Libyan Expatriates In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Demographics of Libya is the demography of Libya, specifically covering population density,
 Historically Berber, over the centuries, Libya has been occupied by the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Italians. The Phoenicians had a big impact on Libya. Many of the coastal towns and cities of Libya were founded by the Phoenicians as trade outposts within the southern Mediterranean coast in order to facilitate the Phoenician business activities in the area. Starting in the 8th century BC, Libya was under the rule of the Phoenician Carthage. After the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War, Libya became a Roman province under the name of Tripolitania until the 7th century AD when Libya was conquered by the Arab Muslims as part of the
Historically Berber, over the centuries, Libya has been occupied by the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Italians. The Phoenicians had a big impact on Libya. Many of the coastal towns and cities of Libya were founded by the Phoenicians as trade outposts within the southern Mediterranean coast in order to facilitate the Phoenician business activities in the area. Starting in the 8th century BC, Libya was under the rule of the Phoenician Carthage. After the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War, Libya became a Roman province under the name of Tripolitania until the 7th century AD when Libya was conquered by the Arab Muslims as part of the
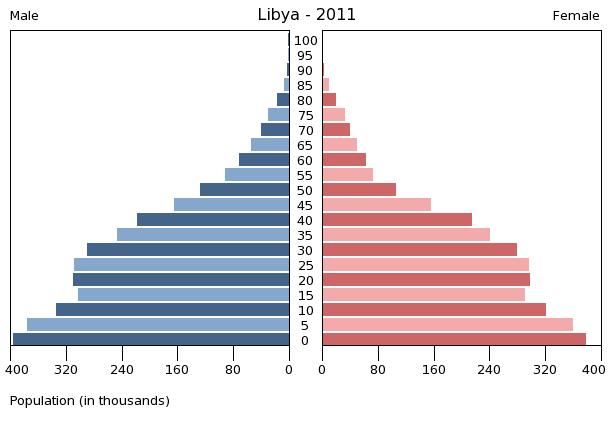
 Libya has a small population residing in a large land area. Population density is about 50 persons per km² (130/sq. mi.) in the two northern regions of
Libya has a small population residing in a large land area. Population density is about 50 persons per km² (130/sq. mi.) in the two northern regions of
 :0-14 years: 33.65% (male 1,184,755/female 1,134,084)
:15-24 years: 15.21% (male 534,245/female 513,728)
:25-54 years: 41.57% (male 1,491,461/female 1,373,086)
:55-64 years: 5.52% (male 186,913/female 193,560)
:65 years and over: 4.04% (male 129,177/female 149,526) (2020 est.)
:0-14 years: 25.53% (male 882,099/ female 842,320)
:15-24 years: 16.81% (male 582,247/ female 553,004)
:25-54 years: 47.47% (male 1,684,019/ female 1,522,027)
:55-64 years: 5.77% (male 197,196/ female 192,320)
:65 years and over: 4.43% (male 147,168/ female 152,107) (2018 est.)
:0-14 years: 33.65% (male 1,184,755/female 1,134,084)
:15-24 years: 15.21% (male 534,245/female 513,728)
:25-54 years: 41.57% (male 1,491,461/female 1,373,086)
:55-64 years: 5.52% (male 186,913/female 193,560)
:65 years and over: 4.04% (male 129,177/female 149,526) (2020 est.)
:0-14 years: 25.53% (male 882,099/ female 842,320)
:15-24 years: 16.81% (male 582,247/ female 553,004)
:25-54 years: 47.47% (male 1,684,019/ female 1,522,027)
:55-64 years: 5.77% (male 197,196/ female 192,320)
:65 years and over: 4.43% (male 147,168/ female 152,107) (2018 est.)
 The foreign population is estimated at 3%, most of whom are migrant workers in the oil industry from Tunisia and Egypt, but also including small numbers of Greeks,
The foreign population is estimated at 3%, most of whom are migrant workers in the oil industry from Tunisia and Egypt, but also including small numbers of Greeks,
Ethnologue report for Libya
Languages of Libya *
Looklex Encyclopedia
Attribution * {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Libya
ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, and religious affiliations, as well as other aspects of the Libyan population. The Libyan population resides in the country of Libya, a territory located on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa, to the west of and adjacent to Egypt. Libyans live in Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
. It is the capital of the country and first in terms of urban population, as well as Benghazi
Benghazi () , ; it, Bengasi; tr, Bingazi; ber, Bernîk, script=Latn; also: ''Bengasi'', ''Benghasi'', ''Banghāzī'', ''Binghāzī'', ''Bengazi''; grc, Βερενίκη (''Berenice'') and ''Hesperides''., group=note (''lit. Son of he Ghazi ...
, Libya's second largest city.
History
 Historically Berber, over the centuries, Libya has been occupied by the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Italians. The Phoenicians had a big impact on Libya. Many of the coastal towns and cities of Libya were founded by the Phoenicians as trade outposts within the southern Mediterranean coast in order to facilitate the Phoenician business activities in the area. Starting in the 8th century BC, Libya was under the rule of the Phoenician Carthage. After the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War, Libya became a Roman province under the name of Tripolitania until the 7th century AD when Libya was conquered by the Arab Muslims as part of the
Historically Berber, over the centuries, Libya has been occupied by the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, and Italians. The Phoenicians had a big impact on Libya. Many of the coastal towns and cities of Libya were founded by the Phoenicians as trade outposts within the southern Mediterranean coast in order to facilitate the Phoenician business activities in the area. Starting in the 8th century BC, Libya was under the rule of the Phoenician Carthage. After the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War, Libya became a Roman province under the name of Tripolitania until the 7th century AD when Libya was conquered by the Arab Muslims as part of the Arab conquest of North Africa
The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb ( ar, الْفَتْحُ الإسلَامِيُّ لِلْمَغرِب) continued the century of rapid Muslim conquests following the death of Muhammad in 632 and into the Byzantine-controlled territories of ...
, and Arab migrations to the region began since then. In the 11th century, major migrations of Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym ( ar, بنو سليم) is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Is ...
from the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
to Libya began, with other nomadic tribes from Eastern Arabia. Centuries after that, the Ottoman Empire conquered Libya in 1551. It remained in control of its territory until 1911 when the country was conquered by Italy. In the 18th century Libya was used as the base for various pirates.the story of the Awlad Sulayman, an Arab group from present-day Libia who dominated northern Lake Chad in the 19th century,. Since the Middle Ages, the populations of this region have shared close political, economic and social ties maintained by the mobility specific to the nomadic way of life. These relationships, fluid due to the difficulties of surviving in this difficult environment, have always been structured in turn, through conflict and cooperation, both of which produced rapidly changing alliances. In the middle of the 18th century, the Awlad Sulayman carved out a vast area of influence for themselves in Sirte and Fezzan by force of arms and by their alliances with neighboring peoples and the Libian administration. Defeated by the Ottoman administration in Tripoli at the end of the 1830s, the survivors of the Awlad Sulayman took refuge in the Lake Chad basin where they reconstituted the conditions for their success in Libya; they controlled trans-Saharan trade and maintained their links with Libian society. Despite the limits imposed on their action by the French colonization of Chad and the Italian colonization of Libia; the Awlad Sulayman retained regional influence during colonial times and appear to maintain it today.
In the Second World War Libya was one of the main battlegrounds of North Africa. During the war, the territory was under an Anglo-French military government until it was overrun by the Axis Powers, who, in turn, were defeated by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in 1943.
In 1951, the country was granted independence by the United Nations, being governed by King Idris
Muhammad Idris bin Muhammad al-Mahdi as-Senussi ( ar, إدريس, Idrīs; 13 March 1890 – 25 May 1983) was a Libyan political and religious leader who was King of Libya from 24 December 1951 until his overthrow on 1 September 1969. He ruled ov ...
. In 1969, a military coup led by Muammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by ''The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
resulted in the overthrow of King Idris I. Gaddafi then established an anti-Western leadership. In 1970, Gaddafi ordered all British and American military bases closed.
The Libyan population has increased rapidly after 1969. They were only 2 million in 1968, and 5 million in 2006. . Many migrant workers came to Libya since 1969. Among the workers were construction workers and laborers from Tunisia, teachers and laborers from Egypt, teachers from Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, and doctors and nurses from Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. 1,000,000 workers, mainly from other neighboring African countries like Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, Niger, Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
and Mali, migrated to Libya in the 1990s, after changes were made to Libya's Pan-African policies.http://www.temehu.com/Libyan-People.htm Temehu. Libyan people and Ethnic tribes. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
Gaddafi used money from the sale of oil to improve the living conditions of the population and to assist Palestinian guerrillas in their fight against the Israelis. In 1979, Libya fought in Uganda to assist the government of Idi Amin in the Ugandan Civil War, and in 1981, fought in the Libyan-Chadian War. Libya had occupied the Aozou Strip; however, in 1990 the International Court of Justice submitted the case and allowed the full recuperation of territory to Chad.
In September 2008, Italy and Libya signed a memorandum by which Italy would pay $5 billion over the next 20 years to compensate Libya for its dominion over Libya for its reign of 30 years.http://www.hejleh.com/countries/libya.html The Country & People of Libya. Posted 2003. Retrieved January 4, 2012, to 23:53 pm.
Since 2011, the country is swept by Libyan Civil War, which broke out between the Anti-Gaddafi rebels and the Pro-Gaddafi government in 2011, culminating in the death and overthrow of Gaddafi. Nevertheless, even today Libya still continues to generate problems within the area and beyond, greatly affecting its population and the migrant route to Europe.
Population

 Libya has a small population residing in a large land area. Population density is about 50 persons per km² (130/sq. mi.) in the two northern regions of
Libya has a small population residing in a large land area. Population density is about 50 persons per km² (130/sq. mi.) in the two northern regions of Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province o ...
and Cyrenaica, but falls to less than one person per km² (2.7/sq. mi.) elsewhere. Ninety percent of the people live in less than 10% of the area, primarily along the coast. About 90% of the population is urban, mostly concentrated in the four largest cities, Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
, Benghazi
Benghazi () , ; it, Bengasi; tr, Bingazi; ber, Bernîk, script=Latn; also: ''Bengasi'', ''Benghasi'', ''Banghāzī'', ''Binghāzī'', ''Bengazi''; grc, Βερενίκη (''Berenice'') and ''Hesperides''., group=note (''lit. Son of he Ghazi ...
, Misrata
Misrata ( ; also spelled Misurata or Misratah; ar, مصراتة, Miṣrāta ) is a city in the Misrata District in northwestern Libya, situated to the east of Tripoli and west of Benghazi on the Mediterranean coast near Cape Misrata. With ...
and Bayda. As of 2019, twenty-eight percent of the population is estimated to be under the age of 15, but this proportion has decreased considerably during the past decades. The majority of the population of Libya is composed of Arabs.
Age distribution
Data taken from United Nations Demographic Yearbook 2020 Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (1.VII.2015):Population history
Population census
Eight population censuses have been carried out in Libya, the first in 1931 and the most recent one in 2006. The population multiplied sixfold between 1931 and 2006.Vital statistics
During the past 60 years the demographic situation of Libya changed considerably. Since the 1950s, life expectancy increased steadily and the infant mortality rates decreased. As the fertility rates remained high until the 1980s (the number of births tripled between 1950–55 and 1980–85), population growth was very high for three decades. However, after 1985 a fast decrease in fertility was observed from over 7 children per woman in the beginning of the 1980s to less than 3 in 2005-2010. Because of this decrease in fertility the population growth slowed down and also the proportion of Libyans under the age of 15 decreased from 45% in 1985 to 29% in 2010.Births and deaths
Source: UN DESA, World Population Prospects, 2022Other demographic statistics
Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022. *One birth every 4 minutes *One death every 15 minutes *One net migrant every 288 minutes *Net gain of one person in the population of libya every 6 minutes..CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from theCIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
.
Population
:7,137,931 (2022 est.) :6,754,507 (July 2018 est.) :note: immigrants make up just over 12% of the total population, according to UN data (2019)Religions
:Muslim (official; virtually all Sunni) 96.6%, Christian 2.7%, Buddhist <1%, Hindu <1%, Jewish <1%, folk religion <1%, other <1%, unafilliated <1% (2020 est.) :note: non-Sunni Muslims include native Ibadhi Muslims (<1% of the population) and foreign MuslimsAge structure
 :0-14 years: 33.65% (male 1,184,755/female 1,134,084)
:15-24 years: 15.21% (male 534,245/female 513,728)
:25-54 years: 41.57% (male 1,491,461/female 1,373,086)
:55-64 years: 5.52% (male 186,913/female 193,560)
:65 years and over: 4.04% (male 129,177/female 149,526) (2020 est.)
:0-14 years: 25.53% (male 882,099/ female 842,320)
:15-24 years: 16.81% (male 582,247/ female 553,004)
:25-54 years: 47.47% (male 1,684,019/ female 1,522,027)
:55-64 years: 5.77% (male 197,196/ female 192,320)
:65 years and over: 4.43% (male 147,168/ female 152,107) (2018 est.)
:0-14 years: 33.65% (male 1,184,755/female 1,134,084)
:15-24 years: 15.21% (male 534,245/female 513,728)
:25-54 years: 41.57% (male 1,491,461/female 1,373,086)
:55-64 years: 5.52% (male 186,913/female 193,560)
:65 years and over: 4.04% (male 129,177/female 149,526) (2020 est.)
:0-14 years: 25.53% (male 882,099/ female 842,320)
:15-24 years: 16.81% (male 582,247/ female 553,004)
:25-54 years: 47.47% (male 1,684,019/ female 1,522,027)
:55-64 years: 5.77% (male 197,196/ female 192,320)
:65 years and over: 4.43% (male 147,168/ female 152,107) (2018 est.)
Median age
:total: 25.8 years. Country comparison to the world: 156th :male: 25.9 years :female: 25.7 years (2020 est.) :total: 29.4 years :male: 29.5 years :female: 29.2 years (2018 est.)Population growth rate
:1.65% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 57th :1.45% (2018 est.)Birth rate
:21.56 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 62th :17.2 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)Death rate
:3.45 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 221st :3.7 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)Net migration rate
:-1.61 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 161st :0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)Total fertility rate
:3.09 children born/woman (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 46th :3.71 children born/woman (2000 est.) :3.01 children born/woman (2010 est.) :2.12 children born/woman (2012 est.) :2.03 children born/woman (2018 est.)Contraceptive prevalence rate
:27.7% (2014)Urbanization
:urban population: 80.1% of total population (2018) :rate of urbanization: 1.68% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Sex ratio
:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female :0–14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female :15–24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female :25–54 years: 1.1 male(s)/female :55–64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female :65 years and over: 1.01 male(s)/female :total population: 1.07 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Infant mortality rate
:total: 10.5 deaths/1,000 live births :male: 11.3 deaths/1,000 live births :female: 9.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)Urbanization
:urban population: 81.3% of total population (2022) :rate of urbanization: 1.45% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)Life expectancy at birth
:Total population: 73.08 years. (2020 est.) : :Male: 70.27 years. (2020 est.) :Female: 76.11 years. (2020 est.) : : : :Total population: 73.44 years. (2022 est.) :Male: 70.6 years. (2022 est.) : :Female: 76.46 years. (2022 est.) :Country comparison to the world: 110rdLiteracy
:Definition: The percentage of the population of a given age group that can read and write :Total population: 91% :Male: 96.7% :Female: 85.6% (2015)Ethnic and tribal groups
Ethnic groups
97% of Libya's population is made up of Arabs andBerbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
, of which 92% are Arabs and 5% are Berbers.
The majority of the population of Libya is primarily of Arab ancestral origin. Unofficial estimates put the number of Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
in Libya at around 600,000, about 10% of the population of Libya. Among the Berber groups are the minority Berber populations of Zuwarah and the Nafusa Mountains, and the nomadic Tuareg, who inhabit the southwestern areas as well as parts of southeastern Algeria, northern Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso. In the southeast, there are small populations of Toubou (Tibbu). They occupy about a quarter of the country and also inhabit Niger and Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
. Among foreign residents, the largest groups are from other African nations, including citizens of other North African nations (primarily Egyptians) and West Africans.
Tribal groups
Libyan society is to a large extent structured along tribal lines, with more than 20 major tribal groups. The major tribal groups of Libya in 2011 were listed: * Tripolitan settled tribes: Misurata Ahali, Misurata Karagula, Geryan, Zawia, Misalata, Zwara Berber, Khumus * Tripolitan Bedouin tribes:Warfalla
The Warfalla ( ar, ورفلة) is a tribe that resides in the west of Libya, in the town of Bani Walid, their stronghold. Usually estimated to be Libya’s largest tribe with up to one million of the total population of about 6 million people, the ...
, Tarhona, Al-Zintan, Al-Rijban, Awlad Suleiman
*Cyrenaican
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
Bedouin tribes: Al-Awagir, Al-Abaydat, Drasa, Al-Barasa, Al-Fawakhir, Al-Zuwayya, Al-Majabra
*Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar G ...
Bedouin: Awlad Suleiman, Qadhadhfa
The Qadhadhfa (also ''al-Qaddafa'', ''Gaddadfa'', ''Qaddadfa'', ''Gaddafa''; ar, القذاذفـة) is one of the Arab Ashraf tribes in Libya, living in the Sirte District in present-day northwestern Libya. They are traditionally counted among ...
, Al-Magarha, Al-Magharba, Al-Riyyah, Al-Haraba, Al-Zuwaid, Al-Guwaid
* Fezzan: Awlad Suleiman, Hutman, Hassawna, Toubou, Tuareg
* Kufra: Al-Zuwayya; Toubou
Some of the ancient Berber tribes include: Adyrmachidae, Auschisae, Es'bet, Temeh'u, Teh'nu, Rebu, Kehek, KeyKesh, Imukehek, Meshwesh, Macetae, Macatutae, Nasamones, Nitriotae, and Tautamaei.
the major tribal groups of Libya, by region, were as follows:
* Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province o ...
: alawana-Souk El Joma'a, AL-Mahameed, Warfalla, Tarhona, Misurata tribes, Al-Jawary, Siyan Tribe, The Warshfana tribes, Zawia Groups, Ghryan Tribes, AL-Asabea, Al-Fwatir, Awlad Busayf, Zintan, Al-jbalya, Zwara, Alajelat, Al-Nawael tribe, Alalqa tribe, Al-Rijban, al Mashashi, Amaym.
* Cyrenaica: AJ-JWAZY, Al-Awagir, Magharba, Al-Abaydat, Drasa, Al-Barasa, Al-Fawakhir, Zuwayya, Majabra, Awama, Minfa, Taraki, alawana, Shwa'ir and in Kufra Zuwayya, Toubou.
* Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar G ...
: Awlad Suleiman, Qadhadhfa, Magharba, Al-Hosoon, Ferrjan
* Fezzan: Awlad Suleiman, Al-Riyyah, Magarha, Al-Zuwaid, Al-Hutman, Al-Hassawna; Toubou, Tuareg.
* Kufra: Zuwayya; Toubou.
Foreign population
 The foreign population is estimated at 3%, most of whom are migrant workers in the oil industry from Tunisia and Egypt, but also including small numbers of Greeks,
The foreign population is estimated at 3%, most of whom are migrant workers in the oil industry from Tunisia and Egypt, but also including small numbers of Greeks, Maltese
Maltese may refer to:
* Someone or something of, from, or related to Malta
* Maltese alphabet
* Maltese cuisine
* Maltese culture
* Maltese language, the Semitic language spoken by Maltese people
* Maltese people, people from Malta or of Malte ...
, Italians, Pakistanis
Pakistanis ( ur, , translit=Pākistānī Qaum, ) are the citizens and nationals of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. According to the 2017 Pakistani national census, the population of Pakistan stood at over 213 million people, making it the w ...
, Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
, Turks, Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, and people from former Yugoslavia. Due to the Libyan Civil War, most of these migrant workers have returned to their homelands or simply left the country for a different one, however a good minority still work in Libya.
According to news accounts in Allafrica.com, and the Libya Herald, between 1 million and 2 million Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
are resident in Libya with Sudanese
Sudanese or Sudanic may refer to:
*pertaining to the country of Sudan
**the people of Sudan, see Demographics of Sudan
*pertaining to Sudan (region)
**Sudanic languages
**Sudanic race, subtype of the Africoid racial category
See also
*Sudanese Civ ...
and Tunisians numbering in the hundreds to thousands. There's also up to a million undocumented migrants mainly from sub-saharan africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
residing in Libya.
Genetics
Y-chromosome
Analysis of Y-chromosome have found that the Libyan population is characterized by the high frequency of haplogroup J1-M267 (39.5%) andhaplogroup E-M81
E-Z827, also known as E1b1b1b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the parent lineage to the E-Z830 and E-L19 subclades, and defines their common phylogeny. The former is predominantly found in the Middle East; the latter is most ...
(33.7%).
Listed here are the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of sh ...
in Libya.
Religions
The vast majority Libyans are nominallySunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagree ...
. Almost 3% of the population is Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, with some local Christian church adherents in Eastern Libya - the Copts
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since antiquity. Most ethnic Copts are C ...
. A small Jewish community historically lived in Libya since antiquity (see History of the Jews in Libya), but the almost the entire Jewish community in Libya eventually fled
''Fled'' is a 1996 American buddy action comedy film directed by Kevin Hooks. It stars Laurence Fishburne and Stephen Baldwin as two prisoners chained together who flee during an escape attempt gone bad.
Plot
An interrogator prepares a man to ...
the country for Italy, Israel, or the United States, particularly after anti-Jewish riots
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
in the wake of the 1967 Six-Day War between Arab countries and Israel. The final Jew in Libya, Esmeralda Meghnagi, died in 2002 ending the several millennia long Jewish ancestral body in Libya.
Culture
Cuisine
Libyan cuisine is mainly Arab and Mediterranean with Italian influence. Notable dishes include Shorba Arabiya, or Arabian soup, which is a thick, highly spiced soup. Like other Maghrebi countries, couscous and tajine are traditional of Libya.Bazeen
Bazin ( ar, البازين, pronounced , is an unleavened bread in the cuisine of Libya prepared with barley, water and salt. Bazin is prepared by boiling barley flour in water and then beating it to create a dough using a ''magraf'', which is a u ...
is a traditional Libyan food, made from a mix of barley flour and a small amount of plain flour.
Music
Libyan music is largely Arab in nature, however someAndalusi The Arabic '' nisbah'' (attributive title) Al-Andalusi denotes an origin from Al-Andalus. Al-Andalusi may refer to:
* Abu Hayyan al-Gharnati
* Ibn Hazm
* Ibn Juzayy
* Ibn 'Atiyya
* Said Al-Andalusi
* Yaʿīsh ibn Ibrāhīm al-Umawī
See also
* A ...
and Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
cultures also exist. Libyan origin instruments are the Zukra The zukra (zokra, zoughara, ar, زكرة) is a Libyan bagpipe with a double-chanter terminating in two cow horns; it is similar in construction to the Tunisian ''mizwad''.
The instrument is played as a bagpipe in the south and west of Libya, but p ...
(a bagpipe), a flute (made of bamboo), the tambourine, the oud (a fretless lute) and the darbuka
The goblet drum (also chalice drum, tarabuka, tarabaki, darbuka, darabuka, derbake, debuka, doumbek, dumbec, dumbeg, dumbelek, toumperleki, tumbak, or zerbaghali; arz, دربوكة / Romanized: ) is a single-head membranophone with a goblet- ...
(a goblet drum held sideways and played with the fingers). Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and A ...
poet-singers had a great influence on the musical folklore of Libya, particularly the style of '' huda'', the camel driver's song.
Language
The official language of Libya isStandard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also refe ...
, while the most prevalent spoken language is Libyan Arabic
Libyan Arabic ( ar, ليبي, Lībī) is a variety of Arabic spoken mainly in Libya, and neighboring countries. It can be divided into two major dialect areas; the eastern centred in Benghazi and Bayda, and the western centred in Tripoli and M ...
. Arabic varieties are partly spoken by immigrant workers and partly by local Libyan populations. These varieties include Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
, Tunisian, Sudanese
Sudanese or Sudanic may refer to:
*pertaining to the country of Sudan
**the people of Sudan, see Demographics of Sudan
*pertaining to Sudan (region)
**Sudanic languages
**Sudanic race, subtype of the Africoid racial category
See also
*Sudanese Civ ...
, Moroccan, Yemeni, Hassaniya and South Levantine Arabic. Minority Berber languages
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber commun ...
are still spoken by the Tuareg, a rural Berber population inhabiting Libya's south, and is spoken by about 300,000 in the north, about 5% of the Libyan population.
Indigenous minority languages in Libya:Languages of Libya *
Berber languages
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber commun ...
: ca. 305,000 speakers (5% of the population)
**Nafusi
Nafusi (also spelt Nefusi; ber, Ažbali / Maziɣ / Mazoɣ, script=Latn, label=in Nafusi) is a Berber language spoken in the Nafusa Mountains (), a large area in northwestern Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State ...
: 184,000 speakers (2006) (3%)
**Tamahaq
Tamahaq (''Tahaggart Tamahaq'', ''Tamahaq Tahaggart'') is the only known Northern Tuareg language, spoken in Algeria, western Libya and northern Niger. It varies little from the Southern Tuareg languages of the Aïr Mountains, Azawagh and Adagh ...
: 47,000 speakers (2006) (<1%)
**Ghadamès
Ghadames or Ghadamis (Berber: ''ʕadémis''; ar, غدامس, Libyan vernacular: ''ɣdāməs'', Latin: ''Cidamus, Cydamus'', it, Gadames) is an oasis Berber town in the Nalut District of the Tripolitania region in northwestern Libya.
The indi ...
: 30,000 speakers (2006) (<1%)
**Sawknah
Sokna (also ''Sawknah'', ''Sukna''; native name: Tasuknit) is a presumably extinct Eastern Berber language which was spoken in the town of Sokna (''Isuknan'') and the village of Fuqaha in northeastern Fezzan in Libya. According to Václav Blaž ...
: 5,600 speakers (2006) (<1%)
** Awjilah: 3,000 speakers (2000) (<1%)
*Domari
Domari is an endangered Indo-Aryan language, spoken by Dom people scattered across the Middle East and North Africa. The language is reported to be spoken as far north as Azerbaijan and as far south as central Sudan, in Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Palest ...
: ca. 33,000 speakers (2006) (<1%)
*Tedaga
The Teda language, also known as Tedaga, is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Teda, a northern subgroup of the Toubou people that inhabits southern Libya, northern Chad and eastern Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type ...
: 2,000 speakers (<1%)
Non-Arabic languages had largely been spoken by foreign workers (who had been massively employed in Libya in various infrastructure projects prior to the 2011 civil war), and those languages with more than 10,000 speakers included Punjabi, Urdu, Mandarin, Cantonese, Korean, Sinhala, Bengal, Tamil, Tagalog, French, Italian, Ukrainian, Serbian, and English.
See also
*Health in Libya A health care crisis currently exists in Libya due to the ongoing conflict.
History
There has been a crisis in the health system in Libya in the past six years following the Libyan Civil War (2011), Libyan Revolution in 2011. Prior to the Libyan ...
* List of Ashraf tribes in Libya
Libyan society is composed of several tribes. The word (, ) refers to persons claiming descent from the family of the prophet Muhammad, often but not exclusively by way of his daughter Fatimah. The word is the plural of ('noble', 'highborn'), ...
References
External links
Looklex Encyclopedia
Attribution * {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Libya