Liguria In Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
it, Ligure , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST =
· 10th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITC , website = , footnotes = Liguria (; lij, Ligûria ; french: Ligurie) is a region of north-western Italy; its
 The narrow strip of land is bordered by the
The narrow strip of land is bordered by the
 Copper begins to be mined from the middle of the
Copper begins to be mined from the middle of the

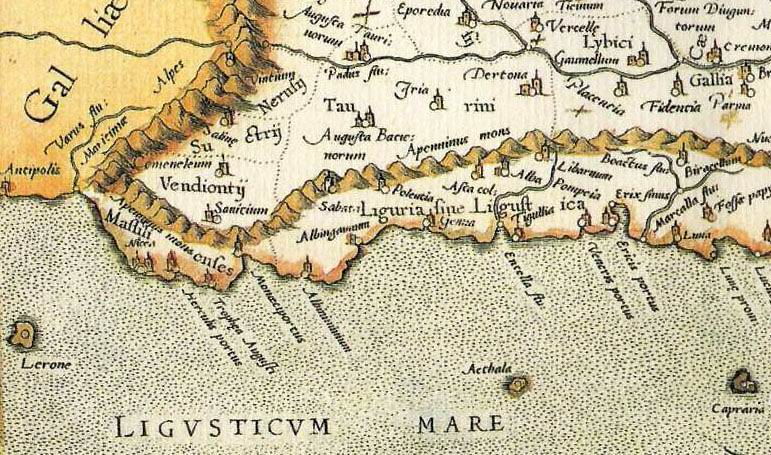

 During the first
During the first
 Between the 4th and the 10th centuries, Liguria was dominated by the Byzantines, the Lombards of King
Between the 4th and the 10th centuries, Liguria was dominated by the Byzantines, the Lombards of King  Between the 11th century (when the Genoese ships played a major role in the first crusade, carrying knights and troops to the Middle-East for a fee) and the 15th century, the Republic of Genoa experienced an extraordinary political and commercial success (mainly spice trades with the Orient). It was one of the most powerful maritime republics in the Mediterranean from the 12th to the 14th century: after the decisive victory in the Battle of Meloria (1284), it acquired control over the Tyrrhenian Sea and was present in the nerve centres of power during the last phase of the Byzantine empire, having colonies up to Black Sea and
Between the 11th century (when the Genoese ships played a major role in the first crusade, carrying knights and troops to the Middle-East for a fee) and the 15th century, the Republic of Genoa experienced an extraordinary political and commercial success (mainly spice trades with the Orient). It was one of the most powerful maritime republics in the Mediterranean from the 12th to the 14th century: after the decisive victory in the Battle of Meloria (1284), it acquired control over the Tyrrhenian Sea and was present in the nerve centres of power during the last phase of the Byzantine empire, having colonies up to Black Sea and
 The alternation of French and Milanese dominions over Liguria went on until the first half of the 16th century. The French influence ceased in 1528, when Andrea Doria allied with the powerful king of Spain and imposed an aristocratic government, which gave the republic relative stability for about 250 years.
The alternation of French and Milanese dominions over Liguria went on until the first half of the 16th century. The French influence ceased in 1528, when Andrea Doria allied with the powerful king of Spain and imposed an aristocratic government, which gave the republic relative stability for about 250 years.
 Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus's speculative proposal to reach the East Indies by sailing westward received the support of the Spanish crown, which saw in it an opportunity to gain the upper hand over rival powers in the contest for the lucrative spice trade with Asia. During his first voyage in 1492, instead of reaching Japan as he had intended, Columbus landed in the Bahamas archipelago, at a locale he named ''San Salvador''. Over the course of three more voyages, Columbus visited the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as the
Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus's speculative proposal to reach the East Indies by sailing westward received the support of the Spanish crown, which saw in it an opportunity to gain the upper hand over rival powers in the contest for the lucrative spice trade with Asia. During his first voyage in 1492, instead of reaching Japan as he had intended, Columbus landed in the Bahamas archipelago, at a locale he named ''San Salvador''. Over the course of three more voyages, Columbus visited the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as the
 The population density of Liguria is much higher than the national average (300 inhabitants per km2, or 770 per mi2), being only less than Campania's,
The population density of Liguria is much higher than the national average (300 inhabitants per km2, or 770 per mi2), being only less than Campania's,
 Ligurian agriculture has increased its specialisation pattern in high-quality products (flowers, wine,
Ligurian agriculture has increased its specialisation pattern in high-quality products (flowers, wine, 
 Steel, once a major industry during the booming 1950s and 1960s, phased out after the late 1980s crisis, as Italy moved away from the heavy industry to pursue more technologically advanced and less polluting production. So the Ligurian industry has turned towards a widely diversified range of high-quality and high-tech products (food, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and electronics, petrochemicals, aerospace etc.). Nonetheless, the region still maintains a flourishing shipbuilding sector (yacht construction and maintenance, cruise liner building, military shipyards).
In the services sector, the gross value-added per worker in Liguria is 4% above the national average. This is due to the increasing diffusion of modern technologies, particularly in commerce and tourism.
Steel, once a major industry during the booming 1950s and 1960s, phased out after the late 1980s crisis, as Italy moved away from the heavy industry to pursue more technologically advanced and less polluting production. So the Ligurian industry has turned towards a widely diversified range of high-quality and high-tech products (food, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and electronics, petrochemicals, aerospace etc.). Nonetheless, the region still maintains a flourishing shipbuilding sector (yacht construction and maintenance, cruise liner building, military shipyards).
In the services sector, the gross value-added per worker in Liguria is 4% above the national average. This is due to the increasing diffusion of modern technologies, particularly in commerce and tourism.
 The politics of Liguria takes place in a framework of a
The politics of Liguria takes place in a framework of a

 Liguria is the original source of pesto, one of the most popular sauces in Italian cuisine, made with fresh basil,
Liguria is the original source of pesto, one of the most popular sauces in Italian cuisine, made with fresh basil,
Official Region website
Video Introduction to Liguria
{{coord, 44, 27, 00, N, 8, 46, 00, E, display=title Regions of Italy NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Wine regions of Italy
it, Ligure , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST =
CEST CEST or cest may refer to:
* Central European Summer Time (UTC+2), daylight saving time observed in the central European time zone
* Cognitive-Experiential Self-Theory
* Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer, a subset of Magnetization transfer in ...
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code_type = ISO 3166 code
ISO 3166 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, special areas of geographical interest, and their principal subdivisions (e.g., pr ...
, area_code = IT-42
, blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal)
, blank_info_sec1 = €49.9 billion (2018)
, blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
, blank1_info_sec1 = €32,100 (2018)
, blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019)
, blank2_info_sec1 = 0.898· 10th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITC , website = , footnotes = Liguria (; lij, Ligûria ; french: Ligurie) is a region of north-western Italy; its
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
mountain range and is roughly coextensive with the former territory of the Republic of Genoa. Liguria is bordered by France ( Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur) to the west, Piedmont to the north, and Emilia-Romagna and Tuscany to the east. It rests on the Ligurian Sea, and has a population of 1,557,533. The region is part of the Alps–Mediterranean Euroregion
The Alps–Mediterranean Euroregion (transnational co-operation structure) was created on 10 July 2007 between three Italian regions (Piedmont, Liguria and Aosta Valley) and two French regions (Rhône-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur). It ha ...
.
Etymology
The name ''Liguria'' predates Latin and is of obscure origin. The Latin adjectives (as in ) and ''Liguscus'' reveal the original root of the name, ''ligusc-'': in the Latin name -sc- was shortened to -s-, and later turned into the -r- of , according torhotacism
Rhotacism () or rhotacization is a sound change that converts one consonant (usually a voiced alveolar consonant: , , , or ) to a rhotic consonant in a certain environment. The most common may be of to . When a dialect or member of a language fa ...
. Compare grc, λίγυς, translit=Lígus, translation=a Ligurian, a person from Liguria whence . The name derives from the ancient Ligures people, although the territory of this people was much larger than the current administrative region; it included all of North-west Italy south to the Po river
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ligurian language (ancient), Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira (river), Mair ...
, and south-eastern France.
Some scholars see a possible connection with Old European languages
The Paleo-European languages, or Old European languages, are the mostly unknown languages that were spoken in Europe prior to the spread of the Indo-European and Uralic families caused by the Bronze Age invasion from the Eurasian steppe of pastor ...
, as the formant -sc- (-sk-) is also present in names like Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
**Etruscan ...
, Euskadi (the endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
of the Basques), and Gascon. Since these are all coastal regions, the shared formant may relate to a shared descent from pre-Indo-European, maritime peoples, and/or the hypothetical Tyrsenian and Vasconic
The Vasconic languages (from Latin 'Basque') are a putative family of languages that includes Basque and the extinct Aquitanian language. The extinct Iberian language is sometimes putatively included.
The concept of the Vasconic languages is ...
language families respectively. This argument is weakened, however, by the fact that the name Etruscan is a relatively late exonym and the relevant endonym, used of the Etruscans themselves, was ''Rasenna'' or ''Raśna''. (In Greek this mutated into ''Tursēnoi'' and ''Tyrrēnoi''; in Latin it became ''Etruria'' and ''Tuscia'', whence the name of the modern Tuscany or ''Toscana''.)
Geography
 The narrow strip of land is bordered by the
The narrow strip of land is bordered by the sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
, the Alps and the Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
. Some mountains rise above ; the watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
line runs at an average altitude of about . The highest point of the region is the summit of Monte Saccarello ().
Liguria is the third smallest Italian region after Aosta Valley and Molise, but is also one of the most densely populated, with a population density of 287 ab/km², much higher than the national average, and is fourth place after Campania, Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
and Lazio. However, there is much difference between inland mountain areas and coastal areas.
The region is crossed east to west by the Ligurian Alps and the Ligurian Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
that form an interrupted chain, but discontinuous in its morphology, with stretches where the Alpine/Apennine ridge is extremely compact and high aligning very high mountain groups (north to Ventimiglia, a series of massifs which became French after the Second World War, rises up to altitudes of 2700-3000 m) while in other stretches (for example in the hinterland of Savona and Genoa) the mountain barrier is not very high and deeply crossed by short valleys and passes that do not reach 500 m above sea level ( Bochetta di Altare, Passo dei Giovi, Crocetta d'Orero).
The winding arched extension goes from Ventimiglia to La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
. Of this, are mountainous (65% of the total) and are hills (35% of the total). Liguria's natural reserves cover 12% of the entire region, or of land. They are made up of one national reserve, six large parks, two smaller parks and three nature reserves.
The continental shelf is very narrow and so steep it descends almost immediately to considerable depths along its coastline. Except for the Portovenere and Portofino promontories, the coast is generally not very jagged and is often high. At the mouths of the biggest watercourses are small beaches, but there are no deep bays and natural harbours except at Genoa and La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
.
The hills lying immediately beyond the coast together with the sea account for a mild climate year-round. Average winter temperatures are and summer temperatures are , which make for a pleasant stay even in the dead of winter. Rainfall can be abundant at times, as mountains very close to the coast create an orographic
Orography is the study of the topographic relief of mountains, and can more broadly include hills, and any part of a region's elevated terrain. Orography (also known as ''oreography'', ''orology'' or ''oreology'') falls within the broader discipl ...
effect. Genoa and La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
can see up to of rain in a year; other areas instead show the normal Mediterranean rainfall of annually.
Prehistory
 Copper begins to be mined from the middle of the
Copper begins to be mined from the middle of the 4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
in Liguria with the Libiola and Monte Loreto mines dated to 3700 BC..
These are the oldest copper mines in the western Mediterranean basin.
The foundation of Genoa
The Genoa area has been inhabited since the fifth or fourth millennium BC. In ancient times this area was inhabited by Ligures (ancient people after whom Liguria is named). According to excavations carried out in the city between 1898 and 1910, the Ligure population that lived in Genoa maintained trade relations with the Etruscans and the Greeks, since several objects from these populations were found. In the 5th century BC the first town, or oppidum, was founded at the top of the hill today called Castello (Castle), which is now inside the medieval old town. The ancient Ligurian city was known as Stalia (Σταλìα), referred to in this way by Artemidorus Ephesius and Pomponius Mela; this toponym is possibly preserved in the name of Staglieno, some from the coast. Stalia had an alliance with Rome through a ''foedus aequum'' (equal pact) in the course of theSecond Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
(218-201 BC). The Carthaginians accordingly destroyed it in 209 BC. The town was rebuilt and, after the Carthaginian Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three yea ...
ended in 146 BC, it received municipal rights. The original ''castrum'' then expanded towards the current areas of Santa Maria di Castello and the San Lorenzo promontory. Trade goods included skins, timber, and honey. Goods were moved to and from Genoa's hinterland, including major cities like Tortona
Tortona (; pms, Torton-a , ; lat, Dhertona) is a ''comune'' of Piemonte, in the Province of Alessandria, Italy. Tortona is sited on the right bank of the Scrivia between the plain of Marengo and the foothills of the Ligurian Apennines.
History ...
and Piacenza. An amphitheater was also found there among other archaeological remains from the Roman period.
History
Roman times


 During the first
During the first Punic War
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three yea ...
, the ancient Ligurians were divided, some of them siding with Carthage, others, including the inhabitants of Stalia (later Genoa), with Rome. Under Augustus, Liguria was designated a region of Italy (''Regio IX Liguria'') stretching from the coast to the banks of the Po River
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ligurian language (ancient), Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira (river), Mair ...
. The great Roman roads (Aurelia and Julia Augusta on the coast, Postumia and Aemilia Scauri towards the inland) helped strengthen territorial unity and increase communication and trade. Important towns developed on the coast, of which evidence is left in the ruins of Albenga, Ventimiglia and Luni.
Middle Ages
 Between the 4th and the 10th centuries, Liguria was dominated by the Byzantines, the Lombards of King
Between the 4th and the 10th centuries, Liguria was dominated by the Byzantines, the Lombards of King Rothari
Rothari (or Rothair) ( 606 – 652), of the Harodingi, house of Arodus, was king of the Lombards from 636 to 652; previously he had been duke of Brescia. He succeeded Arioald, who was an Arianism, Arian like himself, and was one of the most energe ...
(about 641) and the Franks (about 774). It was also invaded by Saracen and Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
raiders. In the 10th century, once the danger of pirates decreased, the Ligurian territory was divided into three marches: Obertenga (east), Arduinica (west) and Aleramica (centre). In the 11th and 12th centuries, the marches were split into fees, and then with the strengthening of the bishops' power, the feudal structure began to partially weaken. The main Ligurian towns, especially on the coast, became city-states, over which Genoa soon extended its rule. Inland, however, fiefs belonging to noble families survived for a very long time.
 Between the 11th century (when the Genoese ships played a major role in the first crusade, carrying knights and troops to the Middle-East for a fee) and the 15th century, the Republic of Genoa experienced an extraordinary political and commercial success (mainly spice trades with the Orient). It was one of the most powerful maritime republics in the Mediterranean from the 12th to the 14th century: after the decisive victory in the Battle of Meloria (1284), it acquired control over the Tyrrhenian Sea and was present in the nerve centres of power during the last phase of the Byzantine empire, having colonies up to Black Sea and
Between the 11th century (when the Genoese ships played a major role in the first crusade, carrying knights and troops to the Middle-East for a fee) and the 15th century, the Republic of Genoa experienced an extraordinary political and commercial success (mainly spice trades with the Orient). It was one of the most powerful maritime republics in the Mediterranean from the 12th to the 14th century: after the decisive victory in the Battle of Meloria (1284), it acquired control over the Tyrrhenian Sea and was present in the nerve centres of power during the last phase of the Byzantine empire, having colonies up to Black Sea and Crimean
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
.
After the introduction of the title of doge for life (1339) and the election of Simone Boccanegra, Genoa resumed its struggles against the Marquis of Finale
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman w ...
and the Counts of Laigueglia
Laigueglia (; lij, L'Aigheuja, ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Savona, in Liguria (northern Italy in 1812), nearby the Capo Mele Lighthouse.
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Laigueglia is twinned with:
* Hö ...
and it conquered again the territories of Finale
Finale may refer to:
Pieces of music
* Finale (music), the last movement of a piece
* ''Finale'' (album), a 1977 album by Loggins and Messina
* "Finale B", a 1996 song from the rock opera ''Rent''
* "Finale", a song by Anthrax from ''State of Eu ...
, Oneglia
Oneglia ( lij, Inêia or ) is a former town in northern Italy on the Ligurian coast, in 1923 joined to Porto Maurizio to form the Comune of Imperia. The name is still used for the suburb.Roy Palmer Domenico, ''The regions of Italy: a reference gu ...
and Porto Maurizio
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropol ...
. In spite of its military and commercial successes, Genoa fell prey to the internal factions which put pressure on its political structure. Due to the vulnerable situation, the rule of the republic went to the hands of the Visconti family
Visconti is a surname which may refer to:
Italian noble families
* Visconti of Milan, ruled Milan from 1277 to 1447
** Visconti di Modrone, collateral branch of the Visconti of Milan
* Visconti of Pisa and Sardinia, ruled Gallura in Sardinia from ...
of Milan. After their expulsion by the popular forces under Boccanegra's lead, the republic remained in Genoese hands until 1396, when the internal instability led the doge Antoniotto Adorno Antoniotto Adorno may refer to the following:
* Antoniotto I Adorno (1340–1398), Doge of the Republic of Genoa (1378, 1384–1390, 1391–1392, 1394–1396)
* Antoniotto II Adorno
Antoniotto II Adorno (c. 1479 – 12 September 1528) was Do ...
to surrender the title of Seignior of Genoa to the king of France. The French were driven away in 1409 and Liguria went back under Milanese control in 1421, thus remaining until 1435.
Early modern
 The alternation of French and Milanese dominions over Liguria went on until the first half of the 16th century. The French influence ceased in 1528, when Andrea Doria allied with the powerful king of Spain and imposed an aristocratic government, which gave the republic relative stability for about 250 years.
The alternation of French and Milanese dominions over Liguria went on until the first half of the 16th century. The French influence ceased in 1528, when Andrea Doria allied with the powerful king of Spain and imposed an aristocratic government, which gave the republic relative stability for about 250 years.
 Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus's speculative proposal to reach the East Indies by sailing westward received the support of the Spanish crown, which saw in it an opportunity to gain the upper hand over rival powers in the contest for the lucrative spice trade with Asia. During his first voyage in 1492, instead of reaching Japan as he had intended, Columbus landed in the Bahamas archipelago, at a locale he named ''San Salvador''. Over the course of three more voyages, Columbus visited the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as the
Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus's speculative proposal to reach the East Indies by sailing westward received the support of the Spanish crown, which saw in it an opportunity to gain the upper hand over rival powers in the contest for the lucrative spice trade with Asia. During his first voyage in 1492, instead of reaching Japan as he had intended, Columbus landed in the Bahamas archipelago, at a locale he named ''San Salvador''. Over the course of three more voyages, Columbus visited the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
coast of Venezuela and Central America, claiming them for the Spanish Empire.
The value of trade routes through Genoa to the Near East declined during the Age of Discovery, when Portuguese explorers discovered routes to Asia around the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is t ...
. The international crises of the seventeenth century, which ended for Genoa with the 1684 bombardment by Louis XIV's fleet, restored French influence over the republic. Consequently, the Ligurian territory was crossed by the Piedmontese and Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
armies when these two states came into conflict with France. Austria occupied Genoa in 1746, but the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
troops were driven away by a popular insurrection. Napoleon's first Italian campaign marked the end of the oligarchic Genoese state, which was transformed into the Ligurian Republic, modelled on the French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
. After the union of Oneglia and Loano (1801), Liguria was annexed to the French Empire
French Empire (french: Empire Français, link=no) may refer to:
* First French Empire, ruled by Napoleon I from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815 and by Napoleon II in 1815, the French state from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815
* Second French Empire, led by Nap ...
(1805) and divided by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
into three departments: Montenotte (department)
Montenotte was a department of the First French Empire in present-day Italy. It was named after the village Montenotte near Savona to commemorate the Battle of Montenotte in 1796. It was formed in 1805, when the Ligurian Republic (formerly the Re ...
, with capital Savona
Savona (; lij, Sann-a ) is a seaport and ''comune'' in the west part of the northern Italy, Italian region of Liguria, capital of the Province of Savona, in the Riviera di Ponente on the Mediterranean Sea.
Savona used to be one of the chie ...
, Gênes, with capital Genoa and the department of the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
, with the capital Chiavari.
Late modern and contemporary
After a short period of independence in 1814, the Congress of Vienna (1815) decided that Liguria should be annexed to the Kingdom of Sardinia. The Genoese uprising against the House of Savoy in 1821, which was put down with great bloodshed, aroused the population's national sentiments. Some of the most prestigious figures of '' Risorgimento'' were born in Liguria ( Giuseppe Mazzini, Mameli,Nino Bixio
Gerolamo "Nino" Bixio (, ; 2 October 1821 – 16 December 1873) was an Italian general, patriot and politician, one of the most prominent figures in the Italian unification.
Life and career
He was born Gerolamo Bixio in Genoa. While still a boy, ...
). Italian patriot and general Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
, who was born in the neighbouring Nice (then part of the Sardinian state), started his Expedition of the Thousand on the evening of 5 May 1860 from a rock in Quarto, a quarter of Genoa.
In late 19th and early 20th century, the region's economic growth was remarkable: steel mills and ship yards flourished along the coast from Imperia
Imperia (; lij, Inpêia or ) is a coastal city and ''comune'' in the Regions of Italy, region of Liguria, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Imperia, and historically it was capital of the ''Intemelia'' district of Liguria. Benito Muss ...
to La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
, while the port of Genoa became the main commercial hub of industrializing Northern Italy. During the tragic period of the Second World War, Liguria experienced heavy bombings, hunger and two years of occupation by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
troops, against whom a liberation struggle was led—among the most effective in Italy. When Allied troops eventually entered Genoa, they were welcomed by Italian partisans who, in a successful insurrection, had freed the city and accepted the surrender of the local German command. For this feat, the city has been awarded the gold medal for military valour.
Demographics
 The population density of Liguria is much higher than the national average (300 inhabitants per km2, or 770 per mi2), being only less than Campania's,
The population density of Liguria is much higher than the national average (300 inhabitants per km2, or 770 per mi2), being only less than Campania's, Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
's and Lazio's. In the Metropolitan City of Genoa, it reaches almost 500 inhabitants per km2, whereas in the provinces of Imperia
Imperia (; lij, Inpêia or ) is a coastal city and ''comune'' in the Regions of Italy, region of Liguria, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Imperia, and historically it was capital of the ''Intemelia'' district of Liguria. Benito Muss ...
and Savona
Savona (; lij, Sann-a ) is a seaport and ''comune'' in the west part of the northern Italy, Italian region of Liguria, capital of the Province of Savona, in the Riviera di Ponente on the Mediterranean Sea.
Savona used to be one of the chie ...
it is less than 200 inhabitants per km2. The Spanish traveller Pedro Tafur
Pedro Tafur (or Pero Tafur) (c. 1410 – c. 1484) was a traveller, historian and writer from Castile (modern day Spain). Born in Córdoba, to a branch of the noble house of Guzmán,He dedicated his manuscript to Don Fernando de Guzmán, Chief Co ...
, noting it from sea in 1436, remarked "To one who does not know it, the whole coast from Savona to Genoa looks like one continuous city, so well inhabited is it, and so thickly studded with houses," and today over 80% of the regional population still lives permanently near to the coast, where all the four major cities above 50,000 are located: Genoa (pop. 610,000), La Spezia
La Spezia (, or , ; in the local Spezzino dialect) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second largest city ...
(pop. 95,000), Savona
Savona (; lij, Sann-a ) is a seaport and ''comune'' in the west part of the northern Italy, Italian region of Liguria, capital of the Province of Savona, in the Riviera di Ponente on the Mediterranean Sea.
Savona used to be one of the chie ...
(pop. 62,000) and Sanremo (pop. 56,000).
The population of Liguria has been declining from 1971 to 2001, most markedly in the cities of Genoa, Savona and La Spezia. The age pyramid now looks more like a 'mushroom' resting on a fragile base. The negative trend has been partially interrupted only in the last decade when, after a successful economic recovery, the region has attracted consistent fluxes of immigrants. , the Italian national institute of statistics, ISTAT, estimated that 90,881 foreign-born immigrants live in Liguria, equal to 5.8% of the total regional population.
Economy
olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: f ...
) and has thus managed to maintain the gross value-added per worker at a level much higher than the national average (the difference was about 42% in 1999). The value of flower production represents over 75% of the agriculture sector turnover, followed by animal farming (11.2%) and vegetable growing (6.4%).

 Steel, once a major industry during the booming 1950s and 1960s, phased out after the late 1980s crisis, as Italy moved away from the heavy industry to pursue more technologically advanced and less polluting production. So the Ligurian industry has turned towards a widely diversified range of high-quality and high-tech products (food, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and electronics, petrochemicals, aerospace etc.). Nonetheless, the region still maintains a flourishing shipbuilding sector (yacht construction and maintenance, cruise liner building, military shipyards).
In the services sector, the gross value-added per worker in Liguria is 4% above the national average. This is due to the increasing diffusion of modern technologies, particularly in commerce and tourism.
Steel, once a major industry during the booming 1950s and 1960s, phased out after the late 1980s crisis, as Italy moved away from the heavy industry to pursue more technologically advanced and less polluting production. So the Ligurian industry has turned towards a widely diversified range of high-quality and high-tech products (food, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and electronics, petrochemicals, aerospace etc.). Nonetheless, the region still maintains a flourishing shipbuilding sector (yacht construction and maintenance, cruise liner building, military shipyards).
In the services sector, the gross value-added per worker in Liguria is 4% above the national average. This is due to the increasing diffusion of modern technologies, particularly in commerce and tourism.
Transport
A good motorways network ( in 2000) makes communications with the border regions relatively easy. The main motorway is located along the coastline, connecting the main ports of Nice (in France), Savona, Genoa and La Spezia. The number of passenger cars per 1000 inhabitants (524 in 2001) is below the national average (584). In average, about 17 million tonnes of cargo are shipped from the main ports of the region and about 57 million tonnes enter the region. The Port of Genoa, with a trade volume of 58.6 million tonnes it is the first port of Italy, the second in terms oftwenty-foot equivalent units
The twenty-foot equivalent unit (abbreviated TEU or teu) is an inexact unit of cargo capacity, often used for container ships and container ports.Rowlett, 2004. It is based on the volume of a intermodal container, a standard-sized metal box whic ...
after the port of transshipment of Gioia Tauro, with a trade volume of 1.86 million TEUs. The main destinations for the cargo-passenger traffic are Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, Barcelona and Canary Islands.
Economical Statistic
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 49.9 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 2.8% of Italy's economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 32,000 euros or 106% of the EU27 average in the same year. The unemployment rate stood at 8.3% in 2020 and was slightly lower than the national average.Government and politics
 The politics of Liguria takes place in a framework of a
The politics of Liguria takes place in a framework of a presidential
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese fu ...
representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Government is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Regional Government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Regional Council.
The Regional Government is presided by the Governor, who is elected for a five-year term, and is composed by the President and the Ministers, who are currently 11, including a vice president.
The Regional Council of is composed of 40 members and it is elected for a five-year term, but, if the President suffers a vote of no confidence, resigns or dies, under the ''simul stabunt vel simul cadent'' clause (introduced in 1999), also the council will be dissolved and there will be a fresh election.
In the last regional election, which took place on 31 May 2015, Giovanni Toti (Forza Italia
Forza ItaliaThe name is not usually translated into English: ''forza'' is the second-person singular imperative of ''forzare'', in this case translating to "to compel" or "to press", and so means something like "Forward, Italy", "Come on, Ital ...
) defeated Raffaella Paita (Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
), after 10 years of regional left-wing government by Claudio Burlando (Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
).
At both national and local level, Liguria is considered a swing region, where no one of the two political blocs is dominant, with the two eastern provinces leaning left, and the two western provinces right.
Liguria is one of 20 regions (administrative divisions) of Italy.
Administrative divisions
Liguria is divided into four provinces:Culture
Cuisine
 Liguria is the original source of pesto, one of the most popular sauces in Italian cuisine, made with fresh basil,
Liguria is the original source of pesto, one of the most popular sauces in Italian cuisine, made with fresh basil, pine kernel
Pine nuts, also called piñón (), pinoli (), pignoli or chilgoza (), are the edible seeds of pines (family Pinaceae, genus ''Pinus''). According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, only 29 species provide edible nuts, while 20 are trade ...
s, olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: f ...
, garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
and Parmesan cheese.
Seafood
Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs (e.g. bivalve molluscs such as clams, oysters and mussels, and cephalopods such as octopus an ...
is a major staple of Mediterranean cuisine, the Ligurian variety being no exception, as the sea has been part of the region's culture since its beginning. ''Ciuppin'' soup is made from fish leftovers and stale bread, flavoured with white wine, onion, and garlic.
Vegetables, especially beans, are important in Ligurian cooking. ''Mesciua'' soup is made from beans, olive oil and farro (old kinds of wheat including emmer). The Badalucco, Conio and Pigna Beans are a Slow Food Presidium.
Ligurian pasta includes ''trenette
Trenette () is a type of narrow, flat, dried pasta from Genoa and Liguria; it is similar to both linguine and fettuccine. ''Trenette'' is the plural of ''trenetta'', but is only used in the plural and is probably a diminutive of the Genoese ''tre ...
'' and '' trofie'', and the fresh pasta pockets called ''pansòuti''.
Sports
The two main men's football clubs areGenoa C.F.C.
Genoa Cricket and Football Club, commonly referred to as Genoa (), is a professional football club based in Genoa, Liguria, Italy, that competes in , the second division of the Italian football league system.
Established in 1893, Genoa is ...
and U.C. Sampdoria, which have played for decades in Serie A. They share the Stadio Luigi Ferraris
The Stadio comunale Luigi Ferraris, also known as the Marassi from the name of the neighbourhood where it is located, is a multi-use stadium in Genoa, Italy. The home of Genoa C.F.C. and U.C. Sampdoria football clubs, it opened in 1911 and is ...
, and face each other in the Derby della Lanterna
The Derby della Lanterna, Italian for the "Derby of the Lantern", is Genoa's local derby, played by Genoa C.F.C and U.C. Sampdoria. It takes place at the Stadio Luigi Ferraris, which both clubs share.
Background
The derby's name is derived from t ...
. The third most successful club is Spezia Calcio
Spezia Calcio is a professional Association football, football club based in La Spezia, Liguria, Italy. Spezia Calcio was founded in 1906 by the Swiss banker Hermann Hurni (or Hurny in some documents), who played for the early Crystal Palace am ...
, which debuted in Serie A in 2020.
Pro Recco is a men's water polo club that has a record 33 Serie A1 titles and 9 LEN Champions League titles.
The Milan–San Remo
Milan–San Remo (in Italian ''Milano-Sanremo''), also called "''The Spring classic''" or "''La Classicissima''", is an annual road cycling race between Milan and Sanremo, in Northwest Italy. With a distance of 298 km (~185.2 miles) it is t ...
is one of the most prestigious one-day road cycling races in the world.
The Rallye Sanremo Rallye Sanremo is a rally competition held in Sanremo, Italy. Except for the 1995 event, the event was part of the FIA World Rally Championship schedule from the 1973 season to the 2003 season. Currently, it is a round of the Intercontinental Rally ...
auto race was part of the World Rally Championship from 1973 to 2003.
See also
* Italian RivieraReferences
External links
Official Region website
Video Introduction to Liguria
{{coord, 44, 27, 00, N, 8, 46, 00, E, display=title Regions of Italy NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Wine regions of Italy