Liberty Foundation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word
 The modern concept of political liberty has its origins in the Greek concepts of freedom and slavery. To be free, to the Greeks, was not to have a master, to be independent from a master (to live as one likes). That was the original Greek concept of freedom. It is closely linked with the concept of democracy, as Aristotle put it:
:"This, then, is one note of liberty which all democrats affirm to be the principle of their state. Another is that a man should live as he likes. This, they say, is the privilege of a freeman, since, on the other hand, not to live as a man likes is the mark of a slave. This is the second characteristic of democracy, whence has arisen the claim of men to be ruled by none, if possible, or, if this is impossible, to rule and be ruled in turns; and so it contributes to the freedom based upon equality."
This applied only to free men. In Athens, for instance, women could not vote or hold office and were legally and socially dependent on a male relative.
The populations of the
The modern concept of political liberty has its origins in the Greek concepts of freedom and slavery. To be free, to the Greeks, was not to have a master, to be independent from a master (to live as one likes). That was the original Greek concept of freedom. It is closely linked with the concept of democracy, as Aristotle put it:
:"This, then, is one note of liberty which all democrats affirm to be the principle of their state. Another is that a man should live as he likes. This, they say, is the privilege of a freeman, since, on the other hand, not to live as a man likes is the mark of a slave. This is the second characteristic of democracy, whence has arisen the claim of men to be ruled by none, if possible, or, if this is impossible, to rule and be ruled in turns; and so it contributes to the freedom based upon equality."
This applied only to free men. In Athens, for instance, women could not vote or hold office and were legally and socially dependent on a male relative.
The populations of the
 The
The
"Chapter I: Introductory"
''On Liberty''.
 England (and, following the
England (and, following the
 According to the 1776 United States Declaration of Independence, all people have a natural right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness". But this declaration of liberty was troubled from the outset by the institutionalization of legalized Black slavery. Slave owners argued that their liberty was paramount since it involved property, their slaves, and that Blacks had no rights that any White man was obliged to recognize. The Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott decision, upheld this principle. It was not until 1866, following the Civil War, that the US Constitution was amended to extend limited rights to persons of color, and not until 1920 that voting rights were extended to women.
By the later half of the 20th century, liberty was expanded further to prohibit government interference with personal choices. In the United States Supreme Court decision '' Griswold v. Connecticut'', Justice William O. Douglas argued that liberties relating to personal relationships, such as marriage, have a unique primacy of place in the hierarchy of freedoms. Jacob M. Appel has summarized this principle:
In modern America, various competing ideologies have divergent views about how best to promote liberty. Liberals in the original sense of the word see equality as a necessary component of freedom. Progressives stress freedom from business monopoly as essential. Right-wing libertarians disagree, and see economic and individual freedom as best. The Tea Party movement sees the "big government" as the enemy of freedom. Other major participants in the modern American right-wing libertarian movement include the Libertarian Party, the Free State Project, and the Mises Institute.
According to the 1776 United States Declaration of Independence, all people have a natural right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness". But this declaration of liberty was troubled from the outset by the institutionalization of legalized Black slavery. Slave owners argued that their liberty was paramount since it involved property, their slaves, and that Blacks had no rights that any White man was obliged to recognize. The Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott decision, upheld this principle. It was not until 1866, following the Civil War, that the US Constitution was amended to extend limited rights to persons of color, and not until 1920 that voting rights were extended to women.
By the later half of the 20th century, liberty was expanded further to prohibit government interference with personal choices. In the United States Supreme Court decision '' Griswold v. Connecticut'', Justice William O. Douglas argued that liberties relating to personal relationships, such as marriage, have a unique primacy of place in the hierarchy of freedoms. Jacob M. Appel has summarized this principle:
In modern America, various competing ideologies have divergent views about how best to promote liberty. Liberals in the original sense of the word see equality as a necessary component of freedom. Progressives stress freedom from business monopoly as essential. Right-wing libertarians disagree, and see economic and individual freedom as best. The Tea Party movement sees the "big government" as the enemy of freedom. Other major participants in the modern American right-wing libertarian movement include the Libertarian Party, the Free State Project, and the Mises Institute.
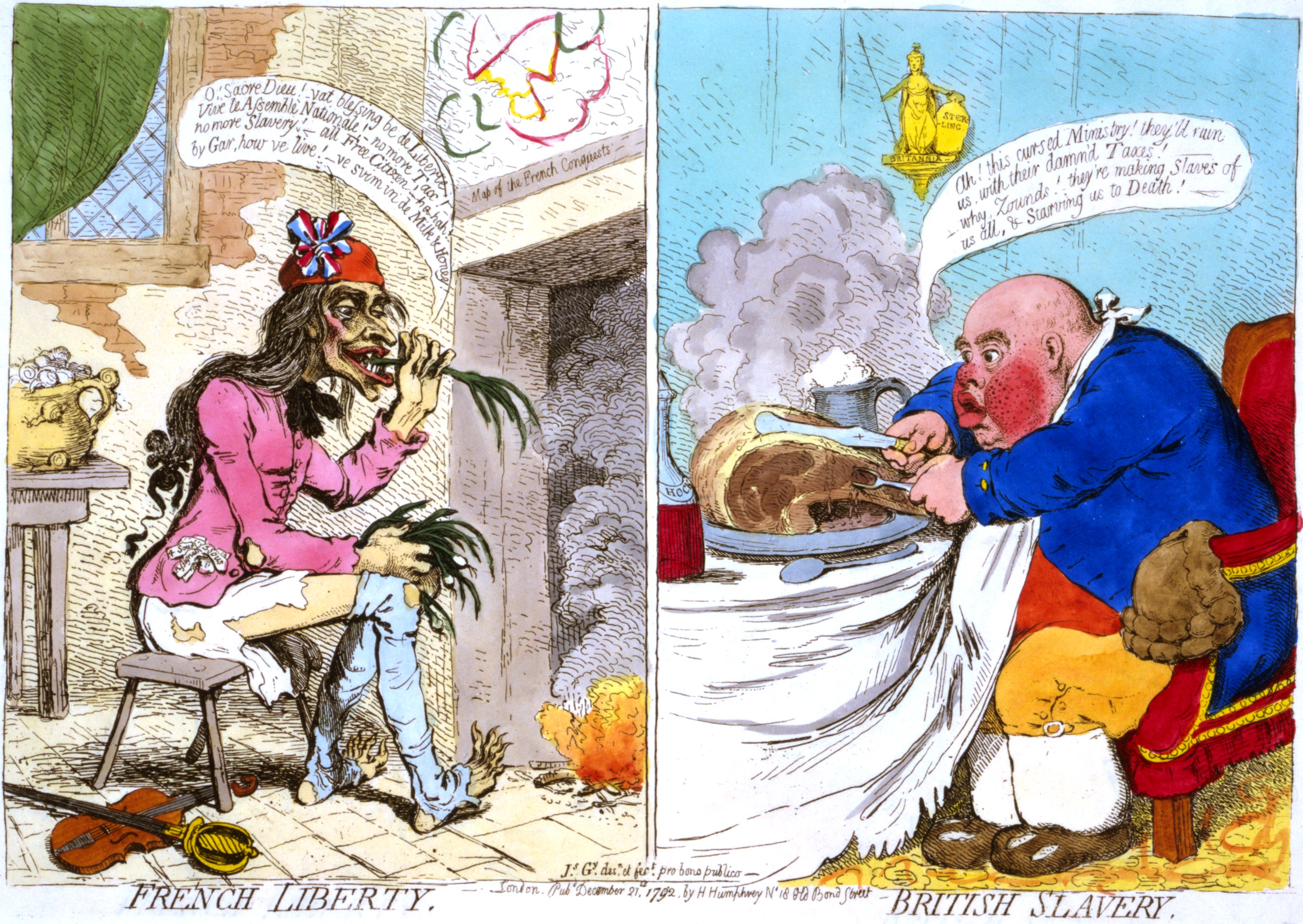
 France supported the Americans in their revolt against English rule and, in 1789, overthrew their own monarchy, with the cry of "Liberté, égalité, fraternité". The bloodbath that followed, known as the
France supported the Americans in their revolt against English rule and, in 1789, overthrew their own monarchy, with the cry of "Liberté, égalité, fraternité". The bloodbath that followed, known as the
 Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom
Freedom is understood as either having the ability to act or change without constraint or to possess the power and resources to fulfill one's purposes unhindered. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving on ...
.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society from control or oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one's way of life, behavior, or political views. In theology, liberty is freedom from the effects of "sin, spiritual servitude, rworldly ties".
Sometimes liberty is differentiated from freedom by using the word "freedom" primarily, if not exclusively, to mean the ability to do as one wills and what one has the power to do; and using the word "liberty" to mean the absence of arbitrary restraints, taking into account the rights of all involved. In this sense, the exercise of liberty is subject to capability and limited by the rights of others. Thus liberty entails the responsible use of freedom under the rule of law
The rule of law is the political philosophy that all citizens and institutions within a country, state, or community are accountable to the same laws, including lawmakers and leaders. The rule of law is defined in the ''Encyclopedia Britannica ...
without depriving anyone else of their freedom. Liberty can be taken away as a form of punishment. In many countries, people can be deprived of their liberty if they are convicted of criminal acts.
Liberty originates from the Latin word , derived from the name of the goddess Libertas, who, along with more modern personifications, is often used to portray the concept, and the archaic Roman god Liber. The word "liberty" is often used in slogans, such as in " life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness" and "'' Liberté, égalité, fraternité''".
Philosophy and metaphysics
Philosophers from the earliest times have considered the question of liberty. Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius (121–180 AD) wrote: According to compatibilist Thomas Hobbes (1588–1679):John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
(1632–1704) rejected that definition of liberty. While not specifically mentioning Hobbes, he attacks Sir Robert Filmer who had the same definition. According to Locke:
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
(1806–1873), in his work, '' On Liberty'', was the first to recognize the difference between liberty as the freedom to act and liberty as the absence of coercion.
In his book '' Two Concepts of Liberty'', Isaiah Berlin
Sir Isaiah Berlin (6 June 1909 – 5 November 1997) was a Russian-British social and political theorist, philosopher, and historian of ideas. Although he became increasingly averse to writing for publication, his improvised lectures and talks ...
formally framed the differences between two perspectives as the distinction between two opposite concepts of liberty: positive liberty and negative liberty. The latter designates a negative condition in which an individual is protected from tyranny and the arbitrary exercise of authority
In the fields of sociology and political science, authority is the legitimate power of a person or group over other people. In a civil state, ''authority'' is practiced in ways such a judicial branch or an executive branch of government.''The N ...
, while the former refers to the liberty that comes from self-mastery, the freedom from inner compulsions such as weakness and fear.
Politics
History
 The modern concept of political liberty has its origins in the Greek concepts of freedom and slavery. To be free, to the Greeks, was not to have a master, to be independent from a master (to live as one likes). That was the original Greek concept of freedom. It is closely linked with the concept of democracy, as Aristotle put it:
:"This, then, is one note of liberty which all democrats affirm to be the principle of their state. Another is that a man should live as he likes. This, they say, is the privilege of a freeman, since, on the other hand, not to live as a man likes is the mark of a slave. This is the second characteristic of democracy, whence has arisen the claim of men to be ruled by none, if possible, or, if this is impossible, to rule and be ruled in turns; and so it contributes to the freedom based upon equality."
This applied only to free men. In Athens, for instance, women could not vote or hold office and were legally and socially dependent on a male relative.
The populations of the
The modern concept of political liberty has its origins in the Greek concepts of freedom and slavery. To be free, to the Greeks, was not to have a master, to be independent from a master (to live as one likes). That was the original Greek concept of freedom. It is closely linked with the concept of democracy, as Aristotle put it:
:"This, then, is one note of liberty which all democrats affirm to be the principle of their state. Another is that a man should live as he likes. This, they say, is the privilege of a freeman, since, on the other hand, not to live as a man likes is the mark of a slave. This is the second characteristic of democracy, whence has arisen the claim of men to be ruled by none, if possible, or, if this is impossible, to rule and be ruled in turns; and so it contributes to the freedom based upon equality."
This applied only to free men. In Athens, for instance, women could not vote or hold office and were legally and socially dependent on a male relative.
The populations of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
enjoyed some degree of freedom. Citizens of all religions and ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
s were given the same rights and had the same freedom of religion, women had the same rights as men, and slavery was abolished (550 BC). All the palaces of the kings of Persia were built by paid workers in an era when slaves typically did such work.
In the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
of ancient India, citizens of all religions and ethnic groups had some rights to freedom
Freedom is understood as either having the ability to act or change without constraint or to possess the power and resources to fulfill one's purposes unhindered. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving on ...
, tolerance
Tolerance or toleration is the state of tolerating, or putting up with, conditionally.
Economics, business, and politics
* Toleration Party, a historic political party active in Connecticut
* Tolerant Systems, the former name of Veritas Software ...
, and equality. The need for tolerance on an egalitarian basis can be found in the Edicts of Ashoka the Great, which emphasize the importance of tolerance in public policy by the government. The slaughter or capture of prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
also appears to have been condemned by Ashoka. Slavery also appears to have been non-existent in the Maurya Empire. However, according to Hermann Kulke and Dietmar Rothermund, "Ashoka's orders seem to have been resisted right from the beginning."
Roman law also embraced certain limited forms of liberty, even under the rule of the Roman Emperors. However, these liberties were accorded only to Roman citizens. Many of the liberties enjoyed under Roman law endured through the Middle Ages, but were enjoyed solely by the nobility, rarely by the common man. The idea of inalienable and universal liberties had to wait until the Age of Enlightenment.
Social contract
 The
The social contract
In moral and political philosophy
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships betw ...
theory, most influentially formulated by Hobbes, John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
and Rousseau (though first suggested by Plato in '' The Republic''), was among the first to provide a political classification of rights, in particular through the notion of sovereignty and of natural rights
Some philosophers distinguish two types of rights, natural rights and legal rights.
* Natural rights are those that are not dependent on the laws or customs of any particular culture or government, and so are ''universal'', ''fundamental'' and ...
. The thinkers of the Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
reasoned that law governed both heavenly and human affairs, and that law gave the king his power, rather than the king's power giving force to law. This conception of law would find its culmination in the ideas of Montesquieu. The conception of law as a relationship between individuals, rather than families, came to the fore, and with it the increasing focus on individual liberty as a fundamental reality, given by " Nature and Nature's God," which, in the ideal state, would be as universal as possible.
In '' On Liberty'', John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
sought to define the "...nature and limits of the power which can be legitimately exercised by society over the individual," and as such, he describes an inherent and continuous antagonism between liberty and authority and thus, the prevailing question becomes "how to make the fitting adjustment between individual independence and social control".Mill, J. S. (1869)"Chapter I: Introductory"
''On Liberty''.
Origins of political freedom
England and Great Britain
 England (and, following the
England (and, following the Act of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the te ...
, Great Britain), laid down the cornerstones of the concept of individual liberty.
Timeline:
* 1066 – as a condition of his coronation William the Conqueror assented to the London Charter of Liberties which guaranteed the "Saxon" liberties of the City of London.
* 1100 – the Charter of Liberties is passed which sets out certain liberties of nobles, church officials and individuals.
* 1166 – Henry II of England transformed English law by passing the Assize of Clarendon
The Assize of Clarendon was an act of Henry II of England in 1166 that began a transformation of English law and led to trial by jury in common law countries worldwide, and that established assize courts.
Prior systems for deciding the winning ...
. The act, a forerunner to trial by jury, started the abolition of trial by combat and trial by ordeal.
* 1187-1189 – publication of Tractatus de legibus et consuetudinibus regni Anglie which contains authoritative definitions of freedom and servitude.
* 1215 – Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
was enacted, becoming the cornerstone of liberty in first England, then Great Britain, and later the world.
* 1628 – the English Parliament passed the Petition of Right which set out specific liberties of English subjects.
* 1679 – the English Parliament passed the Habeas Corpus Act which outlawed unlawful or arbitrary imprisonment.
* 1689 – the Bill of Rights granted "freedom of speech in Parliament", and reinforced many existing civil rights in England. The Scots law equivalent the Claim of Right is also passed.
* 1772 – the Somerset v Stewart judgement found that slavery was unsupported by common law in England and Wales.
* 1859 – an essay by the philosopher John Stuart Mill, entitled '' On Liberty'', argued for toleration and individuality. "If any opinion is compelled to silence, that opinion may, for aught we can certainly know, be true. To deny this is to assume our own infallibility."
* 1948 – British representatives attempted to but were prevented from adding a legal framework to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. (It was not until 1976 that the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights came into force, giving a legal status to most of the Declaration.)
* 1958 – '' Two Concepts of Liberty'', by Isaiah Berlin
Sir Isaiah Berlin (6 June 1909 – 5 November 1997) was a Russian-British social and political theorist, philosopher, and historian of ideas. Although he became increasingly averse to writing for publication, his improvised lectures and talks ...
, identified "negative liberty" as an obstacle, as distinct from "positive liberty" which promotes self-mastery and the concepts of freedom.
United States
 According to the 1776 United States Declaration of Independence, all people have a natural right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness". But this declaration of liberty was troubled from the outset by the institutionalization of legalized Black slavery. Slave owners argued that their liberty was paramount since it involved property, their slaves, and that Blacks had no rights that any White man was obliged to recognize. The Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott decision, upheld this principle. It was not until 1866, following the Civil War, that the US Constitution was amended to extend limited rights to persons of color, and not until 1920 that voting rights were extended to women.
By the later half of the 20th century, liberty was expanded further to prohibit government interference with personal choices. In the United States Supreme Court decision '' Griswold v. Connecticut'', Justice William O. Douglas argued that liberties relating to personal relationships, such as marriage, have a unique primacy of place in the hierarchy of freedoms. Jacob M. Appel has summarized this principle:
In modern America, various competing ideologies have divergent views about how best to promote liberty. Liberals in the original sense of the word see equality as a necessary component of freedom. Progressives stress freedom from business monopoly as essential. Right-wing libertarians disagree, and see economic and individual freedom as best. The Tea Party movement sees the "big government" as the enemy of freedom. Other major participants in the modern American right-wing libertarian movement include the Libertarian Party, the Free State Project, and the Mises Institute.
According to the 1776 United States Declaration of Independence, all people have a natural right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness". But this declaration of liberty was troubled from the outset by the institutionalization of legalized Black slavery. Slave owners argued that their liberty was paramount since it involved property, their slaves, and that Blacks had no rights that any White man was obliged to recognize. The Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott decision, upheld this principle. It was not until 1866, following the Civil War, that the US Constitution was amended to extend limited rights to persons of color, and not until 1920 that voting rights were extended to women.
By the later half of the 20th century, liberty was expanded further to prohibit government interference with personal choices. In the United States Supreme Court decision '' Griswold v. Connecticut'', Justice William O. Douglas argued that liberties relating to personal relationships, such as marriage, have a unique primacy of place in the hierarchy of freedoms. Jacob M. Appel has summarized this principle:
In modern America, various competing ideologies have divergent views about how best to promote liberty. Liberals in the original sense of the word see equality as a necessary component of freedom. Progressives stress freedom from business monopoly as essential. Right-wing libertarians disagree, and see economic and individual freedom as best. The Tea Party movement sees the "big government" as the enemy of freedom. Other major participants in the modern American right-wing libertarian movement include the Libertarian Party, the Free State Project, and the Mises Institute.
France
 France supported the Americans in their revolt against English rule and, in 1789, overthrew their own monarchy, with the cry of "Liberté, égalité, fraternité". The bloodbath that followed, known as the
France supported the Americans in their revolt against English rule and, in 1789, overthrew their own monarchy, with the cry of "Liberté, égalité, fraternité". The bloodbath that followed, known as the reign of terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public executions took place in response to revolutionary fervour, ...
, soured many people on the idea of liberty. Edmund Burke, considered one of the fathers of conservatism, wrote "The French had shewn themselves the ablest architects of ruin that had hitherto existed in the world."
Ideologies
Liberalism
According to the ''Concise Oxford Dictionary of Politics'', liberalism is "the belief that it is the aim of politics to preserve individual rights and to maximize freedom of choice". But they point out that there is considerable discussion about how to achieve those goals. Every discussion of freedom depends on three key components: who is free, what they are free to do, and what forces restrict their freedom. John Gray argues that the core belief of liberalism is toleration. Liberals allow others freedom to do what they want, in exchange for having the same freedom in return. This idea of freedom is personal rather than political. William Safire points out that liberalism is attacked by both the Right and the Left: by the Right for defending such practices as abortion, homosexuality, and atheism, and by the Left for defending free enterprise and the rights of the individual over the collective.Libertarianism
According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', libertarians hold liberty as their primary political value. Their approach to implementing liberty involves opposing any governmental coercion, aside from that which is necessary to prevent individuals from coercing each other. Libertarianism is guided by the principle commonly known as the Non-Aggression Principle (NAP). The Non-Aggression Principle asserts that aggression against an individual or an individual's property is always an immoral violation of one's life, liberty, and property rights. Utilizing deceit instead of consent to achieve ends is also a violation of the Non-Aggression principle. Therefore, under the framework of the Non-Aggression principle, rape, murder, deception, involuntary taxation, government regulation, and other behaviors that initiate aggression against otherwise peaceful individuals are considered violations of this principle. This principle is most commonly adhered to by libertarians. A common elevator pitch for this principle is, "Good ideas don't require force."Republican liberty
According to republican theorists of freedom, like the historianQuentin Skinner
Quentin Robert Duthie Skinner (born 26 November 1940) is a British intellectual historian. He is regarded as one of the founders of the Cambridge School of the history of political thought. He has won numerous prizes for his work, including th ...
or the philosopher Philip Pettit, one's liberty should not be viewed as the absence of interference in one's actions, but as non-domination. According to this view, which originates in the Roman Digest
Digest may refer to:
Biology
*Digestion of food
*Restriction digest
Literature and publications
*''The Digest'', formerly the English and Empire Digest
*Digest size magazine format
* ''Digest'' (Roman law), also known as ''Pandects'', a digest ...
, to be a ''liber homo'', a free man, means not being subject to another's arbitrary will, that is to say, dominated by another. They also cite Machiavelli who asserted that you must be a member of a free self-governing civil association, a republic, if you are to enjoy individual liberty.
The predominance of this view of liberty among parliamentarians during the English Civil War resulted in the creation of the liberal concept of freedom as non-interference in Thomas Hobbes' Leviathan.
Socialism
Socialists view freedom as a concrete situation as opposed to a purely abstract ideal. Freedom is a state of being where individuals haveagency
Agency may refer to:
Organizations
* Institution, governmental or others
** Advertising agency or marketing agency, a service business dedicated to creating, planning and handling advertising for its clients
** Employment agency, a business that ...
to pursue their creative interests unhindered by coercive social relationships, specifically those they are forced to engage in as a requisite for survival under a given social system. Freedom thus requires both the material economic conditions that make freedom possible alongside social relationships and institutions conducive to freedom.
The socialist conception of freedom is closely related to the socialist view of creativity and individuality. Influenced by Karl Marx's concept of alienated labor, socialists understand freedom to be the ability for an individual to engage in creative work in the absence of alienation, where "alienated labor" refers to work people are forced to perform and un-alienated work refers to individuals pursuing their own creative interests.
Marxism
For Karl Marx, meaningful freedom is only attainable in a communist society characterized by superabundance and free access. Such a social arrangement would eliminate the need for alienated labor and enable individuals to pursue their own creative interests, leaving them to develop and maximize their full potentialities. This goes alongside Marx's emphasis on the ability of socialism and communism progressively reducing the average length of the workday to expand the "realm of freedom", or discretionary free time, for each person. Marx's notion of communist society and human freedom is thus radically individualistic.Anarchism
While many anarchists see freedom slightly differently, all oppose authority, including the authority of the state, of capitalism, and of nationalism. For the Russian revolutionary anarchist Mikhail Bakunin, liberty did not mean an abstract ideal but a concrete reality based on the equal liberty of others. In a positive sense, liberty consists of "the fullest development of all the faculties and powers of every human being, by education, by scientific training, and by material prosperity." Such a conception of liberty is "eminently social, because it can only be realized in society," not in isolation. In a negative sense, liberty is "the revolt of the individual against all divine, collective, and individual authority."Cultural prerequisites
Some authors have suggested that a virtuous culture must exist as a prerequisite for liberty. Benjamin Franklin stated that "only a virtuous people are capable of freedom. As nations become corrupt and vicious, they have more need of masters." Madison likewise declared: "To suppose that any form of government will secure liberty or happiness without any virtue in the people, is a chimerical idea." John Adams acknowledged: "Our constitution was made only for a moral and religious people. It is wholly inadequate to the government of any other."John R. Howe, Jr., The Changing Political Thought of John Adams 165 (1966) (quoting from John Adams' "Reply to the Massachusetts Militia," Oct. 11, 1789).Historical writings on liberty
* * * *See also
*Civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
* Cognitive liberty
* Free will
* Gratis versus Libre
* '' Liberté, égalité, fraternité''
* Liberty (personification)
* List of freedom indices
* Political freedom
Political freedom (also known as political autonomy or political agency) is a central concept in history and political thought and one of the most important features of democratic societies.Hannah Arendt, "What is Freedom?", ''Between Past and F ...
* Real freedom
* Rule according to higher law
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
* * {{Authority control Concepts in ethics Concepts in metaphysics Free will Happiness Political concepts Social concepts Virtue