Linear Polarization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
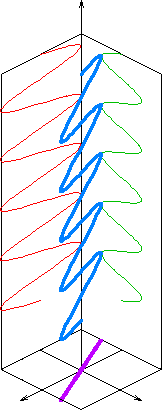 In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the
Animation of Linear Polarization (on YouTube)Comparison of Linear Polarization with Circular and Elliptical Polarizations (YouTube Animation)
{{FS1037C Polarization (waves) ja:直線偏光 pl:Polaryzacja_fali#Polaryzacja_liniowa
 In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ...
vector or magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See ''polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
'' and '' plane of polarization'' for more information.
The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave is defined by the direction of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ...
vector. For example, if the electric field vector is vertical (alternately up and down as the wave travels) the radiation is said to be vertically polarized.
Mathematical description
The classicalsinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in m ...
plane wave solution of the electromagnetic wave equation
The electromagnetic wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation that describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves through a medium or in a vacuum. It is a three-dimensional form of the wave equation. The homogeneous form ...
for the electric and magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particle ...
fields is (cgs units)
:
:
for the magnetic field, where k is the wavenumber,
:
is the angular frequency of the wave, and is the speed of light.
Here is the amplitude of the field and
:
is the Jones vector
In optics, polarized light can be described using the Jones calculus, discovered by R. C. Jones in 1941. Polarized light is represented by a Jones vector, and linear optical elements are represented by ''Jones matrices''. When light crosses an op ...
in the x-y plane.
The wave is linearly polarized when the phase angles are equal,
:.
This represents a wave polarized at an angle with respect to the x axis. In that case, the Jones vector can be written
:.
The state vectors for linear polarization in x or y are special cases of this state vector.
If unit vectors are defined such that
:
and
:
then the polarization state can be written in the "x-y basis" as
:.
See also
*Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions of the electromagnetic wave equation
Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions are particular solutions to the electromagnetic wave equation.
The general solution of the electromagnetic wave equation in homogeneous, linear, time-independent media can be written as a linear superposition of ...
*Polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
** Circular polarization
** Elliptical polarization
** Plane of polarization
* Photon polarization
References
*External links
Animation of Linear Polarization (on YouTube)
{{FS1037C Polarization (waves) ja:直線偏光 pl:Polaryzacja_fali#Polaryzacja_liniowa