Lincolnshire Volunteer Artillery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East Midlands of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea to the east. It borders Norfolk to the south-east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south-west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north-west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders Northamptonshire in the south for just , England's shortest county boundary. The county town is Lincoln, England, Lincoln, where the county council is also based.
The Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Lincolnshire consists of the non-metropolitan county of Lincolnshire and the area covered by the unitary authority, unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire. Part of the ceremonial county is in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, and most is in the East Midlands region. The county is the List of ceremonial counties of England, second-largest of the English ceremonial counties and one that is predominantly agricultural in land use. The county is fourth-largest of the two-tier counties, as the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire are not included.
The county has several geographical sub-regions, including the rolling chalk hills of the Lincolnshire Wolds, the The Fens, Lincolnshire Fens (south-east Lincolnshire), the Carrs (similar to the Fens but in north Lincolnshire), the industrial Humber, Humber Estuary and North Sea coast around Grimsby and Scunthorpe, and in the south-west of the county, the Kesteven Uplands, rolling limestone hills in the district of South Kesteven.
 During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the Corieltauvi people. The language of the area at that time would have been Common Brittonic, the precursor to modern Welsh. The name ''Lincoln'' was derived from Lindum Colonia.
Large numbers of Germanic speakers from continental Europe settled in the region following the withdrawal of the Romans. Though these were later identified as Angles, it is unlikely that they migrated as part of an organized tribal group. Thus, the main language of the region quickly became Old English. However, it is possible that Brittonic continued to be spoken in some communities as late as the eighth century.
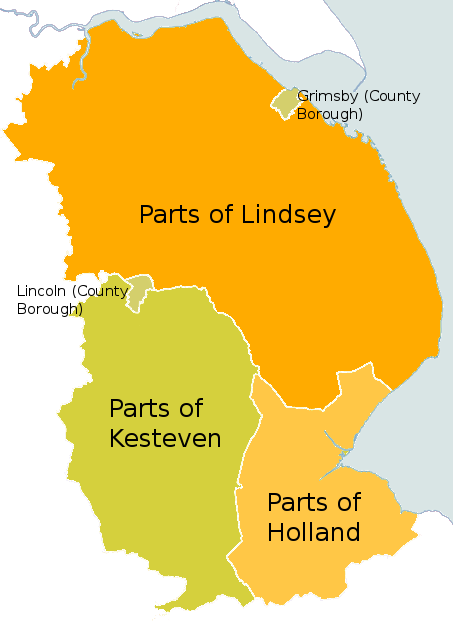
Modern-day Lincolnshire is derived from the merging of the territory of the Kingdom of Lindsey with that controlled by the Danelaw borough of Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford. For some time the entire county was called "Lindsey", and it is recorded as such in the 11th-century ''Domesday Book.'' Later, the name Lindsey (government district), Lindsey was applied to the northern core, around Lincoln. This emerged as one of the three Parts of Lincolnshire, along with the Parts of Holland, Lincolnshire, Holland in the south-east, and the Parts of Kesteven in the south-west, which each had separate Quarter Sessions as their county administrations.
In 1888 when county councils were set up, Lindsey, Holland and Kesteven each received separate ones. These survived until 1974, when Holland, Kesteven, and most of Lindsey were unified into Lincolnshire. The northern part of Lindsey, including Scunthorpe Municipal Borough and Grimsby County Borough, was incorporated into the newly formed shire county, non-metropolitan county of Humberside, along with most of the East Riding of Yorkshire.
During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the Corieltauvi people. The language of the area at that time would have been Common Brittonic, the precursor to modern Welsh. The name ''Lincoln'' was derived from Lindum Colonia.
Large numbers of Germanic speakers from continental Europe settled in the region following the withdrawal of the Romans. Though these were later identified as Angles, it is unlikely that they migrated as part of an organized tribal group. Thus, the main language of the region quickly became Old English. However, it is possible that Brittonic continued to be spoken in some communities as late as the eighth century.
Modern-day Lincolnshire is derived from the merging of the territory of the Kingdom of Lindsey with that controlled by the Danelaw borough of Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford. For some time the entire county was called "Lindsey", and it is recorded as such in the 11th-century ''Domesday Book.'' Later, the name Lindsey (government district), Lindsey was applied to the northern core, around Lincoln. This emerged as one of the three Parts of Lincolnshire, along with the Parts of Holland, Lincolnshire, Holland in the south-east, and the Parts of Kesteven in the south-west, which each had separate Quarter Sessions as their county administrations.
In 1888 when county councils were set up, Lindsey, Holland and Kesteven each received separate ones. These survived until 1974, when Holland, Kesteven, and most of Lindsey were unified into Lincolnshire. The northern part of Lindsey, including Scunthorpe Municipal Borough and Grimsby County Borough, was incorporated into the newly formed shire county, non-metropolitan county of Humberside, along with most of the East Riding of Yorkshire.
 A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire. These two areas became part of Lincolnshire for ceremonial purposes, such as the Lord-Lieutenant, Lord-Lieutenancy, but are not covered by the Lincolnshire police; they are in the Yorkshire and the Humber region.
The remaining districts of Lincolnshire are Boston (borough), Boston, East Lindsey, Lincoln, North Kesteven, South Holland, England, South Holland, South Kesteven, and West Lindsey. They are part of the East Midlands region.
The area was shaken by the 27 February 2008 Lincolnshire earthquake, reaching between 4.7 and 5.3 on the Richter magnitude scale; it was one of the largest earthquakes to affect Britain in recent years.
Lincolnshire is home to Woolsthorpe Manor, birthplace and home of Sir Isaac Newton. He attended The King's School, Grantham. Its library has preserved his signature, carved into a window sill when he was a youth.
A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire. These two areas became part of Lincolnshire for ceremonial purposes, such as the Lord-Lieutenant, Lord-Lieutenancy, but are not covered by the Lincolnshire police; they are in the Yorkshire and the Humber region.
The remaining districts of Lincolnshire are Boston (borough), Boston, East Lindsey, Lincoln, North Kesteven, South Holland, England, South Holland, South Kesteven, and West Lindsey. They are part of the East Midlands region.
The area was shaken by the 27 February 2008 Lincolnshire earthquake, reaching between 4.7 and 5.3 on the Richter magnitude scale; it was one of the largest earthquakes to affect Britain in recent years.
Lincolnshire is home to Woolsthorpe Manor, birthplace and home of Sir Isaac Newton. He attended The King's School, Grantham. Its library has preserved his signature, carved into a window sill when he was a youth.
File: Belton House 2006 Giano.jpg, Belton House
File: Stump&Ingram.jpeg, St Botolph's Church, Boston, Boston Stump
File: Gainsborough Old Hall.jpg, Gainsborough Old Hall
File: Harlaxton manor.jpg, Harlaxton Manor
File: Normanby Hall, Lincs (geograph 56340).jpg, Normanby Hall
File: Tattershall Castle, 2006.jpg, Tattershall Castle, Lincolnshire, Tattershall Castle
File: Thornton Abbey Gatehouse1.jpg, Thornton Abbey
File:Louth Church in 2021.jpg, St James' Church, Louth
 Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of wheat, barley, sugar beet, and oilseed rape. In south Lincolnshire, where the soil is particularly rich in nutrients, some of the most common crops include potatoes, cabbages, cauliflowers, and onions. Lincolnshire farmers often break world records for crop yields. South Lincolnshire is also home to one of the UK's leading agricultural experiment stations, located in Sutton Bridge and operated by the Potato Council; Sutton Bridge Crop Storage Research engages in research for the British potato industry.
The Lincoln sheep, Lincoln Longwool is a rare breed of sheep, named after the region, which was developed both for wool and mutton, at least 500 years ago, and has the longest fleece of any sheep breed. The Lincoln Red is an old breed of beef cattle, originating from the county. In the mid 20th century most farms in Lincolnshire moved away from mixed farming to specialise in arable cropping, partly due to cheap wool imports, partly to take advantage of efficiencies of scale and partly because the drier land on the eastern side of England is particularly suitable for arable cropping.
Mechanization and Modernization Agreement 1960, Mechanization around 1900 greatly diminished the number of workers required to operate the county's relatively large farms, and the proportion of workers in the agricultural sector dropped substantially during this period. Several major engineering companies developed in Lincoln, Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough and Grantham to support those changes. Among these was William Foster & Co Ltd, Fosters of Lincoln, which built the first tank, and Richard Hornsby & Sons of Grantham. Most such industrial companies left during late 20th-century restructuring.
Today, Immigration to Europe, immigrant workers, mainly from Enlargement of the European Union, new member states of the European Union in Central and Eastern Europe, comprise a large component of the seasonal agricultural workforce, particularly in the south of the county. Here more labour-intensive crops are produced, such as small vegetables and cut flowers. This seasonal influx of migrant labour occasionally causes tension between the migrant workforce and local people, in a county which had been relatively unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. Agricultural training is provided at Riseholme College and in 2016 the University of Lincoln opened the Lincoln Institute for Agri-Food Technology.
Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of wheat, barley, sugar beet, and oilseed rape. In south Lincolnshire, where the soil is particularly rich in nutrients, some of the most common crops include potatoes, cabbages, cauliflowers, and onions. Lincolnshire farmers often break world records for crop yields. South Lincolnshire is also home to one of the UK's leading agricultural experiment stations, located in Sutton Bridge and operated by the Potato Council; Sutton Bridge Crop Storage Research engages in research for the British potato industry.
The Lincoln sheep, Lincoln Longwool is a rare breed of sheep, named after the region, which was developed both for wool and mutton, at least 500 years ago, and has the longest fleece of any sheep breed. The Lincoln Red is an old breed of beef cattle, originating from the county. In the mid 20th century most farms in Lincolnshire moved away from mixed farming to specialise in arable cropping, partly due to cheap wool imports, partly to take advantage of efficiencies of scale and partly because the drier land on the eastern side of England is particularly suitable for arable cropping.
Mechanization and Modernization Agreement 1960, Mechanization around 1900 greatly diminished the number of workers required to operate the county's relatively large farms, and the proportion of workers in the agricultural sector dropped substantially during this period. Several major engineering companies developed in Lincoln, Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough and Grantham to support those changes. Among these was William Foster & Co Ltd, Fosters of Lincoln, which built the first tank, and Richard Hornsby & Sons of Grantham. Most such industrial companies left during late 20th-century restructuring.
Today, Immigration to Europe, immigrant workers, mainly from Enlargement of the European Union, new member states of the European Union in Central and Eastern Europe, comprise a large component of the seasonal agricultural workforce, particularly in the south of the county. Here more labour-intensive crops are produced, such as small vegetables and cut flowers. This seasonal influx of migrant labour occasionally causes tension between the migrant workforce and local people, in a county which had been relatively unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. Agricultural training is provided at Riseholme College and in 2016 the University of Lincoln opened the Lincoln Institute for Agri-Food Technology.
 Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by single carriageway Great Britain road numbering scheme, A roads and local roads (B roads) as opposed to Controlled-access highway, motorways and dual carriageways – the administrative county of Lincolnshire is one of the few UK counties without a motorway, and until several years ago, it was said that there was only about of dual carriageway in the whole of Lincolnshire. The M180 motorway passes through North Lincolnshire, splitting into two dual carriageway trunk roads to the Humber Bridge and Grimsby, and the A46 road, A46 is now dual carriageway between Newark-on-Trent and Lincoln.
The low population density of the county means that the number of railway stations and train services is very low considering the county's large area. Many of the county's railway stations were permanently closed following the Beeching cuts, Beeching Report of 1963. The most notable reopening has been the line and two stations between Lincoln and Sleaford, which reopened within months of the Beeching closure. Most other closed lines in the county were long ago lifted and much of the trackbed has returned to agricultural use.
Prior to 1970, a through train service operated between Cleethorpes railway station, Cleethorpes and London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross via Louth railway station, Louth, Boston railway station, Boston and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. The part of this line in Grimsby is now the A16 road (England), A16 road, preventing reinstatement as a railway line, and a small section of the line is now the Lincolnshire Wolds Railway, with an extension towards Louth in progress.
A daily through train service operated between Cleethorpes and London King's Cross via Grimsby railway station, Grimsby, Market Rasen railway station, Market Rasen and Lincoln railway station, Lincoln Central until the late 1980s. The ''Humberlincs Executive'', as the service was known, was operated by an InterCity 125, but was discontinued following the electrification of the East Coast Main Line. Passengers now have to change trains at Newark North Gate railway station, Newark North Gate when travelling to and from London. However, the East Coast Main Line passes through the western edge of the county and one can catch direct trains to London from Grantham railway station, Grantham.
Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by single carriageway Great Britain road numbering scheme, A roads and local roads (B roads) as opposed to Controlled-access highway, motorways and dual carriageways – the administrative county of Lincolnshire is one of the few UK counties without a motorway, and until several years ago, it was said that there was only about of dual carriageway in the whole of Lincolnshire. The M180 motorway passes through North Lincolnshire, splitting into two dual carriageway trunk roads to the Humber Bridge and Grimsby, and the A46 road, A46 is now dual carriageway between Newark-on-Trent and Lincoln.
The low population density of the county means that the number of railway stations and train services is very low considering the county's large area. Many of the county's railway stations were permanently closed following the Beeching cuts, Beeching Report of 1963. The most notable reopening has been the line and two stations between Lincoln and Sleaford, which reopened within months of the Beeching closure. Most other closed lines in the county were long ago lifted and much of the trackbed has returned to agricultural use.
Prior to 1970, a through train service operated between Cleethorpes railway station, Cleethorpes and London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross via Louth railway station, Louth, Boston railway station, Boston and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. The part of this line in Grimsby is now the A16 road (England), A16 road, preventing reinstatement as a railway line, and a small section of the line is now the Lincolnshire Wolds Railway, with an extension towards Louth in progress.
A daily through train service operated between Cleethorpes and London King's Cross via Grimsby railway station, Grimsby, Market Rasen railway station, Market Rasen and Lincoln railway station, Lincoln Central until the late 1980s. The ''Humberlincs Executive'', as the service was known, was operated by an InterCity 125, but was discontinued following the electrification of the East Coast Main Line. Passengers now have to change trains at Newark North Gate railway station, Newark North Gate when travelling to and from London. However, the East Coast Main Line passes through the western edge of the county and one can catch direct trains to London from Grantham railway station, Grantham.

 Most rail services are currently operated by East Midlands Railway and Northern Trains. London North Eastern Railway and CrossCountry have services which pass through the county, with London North Eastern Railway frequently passing and stopping at Grantham on the East Coast Main Line and a service every other hour to Lincoln railway station, Lincoln, while CrossCountry trains stop at Stamford on their way between Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham and Stansted Airport railway station, Stansted Airport. Stations along the Humber are served by TransPennine Express services between Manchester Airport railway station, Manchester Airport and Cleethorpes. One of the most infrequent services in the UK is in Lincolnshire: the Sheffield railway station, Sheffield-Gainsborough Central railway station, Gainsborough Central-Cleethorpes line has passenger trains only on a Saturday, with three trains in both directions. This line is, however, used for freight.
On 22 May 2011 East Coast (train operating company), East Coast started a Lincoln-London service, initially one train a day each way, and there is a northbound service on a Sunday. This was increased in 2019 to a service every two hours. East Midlands Railway also run a daily (Mon-Sat) service each way between Lincoln and St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras, though this is a stopping service which takes around three hours via Nottingham railway station, Nottingham, compared to London North Eastern Railway's service to London King's Cross which takes around 1 hour 50 minutes.
The only airport in Lincolnshire is Humberside Airport, near Brigg. East Midlands Airport the main airport servicing the East Midlands is within travelling distance of the county. Doncaster Sheffield Airport near Doncaster is within travelling distance of much of Lincolnshire.
The county's biggest bus companies are Stagecoach Grimsby-Cleethorpes (formerly Grimsby-Cleethorpes Transport) and Stagecoach in Lincolnshire, (formerly Lincolnshire Road Car). There are several smaller bus companies, including Brylaine of Boston, Delaine Buses and Hornsby's of Scunthorpe.
A Sustrans cycle route runs from Lincoln to Boston in the south of the county.
Most rail services are currently operated by East Midlands Railway and Northern Trains. London North Eastern Railway and CrossCountry have services which pass through the county, with London North Eastern Railway frequently passing and stopping at Grantham on the East Coast Main Line and a service every other hour to Lincoln railway station, Lincoln, while CrossCountry trains stop at Stamford on their way between Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham and Stansted Airport railway station, Stansted Airport. Stations along the Humber are served by TransPennine Express services between Manchester Airport railway station, Manchester Airport and Cleethorpes. One of the most infrequent services in the UK is in Lincolnshire: the Sheffield railway station, Sheffield-Gainsborough Central railway station, Gainsborough Central-Cleethorpes line has passenger trains only on a Saturday, with three trains in both directions. This line is, however, used for freight.
On 22 May 2011 East Coast (train operating company), East Coast started a Lincoln-London service, initially one train a day each way, and there is a northbound service on a Sunday. This was increased in 2019 to a service every two hours. East Midlands Railway also run a daily (Mon-Sat) service each way between Lincoln and St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras, though this is a stopping service which takes around three hours via Nottingham railway station, Nottingham, compared to London North Eastern Railway's service to London King's Cross which takes around 1 hour 50 minutes.
The only airport in Lincolnshire is Humberside Airport, near Brigg. East Midlands Airport the main airport servicing the East Midlands is within travelling distance of the county. Doncaster Sheffield Airport near Doncaster is within travelling distance of much of Lincolnshire.
The county's biggest bus companies are Stagecoach Grimsby-Cleethorpes (formerly Grimsby-Cleethorpes Transport) and Stagecoach in Lincolnshire, (formerly Lincolnshire Road Car). There are several smaller bus companies, including Brylaine of Boston, Delaine Buses and Hornsby's of Scunthorpe.
A Sustrans cycle route runs from Lincoln to Boston in the south of the county.
Northern Lincolnshire and Goole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Some of the larger hospitals in the county include: *Diana Princess of Wales Hospital, Grimsby *Scunthorpe General Hospital *Pilgrim Hospital, Boston Pilgrim Hospital *Lincoln County Hospital Since April 1994, Lincolnshire has had an Air Air ambulances in the United Kingdom, Ambulance service. The air ambulance is stationed at RAF Waddington near Lincoln and can reach emergencies in Lincolnshire within 25 minutes. An A&E hospital is only 10 minutes away by helicopter from any accident in Lincolnshire.
Black Sluice Internal Drainage BoardWitham 4th District IDBLindsey Marsh Drainage Board
, or th
Welland and Deepings Internal Drainage Board
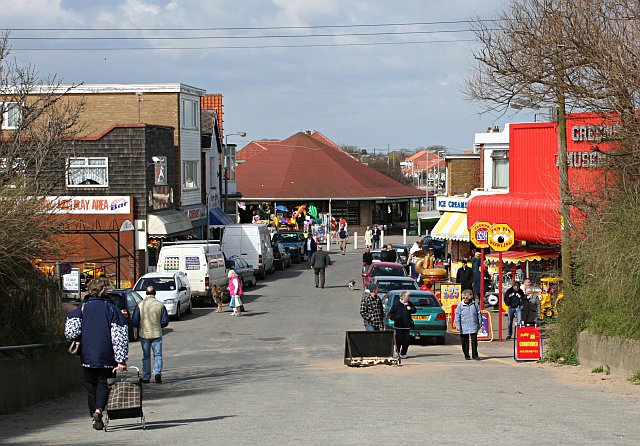



 The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the East Midlands and parts of Yorkshire. There are three main coastal resorts in Lincolnshire and several smaller village resorts.
The main county seaside resort of Skegness with its famous The Jolly Fisherman, Jolly Fisherman mascot and famous slogan "Skegness is so bracing", together with its neighbouring large village coastal resorts of Ingoldmells and Chapel St Leonards, provides the biggest concentration of resorts along the Lincolnshire Coast, with many large caravan and holiday sites. The resort offers many amusements, beaches, leisure activities and shops, as well as Butlins Skegness, Fantasy Island (UK amusement park), Fantasy Island, Church Farm Museum, Natureland Seal Sanctuary, Skegness Stadium, Skegness Pier#Pier, Skegness Pier and several well-known local golf courses. There are good road, bus and rail links to the rest of the county.
The second largest group of resorts along the coast is the seaside town of Mablethorpe, famous for its golden sands, and the neighbouring village resorts of Trusthorpe and Sutton-on-Sea. This area also offers leisure activities and has large caravan and holiday sites. But the area is less developed, with fewer amusement arcades and nightclubs, and poorer road links to the rest of the county; but the area offers a more traditional seaside setting.
The third group of resorts includes the seaside town of Cleethorpes and the large village resort of Humberston within North East Lincolnshire. It has the Cleethorpes Coast Light Railway and Cleethorpes Pier along with its local golf courses and caravan and holiday sites, whilst it is also the former site of Pleasure Island Family Theme Park. Cleethorpes is well-served by road and rail; it is easily accessible from the M180 motorway, M180 and the TransPennine Express route to Manchester.
Nature is an attraction for many tourists: the south-east of the county is mainly fenland that attracts many species of birds, as do the national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves at Gibraltar Point, Lincolnshire, Gibraltar Point, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe Dunes National Nature Reserve, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe and Donna Nook, which also contains a large grey seal colony which is popular with visitors.
The market towns of the Lincolnshire Wolds Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth, Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, Caistor and Spilsby are also attractive, with several having historically important buildings, such as Alford Manor House, St James' Church, Louth, St James' Church and Bolingbroke Castle. The Wolds are popular for cycling and walking, with regular events such as the Lincolnshire Wolds Walking Festival.
The city of Lincoln, England, Lincoln is home to many tourist attractions including Lincoln Castle, Lincoln Cathedral, The Engine Shed, Steep Hill, International Bomber Command Centre and Guildhall and Stonebow, Lincoln, Guildhall and Stonebow among other historical landmarks and listed buildings. The city acts as one of the many tourist centres in the East Midlands Region.
The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the East Midlands and parts of Yorkshire. There are three main coastal resorts in Lincolnshire and several smaller village resorts.
The main county seaside resort of Skegness with its famous The Jolly Fisherman, Jolly Fisherman mascot and famous slogan "Skegness is so bracing", together with its neighbouring large village coastal resorts of Ingoldmells and Chapel St Leonards, provides the biggest concentration of resorts along the Lincolnshire Coast, with many large caravan and holiday sites. The resort offers many amusements, beaches, leisure activities and shops, as well as Butlins Skegness, Fantasy Island (UK amusement park), Fantasy Island, Church Farm Museum, Natureland Seal Sanctuary, Skegness Stadium, Skegness Pier#Pier, Skegness Pier and several well-known local golf courses. There are good road, bus and rail links to the rest of the county.
The second largest group of resorts along the coast is the seaside town of Mablethorpe, famous for its golden sands, and the neighbouring village resorts of Trusthorpe and Sutton-on-Sea. This area also offers leisure activities and has large caravan and holiday sites. But the area is less developed, with fewer amusement arcades and nightclubs, and poorer road links to the rest of the county; but the area offers a more traditional seaside setting.
The third group of resorts includes the seaside town of Cleethorpes and the large village resort of Humberston within North East Lincolnshire. It has the Cleethorpes Coast Light Railway and Cleethorpes Pier along with its local golf courses and caravan and holiday sites, whilst it is also the former site of Pleasure Island Family Theme Park. Cleethorpes is well-served by road and rail; it is easily accessible from the M180 motorway, M180 and the TransPennine Express route to Manchester.
Nature is an attraction for many tourists: the south-east of the county is mainly fenland that attracts many species of birds, as do the national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves at Gibraltar Point, Lincolnshire, Gibraltar Point, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe Dunes National Nature Reserve, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe and Donna Nook, which also contains a large grey seal colony which is popular with visitors.
The market towns of the Lincolnshire Wolds Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth, Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, Caistor and Spilsby are also attractive, with several having historically important buildings, such as Alford Manor House, St James' Church, Louth, St James' Church and Bolingbroke Castle. The Wolds are popular for cycling and walking, with regular events such as the Lincolnshire Wolds Walking Festival.
The city of Lincoln, England, Lincoln is home to many tourist attractions including Lincoln Castle, Lincoln Cathedral, The Engine Shed, Steep Hill, International Bomber Command Centre and Guildhall and Stonebow, Lincoln, Guildhall and Stonebow among other historical landmarks and listed buildings. The city acts as one of the many tourist centres in the East Midlands Region.
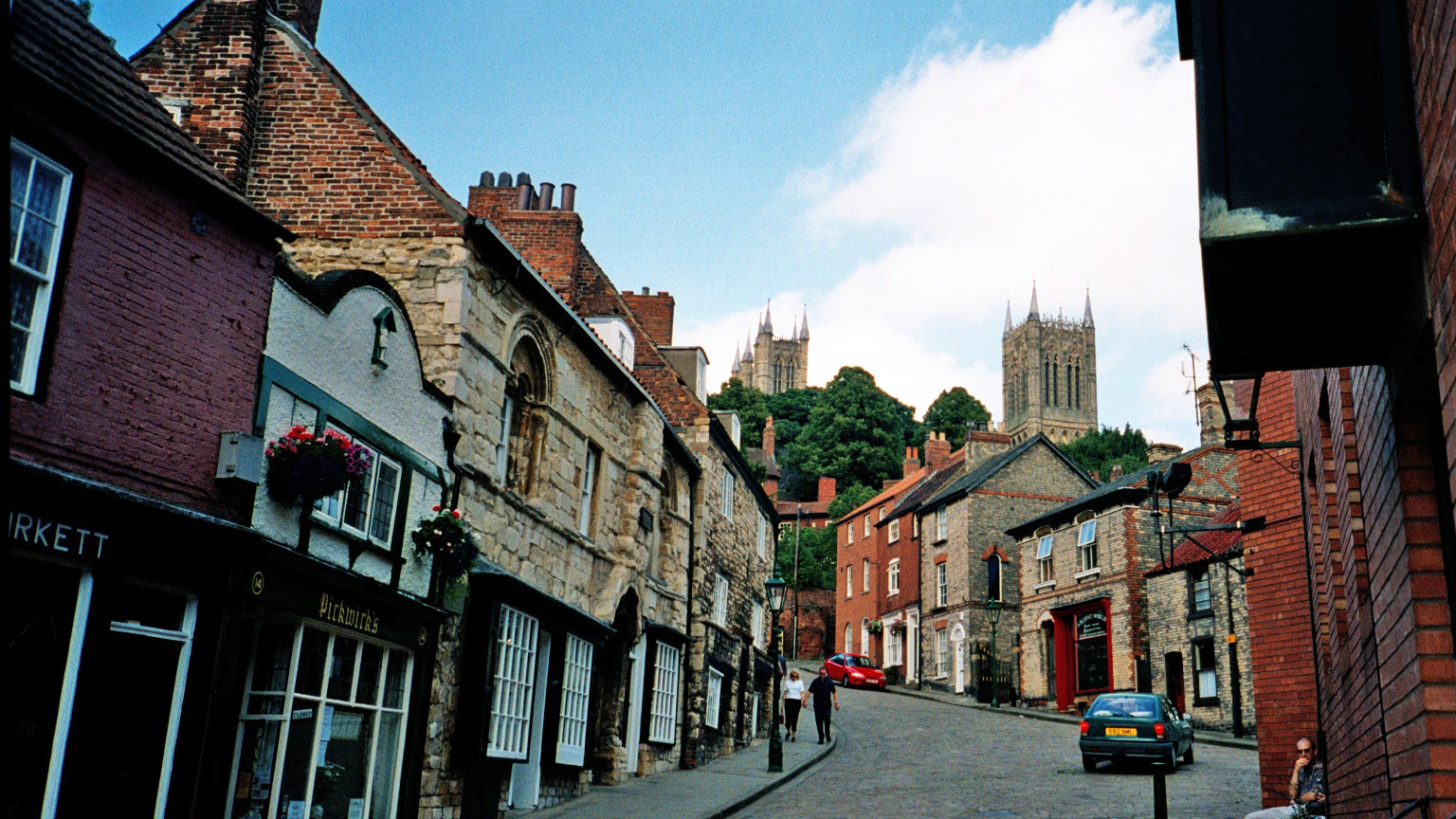
 Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection (Lincolnshire), The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection (Lincolnshire), The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
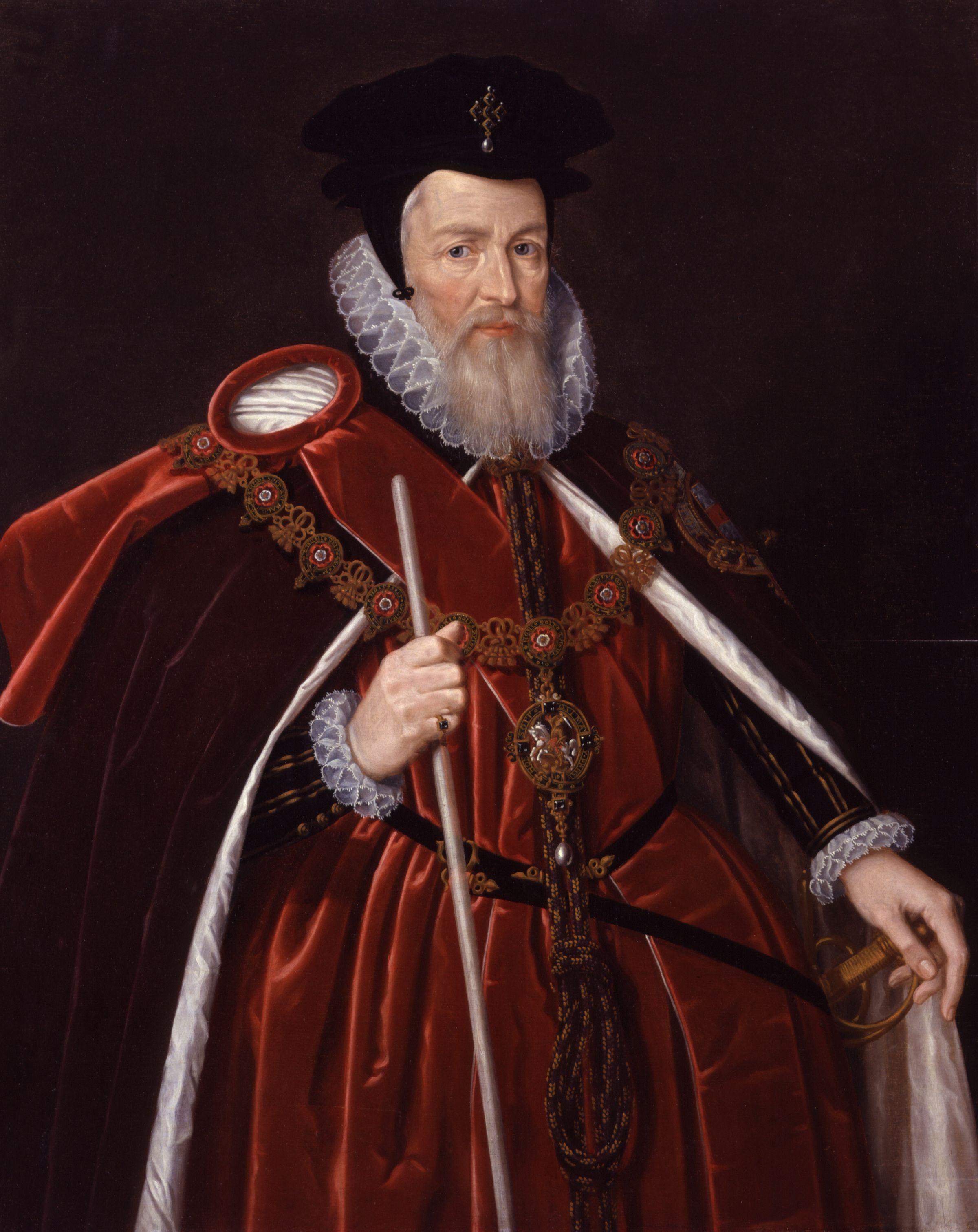
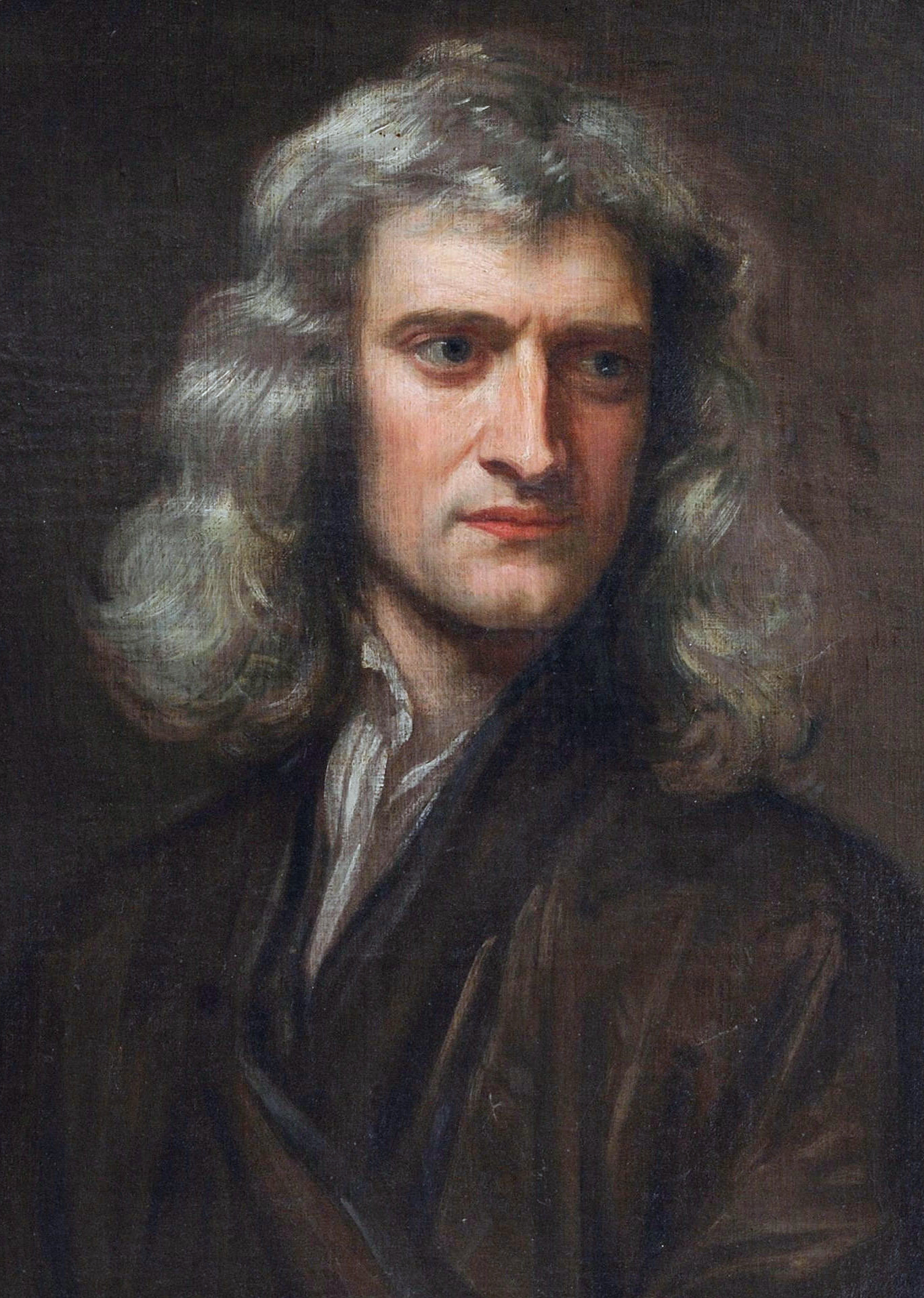






 The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
 Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
*Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with parsley (other ingredients are normally kept secret), and served cold.
*Haslet – a type of pork loaf, also flavoured with sage (pronounced HAYSS-let or AYSS-let in Lincolnshire but HAZ-let in many other parts of the country).
*Lincolnshire sausages – most butchers in Lincolnshire have their own secret recipe for these and a competition is held each year to judge the best sausages in the county. Traditional Lincolnshire sausages are made entirely from minced pork, stale bread crumb (rusk is used nowadays) pepper, sage and salt. The skins should be natural casings which are made from the intestines of either sheep or pig.
*Pork pies – the same pork butchers will take a pride in their unique recipe for pork pies.
*Giblets, Giblet pie.
*Lamb and mutton, Mutton stuffed with oysters.
*Plum bread – as with Christmas pudding, plum pudding, plum refers to dried fruit, namely currants, raisins and sultanas, sometimes soaked in tea.
*Grantham Gingerbread – a hard white ginger biscuit.
*Lincolnshire Poacher cheese – a cheddar-style cheese produced in Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford. Lincolnshire Poacher has won numerous awards over the years including Supreme Champion at the 1996/7 British Cheese Awards and Best British Cheese at the World Cheese awards in 2001/2.
*Batemans Brewery, Batemans ales – a beer brewed in Wainfleet, Lincolnshire, Wainfleet and served in many pubs in the county and further afield.
*There are several small breweries.
*Grimsby is renowned for its fishing industry, and historically ''Grimsby Fish'' has carried a premium price. Since the decline of the fishing industry following entry to the European Economic Community in the 1970s this is no longer the case, with the majority of fish sold at the town's fish market being brought overland from other ports. However, ''Grimsby Fish'' is still a recognised ''product'', one associated with a particular area that specialises in and has expertise in a particular trade (cf ''Sheffield steel''). In 2009 Traditional Grimsby smoked fish, smoked fish from the town was granted Protected Geographical Indication by the European Union, reflecting the unique smoking methods used by certain local fish companies.
Craft Chocolatiers can be found throughout the county, such as Hansens in Folkingham. In 2013 Redstar Chocolate's ''Duffy's Venezuela Ocumare Milk'' won a gold medal as best bean-to-bar. The factory is in Cleethorpes.
Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
*Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with parsley (other ingredients are normally kept secret), and served cold.
*Haslet – a type of pork loaf, also flavoured with sage (pronounced HAYSS-let or AYSS-let in Lincolnshire but HAZ-let in many other parts of the country).
*Lincolnshire sausages – most butchers in Lincolnshire have their own secret recipe for these and a competition is held each year to judge the best sausages in the county. Traditional Lincolnshire sausages are made entirely from minced pork, stale bread crumb (rusk is used nowadays) pepper, sage and salt. The skins should be natural casings which are made from the intestines of either sheep or pig.
*Pork pies – the same pork butchers will take a pride in their unique recipe for pork pies.
*Giblets, Giblet pie.
*Lamb and mutton, Mutton stuffed with oysters.
*Plum bread – as with Christmas pudding, plum pudding, plum refers to dried fruit, namely currants, raisins and sultanas, sometimes soaked in tea.
*Grantham Gingerbread – a hard white ginger biscuit.
*Lincolnshire Poacher cheese – a cheddar-style cheese produced in Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford. Lincolnshire Poacher has won numerous awards over the years including Supreme Champion at the 1996/7 British Cheese Awards and Best British Cheese at the World Cheese awards in 2001/2.
*Batemans Brewery, Batemans ales – a beer brewed in Wainfleet, Lincolnshire, Wainfleet and served in many pubs in the county and further afield.
*There are several small breweries.
*Grimsby is renowned for its fishing industry, and historically ''Grimsby Fish'' has carried a premium price. Since the decline of the fishing industry following entry to the European Economic Community in the 1970s this is no longer the case, with the majority of fish sold at the town's fish market being brought overland from other ports. However, ''Grimsby Fish'' is still a recognised ''product'', one associated with a particular area that specialises in and has expertise in a particular trade (cf ''Sheffield steel''). In 2009 Traditional Grimsby smoked fish, smoked fish from the town was granted Protected Geographical Indication by the European Union, reflecting the unique smoking methods used by certain local fish companies.
Craft Chocolatiers can be found throughout the county, such as Hansens in Folkingham. In 2013 Redstar Chocolate's ''Duffy's Venezuela Ocumare Milk'' won a gold medal as best bean-to-bar. The factory is in Cleethorpes.
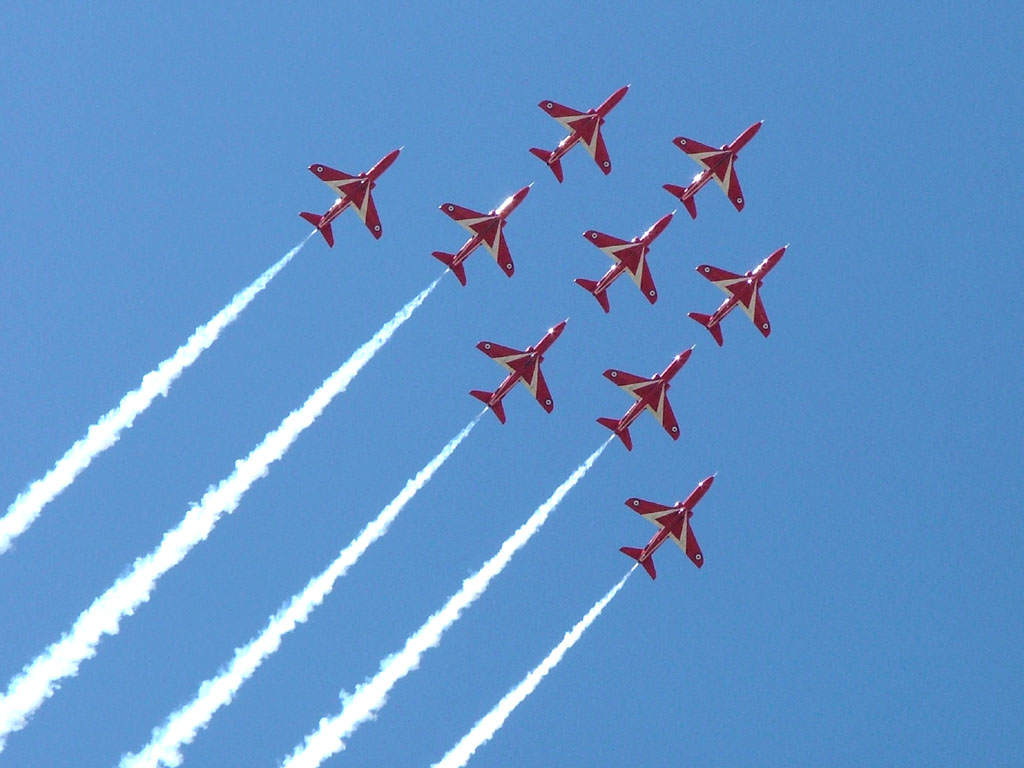 Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne, Lincolnshire, Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The Haxey Hood village competition takes place every January, as it has for over 700 years.
Stamford's Mid-Lent fair sees showmen converge on the town the week after Mothering Sunday, with rides and sideshows filling Broad Street, the Sheepmarket and the Meadows for a week. Stalls selling Grantham gingerbread and nougat are a traditional feature. The following week sees them in Grantham, on the way north for the Summer
Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne, Lincolnshire, Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The Haxey Hood village competition takes place every January, as it has for over 700 years.
Stamford's Mid-Lent fair sees showmen converge on the town the week after Mothering Sunday, with rides and sideshows filling Broad Street, the Sheepmarket and the Meadows for a week. Stalls selling Grantham gingerbread and nougat are a traditional feature. The following week sees them in Grantham, on the way north for the Summer
Roger Tuby
brings a small funfair to Bourne and then to Spalding in Spring and returns in Autumn at the end of the season. The villages of Tetford and Salmonby hold an annual Scarecrow Festival in May every year. The Belchford Downhill Challenge which is held every two years: soapbox racers race down the hill at up to 30 km/h. The turnout has been up to 1,000. Lincoln Christmas Market, a street market held throughout the historic area of the city at the start of December, is one of the largest Christmas markets in Europe, attracting over 250,000 people over the four-day event. Around the same time, Christmas lights are turned on in Bourne, Sleaford, Skegness, and other towns. Throughout the summer the Stamford Shakespeare Company presents the Bard's plays in the open-air theatre at Tolethorpe Hall, which is actually in Rutland. The Spalding, Lincolnshire, Spalding Flower Parade was held in late spring every year between 1959 and 2013. Colourful floats decorated with tulip heads competed for a cup.
 The main sports played in the county are Association football, football, cricket and rugby union. Lincolnshire does not have a high sporting profile, mainly due to the lack of facilities and high-profile football teams. Probably the most well-known sporting venues in Lincolnshire are Cadwell Park near Louth, where a round of the British Motorbike Championship is held on the last Monday of August every year and the racecourse at Market Rasen
*Three teams from Lincolnshire play in the Football League: Lincoln City F.C., Lincoln City play in Football League One, Grimsby Town FC, Grimsby Town play in Football League Two. In non-league football Scunthorpe United F.C., Scunthorpe United play in the National League (division), National League, while Boston United F.C., Boston United and Gainsborough Trinity F.C., Gainsborough Trinity play in the Football Conference North. A meeting between any of these clubs is a Lincolnshire derby; the most prominent meeting, having happened across English football league system, four of the top five tiers of English football, is Lincoln City vs Grimsby Town.
*In cricket Lincolnshire County Cricket Club, Lincolnshire are a minor county and play in the Minor Counties Championship.
*In field hockey, hockey Lindum Hockey Club play in the north of Lincoln.
*Scunthorpe Rugby Club are the most notable rugby union team from Lincolnshire, and will play in the fifth level of the English league system in the 2017–18 season. Other notable teams include Market Rasen and Louth RUFC, Lincoln RFC, and Boston Rugby Club.
*Lincolnshire is home to one racecourse, at Market Rasen Racecourse, Market Rasen.
*Cadwell Park is the only motor-racing course in Lincolnshire. There is a speedway track in Scunthorpe, home of the Scunthorpe Scorpions, and stock-car racing at a stadium at Orby, near Skegness.
*Lincolnshire has an American Football club, the Lincolnshire Bombers, which has existed in its current guise since 2005.
*Lincolnshire is home to the UK roller derby team, the Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Girls, which is sponsored by Motörhead.
The main sports played in the county are Association football, football, cricket and rugby union. Lincolnshire does not have a high sporting profile, mainly due to the lack of facilities and high-profile football teams. Probably the most well-known sporting venues in Lincolnshire are Cadwell Park near Louth, where a round of the British Motorbike Championship is held on the last Monday of August every year and the racecourse at Market Rasen
*Three teams from Lincolnshire play in the Football League: Lincoln City F.C., Lincoln City play in Football League One, Grimsby Town FC, Grimsby Town play in Football League Two. In non-league football Scunthorpe United F.C., Scunthorpe United play in the National League (division), National League, while Boston United F.C., Boston United and Gainsborough Trinity F.C., Gainsborough Trinity play in the Football Conference North. A meeting between any of these clubs is a Lincolnshire derby; the most prominent meeting, having happened across English football league system, four of the top five tiers of English football, is Lincoln City vs Grimsby Town.
*In cricket Lincolnshire County Cricket Club, Lincolnshire are a minor county and play in the Minor Counties Championship.
*In field hockey, hockey Lindum Hockey Club play in the north of Lincoln.
*Scunthorpe Rugby Club are the most notable rugby union team from Lincolnshire, and will play in the fifth level of the English league system in the 2017–18 season. Other notable teams include Market Rasen and Louth RUFC, Lincoln RFC, and Boston Rugby Club.
*Lincolnshire is home to one racecourse, at Market Rasen Racecourse, Market Rasen.
*Cadwell Park is the only motor-racing course in Lincolnshire. There is a speedway track in Scunthorpe, home of the Scunthorpe Scorpions, and stock-car racing at a stadium at Orby, near Skegness.
*Lincolnshire has an American Football club, the Lincolnshire Bombers, which has existed in its current guise since 2005.
*Lincolnshire is home to the UK roller derby team, the Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Girls, which is sponsored by Motörhead.

 The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "Lincolnshire Poacher (folk song), The Lincolnshire Poacher", which dates from around 1776. A version of the song was the theme for BBC Radio Lincolnshire for many years.
According to a 2002 marketing campaign by the charity Plantlife, the County flowers of the United Kingdom, county flower of Lincolnshire is the common dog-violet.
In August 2005, BBC Radio Lincolnshire and ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine launched a vote for a flag of Lincolnshire to represent the county. Six competing designs were voted upon by locals and the winning submission was unveiled in October 2005. Lincoln has its own flag – St George's flag with a Fleur-de-Lys.
The Lincoln Imp has symbolised cathedral, city and county for many years. In 2006 it was replaced as the brand of Lincolnshire County Council by the stylised version seen on the header her
The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "Lincolnshire Poacher (folk song), The Lincolnshire Poacher", which dates from around 1776. A version of the song was the theme for BBC Radio Lincolnshire for many years.
According to a 2002 marketing campaign by the charity Plantlife, the County flowers of the United Kingdom, county flower of Lincolnshire is the common dog-violet.
In August 2005, BBC Radio Lincolnshire and ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine launched a vote for a flag of Lincolnshire to represent the county. Six competing designs were voted upon by locals and the winning submission was unveiled in October 2005. Lincoln has its own flag – St George's flag with a Fleur-de-Lys.
The Lincoln Imp has symbolised cathedral, city and county for many years. In 2006 it was replaced as the brand of Lincolnshire County Council by the stylised version seen on the header her
which has lost even the unique pose of the carving.
Lincolnshire County Council websiteLincs FM websiteVisitlincolnshire.com
Lindcolne Skipfierde
Lincolnshire'
Anglo-Saxon, Viking and Norman
re-enactment and living history group
Lincolnshire Show official websitePathe newsreel of motor tractors at 1919 agricultural show, thought to be Lincoln show
Images of Lincolnshire
at the English Heritage Archive {{Authority control Lincolnshire, Non-metropolitan counties East Midlands NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Counties of England established in antiquity
History
 During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the Corieltauvi people. The language of the area at that time would have been Common Brittonic, the precursor to modern Welsh. The name ''Lincoln'' was derived from Lindum Colonia.
Large numbers of Germanic speakers from continental Europe settled in the region following the withdrawal of the Romans. Though these were later identified as Angles, it is unlikely that they migrated as part of an organized tribal group. Thus, the main language of the region quickly became Old English. However, it is possible that Brittonic continued to be spoken in some communities as late as the eighth century.
Modern-day Lincolnshire is derived from the merging of the territory of the Kingdom of Lindsey with that controlled by the Danelaw borough of Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford. For some time the entire county was called "Lindsey", and it is recorded as such in the 11th-century ''Domesday Book.'' Later, the name Lindsey (government district), Lindsey was applied to the northern core, around Lincoln. This emerged as one of the three Parts of Lincolnshire, along with the Parts of Holland, Lincolnshire, Holland in the south-east, and the Parts of Kesteven in the south-west, which each had separate Quarter Sessions as their county administrations.
In 1888 when county councils were set up, Lindsey, Holland and Kesteven each received separate ones. These survived until 1974, when Holland, Kesteven, and most of Lindsey were unified into Lincolnshire. The northern part of Lindsey, including Scunthorpe Municipal Borough and Grimsby County Borough, was incorporated into the newly formed shire county, non-metropolitan county of Humberside, along with most of the East Riding of Yorkshire.
During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the Corieltauvi people. The language of the area at that time would have been Common Brittonic, the precursor to modern Welsh. The name ''Lincoln'' was derived from Lindum Colonia.
Large numbers of Germanic speakers from continental Europe settled in the region following the withdrawal of the Romans. Though these were later identified as Angles, it is unlikely that they migrated as part of an organized tribal group. Thus, the main language of the region quickly became Old English. However, it is possible that Brittonic continued to be spoken in some communities as late as the eighth century.
Modern-day Lincolnshire is derived from the merging of the territory of the Kingdom of Lindsey with that controlled by the Danelaw borough of Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford. For some time the entire county was called "Lindsey", and it is recorded as such in the 11th-century ''Domesday Book.'' Later, the name Lindsey (government district), Lindsey was applied to the northern core, around Lincoln. This emerged as one of the three Parts of Lincolnshire, along with the Parts of Holland, Lincolnshire, Holland in the south-east, and the Parts of Kesteven in the south-west, which each had separate Quarter Sessions as their county administrations.
In 1888 when county councils were set up, Lindsey, Holland and Kesteven each received separate ones. These survived until 1974, when Holland, Kesteven, and most of Lindsey were unified into Lincolnshire. The northern part of Lindsey, including Scunthorpe Municipal Borough and Grimsby County Borough, was incorporated into the newly formed shire county, non-metropolitan county of Humberside, along with most of the East Riding of Yorkshire.
 A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire. These two areas became part of Lincolnshire for ceremonial purposes, such as the Lord-Lieutenant, Lord-Lieutenancy, but are not covered by the Lincolnshire police; they are in the Yorkshire and the Humber region.
The remaining districts of Lincolnshire are Boston (borough), Boston, East Lindsey, Lincoln, North Kesteven, South Holland, England, South Holland, South Kesteven, and West Lindsey. They are part of the East Midlands region.
The area was shaken by the 27 February 2008 Lincolnshire earthquake, reaching between 4.7 and 5.3 on the Richter magnitude scale; it was one of the largest earthquakes to affect Britain in recent years.
Lincolnshire is home to Woolsthorpe Manor, birthplace and home of Sir Isaac Newton. He attended The King's School, Grantham. Its library has preserved his signature, carved into a window sill when he was a youth.
A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire. These two areas became part of Lincolnshire for ceremonial purposes, such as the Lord-Lieutenant, Lord-Lieutenancy, but are not covered by the Lincolnshire police; they are in the Yorkshire and the Humber region.
The remaining districts of Lincolnshire are Boston (borough), Boston, East Lindsey, Lincoln, North Kesteven, South Holland, England, South Holland, South Kesteven, and West Lindsey. They are part of the East Midlands region.
The area was shaken by the 27 February 2008 Lincolnshire earthquake, reaching between 4.7 and 5.3 on the Richter magnitude scale; it was one of the largest earthquakes to affect Britain in recent years.
Lincolnshire is home to Woolsthorpe Manor, birthplace and home of Sir Isaac Newton. He attended The King's School, Grantham. Its library has preserved his signature, carved into a window sill when he was a youth.
Geography
The geographical layout of Lincolnshire is quite extensive and mostly separated by many rivers and rolling countryside. The north of the county begins from where the Isle of Axholme is located near the meeting points of the rivers River Great Ouse, Ouse and River Trent, Trent near to the River Humber, Humber. From there, the southside of the Humber, Humber esturary forms the border between Lincolnshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire. From there, the south bank of the Humber Estuary where the Humber Bridge crosses the estuary at Barton upon Humber, is used primarily for the shipping ports at Immingham, New Holland, Lincolnshire, New Holland and Grimsby. From there, the rest of the southern bank forms the Lincolnshire Coast from Cleethorpes to Mablethorpe and then onto Skegness. From Skegness, the rest of the Lincolnshire Coastline forms the sea boundary and border with Norfolk at the The Wash, Wash. The coast then at Boston, Lincolnshire, Boston becomes the meeting point of the rivers River Welland, Welland and River Haven, Haven. The rest of the county boundary runs roughly to the point of Sutton Bridge, which is separated from Norfolk by the River Nene which begins to branch off from the North Sea. The border with Lincolnshire to Cambridgeshire begins at Crowland, Market Deeping and Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford which form the southern boundary of the county with both Peterborough, Rutland and briefly Northamptonshire. From there, the border with Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire begins at Sleaford, Grantham, Lincoln, Lincolnshire, Lincoln and Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough. From Gainsborough, the border with South Yorkshire begins at Haxey and Epworth, Lincolnshire, Epworth before looping back to the original north of the county near Scunthorpe with East Riding of Yorkshire at the Isle of Axholme and Goole. Bedrock in Lincolnshire features Jurassic limestone (near Lincoln) and Cretaceous chalk (north-east). The area around Woodhall Spa and Kirkby on Bain is dominated by gravel and sand. For much of prehistory, Lincolnshire was under tropical seas, and most fossils found in the county are marine invertebrates. Marine vertebrates have also been found including ichthyosaurus and plesiosaur. The highest point in Lincolnshire is Wolds Top (), at Normanby le Wold. Some parts of the Fens may be below sea level. The nearest mountains are in Derbyshire. The biggest rivers in Lincolnshire are the River Trent, Trent, running northwards from Staffordshire up the western edge of the county to the Humber estuary, and the River Witham, Witham, which begins in Lincolnshire at South Witham and runs for through the middle of the county, eventually emptying into the North Sea at The Wash. The Humber estuary, on Lincolnshire's northern border, is also fed by the River Ouse, Yorkshire, River Ouse. The Wash is also the mouth of the River Welland, Welland, the River Nene, Nene and the Great Ouse. Lincolnshire's geography is fairly varied, but consists of several distinct areas: * Lincolnshire Wolds: area of rolling hills in the north-east of the county designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty * The Fens: dominating the south-east quarter of the county * Lincolnshire Marsh, The Marshes: running along the coast of the county * Lincoln Cliff, Lincoln Edge or Cliff: limestone escarpment running north–south along the western half of the county Lincolnshire's most well-known nature reserves include Gibraltar Point, Lincolnshire, Gibraltar Point National Nature Reserve, Whisby Moor#Whisby Nature Park, Whisby Nature Park Local Nature Reserve, Donna Nook National Nature Reserve, RSPB Frampton Marsh and the Humberhead Levels, Humberhead Peatlands National Nature Reserve. Although the Lincolnshire countryside is intensively farmed, there are many biodiverse wetland areas, as well as rare Bardney Limewoods, limewood forests. Much of the county was once wet fenland (see The Fens). From bones, we can tell that animal species formerly found in Lincolnshire include woolly mammoth, woolly rhinoceros, tarpan, wild horse, wolf, wild boar and beaver. Species which have recently returned to Lincolnshire after extirpation include little egret, Eurasian spoonbill, European otter and red kite.Governance
Lincolnshire County Council is Conservative Party (UK), Conservative controlled, as are six of its seven district councils (Lincoln City Council is controlled by Labour Party (UK), Labour). Two further districts - North East Lincolnshire and North Lincolnshire - are unitary authorities. They were previously districts of Humberside, Humberside county from 1974. In 1996, Humberside was abolished along with its county council. However some services in those districts are still shared with the East Riding of Yorkshire ceremonial county, rather than the rest of Lincolnshire. Lincolnshire is represented by 11 Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs). As of the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 general election, all 11 constituencies are represented by the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party.Economy
This is a chart of trend of regional gross value added of Lincolnshire at current basic prices, according to the Office for National Statistics with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling. : includes hunting and forestry : includes energy and construction : includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured Notable businesses based in Lincolnshire include the Lincs FM Group, Young's Seafood, Openfield and the Lincolnshire Co-operative (whose membership includes about one quarter of the population of the county).Agriculture
 Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of wheat, barley, sugar beet, and oilseed rape. In south Lincolnshire, where the soil is particularly rich in nutrients, some of the most common crops include potatoes, cabbages, cauliflowers, and onions. Lincolnshire farmers often break world records for crop yields. South Lincolnshire is also home to one of the UK's leading agricultural experiment stations, located in Sutton Bridge and operated by the Potato Council; Sutton Bridge Crop Storage Research engages in research for the British potato industry.
The Lincoln sheep, Lincoln Longwool is a rare breed of sheep, named after the region, which was developed both for wool and mutton, at least 500 years ago, and has the longest fleece of any sheep breed. The Lincoln Red is an old breed of beef cattle, originating from the county. In the mid 20th century most farms in Lincolnshire moved away from mixed farming to specialise in arable cropping, partly due to cheap wool imports, partly to take advantage of efficiencies of scale and partly because the drier land on the eastern side of England is particularly suitable for arable cropping.
Mechanization and Modernization Agreement 1960, Mechanization around 1900 greatly diminished the number of workers required to operate the county's relatively large farms, and the proportion of workers in the agricultural sector dropped substantially during this period. Several major engineering companies developed in Lincoln, Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough and Grantham to support those changes. Among these was William Foster & Co Ltd, Fosters of Lincoln, which built the first tank, and Richard Hornsby & Sons of Grantham. Most such industrial companies left during late 20th-century restructuring.
Today, Immigration to Europe, immigrant workers, mainly from Enlargement of the European Union, new member states of the European Union in Central and Eastern Europe, comprise a large component of the seasonal agricultural workforce, particularly in the south of the county. Here more labour-intensive crops are produced, such as small vegetables and cut flowers. This seasonal influx of migrant labour occasionally causes tension between the migrant workforce and local people, in a county which had been relatively unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. Agricultural training is provided at Riseholme College and in 2016 the University of Lincoln opened the Lincoln Institute for Agri-Food Technology.
Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of wheat, barley, sugar beet, and oilseed rape. In south Lincolnshire, where the soil is particularly rich in nutrients, some of the most common crops include potatoes, cabbages, cauliflowers, and onions. Lincolnshire farmers often break world records for crop yields. South Lincolnshire is also home to one of the UK's leading agricultural experiment stations, located in Sutton Bridge and operated by the Potato Council; Sutton Bridge Crop Storage Research engages in research for the British potato industry.
The Lincoln sheep, Lincoln Longwool is a rare breed of sheep, named after the region, which was developed both for wool and mutton, at least 500 years ago, and has the longest fleece of any sheep breed. The Lincoln Red is an old breed of beef cattle, originating from the county. In the mid 20th century most farms in Lincolnshire moved away from mixed farming to specialise in arable cropping, partly due to cheap wool imports, partly to take advantage of efficiencies of scale and partly because the drier land on the eastern side of England is particularly suitable for arable cropping.
Mechanization and Modernization Agreement 1960, Mechanization around 1900 greatly diminished the number of workers required to operate the county's relatively large farms, and the proportion of workers in the agricultural sector dropped substantially during this period. Several major engineering companies developed in Lincoln, Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough and Grantham to support those changes. Among these was William Foster & Co Ltd, Fosters of Lincoln, which built the first tank, and Richard Hornsby & Sons of Grantham. Most such industrial companies left during late 20th-century restructuring.
Today, Immigration to Europe, immigrant workers, mainly from Enlargement of the European Union, new member states of the European Union in Central and Eastern Europe, comprise a large component of the seasonal agricultural workforce, particularly in the south of the county. Here more labour-intensive crops are produced, such as small vegetables and cut flowers. This seasonal influx of migrant labour occasionally causes tension between the migrant workforce and local people, in a county which had been relatively unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. Agricultural training is provided at Riseholme College and in 2016 the University of Lincoln opened the Lincoln Institute for Agri-Food Technology.
Central Lincolnshire
This area covers North Kesteven, Lincoln and West Lindsey. It helps with development and economic planning around the three districts.Politics
Services and retail
According to an Intra-governmental Group on Geographic Information (IGGI) study in 2000, the town centres were ranked by area thus (including North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire areas): *Lincoln, England, Lincoln *Grantham *Grimsby *Boston, Lincolnshire, Boston and Scunthorpe (equal) *Spalding, Lincolnshire, Spalding *Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford *Skegness *Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth *Sleaford *Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough *Brigg *Cleethorpes *Bourne, Lincolnshire, Bourne *Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle and Mablethorpe (equal)Public services
Education
Lincolnshire is one of the few counties in the UK that still uses the 11-plus to decide who may attend grammar schools in the United Kingdom, grammar school. As a result, many towns in Lincolnshire have both a grammar school and a secondary modern school. Lincolnshire's rural character means that some larger villages also have primary schools and are served by buses to nearby high schools. Lincoln itself, however, is primarily non-selective, as is the area within a radius of about seven miles. In this area, almost all children attend comprehensive schools, though it is still possible to opt into the 11-plus system. This gives rise to the unusual result that those who pass the Eleven plus can attend a Grammar School outside the Lincoln Comprehensive area, but those who do not pass still attend a (partly non-selective) Comprehensive school.Transport
 Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by single carriageway Great Britain road numbering scheme, A roads and local roads (B roads) as opposed to Controlled-access highway, motorways and dual carriageways – the administrative county of Lincolnshire is one of the few UK counties without a motorway, and until several years ago, it was said that there was only about of dual carriageway in the whole of Lincolnshire. The M180 motorway passes through North Lincolnshire, splitting into two dual carriageway trunk roads to the Humber Bridge and Grimsby, and the A46 road, A46 is now dual carriageway between Newark-on-Trent and Lincoln.
The low population density of the county means that the number of railway stations and train services is very low considering the county's large area. Many of the county's railway stations were permanently closed following the Beeching cuts, Beeching Report of 1963. The most notable reopening has been the line and two stations between Lincoln and Sleaford, which reopened within months of the Beeching closure. Most other closed lines in the county were long ago lifted and much of the trackbed has returned to agricultural use.
Prior to 1970, a through train service operated between Cleethorpes railway station, Cleethorpes and London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross via Louth railway station, Louth, Boston railway station, Boston and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. The part of this line in Grimsby is now the A16 road (England), A16 road, preventing reinstatement as a railway line, and a small section of the line is now the Lincolnshire Wolds Railway, with an extension towards Louth in progress.
A daily through train service operated between Cleethorpes and London King's Cross via Grimsby railway station, Grimsby, Market Rasen railway station, Market Rasen and Lincoln railway station, Lincoln Central until the late 1980s. The ''Humberlincs Executive'', as the service was known, was operated by an InterCity 125, but was discontinued following the electrification of the East Coast Main Line. Passengers now have to change trains at Newark North Gate railway station, Newark North Gate when travelling to and from London. However, the East Coast Main Line passes through the western edge of the county and one can catch direct trains to London from Grantham railway station, Grantham.
Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by single carriageway Great Britain road numbering scheme, A roads and local roads (B roads) as opposed to Controlled-access highway, motorways and dual carriageways – the administrative county of Lincolnshire is one of the few UK counties without a motorway, and until several years ago, it was said that there was only about of dual carriageway in the whole of Lincolnshire. The M180 motorway passes through North Lincolnshire, splitting into two dual carriageway trunk roads to the Humber Bridge and Grimsby, and the A46 road, A46 is now dual carriageway between Newark-on-Trent and Lincoln.
The low population density of the county means that the number of railway stations and train services is very low considering the county's large area. Many of the county's railway stations were permanently closed following the Beeching cuts, Beeching Report of 1963. The most notable reopening has been the line and two stations between Lincoln and Sleaford, which reopened within months of the Beeching closure. Most other closed lines in the county were long ago lifted and much of the trackbed has returned to agricultural use.
Prior to 1970, a through train service operated between Cleethorpes railway station, Cleethorpes and London King's Cross railway station, London King's Cross via Louth railway station, Louth, Boston railway station, Boston and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. The part of this line in Grimsby is now the A16 road (England), A16 road, preventing reinstatement as a railway line, and a small section of the line is now the Lincolnshire Wolds Railway, with an extension towards Louth in progress.
A daily through train service operated between Cleethorpes and London King's Cross via Grimsby railway station, Grimsby, Market Rasen railway station, Market Rasen and Lincoln railway station, Lincoln Central until the late 1980s. The ''Humberlincs Executive'', as the service was known, was operated by an InterCity 125, but was discontinued following the electrification of the East Coast Main Line. Passengers now have to change trains at Newark North Gate railway station, Newark North Gate when travelling to and from London. However, the East Coast Main Line passes through the western edge of the county and one can catch direct trains to London from Grantham railway station, Grantham.

Health care
The United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust is one of the largest trusts in the country, employing almost 4,000 staff and with an annual budget of over £200 million. The north of the county is served by thNorthern Lincolnshire and Goole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Some of the larger hospitals in the county include: *Diana Princess of Wales Hospital, Grimsby *Scunthorpe General Hospital *Pilgrim Hospital, Boston Pilgrim Hospital *Lincoln County Hospital Since April 1994, Lincolnshire has had an Air Air ambulances in the United Kingdom, Ambulance service. The air ambulance is stationed at RAF Waddington near Lincoln and can reach emergencies in Lincolnshire within 25 minutes. An A&E hospital is only 10 minutes away by helicopter from any accident in Lincolnshire.
Drainage
Separately to the commercial water companies the low-lying parts of the county are drained by various internal drainage boards, such as thBlack Sluice Internal Drainage Board
, or th
Welland and Deepings Internal Drainage Board
Towns and villages
In terms of population, the 12 biggest settlements in the county by population are: *Lincoln, Lincolnshire, Lincoln (Population: 97,541) *Grimsby (Population: 88,243) *Scunthorpe (Population: 82,334) *Grantham (Population: 44,580) *Cleethorpes (Population: 38,996) *Boston, Lincolnshire, Boston (Population: 35,124) *Spalding, Lincolnshire, Spalding (Population: 34,613) *Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough (Population: 22,841) *Stamford, Lincolnshire, Stamford (Population: 19,701) *Skegness (Population: 19,579) *Sleaford (Population: 17,671) *Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth (Population, 16,419) A small part of the Thorne and Hatfield Moors#Location, Thorne Waste area of the town of Thorne, South Yorkshire, Thorne in South Yorkshire, known as the Yorkshire Triangle, currently falls under North Lincolnshire.Tourism

 The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the East Midlands and parts of Yorkshire. There are three main coastal resorts in Lincolnshire and several smaller village resorts.
The main county seaside resort of Skegness with its famous The Jolly Fisherman, Jolly Fisherman mascot and famous slogan "Skegness is so bracing", together with its neighbouring large village coastal resorts of Ingoldmells and Chapel St Leonards, provides the biggest concentration of resorts along the Lincolnshire Coast, with many large caravan and holiday sites. The resort offers many amusements, beaches, leisure activities and shops, as well as Butlins Skegness, Fantasy Island (UK amusement park), Fantasy Island, Church Farm Museum, Natureland Seal Sanctuary, Skegness Stadium, Skegness Pier#Pier, Skegness Pier and several well-known local golf courses. There are good road, bus and rail links to the rest of the county.
The second largest group of resorts along the coast is the seaside town of Mablethorpe, famous for its golden sands, and the neighbouring village resorts of Trusthorpe and Sutton-on-Sea. This area also offers leisure activities and has large caravan and holiday sites. But the area is less developed, with fewer amusement arcades and nightclubs, and poorer road links to the rest of the county; but the area offers a more traditional seaside setting.
The third group of resorts includes the seaside town of Cleethorpes and the large village resort of Humberston within North East Lincolnshire. It has the Cleethorpes Coast Light Railway and Cleethorpes Pier along with its local golf courses and caravan and holiday sites, whilst it is also the former site of Pleasure Island Family Theme Park. Cleethorpes is well-served by road and rail; it is easily accessible from the M180 motorway, M180 and the TransPennine Express route to Manchester.
Nature is an attraction for many tourists: the south-east of the county is mainly fenland that attracts many species of birds, as do the national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves at Gibraltar Point, Lincolnshire, Gibraltar Point, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe Dunes National Nature Reserve, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe and Donna Nook, which also contains a large grey seal colony which is popular with visitors.
The market towns of the Lincolnshire Wolds Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth, Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, Caistor and Spilsby are also attractive, with several having historically important buildings, such as Alford Manor House, St James' Church, Louth, St James' Church and Bolingbroke Castle. The Wolds are popular for cycling and walking, with regular events such as the Lincolnshire Wolds Walking Festival.
The city of Lincoln, England, Lincoln is home to many tourist attractions including Lincoln Castle, Lincoln Cathedral, The Engine Shed, Steep Hill, International Bomber Command Centre and Guildhall and Stonebow, Lincoln, Guildhall and Stonebow among other historical landmarks and listed buildings. The city acts as one of the many tourist centres in the East Midlands Region.
The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the East Midlands and parts of Yorkshire. There are three main coastal resorts in Lincolnshire and several smaller village resorts.
The main county seaside resort of Skegness with its famous The Jolly Fisherman, Jolly Fisherman mascot and famous slogan "Skegness is so bracing", together with its neighbouring large village coastal resorts of Ingoldmells and Chapel St Leonards, provides the biggest concentration of resorts along the Lincolnshire Coast, with many large caravan and holiday sites. The resort offers many amusements, beaches, leisure activities and shops, as well as Butlins Skegness, Fantasy Island (UK amusement park), Fantasy Island, Church Farm Museum, Natureland Seal Sanctuary, Skegness Stadium, Skegness Pier#Pier, Skegness Pier and several well-known local golf courses. There are good road, bus and rail links to the rest of the county.
The second largest group of resorts along the coast is the seaside town of Mablethorpe, famous for its golden sands, and the neighbouring village resorts of Trusthorpe and Sutton-on-Sea. This area also offers leisure activities and has large caravan and holiday sites. But the area is less developed, with fewer amusement arcades and nightclubs, and poorer road links to the rest of the county; but the area offers a more traditional seaside setting.
The third group of resorts includes the seaside town of Cleethorpes and the large village resort of Humberston within North East Lincolnshire. It has the Cleethorpes Coast Light Railway and Cleethorpes Pier along with its local golf courses and caravan and holiday sites, whilst it is also the former site of Pleasure Island Family Theme Park. Cleethorpes is well-served by road and rail; it is easily accessible from the M180 motorway, M180 and the TransPennine Express route to Manchester.
Nature is an attraction for many tourists: the south-east of the county is mainly fenland that attracts many species of birds, as do the national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves at Gibraltar Point, Lincolnshire, Gibraltar Point, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe Dunes National Nature Reserve, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe and Donna Nook, which also contains a large grey seal colony which is popular with visitors.
The market towns of the Lincolnshire Wolds Louth, Lincolnshire, Louth, Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, Caistor and Spilsby are also attractive, with several having historically important buildings, such as Alford Manor House, St James' Church, Louth, St James' Church and Bolingbroke Castle. The Wolds are popular for cycling and walking, with regular events such as the Lincolnshire Wolds Walking Festival.
The city of Lincoln, England, Lincoln is home to many tourist attractions including Lincoln Castle, Lincoln Cathedral, The Engine Shed, Steep Hill, International Bomber Command Centre and Guildhall and Stonebow, Lincoln, Guildhall and Stonebow among other historical landmarks and listed buildings. The city acts as one of the many tourist centres in the East Midlands Region.
Culture

 Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection (Lincolnshire), The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection (Lincolnshire), The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
People
Those born in Lincolnshire are sometimes given the nickname of Yellowbelly (Lincolnshire), Yellowbellies (often spelt "Yeller Bellies", to reflect the pronunciation of the phrase by the typical Lincolnshire farmer). The origin of this term is debated, but is most commonly believed to derive from the uniform of the 10th Regiment of Foot (later the Lincolnshire Regiment) which featured yellow facings. For this reason, the coat of arms of Lincolnshire County Council is supported by two officers of the regiment.Notable people






 The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
Born before 1701
* Guthlac of Crowland (674–715), Christian saint * Æthelhard (8th century-805), Archbishop of Canterbury * Hereward the Wake (c.1035-c.1072), Anglo-Saxon nobleman * Lucy of Bolingbroke (1074–1136), countess of Chester * Gilbert of Sempringham (c.1085–1190), Saint and Founder of the Gilbertine Order * Aaron of Lincoln (c.1125–1186), financier * Hugh of Lincoln (1135/40-1200), Bishop of Lincoln * Stephen Langton (c.1150–1228), Archbishop of Canterbury * Nicolaa de la Haye (c.1150–1230), landowner and administrator * Robert Grosseteste (c.1175–1253), Bishop of Lincoln * Berechiah de Nicole (c.1210-c.1270), Tosafist * Eleanor of Castile (1241–1290), wife of Edward I of England, Edward I * Little Saint Hugh of Lincoln (1246–1255), murder victim, falsely attributed to blood libel * Katherine Swynford (c.1350–1403), third wife of John of Gaunt * Henry IV of England (1367–1413), King of England * Richard Foxe (1458–1528), bishop and founder of Corpus Christi College, Oxford * John Taverner (c1490-1545), composer and organist * John Whitgift (c.1503–1604), Archbishop of Canterbury * John Foxe (c.1516–1587), author of ''Foxe's Book of Martyrs'' * William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley (1520–1598), Chief Advisor to Queen Elizabeth I * Anne Askew (1521–1546), Protestant martyr * William Byrd (1539–1623), composer * John Smyth (Baptist minister), John Smyth (c.1554-c.1612), founder of the Baptist denomination * Robert Tighe (1562–1620), cleric and linguist * Francis Meres (1565/1566-1647), churchman and author * Captain John Smith (1580–1631), leader of the settlement of Jamestown, Virginia * John Cotton (minister), John Cotton (1585–1652), clergyman * Anne Bradstreet (1612–1672), poet * John Leverett (1616-1678/79), penultimate governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony * Simon Patrick (1626–1707), English theologian and bishop * Isaac Newton, Sir Isaac Newton (1642–1726), mathematician and physicist * John Harrison (1693–1776), Marine chronometer, chronometer innovator * William Stukeley (1687–1765), antiquarianBorn 1701–1850
* John Wesley, John (1703–1791) and Charles Wesley (1707–1788), founders of the Methodist movement * Benjamin Huntsman (1704–1776), inventor of crucible steel * Thomas Paine (1737–1809), political activist and philosopher * Joseph Banks (1743–1820), botanist and naturalist * Samuel Eyles Pierce (1746–1829), preacher and theologian * Thomas Scott (commentator), Thomas Scott (1747–1821), Bible commentator and co-founder of the Church Missionary Society * George Bass (1771-c.1803), explorer of Australia * Matthew Flinders (1774–1814), navigator and cartographer * Richard Watson (Methodist), Richard Watson (1781–1833), theologian and Methodist writer * George Davenport (1783–1845), sailor and frontiersman * Peter De Wint (1784–1849), landscape painter * Pishey Thompson (1784–1862), publisher and antiquarian writer * Sir John Franklin (1786–1847), Arctic explorer * Andreas Kalvos (1792–1869), poet * Christopher Wordsworth (1807–1885), Bishop of Lincoln * Alfred Lord Tennyson (1809–1892), poet * Herbert Ingram (1811–1860), journalist * Lady Charlotte Guest (1812–1895), businesswoman and Welsh language translator * George Boole (1815–1864), mathematician * William Marwood (1818–1883), hangman * Jean Ingelow (1820–1897), poet * Charles Frederick Worth (1825–1895), fashion designer * Edward King (bishop of Lincoln), Edward King (1829–1910), Bishop of Lincoln * Charlotte Alington Barnard (1830–1869), ballad composer and hymn writer * Joseph Ruston (1835–1897), engineer and manufacturer *Arnold Rylott (1839–1914), cricketer for Marylebone Cricket Club * George Green (Medal of Honor) (1840–1898), Medal of Honor recipient * Gonville Bromhead (1845–1891), Victoria Cross recipient * Madge Kendal (1848–1935), actressBorn 1851–1950
* Ethel Rudkin (1893–1985), folklorist and archaeologist * Sarah Swift (1854–1937), Royal College of Nursing founder * Frank Bramley (1857–1915), artist * Adrian Woodruffe-Peacock (1858–1922), clergyman and ecologist * William Robertson (British Army officer), William Robertson (1860–1933), Field Marshal * Halford Mackinder (1861–1947), geographer * Thomas Colclough Watson (1867–1917), Victoria Cross recipient * Cyril Bland (1872–1950), cricketer * William Tritton (1875–1946), tank developer * Frank Pick (1878–1941), railway administrator * Sybil Thorndike (1882–1976), actress * Alfred Piccaver (1884–1958), tenor * Arthur Lucan (1885–1954), part of the music hall act Old Mother Riley * Harold Jackson (VC) (1892–1918), Victoria Cross recipient * Charles Richard Sharpe (1889–1963), Victoria Cross recipient * Francis Hill (1899–1980), historian * Frank Whittle (1907–1996), RAF officer * John George Haigh (1909–1949), serial killer * Douglas Bader (1910–1982), RAF flying ace * James Cobban (1910–1999), educator and headmaster * Chad Varah (1911–2007), priest and "The Samaritans" founder * Ted Savage (footballer), Ted Savage (1912–1964), footballer * Guy Gibson (1918–1944), bomber pilot and Victoria Cross recipient * Steve Race (1921–2009), musician and broadcaster * Liz Smith (actress), Liz Smith (1921–2016), actress * Leslie Manser (1922–1942), bomber pilot and Victoria Cross recipient * Brian Tierney (medievalist), Brian Tierney (1922–2019), historian * Nicholas Parsons (1923–2020), radio and TV presenter * Neville Marriner (1924–2016), violinist and conductor * Margaret Thatcher (1925–2013), former Prime Minister * Elizabeth Jennings (poet), Elizabeth Jennings (1926–2001), poet * Brenda Fisher (1927–2022), swimmer * Joan Plowright (born 1929), actress * Jeff Hall (footballer), Jeff Hall (1929–1959), footballer * Colin Dexter (1930–2017), crime writer * Bill Podmore (1931–1994), television producer * Neil McCarthy (actor), Neil McCarthy (1932–1985), actor * Frank Sargeant (bishop), Frank Sargeant (born 1932), retired Anglican bishop * Mervyn Winfield (1932–2014), cricketer * Bernard Codd (1934–2013), motorcycle road racer * Victor Emery (1934–2002), physicist * Mike Pinner (born 1934), football goalkeeper * Bruce Barrymore Halpenny (born 1937), military historian and author * Roy Axe (1937–2010), car designer * Barry Spikings (born 1939), Hollywood producer * John Alderton (born 1940), actor * John Hurt (1940-2017), actor * Jo Kendall (1940-2022), actress * Ted Lewis (writer), Ted Lewis (1940–1982), crime writer * Alec Brader () (born 1942) professional footballer, schoolteacher and youth athletics coach * Graham Oates (footballer, born 1943), Graham Oates (born 1943), footballer * John Hargreaves (cricketer), John Hargreaves (born 1944), cricketer * Tony Jacklin (born 1944), golfer * Roger Scruton (1944–2020), philosopher * Graham Taylor (1944-2017), footballer, club and England national team manager. * Chris Wright (music industry executive), Chris Wright (born 1944), music industry executive and businessman * Patricia Hodge (born 1946), actress * Iain Matthews (born 1946), singer-songwriter and musician * Philip Priestley (born 1946), former British diplomat * Richard Budge (1947–2016), coal mining entrepreneur * Ray Clemence (1948-2020), football goalkeeper * Jim Broadbent (born 1949), actor * Geoff Capes (born 1949), shotputter * Rod Temperton (1949–2016), songwriter, record producer and musician * Bernie Taupin (born 1950), songwriterBorn 1951 onwards
* Brian Bolland (born 1951), comics artist * John Ward (footballer, born 1951), John Ward (born 1951), footballer * David Ward (British politician), David Ward (born 1953), former Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) * Michael Foale (born 1957), astronaut * Jennifer Saunders (born 1958), actress and comedian * Chris Woods (born 1959), football goalkeeper * Lee Chapman (born 1959), footballer * Glenn Cockerill (born 1959), footballer * Simon Garner (born 1959), footballer * Alan Moulder (born 1959), record producer, mixing engineer and audio engineer * John Cridland (born 1961), former Director-General of the Confederation of British Industry (CBI); Chair of Transport for the North (TfN) * Bill Dunham (born 1961), former Deputy Commandant General of the Royal Marines * Colin McFarlane (born 1961), actor * Stephen Sackur (born 1964), broadcaster and journalist * Jonathan Van-Tam (born 1964), specialist in influenza, and former Deputy Chief Medical Officer for England * Helen Fospero (born 1966), newsreader and journalist * Antonio Berardi (born 1968), fashion designer * Beverley Allitt (born 1968), serial killer * Samantha Cameron (born 1971), businesswoman and wife of the former Prime Minister David Cameron * Rae Earl (born 1971), author * Jane Taylor (musician), Jane Taylor (born 1972), singer and musician * Robert Webb (actor), Robert Webb (born 1972), actor, comedian and writer * Jonathan Kerrigan (born 1972), actor * Paul Palmer (swimmer), Paul Palmer (born 1974), swimmer * Abi Titmuss (born 1976), poker player and glamour model * Steve Housham (born 1976), footballer and manager * Danny Butterfield (born 1979), footballer * Colin Furze (born 1979), inventor and YouTube personality * Kelly Adams (born 1979), actress * Sheridan Smith (born 1981), actress * Paul Mayo (born 1981), footballer * Guy Martin (born 1981), motorcycle racer and television presenter * Kevin Clifton (born 1982), professional dancer and actor * Joanne Clifton (born 1983), professional dancer and actress * Carl Hudson (born 1983), musician * Ross Edgley (born 1985), extreme adventurer, ultra-marathon sea swimmer and author * Nicola Roberts (born 1985), singer * Oliver Ryan (born 1985), footballer * Luke Wright (born 1985), cricketer * Lee Frecklington (born 1985), footballer * Kate Haywood (born 1987), swimmer * Sam Clucas (born 1990), footballer * Georgie Twigg (born 1990), hockey player * Sophie Wells (born 1990), para-equestrian * Scott Williams (darts player), Scott Williams (born 1990), darts player * Thomas Turgoose (born 1992), actor * Eliza Butterworth (born 1993), actress * Patrick Bamford (born 1993), footballer * Jack Harvey (racing driver), Jack Harvey (born 1993), racing driver * Hollie Arnold (born 1994), javelin thrower * Ella Henderson (born 1996), singer and songwriter * Holly Humberstone (born 1999), singer and songwriter * Ellis Chapman (born 2001), footballerLocal dialect
In common with most other English English#Northern England, Northern and English English#Midlands, Midlands dialects in England, "flat" ''a'' is preferred, i.e. over , and also traditionally in words like 'water', pronounced ''watter'' (though such a pronunciation is rarely heard nowadays). Similarly, is usually replaced by . Features rather more confined to Lincolnshire include: * Elaboration of Received Pronunciation English or into a complex triphthong approximating, and often Transcription (linguistics), transcribed ''-air-'' or ''-yair-''. For example: 'mate' ; 'beast' ; ''tates'' (potatoes) . * An equivalent elaboration of standard English – commonly in Northern England – into ''-ooa-''. For example, 'boat' . * Insertion of an extra schwa into the standard English diphthong . * Vocabulary: 'duck' as a term of endearment or informal address, 'mardy' meaning upset or angry, ''mowt'' (pronounced like 'mout') for 'might', ''while'' as a substitute for standard English 'until', ''frit'' meaning frightened, ''grufty'' meaning dirty or disgusting, and the inimitable salutation (greeting), salutation ''now then!?'' (hello), sometimes written ''nairn'' to reflect pronunciation. * In the north-east of the county, around Grimsby and Immingham, the Phonological history of English vowels, nurse-square merger can be heard, as is also the case along the east coast of Yorkshire and also in Liverpool. Words that take in RP take in these areas. Lincolnshire has its own dialect "champion", a farmer from the village of Minting called Farmer Wink (real name Robert Carlton), who has produced videos about rural life, narrated in his broad Lincolnshire accent. A resident of Woodhall Spa has published a dictionary of words once prevalent in parts of the county.Music
Lincolnshire was historically associated with the Lincolnshire bagpipes, instruments derided as coarse and unpleasant in contemporary literature, but noted as very popular in the county. The last player, John Hunsley of Middle Manton, died in 1851, and since then the instrument has been extinct. In 1937, Percy Grainger wrote his ''Lincolnshire Posy'' for wind band. The piece is a compilation of folk songs "musical wildflowers" collected by the composer in and around the county of Lincolnshire.Food
 Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
*Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with parsley (other ingredients are normally kept secret), and served cold.
*Haslet – a type of pork loaf, also flavoured with sage (pronounced HAYSS-let or AYSS-let in Lincolnshire but HAZ-let in many other parts of the country).
*Lincolnshire sausages – most butchers in Lincolnshire have their own secret recipe for these and a competition is held each year to judge the best sausages in the county. Traditional Lincolnshire sausages are made entirely from minced pork, stale bread crumb (rusk is used nowadays) pepper, sage and salt. The skins should be natural casings which are made from the intestines of either sheep or pig.
*Pork pies – the same pork butchers will take a pride in their unique recipe for pork pies.
*Giblets, Giblet pie.
*Lamb and mutton, Mutton stuffed with oysters.
*Plum bread – as with Christmas pudding, plum pudding, plum refers to dried fruit, namely currants, raisins and sultanas, sometimes soaked in tea.
*Grantham Gingerbread – a hard white ginger biscuit.
*Lincolnshire Poacher cheese – a cheddar-style cheese produced in Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford. Lincolnshire Poacher has won numerous awards over the years including Supreme Champion at the 1996/7 British Cheese Awards and Best British Cheese at the World Cheese awards in 2001/2.
*Batemans Brewery, Batemans ales – a beer brewed in Wainfleet, Lincolnshire, Wainfleet and served in many pubs in the county and further afield.
*There are several small breweries.
*Grimsby is renowned for its fishing industry, and historically ''Grimsby Fish'' has carried a premium price. Since the decline of the fishing industry following entry to the European Economic Community in the 1970s this is no longer the case, with the majority of fish sold at the town's fish market being brought overland from other ports. However, ''Grimsby Fish'' is still a recognised ''product'', one associated with a particular area that specialises in and has expertise in a particular trade (cf ''Sheffield steel''). In 2009 Traditional Grimsby smoked fish, smoked fish from the town was granted Protected Geographical Indication by the European Union, reflecting the unique smoking methods used by certain local fish companies.
Craft Chocolatiers can be found throughout the county, such as Hansens in Folkingham. In 2013 Redstar Chocolate's ''Duffy's Venezuela Ocumare Milk'' won a gold medal as best bean-to-bar. The factory is in Cleethorpes.
Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
*Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with parsley (other ingredients are normally kept secret), and served cold.
*Haslet – a type of pork loaf, also flavoured with sage (pronounced HAYSS-let or AYSS-let in Lincolnshire but HAZ-let in many other parts of the country).
*Lincolnshire sausages – most butchers in Lincolnshire have their own secret recipe for these and a competition is held each year to judge the best sausages in the county. Traditional Lincolnshire sausages are made entirely from minced pork, stale bread crumb (rusk is used nowadays) pepper, sage and salt. The skins should be natural casings which are made from the intestines of either sheep or pig.
*Pork pies – the same pork butchers will take a pride in their unique recipe for pork pies.
*Giblets, Giblet pie.
*Lamb and mutton, Mutton stuffed with oysters.
*Plum bread – as with Christmas pudding, plum pudding, plum refers to dried fruit, namely currants, raisins and sultanas, sometimes soaked in tea.
*Grantham Gingerbread – a hard white ginger biscuit.
*Lincolnshire Poacher cheese – a cheddar-style cheese produced in Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford. Lincolnshire Poacher has won numerous awards over the years including Supreme Champion at the 1996/7 British Cheese Awards and Best British Cheese at the World Cheese awards in 2001/2.
*Batemans Brewery, Batemans ales – a beer brewed in Wainfleet, Lincolnshire, Wainfleet and served in many pubs in the county and further afield.
*There are several small breweries.
*Grimsby is renowned for its fishing industry, and historically ''Grimsby Fish'' has carried a premium price. Since the decline of the fishing industry following entry to the European Economic Community in the 1970s this is no longer the case, with the majority of fish sold at the town's fish market being brought overland from other ports. However, ''Grimsby Fish'' is still a recognised ''product'', one associated with a particular area that specialises in and has expertise in a particular trade (cf ''Sheffield steel''). In 2009 Traditional Grimsby smoked fish, smoked fish from the town was granted Protected Geographical Indication by the European Union, reflecting the unique smoking methods used by certain local fish companies.
Craft Chocolatiers can be found throughout the county, such as Hansens in Folkingham. In 2013 Redstar Chocolate's ''Duffy's Venezuela Ocumare Milk'' won a gold medal as best bean-to-bar. The factory is in Cleethorpes.
Events
Every year the Lincolnshire Agricultural Society, founded in 1869, stages the Lincolnshire Agricultural Show. It is held on the Wednesday and Thursday of the last whole week of June at its showground at Grange de Lings, a few miles north of Lincoln on the A15 road (Great Britain), A15. The show was first held here in 1958. First held around the year 1884, it is one of the largest agricultural shows in the country, and is attended by around 100,000 people over its two days. The showground is in regular use throughout the year for a wide range of other events and functions. Smaller local agricultural shows, such as the Heckington Show can still be found. Corby Glen sheep fair has been held since 1238. Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne, Lincolnshire, Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The Haxey Hood village competition takes place every January, as it has for over 700 years.
Stamford's Mid-Lent fair sees showmen converge on the town the week after Mothering Sunday, with rides and sideshows filling Broad Street, the Sheepmarket and the Meadows for a week. Stalls selling Grantham gingerbread and nougat are a traditional feature. The following week sees them in Grantham, on the way north for the Summer
Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne, Lincolnshire, Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The Haxey Hood village competition takes place every January, as it has for over 700 years.
Stamford's Mid-Lent fair sees showmen converge on the town the week after Mothering Sunday, with rides and sideshows filling Broad Street, the Sheepmarket and the Meadows for a week. Stalls selling Grantham gingerbread and nougat are a traditional feature. The following week sees them in Grantham, on the way north for the SummerRoger Tuby
brings a small funfair to Bourne and then to Spalding in Spring and returns in Autumn at the end of the season. The villages of Tetford and Salmonby hold an annual Scarecrow Festival in May every year. The Belchford Downhill Challenge which is held every two years: soapbox racers race down the hill at up to 30 km/h. The turnout has been up to 1,000. Lincoln Christmas Market, a street market held throughout the historic area of the city at the start of December, is one of the largest Christmas markets in Europe, attracting over 250,000 people over the four-day event. Around the same time, Christmas lights are turned on in Bourne, Sleaford, Skegness, and other towns. Throughout the summer the Stamford Shakespeare Company presents the Bard's plays in the open-air theatre at Tolethorpe Hall, which is actually in Rutland. The Spalding, Lincolnshire, Spalding Flower Parade was held in late spring every year between 1959 and 2013. Colourful floats decorated with tulip heads competed for a cup.
Sport
 The main sports played in the county are Association football, football, cricket and rugby union. Lincolnshire does not have a high sporting profile, mainly due to the lack of facilities and high-profile football teams. Probably the most well-known sporting venues in Lincolnshire are Cadwell Park near Louth, where a round of the British Motorbike Championship is held on the last Monday of August every year and the racecourse at Market Rasen
*Three teams from Lincolnshire play in the Football League: Lincoln City F.C., Lincoln City play in Football League One, Grimsby Town FC, Grimsby Town play in Football League Two. In non-league football Scunthorpe United F.C., Scunthorpe United play in the National League (division), National League, while Boston United F.C., Boston United and Gainsborough Trinity F.C., Gainsborough Trinity play in the Football Conference North. A meeting between any of these clubs is a Lincolnshire derby; the most prominent meeting, having happened across English football league system, four of the top five tiers of English football, is Lincoln City vs Grimsby Town.
*In cricket Lincolnshire County Cricket Club, Lincolnshire are a minor county and play in the Minor Counties Championship.
*In field hockey, hockey Lindum Hockey Club play in the north of Lincoln.
*Scunthorpe Rugby Club are the most notable rugby union team from Lincolnshire, and will play in the fifth level of the English league system in the 2017–18 season. Other notable teams include Market Rasen and Louth RUFC, Lincoln RFC, and Boston Rugby Club.
*Lincolnshire is home to one racecourse, at Market Rasen Racecourse, Market Rasen.
*Cadwell Park is the only motor-racing course in Lincolnshire. There is a speedway track in Scunthorpe, home of the Scunthorpe Scorpions, and stock-car racing at a stadium at Orby, near Skegness.
*Lincolnshire has an American Football club, the Lincolnshire Bombers, which has existed in its current guise since 2005.
*Lincolnshire is home to the UK roller derby team, the Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Girls, which is sponsored by Motörhead.
The main sports played in the county are Association football, football, cricket and rugby union. Lincolnshire does not have a high sporting profile, mainly due to the lack of facilities and high-profile football teams. Probably the most well-known sporting venues in Lincolnshire are Cadwell Park near Louth, where a round of the British Motorbike Championship is held on the last Monday of August every year and the racecourse at Market Rasen
*Three teams from Lincolnshire play in the Football League: Lincoln City F.C., Lincoln City play in Football League One, Grimsby Town FC, Grimsby Town play in Football League Two. In non-league football Scunthorpe United F.C., Scunthorpe United play in the National League (division), National League, while Boston United F.C., Boston United and Gainsborough Trinity F.C., Gainsborough Trinity play in the Football Conference North. A meeting between any of these clubs is a Lincolnshire derby; the most prominent meeting, having happened across English football league system, four of the top five tiers of English football, is Lincoln City vs Grimsby Town.
*In cricket Lincolnshire County Cricket Club, Lincolnshire are a minor county and play in the Minor Counties Championship.
*In field hockey, hockey Lindum Hockey Club play in the north of Lincoln.
*Scunthorpe Rugby Club are the most notable rugby union team from Lincolnshire, and will play in the fifth level of the English league system in the 2017–18 season. Other notable teams include Market Rasen and Louth RUFC, Lincoln RFC, and Boston Rugby Club.
*Lincolnshire is home to one racecourse, at Market Rasen Racecourse, Market Rasen.
*Cadwell Park is the only motor-racing course in Lincolnshire. There is a speedway track in Scunthorpe, home of the Scunthorpe Scorpions, and stock-car racing at a stadium at Orby, near Skegness.
*Lincolnshire has an American Football club, the Lincolnshire Bombers, which has existed in its current guise since 2005.
*Lincolnshire is home to the UK roller derby team, the Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Girls, which is sponsored by Motörhead.
Symbols
 The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "Lincolnshire Poacher (folk song), The Lincolnshire Poacher", which dates from around 1776. A version of the song was the theme for BBC Radio Lincolnshire for many years.
According to a 2002 marketing campaign by the charity Plantlife, the County flowers of the United Kingdom, county flower of Lincolnshire is the common dog-violet.
In August 2005, BBC Radio Lincolnshire and ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine launched a vote for a flag of Lincolnshire to represent the county. Six competing designs were voted upon by locals and the winning submission was unveiled in October 2005. Lincoln has its own flag – St George's flag with a Fleur-de-Lys.
The Lincoln Imp has symbolised cathedral, city and county for many years. In 2006 it was replaced as the brand of Lincolnshire County Council by the stylised version seen on the header her
The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "Lincolnshire Poacher (folk song), The Lincolnshire Poacher", which dates from around 1776. A version of the song was the theme for BBC Radio Lincolnshire for many years.
According to a 2002 marketing campaign by the charity Plantlife, the County flowers of the United Kingdom, county flower of Lincolnshire is the common dog-violet.
In August 2005, BBC Radio Lincolnshire and ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine launched a vote for a flag of Lincolnshire to represent the county. Six competing designs were voted upon by locals and the winning submission was unveiled in October 2005. Lincoln has its own flag – St George's flag with a Fleur-de-Lys.
The Lincoln Imp has symbolised cathedral, city and county for many years. In 2006 it was replaced as the brand of Lincolnshire County Council by the stylised version seen on the header herwhich has lost even the unique pose of the carving.
Media
Press
The county is home to one daily newspaper, the ''Grimsby Telegraph'' which as the name suggests, is published in the town and whose circulation area ostensibly covers North East Lincolnshire, although it reaches as far south as Louth and Alford and as west as Brigg. There are two further weekly papers which used to be published daily until 2011; the ''Lincolnshire Echo'' is published weekly from Lincoln and covers the majority of the county reaching as far north as Louth, and the ''Scunthorpe Telegraph'' which covers northern Lincolnshire. All three are ultimately owned by the Daily Mail and General Trust. There are also a number of weekly papers serving individual towns published in the county by Johnston Press. One of these, the ''Stamford Mercury'' claims to be Britain's oldest newspaper, although it is now a typical local weekly and no longer covers stories from the whole East Midlands as the archived copies did.Television
With the exception of a small area to the south-west of the county, Lincolnshire is served from the Belmont transmitting station, Belmont transmitter, receiving programmes from ITV Yorkshire and BBC One BBC Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, Yorkshire and Lincolnshire regions. The BBC has, since 2003, provided the area with its twelfth regional service: BBC Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, carrying a local "BBC Look North (East Yorkshire and Lincolnshire), Look North" news programme from the main studio in Kingston upon Hull, Hull, with input from other studios in Lincoln and Grimsby. ITV Yorkshire provides coverage through its evening news programme "Calendar (News), Calendar". Until late 2008 the station provided a separate edition for the Belmont transmitter (although it was still broadcast from Leeds). From January 2009 the area is now covered by a programme that covers the entire ITV Yorkshire region. From 1959 to July 1974 ITV (TV network), ITV programmes were provided by Anglia Television (although some coverage could be received from the Manchester-based Granada Television, Granada and ABC Weekend). Based in Norwich the company had news offices in Grimsby. Following a transmitter change ITV services were provided by Yorkshire Television. This company kept open the offices in Grimsby and opened further facilities in Lincoln, although both of these closed in the mid-1990s. South-west Lincolnshire receives BBC East Midlands and ITV Central which are broadcast from the Waltham transmitting station, Waltham-on-the-Wolds Transmitting Station. Although subject to co-channel interference from the Waltham transmitter, a small number of households in the southern tip of the county are able to receive regional programming from BBC East and ITV Anglia. Many villages just west of the Lincoln Cliff, Lincoln Edge cannot get a signal from Belmont due to Fading, shadowing and instead get their TV from Emley Moor transmitting station, Emley Moor near Huddersfield.Radio
The area is covered by several local radio stations including: *BBC Radio Lincolnshire Can be heard throughout historic Lincolnshire although its broadcast remit is the present county of Lincolnshire *BBC Radio Humberside The counties of northern Lincolnshire that were formerly known as South Humberside *Greatest Hits Radio Lincolnshire Grimsby, Cleethorpes and Immingham *Heart East Peterborough and South Lincolnshire *Lincs FM Historic Lincolnshire *Siren FM Lincoln *Tulip Radio Spalding and South Holland *Viking FM Northern Lincolnshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire, East Yorkshire, formerly the constituent areas of HumbersideMilitary
Air
Because of its flat geography and low population density, Lincolnshire is an ideal place for airfields, and the Air Ministry built prolifically with the county hosting nearly seventy separate air bases. It became known as "bomber county". Since the end of the Second World War most of these airfields or stations were decommissioned, but the RAF retains a significant footprint in Lincolnshire for the air defence of the United Kingdom and aircrew training. For more information on former bases, see List of former RAF stations. Two major front-line bases located in Lincolnshire are RAF Coningsby, which is one of only two RAF Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) Stations in the United Kingdom and home to the Eurofighter Typhoon jet fighters, and RAF Waddington, where most of the RAF's Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance aircraft are based. Other stations in Lincolnshire include RAF Cranwell, home to all Air Force Basic Officer Training for the Royal Air Force; RAF Scampton, home base to the Red Arrows Aerobatic Team and former base of the Avro Vulcan nuclear strike V bomber-force; RAF Barkston Heath, a training airfield; and minor bases such as RAF Kirton in Lindsey, RAF Donna Nook and RAF Digby. Lincolnshire is also home to two active RAF and NATO-allied air weapons training bombing ranges, located along The Wash and north Lincolnshire coastline—RAF Holbeach active since 1926 (originally part of the former RAF Sutton Bridge station) and RAF Donna Nook, Donna Nook. The RAF Wainfleet range was decommissioned in 2010.Army
The Army runs Sobraon Barracks, home of 160 (Lincoln) Squadron, Royal Logistic Corps (RLC), as well as Prince William of Gloucester Barracks, Grantham, home to the national specialist logistics units. In November 2016 the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence announced that the Grantham site would close in 2020.Places of interest
See also
*''Outline of England'' *Custos Rotulorum of Lincolnshire – List of Keepers of the Rolls for Lincolnshire *Earl of Lincoln is a title that has been created eight times in the Peerage of England and is currently represented. *High Sheriff of Lincolnshire *Lincolnshire (UK Parliament constituency) List of MPs for the Lincolnshire constituency *Lincs Wind Farm *Lists **List of bridges and viaducts in Lincolnshire **List of churches in Lincolnshire **List of civil parishes in Lincolnshire **List of companies in Lincolnshire – Both current and former **List of forests and woodland in Lincolnshire **List of monastic houses in Lincolnshire **List of museums in Lincolnshire **List of parliamentary constituencies in Lincolnshire **List of places in Lincolnshire **List of public art in Lincolnshire **List of Roman Sites in Lincolnshire, List of Roman sites in Lincolnshire **List of schools in Lincolnshire **List of watermills in Lincolnshire **List of Waterways in Lincolnshire, List of waterways in Lincolnshire **List of windmills in Lincolnshire *Lord Lieutenant of Lincolnshire *Stamford Senior Youth Theatre *1185 East Midlands earthquakeReferences
Bibliography
*External links
Lincolnshire County Council website
Lindcolne Skipfierde
Lincolnshire'
Anglo-Saxon, Viking and Norman
re-enactment and living history group
Lincolnshire Show official website
Images of Lincolnshire
at the English Heritage Archive {{Authority control Lincolnshire, Non-metropolitan counties East Midlands NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Counties of England established in antiquity