Lingual Tonsils on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The lingual tonsils are a collection of
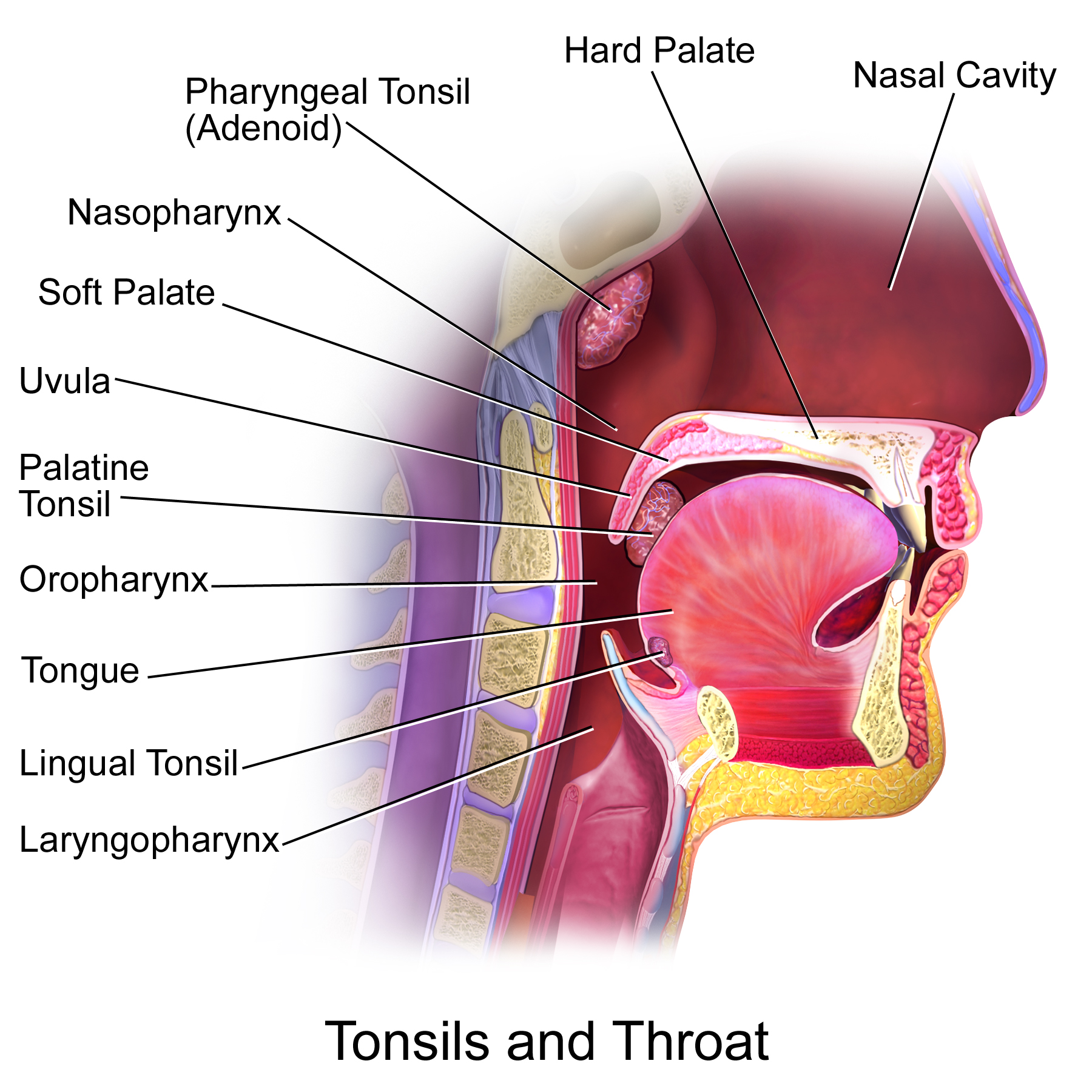 Like other lymphatic tissues, the function of lingual tonsils is to prevent infections. These tonsils contain B and T lymphocytes which get activated when harmful bacteria and viruses come in contact with tonsils. B lymphocytes kill pathogens by producing antibodies against them, while T lymphocytes directly kill them by engulfing them or indirectly by stimulating other cells of the immune system.
Like other lymphatic tissues, the function of lingual tonsils is to prevent infections. These tonsils contain B and T lymphocytes which get activated when harmful bacteria and viruses come in contact with tonsils. B lymphocytes kill pathogens by producing antibodies against them, while T lymphocytes directly kill them by engulfing them or indirectly by stimulating other cells of the immune system.
File:Slide1sss.JPG, Lingual tonsil
File:Slide7ttt.JPG, Lingual tonsil
File:Slide12uuu.JPG, Lingual tonsils
Pictures at usc.edu
* * * (labeled as 'lymphoid tissue')]
Lingual Tonsil
lymphatic tissue
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste bu ...
. This lymphatic tissue consists of the lymphatic nodules rich in cells of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
( immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate the immune response when the lingual tonsils get in contact with invading microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s (pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room ...
or parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
).
Structure
Microanatomy
Lingual tonsils are covered externally by stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium that invaginates inward forming crypts. Beneath the epithelium is a layer of lymphoid nodules containing lymphocytes. Mucous glands located at the root of tongue are drained through several ducts into the crypt of lingual tonsils. Secretions of these mucous glands keep the crypt clean and free of any debris.Blood supply
Lingual tonsils are located on posterior aspect of tongue which is supplied through: * Lingual artery, branch of external carotid artery * Tonsillar branch of facial artery *Ascending and descending palatine arteries * Ascending pharyngeal branch of external carotid arteryNerve supply
Lingual tonsils are innervated by tonsillar nerves from the tonsilar plexus, formed by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.Function
 Like other lymphatic tissues, the function of lingual tonsils is to prevent infections. These tonsils contain B and T lymphocytes which get activated when harmful bacteria and viruses come in contact with tonsils. B lymphocytes kill pathogens by producing antibodies against them, while T lymphocytes directly kill them by engulfing them or indirectly by stimulating other cells of the immune system.
Like other lymphatic tissues, the function of lingual tonsils is to prevent infections. These tonsils contain B and T lymphocytes which get activated when harmful bacteria and viruses come in contact with tonsils. B lymphocytes kill pathogens by producing antibodies against them, while T lymphocytes directly kill them by engulfing them or indirectly by stimulating other cells of the immune system.
Clinical significance
Cancer
Squamous cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
carcinoma is a type of neoplasm that can affect lingual tonsils.
Sleep apnea
Enlarged or hypertrophic lingual tonsils have the potential to cause or exacerbate sleep apnea.Additional images
External links
Pictures at usc.edu
* * * (labeled as 'lymphoid tissue')]
Lingual Tonsil
References
{{Authority control Lymphatics of the head and neck Tongue Tonsil