The status and future of acupuncture mechanism research.
J Altern Complement Med 14(7): 861–869. In practice, acupuncture points are located by a combination of anatomical landmarks, palpation, and feedback from the patient.
2014
listing 361 classical acupuncture points organized according to the fourteen meridians, eight extra meridians, 48 extra points, and scalp acupuncture points,Regional Office for the Western Pacific, WHO. 1991
A Proposed Standard International Acupuncture Nomenclature Report of a WHO Scientific Group
(pdf).
Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature
' in 1993, focused on the 361 classical acupuncture points.Regional Office for the Western Pacific, WHO. 1993
Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature, 2nd ed
(pdf).
Archived from the original on 28 February 2011
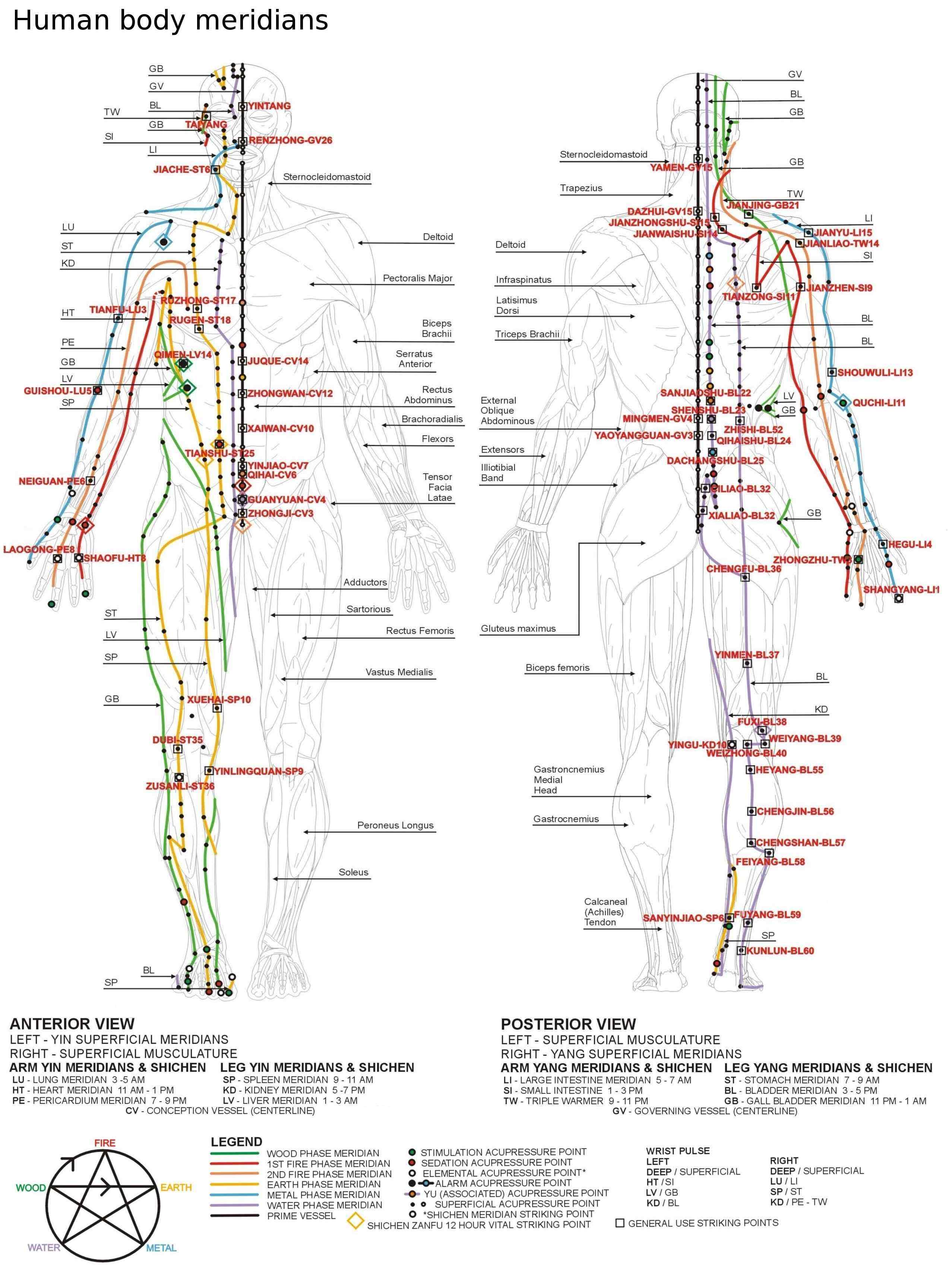
Retrieved Sep-05-2014. Each acupuncture point is identified by the meridian on which it is located and its number in the point sequence on that channel. For example, ''Lu-9'' identifies the 9th acupuncture point on the lung meridian. The only ambiguity with this unique systemized method is on the urinary bladder meridian, where the outer line of 14 points found on the back near the spine are inserted in one of two ways; following the last point of the inner line along the spine () and resuming with the point found in the crease of the buttocks (), or following the point in the center of the crease of the knee () and resuming with the point just below that (), found in the bifurcation of the gastrocnemius muscle. Although classification of the extra points often tries to utilize a similar shortcut method, where a numbered sequence along an assigned body part is used, there is no commonly agreed-upon system and therefore universal identification of these points relies on the original naming system of traditional Chinese characters. The tables in this article follow the WHO numbering scheme to identify the acupuncture points of the main channels. For extra points the tables follow the numbering scheme found in ''A Manual of Acupuncture''.
acupuncture point
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientifi ...
s, locations on the body used in acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientifi ...
, acupressure
Acupressure is an alternative medicine technique often used in conjunction with acupuncture or reflexology. It is based on the concept of life energy, which flows through "meridians" in the body. In treatment, physical pressure is applied to ac ...
, and other treatment systems based on Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM).
Locations and basis
More than four hundred acupuncture points have been described, with the majority located on one of the twenty main cutaneous and subcutaneous meridians, pathways which run throughout the body and according to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) transport qi (). Twelve of these major meridians, commonly referred to as "the primary meridians", are bilateral and practitioners associate them with internal organs. The remaining eight meridians are designated as "extraordinary", and are also bilateral except for three, one that encircles the body near the waist, and two that run along the midline of the body. Only those two extraordinary meridians that run along the midline contain their own points, the remaining six comprise points from the aforementioned twelve primary meridians. There are also points that are not located on the fourteen major meridians but do lie in the complete nexus referred to as ''jing luo'' (). Such outliers are often referred to as "extra points".Deadman, P, Baker K, Al-Khafaji, M. 2007. A Manual of Acupuncture, 2nd Edition. Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications. . There is no anatomical and physiological basis for acupuncture points and meridians.Napadow V, Ahn A, Longhurst J, et al. 2008The status and future of acupuncture mechanism research.
J Altern Complement Med 14(7): 861–869. In practice, acupuncture points are located by a combination of anatomical landmarks, palpation, and feedback from the patient.
Twelve Primary Meridians
Eight Extraordinary Meridians
The eight extraordinary meridians () are of pivotal importance in the study ofQigong
''Qigong'' (), ''qi gong'', ''chi kung'', ''chi 'ung'', or ''chi gung'' () is a system of coordinated body-posture and movement, breathing, and meditation
used for the purposes of health, spirituality, and martial-arts training. With roots in ...
(氣功; Chi kung), T'ai chi ch'uan
Tai chi (), short for Tai chi ch'üan ( zh, s=太极拳, t=太極拳, first=t, p=Tàijíquán, labels=no), sometimes called "shadowboxing", is an neijia, internal Chinese martial art practiced for defense training, health benefits and medita ...
(太極拳), and Chinese alchemy
Chinese alchemy is an ancient Chinese scientific and technological approach to alchemy, a part of the larger tradition of Taoist / Daoist body-spirit cultivation developed from the traditional Chinese understanding of medicine and the body. Accor ...
. Though many are listed, only the Governing Vessel and the Conception Vessel meridians have points not associated with the previous 12 meridians.
Nomenclature
Some acupuncture points have several traditional names, for example ''tài yuān'' () and ''gui xin'' () are two names used for the 9th acupuncture point on the lung meridian. TheWorld Health Organization (WHO)
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
published ''A Proposed Standard International Acupuncture Nomenclature Report'' in 1991 an2014
listing 361 classical acupuncture points organized according to the fourteen meridians, eight extra meridians, 48 extra points, and scalp acupuncture points,Regional Office for the Western Pacific, WHO. 1991
A Proposed Standard International Acupuncture Nomenclature Report of a WHO Scientific Group
(pdf).
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
. Retrieved Sep-05-2014. and published Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature
' in 1993, focused on the 361 classical acupuncture points.Regional Office for the Western Pacific, WHO. 1993
Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature, 2nd ed
(pdf).
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
Archived from the original on 28 February 2011
Retrieved Sep-05-2014. Each acupuncture point is identified by the meridian on which it is located and its number in the point sequence on that channel. For example, ''Lu-9'' identifies the 9th acupuncture point on the lung meridian. The only ambiguity with this unique systemized method is on the urinary bladder meridian, where the outer line of 14 points found on the back near the spine are inserted in one of two ways; following the last point of the inner line along the spine () and resuming with the point found in the crease of the buttocks (), or following the point in the center of the crease of the knee () and resuming with the point just below that (), found in the bifurcation of the gastrocnemius muscle. Although classification of the extra points often tries to utilize a similar shortcut method, where a numbered sequence along an assigned body part is used, there is no commonly agreed-upon system and therefore universal identification of these points relies on the original naming system of traditional Chinese characters. The tables in this article follow the WHO numbering scheme to identify the acupuncture points of the main channels. For extra points the tables follow the numbering scheme found in ''A Manual of Acupuncture''.
Lung meridian
Abbreviated as LU, named "The Lung channel of Hand, Greater Yin". This refers to the meridian starting in the arm, thelung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
's association with yin
Yin may refer to:
*the dark force in the yin and yang from traditional Chinese philosophy and medicine
*Yīn (surname) (), a Chinese surname
*Yǐn (surname) (), a Chinese surname
*Shang dynasty, also known as the Yin dynasty
**Yinxu or Yin, the S ...
, and that it is considered more easy to find.
Large intestine meridian
Abbreviated as LI or CO (colon), named "The Large Intestine channel of Hand, Yang Bright".Stomach meridian
Abbreviated as ST, named "The Stomach channel of Foot, Yang Bright".Spleen meridian
Abbreviated as SP, named "The Spleen channel of Foot, Greater Yin".Heart meridian
Abbreviated as HE, HT or H, named "The Heart channel of Hand, Lesser Yin".Small intestine meridian
Abbreviated as SI, named "The Small Intestine channel of Hand, Greater Yang".Bladder meridian
Abbreviated as BL or UB (urinary bladder), described in Chinese as "The Bladder channel of Foot, Greater Yang". An alternative numbering scheme for the "appended part" (beginning with Bl-41 in the list below), which places the outer line along the spine after Bl-35 () instead of Bl-40 (), will be noted in the ''Alternative names'' column.Kidney meridian
Abbreviated as KI or K, described in Chinese as or "The Kidney channel of Foot, Lesser Yin".Pericardium meridian
Abbreviated as PC or P, named "The Pericardium channel of Hand, Faint Yin".Triple burner meridian
Also known as San Jiao, triple-heater, triple-warmer or triple-energizer, abbreviated as TB or SJ or TE and named "The Sanjiao channel of Hand, Lesser Yang".Gallbladder meridian
Abbreviated as GB, this meridian is named "The Gallbladder channel of Foot, Lesser Yang".Liver meridian
Abbreviated as LR or LV, named "The Liver channel of Foot, Faint Yin".Governing vessel
Also known as Du, abbreviated as GV and named "The Governing Vessel".Conception vessel
Also known as Ren, Directing Vessel, abbreviated as CV and named "The Conception Vessel".Extra points
There is no agreed-on naming scheme for extra points on the body. This first table follows the numbering scheme of Peter Deadman. This second table names meridians as they appear in the table.Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:List of Acupuncture Points *Acupuncture points
This article provides a comprehensive list of acupuncture points, locations on the body used in acupuncture, acupressure, and other treatment systems based on Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM).
Locations and basis
More than four hundred ...