Limnoria lignorum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Limnoria lignorum'', commonly known as the gribble, is a
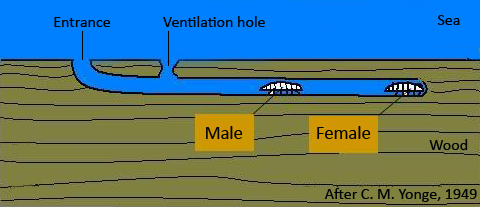 ''Limnoria lignorum'' is a wood borer and in favourable conditions can be present in large numbers, with densities of as many as four hundred individuals per of wood. The isopods are very small and the damage is at first confined to near the surface of the wood. The tunnels are about in diameter and usually follow the line of less-lignified material. As the upper layer of wood crumbles away under this onslaught, deeper parts of the timber are attacked and in time, pilings and other wooden structures are eaten away.
''Limnoria lignorum'' ingest wood fragments as they burrow. They do not seem to house bacteria in their gut that are able to digest
''Limnoria lignorum'' is a wood borer and in favourable conditions can be present in large numbers, with densities of as many as four hundred individuals per of wood. The isopods are very small and the damage is at first confined to near the surface of the wood. The tunnels are about in diameter and usually follow the line of less-lignified material. As the upper layer of wood crumbles away under this onslaught, deeper parts of the timber are attacked and in time, pilings and other wooden structures are eaten away.
''Limnoria lignorum'' ingest wood fragments as they burrow. They do not seem to house bacteria in their gut that are able to digest
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of isopod
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, an ...
in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Limnoriidae
A gribble /ˈgɹɪbəl/ (or gribble worm) is any of about 56 species of marine isopod from the family Limnoriidae. They are mostly pale white and small ( long) crustaceans, although ''Limnoria stephenseni'' from subantarctic waters can reach .
...
. It is found in shallow water in the North Atlantic and North Pacific Ocean where it tunnels into wood and attacks and destroys submerged wooden structures.
Description
''Limnoria lignorum'' grows to a maximum length of but a more usual size range is . It is a yellowish colour and is about three times as long as it is broad. It has awoodlouse
A woodlouse (plural woodlice) is an isopod crustacean from the polyphyleticThe current consensus is that Oniscidea is actually triphyletic suborder Oniscidea within the order Isopoda. They get their name from often being found in old wood. ...
-like body with fourteen segments. It bores its way into wood to a depth of about .
Distribution
''Limnoria lignorum'' is found in the boreal and temperate seas of the northern Atlantic Ocean and North Sea and it is also known from the west coast of North America. Its range extends from Norway southwards to France, and from the Gulf of St Lawrence southwards toCobscook Bay
Cobscook Bay is located in Washington County in the state of Maine. It opens into Passamaquoddy Bay, within the Bay of Fundy. Cobscook Bay is immediately south of the island city of Eastport, the main island of which (Moose Island) straddles the ...
and Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of mainland Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer mont ...
. Its depth range is from the littoral zone
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas ...
to a depth of about It is unclear from exactly where it originated because it has spread widely, aided in its dispersal by tunnelling into the hulls of wooden ships and inside floating driftwood
__NOTOC__
Driftwood is wood that has been washed onto a shore or beach of a sea, lake, or river by the action of winds, tides or waves.
In some waterfront areas, driftwood is a major nuisance. However, the driftwood provides shelter and fo ...
. It was first described by the German zoologist Martin Rathke
Martin Heinrich Rathke (25 August 1793, Danzig – 3 September 1860, Königsberg) was a German embryologist and anatomist. Along with Karl Ernst von Baer and Christian Heinrich Pander, he is recognized as one of the founders of modern embryol ...
in 1799 from a location
In geography, location or place are used to denote a region (point, line, or area) on Earth's surface or elsewhere. The term ''location'' generally implies a higher degree of certainty than ''place'', the latter often indicating an entity with an ...
is Norway.
Biology
 ''Limnoria lignorum'' is a wood borer and in favourable conditions can be present in large numbers, with densities of as many as four hundred individuals per of wood. The isopods are very small and the damage is at first confined to near the surface of the wood. The tunnels are about in diameter and usually follow the line of less-lignified material. As the upper layer of wood crumbles away under this onslaught, deeper parts of the timber are attacked and in time, pilings and other wooden structures are eaten away.
''Limnoria lignorum'' ingest wood fragments as they burrow. They do not seem to house bacteria in their gut that are able to digest
''Limnoria lignorum'' is a wood borer and in favourable conditions can be present in large numbers, with densities of as many as four hundred individuals per of wood. The isopods are very small and the damage is at first confined to near the surface of the wood. The tunnels are about in diameter and usually follow the line of less-lignified material. As the upper layer of wood crumbles away under this onslaught, deeper parts of the timber are attacked and in time, pilings and other wooden structures are eaten away.
''Limnoria lignorum'' ingest wood fragments as they burrow. They do not seem to house bacteria in their gut that are able to digest lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity ...
, as is the case in some other wood-boring species, and seem to rely on their cellulolytic enzymes to digest cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
. They may also feed on fungal hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
directly or may consume them indirectly in wood that is already softened as a result of attack by fungi and bacteria. The enzymes it produces to break up wood into sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
s which it can digest are being investigated for producing biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (E ...
.
The eggs of ''Limnoria lignorum'' are retained by the female in the brood pouch under her thorax. The eggs hatch directly into manca
The manca (plural: ''mancae'') is the post- larval juvenile in some crustaceans. The manca stage is the defining characteristic of a clade called Mancoida which comprises all the member of the Peracarida except the Amphipoda. Mancae closely rese ...
e, juveniles that are miniature versions of the adult, which means there is no free-living larval stage to aid dispersal of this species. It has been shown that the water temperature influences reproductive processes. Little tunnelling or reproduction takes place during the winter but activity starts earlier in the year and continues later, and the young develop more rapidly under the warmer conditions that exist near the exit of a water cooling system.
Effect on piers
It has been known to damagewood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
en piles in pier
image:Brighton Pier, Brighton, East Sussex, England-2Oct2011 (1).jpg, Seaside pleasure pier in Brighton, England. The first seaside piers were built in England in the early 19th century.
A pier is a raised structure that rises above a body of ...
s, something first observed in 1810 by Robert Stevenson Robert Stevenson may refer to:
* Robert Stevenson (actor and politician) (1915–1975), American actor and politician
* Robert Stevenson (civil engineer) (1772–1850), Scottish lighthouse engineer
* Robert Stevenson (director) (1905–1986), Engl ...
in the timbers he used in constructing the Bell Rock Lighthouse
The Bell Rock Lighthouse, off the coast of Angus, Scotland, is the world's oldest surviving sea-washed lighthouse. It was built between 1807 and 1810 by Robert Stevenson on the Bell Rock (also known as Inchcape) in the North Sea, east of the ...
. In 1830 the Trinity Chain Pier
Trinity Chain Pier, originally called Trinity Pier of Suspension, was built in Trinity, Edinburgh, Scotland in 1821. The pier was designed by Samuel Brown, a pioneer of chains and suspension bridges. It was intended to serve ferry traffic on ...
had to be almost completely rebuilt after attack from the organism. The use of creosote
Creosote is a category of carbonaceous chemicals formed by the distillation of various tars and pyrolysis of plant-derived material, such as wood or fossil fuel. They are typically used as preservatives or antiseptics.
Some creosote types were ...
does not protect wood against it.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q3858142 Isopoda Crustaceans described in 1799