Ligurian (ancient Language) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ligurian language was spoken in pre-Roman times and into the Roman era by an ancient people of north-western

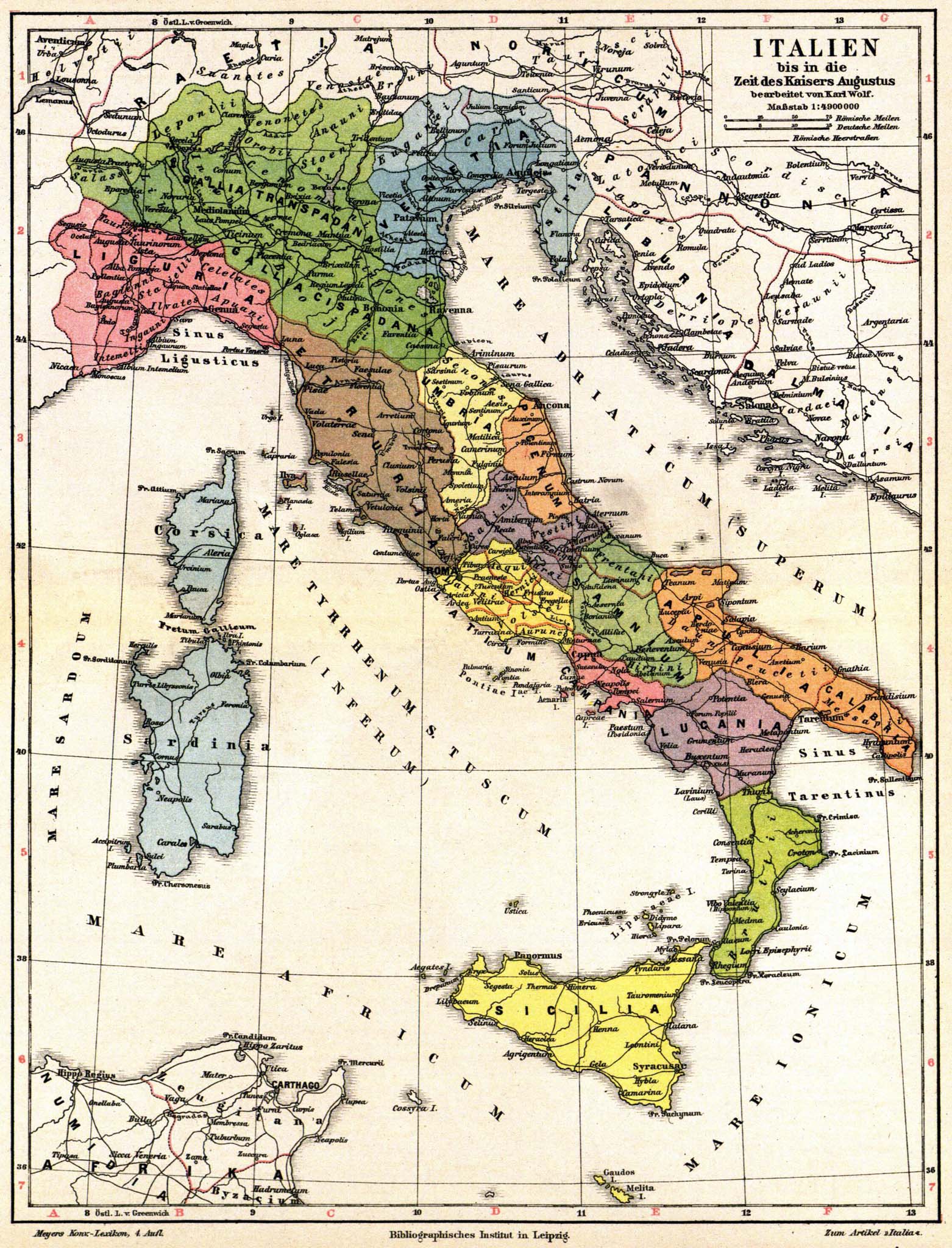

Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
and current south-eastern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
known as the Ligures
The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named.
Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian regio ...
.
Very little is known about ancient Ligurian; the lack of inscriptions and the unknown origin of the Ligurian people prevent its certain linguistic classification as a Pre-Indo-European or an Indo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
. The linguistic hypotheses are mainly based on toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
and onomastics
Onomastics (or, in older texts, onomatology) is the study of the etymology, history, and use of proper names. An ''orthonym'' is the proper name of the object in question, the object of onomastic study.
Onomastics can be helpful in data mining, w ...
.
Ancient sources


Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
indicates that the Ligurians were different from the Celts:
Because of the strong Celtic influences on the language and culture, the Ligurians were known in antiquity as ''Celto-Ligurians'' (in Greek ''Keltolígues'') in some other sources.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
wrote that '' sigunnai'' meant 'hucksters, peddlers' among the Ligurians who lived above Massilia
Massalia (Greek: Μασσαλία; Latin: Massilia; modern Marseille) was an ancient Greek colony founded ca. 600 BC on the Mediterranean coast of present-day France, east of the river Rhône, by Ionian Greek settlers from Phocaea, in Western An ...
.
Ligurian as a Pre-Indo-European language
Scholars, such as Ernst Gamillscheg, Pia Laviosa Zambotti andYakov Malkiel
Yakov Malkiel (July 22, 1914 – April 24, 1998) was a U.S. (Russian-born) Romance etymologist and philologist. His specialty was the development of Latin words, roots, prefixes, and suffixes in modern Romance languages, particularly Spanish. ...
, posit that ancient Ligurian was a pre-Indo-European language, with significant late Indo-European influence, especially Celtic (Gallic) and Italic (Latin), superimposed on the original language.
Their thesis is that the Ligurians were survivors of the ancient pre-Indo-European populations that had occupied Europe, at least from the fifth millennium BC. These populations would have had languages of their own families, which they would have preserved until the onset of waves of Indo-European migration
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
. Later, the latter would conquer the territories, imposing their culture and language on the Ligurians.
Ligurian as an Indo-European language and its relationship with Celtic
Xavier Delamarre
Xavier Delamarre (; born 5 June 1954) is a French linguist, lexicographer, and diplomat. He is regarded as one of the world's foremost authorities on the Gaulish language.
Since 2019, he has been an associate researcher for the CNRS- PSL AOrOc l ...
argues that Ligurian was a Celtic language
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
, similar to, but not the same as, Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium ...
. His argument hinges on two points: firstly, the Ligurian place-name ''Genua'' (modern Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
, located near a river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
mouth) is claimed by Delamarre to derive from PIE
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), swe ...
*''ǵenu-'', "chin(bone)". Many Indo-European languages use 'mouth' to mean the part of a river which meets the sea or a lake, but it is only in Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
for which reflexes of PIE *''ǵenu-'' mean 'mouth'. Besides Genua, which is considered Ligurian, this is found also in ''Genava'' (modern Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
), which may be Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium ...
. However, ''Genua'' and ''Genava'' may well derive from another PIE root with the form *''ǵonu-'', which means "knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
" (so in Pokorny, IEW).
Delamarre's second point is Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
's mention that during the Battle of Aquae Sextiae
The Battle of Aquae Sextiae (Aix-en-Provence) took place in 102 BC. After a string of Roman defeats (see: the Battle of Noreia, the Battle of Burdigala, and the Battle of Arausio), the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and A ...
in 102 BC, the Ambrones
The Ambrones ( grc, Ἄμβρωνες) were an ancient tribe mentioned by Roman authors. They are generally believed to have been a Germanic tribe from Jutland.
In the late 2nd century BC, along with the fellow Cimbri and Teutons, the Ambrones m ...
(who were a Germanic tribe
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginn ...
from Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
) began to shout ''"Ambrones!"'' as their battle cry
A battle cry or war cry is a yell or chant taken up in battle, usually by members of the same combatant group.
Battle cries are not necessarily articulate (e.g. "Eulaliaaaa!", "Alala"..), although they often aim to invoke patriotic or religious ...
; the Ligurian troops fighting for the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, on hearing this cry, found that it was identical to an ancient name in their country which the Ligurians often used when speaking of their descent (''outôs kata genos onomazousi Ligues''), so they returned the shout, ''"Ambrones!"''.
A risk of circular logic has been pointed out – if it is believed that the Ligurians are non-Celtic, and if many place names and tribal names that classical authors state are Ligurian seem to be Celtic, it is incorrect to discard all the Celtic ones when collecting Ligurian words and to use this edited corpus to demonstrate that Ligurian is non-Celtic or non-Indo-European.
The Ligurian-Celtic question is also discussed by Guy Barruol
Guy Barruol (born 10 June 1934) is a French historian and archaeologist. He is director of research emeritus at the CNRS.
Biography
Guy Barruol was born on 10 June 1934 in Mazan, Vaucluse, the son of Jean Barruol (1898–1982), a local histori ...
in his 1969 paper ''The Pre-Roman Peoples of South-East Gaul: Study of Historical Geography''.
Ligurian as substrate
French historian and philologistMarie Henri d'Arbois de Jubainville
Marie Henri d'Arbois de Jubainville (; 5 December 1827 – 26 February 1910) was a French historian, philologist and Celtic scholar.
Career
He qualified as a lawyer in 1850, and entered a seminary with the intention of becoming a Catholic priest, ...
held that Ligurian was the first Indo-European language spoken in Western Europe and was related to Sicel
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, bu ...
. In his work ''Premiers Habitants de l'Europe'' (2nd edition 1889–1894), Jubainville proposed an early Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
substrate language for Corsica, Sardinia, eastern Spain, southern France and western Italy, based on the occurrence there of place names ending in ''-asco'', ''-asca'', ''-usco'', ''-osco'', ''-osca'' as well as ''-inco'', ''-inca''. For examples of the Corsican toponymy cited by Jubainville, see Prehistory of Corsica
The prehistory of Corsica is analogous to the prehistories of the other islands in the Mediterranean Sea, such as Sicily, Sardinia, Malta and Cyprus, which could only be accessed by boat and featured cultures that were to some degree insular; t ...
.
Other linguists expanded on the idea. Julius Pokorny
Julius Pokorny (12 June 1887 – 8 April 1970) was an Austrian-Czech linguist and scholar of the Celtic languages, particularly Irish, and a supporter of Irish nationalism. He held academic posts in Austrian and German universities.
Early life a ...
adapted it as the basis for his Illyro-Venetic theory. Paul Kretschmer Paul Kretschmer (2 May 1866 – 9 March 1956) was a German linguist who studied the earliest history and interrelations of the Indo-European languages and showed how they were influenced by non-Indo-European languages, such as Etruscan.
Biography ...
saw evidence for Ligurian in Lepontic
Lepontic is an ancient Alps, Alpine Celtic languageJohn T. Koch (ed.) ''Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia'' ABC-CLIO (2005) that was spoken in parts of Rhaetia and Cisalpine Gaul (now Northern Italy) between 550 and 100 BC. Lepontic i ...
inscriptions, now seen as Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
. Hans Krahe
Hans Krahe (7 February 1898 – 25 June 1965) was a German philologist and linguist, specializing over many decades in the Illyrian languages. He was born in Gelsenkirchen.
Work
Between 1936 and 1946 he was a professor at the University of W ...
, focusing on river names, converted the concept into his theory of the Old European hydronymy
Old European (german: Alteuropäisch) is the term used by Hans Krahe (1964) for the language of the oldest reconstructed stratum of European hydronymy (river names) in Central and Western Europe.Hans Krahe, ''Unsere ältesten Flussnamen'', Wiesbad ...
.
See also
*Prehistory of Corsica
The prehistory of Corsica is analogous to the prehistories of the other islands in the Mediterranean Sea, such as Sicily, Sardinia, Malta and Cyprus, which could only be accessed by boat and featured cultures that were to some degree insular; t ...
References
Sources
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ligurian Language (Ancient) Languages of ancient Italy Extinct languages of Italy Unclassified Indo-European languages Unclassified languages of Europe Ligures Languages attested from the 3rd century BC Languages extinct in the 1st century BC Pre-Indo-European languages Gallo-Roman culture Linguistic strata Italo-Celtic