Lichfield City F.C. Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lichfield () is a cathedral city and civil parish in
 The early history of Lichfield is obscure. The first authentic record of Lichfield occurs in
The early history of Lichfield is obscure. The first authentic record of Lichfield occurs in  In 1102 Bishop Peter's successor,
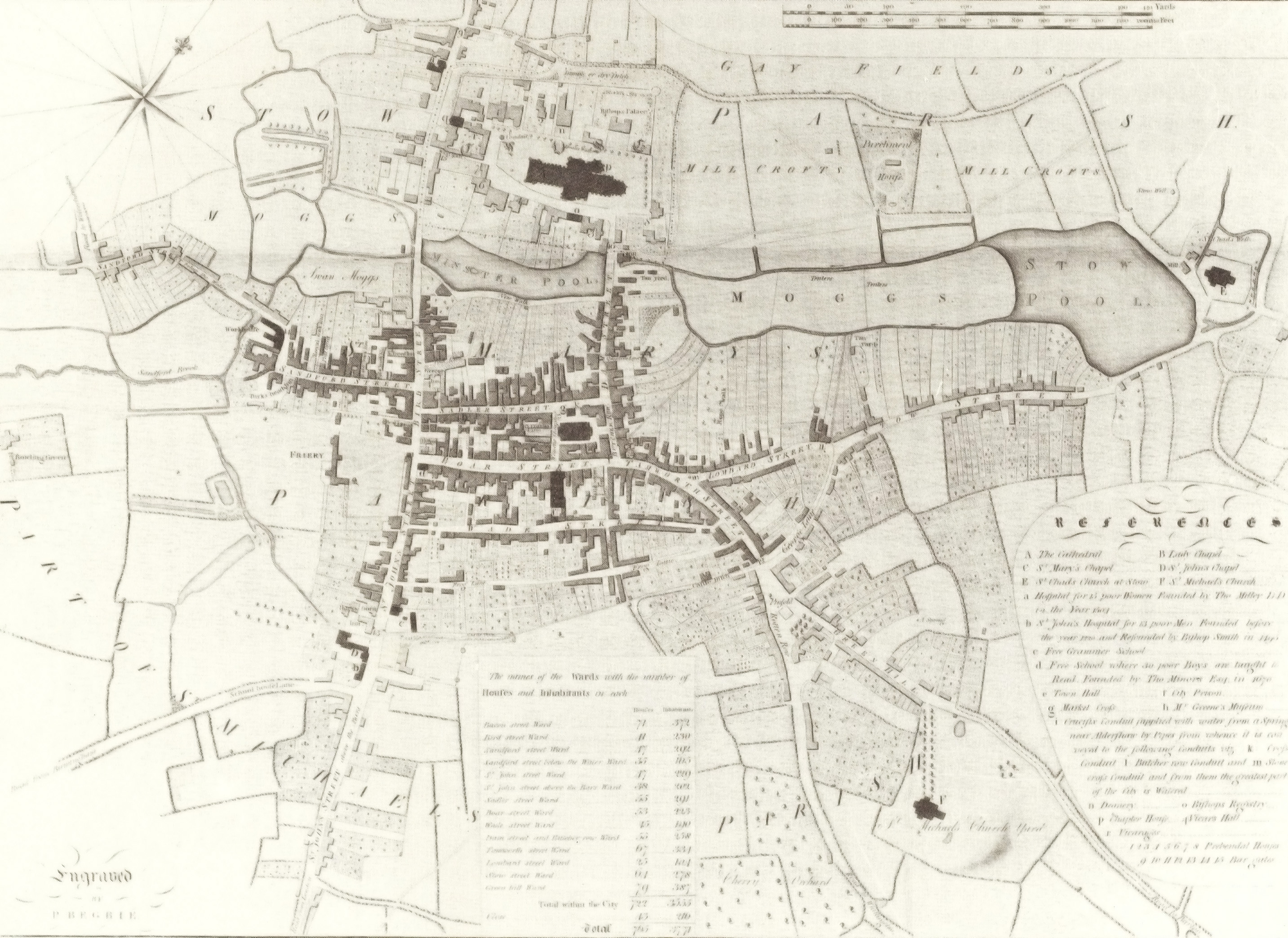
In 1102 Bishop Peter's successor,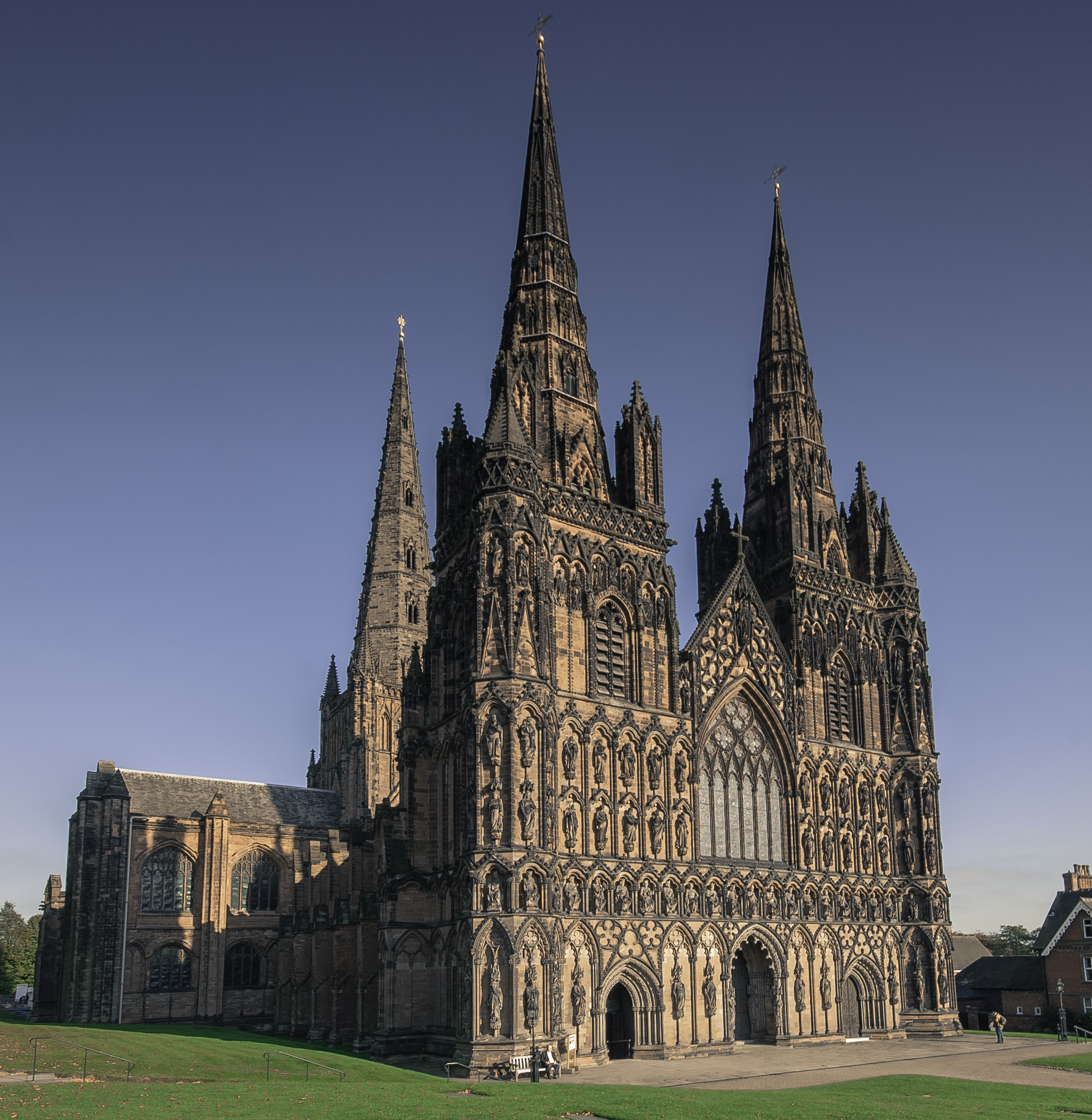  Bishop Roger de Clinton was responsible for transforming the scattered settlements to the south of Minster Pool into the ladder-plan streets existing today. Market Street, Wade Street, Bore Street and Frog Lane linked Dam Street, Conduit Street and Bakers Lane on one side with Bird Street and St John Street on the other. Bishop de Clinton also fortified the cathedral close and enclosed the town with a bank and ditch, and gates were set up where roads into the town crossed the ditch. In 1291 Lichfield was severely damaged by a fire which destroyed most of the town; however the Cathedral and Close survived unscathed.
In 1387
Bishop Roger de Clinton was responsible for transforming the scattered settlements to the south of Minster Pool into the ladder-plan streets existing today. Market Street, Wade Street, Bore Street and Frog Lane linked Dam Street, Conduit Street and Bakers Lane on one side with Bird Street and St John Street on the other. Bishop de Clinton also fortified the cathedral close and enclosed the town with a bank and ditch, and gates were set up where roads into the town crossed the ditch. In 1291 Lichfield was severely damaged by a fire which destroyed most of the town; however the Cathedral and Close survived unscathed.
In 1387
 The policies of
The policies of 
 In the English Civil War, Lichfield was divided. The cathedral authorities, supported by some of the townsfolk, were for the king, but the townsfolk generally sided with the Parliament. This led to the fortification of the close in 1643. Lichfield's position as a focus of supply routes had an important strategic significance during the war, and both forces were anxious for control of the city. The Parliamentary commander Lord Brooke led an assault on the fortified close, but was killed by a deflected bullet on St Chad's day in 1643, an accident welcomed as a miracle by the Royalists. The close subsequently yielded to the Parliamentarians, but was retaken by
In the English Civil War, Lichfield was divided. The cathedral authorities, supported by some of the townsfolk, were for the king, but the townsfolk generally sided with the Parliament. This led to the fortification of the close in 1643. Lichfield's position as a focus of supply routes had an important strategic significance during the war, and both forces were anxious for control of the city. The Parliamentary commander Lord Brooke led an assault on the fortified close, but was killed by a deflected bullet on St Chad's day in 1643, an accident welcomed as a miracle by the Royalists. The close subsequently yielded to the Parliamentarians, but was retaken by
Christopher Pincher , In your Area , Map
and was elected as the Conservative Member in May 2010, and was re-elected in May 2015, June 2017 and December 2019 with a majority of 19,634.
 Lichfield's wealth grew along with its importance as an ecclesiastical centre. The original settlement prospered as the place where pilgrims gathered to worship at the shrine of St Chad: this practice continued until the Reformation, when the shrine was destroyed.
In the Middle Ages, the main industry in Lichfield was making woollen cloth; there was also a leather industry. Much of the surrounding area was open pasture, and there were many surrounding farms.
In the 18th century, Lichfield became a busy coaching centre. Inns and hostelries grew up to provide accommodation, and industries dependent on the coaching trade such as coach builders, corn and hay merchants, saddlers and tanneries began to thrive. The main source of wealth to the city came from the money generated by its many visitors. The invention of the railways saw a decline in coach travel, and with it came the decline in Lichfield's prosperity.
By the end of the 19th century, brewing was the principal industry, and in the neighbourhood were large market gardens which provided food for the growing populations of nearby Birmingham and the Black Country.
Today there are a number of light industrial areas, predominantly in the east of the city, not dominated by any one particular industry. The district is famous for two local manufacturers: Armitage Shanks, makers of baths/bidets and showers, and Arthur Price, Arthur Price of England, master cutlers and silversmiths. Many residents commute to Birmingham.
Lichfield District Council has predicted that, once completed, the new Friarsgate retail and leisure development could attract 11,000 more visitors to the city every month, generating annual sales of around £61 million and creating hundreds of jobs in the city.
The city is home to Central England Co-operative (and its predecessor Midlands Co-operative Society), the second largest independent consumer co-operative in the UK.
Lichfield's wealth grew along with its importance as an ecclesiastical centre. The original settlement prospered as the place where pilgrims gathered to worship at the shrine of St Chad: this practice continued until the Reformation, when the shrine was destroyed.
In the Middle Ages, the main industry in Lichfield was making woollen cloth; there was also a leather industry. Much of the surrounding area was open pasture, and there were many surrounding farms.
In the 18th century, Lichfield became a busy coaching centre. Inns and hostelries grew up to provide accommodation, and industries dependent on the coaching trade such as coach builders, corn and hay merchants, saddlers and tanneries began to thrive. The main source of wealth to the city came from the money generated by its many visitors. The invention of the railways saw a decline in coach travel, and with it came the decline in Lichfield's prosperity.
By the end of the 19th century, brewing was the principal industry, and in the neighbourhood were large market gardens which provided food for the growing populations of nearby Birmingham and the Black Country.
Today there are a number of light industrial areas, predominantly in the east of the city, not dominated by any one particular industry. The district is famous for two local manufacturers: Armitage Shanks, makers of baths/bidets and showers, and Arthur Price, Arthur Price of England, master cutlers and silversmiths. Many residents commute to Birmingham.
Lichfield District Council has predicted that, once completed, the new Friarsgate retail and leisure development could attract 11,000 more visitors to the city every month, generating annual sales of around £61 million and creating hundreds of jobs in the city.
The city is home to Central England Co-operative (and its predecessor Midlands Co-operative Society), the second largest independent consumer co-operative in the UK.


 There are many parks, gardens and open spaces in the city. The city centre park is Beacon Park, which hosts a range of community events and activities throughout the year. Also in the city centre are two lakes, Minster Pool and Stowe Pool. The Garden of Remembrance, a memorial garden laid out in 1920 after World War I, is located on Bird Street. Many other parks are located on the outskirts of the city: these include Brownsfield Park, Darnford Park, Shortbutts Park, Stychbrook Park, Saddlers Wood and Christian Fields.
There are two public sports and leisure facilities in the city. Friary Grange Leisure Centre in the north-west of the city offers racket sports, a swimming pool, and sports hall and fitness gym. King Edward VI Leisure Centre in the south of the city offers racket sports, a sports hall and an artificial turf pitch.
Lichfield Library and Record Office was located on the corner of St John Street and The Friary. The building also included an adult education centre and a small art gallery. The library occupied this building in 1989, when it moved from the Lichfield Free Library and Museum on Bird Street. The library moved into the newly renovated St Mary's church on Market Square in 2018
The city is served by the Samuel Johnson Community Hospital located on Trent Valley Road. This hospital replaced the now-demolished Victoria Hospital in 2006.
There are many parks, gardens and open spaces in the city. The city centre park is Beacon Park, which hosts a range of community events and activities throughout the year. Also in the city centre are two lakes, Minster Pool and Stowe Pool. The Garden of Remembrance, a memorial garden laid out in 1920 after World War I, is located on Bird Street. Many other parks are located on the outskirts of the city: these include Brownsfield Park, Darnford Park, Shortbutts Park, Stychbrook Park, Saddlers Wood and Christian Fields.
There are two public sports and leisure facilities in the city. Friary Grange Leisure Centre in the north-west of the city offers racket sports, a swimming pool, and sports hall and fitness gym. King Edward VI Leisure Centre in the south of the city offers racket sports, a sports hall and an artificial turf pitch.
Lichfield Library and Record Office was located on the corner of St John Street and The Friary. The building also included an adult education centre and a small art gallery. The library occupied this building in 1989, when it moved from the Lichfield Free Library and Museum on Bird Street. The library moved into the newly renovated St Mary's church on Market Square in 2018
The city is served by the Samuel Johnson Community Hospital located on Trent Valley Road. This hospital replaced the now-demolished Victoria Hospital in 2006.
 * Lichfield Cathedral - The only medieval cathedral in Europe with three spires. The present building was started in 1195, and completed by the building of the Lady Chapel in the 1330s. It replaced a Norman building begun in 1085 which had replaced one, or possibly two, Saxon buildings from the seventh century.
* Cathedral Close - Surrounding the cathedral, the close contains many buildings of architectural interest.
*Samuel Johnson Birthplace Museum - A museum to Samuel Johnson's life, work and personality.
*Erasmus Darwin House - Home to Erasmus Darwin, the house was restored to create a museum which opened to the public in 1999.
*Lichfield Museum - in St Mary's Church, Lichfield, St Mary's Church in the market square, an exhibition of 2,000 years of Lichfield's history.
*Lichfield Guildhall - a historic building in the centre of Lichfield, located in Bore Street, it has been central to the government of the city for over 600 years.
*Bishop's Palace, Lichfield, Bishop's Palace - Built in 1687, the palace was the residence of the Bishop of Lichfield until 1954; it is now used by the Cathedral School.
*Dr Milley's Hospital - Located on Beacon Street, it dates back to 1504 and was a women's hospital.
*Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs, Lichfield, Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs - A distinctive Tudor building with a row of eight brick chimneys. This was built outside the city walls (barrs) to provide accommodation for travellers arriving after the city gates were closed. It now provides homes for elderly people and has an adjacent Chapel.
*The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, Church of St Chad - A 12th-century church, though extensively restored; near the church is a reconstruction of 'St Chad's Well', where the 7th-century churchman St Chad, Ceadda, St Chad is said to have prayed and baptised people.
*St Michael on Greenhill - Overlooking the city, the ancient churchyard is one of the largest in the country at .
*Christ Church, Lichfield, Christ Church - An outstanding example of Victorian ecclesiastical architecture and a grade II* listed building.
*The Market Square - In the centre of the city, the square contains two statues, one of Samuel Johnson overlooking the house in which he was born, and one of his great friend and biographer, James Boswell.
*Beacon Park - An public park in the centre of the city, used for many sporting and recreational activities.
*Minster Pool & Stowe Pool - The two lakes occupying 16 acres in the heart of Lichfield: Stowe Pool is designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest, SSSI site as it is home to native White-Clawed Crayfish. By Stowe Pool stands Johnson's Willow, a descendant of the original enormous tree which was much admired and visited by Samuel Johnson. In 2021 a fifth descendant was installed.
*The Franciscan Friary,Lichfield, The Franciscan Friary - The ruins of the former Friary in Lichfield, now classed as a Scheduled monument, Scheduled Ancient Monument.
*Lichfield Clock Tower - A Grade II listed 19th century clock tower, located south of Festival Gardens.
* Letocetum - The remains of a Roman staging post and bath house, in the village of Wall, south of the city.
*Staffordshire Regiment Museum - east of the city in Whittington, Staffordshire, Whittington, the museum covers the regiment's history, activities and members, and includes photographs, uniforms, weapons, medals, artefacts, memorabilia and regimental regalia. Outdoors is a replica trench from World War I, and several armoured fighting vehicles.
*National Memorial Arboretum - north east of the city in Alrewas, the Arboretum is a national site of remembrance and contains many memorials to the armed services.
* Lichfield Cathedral - The only medieval cathedral in Europe with three spires. The present building was started in 1195, and completed by the building of the Lady Chapel in the 1330s. It replaced a Norman building begun in 1085 which had replaced one, or possibly two, Saxon buildings from the seventh century.
* Cathedral Close - Surrounding the cathedral, the close contains many buildings of architectural interest.
*Samuel Johnson Birthplace Museum - A museum to Samuel Johnson's life, work and personality.
*Erasmus Darwin House - Home to Erasmus Darwin, the house was restored to create a museum which opened to the public in 1999.
*Lichfield Museum - in St Mary's Church, Lichfield, St Mary's Church in the market square, an exhibition of 2,000 years of Lichfield's history.
*Lichfield Guildhall - a historic building in the centre of Lichfield, located in Bore Street, it has been central to the government of the city for over 600 years.
*Bishop's Palace, Lichfield, Bishop's Palace - Built in 1687, the palace was the residence of the Bishop of Lichfield until 1954; it is now used by the Cathedral School.
*Dr Milley's Hospital - Located on Beacon Street, it dates back to 1504 and was a women's hospital.
*Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs, Lichfield, Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs - A distinctive Tudor building with a row of eight brick chimneys. This was built outside the city walls (barrs) to provide accommodation for travellers arriving after the city gates were closed. It now provides homes for elderly people and has an adjacent Chapel.
*The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, Church of St Chad - A 12th-century church, though extensively restored; near the church is a reconstruction of 'St Chad's Well', where the 7th-century churchman St Chad, Ceadda, St Chad is said to have prayed and baptised people.
*St Michael on Greenhill - Overlooking the city, the ancient churchyard is one of the largest in the country at .
*Christ Church, Lichfield, Christ Church - An outstanding example of Victorian ecclesiastical architecture and a grade II* listed building.
*The Market Square - In the centre of the city, the square contains two statues, one of Samuel Johnson overlooking the house in which he was born, and one of his great friend and biographer, James Boswell.
*Beacon Park - An public park in the centre of the city, used for many sporting and recreational activities.
*Minster Pool & Stowe Pool - The two lakes occupying 16 acres in the heart of Lichfield: Stowe Pool is designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest, SSSI site as it is home to native White-Clawed Crayfish. By Stowe Pool stands Johnson's Willow, a descendant of the original enormous tree which was much admired and visited by Samuel Johnson. In 2021 a fifth descendant was installed.
*The Franciscan Friary,Lichfield, The Franciscan Friary - The ruins of the former Friary in Lichfield, now classed as a Scheduled monument, Scheduled Ancient Monument.
*Lichfield Clock Tower - A Grade II listed 19th century clock tower, located south of Festival Gardens.
* Letocetum - The remains of a Roman staging post and bath house, in the village of Wall, south of the city.
*Staffordshire Regiment Museum - east of the city in Whittington, Staffordshire, Whittington, the museum covers the regiment's history, activities and members, and includes photographs, uniforms, weapons, medals, artefacts, memorabilia and regimental regalia. Outdoors is a replica trench from World War I, and several armoured fighting vehicles.
*National Memorial Arboretum - north east of the city in Alrewas, the Arboretum is a national site of remembrance and contains many memorials to the armed services.


 In addition to nine primary schools and one infant school, Lichfield has three secondary schools:
* The Friary School
* King Edward VI School, Lichfield, King Edward VI School (''formerly Lichfield Grammar School'')
* Nether Stowe School, a comprehensive school with specialist Maths and Computing college status
There are two independent schools:
*Lichfield Cathedral School: A co-educational school for ages 3 to 18, based in the Cathedral Close and Longdon, Staffordshire, Longdon.
*Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes School: A DfES Approved Special School for dyslexic children.
The Lichfield campus of Staffordshire University and South Staffordshire College is located on the Friary. This campus facility was opened in 1998 and offers further and higher education courses up to and including master's degrees. A £3 million school of art, design and media, housed in purpose-built accommodation, opened in 2006. This facility received the highest possible grade of 'outstanding provision' in the latest Ofsted inspection report.
In addition to nine primary schools and one infant school, Lichfield has three secondary schools:
* The Friary School
* King Edward VI School, Lichfield, King Edward VI School (''formerly Lichfield Grammar School'')
* Nether Stowe School, a comprehensive school with specialist Maths and Computing college status
There are two independent schools:
*Lichfield Cathedral School: A co-educational school for ages 3 to 18, based in the Cathedral Close and Longdon, Staffordshire, Longdon.
*Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes School: A DfES Approved Special School for dyslexic children.
The Lichfield campus of Staffordshire University and South Staffordshire College is located on the Friary. This campus facility was opened in 1998 and offers further and higher education courses up to and including master's degrees. A £3 million school of art, design and media, housed in purpose-built accommodation, opened in 2006. This facility received the highest possible grade of 'outstanding provision' in the latest Ofsted inspection report.




 * Ceatta of Lichfield, an obscure 11th century Anglo Saxon saint of the Catholic Church.
* Ceatta of Lichfield, an obscure 11th century Anglo Saxon saint of the Catholic Church.



 * Alasdair Steele-Bodger CBE, FRCVS (1924–2008), veterinary surgeon
* Elaine Horseman (1925–1999), author
* Denis Alva Parsons MBE, ARBS (1934–2012), sculptor
* Michael Laskey (born 1944), poet and editor
* John Hinch (musician), John Hinch (1947–2021) drummer, original drummer of Judas Priest
* Louis Lillywhite, Lieutenant General Louis Lillywhite CB, MBE, QHS (born 1948) retired British Army physician, Surgeon-General (United Kingdom), Surgeon-General 2006/2009
* Phil Ford (writer), Phil Ford (born 1950), television writer
* Charles Lambert (author), Charles Lambert (born 1953) novelist and short-story writer
* Richard Allinson (born 1958), broadcaster, early morning weekend show on BBC Radio 2
* David Charles Manners (born 1965), theatre designer, author and charity founder
* Mark Thwaite (born 1965), guitarist with rock bands The Mission (band), The Mission, Tricky (musician), Tricky, & Peter Murphy (musician), Peter Murphy
* Julian Argüelles (born 1966), jazz saxophonist
* Helen Baxendale (born 1970), actress
* Richie Edwards (born 1974), bassist with rock bands The Darkness (band), the Darkness and Stone Gods
* Adrian Poynton (born 1979), screenwriter, playwright and stand-up comedian
* Sian Brooke (born 1980), actress
* Bryn Fowler (born 1982), musician, bassist and backing vocalist in the band the Holloways
* Siobhan Dillon (born 1984), singer and actress
* Michael Lieber (born 1988), novelist (alumnus of Lichfield's Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes Hall)
* Alasdair Steele-Bodger CBE, FRCVS (1924–2008), veterinary surgeon
* Elaine Horseman (1925–1999), author
* Denis Alva Parsons MBE, ARBS (1934–2012), sculptor
* Michael Laskey (born 1944), poet and editor
* John Hinch (musician), John Hinch (1947–2021) drummer, original drummer of Judas Priest
* Louis Lillywhite, Lieutenant General Louis Lillywhite CB, MBE, QHS (born 1948) retired British Army physician, Surgeon-General (United Kingdom), Surgeon-General 2006/2009
* Phil Ford (writer), Phil Ford (born 1950), television writer
* Charles Lambert (author), Charles Lambert (born 1953) novelist and short-story writer
* Richard Allinson (born 1958), broadcaster, early morning weekend show on BBC Radio 2
* David Charles Manners (born 1965), theatre designer, author and charity founder
* Mark Thwaite (born 1965), guitarist with rock bands The Mission (band), The Mission, Tricky (musician), Tricky, & Peter Murphy (musician), Peter Murphy
* Julian Argüelles (born 1966), jazz saxophonist
* Helen Baxendale (born 1970), actress
* Richie Edwards (born 1974), bassist with rock bands The Darkness (band), the Darkness and Stone Gods
* Adrian Poynton (born 1979), screenwriter, playwright and stand-up comedian
* Sian Brooke (born 1980), actress
* Bryn Fowler (born 1982), musician, bassist and backing vocalist in the band the Holloways
* Siobhan Dillon (born 1984), singer and actress
* Michael Lieber (born 1988), novelist (alumnus of Lichfield's Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes Hall)
SoccerBase Database
retrieved December 2017 347 pro appearances
* Stuart Ryder (born 1973), former Walsall F.C. and England U21 footballer
* Adam Wilcox (racing driver), Adam Wilcox (born 1976), racing driver
* Robert Rock (born 1977), professional golfer on the PGA European Tour, formerly a coach at Swingers Golf Centre
* Gary Mason (motorcycle racer), Gary Mason (born 1979), motorcycle racer in the British Superbike Championship
* James Austin (judoka), James Austin (born 1983) judoka, competed at the 2012 Summer Olympics
* Adam Christodoulou (born 1989), racing driver
Lichfield City Council
Visit Lichfield - Travel and Tourism body
* * {{Authority control Lichfield, Burial sites of the House of Icel Cities in the West Midlands (region) Civil parishes in Staffordshire Towns in Staffordshire
Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
, England. Lichfield is situated roughly south-east of the county town of Stafford
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It lies about north of Wolverhampton, south of Stoke-on-Trent and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 70,145 in t ...
, south-east of Rugeley, north-east of Walsall, north-west of Tamworth and south-west of Burton Upon Trent. At the time of the 2011 Census, the population was estimated at 32,219 and the wider Lichfield District at 100,700.
Notable for its three-spired medieval cathedral, Lichfield was the birthplace of Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
, the writer of the first authoritative '' Dictionary of the English Language''. The city's recorded history began when Chad of Mercia arrived to establish his Bishopric in 669 AD and the settlement grew as the ecclesiastical centre of Mercia. In 2009, the Staffordshire Hoard, the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
gold and silver metalwork, was found south-west of Lichfield.
The development of the city was consolidated in the 12th century under Roger de Clinton, who fortified the Cathedral Close and also laid out the town with the ladder-shaped street pattern that survives to this day. Lichfield's heyday was in the 18th century, when it developed into a thriving coaching city. This was a period of great intellectual activity; the city was the home of many famous people including Samuel Johnson, David Garrick
David Garrick (19 February 1717 – 20 January 1779) was an English actor, playwright, theatre manager and producer who influenced nearly all aspects of European theatrical practice throughout the 18th century, and was a pupil and friend of Sa ...
, Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet.
His poems ...
and Anna Seward, prompting Johnson's remark that Lichfield was "a city of philosophers".
Today, the city still retains its old importance as an ecclesiastical centre, and its industrial and commercial development has been limited. The centre of the city has over 230 listed buildings (including many examples of Georgian architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, Georg ...
) and preserves much of its historic character.
Etymology
The origin of the modern name "Lichfield" is twofold. At Wall, south of the current city, there was a Romano-British village, Letocetum, aCommon Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
place name meaning "Greywood", "grey" perhaps referring to varieties of tree prominent in the landscape such as ash and elm. This passed into Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
as ''Lyccid'', cf. owl, Luitcoyt, to which was appended ang, feld "open country". This word is the origin of the word "Lichfield". The form "Licitfelda" is recorded c. 710 - c. 720.
Popular etymology has it that a thousand Christians were martyred in Lichfield around AD 300 during the reign of Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
and that the name Lichfield actually means "field of the dead" (see '' lich''). There is no evidence to support this legend, as with many folk etymologies.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
The earliest evidence of settlement isMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
flints discovered on the high ground of the cemetery at St Michael on Greenhill
St Michael on Greenhill is a parish church in Lichfield, Staffordshire in the United Kingdom, located on the high ground of Greenhill in the east of the city. A church has been on the present site since at least 1190 but the current building dat ...
, which may indicate an early flint industry. Traces of Neolithic settlement have been discovered on the south side of the sandstone ridge occupied by Lichfield Cathedral.
south-west of Lichfield, near the point where Icknield Street crosses Watling Street, was the site of Letocetum (the Brittonic *Lētocaiton, "Greywood"). Established in AD 50 as a Roman military fortress, it had become a civilian settlement ( vicus) with a bath house and a mansio
In the Roman Empire, a ''mansio'' (from the Latin word ''mansus,'' the perfect passive participle of ''manere'' "to remain" or "to stay") was an official stopping place on a Roman road, or ''via'', maintained by the central government for the use ...
by the 2nd century. Letocetum fell into decline by the 4th century and the Romans had left by the 5th century. There have been scattered Romano-British finds in Lichfield and it is possible that a burial discovered beneath the cathedral in 1751 was Romano-British. There is no evidence of what happened to Letocetum after the Romans left; however, Lichfield may have emerged as the inhabitants of Letocetum relocated during its decline. A (" Fort Greywood") was listed by Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
among the 28 cities of Britain in his '' Historia Brittonum'', although these were largely historic remembrances of early Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the Anglo-Saxon settlement. The term was originally used to describe archaeological remains found in 5th- and 6th-century AD sites that hint ...
.
Middle Ages
 The early history of Lichfield is obscure. The first authentic record of Lichfield occurs in
The early history of Lichfield is obscure. The first authentic record of Lichfield occurs in Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
's history, where it is called ''Licidfelth'' and mentioned as the place where St Chad
Chad of Mercia (died 2 March 672) was a prominent 7th-century Anglo-Saxon Catholic monk who became abbot of several monasteries, Bishop of the Northumbrians and subsequently Bishop of the Mercians and Lindsey People. He was later canonised ...
fixed the episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
of the Mercians in 669. The first Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
king of Mercia, Wulfhere, donated land at Lichfield for St Chad to build a monastery. It was because of this that the ecclesiastical centre of Mercia became settled as the Diocese of Lichfield, which was approximately northwest of the seat of the Mercian kings at Tamworth.
In July 2009, the Staffordshire Hoard, the largest collection of Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
gold ever found, was discovered in a field in the parish of Hammerwich, south-west of Lichfield; it was probably deposited in the 7th century.
The first cathedral was built on the present site in 700 when Bishop Hædde
Hædde (died 705) was a medieval monk and Bishop of Winchester.
Life
Hædde is believed to have been born in Headingley, Leeds, and became a monk of Whitby Abbey.Benedictine Monks of Ramsgate. ''The Book of Saints'' p.254Hunt. ''Dictionary of N ...
built a new church to house the bones of St Chad, which had become the centre of a sacred shrine to many pilgrims when he died in 672. The burial in the cathedral of the kings of Mercia, Wulfhere in 674 and Ceolred
Ceolred (died 716) was King of Mercia from 709 to 716.
Mercia at the end of the 7th century
By the end of the 7th century, England was almost entirely divided into kingdoms ruled by the Anglo-Saxons, who had come to Britain two hundred years ...
in 716, further increased the city's prestige.From: 'Lichfield: History to c.1500', A History of the County of Stafford: Volume 14: Lichfield (1990), pp. 4–14. URL: http://www.british-history.ac.uk/report.aspx?compid=42336 Date accessed: 24 July 2009. In 786 King Offa
Offa (died 29 July 796 AD) was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æt ...
made the city an archbishopric with authority over all the bishops from the Humber to the River Thames; his appointee was Archbishop Hygeberht. This may have been motivated by Offa's desire to have an archbishop consecrate his son Ecgfrith Ecgfrith ( ang, Ecgfrið) was the name of several Anglo-Saxon kings in England, including:
* Ecgfrith of Northumbria, died 685
* Ecgfrith of Mercia
Ecgfrith was king of Mercia from 29 July to December 796. He was the son of Offa, one of the m ...
as king, since it is possible Jænberht
Jænberht (died 12 August 792) was a medieval monk, and later the abbot, of St Augustine's Abbey, Canterbury who was named Archbishop of Canterbury in 765. As archbishop, he had a difficult relationship with King Offa of Mercia, who at one point ...
refused to perform the ceremony, which took place in 787. After King Offa's death in 796, Lichfield's power waned; in 803 the primacy was restored to Canterbury by Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlemagne's position b ...
after only 16 years.
The '' Historia Brittonum'' lists the city as one of the 28 cities of Britain around AD 833.
During the 9th century, Mercia was devastated by Danish Vikings. Lichfield itself was unwalled and the cathedral was despoiled, so Bishop Peter moved the see to the fortified and wealthier Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
in 1075. At the time of the Domesday Book survey (1086), Lichfield was held by the bishop of Chester; Lichfield was listed as a small village. The lord of the manor was the Bishop of Chester until the reign of Edward VI. In 1102 Bishop Peter's successor,
In 1102 Bishop Peter's successor, Robert de Limesey __NOTOC__
Robert de Limesey (died 1117) was a medieval cleric. He became Bishop of Chester in 1085, then his title changed to Bishop of Coventry when the see was moved in 1102.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 253
Robert was a ...
, transferred the see from Chester to Coventry. The Bishop of Coventry and Lichfield had seats in both locations; work on the present Gothic cathedral at Lichfield began in 1195. (In 1837 the see of Lichfield acquired independent status, and the style 'Bishop of Lichfield' was adopted.)
 Bishop Roger de Clinton was responsible for transforming the scattered settlements to the south of Minster Pool into the ladder-plan streets existing today. Market Street, Wade Street, Bore Street and Frog Lane linked Dam Street, Conduit Street and Bakers Lane on one side with Bird Street and St John Street on the other. Bishop de Clinton also fortified the cathedral close and enclosed the town with a bank and ditch, and gates were set up where roads into the town crossed the ditch. In 1291 Lichfield was severely damaged by a fire which destroyed most of the town; however the Cathedral and Close survived unscathed.
In 1387
Bishop Roger de Clinton was responsible for transforming the scattered settlements to the south of Minster Pool into the ladder-plan streets existing today. Market Street, Wade Street, Bore Street and Frog Lane linked Dam Street, Conduit Street and Bakers Lane on one side with Bird Street and St John Street on the other. Bishop de Clinton also fortified the cathedral close and enclosed the town with a bank and ditch, and gates were set up where roads into the town crossed the ditch. In 1291 Lichfield was severely damaged by a fire which destroyed most of the town; however the Cathedral and Close survived unscathed.
In 1387 Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father died ...
gave a charter for the foundation of the guild of St Mary and St John the Baptist; this guild functioned as the local government, until its dissolution by Edward VI, who incorporated the town in 1548.
Early Modern
 The policies of
The policies of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
had a dramatic effect on Lichfield. The Reformation brought the disappearance of pilgrim traffic following the destruction of St Chad's shrine in 1538, which was a major loss to the city's economic prosperity. That year too the Franciscan Friary was dissolved, the site becoming a private estate. Further economic decline followed the outbreak of plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
in 1593, which resulted in the death of over a third of the entire population.
Three people were burned at the stake for heresy under Mary I. The last public burning at the stake for heresy in England took place in Lichfield, when Edward Wightman
Edward Wightman (1566 – 11 April 1612) was an English Radical Reformation, radical Anabaptist Minister (Christianity), minister, executed at Lichfield on charges of heresy. He was the last person to be Execution by burning, burned at the stake ...
from Burton upon Trent was executed by burning in the Market Place on 11 April 1612 for promoting himself as the divine Paraclete
Paraclete ( grc, παράκλητος, la, paracletus) means 'advocate' or 'helper'. In Christianity, the term ''paraclete'' most commonly refers to the Holy Spirit.
Etymology
''Paraclete'' comes from the Koine Greek word (). A combination o ...
and Saviour of the world.

 In the English Civil War, Lichfield was divided. The cathedral authorities, supported by some of the townsfolk, were for the king, but the townsfolk generally sided with the Parliament. This led to the fortification of the close in 1643. Lichfield's position as a focus of supply routes had an important strategic significance during the war, and both forces were anxious for control of the city. The Parliamentary commander Lord Brooke led an assault on the fortified close, but was killed by a deflected bullet on St Chad's day in 1643, an accident welcomed as a miracle by the Royalists. The close subsequently yielded to the Parliamentarians, but was retaken by
In the English Civil War, Lichfield was divided. The cathedral authorities, supported by some of the townsfolk, were for the king, but the townsfolk generally sided with the Parliament. This led to the fortification of the close in 1643. Lichfield's position as a focus of supply routes had an important strategic significance during the war, and both forces were anxious for control of the city. The Parliamentary commander Lord Brooke led an assault on the fortified close, but was killed by a deflected bullet on St Chad's day in 1643, an accident welcomed as a miracle by the Royalists. The close subsequently yielded to the Parliamentarians, but was retaken by Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist cavalr ...
in the same year; on the collapse of the Royalist cause in 1646 it again surrendered. The cathedral suffered extensive damage from the war, including the complete destruction of the central spire. It was restored at the Restoration under the supervision of Bishop Hacket, and thanks in part to the generosity of King Charles II.
Lichfield started to develop a lively coaching trade as a stop-off on the busy route between London and Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
from the 1650s onwards, making it Staffordshire's most prosperous town. In the 18th century, and then reaching its peak in the period from 1800 to 1840, the city thrived as a busy coaching city on the main routes from London to the north-west and Birmingham to the north-east. It also became a centre of great intellectual activity, being the home of many famous people including Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
, David Garrick
David Garrick (19 February 1717 – 20 January 1779) was an English actor, playwright, theatre manager and producer who influenced nearly all aspects of European theatrical practice throughout the 18th century, and was a pupil and friend of Sa ...
, Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet.
His poems ...
and Anna Seward; this prompted Johnson's remark that Lichfield was "a city of philosophers". In the 1720s Daniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe (; born Daniel Foe; – 24 April 1731) was an English writer, trader, journalist, pamphleteer and spy. He is most famous for his novel ''Robinson Crusoe'', published in 1719, which is claimed to be second only to the Bible in its ...
described Lichfield as 'a fine, neat, well-built, and indifferent large city', the principal town in the region after Chester.From: 'Lichfield: From the Reformation to c.1800', A History of the County of Stafford: Volume 14: Lichfield (1990), pp. 14-24. URL: http://www.british-history.ac.uk/report.aspx?compid=42337 Date accessed: 24 July 2009. During the late 18th and early 19th century much of the medieval city was rebuilt with the red-brick Georgian style buildings still to be seen today. Also during this time, the city's infrastructure underwent great improvements, with underground sewerage systems, paved streets and gas-powered street lighting. An infantry regiment of the British Army was formed at Lichfield in 1705 by Col. Luke Lillingstone
Luke Lillingstone or Lillingston (1653–1713) was a British Army general who accompanied William of Orange to England in 1688.
Early life
Lillingstone's surname is variably spelled Lillingstone, Lillingston and Lillingstein. He was born to Co ...
in the King's Head tavern in Bird Street. In 1751 it became the 38th Regiment of Foot, and in 1783 the 1st Staffordshire Regiment; after reorganisation in 1881 it became the 1st battalion of the South Staffordshire Regiment.
Late Modern and contemporary
The arrival of the Industrial Revolution and the railways in 1837 signalled the end of Lichfield's position as an important staging post for coaching traffic. While nearby Birmingham (and its population) expanded greatly during the Industrial Revolution, Lichfield remained largely unchanged in character. The first council houses were built in the Dimbles area of the city in the 1930s. The outbreak of World War II brought over 2,000 evacuees from industrialised areas. However, due to the lack of heavy industry in the city, Lichfield escaped lightly, although there were air raids in 1940 and 1941 and three Lichfeldians were killed. Just outside the city,Wellington Bomber
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson; a key feature of the aircraft is its ...
s flew out of Fradley Aerodrome, which was known as RAF Lichfield. After the war the council built many new houses in the 1960s, including some high-rise flats, while the late 1970s and early 1980s saw the construction of a large housing estate at Boley Park in the south-east of the city. The city's population tripled between 1951 and the late 1980s.
The city has continued expanding to the west. The Darwin Park housing estate has been under development for a number of years and has swelled the city's population by approximately 3,000. Plans have been approved for Friarsgate, a new £100 million shopping and leisure complex opposite Lichfield City Station
Lichfield City is one of two railway stations serving the city of Lichfield, in Staffordshire, England. It is situated in the city-centre, and is towards the northern end of the Cross-City Line northeast of Birmingham New Street. The stati ...
. The police station, bus station, Ford garage and multi-storey car park will be demolished to make way for 22,000 m2 of retail space and 2,000 m2 of leisure facilities, consisting of a flagship department store, six-screen cinema, hotel, 37 individual shops and 56 flats. These plans have not gone ahead.
Governance
Local government
Historically the Bishop of Lichfield had authority over the city. It was not until 1548, with Edward VI's charter, that Lichfield had any form of secular government. As a reward for the support given to Mary I by the bailiffs and citizens during the Duke of Northumberland's attempt to prevent her accession, the Queen issued a new charter in 1553, confirming the 1548 charter and in addition granting the city its own Sheriff. The same charter made Lichfield a county separate from the rest ofStaffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
. It remained so until 1888.
The City Council (not to be confused with Lichfield District Council, which has authority over a wider area than Lichfield city) has 28 members (from the nine wards of Boley Park, Burton Old Road West, Chadsmead, Curborough, Garrick Road, Leamonsley, St John's, Pentire Road and Stowe), who are elected every four years. After the 2019 parish council elections, the Conservatives remained in overall control, with the 28 seats being divided between the Conservatives (16), the Liberal Democrats (8), Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
(3) and Independent (1) who subsequently joined the Labour group. The Right Worshipful
Worship is an honorific prefix for mayors, justices of the peace and magistrates in present or former Commonwealth realms. In spoken address, these officials are addressed as Your Worship or referred to as His Worship, Her Worship, or Their Wor ...
the Mayor of Lichfield (currently Councillor Robert Yardley) is the civic head of the council and chairs council meetings. The council also appoints a Leader of Council to be the main person responsible for leadership of the council's political and policy matters. The council's current Leader is Councillor Mark Warfield. Lichfield is one of only 15 towns and cities in England and Wales which appoints a Sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
.
Members of Parliament
The Lichfield constituency sent two members to the parliament of 1304 and to a few succeeding parliaments, but the representation did not become regular until 1552; in 1867 it lost one member, and in 1885 its representation was merged into that of the county. The Lichfield constituency was abolished in 1950 and replaced with the Lichfield and Tamworth constituency. This constituency lasted until 1983, when it was replaced with the Mid Staffordshire constituency. Based on the resident's location in Lichfield Distrist, there are technically two MPs. The current Member of Parliament for Lichfield, including the whole of the City, is the Conservative Michael Fabricant, who has been MP for Lichfield since 1997. Fabricant was first elected for the Mid Staffordshire constituency in1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: 1992 Los Angeles riots, Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the Police brutality, police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment buildi ...
, regaining the seat for the Conservatives following Sylvia Heal
Dame Sylvia Lloyd Heal (''née'' Fox; born 20 July 1942) is a British Labour Party politician who was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Halesowen and Rowley Regis from 1997 to 2010, having previously been the MP for Mid Staffordshire from 1 ...
's victory for Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
at the 1990 by-election
Year 199 ( CXCIX) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was sometimes known as year 952 '' Ab urbe condita''. The denomination 199 for this year has been used since the ...
. Fabricant took the seat with a majority of 6,236 and has remained a Member of Parliament since. The Mid Staffordshire seat was abolished at the 1997 general election, but Fabricant contested and won the Lichfield constituency, which partially replaced it, by just 238 votes. He has remained the Lichfield MP since, increasing his majority to 4,426 in 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which Casualties of the September 11 attacks, killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a Participants in ...
, 7,080 in 2005 United Kingdom general election, 2005, 17,683 in 2010 United Kingdom general election, 2010, 18,189 in 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015, 18,581 in 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 and 23,638 in 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019.
Christopher Pincher is current Member of Parliament for Tamworth and areas of Lichfield District (seChristopher Pincher , In your Area , Map
and was elected as the Conservative Member in May 2010, and was re-elected in May 2015, June 2017 and December 2019 with a majority of 19,634.
Geography
Lichfield covers an area of approximately in the south-east of the county of Staffordshire in the West Midlands region of England. It is approximately north of Birmingham and north-west of London. The city is located between the high ground of Cannock Chase to the west and the valleys of the Rivers River Trent, Trent and River Tame, West Midlands, Tame to the east. It is underlain by red sandstone, deposited during the arid desert conditions of the Triassic period. Keuper marl, Mercia Mudstone underlies the north and north-eastern edges of the city towards Curborough and Elmhurst, Elmhurst and Curborough. The red sandstone underlying the majority of Lichfield is present in many of its ancient buildings, including Lichfield Cathedral and the The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, Church of St Chad. The ground within the city slopes down from 116m in the north-west to 86m on the sandstone shelf where Lichfield Cathedral stands. To the south and east of the city centre is a ridge which reaches 103 m atSt Michael on Greenhill
St Michael on Greenhill is a parish church in Lichfield, Staffordshire in the United Kingdom, located on the high ground of Greenhill in the east of the city. A church has been on the present site since at least 1190 but the current building dat ...
. Boley Park lies on top of a ridge with its highest point on Borrowcop Hill at 113m. To the south-east the level drops to 69 m where Tamworth Road crosses the city boundary into Freeford. There is another high ridge south-west of the city where there are two high points, one at Berry Hill Farm at 123 m and the other on Harehurst Hill near the city boundary at Aldershawe where the level reaches 134 m.
The city is built on the two sides of a shallow valley, into which flow two streams from the west, the Trunkfield Brook and the Leamonsley Brook, and out of which the Curborough Brook runs to the north-east, eventually flowing into the River Trent. The two streams have been dammed south of the cathedral on Dam Street to form Minster Pool and near St Chad's Road to form Stowe Pool.
Suburbs
* Boley Park * Chadsmead * Christ Church * Darwin Park * The Dimbles * Leomansley * Nether Stowe * Sandfields * Stowe * Streethay * Trent ValleyDemography
At the time of the 2011 census, the population of the City of Lichfield was 32,219. Lichfield is 96.5% white and 66.5% Christian. 51% of the population over 16 were married. 64% were employed and 21% of the people were retired. All of these figures were higher than the national average.Economy
 Lichfield's wealth grew along with its importance as an ecclesiastical centre. The original settlement prospered as the place where pilgrims gathered to worship at the shrine of St Chad: this practice continued until the Reformation, when the shrine was destroyed.
In the Middle Ages, the main industry in Lichfield was making woollen cloth; there was also a leather industry. Much of the surrounding area was open pasture, and there were many surrounding farms.
In the 18th century, Lichfield became a busy coaching centre. Inns and hostelries grew up to provide accommodation, and industries dependent on the coaching trade such as coach builders, corn and hay merchants, saddlers and tanneries began to thrive. The main source of wealth to the city came from the money generated by its many visitors. The invention of the railways saw a decline in coach travel, and with it came the decline in Lichfield's prosperity.
By the end of the 19th century, brewing was the principal industry, and in the neighbourhood were large market gardens which provided food for the growing populations of nearby Birmingham and the Black Country.
Today there are a number of light industrial areas, predominantly in the east of the city, not dominated by any one particular industry. The district is famous for two local manufacturers: Armitage Shanks, makers of baths/bidets and showers, and Arthur Price, Arthur Price of England, master cutlers and silversmiths. Many residents commute to Birmingham.
Lichfield District Council has predicted that, once completed, the new Friarsgate retail and leisure development could attract 11,000 more visitors to the city every month, generating annual sales of around £61 million and creating hundreds of jobs in the city.
The city is home to Central England Co-operative (and its predecessor Midlands Co-operative Society), the second largest independent consumer co-operative in the UK.
Lichfield's wealth grew along with its importance as an ecclesiastical centre. The original settlement prospered as the place where pilgrims gathered to worship at the shrine of St Chad: this practice continued until the Reformation, when the shrine was destroyed.
In the Middle Ages, the main industry in Lichfield was making woollen cloth; there was also a leather industry. Much of the surrounding area was open pasture, and there were many surrounding farms.
In the 18th century, Lichfield became a busy coaching centre. Inns and hostelries grew up to provide accommodation, and industries dependent on the coaching trade such as coach builders, corn and hay merchants, saddlers and tanneries began to thrive. The main source of wealth to the city came from the money generated by its many visitors. The invention of the railways saw a decline in coach travel, and with it came the decline in Lichfield's prosperity.
By the end of the 19th century, brewing was the principal industry, and in the neighbourhood were large market gardens which provided food for the growing populations of nearby Birmingham and the Black Country.
Today there are a number of light industrial areas, predominantly in the east of the city, not dominated by any one particular industry. The district is famous for two local manufacturers: Armitage Shanks, makers of baths/bidets and showers, and Arthur Price, Arthur Price of England, master cutlers and silversmiths. Many residents commute to Birmingham.
Lichfield District Council has predicted that, once completed, the new Friarsgate retail and leisure development could attract 11,000 more visitors to the city every month, generating annual sales of around £61 million and creating hundreds of jobs in the city.
The city is home to Central England Co-operative (and its predecessor Midlands Co-operative Society), the second largest independent consumer co-operative in the UK.
Culture and community


Culture
The Lichfield Bower, Lichfield Greenhill Bower takes place annually on Spring Bank Holiday. Originating from a celebration that was held after the Court of Arraye in the 12th century, the festival has evolved into its modern form, but has kept many of its ancient traditions. After a recreation of the Court of Arraye at the Lichfield Guildhall, Guildhall, a procession of marching bands, Morris dance, morris men and carnival floats makes its way through the city and the Bower Queen is crowned outside the Guildhall. There is a funfair in the city centre, and another fair and jamboree in Beacon Park. The Lichfield Festival, an international arts festival, has taken place every July for 30 years. The festival is a celebration of classical music, dance, drama, film, jazz, literature, poetry, visual arts and world music. Events take place at many venues around the city but centre on Lichfield Cathedral and the Lichfield Garrick Theatre, Garrick Theatre. Popular events include the medieval market in the Cathedral Close and the fireworks display which closes the festival. Triennially the Lichfield Mystery Play, Mysteries, the biggest community theatre event in the country, takes place at the cathedral and in the Market Place. It consists of a play cycle, cycle of 24 medieval-style plays involving over 600 amateur actors. Other weekend summer festivals include the Lichfield Folk festival, Folk Festival and The Lichfield Cask ale, Real Ale, Jazz and Blues Festival. Lichfield Heritage Weekend, incorporating Samuel Johnson, Dr Johnson's Birthday Celebrations, takes place on the third weekend in September with a variety of civic events including live music and free historical tours of local landmarks.Community facilities
Places of interest
 * Lichfield Cathedral - The only medieval cathedral in Europe with three spires. The present building was started in 1195, and completed by the building of the Lady Chapel in the 1330s. It replaced a Norman building begun in 1085 which had replaced one, or possibly two, Saxon buildings from the seventh century.
* Cathedral Close - Surrounding the cathedral, the close contains many buildings of architectural interest.
*Samuel Johnson Birthplace Museum - A museum to Samuel Johnson's life, work and personality.
*Erasmus Darwin House - Home to Erasmus Darwin, the house was restored to create a museum which opened to the public in 1999.
*Lichfield Museum - in St Mary's Church, Lichfield, St Mary's Church in the market square, an exhibition of 2,000 years of Lichfield's history.
*Lichfield Guildhall - a historic building in the centre of Lichfield, located in Bore Street, it has been central to the government of the city for over 600 years.
*Bishop's Palace, Lichfield, Bishop's Palace - Built in 1687, the palace was the residence of the Bishop of Lichfield until 1954; it is now used by the Cathedral School.
*Dr Milley's Hospital - Located on Beacon Street, it dates back to 1504 and was a women's hospital.
*Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs, Lichfield, Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs - A distinctive Tudor building with a row of eight brick chimneys. This was built outside the city walls (barrs) to provide accommodation for travellers arriving after the city gates were closed. It now provides homes for elderly people and has an adjacent Chapel.
*The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, Church of St Chad - A 12th-century church, though extensively restored; near the church is a reconstruction of 'St Chad's Well', where the 7th-century churchman St Chad, Ceadda, St Chad is said to have prayed and baptised people.
*St Michael on Greenhill - Overlooking the city, the ancient churchyard is one of the largest in the country at .
*Christ Church, Lichfield, Christ Church - An outstanding example of Victorian ecclesiastical architecture and a grade II* listed building.
*The Market Square - In the centre of the city, the square contains two statues, one of Samuel Johnson overlooking the house in which he was born, and one of his great friend and biographer, James Boswell.
*Beacon Park - An public park in the centre of the city, used for many sporting and recreational activities.
*Minster Pool & Stowe Pool - The two lakes occupying 16 acres in the heart of Lichfield: Stowe Pool is designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest, SSSI site as it is home to native White-Clawed Crayfish. By Stowe Pool stands Johnson's Willow, a descendant of the original enormous tree which was much admired and visited by Samuel Johnson. In 2021 a fifth descendant was installed.
*The Franciscan Friary,Lichfield, The Franciscan Friary - The ruins of the former Friary in Lichfield, now classed as a Scheduled monument, Scheduled Ancient Monument.
*Lichfield Clock Tower - A Grade II listed 19th century clock tower, located south of Festival Gardens.
* Letocetum - The remains of a Roman staging post and bath house, in the village of Wall, south of the city.
*Staffordshire Regiment Museum - east of the city in Whittington, Staffordshire, Whittington, the museum covers the regiment's history, activities and members, and includes photographs, uniforms, weapons, medals, artefacts, memorabilia and regimental regalia. Outdoors is a replica trench from World War I, and several armoured fighting vehicles.
*National Memorial Arboretum - north east of the city in Alrewas, the Arboretum is a national site of remembrance and contains many memorials to the armed services.
* Lichfield Cathedral - The only medieval cathedral in Europe with three spires. The present building was started in 1195, and completed by the building of the Lady Chapel in the 1330s. It replaced a Norman building begun in 1085 which had replaced one, or possibly two, Saxon buildings from the seventh century.
* Cathedral Close - Surrounding the cathedral, the close contains many buildings of architectural interest.
*Samuel Johnson Birthplace Museum - A museum to Samuel Johnson's life, work and personality.
*Erasmus Darwin House - Home to Erasmus Darwin, the house was restored to create a museum which opened to the public in 1999.
*Lichfield Museum - in St Mary's Church, Lichfield, St Mary's Church in the market square, an exhibition of 2,000 years of Lichfield's history.
*Lichfield Guildhall - a historic building in the centre of Lichfield, located in Bore Street, it has been central to the government of the city for over 600 years.
*Bishop's Palace, Lichfield, Bishop's Palace - Built in 1687, the palace was the residence of the Bishop of Lichfield until 1954; it is now used by the Cathedral School.
*Dr Milley's Hospital - Located on Beacon Street, it dates back to 1504 and was a women's hospital.
*Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs, Lichfield, Hospital of St John Baptist without the Barrs - A distinctive Tudor building with a row of eight brick chimneys. This was built outside the city walls (barrs) to provide accommodation for travellers arriving after the city gates were closed. It now provides homes for elderly people and has an adjacent Chapel.
*The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, Church of St Chad - A 12th-century church, though extensively restored; near the church is a reconstruction of 'St Chad's Well', where the 7th-century churchman St Chad, Ceadda, St Chad is said to have prayed and baptised people.
*St Michael on Greenhill - Overlooking the city, the ancient churchyard is one of the largest in the country at .
*Christ Church, Lichfield, Christ Church - An outstanding example of Victorian ecclesiastical architecture and a grade II* listed building.
*The Market Square - In the centre of the city, the square contains two statues, one of Samuel Johnson overlooking the house in which he was born, and one of his great friend and biographer, James Boswell.
*Beacon Park - An public park in the centre of the city, used for many sporting and recreational activities.
*Minster Pool & Stowe Pool - The two lakes occupying 16 acres in the heart of Lichfield: Stowe Pool is designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest, SSSI site as it is home to native White-Clawed Crayfish. By Stowe Pool stands Johnson's Willow, a descendant of the original enormous tree which was much admired and visited by Samuel Johnson. In 2021 a fifth descendant was installed.
*The Franciscan Friary,Lichfield, The Franciscan Friary - The ruins of the former Friary in Lichfield, now classed as a Scheduled monument, Scheduled Ancient Monument.
*Lichfield Clock Tower - A Grade II listed 19th century clock tower, located south of Festival Gardens.
* Letocetum - The remains of a Roman staging post and bath house, in the village of Wall, south of the city.
*Staffordshire Regiment Museum - east of the city in Whittington, Staffordshire, Whittington, the museum covers the regiment's history, activities and members, and includes photographs, uniforms, weapons, medals, artefacts, memorabilia and regimental regalia. Outdoors is a replica trench from World War I, and several armoured fighting vehicles.
*National Memorial Arboretum - north east of the city in Alrewas, the Arboretum is a national site of remembrance and contains many memorials to the armed services.
Transport


Railway
Lichfield is served by two railway stations: Lichfield City railway station, Lichfield City and Lichfield Trent Valley railway station, Lichfield Trent Valley, both built by the London and North Western Railway. These stations are now on the Cross-City Line to Redditch railway station, Redditch via Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham. Additionally, Trent Valley station is on the West Coast Main Line with semi-fast services between Euston railway station, London Euston, Stoke-on-Trent railway station, Stoke-on-Trent, Stafford railway station, Stafford and Crewe railway station, Crewe. Despite being north of Birmingham, trains to London Euston can take as little as 1 hour 9 minutes. Lichfield City is located in the city centre and Lichfield Trent Valley is located or 20 minutes walk north-east of the city centre.Buses
Lichfield has regular bus services in and around the city, in addition to longer distance services. The bus station is located on Birmingham Road, opposite Lichfield City railway station, although as part of the Friarsgate development plans have been approved for it to be moved next to the railway station. Arriva Midlands, Diamond West Midlands, Diamond Bus, D&G Bus, Select Bus, Midland Classic and National Express West Midlands are the main bus operators in Lichfield. These companies run regular services to Birmingham, Aldridge, Brownhills, Burntwood, Rugeley, Burton upon Trent,Stafford
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It lies about north of Wolverhampton, south of Stoke-on-Trent and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 70,145 in t ...
, Sutton Coldfield, Tamworth and Walsall.
Lichfield has college services for the Rodbaston campus of South Staffordshire College, run by Midland Classic, and school-only journeys for local high schools. Seasonal bus routes run for Boots and Amazon employees only are usually operated by Midland Classic and National Express West Midlands.
Road
Lichfield is centrally located on the Roads in the United Kingdom, UK road network. Historically, the Roman roads in Britain, Roman roads of Watling Street and Icknield Street, Ryknild Street crossed south of the city at Letocetum; today, they follow much of the same routes as the A5 road (Great Britain), A5 and A38 road, A38. The A5 runs west towards Wales and south-east towards Tamworth. The A38 runs south to Birmingham and north-east to Derby. Running along the western perimeter of the city is the A51 road, which runs north to Chester and south-east to Tamworth. The nearest motorway junction is T5 of the M6 Toll, located south of the city. Junction 9 of the M42 motorway, M42 and junction 4A of the M6 motorway, M6 are and to the south respectively.Canal
Lichfield Canal was historically part of the Wyrley and Essington Canal and ran south of the city from 1797 until it was abandoned in 1955. Starting in the 1990s, a works programme started to restore the canal along much of its original route and make it navigable by 2025. As of 2011, none of the stretch of canal is navigable. The nearest navigable canal to Lichfield is the Coventry Canal which runs through Streethay.Air
Two nearby airports serve Lichfield: Birmingham Airport is to the south and East Midlands Airport is to the north-east.Education

 In addition to nine primary schools and one infant school, Lichfield has three secondary schools:
* The Friary School
* King Edward VI School, Lichfield, King Edward VI School (''formerly Lichfield Grammar School'')
* Nether Stowe School, a comprehensive school with specialist Maths and Computing college status
There are two independent schools:
*Lichfield Cathedral School: A co-educational school for ages 3 to 18, based in the Cathedral Close and Longdon, Staffordshire, Longdon.
*Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes School: A DfES Approved Special School for dyslexic children.
The Lichfield campus of Staffordshire University and South Staffordshire College is located on the Friary. This campus facility was opened in 1998 and offers further and higher education courses up to and including master's degrees. A £3 million school of art, design and media, housed in purpose-built accommodation, opened in 2006. This facility received the highest possible grade of 'outstanding provision' in the latest Ofsted inspection report.
In addition to nine primary schools and one infant school, Lichfield has three secondary schools:
* The Friary School
* King Edward VI School, Lichfield, King Edward VI School (''formerly Lichfield Grammar School'')
* Nether Stowe School, a comprehensive school with specialist Maths and Computing college status
There are two independent schools:
*Lichfield Cathedral School: A co-educational school for ages 3 to 18, based in the Cathedral Close and Longdon, Staffordshire, Longdon.
*Maple Hayes, Maple Hayes School: A DfES Approved Special School for dyslexic children.
The Lichfield campus of Staffordshire University and South Staffordshire College is located on the Friary. This campus facility was opened in 1998 and offers further and higher education courses up to and including master's degrees. A £3 million school of art, design and media, housed in purpose-built accommodation, opened in 2006. This facility received the highest possible grade of 'outstanding provision' in the latest Ofsted inspection report.
Religion and beliefs
Some 66.5% of the people in the Lichfield parish area polled as part of the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census described themselves as Christian. Lichfield has held a religious importance since St Chad became the first Bishop of Lichfield and built a monastery in 669 AD. After Chad's death in 672 AD he was buried in anAnglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
church which later became part of Lichfield Cathedral.
Anglicanism predominates, with three parishes as well as the cathedral. St Michael on Greenhill, Lichfield, St Michael's and St Mary's Church, Lichfield, St Mary's serve one parish and Christ Church, Lichfield, Christ Church and The Church of St Chad, Lichfield, St Chad's serve the other two. Lichfield is within the Diocese of Lichfield and represented by Michael Ipgrave, the current Bishop of Lichfield.
There are two Catholic Church, Roman Catholic churches, Holy Cross and SS Peter & Paul, which are part of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Birmingham, Archdiocese of Birmingham. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has a meeting house on Purcell Avenue on the north side of the city. In the city centre there is a Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist church and Wade Street Church, which is a United Reformed Church, United Reformed and Baptists, Baptist church. There is a Pentecostalism, Pentecostal Church under the name Emmanuel Christian Centre in Nether Stowe and the Christadelphians, Christadelphian Hall on Station Road. Jehovah's Witnesses have a Kingdom Hall on Lombard Street.
There are five faith schools in the city, all of which are primary schools. St Michael's C of E School, Christ Church C of E School and St Chad's C of E (VC) School are all Church of England faith schools. St Joseph's RC School and SS Peter & Paul School are Roman Catholic faith schools.
Sport
Historically Rugby Union, rugby was more popular in the city than soccer, football largely due to the fact that it was the main sport at King Edward VI School (Lichfield), Lichfield Grammar School. However, both sports have remained at amateur level. Lichfield Rugby Union Football Club was founded in 1874. As of the 2011–12 season they play in the Midlands 1 West League, which is the 6th level of the English rugby union system, English Rugby Union system. The team plays at Cooke Fields, located south east of the city on Tamworth Road, behind the Horse and Jockey public house. AFC Lichfield are an FA Chartered Standard community youth football club and currently have teams playing in the Lichfield & District Recreational League at all levels from under 6 to under 18. AFC Lichfield also boast a football academy offering FA coaching to boys and girls aged 4–8 years. Lichfield City F.C. play in the Premier Division of the Midland Football League (2014), Midland Football League after promotion in 2012. The 1st team play at Brownsfield Park. LCFC are a FA Charter Community club with teams from under 7s to adults. Lichfield Diamonds LFC is at the forefront of girls' football in Staffordshire, being the first all female club to achieve Charter Standard Status. The team plays at the Collins Hill Sports Ground. Lichfield Cricket Club currently play in the Third Division of the Birmingham and District Premier League. They also play at the Collins Hill Sports Ground. Lichfield is served by four golf courses, including the local authority 18-hole course at Beacon Park. The others are: Darnford Moors Golf Club, a new facility in the south of the city which provides a 9-hole pay and play facility, and the Robert Rock Academy, a driving range and coaching academy; Lichfield Country Club, based in Elmhurst, Staffordshire, Elmhurst, which boasts an 18-hole par 72 championship course and the English Midlands, Midlands' first American-specification 9 hole par 3 course; and Whittington Heath Golf Club, an 18-hole par 70 course south-east of the city, laid out on heath (habitat), heathland and woodland. Lichfield Archers were formed over 40 years ago and shoot at Christian Fields, where they have 20-yard indoor and 100-yard outdoor ranges. Apart from club competitions, the club also holds Inter-County and Inter-Club shoots and have held the Staffordshire Outdoor Championshipe at Christian Fields Lichfield Hockey Club located on Collins Hill Sports Ground on Eastern Avenue is a highly successful club for both men and women, and has a large junior section. The women's section boasts six Saturday teams competing at varying levels and the men's side has over ten teams. On 21 March 2015 the men's section won the league with a 3–2 win over Barton, meaning they were promoted to national league for the forthcoming season of 2015/16. The Wandering Angels, a team from Lichfield in Staffordshire took part in the first known Womens FA Cup Match on 1 November 1970 against Leicester City Supporters Ladies FC.Notable Lichfeldians




 * Ceatta of Lichfield, an obscure 11th century Anglo Saxon saint of the Catholic Church.
* Ceatta of Lichfield, an obscure 11th century Anglo Saxon saint of the Catholic Church.
16th c.
*Edward Wightman
Edward Wightman (1566 – 11 April 1612) was an English Radical Reformation, radical Anabaptist Minister (Christianity), minister, executed at Lichfield on charges of heresy. He was the last person to be Execution by burning, burned at the stake ...
(?1566–1612), last person in England to be burnt at the stake for heresy, in the Market Place of Lichfield
* Edmund Gennings (1567–1591), Jesuit priest and martyr
17th c.
* Thomas Minors (1609–1677) merchant, politician, MP from 1654 to 1660 and ''commissioner for scandalous ministers'' * Michael Biddulph (died 1666), Michael Biddulph (1610–1666) elected MP for Lichfield (UK Parliament constituency), Lichfield in 1660 in the Convention Parliament * Elias Ashmole (1617–1692), antiquary, politician, astrologer and alchemist. founder of Ashmolean Museum * Edward Wetenhall (1636–1713), English bishop of the Church of Ireland * Gregory King (1648–1712), genealogist, engraver and statistician * John Floyer (physician), John Floyer (1649 in Hints, Staffordshire, Hints – 1734), physician and author * Richard Dyott (died 1719), Richard Dyott (1667–1719) elected MP for Lichfield (UK Parliament constituency), Lichfield 1690/1695, re-elected 1698/1708, elected again 1710/1715 * Joseph Addison (1672–1719), essayist, poet, playwright, and politician. * Gilbert Walmisley (1680–1751), barrister, friend ofSamuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
, buried in a vault near the south side of Lichfield Cathedral.
* Theophilus Levett (1693–1746), attorney, town clerk of Lichfield, politician and landowner,
18th c.
* John Wyatt (inventor), John Wyatt (1700–1766), inventor, particularly of a spinning machine * Thomas Newton (1704–1782), cleric, biblical scholar and Bishop of Bristol, 1761 to 1782. *Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford ...
(1709–1784), often referred to as ''Dr Johnson'', was an English writer, poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor, and lexicographer
* Richard Greene (antiquary), Richard Greene (1716–1793) antiquary and collector of curiosities.
* David Garrick
David Garrick (19 February 1717 – 20 January 1779) was an English actor, playwright, theatre manager and producer who influenced nearly all aspects of European theatrical practice throughout the 18th century, and was a pupil and friend of Sa ...
(1717–1779), actor, playwright, producer and theatre manager
* Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet.
His poems ...
(1731–1802), scientist, inventor and grandfather of Charles Darwin
* Anna Seward (1742–1809), romantic poet, memorialist and letter writer
* Richard Lovell Edgeworth (1744–1817), politician, writer, inventor, lived at Stowe House
* Theophilus Houlbrooke (1745–1824), minister and amateur botanist, President of the Liverpool Athenaeum from 1809 to 1813
* General Richard Vyse (1746–1825), general and MP for Beverley (UK Parliament constituency), Beverley in 1806
* Joseph Potter (architect), Joseph Potter (1756–1842) architect and builder, considerable practice in Staffordshire and neighbouring counties
* Thomas Day (writer), Thomas Day (1748–1789), author and abolitionist, lived for a time at Stowe House
* Henry Salt (Egyptologist), Henry Salt (1780–1827), antiquarian; gave Egyptian collection to the British Museum
* Admiral of the Fleet Sir William Parker, 1st Baronet, of Shenstone (1781–1866), a Royal Navy officer
19th c.
* John Hewitt (antiquary), John Hewitt (1807–1878), antiquarian * James Fowler (architect), James Fowler (1828–1892), aka "Fowler of Louth", a Victorian ecclesiastical architect * Richard Garnett (writer), Richard Garnett (1835–1906), scholar, librarian, biographer and poet * Walter Noel Hartley (1845–1913), chemist and pioneer of spectroscopy * Frederic King (1853–1933), baritone * Lieutenant-Colonel Michael Swinfen-Broun JP (1858-1948), soldier, magistrate, High Sheriff of Staffordshire, High Sheriff and Deputy Lieutenant of Staffordshire * Mary Alice Eleanor Richards, British botanist and prolific collector of Zambian plants20th c.



Sport
* Tommy Skelton (1856–1900), jockey, rode the winner of the Grand National 1886, ''Old Joe'' * Roly Harper (1881–1949), professional footballer, born in Lichfield * Noel George (1897–1929), goalkeeper for Wolverhampton Wanderers F.C., Wolves, died of a disease of the gums * Roger Pearman (cricketer), Roger Pearman (1943–2009), cricketer and cricket administrator * Tom Leadbitter (1945–1995), scrambles, motorcycle speedway and grasstrack rider * Jason Robinson (cricketer), Jason Robinson (born 1965), cricketer * Ian Wright (footballer, born 1972), Ian Wright (born 1972) former footballer,retrieved December 2017
Twinnings
Following the Second World War, to try and help prevent another global conflict and to ease relations between, and stop prejudices against nations, the City of Lichfield was twinned with: Daily newspapers from Limburg and Sainte-Foy are available at Lichfield Library.See also
* ''The Beaux' Stratagem'' by George Farquhar, play set in Lichfield in 1707 * Bishop of Lichfield, Bishops of Lichfield * Earl of Lichfield * Listed buildings in Lichfield * Garrick Theatre (Lichfield), Garrick Theatre * Heart of England Way * Lichfield Bower * Lichfield Canal * Lichfield Cricket Club * Lichfield Gospels, The Lichfield Gospels * Lichfield Rugby Union Football Club * RAF LichfieldReferences
External links
Lichfield City Council
Visit Lichfield - Travel and Tourism body
* * {{Authority control Lichfield, Burial sites of the House of Icel Cities in the West Midlands (region) Civil parishes in Staffordshire Towns in Staffordshire