Lion Sermon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large
 ''Felis leo'' was the
''Felis leo'' was the
 In the 19th and 20th centuries, several lion
In the 19th and 20th centuries, several lion
 Other lion subspecies or
Other lion subspecies or
 The ''Panthera''
The ''Panthera''
 African lions live in scattered populations across sub-Saharan Africa. The lion prefers grassy plains and
African lions live in scattered populations across sub-Saharan Africa. The lion prefers grassy plains and
 Although adult lions have no natural predators, evidence suggests most die violently from attacks by humans or other lions. Schaller, p. 183. Lions often inflict serious injuries on members of other prides they encounter in territorial disputes or members of the home pride when fighting at a kill. Schaller, pp. 188–89. Crippled lions and cubs may fall victim to hyenas and leopards or be trampled by buffalo or elephants. Careless lions may be maimed when hunting prey. Schaller, pp. 189–90.
Ticks commonly infest the ears, neck and groin regions of the lions. Schaller, p. 184. Adult forms of several tapeworm species of the genus ''Taenia (tapeworm), Taenia'' have been isolated from lion intestines, having been ingested as larvae in antelope meat. Lions in the Ngorongoro Crater were afflicted by an outbreak of stable fly (''Stable fly, Stomoxys calcitrans'') in 1962, resulting in lions becoming emaciated and covered in bloody, bare patches. Lions sought unsuccessfully to evade the biting flies by climbing trees or crawling into hyena burrows; many died or migrated and the local population dropped from 70 to 15 individuals. A more recent outbreak in 2001 killed six lions.
Captive lions have been infected with canine distemper virus (CDV) since at least the mid-1970s. CDV is spread by domestic dogs and other carnivores; a 1994 outbreak in Serengeti National Park resulted in many lions developing neurological symptoms such as seizures. During the outbreak, several lions died from pneumonia and encephalitis. Feline immunodeficiency virus and lentivirus also affect captive lions.
Although adult lions have no natural predators, evidence suggests most die violently from attacks by humans or other lions. Schaller, p. 183. Lions often inflict serious injuries on members of other prides they encounter in territorial disputes or members of the home pride when fighting at a kill. Schaller, pp. 188–89. Crippled lions and cubs may fall victim to hyenas and leopards or be trampled by buffalo or elephants. Careless lions may be maimed when hunting prey. Schaller, pp. 189–90.
Ticks commonly infest the ears, neck and groin regions of the lions. Schaller, p. 184. Adult forms of several tapeworm species of the genus ''Taenia (tapeworm), Taenia'' have been isolated from lion intestines, having been ingested as larvae in antelope meat. Lions in the Ngorongoro Crater were afflicted by an outbreak of stable fly (''Stable fly, Stomoxys calcitrans'') in 1962, resulting in lions becoming emaciated and covered in bloody, bare patches. Lions sought unsuccessfully to evade the biting flies by climbing trees or crawling into hyena burrows; many died or migrated and the local population dropped from 70 to 15 individuals. A more recent outbreak in 2001 killed six lions.
Captive lions have been infected with canine distemper virus (CDV) since at least the mid-1970s. CDV is spread by domestic dogs and other carnivores; a 1994 outbreak in Serengeti National Park resulted in many lions developing neurological symptoms such as seizures. During the outbreak, several lions died from pneumonia and encephalitis. Feline immunodeficiency virus and lentivirus also affect captive lions.
 When resting, lion socialisation occurs through a number of behaviours; the animal's expressive movements are highly developed. The most common peaceful, tactile gestures are Bunting_(animal_behavior), head rubbing and social licking, Schaller, p. 85. which have been compared with the role of allogrooming among primates. Head rubbing—nuzzling the forehead, face and neck against another lion—appears to be a form of greeting and is seen often after an animal has been apart from others or after a fight or confrontation. Males tend to rub other males, while cubs and females rub females. Schaller, pp. 85–88. Social licking often occurs in tandem with head rubbing; it is generally mutual and the recipient appears to express pleasure. The head and neck are the most common parts of the body licked; this behaviour may have arisen out of utility because lions cannot lick these areas themselves. Schaller, pp. 88–91.
Lions have an array of facial expressions and body postures that serve as visual gestures. Schaller, pp. 103–117. A common facial expression is the "grimace face" or flehmen response, which a lion makes when sniffing chemical signals and involves an open mouth with bared teeth, raised muzzle, wrinkled nose closed eyes and relaxed ears. Lions also use chemical and visual marking; males will Territory (animal)#Scent marking, spray and scrape plots of ground and objects within the territory.
The lion's repertoire of vocalisations is large; variations in intensity and pitch appear to be central to communication. Most lion vocalisations are variations of growling, snarling, meowing and roaring. Other sounds produced include purring, puffing, bleating and humming. Roaring is used to advertise its presence. Lions most often roar at night, a sound that can be heard from a distance of . Schaller, pp. 103–113. They tend to roar in a very characteristic manner starting with a few deep, long roars that subside into a series of shorter ones.
When resting, lion socialisation occurs through a number of behaviours; the animal's expressive movements are highly developed. The most common peaceful, tactile gestures are Bunting_(animal_behavior), head rubbing and social licking, Schaller, p. 85. which have been compared with the role of allogrooming among primates. Head rubbing—nuzzling the forehead, face and neck against another lion—appears to be a form of greeting and is seen often after an animal has been apart from others or after a fight or confrontation. Males tend to rub other males, while cubs and females rub females. Schaller, pp. 85–88. Social licking often occurs in tandem with head rubbing; it is generally mutual and the recipient appears to express pleasure. The head and neck are the most common parts of the body licked; this behaviour may have arisen out of utility because lions cannot lick these areas themselves. Schaller, pp. 88–91.
Lions have an array of facial expressions and body postures that serve as visual gestures. Schaller, pp. 103–117. A common facial expression is the "grimace face" or flehmen response, which a lion makes when sniffing chemical signals and involves an open mouth with bared teeth, raised muzzle, wrinkled nose closed eyes and relaxed ears. Lions also use chemical and visual marking; males will Territory (animal)#Scent marking, spray and scrape plots of ground and objects within the territory.
The lion's repertoire of vocalisations is large; variations in intensity and pitch appear to be central to communication. Most lion vocalisations are variations of growling, snarling, meowing and roaring. Other sounds produced include purring, puffing, bleating and humming. Roaring is used to advertise its presence. Lions most often roar at night, a sound that can be heard from a distance of . Schaller, pp. 103–113. They tend to roar in a very characteristic manner starting with a few deep, long roars that subside into a series of shorter ones.
 The last refuge of the Asiatic lion population is the Gir National Park and surrounding areas in the Saurashtra (region), region of Saurashtra or Kathiawar Peninsula in
The last refuge of the Asiatic lion population is the Gir National Park and surrounding areas in the Saurashtra (region), region of Saurashtra or Kathiawar Peninsula in
 Lions imported to Europe before the middle of the 19th century were possibly foremost Barbary lions from North Africa, or Cape lions from Southern Africa. Another 11 animals thought to be Barbary lions kept in Addis Ababa Zoo are descendants of animals owned by Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia, Emperor Haile Selassie. WildLink International in collaboration with Oxford University launched an ambitious International Barbary lion#The Barbary Lion Project, Barbary Lion Project with the aim of identifying and breeding Barbary lions in captivity for eventual reintroduction into a national park in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. However, a genetic analysis showed that the captive lions at Addis Ababa Zoo were not Barbary lions, but rather closely related to wild lions in Chad and Cameroon.
In 1982, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums started a Species Survival Plan for the Asiatic lion to increase its chances of survival. In 1987, it was found that most lions in North American zoos were hybrids between African and Asiatic lions. Breeding programs need to note origins of the participating animals to avoid cross-breeding different subspecies and thus reducing their conservation value. Captive breeding of lions was halted to eliminate individuals of unknown origin and Pedigree (animal), pedigree. Wild-born lions were imported to American zoos from Africa between 1989 and 1995. Breeding was continued in 1998 in the frame of an African lion Species Survival Plan.
About 77% of the captive lions registered in the International Species Information System in 2006 were of unknown origin; these animals might have carried genes that are extinct in the wild and may therefore be important to the maintenance of the overall genetic variability of the lion.
Lions imported to Europe before the middle of the 19th century were possibly foremost Barbary lions from North Africa, or Cape lions from Southern Africa. Another 11 animals thought to be Barbary lions kept in Addis Ababa Zoo are descendants of animals owned by Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia, Emperor Haile Selassie. WildLink International in collaboration with Oxford University launched an ambitious International Barbary lion#The Barbary Lion Project, Barbary Lion Project with the aim of identifying and breeding Barbary lions in captivity for eventual reintroduction into a national park in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. However, a genetic analysis showed that the captive lions at Addis Ababa Zoo were not Barbary lions, but rather closely related to wild lions in Chad and Cameroon.
In 1982, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums started a Species Survival Plan for the Asiatic lion to increase its chances of survival. In 1987, it was found that most lions in North American zoos were hybrids between African and Asiatic lions. Breeding programs need to note origins of the participating animals to avoid cross-breeding different subspecies and thus reducing their conservation value. Captive breeding of lions was halted to eliminate individuals of unknown origin and Pedigree (animal), pedigree. Wild-born lions were imported to American zoos from Africa between 1989 and 1995. Breeding was continued in 1998 in the frame of an African lion Species Survival Plan.
About 77% of the captive lions registered in the International Species Information System in 2006 were of unknown origin; these animals might have carried genes that are extinct in the wild and may therefore be important to the maintenance of the overall genetic variability of the lion.
 Lions do not usually hunt humans but some (usually males) seem to seek them out. One well-publicised case is the Tsavo maneaters; in 1898, 28 officially recorded railway workers building the Uganda Railway, Kenya-Uganda Railway were taken by lions over nine months during the construction of a bridge in Kenya. The hunter who killed the lions wrote a book detailing the animals' predatory behaviour; they were larger than normal and lacked manes, and one seemed to suffer from tooth decay. The infirmity theory, including tooth decay, is not favoured by all researchers; an analysis of teeth and jaws of man-eating lions in museum collections suggests that while tooth decay may explain some incidents, prey depletion in human-dominated areas is a more likely cause of lion predation on humans. Sick or injured animals may be more prone to man-eating but the behaviour is not unusual, nor necessarily aberrant.
Lions' proclivity for man-eating has been systematically examined. American and Tanzanian scientists report that man-eating behaviour in rural areas of Tanzania increased greatly from 1990 to 2005. At least 563 villagers were attacked and many eaten over this period. The incidents occurred near Selous Game Reserve, Selous National Park in Rufiji River, Rufiji District and in Lindi Region, Lindi Province near the Mozambican border. While the expansion of villages into bush country is one concern, the authors argue conservation policy must mitigate the danger because in this case, conservation contributes directly to human deaths. Cases in Lindi in which lions seize humans from the centres of substantial villages have been documented. Another study of 1,000 people attacked by lions in southern Tanzania between 1988 and 2009 found that the weeks following the full moon, when there was less moonlight, were a strong indicator of increased night-time attacks on people.
According to Robert R. Frump, Mozambican refugees regularly crossing Kruger National Park, South Africa, at night are attacked and eaten by lions; park officials have said man-eating is a problem there. Frump said thousands may have been killed in the decades after apartheid sealed the park and forced refugees to cross the park at night. For nearly a century before the border was sealed, Mozambicans had regularly crossed the park in daytime with little harm.
Lions do not usually hunt humans but some (usually males) seem to seek them out. One well-publicised case is the Tsavo maneaters; in 1898, 28 officially recorded railway workers building the Uganda Railway, Kenya-Uganda Railway were taken by lions over nine months during the construction of a bridge in Kenya. The hunter who killed the lions wrote a book detailing the animals' predatory behaviour; they were larger than normal and lacked manes, and one seemed to suffer from tooth decay. The infirmity theory, including tooth decay, is not favoured by all researchers; an analysis of teeth and jaws of man-eating lions in museum collections suggests that while tooth decay may explain some incidents, prey depletion in human-dominated areas is a more likely cause of lion predation on humans. Sick or injured animals may be more prone to man-eating but the behaviour is not unusual, nor necessarily aberrant.
Lions' proclivity for man-eating has been systematically examined. American and Tanzanian scientists report that man-eating behaviour in rural areas of Tanzania increased greatly from 1990 to 2005. At least 563 villagers were attacked and many eaten over this period. The incidents occurred near Selous Game Reserve, Selous National Park in Rufiji River, Rufiji District and in Lindi Region, Lindi Province near the Mozambican border. While the expansion of villages into bush country is one concern, the authors argue conservation policy must mitigate the danger because in this case, conservation contributes directly to human deaths. Cases in Lindi in which lions seize humans from the centres of substantial villages have been documented. Another study of 1,000 people attacked by lions in southern Tanzania between 1988 and 2009 found that the weeks following the full moon, when there was less moonlight, were a strong indicator of increased night-time attacks on people.
According to Robert R. Frump, Mozambican refugees regularly crossing Kruger National Park, South Africa, at night are attacked and eaten by lions; park officials have said man-eating is a problem there. Frump said thousands may have been killed in the decades after apartheid sealed the park and forced refugees to cross the park at night. For nearly a century before the border was sealed, Mozambicans had regularly crossed the park in daytime with little harm.
 The lion is one of the most widely recognised animal symbols in human culture. It has been extensively depicted in sculptures and paintings, on national flags, and in contemporary films and literature. It appeared as a symbol for strength and nobility in cultures across Europe, Asia and Africa, despite incidents of attacks on people. The lion has been depicted as "king of the jungle" and "king of beasts", and thus became a popular symbol for royalty and stateliness. The lion is also used as a symbol of sporting teams.
The lion is one of the most widely recognised animal symbols in human culture. It has been extensively depicted in sculptures and paintings, on national flags, and in contemporary films and literature. It appeared as a symbol for strength and nobility in cultures across Europe, Asia and Africa, despite incidents of attacks on people. The lion has been depicted as "king of the jungle" and "king of beasts", and thus became a popular symbol for royalty and stateliness. The lion is also used as a symbol of sporting teams.
 The lion was a prominent symbol in ancient Mesopotamia from Sumer up to Assyrian and Babylonian times, where it was strongly associated with kingship. Lions were among the major symbols of the goddess Inanna/Ishtar. The Lion of Babylon was the foremost symbol of the Babylonian Empire. The Lion of Judah is the biblical emblem of the tribe of Judah and the later Kingdom of Judah. Lions are frequently mentioned in the Bible, notably in the Book of Daniel, in which the Daniel (biblical figure), eponymous hero refuses to worship Darius the Mede, King Darius and is forced to sleep in Daniel in the lions' den, the lions' den where he is miraculously unharmed (). In the Book of Judges, Samson kills a lion as he travels to visit a Philistine woman.().
Indo-Persian chroniclers regarded the lion as keeper of order in the realm of animals. The Sanskrit word ''mrigendra'' signifies a lion as king of animals in general or deer in particular. Narasimha, the man-lion, is one of ten avatars of the Hinduism, Hindu god Vishnu. Singh is an History of India, ancient Indian Vedic Sanskrit, vedic name meaning "lion", dating back over 2,000 years. It was originally used only by Rajputs, a Hindu Kshatriya or military caste but is used by millions of Hindu Rajputs and more than twenty million Sikhs today. The Lion Capital of Ashoka, erected by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century CE, depicts four lions standing back to back. It was made the National Emblem of India in 1950. The lion is also symbolic for the Sinhalese people, the term derived from the Sanskrit ''Sinhala'', meaning "of lions" while a sword-wielding lion is the central figure on the national flag of Sri Lanka.
The lion is a common motif in Chinese art; it was first used in art during the late Spring and Autumn period (fifth or sixth century BC) and became more popular during the Han Dynasty (206 BCAD 220) when imperial guardian lions started to be placed in front of imperial palaces for protection. Because lions have never been native to China, early depictions were somewhat unrealistic; after the introduction of Buddhist art to China in the Tang Dynasty after the sixth century AD, lions were usually depicted wingless with shorter, thicker bodies and curly manes. The lion dance is a traditional dance in Chinese culture in which performers in lion costumes mimic a lion's movements, often with musical accompaniment from cymbals, drums and gongs. They are performed at Chinese New Year, the Mid-Autumn Festival, August Moon Festival and other celebratory occasions for good luck.
The lion was a prominent symbol in ancient Mesopotamia from Sumer up to Assyrian and Babylonian times, where it was strongly associated with kingship. Lions were among the major symbols of the goddess Inanna/Ishtar. The Lion of Babylon was the foremost symbol of the Babylonian Empire. The Lion of Judah is the biblical emblem of the tribe of Judah and the later Kingdom of Judah. Lions are frequently mentioned in the Bible, notably in the Book of Daniel, in which the Daniel (biblical figure), eponymous hero refuses to worship Darius the Mede, King Darius and is forced to sleep in Daniel in the lions' den, the lions' den where he is miraculously unharmed (). In the Book of Judges, Samson kills a lion as he travels to visit a Philistine woman.().
Indo-Persian chroniclers regarded the lion as keeper of order in the realm of animals. The Sanskrit word ''mrigendra'' signifies a lion as king of animals in general or deer in particular. Narasimha, the man-lion, is one of ten avatars of the Hinduism, Hindu god Vishnu. Singh is an History of India, ancient Indian Vedic Sanskrit, vedic name meaning "lion", dating back over 2,000 years. It was originally used only by Rajputs, a Hindu Kshatriya or military caste but is used by millions of Hindu Rajputs and more than twenty million Sikhs today. The Lion Capital of Ashoka, erected by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century CE, depicts four lions standing back to back. It was made the National Emblem of India in 1950. The lion is also symbolic for the Sinhalese people, the term derived from the Sanskrit ''Sinhala'', meaning "of lions" while a sword-wielding lion is the central figure on the national flag of Sri Lanka.
The lion is a common motif in Chinese art; it was first used in art during the late Spring and Autumn period (fifth or sixth century BC) and became more popular during the Han Dynasty (206 BCAD 220) when imperial guardian lions started to be placed in front of imperial palaces for protection. Because lions have never been native to China, early depictions were somewhat unrealistic; after the introduction of Buddhist art to China in the Tang Dynasty after the sixth century AD, lions were usually depicted wingless with shorter, thicker bodies and curly manes. The lion dance is a traditional dance in Chinese culture in which performers in lion costumes mimic a lion's movements, often with musical accompaniment from cymbals, drums and gongs. They are performed at Chinese New Year, the Mid-Autumn Festival, August Moon Festival and other celebratory occasions for good luck.
 Lion-headed figures and amulets were excavated in tombs in the Greek islands of Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Paros and Chios. They are associated with the Egyptian deity Sekhmet and date to the early Iron Age between the 9th and 6th centuries BC. The lion is featured in several of Aesop's fables, notably The Lion and the Mouse. The Nemean lion was symbolic in ancient Greece and Rome, represented as the constellation and zodiac sign Leo (astrology), Leo, and described in mythology, where it was killed and worn by the hero Heracles, symbolising victory over death. Lancelot and Gawain were also heroes slaying lions in the
Lion-headed figures and amulets were excavated in tombs in the Greek islands of Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Paros and Chios. They are associated with the Egyptian deity Sekhmet and date to the early Iron Age between the 9th and 6th centuries BC. The lion is featured in several of Aesop's fables, notably The Lion and the Mouse. The Nemean lion was symbolic in ancient Greece and Rome, represented as the constellation and zodiac sign Leo (astrology), Leo, and described in mythology, where it was killed and worn by the hero Heracles, symbolising victory over death. Lancelot and Gawain were also heroes slaying lions in the
cat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
of the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
''Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family (biology), family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as co ...
'' native to Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother wasp ...
, forming groups called ''prides''. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
s. The lion is an apex
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
Arts and media Fictional entities
* Apex (comics), a teenaged super villainess in the Marvel Universe
* Ape-X, a super-intelligent ape in the Squadron Supreme universe
*Apex ...
and keystone predator
A keystone species is a species which has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance, a concept introduced in 1969 by the zoologist Robert T. Paine. Keystone species play a critical role in maintaini ...
; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, lions typically don't actively seek out and prey on humans.
The lion inhabits grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
s, savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
s and shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It m ...
s. It is usually more diurnal than other wild cats, but when persecuted, it adapts to being active at night and at twilight. During the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period, the lion ranged throughout Africa and Eurasia from Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (al ...
to India, but it has been reduced to fragmented populations in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
and one population in western India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Union te ...
. It has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
since 1996 because populations in African countries have declined by about 43% since the early 1990s. Lion populations are untenable outside designated protected areas. Although the cause of the decline is not fully understood, habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and conflicts with humans are the greatest causes for concern.
One of the most widely recognised animal symbols in human culture, the lion has been extensively depicted in sculptures and paintings, on national flags, and in contemporary films and literature. Lions have been kept in menagerie
A menagerie is a collection of captive animals, frequently exotic, kept for display; or the place where such a collection is kept, a precursor to the modern Zoo, zoological garden.
The term was first used in 17th-century France, in reference to ...
s since the time of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
and have been a key species sought for exhibition in zoological garden
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zool ...
s across the world since the late 18th century. Cultural depictions of lions
Cultural depictions of lions are known in countries of Afro-Eurasia. The lion has been an important symbol to humans for tens of thousands of years. The earliest graphic representations feature lions as organized hunters with great strength, str ...
were prominent in Ancient Egypt, and depictions have occurred in virtually all ancient and medieval cultures in the lion's historic and current range.
Etymology
The English word ''lion'' is derived viaAnglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
*Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 ...
from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
(nominative: ), which in turn was a borrowing from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
. The Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
word may also be related. The generic name ''Panthera'' is traceable to the classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later periods ...
word 'panthēra' and the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
word πάνθηρ 'panther'.
Taxonomy
scientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
used by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in 1758, who described the lion in his work ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''. The genus name ''Panthera'' was coined by Lorenz Oken
Lorenz Oken (1 August 1779 – 11 August 1851) was a German naturalist, botanist, biologist, and ornithologist.
Oken was born Lorenz Okenfuss (german: Okenfuß) in Bohlsbach (now part of Offenburg), Ortenau, Baden, and studied natural history and ...
in 1816. Between the mid-18th and mid-20th centuries, 26 lion specimen
Specimen may refer to:
Science and technology
* Sample (material), a limited quantity of something which is intended to be similar to and represent a larger amount
* Biological specimen or biospecimen, an organic specimen held by a biorepository ...
s were described and proposed as subspecies, of which 11 were recognised as valid in 2005. They were distinguished mostly by the size and colour of their manes and skins.
Subspecies
 In the 19th and 20th centuries, several lion
In the 19th and 20th centuries, several lion type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
s were described and proposed as subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, with about a dozen recognised as valid taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
until 2017. Between 2008 and 2016, IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
assessors used only two subspecific names: ''P. l. leo'' for African lion populations, and ''P. l. persica'' for the Asiatic lion population. In 2017, the Cat Classification Task Force of the Cat Specialist Group revised lion taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
, and recognises two subspecies based on results of several phylogeographic
Phylogeography is the study of the historical processes that may be responsible for the past to present geographic distributions of genealogical lineages. This is accomplished by considering the geographic distribution of individuals in light of ge ...
studies on lion evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, namely:
* ''P. l. leo'' − the nominate
Nomination is part of the process of selecting a candidate for either election to a public office, or the bestowing of an honor or award. A collection of nominees narrowed from the full list of candidates is a short list.
Political office
In the ...
lion subspecies includes the Asiatic lion
The Asiatic lion is a population of ''Panthera leo leo'' that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat ...
, the regionally extinct
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
Barbary lion
The Barbary lion, also called the North African lion, Berber lion, Atlas lion, and Egyptian lion, is an extinct population of the lion subspecies ''Panthera leo leo''. It lived in the mountains and deserts of the Barbary Coast of North Africa, f ...
, and lion populations in West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
and northern parts of Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
. Synonyms
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
include ''P. l. persica'' , ''P. l. senegalensis'' , ''P. l. kamptzi'' , and ''P. l. azandica'' . Multiple authors referred to it as 'northern lion' and 'northern subspecies'.
* ''P. l. melanochaita'' − includes the extinct Cape lion and lion populations in East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
n regions. Synonyms include ''P. l. somaliensis'' , ''P. l. massaica'' , ''P. l. sabakiensis'' , ''P. l. bleyenberghi'' , ''P. l. roosevelti'' , ''P. l. nyanzae'' , ''P. l. hollisteri'' , ''P. l. krugeri'' , ''P. l. vernayi'' , and ''P. l. webbiensis'' . It has been referred to as 'southern subspecies' and 'southern lion'.
However, there seems to be some degree of overlap between both groups in northern Central Africa. DNA analysis from a more recent study indicates, that Central African lions are derived from both northern and southern lions, as they cluster with ''P. leo leo'' in mtDNA-based phylogenies whereas their genomic DNA indicates a closer relationship with P. ''leo melanochaita''.
Lion samples from some parts of the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
cluster genetically with those from Cameroon and Chad, while lions from other areas of Ethiopia cluster with samples from East Africa. Researchers therefore assume Ethiopia is a contact zone between the two subspecies. Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
-wide data of a wild-born historical lion sample from Sudan showed that it clustered with ''P. l. leo'' in mtDNA-based phylogenies, but with a high affinity to ''P. l. melanochaita''. This result suggested that the taxonomic position of lions in Central Africa may require revision.
Fossil records
 Other lion subspecies or
Other lion subspecies or sister species
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
to the modern lion existed in prehistoric times:
*'' P. l. sinhaleyus'' was a fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
carnassial
Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified f ...
excavated in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, which was attributed to a lion. It is thought to have become extinct around 39,000 years ago.
* ''P. leo fossilis'' was larger than the modern lion and lived in the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The ...
. Bone fragments were excavated in caves in the United Kingdom, Germany, Italy and Czech Republic.
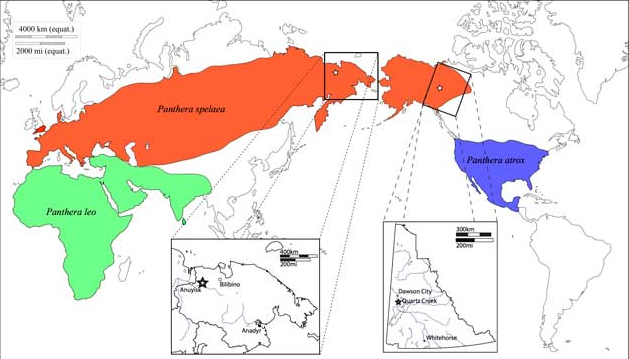
*'' P. spelaea'', or the cave lion, lived in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
and Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
during the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of ...
. It became extinct due to climate warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
or human expansion latest by 11,900 years ago. Bone fragments excavated in European, North Asian, Canadian and Alaskan caves indicate that it ranged from Europe across Siberia into western Alaska. It likely derived from ''P. fossilis'', and was genetically isolated and highly distinct from the modern lion in Africa and Eurasia. It is depicted in Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
cave paintings, ivory carvings, and clay busts.
* ''P. atrox'', or the American lion, ranged in the Americas from Canada to possibly Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ...
. It arose when a cave lion population in Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
became isolated south of the Cordilleran Ice Sheet about 370,000 years ago. A fossil from Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
dates to 11,355 ± 55 years ago.
Evolution
 The ''Panthera''
The ''Panthera'' lineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populati ...
is estimated to have genetically diverged from the common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
of the Felidae
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the ...
around to ,
and the geographic origin of the genus is most likely northern Central Asia.
Results of analyses differ in the phylogenetic relationship of the lion; it was thought to form a sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
with the jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus '' Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
(''P. onca'') that diverged , but also with the leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
(''P. pardus'') that diverged to . Hybridisation between lion and snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia''), also known as the ounce, is a Felidae, felid in the genus ''Panthera'' native to the mountain ranges of Central Asia, Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable species, Vulnerable on the IUCN Red ...
(''P. uncia'') ancestors possibly continued until about 2.1 million years ago. The lion-leopard clade was distributed in the Asian and African Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sibe ...
since at least the early Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Olduvai Gorge
The Olduvai Gorge or Oldupai Gorge in Tanzania is one of the most important paleoanthropology, paleoanthropological localities in the world; the many sites exposed by the gorge have proven invaluable in furthering understanding of early human ev ...
in Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
and are estimated to be up to 2 million years old.
Estimates for the divergence time of the modern and cave lion lineages range from 529,000 to 392,000 years ago based on mutation rate
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates ...
per generation time of the modern lion. There is no evidence for gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent a ...
between the two lineages, indicating that they did not share the same geographic area. The Eurasian and American cave lions became extinct at the end of the last glacial period without mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
descendants on other continents. The modern lion was probably widely distributed in Africa during the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The ...
and started to diverge in sub-Saharan Africa during the Late Pleistocene. Lion populations in East and Southern Africa became separated from populations in West and North Africa when the equatorial rainforest expanded 183,500 to 81,800 years ago. They shared a common ancestor probably between 98,000 and 52,000 years ago. Due to the expansion of the Sahara between 83,100 and 26,600 years ago, lion populations in West and North Africa became separated. As the rainforest decreased and thus gave rise to more open habitats, lions moved from West to Central Africa. Lions from North Africa dispersed to southern Europe and Asia between 38,800 and 8,300 years ago.
Extinction of lions in southern Europe, North Africa and the Middle East interrupted gene flow between lion populations in Asia and Africa. Genetic evidence revealed numerous mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
s in lion samples from East and Southern Africa, which indicates that this group has a longer evolutionary history than genetically less diverse lion samples from Asia and West and Central Africa. A whole genome-wide sequence of lion samples showed that samples from West Africa shared alleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
with samples from Southern Africa, and samples from Central Africa shared alleles with samples from Asia. This phenomenon indicates that Central Africa was a melting pot of lion populations after they had become isolated, possibly migrating through corridors in the Nile Basin
The Nile Basin is the part of Africa drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
Besides being the second largest hydrographic basin in Africa, the Nile Basin is effectively the most notable drainage basin on the continent. It covers approxim ...
during the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
.
Hybrids
In zoos, lions have been bred with tigers to create hybrids for the curiosity of visitors or for scientific purpose. Theliger
The liger is a hybrid offspring of a male lion (''Panthera leo'') and a female tiger (''Panthera tigris''). The liger has parents in the same genus but of different species. The liger is distinct from the similar hybrid called the tigon, and ...
is bigger than a lion and a tiger, whereas most tigon
A tigon (), tiglon () (portmanteau of ''tiger'' and ''lion''), or tion () is the hybrid offspring of a male tiger (''Panthera tigris'') and a female lion (''Panthera leo'').
s are relatively small compared to their parents because of reciprocal gene effects. The leopon
A leopon (portmanteau of ''leopard'' and ''lion'') is the hybrid offspring of a male leopard and a female lion. The head of the animal is similar to that of a lion while the rest of the body carries similarities to leopards. These hybrids are p ...
is a hybrid between a lion and leopard.
Description
The lion is a muscular, broad-chested cat with a short, rounded head, a reduced neck and round ears. Its fur varies in colour from light buff to silvery grey, yellowish red and dark brown. The colours of the underparts are generally lighter. A new-born lion has darkspots
Spot or SPOT may refer to:
Places
* Spot, North Carolina, a community in the United States
* The Spot, New South Wales, a locality in Sydney, Australia
* South Pole Traverse, sometimes called the South Pole Overland Traverse
People
* Spot (produ ...
, which fade as the cub reaches adulthood, although faint spots often may still be seen on the legs and underparts. The lion is the only member of the cat family that displays obvious sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
. Males have broader heads and a prominent mane that grows downwards and backwards covering most of the head, neck, shoulders, and chest. The mane is typically brownish and tinged with yellow, rust and black hairs.
The tail of all lions ends in a dark, hairy tuft that in some lions conceals an approximately -long, hard "spine" or "spur" that is formed from the final, fused sections of tail bone. The functions of the spur are unknown. The tuft is absent at birth and develops at around months of age. It is readily identifiable by the age of seven months. Schaller, pp. 28–30.
Of the living felid species, the lion is rivaled only by the tiger in length, weight, and height at the shoulder. Its skull is very similar to that of the tiger, although the frontal region is usually more depressed and flattened, and has a slightly shorter postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
region and broader nasal openings than those of the tiger. Due to the amount of skull variation in the two species, usually only the structure of the lower jaw can be used as a reliable indicator of species.
Skeletal muscles of the lion make up 58.8% of its body weight and represents the highest percentage of muscles among mammals.
Size
The size and weight of adult lions varies across global range and habitats. Accounts of a few individuals that were larger than average exist from Africa and India.Mane
The male lion's mane is the most recognisable feature of the species. It may have evolved around 320,000–190,000 years ago. It starts growing when lions are about a year old. Mane colour varies and darkens with age; research shows its colour and size are influenced by environmental factors such as average ambient temperature. Mane length apparently signals fighting success in male–male relationships; darker-maned individuals may have longer reproductive lives and higher offspring survival, although they suffer in the hottest months of the year. The presence, absence, colour and size of the mane are associated with genetic precondition, sexual maturity, climate andtestosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
production; the rule of thumb is that a darker, fuller mane indicates a healthier animal. In Serengeti National Park
The Serengeti National Park is a large national park in northern Tanzania that stretches over . It is located entirely in eastern Mara Region and north east portion of Simiyu Region and contains over of virgin savanna. The park was established in ...
, female lions favour males with dense, dark manes as mates. Cool ambient temperature in European and North American zoos may result in a heavier mane. Asiatic lions usually have sparser manes than average African lions.
Almost all male lions in Pendjari National Park
The Pendjari National Park (french: Parc National de la Pendjari) lies in north western Benin, adjoining the Arli National Park in Burkina Faso. Named for the Pendjari River, the national park is known for its wildlife and is home to some of the ...
are either maneless or have very short manes. Maneless lion
The term "maneless lion" or "scanty mane lion" often refers to a male lion without a mane, or with a weak one. The purpose of the mane is thought to protect the lion in territorial fights. Although lions are known for their mane, not all males ...
s have also been reported in Senegal, in Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
's Dinder National Park
Dinder National Park is a national park and biosphere reserve in eastern Sudan, and is connected to Ethiopia's Alitash National Park.
Location
Dinder lies approximately southeast of Khartoum, on either side of the Dinder River bounded to the n ...
and in Tsavo East National Park
Tsavo East National Park is one of the oldest and largest parks in Kenya at 13,747 square kilometres. Situated in a semi-arid area previously known as the Taru Desert it opened in April 1948, and is located near the town of Voi in the Taita ...
, Kenya. The original male white lion from Timbavati
The Timbavati Private Nature Reserve is located at the border line between Hoedspruit (in Limpopo) and Acornhoek (in Mpumalanga), north of the Sabi Sand Private Game Reserve on the western edge of Kruger National Park. Geographically and poli ...
in South Africa was also maneless. The hormone testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
has been linked to mane growth; castrated
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceut ...
lions often have little to no mane because the removal of the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s inhibits testosterone production. Increased testosterone may be the cause of maned lionesses reported in northern Botswana.
Colour variation
The white lion is a raremorph
Morph may refer to:
Biology
* Morph (zoology), a visual or behavioral difference between organisms of distinct populations in a species
* Muller's morphs, a classification scheme for genetic mutations
* "-morph", a suffix commonly used in tax ...
with a genetic condition called leucism
Leucism () is a wide variety of conditions that result in the partial loss of pigmentation in an animal—causing white, pale, or patchy coloration of the skin, hair, feathers, scales, or cuticles, but not the eyes. It is occasionally spelled ' ...
which is caused by a double recessive allele
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
. It is not albino; it has normal pigmentation in the eyes and skin. White lions have occasionally been encountered in and around Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
and the adjacent Timbavati Private Game Reserve
The Timbavati Private Nature Reserve is located at the border line between Hoedspruit (in Limpopo) and Acornhoek (in Mpumalanga), north of the Sabi Sand Private Game Reserve on the western edge of Kruger National Park. Geographically and politi ...
in eastern South Africa. They were removed from the wild in the 1970s, thus decreasing the white lion gene pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species.
Description
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can surv ...
. Nevertheless, 17 births have been recorded in five prides between 2007 and 2015. White lions are selected for breeding in captivity. They have reportedly been bred in camps in South Africa for use as trophies to be killed during canned hunt
A canned hunt is a trophy hunt which is not " fair chase", typically by having game animals kept in a confined area such as in a fenced ranch (i.e. "canned") to prevent the animals' escape and make tracking easier for the hunter, in order to inc ...
s.
Distribution and habitat
 African lions live in scattered populations across sub-Saharan Africa. The lion prefers grassy plains and
African lions live in scattered populations across sub-Saharan Africa. The lion prefers grassy plains and savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to rea ...
s, scrub bordering rivers and open woodlands with bushes. It rarely enters closed forests. On Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
, the lion has been recorded up to an elevation of and close to the snow line on Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the second-highest in Africa, after Kilimanjaro. The highest peaks of the mountain are Batian (), Nelion () and Point Lenana (). Mount Kenya is locat ...
. Savannahs with an annual rainfall of make up the majority of lion habitat in Africa, estimated at at most, but remnant populations are also present in tropical moist forests in West Africa and montane
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial f ...
forests in East Africa. The Asiatic lion now survives only in and around Gir National Park
Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary, also known as Sasan Gir, is a forest, national park, and wildlife sanctuary near Talala Gir in Gujarat, India. It is located north-east of Somnath, south-east of Junagadh and south-west of Amreli ...
in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, western India. Its habitat is a mixture of dry savannah forest and very dry, deciduous scrub forest
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It ma ...
.
Historical range
In Africa, the range of the lion originally spanned most of the centralAfrican rainforest
Although tropical Africa is mostly familiar to the West for its rainforests, this biogeographic realm of Africa is far more diverse. While the tropics are thought of as regions with hot moist climates, which are caused by latitude and the trop ...
zone and the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
desert. Schaller, p. 5. In the 1960s, it became extinct in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, except in the southern part of Sudan.
In southern Europe and Asia, the lion once ranged in regions where climatic conditions supported an abundance of prey. In Greece, it was common as reported by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
in 480 BC; it was considered rare by 300 BC and extirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
by AD 100. It was present in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
until the 10th century. It lived in Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
until the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, and in Southwest Asia until the late 19th century. By the late 19th century, it had been extirpated in most of Turkey. The last live lion in Iran was sighted in 1942 about northwest of Dezful
Dezful ( fa, دزفول, pronounced , Dezfuli dialect: Desfil, pronounced ) also Romanized as Dezfūl and Dezfool; also known as Dīzfūl and Ab I Diz is a city and capital of Dezful County, Khuzestan Province, Iran. At the 2011 census, its popul ...
, although the corpse of a lioness was found on the banks of the Karun
The Karun ( fa, کارون, ) is the Iranian river with the highest water flow, and its only navigable river. It is long. It rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari people, Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tribut ...
river in Khūzestān Province
Khuzestan Province (also spelled Xuzestan; fa, استان خوزستان ''Ostān-e Xūzestān'') is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the southwest of the country, bordering Iraq and the Persian Gulf. Its capital is Ahvaz and it covers ...
in 1944. It once ranged from Sind
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
in Pakistan to Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and the Narmada River in central India.
Behaviour and ecology
Lions spend much of their time resting; they are inactive for about twenty hours per day. Schaller, p. 122. Although lions can be active at any time, their activity generally peaks after dusk with a period of socialising, grooming and defecating. Intermittent bursts of activity continue until dawn, when hunting most often takes place. They spend an average of two hours a day walking and fifty minutes eating. Schaller, pp. 120–21.Group organisation
The lion is the most social of all wild felid species, living in groups of related individuals with their offspring. Such a group is called a "pride
Pride is defined by Merriam-Webster as "reasonable self-esteem" or "confidence and satisfaction in oneself". A healthy amount of pride is good, however, pride sometimes is used interchangeably with "conceit" or "arrogance" (among other words) wh ...
". Groups of male lions are called "coalitions". Schaller, p. 33. Females form the stable social unit
The term "level of analysis" is used in the social sciences to point to the location, size, or scale of a research target.
"Level of analysis" is distinct from the term "unit of observation" in that the former refers to a more or less integrated s ...
in a pride and do not tolerate outside females. Schaller, p. 37. Membership changes only with the births and deaths of lionesses, Schaller, p. 39. although some females leave and become nomadic. Schaller, p. 44. The average pride consists of around 15 lions, including several adult females and up to four males and their cubs of both sexes. Large prides, consisting of up to 30 individuals, have been observed. The sole exception to this pattern is the Tsavo lion
''Panthera leo melanochaita'' is a lion subspecies in Southern and East Africa. In this part of Africa, lion populations are regionally extinct in Lesotho, Djibouti and Eritrea, and are threatened by loss of habitat and prey base, killing by local ...
pride that always has just one adult male. Male cubs are excluded from their maternal pride when they reach maturity at around two or three years of age.
Some lions are "nomads" that range widely and move around sporadically, either in pairs or alone. Pairs are more frequent among related males who have been excluded from their birth pride. A lion may switch lifestyles; nomads can become residents and vice versa. Interactions between prides and nomads tend to be hostile, although pride females in estrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
allow nomadic males to approach them. Males spend years in a nomadic phase before gaining residence in a pride. A study undertaken in the Serengeti National Park revealed that nomadic coalitions gain residency at between 3.5 and 7.3 years of age. In Kruger National Park, dispersing male lions move more than away from their natal pride in search of their own territory. Female lions stay closer to their natal pride. Therefore, female lions in an area are more closely related to each other than male lions in the same area.
The area occupied by a pride is called a "pride area" whereas that occupied by a nomad is a "range". Males associated with a pride tend to stay on the fringes, patrolling their territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
. The reasons for the development of sociality
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother wasp ...
in lionesses—the most pronounced in any cat species—are the subject of much debate. Increased hunting success appears to be an obvious reason, but this is uncertain upon examination; coordinated hunting allows for more successful predation but also ensures non-hunting members reduce ''per capita'' calorific intake. Some females, however, take a role raising cubs that may be left alone for extended periods. Members of the pride tend to regularly play the same role in hunts and hone their skills. The health of the hunters is the primary need for the survival of the pride; hunters are the first to consume the prey at the site it is taken. Other benefits include possible kin selection
Kin selection is the evolutionary strategy that favours the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even when at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction. Kin altruism can look like Altruism in animals, altruistic behavio ...
, sharing food within the family, protecting the young, maintaining territory, and individual insurance against injury and hunger.
Both males and females defend the pride against intruders, but the male lion is better-suited for this purpose due to its stockier, more powerful build. Some individuals consistently lead the defence against intruders, while others lag behind. Lions tend to assume specific roles in the pride; slower-moving individuals may provide other valuable services to the group. Alternatively, there may be rewards associated with being a leader that fends off intruders; the rank of lionesses in the pride is reflected in these responses. The male or males associated with the pride must defend their relationship with the pride from outside males who may attempt to usurp them.
Asiatic lion prides differ in group composition. Male Asiatic lions are solitary or associate with up to three males, forming a loose pride while females associate with up to 12 other females, forming a stronger pride together with their cubs. Female and male lions associate only when mating. Coalitions of males hold territory for a longer time than single lions. Males in coalitions of three or four individuals exhibit a pronounced hierarchy, in which one male dominates the others and mates more frequently.
Hunting and diet
The lion is ageneralist
A generalist is a person with a wide array of knowledge on a variety of subjects, useful or not. It may also refer to:
Occupations
* a physician who provides general health care, as opposed to a medical specialist; see also:
** General pract ...
hypercarnivore
A hypercarnivore is an animal which has a diet that is more than 70% meat, either via active predation or by scavenging. The remaining non-meat diet may consist of non-animal foods such as fungi, fruits or other plant material. Some extant examp ...
and is considered to be both an apex and keystone predator due to its wide prey spectrum. Its prey consists mainly of ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
s weighing , particularly blue wildebeest
The blue wildebeest (''Connochaetes taurinus''), also called the common wildebeest, white-bearded gnu or brindled gnu, is a large antelope and one of the two species of wildebeest. It is placed in the genus '' Connochaetes'' and family Bovidae, a ...
, plains zebra
The plains zebra (''Equus quagga'', formerly ''Equus burchellii''), also known as the common zebra, is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of ...
, African buffalo, gemsbok
The gemsbok or South African oryx (''Oryx gazella'') is a large antelope in the genus ''Oryx''. It is native to the extremely dry, arid regions of Southern Africa; notably, the Kalahari Desert. Some authorities formerly classified the East Afric ...
and giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
. They also hunt common warthog
The common warthog (''Phacochoerus africanus'') is a wild member of the pig family (Suidae) found in grassland, savanna, and woodland in sub-Saharan Africa. In the past, it was commonly treated as a subspecies of ''P. aethiopicus'', but today th ...
depending on availability, despite weighing less than the preferred weight range. In India, chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
and sambar deer
The sambar (''Rusa unicolor'') is a large deer native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia that is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 2008. Populations have declined substantially due to severe hunting, local ins ...
are the most common wild prey, while livestock contributes significantly to lion kills outside protected areas. They usually avoid fully grown adult elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae an ...
s, rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species o ...
es and hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
and small prey like dik-dik
A dik-dik is the name for any of four species of small antelope in the genus ''Madoqua'' that live in the bushlands of eastern and southern Africa.
Dik-diks stand about at the shoulder, are long, weigh and can live for up to 10 years. Dik- ...
, hyrax
Hyraxes (), also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between long and weigh between . They are superficially simil ...
es, hare
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores, and live solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are able to fend for themselves shortly after birth. The ge ...
s and monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s. Unusual prey include porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizont ...
s and small reptiles. Lions kill other predators but seldom consume them.
Young lions first display stalking behaviour at around three months of age, although they do not participate in hunting until they are almost a year old and begin to hunt effectively when nearing the age of two. Schaller, p. 153. Single lions are capable of bringing down zebra and wildebeest, while larger prey like buffalo and giraffe are riskier. In Chobe National Park
Chobe National Park is Botswana's first national park, and also the most biologically diverse. Located in the north of the country, it is Botswana's third largest park, after Central Kalahari Game Reserve and Gemsbok National Park, and has one of ...
, large prides have been observed hunting African bush elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana'') is one of two extant African elephant species and one of three extant elephant species. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with bulls reaching a shoulder height of up to and a body ...
s up to around 15 years old in exceptional cases, with the victims being calves, juveniles, and even subadults. In typical hunts, each lioness has a favoured position in the group, either stalking prey on the "wing", then attacking, or moving a smaller distance in the centre of the group and capturing prey fleeing from other lionesses. Males attached to prides do not usually participate in group hunting. Some evidence suggests, however, that males are just as successful as females; they are typically solo hunters who ambush prey in small bushland.
Lions are not particularly known for their stamina. For instance, a lioness's heart comprises only 0.57% of her body weight and a male's is about 0.45% of his body weight, whereas a hyena's heart comprises almost 1% of its body weight. Thus, lions run quickly only in short bursts at about and need to be close to their prey before starting the attack. Schaller, pp. 233, 247–248 One study in 2018 recorded a lion running at a top speed of . They take advantage of factors that reduce visibility; many kills take place near some form of cover or at night. Schaller, p. 237. The lion's attack is short and powerful; they attempt to catch prey with a fast rush and final leap. They usually pull it down by the rump and kill by a strangling bite to the throat. They also kill prey by enclosing its muzzle in their jaws. Male lions usually aim for the backs or hindquarters of rivals, rather than their necks.
Lions typically consume prey at the location of the hunt but sometimes drag large prey into cover. They tend to squabble over kills, particularly the males. Cubs suffer most when food is scarce but otherwise all pride members eat their fill, including old and crippled lions, which can live on leftovers. Large kills are shared more widely among pride members. Schaller, p. 133. An adult lioness requires an average of about of meat per day while males require about . Lions gorge themselves and eat up to in one session. If it is unable to consume all of the kill, it rests for a few hours before continuing to eat. On hot days, the pride retreats to shade with one or two males standing guard. Schaller, pp. 270–76. Lions defend their kills from scavengers such as vultures and hyenas.
Lions scavenge on carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
when the opportunity arises, scavenging animals dead from natural causes such as disease or those that were killed by other predators. Scavenging lions keep a constant lookout for circling vultures, which indicate the death or distress of an animal. Schaller, p. 213–216. Most carrion on which both hyenas and lions feed upon are killed by hyenas rather than lions. Carrion is thought to provide a large part of lion diet.
Predatory competition
Lions andspotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s occupy a similar ecological niche and compete for prey and carrion; a review of data across several studies indicates a dietary overlap of 58.6%. Lions typically ignore hyenas unless they are on a kill or are being harassed, while the latter tend to visibly react to the presence of lions with or without the presence of food. In the Ngorongoro crater
The Ngorongoro Conservation Area (, ) is a protected area and a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Ngorongoro District, west of Arusha City in Arusha Region, within the Crater Highlands geological area of northern Tanzania. The area is nam ...
, lions subsist largely on kills stolen from hyenas, causing them to increase their kill rate. In Botswana's Chobe National Park, the situation is reversed as hyenas there frequently challenge lions and steal their kills, obtaining food from 63% of all lion kills. When confronted on a kill, hyenas may either leave or wait patiently at a distance of until the lions have finished. Schaller, p. 272. Hyenas feed alongside lions and force them off a kill. The two species attack one another even when there is no food involved for no apparent reason. Schaller, pp. 273–74. Lion predation can account for up to 71% of hyena deaths in Etosha National Park
Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. ...
. Hyenas have adapted by frequently mobbing lions that enter their home ranges. When the lion population in Kenya's Masai Mara National Reserve
Maasai Mara, also sometimes spelled Masai Mara and locally known simply as The Mara, is a large national game reserve in Narok, Kenya, contiguous with the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania. It is named in honor of the Maasai people, the ancest ...
declined, the spotted hyena population increased rapidly.
Lions tend to dominate cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
s and leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s, steal their kills and kill their cubs and even adults when given the chance. Cheetahs often lose their kills to lions or other predators. A study in the Serengeti ecosystem revealed that lions killed at least 17 of 125 cheetah cubs born between 1987 and 1990. Cheetahs avoid their competitors by hunting at different times and habitats. Leopards take refuge in trees, but lionesses occasionally attempt to climb up and retrieve their kills. Schaller, p. 293.
Lions similarly dominate African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called the painted dog or Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a native species to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Ly ...
s, taking their kills and slaying pups or adult dogs. Population densities of wild dogs are low in areas where lions are more abundant. However, there are a few reported cases of old and wounded lion falling prey to wild dogs. Schaller, p. 188. Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern ...
s may also kill and eat lions, evidenced by the occasional lion claw found in crocodile stomachs.
Reproduction and life cycle
Most lionesses reproduce by the time they are four years of age. Schaller, p. 29. Lions do not mate at a specific time of year and the females arepolyestrous
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
. Schaller, p. 174. Like those of other cats, the male lion's penis has spines that point backward. During withdrawal of the penis, the spines rake the walls of the female's vagina, which may cause ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized ...
. A lioness may mate with more than one male when she is in heat
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
. Schaller, p. 142. Generation length of the lion is about seven years. The average gestation period is around 110days; the female gives birth to a litter of between one and four cubs in a secluded den, which may be a thicket, a reed-bed, a cave, or some other sheltered area, usually away from the pride. She will often hunt alone while the cubs are still helpless, staying relatively close to the den.Scott
Scott may refer to:
Places Canada
* Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec
* Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380
* Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Saska ...
, p. 45. Lion cubs are born blind, their eyes opening around seven days after birth. They weigh at birth and are almost helpless, beginning to crawl a day or two after birth and walking around three weeks of age. Schaller, p. 143. To avoid a buildup of scent attracting the attention of predators, the lioness moves her cubs to a new den site several times a month, carrying them one-by-one by the nape of the neck.
Usually, the mother does not integrate herself and her cubs back into the pride until the cubs are six to eight weeks old. Sometimes the introduction to pride life occurs earlier, particularly if other lionesses have given birth at about the same time. When first introduced to the rest of the pride, lion cubs lack confidence when confronted with adults other than their mother. They soon begin to immerse themselves in the pride life, however, playing among themselves or attempting to initiate play with the adults. Lionesses with cubs of their own are more likely to be tolerant of another lioness's cubs than lionesses without cubs. Male tolerance of the cubs varies—one male could patiently let the cubs play with his tail or his mane, while another may snarl and bat the cubs away.
Pride lionesses often synchronise their reproductive cycles and communal rearing and suckling of the young, which suckle indiscriminately from any or all of the nursing females in the pride. The synchronisation of births is advantageous because the cubs grow to being roughly the same size and have an equal chance of survival, and sucklings are not dominated by older cubs. Schaller, p. 147-49. Weaning occurs after six or seven months. Male lions reach maturity at about three years of age and at four to five years are capable of challenging and displacing adult males associated with another pride. They begin to age and weaken at between 10 and 15 years of age at the latest.
When one or more new males oust the previous males associated with a pride, the victors often infanticide (zoology), kill any existing young cubs, perhaps because females do not become fertile and receptive until their cubs mature or die. Females often fiercely defend their cubs from a usurping male but are rarely successful unless a group of three or four mothers within a pride join forces against the male. Cubs also die from starvation and abandonment, and predation by leopards, hyenas and wild dogs. Up to 80% of lion cubs will die before the age of two. Both male and female lions may be ousted from prides to become nomads, although most females usually remain with their birth pride. When a pride becomes too large, however, the youngest generation of female cubs may be forced to leave to find their own territory. When a new male lion takes over a pride, adolescents both male and female may be evicted. Lions of both sexes may be involved in group Homosexuality in animals, homosexual and courtship activities. Males will also head-rub and roll around with each other before simulating sex together.
Health and mortality
Communication
 When resting, lion socialisation occurs through a number of behaviours; the animal's expressive movements are highly developed. The most common peaceful, tactile gestures are Bunting_(animal_behavior), head rubbing and social licking, Schaller, p. 85. which have been compared with the role of allogrooming among primates. Head rubbing—nuzzling the forehead, face and neck against another lion—appears to be a form of greeting and is seen often after an animal has been apart from others or after a fight or confrontation. Males tend to rub other males, while cubs and females rub females. Schaller, pp. 85–88. Social licking often occurs in tandem with head rubbing; it is generally mutual and the recipient appears to express pleasure. The head and neck are the most common parts of the body licked; this behaviour may have arisen out of utility because lions cannot lick these areas themselves. Schaller, pp. 88–91.
Lions have an array of facial expressions and body postures that serve as visual gestures. Schaller, pp. 103–117. A common facial expression is the "grimace face" or flehmen response, which a lion makes when sniffing chemical signals and involves an open mouth with bared teeth, raised muzzle, wrinkled nose closed eyes and relaxed ears. Lions also use chemical and visual marking; males will Territory (animal)#Scent marking, spray and scrape plots of ground and objects within the territory.
The lion's repertoire of vocalisations is large; variations in intensity and pitch appear to be central to communication. Most lion vocalisations are variations of growling, snarling, meowing and roaring. Other sounds produced include purring, puffing, bleating and humming. Roaring is used to advertise its presence. Lions most often roar at night, a sound that can be heard from a distance of . Schaller, pp. 103–113. They tend to roar in a very characteristic manner starting with a few deep, long roars that subside into a series of shorter ones.
When resting, lion socialisation occurs through a number of behaviours; the animal's expressive movements are highly developed. The most common peaceful, tactile gestures are Bunting_(animal_behavior), head rubbing and social licking, Schaller, p. 85. which have been compared with the role of allogrooming among primates. Head rubbing—nuzzling the forehead, face and neck against another lion—appears to be a form of greeting and is seen often after an animal has been apart from others or after a fight or confrontation. Males tend to rub other males, while cubs and females rub females. Schaller, pp. 85–88. Social licking often occurs in tandem with head rubbing; it is generally mutual and the recipient appears to express pleasure. The head and neck are the most common parts of the body licked; this behaviour may have arisen out of utility because lions cannot lick these areas themselves. Schaller, pp. 88–91.
Lions have an array of facial expressions and body postures that serve as visual gestures. Schaller, pp. 103–117. A common facial expression is the "grimace face" or flehmen response, which a lion makes when sniffing chemical signals and involves an open mouth with bared teeth, raised muzzle, wrinkled nose closed eyes and relaxed ears. Lions also use chemical and visual marking; males will Territory (animal)#Scent marking, spray and scrape plots of ground and objects within the territory.
The lion's repertoire of vocalisations is large; variations in intensity and pitch appear to be central to communication. Most lion vocalisations are variations of growling, snarling, meowing and roaring. Other sounds produced include purring, puffing, bleating and humming. Roaring is used to advertise its presence. Lions most often roar at night, a sound that can be heard from a distance of . Schaller, pp. 103–113. They tend to roar in a very characteristic manner starting with a few deep, long roars that subside into a series of shorter ones.
Conservation
The lion is listed as Vulnerable on theIUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
. The Indian population is listed on CITES Appendix I and the African population on CITES Appendix II.
In Africa
Several large and well-managed protected areas in Africa host large lion populations. Where an infrastructure for wildlife tourism has been developed, cash revenue for park management and local communities is a strong incentive for lion conservation. Most lions now live in East and Southern Africa; their numbers are rapidly decreasing, and fell by an estimated 30–50% in the late half of the 20th century. Primary causes of the decline include disease and human interference. In 1975, it was estimated that since the 1950s, lion numbers had decreased by half to 200,000 or fewer. Estimates of the African lion population range between 16,500 and 47,000 living in the wild in 2002–2004. In the Republic of the Congo, Odzala-Kokoua National Park was considered a lion stronghold in the 1990s. By 2014, no lions were recorded in the protected area so the population is considered locally extinct. The West African lion population is isolated from the one in Central Africa, with little or no exchange of breeding individuals. In 2015, it was estimated that this population consists of about 400 animals, including fewer than 250 mature individuals. They persist in three protected areas in the region, mostly in one population in the W National Park, W Arli National Park, A Pendjari National Park, P protected area complex, shared by Benin, Burkina Faso and Niger. This population is listed as Critically Endangered. Field surveys in the W-Arly-Pendjari Complex, WAP ecosystem revealed that lion occupancy is lowest in the W National Park, and higher in areas with permanent staff and thus better protection. A population occurs in Cameroon's Waza National Park, where between approximately 14 and 21 animals persisted as of 2009. In addition, 50 to 150 lions are estimated to be present in Burkina Faso's Arly-Singou ecosystem. In 2015, an adult male lion and a female lion were sighted in Ghana's Mole National Park. These were the first sightings of lions in the country in 39 years. In the same year, a population of up to 200 lions that was previously thought to have beenextirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
was filmed in the Alatash National Park, Ethiopia, close to the Sudanese border.
In 2005, Lion Conservation Strategies were developed for West and Central Africa, and or East and Southern Africa. The strategies seek to maintain suitable habitat, ensure a sufficient wild prey base for lions, reduce factors that lead to further fragmentation of populations, and make lion–human coexistence sustainable. Lion depredation on livestock is significantly reduced in areas where herders keep livestock in improved enclosures. Such measures contribute to mitigating human–lion conflict.
In Asia
 The last refuge of the Asiatic lion population is the Gir National Park and surrounding areas in the Saurashtra (region), region of Saurashtra or Kathiawar Peninsula in
The last refuge of the Asiatic lion population is the Gir National Park and surrounding areas in the Saurashtra (region), region of Saurashtra or Kathiawar Peninsula in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
State, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The population has risen from approximately 180 lions in 1974 to about 400 in 2010. It is geographically isolated, which can lead to inbreeding and reduced genetic diversity. Since 2008, the Asiatic lion has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
. By 2015, the population had grown to 523 individuals inhabiting an area of in Saurashtra. The Asiatic Lion Census conducted in 2017 recorded about 650 individuals.
The presence of numerous human habitations close to the National Park results in conflict between lions, local people and their livestock. Some consider the presence of lions a benefit, as they keep populations of crop damaging herbivores in check. The establishment of a second, independent Asiatic lion population in Kuno Wildlife Sanctuary, located in Madhya Pradesh was planned but in 2017, the Asiatic Lion Reintroduction Project seemed unlikely to be implemented.
Captive breeding
 Lions imported to Europe before the middle of the 19th century were possibly foremost Barbary lions from North Africa, or Cape lions from Southern Africa. Another 11 animals thought to be Barbary lions kept in Addis Ababa Zoo are descendants of animals owned by Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia, Emperor Haile Selassie. WildLink International in collaboration with Oxford University launched an ambitious International Barbary lion#The Barbary Lion Project, Barbary Lion Project with the aim of identifying and breeding Barbary lions in captivity for eventual reintroduction into a national park in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. However, a genetic analysis showed that the captive lions at Addis Ababa Zoo were not Barbary lions, but rather closely related to wild lions in Chad and Cameroon.
In 1982, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums started a Species Survival Plan for the Asiatic lion to increase its chances of survival. In 1987, it was found that most lions in North American zoos were hybrids between African and Asiatic lions. Breeding programs need to note origins of the participating animals to avoid cross-breeding different subspecies and thus reducing their conservation value. Captive breeding of lions was halted to eliminate individuals of unknown origin and Pedigree (animal), pedigree. Wild-born lions were imported to American zoos from Africa between 1989 and 1995. Breeding was continued in 1998 in the frame of an African lion Species Survival Plan.
About 77% of the captive lions registered in the International Species Information System in 2006 were of unknown origin; these animals might have carried genes that are extinct in the wild and may therefore be important to the maintenance of the overall genetic variability of the lion.
Lions imported to Europe before the middle of the 19th century were possibly foremost Barbary lions from North Africa, or Cape lions from Southern Africa. Another 11 animals thought to be Barbary lions kept in Addis Ababa Zoo are descendants of animals owned by Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia, Emperor Haile Selassie. WildLink International in collaboration with Oxford University launched an ambitious International Barbary lion#The Barbary Lion Project, Barbary Lion Project with the aim of identifying and breeding Barbary lions in captivity for eventual reintroduction into a national park in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. However, a genetic analysis showed that the captive lions at Addis Ababa Zoo were not Barbary lions, but rather closely related to wild lions in Chad and Cameroon.
In 1982, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums started a Species Survival Plan for the Asiatic lion to increase its chances of survival. In 1987, it was found that most lions in North American zoos were hybrids between African and Asiatic lions. Breeding programs need to note origins of the participating animals to avoid cross-breeding different subspecies and thus reducing their conservation value. Captive breeding of lions was halted to eliminate individuals of unknown origin and Pedigree (animal), pedigree. Wild-born lions were imported to American zoos from Africa between 1989 and 1995. Breeding was continued in 1998 in the frame of an African lion Species Survival Plan.
About 77% of the captive lions registered in the International Species Information System in 2006 were of unknown origin; these animals might have carried genes that are extinct in the wild and may therefore be important to the maintenance of the overall genetic variability of the lion.
Interactions with humans
In zoos and circuses
Lions are part of a group of exotic animals that have been central to zoo exhibits since the late 18th century. Although many modern zoos are more selective about their exhibits,#Courcy, de Courcy, p. 81-82. there are more than 1,000 African and 100 Asiatic lions in zoos and wildlife parks around the world. They are considered an ambassador species and are kept for tourism, education and conservation purposes. Lions can live over twenty years in captivity; for example, three sibling lions at the Honolulu Zoo lived to the age of 22 in 2007. The first European "zoos" spread among noble and royal families in the 13th century, and until the 17th century were called seraglios. At that time, they came to be calledmenagerie
A menagerie is a collection of captive animals, frequently exotic, kept for display; or the place where such a collection is kept, a precursor to the modern Zoo, zoological garden.
The term was first used in 17th-century France, in reference to ...
s, an extension of the cabinet of curiosities. They spread from France and Italy during the Renaissance to the rest of Europe. In England, although the seraglio tradition was less developed, lions were Tower of London#Menagerie, kept at the Tower of London in a seraglio established by John of England, King John in the 13th century; this was probably stocked with animals from an earlier menagerie started in 1125 by Henry I of England, Henry I at his hunting lodge in Woodstock, Oxfordshire, where according to William of Malmesbury lions had been stocked.#Blunt, Blunt, p. 15.
Lions were kept in cramped and squalid conditions at London Zoo until a larger lion house with roomier cages was built in the 1870s.#Blunt, Blunt, p. 208. Further changes took place in the early 20th century when Carl Hagenbeck designed enclosures with concrete "rocks", more open space and a moat instead of bars, more closely resembling a natural habitat. Hagenbeck designed lion enclosures for both Melbourne Zoo and Sydney's Taronga Zoo; although his designs were popular, the use of bars and caged enclosures prevailed in many zoos until the 1960s.#Courcy, de Courcy, p. 69. In the late 20th century, larger, more natural enclosures and the use of wire mesh or laminated glass instead of lowered dens allowed visitors to come closer than ever to the animals; some attractions such as the Cat Forest/Lion Overlook of Oklahoma City Zoo and Botanical Garden, Oklahoma City Zoological Park placed the den on ground level, higher than visitors.
Lion taming has been part of both established circuses and individual acts such as Siegfried & Roy. The practice began in the early 19th century by Frenchman Henri Martin and American Isaac A. Van Amburgh, Isaac Van Amburgh, who both toured widely and whose techniques were copied by a number of followers. Van Amburgh performed before Queen Victoria in 1838 when he toured Great Britain. Martin composed a pantomime titled ''Les Lions de Mysore'' ("the lions of Mysore"), an idea Amburgh quickly borrowed. These acts eclipsed equestrianism acts as the central display of circus shows and entered public consciousness in the early 20th century with cinema. In demonstrating the superiority of human over animal, lion taming served a purpose similar to animal fights of previous centuries.#Baratay, Baratay & Hardouin-Fugier, p. 187. The ultimate proof of a tamer's dominance and control over a lion is demonstrated by the placing of the tamer's head in the lion's mouth. The now-iconic lion tamer's chair was possibly first used by American Clyde Beatty (1903–1965).
Hunting and games
Lion hunting has occurred since ancient times and was often a royal tradition, intended to demonstrate the power of the king over nature. Such hunts took place in a reserved area in front of an audience. The monarch was accompanied by his men and controls were put in place to increase their safety and ease of killing. The earliest surviving record of lion hunting is an ancient Egyptian inscription dated circa 1380 BC that mentions Pharaoh Amenhotep III killing 102 lions in ten years "with his own arrows". The Assyrian emperor Ashurbanipal had one of his lion hunts depicted on a sequence of Assyrian palace reliefs, palace reliefs , known as the Lion Hunt of Ashurbanipal. Lions were also hunted during the Mughal Empire, where Emperor Jahangir is said to have excelled at it.#Jackson, Jackson, p. 156–159. In Ancient Rome, lions were kept by emperors for Venatio, hunts, Bestiarii, gladiator fights and Damnatio ad bestias, executions. The Maasai people have traditionally viewed the killing of lions as a rite of passage. Historically, lions were hunted by individuals, however, due to reduced lion populations, elders discourage solo lion hunts. During the Scramble for Africa, European colonisation of Africa in the 19th century, the hunting of lions was encouraged because they were considered pests and lion skins were sold for Pound sterling, £1 each. The widely reproduced imagery of the heroic hunter chasing lions would dominate a large part of the century. Trophy hunting of lions in recent years has been met with controversy, notably with the killing of Cecil the lion in mid-2015.Man-eating
 Lions do not usually hunt humans but some (usually males) seem to seek them out. One well-publicised case is the Tsavo maneaters; in 1898, 28 officially recorded railway workers building the Uganda Railway, Kenya-Uganda Railway were taken by lions over nine months during the construction of a bridge in Kenya. The hunter who killed the lions wrote a book detailing the animals' predatory behaviour; they were larger than normal and lacked manes, and one seemed to suffer from tooth decay. The infirmity theory, including tooth decay, is not favoured by all researchers; an analysis of teeth and jaws of man-eating lions in museum collections suggests that while tooth decay may explain some incidents, prey depletion in human-dominated areas is a more likely cause of lion predation on humans. Sick or injured animals may be more prone to man-eating but the behaviour is not unusual, nor necessarily aberrant.
Lions' proclivity for man-eating has been systematically examined. American and Tanzanian scientists report that man-eating behaviour in rural areas of Tanzania increased greatly from 1990 to 2005. At least 563 villagers were attacked and many eaten over this period. The incidents occurred near Selous Game Reserve, Selous National Park in Rufiji River, Rufiji District and in Lindi Region, Lindi Province near the Mozambican border. While the expansion of villages into bush country is one concern, the authors argue conservation policy must mitigate the danger because in this case, conservation contributes directly to human deaths. Cases in Lindi in which lions seize humans from the centres of substantial villages have been documented. Another study of 1,000 people attacked by lions in southern Tanzania between 1988 and 2009 found that the weeks following the full moon, when there was less moonlight, were a strong indicator of increased night-time attacks on people.
According to Robert R. Frump, Mozambican refugees regularly crossing Kruger National Park, South Africa, at night are attacked and eaten by lions; park officials have said man-eating is a problem there. Frump said thousands may have been killed in the decades after apartheid sealed the park and forced refugees to cross the park at night. For nearly a century before the border was sealed, Mozambicans had regularly crossed the park in daytime with little harm.
Lions do not usually hunt humans but some (usually males) seem to seek them out. One well-publicised case is the Tsavo maneaters; in 1898, 28 officially recorded railway workers building the Uganda Railway, Kenya-Uganda Railway were taken by lions over nine months during the construction of a bridge in Kenya. The hunter who killed the lions wrote a book detailing the animals' predatory behaviour; they were larger than normal and lacked manes, and one seemed to suffer from tooth decay. The infirmity theory, including tooth decay, is not favoured by all researchers; an analysis of teeth and jaws of man-eating lions in museum collections suggests that while tooth decay may explain some incidents, prey depletion in human-dominated areas is a more likely cause of lion predation on humans. Sick or injured animals may be more prone to man-eating but the behaviour is not unusual, nor necessarily aberrant.
Lions' proclivity for man-eating has been systematically examined. American and Tanzanian scientists report that man-eating behaviour in rural areas of Tanzania increased greatly from 1990 to 2005. At least 563 villagers were attacked and many eaten over this period. The incidents occurred near Selous Game Reserve, Selous National Park in Rufiji River, Rufiji District and in Lindi Region, Lindi Province near the Mozambican border. While the expansion of villages into bush country is one concern, the authors argue conservation policy must mitigate the danger because in this case, conservation contributes directly to human deaths. Cases in Lindi in which lions seize humans from the centres of substantial villages have been documented. Another study of 1,000 people attacked by lions in southern Tanzania between 1988 and 2009 found that the weeks following the full moon, when there was less moonlight, were a strong indicator of increased night-time attacks on people.
According to Robert R. Frump, Mozambican refugees regularly crossing Kruger National Park, South Africa, at night are attacked and eaten by lions; park officials have said man-eating is a problem there. Frump said thousands may have been killed in the decades after apartheid sealed the park and forced refugees to cross the park at night. For nearly a century before the border was sealed, Mozambicans had regularly crossed the park in daytime with little harm.
Cultural significance
Africa
In sub-Saharan Africa, the lion has been a common character in stories, proverbs and dances, but rarely featured in visual arts. In some cultures, the lion symbolises power and royalty. In the Swahili language, the lion is known as ''simba'' which also means "aggressive", "king" and "strong". Some rulers had the word "lion" in their nickname. Sundiata Keita of the Mali Empire was called "Lion of Mali". The founder of the Waalo kingdom is said to have been raised by lions and returned to his people part-lion to unite them using the knowledge he learned from the lions. In parts of West Africa, lions symbolised the top class of their social hierarchies. In more heavily forested areas where lions were rare, the leopard represented the top of the hierarchy.#Jackson, Jackson, p. 119. In parts of West and East Africa, the lion is associated with healing and provides the connection between Clairvoyance, seers and the supernatural. In other East African traditions, the lion represents laziness. In much of African folklore, the lion is portrayed as having low intelligence and is easily tricked by other animals. The ancient Egyptians portrayed several of their List of war deities, war deities as lionesses, which they revered as fierce hunters. Egyptian deities associated with lions include Sekhmet, Bastet, Bast, Mafdet, Menhit, Pakhet and Tefnut. These deities were often connected with the sun god Ra and his fierce heat, and their dangerous power was invoked to guard people or sacred places. The sphinx, a figure with a lion's body and the head of a human or other creature, represented a pharaoh or deity who had taken on this protective role.Eastern world
Western world
 Lion-headed figures and amulets were excavated in tombs in the Greek islands of Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Paros and Chios. They are associated with the Egyptian deity Sekhmet and date to the early Iron Age between the 9th and 6th centuries BC. The lion is featured in several of Aesop's fables, notably The Lion and the Mouse. The Nemean lion was symbolic in ancient Greece and Rome, represented as the constellation and zodiac sign Leo (astrology), Leo, and described in mythology, where it was killed and worn by the hero Heracles, symbolising victory over death. Lancelot and Gawain were also heroes slaying lions in the
Lion-headed figures and amulets were excavated in tombs in the Greek islands of Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Paros and Chios. They are associated with the Egyptian deity Sekhmet and date to the early Iron Age between the 9th and 6th centuries BC. The lion is featured in several of Aesop's fables, notably The Lion and the Mouse. The Nemean lion was symbolic in ancient Greece and Rome, represented as the constellation and zodiac sign Leo (astrology), Leo, and described in mythology, where it was killed and worn by the hero Heracles, symbolising victory over death. Lancelot and Gawain were also heroes slaying lions in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. In some medieval stories, lions were portrayed as allies and companions. "Lion" was the nickname of several medieval warrior-rulers with a reputation for bravery, such as Richard the Lionheart.
Lions continue to appear in modern literature as characters including the messianic Aslan in the 1950 novel ''The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe'' and ''The Chronicles of Narnia'' series by C. S. Lewis, and the comedic Cowardly Lion in L. Frank Baum's 1900 ''The Wonderful Wizard of Oz''. Lion symbolism was used from the advent of cinema; one of the most iconic and widely recognised lions is Leo the Lion (MGM), Leo, which has been the mascot for Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer studios since the 1920s. The 1966 film ''Born Free'' features Elsa the lioness and is based on the 1960 Born Free (book), non-fiction book with the same title. The lion's role as king of the beasts has been used in the 1994 Disney animated feature film ''The Lion King''.
Lions are frequently Lion (heraldry), depicted on coat of arms, coats of arms, like on the coat of arms of Finland, either as a device on shields or as supporters, but the lioness is used much less frequently. The heraldic lion is particularly common in British arms. It is traditionally depicted in a great variety of Attitude (heraldry), attitudes, although within French heraldry only lions rampant are considered to be lions; feline figures in any other position are instead referred to as leopards.Arthur Fox-Davies, ''A Complete Guide to Heraldry'', T.C. and E.C. Jack, London, 1909, Chapter XI, https://archive.org/details/completeguidetoh00foxduoft.
See also
* List of largest cats * Mapogo lion coalition * ''Roar (1981 film), Roar'' (1981 film) * Tiger versus lionExplanatory notes
References
Citations
Books
* * * * * *External links
* * * * {{Authority control Lions, Apex predators Articles containing video clips Big cats Extant Pliocene first appearances Felids of Africa Mammals described in 1758 Mammals of Sub-Saharan Africa Mammals of South Asia National symbols of Burundi National symbols of Chad National symbols of Eswatini National symbols of Kenya National symbols of Malawi National symbols of Morocco National symbols of Sierra Leone National symbols of Singapore National symbols of South Africa National symbols of Sri Lanka National symbols of the Republic of the Congo National symbols of Togo National symbols of Tunisia Panthera Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Vulnerable animals Vulnerable biota of Africa