Liberal Party of Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Liberal Party of Canada (french: Parti libéral du Canada, region=CA) is a federal political party in Canada. The party espouses the principles of
"Liberal Party".
''The Canadian Encyclopedia''. and generally sits at the centre to
at UBC Press. practising "brokerage politics", attracting support from a broad spectrum of voters. The Liberal Party is the longest-serving and oldest active federal political party in the country, and has dominated federal politics of Canada for much of its history, holding power for almost 70 years of the 20th century. As a result, it has sometimes been referred to as Canada's "natural governing party". The party first came into power in 1873 under Alexander Mackenzie, but were voted out
 Until the early part of the century, the Liberal Party was a loose coalition of local, provincial, and regional bodies with a strong national party leader and caucus, but with an informal and regionalized extra-parliamentary organizational structure. There was no national membership of the party. An individual became a member by joining a provincial Liberal party. Laurier called the party's first national convention in 1893 to unite Liberal supporters behind a programme and build the campaign that successfully brought the party to power in 1896, but no efforts were made to create a formal national organization outside Parliament.
As a result of the party's defeats in the 1911 and 1917 federal elections, Laurier attempted to organize the party on a national level by creating three bodies: the Central Liberal Information Office, the National Liberal Advisory Committee, and the National Liberal Organization Committee. However, the advisory committee became dominated by members of Parliament and all three bodies were underfunded and competed with both local and provincial Liberal associations and the national caucus for authority. The party did organize the national party's second convention in 1919 to elect William Lyon Mackenzie King as Laurier's successor (Canada's first leadership convention), yet following the party's return to power in the 1921 federal election the nascent national party organizations were eclipsed by powerful ministers and local party organizations largely driven by patronage.
As a result of both the party's defeat in the 1930 federal election and the Beauharnois scandal, which highlighted the need for distance between the Liberal Party's parliamentary wing and campaign fundraising,Beauharnois Scandal
Until the early part of the century, the Liberal Party was a loose coalition of local, provincial, and regional bodies with a strong national party leader and caucus, but with an informal and regionalized extra-parliamentary organizational structure. There was no national membership of the party. An individual became a member by joining a provincial Liberal party. Laurier called the party's first national convention in 1893 to unite Liberal supporters behind a programme and build the campaign that successfully brought the party to power in 1896, but no efforts were made to create a formal national organization outside Parliament.
As a result of the party's defeats in the 1911 and 1917 federal elections, Laurier attempted to organize the party on a national level by creating three bodies: the Central Liberal Information Office, the National Liberal Advisory Committee, and the National Liberal Organization Committee. However, the advisory committee became dominated by members of Parliament and all three bodies were underfunded and competed with both local and provincial Liberal associations and the national caucus for authority. The party did organize the national party's second convention in 1919 to elect William Lyon Mackenzie King as Laurier's successor (Canada's first leadership convention), yet following the party's return to power in the 1921 federal election the nascent national party organizations were eclipsed by powerful ministers and local party organizations largely driven by patronage.
As a result of both the party's defeat in the 1930 federal election and the Beauharnois scandal, which highlighted the need for distance between the Liberal Party's parliamentary wing and campaign fundraising,Beauharnois Scandal
at ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' a central coordinating organization, the National Liberal Federation, was created in 1932 with Vincent Massey as its first president. With the Liberal return to power, the national organization languished except for occasional national committee meetings, such as in 1943 when Mackenzie King called a meeting of the federation (consisting of the national caucus and up to seven voting delegates per province) to approve a new platform for the party in anticipation of the end of World War II and prepare for a post-war election. No national convention was held, however, until 1948; the Liberal Party held only three national conventions prior to the 1950s – in 1893, 1919 and 1948. The National Liberal Federation remained largely dependent on provincial Liberal parties and was often ignored and bypassed the parliamentary party in the organization of election campaigns and the development of policy. With the defeat of the Liberals in the 1957 federal election and in particular 1958, reformers argued for the strengthening of the national party organization so it would not be dependent on provincial Liberal parties and patronage. A national executive and Council of presidents, consisting of the presidents of each Liberal riding association, were developed to give the party more co-ordination and national party conventions were regularly held in biennially where previously they had been held infrequently. Over time, provincial Liberal parties in most provinces were separated from provincial wings of the federal party and in a number of cases disaffiliated. By the 1980s, the National Liberal Federation was officially known as the Liberal Party of Canada.
 Under Laurier, and his successor William Lyon Mackenzie King, the Liberals promoted Canadian sovereignty and greater independence within the British Commonwealth. In Imperial Conferences held
throughout the 1920s, Canadian Liberal governments often took the lead in arguing that the United Kingdom and the dominions should have equal status, and against proposals for an 'imperial parliament' that would have subsumed Canadian independence. After the King–Byng Affair of 1926, the Liberals argued that the Governor General of Canada should no longer be appointed on the recommendation of the British government. The decisions of the Imperial Conferences were formalized in the Statute of Westminster, which was actually passed in 1931, the year after the Liberals lost power.
The Liberals also promoted the idea of Canada being responsible for its own foreign and defence policy. Initially, it was Britain which determined external affairs for the dominion. In 1905, Laurier created the Department of External Affairs, and in 1909 he advised
Under Laurier, and his successor William Lyon Mackenzie King, the Liberals promoted Canadian sovereignty and greater independence within the British Commonwealth. In Imperial Conferences held
throughout the 1920s, Canadian Liberal governments often took the lead in arguing that the United Kingdom and the dominions should have equal status, and against proposals for an 'imperial parliament' that would have subsumed Canadian independence. After the King–Byng Affair of 1926, the Liberals argued that the Governor General of Canada should no longer be appointed on the recommendation of the British government. The decisions of the Imperial Conferences were formalized in the Statute of Westminster, which was actually passed in 1931, the year after the Liberals lost power.
The Liberals also promoted the idea of Canada being responsible for its own foreign and defence policy. Initially, it was Britain which determined external affairs for the dominion. In 1905, Laurier created the Department of External Affairs, and in 1909 he advised
 In the period just before and after the
In the period just before and after the
 Under
Under 
 Turner announced that he would resign as leader of the Liberal Party on May 3, 1989. The Liberal Party set a leadership convention for June 23, 1990, in
Turner announced that he would resign as leader of the Liberal Party on May 3, 1989. The Liberal Party set a leadership convention for June 23, 1990, in
 After their election defeat Martin chose not to take on the office of Leader of the Opposition. He stepped down as parliamentary leader of his party on February 1, and the Liberal caucus appointed Bill Graham, MP for Toronto Centre and outgoing Defence Minister, as his interim successor. Martin officially resigned as leader in March, with Graham taking over on an interim basis.
The leadership election was set for December 2, 2006, in
After their election defeat Martin chose not to take on the office of Leader of the Opposition. He stepped down as parliamentary leader of his party on February 1, and the Liberal caucus appointed Bill Graham, MP for Toronto Centre and outgoing Defence Minister, as his interim successor. Martin officially resigned as leader in March, with Graham taking over on an interim basis.
The leadership election was set for December 2, 2006, in
 On November 27, 2008, Minister of Finance Jim Flaherty provided the House of Commons with a fiscal update, within which were plans to cut government spending, suspend the ability of civil servants to strike until 2011, sell off some Crown assets to raise capital, and eliminate the existing $1.95 per vote subsidy parties garner in an election. The opposition parties criticized the fiscal update, and announced they would not support it because it contained no stimulus money to spur Canada's economy and protect workers during the economic crisis. With the Conservative Party only holding a minority of the seats in the House of Commons the government would be defeated if the opposition parties voted against the fiscal update. With the Conservatives unwilling to budge on the proposals outlined in the fiscal update the Liberals and NDP signed an agreement to form a coalition government, with a written pledge of support from the Bloc Québécois. Under the terms of the agreement Dion would be sworn in as Prime Minister, however he would only serve in the position until the next Liberal leader was chosen. Dion contacted Governor General Michaëlle Jean and advised her that he had the confidence of the House of Commons if Prime Minister Harper's government was to fall. However, before the fiscal update could be voted on in the House of Commons Prime Minister Harper requested the Governor General to prorogue parliament until January 26, 2009, which she accepted.
While polls showed Canadians were split on the idea of having either a coalition government or having the Conservatives continue to govern, it was clear that because of Dion's personal popularity they were not comfortable with him becoming Prime Minister. Members of the Liberal Party therefore called on Dion to resign as leader immediately and for an interim leader to be chosen, this person would become the Prime Minister in case the Conservatives were defeated when parliament resumed in January. With an estimated 70 percent of the Liberal caucus wanting Ignatieff to be named interim leader, Dion resigned the post on December 8, 2008 (effective December 10, upon Ignatieff's becoming interim leader). LeBlanc announced on the same day that he was abandoning the Liberal leadership race and endorsing Ignatieff as the next leader. The following day Rae announced he was also dropping out of the race and was placing his "full and unqualified" support to Ignatieff.
On November 27, 2008, Minister of Finance Jim Flaherty provided the House of Commons with a fiscal update, within which were plans to cut government spending, suspend the ability of civil servants to strike until 2011, sell off some Crown assets to raise capital, and eliminate the existing $1.95 per vote subsidy parties garner in an election. The opposition parties criticized the fiscal update, and announced they would not support it because it contained no stimulus money to spur Canada's economy and protect workers during the economic crisis. With the Conservative Party only holding a minority of the seats in the House of Commons the government would be defeated if the opposition parties voted against the fiscal update. With the Conservatives unwilling to budge on the proposals outlined in the fiscal update the Liberals and NDP signed an agreement to form a coalition government, with a written pledge of support from the Bloc Québécois. Under the terms of the agreement Dion would be sworn in as Prime Minister, however he would only serve in the position until the next Liberal leader was chosen. Dion contacted Governor General Michaëlle Jean and advised her that he had the confidence of the House of Commons if Prime Minister Harper's government was to fall. However, before the fiscal update could be voted on in the House of Commons Prime Minister Harper requested the Governor General to prorogue parliament until January 26, 2009, which she accepted.
While polls showed Canadians were split on the idea of having either a coalition government or having the Conservatives continue to govern, it was clear that because of Dion's personal popularity they were not comfortable with him becoming Prime Minister. Members of the Liberal Party therefore called on Dion to resign as leader immediately and for an interim leader to be chosen, this person would become the Prime Minister in case the Conservatives were defeated when parliament resumed in January. With an estimated 70 percent of the Liberal caucus wanting Ignatieff to be named interim leader, Dion resigned the post on December 8, 2008 (effective December 10, upon Ignatieff's becoming interim leader). LeBlanc announced on the same day that he was abandoning the Liberal leadership race and endorsing Ignatieff as the next leader. The following day Rae announced he was also dropping out of the race and was placing his "full and unqualified" support to Ignatieff.
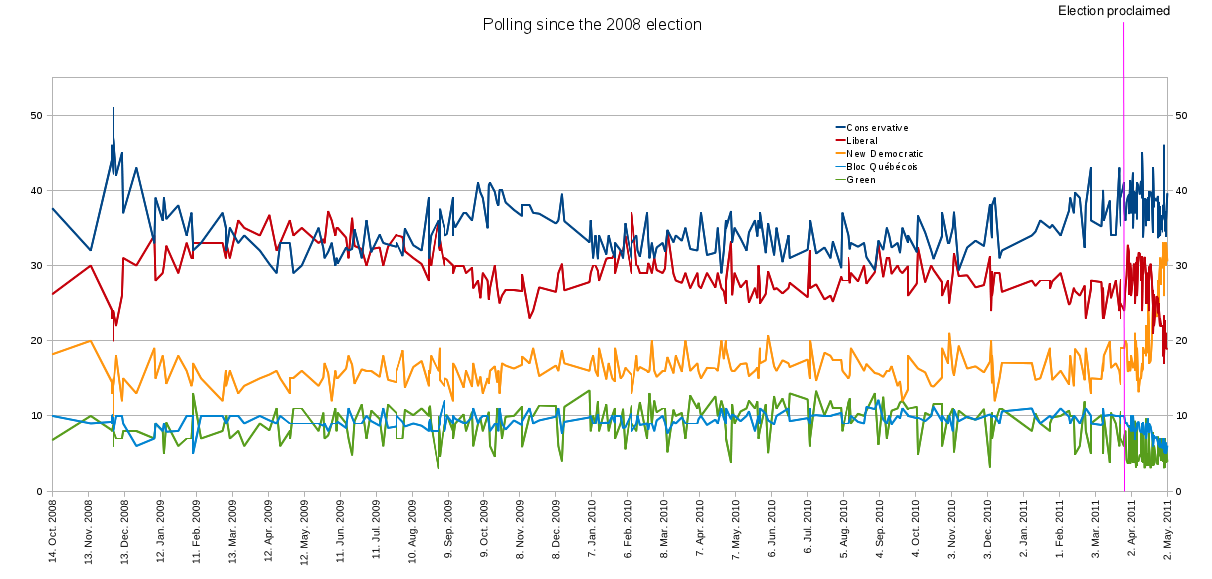 Throughout the Winter of 2008–09, opinion polls showed that while the Ignatieff led Liberals still trailed the Conservatives, their support had stabilized in the low 30 percent range. However, by the time Ignatieff was confirmed as party leader on May 2, 2009, the Liberal Party had a comfortable lead over the governing Conservatives. After a summer where he was accused of being missing in action, Ignatieff announced on August 31, 2009, that the Liberals would not support the minority Conservative government. After this announcement the Liberal Party's poll numbers, which had already declined over the summer, started to fall further behind the Conservatives. On October 1, 2009, the Liberals put forth a non-confidence motion with the hope of defeating the government. However, the NDP abstained from voting and the Conservatives survived the confidence motion.
Throughout the Winter of 2008–09, opinion polls showed that while the Ignatieff led Liberals still trailed the Conservatives, their support had stabilized in the low 30 percent range. However, by the time Ignatieff was confirmed as party leader on May 2, 2009, the Liberal Party had a comfortable lead over the governing Conservatives. After a summer where he was accused of being missing in action, Ignatieff announced on August 31, 2009, that the Liberals would not support the minority Conservative government. After this announcement the Liberal Party's poll numbers, which had already declined over the summer, started to fall further behind the Conservatives. On October 1, 2009, the Liberals put forth a non-confidence motion with the hope of defeating the government. However, the NDP abstained from voting and the Conservatives survived the confidence motion.
 The Liberal Party's attempt to force an election, just a year after the previous one, was reported as a miscalculation, as polls showed that most Canadians did not want another election. Even after the government survived the confidence motion popularity for Ignatieff and his party continued to fall. Over the next year and a half, with the exception of a brief period in early 2010, support for the Liberals remained below 30 percent, and behind the Conservatives. While his predecessor Dion was criticized by the Conservatives as a "weak leader", Ignatieff was attacked as a "political opportunist".
On March 25, 2011, Ignatieff introduced a motion of
The Liberal Party's attempt to force an election, just a year after the previous one, was reported as a miscalculation, as polls showed that most Canadians did not want another election. Even after the government survived the confidence motion popularity for Ignatieff and his party continued to fall. Over the next year and a half, with the exception of a brief period in early 2010, support for the Liberals remained below 30 percent, and behind the Conservatives. While his predecessor Dion was criticized by the Conservatives as a "weak leader", Ignatieff was attacked as a "political opportunist".
On March 25, 2011, Ignatieff introduced a motion of
 On April 14, 2013,
On April 14, 2013,
''Maclean's'' June 20, 2011 online
* Jeffrey, Brooke. ''Divided Loyalties: The Liberal Party of Canada, 1984–2008'' (2010
excerpt and text search
* Jeffrey, Brooke. ''Road to Redemption: The Liberal Party of Canada, 2006-2019'' (2020) * Koop, Royce. "Professionalism, Sociability and the Liberal Party in the Constituencies." ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' (2010) 43#04 pp: 893–913. * * McCall, Christina. ''Grits: an intimate portrait of the Liberal Party'' (Macmillan of Canada, 1982) *
Liberal Party of Canada - Canadian Political Parties and Political Interest Groups
- Web Archive created by the University of Toronto Libraries
The Liberal Party of Canada Constitution
Canadian Encyclopedia entry on the Liberal Party
Liberal Party of Canada fonds
at
liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for ...
,McCall, Christina; Stephen Clarkson"Liberal Party".
''The Canadian Encyclopedia''. and generally sits at the centre to
centre-left
Centre-left politics lean to the left on the left–right political spectrum but are closer to the centre than other left-wing politics. Those on the centre-left believe in working within the established systems to improve social justice. The ...
of the Canadian political spectrum
A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different political positions in relation to one another. These positions sit upon one or more geometric axes that represent independent political dimensions. The expressions polit ...
, with their rival, the Conservative Party, positioned to their right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical th ...
and the New Democratic Party, who at times aligned itself with the Liberals during minority governments, positioned to their left. The party is described as " big tent",PDF copyat UBC Press. practising "brokerage politics", attracting support from a broad spectrum of voters. The Liberal Party is the longest-serving and oldest active federal political party in the country, and has dominated federal politics of Canada for much of its history, holding power for almost 70 years of the 20th century. As a result, it has sometimes been referred to as Canada's "natural governing party". The party first came into power in 1873 under Alexander Mackenzie, but were voted out
five years later
''Five Years Later'' is an album by Ralph Towner and guitarists John Abercrombie (guitarist), John Abercrombie, recorded in 1981 and released by ECM Records, ECM in 1982.
due to the economic conditions at the time. They would not come back to office until 1896; Wilfrid Laurier was prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
from that year until the party's defeat in 1911 and his tenure was marked by several compromises between English and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
Canada. From the early 1920s until the mid-1950s, the Liberal Party under Prime Ministers William Lyon Mackenzie King and Louis St. Laurent
Louis Stephen St. Laurent (''Saint-Laurent'' or ''St-Laurent'' in French, baptized Louis-Étienne St-Laurent; February 1, 1882 – July 25, 1973) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 12th prime minister of Canada from 19 ...
gradually built a Canadian welfare state.
The Liberals' signature policies and legislative decisions include universal health care, the Canada Pension Plan, Canada Student Loans, the establishment of the Royal Canadian Navy, multilateralism, official bilingualism, official multiculturalism
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for "Pluralism (political theory), ethnic pluralism", with the tw ...
, gun control, the patriation of the Constitution of Canada and the establishment of the ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms'' (french: Charte canadienne des droits et libertés), often simply referred to as the ''Charter'' in Canada, is a bill of rights entrenched in the Constitution of Canada, forming the first part ...
'', the '' Clarity Act'', legalizing same-sex marriage, euthanasia, and cannabis, national carbon pricing, and expanded access to abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
.
The Liberal Party, led by Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since ...
since 2013, won a majority government in the 2015 federal election. In both the federal elections of 2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
and 2021, the party was re-elected with a minority government.
History
19th century
Origins
The Liberals are descended from the mid-19th centuryReformers
A reformer is someone who works for reform.
Reformer may also refer to:
*Catalytic reformer, in an oil refinery
*Methane reformer, producing hydrogen
* Steam reformer
*Hydrogen reformer, extracting hydrogen
*Methanol reformer, producing hydrogen f ...
who advocated for responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive bra ...
throughout British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
. These included George Brown, Alexander Mackenzie, Robert Baldwin, William Lyon Mackenzie and the Clear Grits in Upper Canada, Joseph Howe in Nova Scotia, and the Patriotes and Rouges in Lower Canada led by figures such as Louis-Joseph Papineau. The Clear Grits and Parti rouge
The Red Party (french: Parti rouge, or french: Parti démocratique) was a political group that contested elections in the Eastern section of the Province of Canada. It was formed around 1847 by radical French-Canadians inspired by the ideas of Lo ...
sometimes functioned as a united bloc in the legislature of the Province of Canada beginning in 1854, and a united Liberal Party combining both English and French Canadian members was formed in 1861.
Confederation
At the time of Confederation of the former British colonies of Canada (nowOntario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
), New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic Canad ...
, and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native En ...
, the radical Liberals were marginalized by the more pragmatic Conservative coalition assembled under Sir John A. Macdonald. In the 29 years after Confederation, the Liberals were consigned to opposition, with the exception of one stint in government. Alexander Mackenzie was the ''de facto'' leader of the Official Opposition after Confederation and finally agreed to become the first official leader of the Liberal Party in 1873. He was able to lead the party to power for the first time in 1873, after the Macdonald government resigned over the Pacific Scandal. Mackenzie subsequently won the 1874 election and served as Prime Minister for an additional four years. During the five years the Liberal government brought in many reforms, including the replacement of open voting by secret ballot, confining elections to one day and the creation of the Supreme Court of Canada
The Supreme Court of Canada (SCC; french: Cour suprême du Canada, CSC) is the highest court in the judicial system of Canada. It comprises nine justices, whose decisions are the ultimate application of Canadian law, and grants permission to ...
, the Royal Military College of Canada, and the Office of the Auditor General; however, the party was only able to build a solid support base in Ontario and in 1878 lost the government to Macdonald. The Liberals would spend the next 18 years in opposition.
Wilfrid Laurier
In their early history, the Liberals were the party of continentalism and opposition toimperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power ( economic and ...
. The Liberals also became identified with the aspirations of Quebecers as a result of the growing hostility of French Canadians to the Conservatives. The Conservatives lost the support of French Canadians because of the role of Conservative governments in the execution of Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first ...
and their role in the Conscription Crisis of 1917, and especially their opposition to French schools in provinces besides Quebec.
It was not until Wilfrid Laurier became leader that the Liberal Party emerged as a modern party. Laurier was able to capitalize on the Tories' alienation of French Canada by offering the Liberals as a credible alternative. Laurier was able to overcome the party's reputation for anti-clericalism that offended the still-powerful Quebec Roman Catholic Church. In English-speaking Canada, the Liberal Party's support for reciprocity
Reciprocity may refer to:
Law and trade
* Reciprocity (Canadian politics), free trade with the United States of America
** Reciprocal trade agreement, entered into in order to reduce (or eliminate) tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on ...
made it popular among farmers, and helped cement the party's hold in the growing prairie provinces.
Laurier led the Liberals to power in the 1896 election (in which he became the first Francophone Prime Minister) and oversaw a government that increased immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
to settle Western Canada. Laurier's government created the provinces of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North ...
and Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
out of the North-West Territories and promoted the development of Canadian industry.
20th century
Organization
 Until the early part of the century, the Liberal Party was a loose coalition of local, provincial, and regional bodies with a strong national party leader and caucus, but with an informal and regionalized extra-parliamentary organizational structure. There was no national membership of the party. An individual became a member by joining a provincial Liberal party. Laurier called the party's first national convention in 1893 to unite Liberal supporters behind a programme and build the campaign that successfully brought the party to power in 1896, but no efforts were made to create a formal national organization outside Parliament.
As a result of the party's defeats in the 1911 and 1917 federal elections, Laurier attempted to organize the party on a national level by creating three bodies: the Central Liberal Information Office, the National Liberal Advisory Committee, and the National Liberal Organization Committee. However, the advisory committee became dominated by members of Parliament and all three bodies were underfunded and competed with both local and provincial Liberal associations and the national caucus for authority. The party did organize the national party's second convention in 1919 to elect William Lyon Mackenzie King as Laurier's successor (Canada's first leadership convention), yet following the party's return to power in the 1921 federal election the nascent national party organizations were eclipsed by powerful ministers and local party organizations largely driven by patronage.
As a result of both the party's defeat in the 1930 federal election and the Beauharnois scandal, which highlighted the need for distance between the Liberal Party's parliamentary wing and campaign fundraising,Beauharnois Scandal
Until the early part of the century, the Liberal Party was a loose coalition of local, provincial, and regional bodies with a strong national party leader and caucus, but with an informal and regionalized extra-parliamentary organizational structure. There was no national membership of the party. An individual became a member by joining a provincial Liberal party. Laurier called the party's first national convention in 1893 to unite Liberal supporters behind a programme and build the campaign that successfully brought the party to power in 1896, but no efforts were made to create a formal national organization outside Parliament.
As a result of the party's defeats in the 1911 and 1917 federal elections, Laurier attempted to organize the party on a national level by creating three bodies: the Central Liberal Information Office, the National Liberal Advisory Committee, and the National Liberal Organization Committee. However, the advisory committee became dominated by members of Parliament and all three bodies were underfunded and competed with both local and provincial Liberal associations and the national caucus for authority. The party did organize the national party's second convention in 1919 to elect William Lyon Mackenzie King as Laurier's successor (Canada's first leadership convention), yet following the party's return to power in the 1921 federal election the nascent national party organizations were eclipsed by powerful ministers and local party organizations largely driven by patronage.
As a result of both the party's defeat in the 1930 federal election and the Beauharnois scandal, which highlighted the need for distance between the Liberal Party's parliamentary wing and campaign fundraising,Beauharnois Scandalat ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' a central coordinating organization, the National Liberal Federation, was created in 1932 with Vincent Massey as its first president. With the Liberal return to power, the national organization languished except for occasional national committee meetings, such as in 1943 when Mackenzie King called a meeting of the federation (consisting of the national caucus and up to seven voting delegates per province) to approve a new platform for the party in anticipation of the end of World War II and prepare for a post-war election. No national convention was held, however, until 1948; the Liberal Party held only three national conventions prior to the 1950s – in 1893, 1919 and 1948. The National Liberal Federation remained largely dependent on provincial Liberal parties and was often ignored and bypassed the parliamentary party in the organization of election campaigns and the development of policy. With the defeat of the Liberals in the 1957 federal election and in particular 1958, reformers argued for the strengthening of the national party organization so it would not be dependent on provincial Liberal parties and patronage. A national executive and Council of presidents, consisting of the presidents of each Liberal riding association, were developed to give the party more co-ordination and national party conventions were regularly held in biennially where previously they had been held infrequently. Over time, provincial Liberal parties in most provinces were separated from provincial wings of the federal party and in a number of cases disaffiliated. By the 1980s, the National Liberal Federation was officially known as the Liberal Party of Canada.
Canadian sovereignty
 Under Laurier, and his successor William Lyon Mackenzie King, the Liberals promoted Canadian sovereignty and greater independence within the British Commonwealth. In Imperial Conferences held
throughout the 1920s, Canadian Liberal governments often took the lead in arguing that the United Kingdom and the dominions should have equal status, and against proposals for an 'imperial parliament' that would have subsumed Canadian independence. After the King–Byng Affair of 1926, the Liberals argued that the Governor General of Canada should no longer be appointed on the recommendation of the British government. The decisions of the Imperial Conferences were formalized in the Statute of Westminster, which was actually passed in 1931, the year after the Liberals lost power.
The Liberals also promoted the idea of Canada being responsible for its own foreign and defence policy. Initially, it was Britain which determined external affairs for the dominion. In 1905, Laurier created the Department of External Affairs, and in 1909 he advised
Under Laurier, and his successor William Lyon Mackenzie King, the Liberals promoted Canadian sovereignty and greater independence within the British Commonwealth. In Imperial Conferences held
throughout the 1920s, Canadian Liberal governments often took the lead in arguing that the United Kingdom and the dominions should have equal status, and against proposals for an 'imperial parliament' that would have subsumed Canadian independence. After the King–Byng Affair of 1926, the Liberals argued that the Governor General of Canada should no longer be appointed on the recommendation of the British government. The decisions of the Imperial Conferences were formalized in the Statute of Westminster, which was actually passed in 1931, the year after the Liberals lost power.
The Liberals also promoted the idea of Canada being responsible for its own foreign and defence policy. Initially, it was Britain which determined external affairs for the dominion. In 1905, Laurier created the Department of External Affairs, and in 1909 he advised Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
Earl Grey to appoint the first Secretary of State for External Affairs to Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
. It was also Laurier who first proposed the creation of a Canadian Navy in 1910. Mackenzie King recommended the appointment by Governor General Lord Byng
Field Marshal Julian Hedworth George Byng, 1st Viscount Byng of Vimy, (11 September 1862 – 6 June 1935) was a British Army officer who served as Governor General of Canada, the 12th since the Canadian Confederation.
Known to friends as "Bung ...
of Vincent Massey as the first Canadian ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sov ...
to Washington in 1926, marking the Liberal government's insistence on having direct relations with the United States, rather than having Britain act on Canada's behalf.
Social safety net
 In the period just before and after the
In the period just before and after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the party became a champion of 'progressive social policy'. As Prime Minister for most of the time between 1921 and 1948, King introduced several measures that led to the creation of Canada's social safety net. Bowing to popular pressure, he introduced the mother's allowance, a monthly payment to all mothers with young children. He also reluctantly introduced old age pensions when J. S. Woodsworth required it in exchange for his Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF; french: Fédération du Commonwealth Coopératif, FCC); from 1955 the Social Democratic Party of Canada (''french: Parti social démocratique du Canada''), was a federal democratic socialistThe foll ...
party's support of King's minority government.
Louis St. Laurent
Louis Stephen St. Laurent (''Saint-Laurent'' or ''St-Laurent'' in French, baptized Louis-Étienne St-Laurent; February 1, 1882 – July 25, 1973) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 12th prime minister of Canada from 19 ...
succeeded King as Liberal leader and Prime Minister on November 15, 1948. In the 1949 and 1953 federal elections, St. Laurent led the Liberal Party to two large majority governments. As Prime Minister he oversaw the joining of Newfoundland in Confederation as Canada's tenth province, he established equalization payments to the provinces, and continued with social reform with improvements in pensions and health insurance. In 1956, Canada played an important role in resolving the Suez Crisis, and contributed to the United Nations force in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
. Canada enjoyed economic prosperity during St. Laurent's premiership and wartime debts were paid off. The Pipeline Debate proved the Liberal Party's undoing. Their attempt to pass legislation to build a natural gas pipeline from Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
to central Canada was met with fierce disagreement in the House of Commons. In 1957, John Diefenbaker's Progressive Conservatives won a minority government and St. Laurent resigned as Prime Minister and Liberal leader.
Lester B. Pearson was easily elected Liberal leader at the party's 1958 leadership convention. However, only months after becoming Liberal leader, Pearson led the party into the 1958 federal election that saw Diefenbaker's Progressive Conservatives win the largest majority government, by percentage of seats, in Canadian history. The Progressive Conservatives won 206 of the 265 seats in the House of Commons, while the Liberals were reduced to just 48 seats. Pearson remained Liberal leader during this time and in the 1962 election managed to reduce Diefenbaker to a minority government. In the 1963 election Pearson led the Liberal Party back to victory, forming a minority government. Pearson served as Prime Minister for five years, winning a second election in 1965. While Pearson's leadership was considered poor and the Liberal Party never held a majority of the seats in parliament during his premiership, he left office in 1968 with an impressive legacy. Pearson's government introduced Medicare, a new immigration act, the Canada Pension Plan, Canada Student Loans, the Canada Assistance Plan, and adopted the Maple Leaf as Canada's national flag.
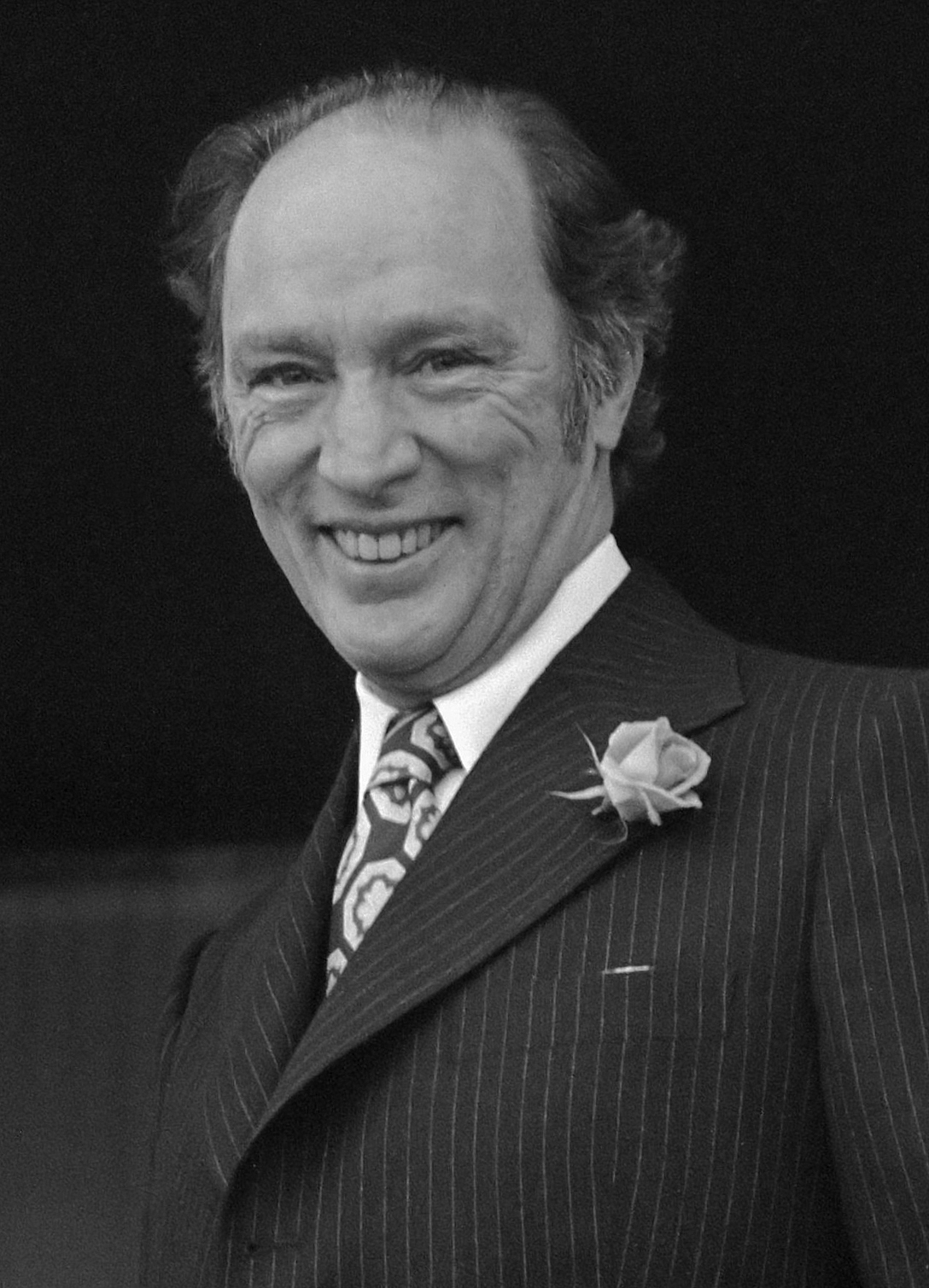
Pierre Trudeau
 Under
Under Pierre Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau ( , ; October 18, 1919 – September 28, 2000), also referred to by his initials PET, was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada from 1968 to 1979 and ...
, the mission of a progressive social policy evolved into the goal of creating a " just society". In the late 1970s, Trudeau stated that his Liberal Party adhered to the " radical centre".Graham, Ron, ed. (1998). ''The Essential Trudeau''. McClelland & Stewart, p. 71. .
The Liberal Party under Trudeau promoted official bilingualism and passed the '' Official Languages Act'', which gave French and English languages equal status in Canada. Trudeau hoped that the promotion of bilingualism would cement Quebec's place in Confederation, and counter growing calls for an independent Quebec. The party hoped the policy would transform Canada into a country where English and French Canadians could live together, and allow Canadians to move to any part of the country without having to lose their language. Although this vision has yet to fully materialize, official bilingualism has helped to halt the decline of the French language outside of Quebec, and to ensure that all federal government services (including radio and television services provided by the government-owned Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (french: Société Radio-Canada), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a federal Crown corporation that receives funding from the governme ...
/ Radio-Canada) are available in both languages throughout the country.
The Trudeau Liberals are also credited with support for state multiculturalism as a means of integrating immigrants into Canadian society without forcing them to shed their culture, leading the party to build a base of support among recent immigrants and their children. This marked the culmination of a decades-long shift in Liberal immigration policy, a reversal of pre-war racial attitudes that spurred discriminatory policies such as the Chinese Immigration Act of 1923
The Chinese Immigration Act, 1923, known today as the Chinese Exclusion Act (the duration of which has been dubbed the Exclusion Era), was an act passed by the government of Liberal Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King, banning most forms o ...
and the MS St. Louis incident.
The most lasting effect of the Trudeau years has been the patriation of the Constitution of Canada and the creation of the ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms'' (french: Charte canadienne des droits et libertés), often simply referred to as the ''Charter'' in Canada, is a bill of rights entrenched in the Constitution of Canada, forming the first part ...
''. Trudeau's Liberals supported the concept of a strong, central government, and fought Quebec separatism, other forms of Quebec nationalism, and the granting of " distinct society" status to Quebec; however, such actions served as rallying cries for sovereigntists, and alienated many Francophone Quebeckers.
The other primary legacy of the Trudeau years has been financial. Net federal debt in fiscal 1968, just before Trudeau became Prime Minister, was about $18 billion CAD, or 26 percent of gross domestic product; by his final year in office, it had ballooned to over 200 billion—at 46 percent of GDP, nearly twice as large relative to the economy.
As the opposition
After Trudeau's retirement in 1984, many Liberals, such as Jean Chrétien and Clyde Wells, continued to adhere to Trudeau's concept of federalism. Others, such as John Turner, supported the failed Meech Lake and Charlottetown Constitutional Accords, which would have recognized Quebec as a "distinct society" and would have increased the powers of the provinces to the detriment of the federal government. Trudeau stepped down as Prime Minister and party leader in 1984, as the Liberals were slipping in polls. At that year's leadership convention, Turner defeated Chrétien on the second ballot to become Prime Minister. Immediately, upon taking office, Turner called a snap election, citing favourable internal polls. However, the party was hurt by numerous patronage appointments, many of which Turner had made supposedly in return for Trudeau retiring early. Also, they were unpopular in their traditional stronghold of Quebec because of the constitution repatriation which excluded that province. The Liberals lost power in the 1984 election, and were reduced to only 40 seats in the House of Commons. The Progressive Conservatives won a majority of the seats in every province, including Quebec. The 95-seat loss was the worst defeat in the party's history, and the worst defeat at the time for a governing party at the federal level. What was more, the New Democratic Party, successor to theCo-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF; french: Fédération du Commonwealth Coopératif, FCC); from 1955 the Social Democratic Party of Canada (''french: Parti social démocratique du Canada''), was a federal democratic socialistThe foll ...
, won only ten fewer seats than the Liberals, and some thought that the NDP under Ed Broadbent would push the Liberals to third-party status.
The party began a long process of reconstruction. A small group of young Liberal MPs, known as the Rat Pack, gained fame by criticizing the Tory government of Brian Mulroney at every turn. Also, despite public and backroom attempts to remove Turner as leader, he managed to consolidate his leadership at the 1986 review.
The 1988 election was notable for Turner's strong opposition to the Canada-U.S. Free Trade Agreement negotiated by Progressive Conservative Prime Minister Brian Mulroney. Although most Canadians voted for parties opposed to free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold ...
, the Tories were returned with a majority government, and implemented the deal. The Liberals recovered from their near-meltdown of 1984, however, winning 83 seats and ending much of the talk of being eclipsed by the NDP, who won 43 seats.
Jean Chrétien
 Turner announced that he would resign as leader of the Liberal Party on May 3, 1989. The Liberal Party set a leadership convention for June 23, 1990, in
Turner announced that he would resign as leader of the Liberal Party on May 3, 1989. The Liberal Party set a leadership convention for June 23, 1990, in Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, maki ...
. Five candidates contested the leadership of the party and former Deputy Prime Minister Jean Chrétien, who had served in every Liberal cabinet since 1965, won on the first ballot. Chrétien's Liberals campaigned in the 1993 election on the promise of renegotiating the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and eliminating the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Just after the writ was dropped for the election, they issued the Red Book, an integrated and coherent approach to economic, social, environmental and foreign policy. This was unprecedented for a Canadian party. Taking full advantage of the inability of Mulroney's successor, Kim Campbell, to overcome a large amount of antipathy toward Mulroney, they won a strong majority government with 177 seats—the third-best performance in party history, and their best since 1949. The Progressive Conservatives were cut down to only two seats, suffering a defeat even more severe than the one they had handed the Liberals nine years earlier. The Liberals were re-elected with a considerably reduced majority in 1997, but nearly tied their 1993 total in 2000.
For the next decade, the Liberals dominated Canadian politics in a fashion not seen since the early years of Confederation. This was because of the destruction of the "grand coalition" of Western socially conservative populists, Quebec nationalists, and fiscal conservatives from Ontario that had supported the Progressive Conservatives in 1984 and 1988. The Progressive Conservatives' Western support, for all practical purposes, transferred en masse to the Western-based Reform Party, which replaced the PCs as the major right-wing party in Canada. However, the new party's agenda was seen as too conservative for most Canadians. It only won one seat east of Manitoba in an election (but gained another in a floor-crossing). Even when Reform restructured into the Canadian Alliance, the party was virtually non-existent east of Manitoba, winning only 66 seats in 2000. Reform/Alliance was the official opposition from 1997 to 2003, but was never able to overcome wide perceptions that it was merely a Western protest party. The Quebec nationalists who had once supported the Tories largely switched their support to the sovereigntist Bloc Québécois, while the Tories' Ontario support largely moved to the Liberals. The PCs would never be a major force in Canadian politics again; while they rebounded to 20 seats in the next election, they won only two seats west of Quebec in the next decade.
Ontario and Quebec combine for a majority of seats in the House of Commons by virtue of Ontario's current population and Quebec's historic population (59 percent of the seats ). As a result, it is very difficult to form even a minority government without substantial support in Ontario and/or Quebec. No party has ever formed a majority government without winning the most seats in either Ontario or Quebec. It is mathematically possible to form a minority government without a strong base in either province, but such an undertaking is politically difficult. The Liberals were the only party with a strong base in both provinces, thus making them the only party capable of forming a government.
There was some disappointment as Liberals were not able to recover their traditional dominant position in Quebec, despite being led by a Quebecer from a strongly nationalist region of Quebec. The Bloc capitalized on discontent with the failure of the 1990 Meech Lake Accord and Chrétien's uncompromising stance on federalism (see below) to win the most seats in Quebec in every election from 1993, onward, even serving as the official opposition from 1993 to 1997. Chrétien's reputation in his home province never recovered after the 1990 leadership convention when rival Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
The son o ...
forced him to declare his opposition to the Meech Lake Accord. However, the Liberals did increase their support in the next two elections because of infighting within the Bloc. In the 1997 election, although the Liberals finished with a thin majority, it was their gains in Quebec which were credited with offsetting their losses in the Maritime provinces. In particular, the 2000 election was a breakthrough for the Liberals after the PQ government's unpopular initiatives regarding consolidation of several Quebec urban areas into "megacities". Many federal Liberals also took credit for Charest's provincial election victory over the PQ in spring 2003. A series of by-elections allowed the Liberals to gain a majority of Quebec ridings for the first time since 1984.
The Chrétien Liberals more than made up for their shortfall in Quebec by building a strong base in Ontario. They reaped a substantial windfall from the votes of fiscally conservative and socially liberal voters who had previously voted Tory, as well as rapid growth in the Greater Toronto Area. They were also able to take advantage of massive vote splitting
Vote splitting is an electoral effect in which the distribution of votes among multiple similar candidates reduces the chance of winning for any of the similar candidates, and increases the chance of winning for a dissimilar candidate.
Vote sp ...
between the Tories and Reform/Alliance in rural areas of the province that had traditionally formed the backbone of provincial Tory governments. Combined with their historic dominance of Metro Toronto and northern Ontario, the Liberals dominated the province's federal politics even as the Tories won landslide majorities at the provincial level. In 1993, for example, the Liberals won all but one seat in Ontario, and came within 123 votes in Simcoe Centre of pulling off the first clean sweep of Canada's most populated province. They were able to retain their position as the largest party in the House by winning all but two seats in Ontario in the 1997 election. The Liberals were assured of at least a minority government once the Ontario results came in, but it was not clear until later in the night that they would retain their majority. In 2000, the Liberals won all but three seats in Ontario.
While the Chrétien Liberals campaigned from the left, their time in power is most marked by the cuts made to many social programs, including health transfers, in order to balance the federal budget. Chrétien had supported the Charlottetown Accord while in opposition, but in power opposed major concessions to Quebec and other provincialist factions. In contrast to their promises during the 1993 campaign, they implemented only minor changes to NAFTA, embraced the free trade concept and—with the exception of the replacement of the GST with the Harmonized Sales Tax in some Atlantic provinces—broke their promise to replace the GST.
After a proposal for Quebec independence was narrowly defeated in the 1995 Quebec referendum, the Liberals passed the " Clarity Act", which outlines the federal government's preconditions for negotiating provincial independence. In Chrétien's final days, he supported same-sex marriage and decriminalizing the possession of small quantities of marijuana. Chrétien displeased the United States government when he pledged on March 17, 2003, that Canada would not support the 2003 invasion of Iraq. A poll released shortly after showed widespread approval of Chrétien's decision by the Canadian public. The poll, which was conducted by EKOS for the ''Toronto Star
The ''Toronto Star'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet daily newspaper. The newspaper is the country's largest daily newspaper by circulation. It is owned by Toronto Star Newspapers Limited, a subsidiary of Torstar Corporation and pa ...
'' and '' La Presse'', found 71 percent of those questioned approved of the government's decision to not enter the United States-led invasion, with 27 percent expressing disapproval.
21st century
Several trends started in 2003 which suggested the end of the Liberal Party's political dominance. Notably, there would be a high turnover of permanent party leaders, in contrast to their predecessors who usually served over two or more elections, particularly Trudeau and Chrétien who each led for over a decade. The Liberals were also hampered by their inability to raise campaign money competitively after Chrétien passed a bill in 2003 which banned corporate donations, even though the Liberals had enjoyed by far the lion's share of this funding because of the then-divided opposition parties. It has been suggested that Chrétien, who had done nothing about election financing for his 10 years in office, could be seen as the idealist as he retired, while his rival and successor Paul Martin would have the burden of having to fight an election under the strict new rules. Simon Fraser University professor Doug McArthur has noted that Martin's leadership campaign used aggressive tactics for the 2003 leadership convention, in attempting to end the contest before it could start by giving the impression that his bid was too strong for any other candidate to beat. McArthur blamed Martin's tactics for the ongoing sag in Liberal fortunes, as it discouraged activists who were not on side.Paul Martin

Paul Martin
Paul Edgar Philippe Martin (born August 28, 1938), also known as Paul Martin Jr., is a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 21st prime minister of Canada and the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
The son o ...
succeeded Chrétien as party leader and prime minister in 2003. Despite the personal rivalry between the two, Martin was the architect of the Liberals' economic policies as Minister of Finance during the 1990s. Chrétien left office with a high approval rating and Martin was expected to make inroads into Quebec and Western Canada, two regions of Canada where the Liberals had not attracted much support since the 1980s and 1990s, respectively. While his cabinet choices provoked some controversy over excluding many Chrétien supporters, it at first did little to hurt his popularity.
The political situation changed with the revelation of the sponsorship scandal, in which advertising agencies supporting the Liberal Party received grossly inflated commissions for their services. Having faced a divided conservative opposition for the past three elections, Liberals were seriously challenged by competition from the newly united Conservative Party led by Stephen Harper. The infighting between Martin and Chrétien's supporters also dogged the party. Nonetheless, by criticizing the Conservatives' social policies, the Liberals were able to draw progressive votes from the NDP which made the difference in several close races. On June 28, 2004 federal election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
, the Martin Liberals retained enough support to continue as the government, though they were reduced to a minority.
In the ensuing months, testimony from the Gomery Commission caused public opinion to turn sharply against the Liberals for the first time in over a decade. Despite the devastating revelations, only two Liberal MPs—David Kilgour
David William Kilgour (February 18, 1941 – April 5, 2022) was a Canadian human rights activist, author, lawyer, and politician. He was also a Senior Fellow to the Raoul Wallenberg Centre for Human Rights.
Kilgour graduated from the Univer ...
(who had crossed the floor
Crossed may refer to:
* ''Crossed'' (comics), a 2008 comic book series by Garth Ennis
* ''Crossed'' (novel), a 2010 young adult novel by Ally Condie
* "Crossed" (''The Walking Dead''), an episode of the television series ''The Walking Dead''
S ...
from the PC Party in 1990) and Pat O'Brien—left the party for reasons other than the scandal. Belinda Stronach, who crossed the floor from the Conservatives to the Liberals, gave Martin the number of votes needed, although barely, to hold onto power when an NDP-sponsored amendment to his budget was passed only by the Speaker's tiebreaking vote on May 19, 2005.
In November, the Liberals dropped in polls following the release of the first Gomery Report. Nonetheless, Martin turned down the NDP's conditions for continued support, as well as rejected an opposition proposal which would schedule a February 2006 election in return for passing several pieces of legislation. The Liberals thus lost the no-confidence vote on November 28; Martin thus became only the fifth prime minister to lose the confidence of the House, but the first to lose on a straight no-confidence motion. Because of the Christmas holiday, Martin advised Governor General Michaëlle Jean to dissolve Parliament and call an election for January 2006.
The Liberal campaign was dogged from start to finish by the sponsorship scandal, which was brought up by a Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
(RCMP) criminal investigation into the leak of the income trust announcement. Numerous gaffes, contrasting with a smoothly run Conservative campaign, put Liberals as many as ten points behind the Conservatives in opinion polling. They managed to recover some of their momentum by election night, but not enough to retain power. They won 103 seats, a net loss of 30 from when the writs were dropped, losing a similar number of seats in Ontario and Quebec to the Tories. However, the Liberals managed to capture the most seats in Ontario for the fifth straight election (54 to the Tories' 40), holding the Conservatives to a minority government. While the Conservatives captured many of Ontario's rural ridings, the Liberals retained most of the population-rich Greater Toronto Area. Many of these ridings, particularly the 905 region, had historically been bellwethers (the Liberals were nearly shut out of this region in 1979 and 1984), but demographic changes have resulted in high Liberal returns in recent years.
Martin resigned as parliamentary leader after the election and stepped down as Liberal leader on March 18, having previously promised to step down if he did not win a plurality.
On May 11, 2006, '' La Presse'' reported that the Government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown-i ...
would file a lawsuit against the Liberal Party to recover all the money missing in the sponsorship program. Scott Brison told reporters that same day that the Liberals has already paid back the $1.14 million into the public purse; however, the Conservatives believed that there was as much as $40 million unaccounted for in the sponsorship program.
Stéphane Dion
 After their election defeat Martin chose not to take on the office of Leader of the Opposition. He stepped down as parliamentary leader of his party on February 1, and the Liberal caucus appointed Bill Graham, MP for Toronto Centre and outgoing Defence Minister, as his interim successor. Martin officially resigned as leader in March, with Graham taking over on an interim basis.
The leadership election was set for December 2, 2006, in
After their election defeat Martin chose not to take on the office of Leader of the Opposition. He stepped down as parliamentary leader of his party on February 1, and the Liberal caucus appointed Bill Graham, MP for Toronto Centre and outgoing Defence Minister, as his interim successor. Martin officially resigned as leader in March, with Graham taking over on an interim basis.
The leadership election was set for December 2, 2006, in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
; however, a number of prominent members such as John Manley, Frank McKenna, Brian Tobin
Brian Vincent Tobin (born October 21, 1954) is a Canadian businessman and former politician. Tobin served as the sixth premier of Newfoundland from 1996 to 2000. Tobin was also a prominent Member of Parliament and served as a cabinet minister i ...
, and Allan Rock had already announced they would not enter the race to succeed Martin. Throughout the campaign 12 candidates came forward to lead the party, but by the time of the leadership convention only eight people remained in the race; Martha Hall Findlay
Martha Hall Findlay (born August 17, 1959) is a Canadian businesswoman, entrepreneur, lawyer and politician who previously served as the president and CEO of the Canada West Foundation, a Calgary-based think tank, and is now senior vice-presi ...
, Stéphane Dion, Michael Ignatieff, Gerard Kennedy, Bob Rae, Scott Brison
Scott A. Brison (born May 10, 1967) is a Canadian former politician from Nova Scotia. Brison served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for the riding of Kings-Hants from the 1997 federal election until July 2000, then from November 2000 to F ...
, Ken Dryden, Joe Volpe
Giuseppe "Joe" Volpe (born September 21, 1947) is a Canadian politician. He represented the Ontario riding of Eglinton-Lawrence as a member of the Liberal Party in the House of Commons of Canada from 1988 until 2011, when he lost his seat t ...
.
Throughout the campaign Ignatieff, Rae, Dion and Kennedy were considered to be the only candidates with enough support to be able to win the leadership, with Ignatieff and Rae being considered the two front-runner
In politics, a front-runner (also spelled frontrunner or front runner) is a leader in an electoral race. While the front-runner in athletic events (the namesake of the political concept) is generally clear, a political front-runner, particularly i ...
s. However polling showed Ignatieff had little room to grow his support, while Dion was the second and third choice among a plurality of delegates. At the leadership convention Ignatieff came out on top on the first ballot with 29.3 percent, With Kennedy's support Dion was able to leapfrog both Rae and Ignatieff on the third ballot, eliminating Rae. On the fourth and final ballot Dion defeated Ignatieff to become leader of the Liberal Party.
Following the leadership race the Liberal Party saw a bounce in support and surpassed the Conservative Party as the most popular party in Canada. However, in the months and years to come the party's support gradually fell. Dion's own popularity lagged considerably behind that of Prime Minister Harper's, and he often trailed NDP leader Jack Layton in opinion polls when Canadians were asked who would make the best Prime Minister.
Dion campaigned on environmental sustainability during the leadership race, and created the "Green Shift" plan following his election as leader. The Green Shift proposed creating a carbon tax
A carbon tax is a tax levied on the carbon emissions required to produce goods and services. Carbon taxes are intended to make visible the "hidden" social costs of carbon emissions, which are otherwise felt only in indirect ways like more s ...
that would be coupled with reductions to income tax rates. The proposal was to tax greenhouse gas emissions, starting at $10 per tonne of and reaching $40 per tonne within four years. The plan was a key policy for the party in the 2008 federal election, but it was not well received and was continuously attacked by both the Conservatives and NDP. On election night the Liberal Party won 26.26 percent of the popular vote and 77 of the 308 seats in the House of Commons. At that time their popular support was the lowest in the party's history, and weeks later Dion announced he would step down as Liberal leader once his successor was chosen.
Leadership campaign and coalition attempt
New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic Canad ...
Member of Parliament Dominic LeBlanc was the first candidate to announce he would seek the leadership of the Liberal Party on October 27, 2008. Days later Bob Rae, who had finished third in 2006, announced he would also be a candidate for the leadership. The party executive met in early November and chose May 2, 2009, as the date to elect the next leader. On November 13 Michael Ignatieff, who finished second in 2006, announced he would also be a candidate.
 On November 27, 2008, Minister of Finance Jim Flaherty provided the House of Commons with a fiscal update, within which were plans to cut government spending, suspend the ability of civil servants to strike until 2011, sell off some Crown assets to raise capital, and eliminate the existing $1.95 per vote subsidy parties garner in an election. The opposition parties criticized the fiscal update, and announced they would not support it because it contained no stimulus money to spur Canada's economy and protect workers during the economic crisis. With the Conservative Party only holding a minority of the seats in the House of Commons the government would be defeated if the opposition parties voted against the fiscal update. With the Conservatives unwilling to budge on the proposals outlined in the fiscal update the Liberals and NDP signed an agreement to form a coalition government, with a written pledge of support from the Bloc Québécois. Under the terms of the agreement Dion would be sworn in as Prime Minister, however he would only serve in the position until the next Liberal leader was chosen. Dion contacted Governor General Michaëlle Jean and advised her that he had the confidence of the House of Commons if Prime Minister Harper's government was to fall. However, before the fiscal update could be voted on in the House of Commons Prime Minister Harper requested the Governor General to prorogue parliament until January 26, 2009, which she accepted.
While polls showed Canadians were split on the idea of having either a coalition government or having the Conservatives continue to govern, it was clear that because of Dion's personal popularity they were not comfortable with him becoming Prime Minister. Members of the Liberal Party therefore called on Dion to resign as leader immediately and for an interim leader to be chosen, this person would become the Prime Minister in case the Conservatives were defeated when parliament resumed in January. With an estimated 70 percent of the Liberal caucus wanting Ignatieff to be named interim leader, Dion resigned the post on December 8, 2008 (effective December 10, upon Ignatieff's becoming interim leader). LeBlanc announced on the same day that he was abandoning the Liberal leadership race and endorsing Ignatieff as the next leader. The following day Rae announced he was also dropping out of the race and was placing his "full and unqualified" support to Ignatieff.
On November 27, 2008, Minister of Finance Jim Flaherty provided the House of Commons with a fiscal update, within which were plans to cut government spending, suspend the ability of civil servants to strike until 2011, sell off some Crown assets to raise capital, and eliminate the existing $1.95 per vote subsidy parties garner in an election. The opposition parties criticized the fiscal update, and announced they would not support it because it contained no stimulus money to spur Canada's economy and protect workers during the economic crisis. With the Conservative Party only holding a minority of the seats in the House of Commons the government would be defeated if the opposition parties voted against the fiscal update. With the Conservatives unwilling to budge on the proposals outlined in the fiscal update the Liberals and NDP signed an agreement to form a coalition government, with a written pledge of support from the Bloc Québécois. Under the terms of the agreement Dion would be sworn in as Prime Minister, however he would only serve in the position until the next Liberal leader was chosen. Dion contacted Governor General Michaëlle Jean and advised her that he had the confidence of the House of Commons if Prime Minister Harper's government was to fall. However, before the fiscal update could be voted on in the House of Commons Prime Minister Harper requested the Governor General to prorogue parliament until January 26, 2009, which she accepted.
While polls showed Canadians were split on the idea of having either a coalition government or having the Conservatives continue to govern, it was clear that because of Dion's personal popularity they were not comfortable with him becoming Prime Minister. Members of the Liberal Party therefore called on Dion to resign as leader immediately and for an interim leader to be chosen, this person would become the Prime Minister in case the Conservatives were defeated when parliament resumed in January. With an estimated 70 percent of the Liberal caucus wanting Ignatieff to be named interim leader, Dion resigned the post on December 8, 2008 (effective December 10, upon Ignatieff's becoming interim leader). LeBlanc announced on the same day that he was abandoning the Liberal leadership race and endorsing Ignatieff as the next leader. The following day Rae announced he was also dropping out of the race and was placing his "full and unqualified" support to Ignatieff.
Michael Ignatieff
With Ignatieff named interim leader of the party (on December 10), the Liberal's poll numbers saw significant gains, after they plummeted with the signing of the coalition agreement. When parliament resumed on January 28, 2009, the Ignatieff Liberals agreed to support the budget as long as it included regular accountability reports, which the Conservatives accepted. This ended the possibility of the coalition government with the New Democrats. Throughout the Winter of 2008–09, opinion polls showed that while the Ignatieff led Liberals still trailed the Conservatives, their support had stabilized in the low 30 percent range. However, by the time Ignatieff was confirmed as party leader on May 2, 2009, the Liberal Party had a comfortable lead over the governing Conservatives. After a summer where he was accused of being missing in action, Ignatieff announced on August 31, 2009, that the Liberals would not support the minority Conservative government. After this announcement the Liberal Party's poll numbers, which had already declined over the summer, started to fall further behind the Conservatives. On October 1, 2009, the Liberals put forth a non-confidence motion with the hope of defeating the government. However, the NDP abstained from voting and the Conservatives survived the confidence motion.
Throughout the Winter of 2008–09, opinion polls showed that while the Ignatieff led Liberals still trailed the Conservatives, their support had stabilized in the low 30 percent range. However, by the time Ignatieff was confirmed as party leader on May 2, 2009, the Liberal Party had a comfortable lead over the governing Conservatives. After a summer where he was accused of being missing in action, Ignatieff announced on August 31, 2009, that the Liberals would not support the minority Conservative government. After this announcement the Liberal Party's poll numbers, which had already declined over the summer, started to fall further behind the Conservatives. On October 1, 2009, the Liberals put forth a non-confidence motion with the hope of defeating the government. However, the NDP abstained from voting and the Conservatives survived the confidence motion.
non-confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
against the Harper government to attempt to force a federal election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
after the government was found to be in Contempt of Parliament, the first such occurrence in Commonwealth history. The House of Commons passed the motion by 156–145.
The Liberals had considerable momentum when the writ was dropped, and Ignatieff successfully squeezed NDP leader Jack Layton out of media attention, by issuing challenges to Harper for one-on-one debates. In the first couple weeks of the campaign, Ignatieff kept his party in second place in the polls, and his personal ratings exceeded that of Layton for the first time. However, opponents frequently criticized Ignatieff's perceived political opportunism, particularly during the leaders debate
A leaders' debate or presidential debate is a public debate held during a general election campaign, where the candidates expose their political opinions and public policy proposals, and criticism of them, to potential voters. They are normally b ...
s when Layton criticized Ignatieff for having a poor attendance record for Commons votes saying "You know, most Canadians, if they don't show up for work, they don't get a promotion". Ignatieff failed to defend himself against these charges, and the debates were said to be a turning point for his party's campaign. Near the end of the campaign, a late surge in support for Layton and the NDP relegated Ignatieff and the Liberals to third in opinion polls.
The Liberals took their biggest loss ever on the May 2, 2011, federal election. The result was a third-place finish, with only 19 percent of the vote and returning 34 seats in the House of Commons. Notably, their support in Toronto and Montreal, their power bases for the last two decades, all but vanished. All told, the Liberals won only 11 seats in Ontario (seven of which were in Toronto) and seven in Quebec (all in Montreal)—their fewest totals in either province. Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
was the only province with majority Liberal seats at 4 out of 7. They also won only four seats west of Ontario. The Conservatives won 40 percent of the vote and formed a majority government, while the NDP formed the Official Opposition winning 31 percent of the vote.
This election marked the first time the Liberals were unable to form either government or the official opposition. Ignatieff was defeated in his own riding, and announced his resignation as Liberal leader shortly after. Bob Rae was chosen as the interim leader on May 25, 2011.
Justin Trudeau
 On April 14, 2013,
On April 14, 2013, Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since ...
, son of former Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau, was elected leader of the Liberal Party on the first ballot, winning 80% of the vote. Following his win, support for the Liberal Party increased considerably, and the party moved into first place in public opinion polls.
An initial surge in support in the polls following Trudeau's election wore off in the following year, in the face of Conservative ad campaign after Trudeau's win attempting to " ainthim as a silly dilettante unfit for public office."
In 2014, Trudeau removed all Liberal senators from the Liberal Party caucus. In announcing this, Trudeau said the purpose of the unelected upper chamber is to act as a check on the power of the prime minister, but the party structure interferes with that purpose. Following this move, Liberal senators chose to keep the designation "Liberal" and sit together as a caucus, albeit not one supported by the Liberal Party of Canada. This independent group continued to refer to itself in publications as the Senate Liberal Caucus until 2019.
By the time the 2015 federal election was called, the Liberals had been knocked back into third place. Trudeau and his advisors planned to mount a campaign based on economic stimulus in the hopes of regaining the mantle of being the party that best represented change from the New Democrats.
Justin Trudeau's Liberals would win the 2015 election with 39.5 percent of the popular vote and 184 seats in dramatic fashion: becoming the first party to win a parliamentary majority after being reduced to third party status in a previous general election, besting Brian Mulroney's record for the largest seat increase by a party in a single election (111 in 1984), and winning the most seats in Quebec for the first time since 1980. Chantal Hébert deemed the result "a Liberal comeback that is headed straight for the history books", while Bloomberg's Josh Wingrove and Theophilos Argitis similarly described it as "capping the biggest political comeback in the country’s history."
At the 2019 federal election, Trudeau's Liberal Party lost 20 seats in the House of Commons (lowering its total from 177 to 157) from the time of dissolution, they still won the most seats of any party—enough seats to allow Trudeau to form a minority government. For the first time since 1979, the party that garnered the largest share of the national popular vote did not win the most seats; the Liberals under Trudeau had 33.1 per cent of the popular vote, while the Conservatives under Andrew Scheer had 34.4 per cent. It was also the first time a government took power with less than 35 per cent of the national popular vote since the Conservatives of John A. Macdonald, in 1867, who had 34.8 per cent of the votes.
In the 2021 federal election, Trudeau and the Liberals secured a third mandate and his second minority government after winning 160 seats. However, the Liberals again came in second in the national popular vote, behind the Conservatives. They received 32.6 percent of the popular vote, the lowest percentage of the national popular vote for a governing party in Canadian history.
In March 2022, Trudeau's Liberal Party agreed to a confidence and supply deal with the New Democratic Party.
Systems and realignment model
Scholars and political experts have recently used a political realignment model to explain what was considered a collapse of a dominant party, and put its condition in long-term perspective. According to recent scholarship, there have been four party systems in Canada at the federal level since Confederation, each with its own distinctive pattern of social support, patronage relationships, leadership styles, and electoral strategies. Steve Patten identifies four party systems in Canada's political history: * The first party system emerged from pre-Confederation colonial politics, had its "heyday" from 1896 to 1911 and lasted until the Conscription Crisis of 1917, and was characterized by local patronage administered by the two largest parties, the Liberals and the Conservatives. * The second system emerged following the First World War, and had its heyday from 1935 and 1957, was characterized byregionalism
Regionalism may refer to:
* Regionalism (art), an American realist modern art movement that was popular during the 1930s
* Regionalism (international relations), the expression of a common sense of identity and purpose combined with the creation a ...
and saw the emergence of several protest parties, such as the Progressives, the Social Credit Party, and the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF; french: Fédération du Commonwealth Coopératif, FCC); from 1955 the Social Democratic Party of Canada (''french: Parti social démocratique du Canada''), was a federal democratic socialistThe foll ...
.
* The third system emerged in 1963 and had its heyday from 1968 to 1983 and began to unravel thereafter. The two largest parties were challenged by a strong third party, the New Democratic Party (successor to the CCF). Campaigns during this era became more national in scope because of electronic media
Electronic media are media that use electronics or electromechanical means for the audience to access the content. This is in contrast to static media (mainly print media), which today are most often created digitally, but do not requir ...
, and involved a greater focus on leadership. The dominant policy of the era was Keynesian economics.
* The fourth party system has involved the rise of the Reform Party, the Bloc Québécois, and the merger of the Canadian Alliance with the Progressive Conservatives. Most parties moved to one-member-one-vote leadership contests, and campaign finance laws were reformed in 2004. The fourth party system has been characterized by market-oriented policies that generally abandoned Keynesian policies, but maintained the welfare state.
Stephen Clarkson (2005) shows how the Liberal Party has dominated all the party systems, using different approaches. It began with a "clientelistic approach" under Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, ( ; ; November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minist ...
, which evolved into a "brokerage" system of the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s under Mackenzie King. The 1950s saw the emergence of a "pan-Canadian system", which lasted until the 1990s. The 1993 election – categorized by Clarkson as an electoral "earthquake" which "fragmented" the party system, saw the emergence of regional politics within a four party-system, whereby various groups championed regional issues and concerns. Clarkson concludes that the inherent bias built into the first-past-the-post system, has chiefly benefited the Liberals.
Principles and policies
The principles of the party are based onliberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for ...
as defined by various liberal theorists
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment a ...
and include individual freedom for present and future generations, responsibility, human dignity, a just society, political freedom, religious freedom, national unity, equality of opportunity, cultural diversity, bilingualism, and multilateralism. From the early twentieth century, the Liberal party has favoured a variety of " big tent" policies from both right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical th ...
and left of the political spectrum
A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different political positions in relation to one another. These positions sit upon one or more geometric axes that represent independent political dimensions. The expressions polit ...
. When it formed the government from 1993 to 2006, it championed balanced budgets, and eliminated the budget deficit completely from the federal budget in 1995 by reducing spending on social programs or delegating them to the provinces, and promised to replace the Goods and Services Tax in the party's famous Red Book. It also legalized same-sex marriage.
2021 party platform
During the 2021 federal election, the Liberal Party of Canada introduced their platform, which included a "Gender and Diversity Impact Summary" for each chapter, as well as six key categories. These included: the pandemic, housing, health care, the economy, climate change, and reconciliation. Key Liberal policies of the 2021 platform included: *Requiring travellers on interprovincial trains, commercial flights, cruise ships, and other federally regulated vessels be vaccinated against COVID-19. *Making an investment of $6 billion—on top of $4 billion already committed—to support the elimination of health system waitlists. *Providing various investments in order to build, preserve, or revitalize 1.4 million new homes by 2025–26. *Allocating funds to spend $2 billion over the next five years on measures to address the legacy of residential schools with “truth, justice, and healing” initiatives. *Re-introducing legislation within the first 100 days in office to eliminate the practice of gay conversion therapy for everyone. *Achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. *Presenting a National Action Plan on Combating Hate by 2022 as part of a renewed Anti-Racism Strategy, including the Black Canadians Justice Strategy. *Updating the committed number to receive 40,000 Afghan refugees. *Creating a minimum tax rule so that everyone who earns enough to qualify for the top bracket pays at least 15% each year (the tax rate paid by people earning less than $49,000), removing their ability to artificially pay no tax through excessive use of deductions and credits. *Establishing a permanent Council of Economic Advisors to provide independent advice to government on long-term growth. The council will be gender- balanced and reflect Canada's diversity. *Reform economic immigration programs to expand pathways to permanent residence for temporary foreign workers and former international students through the Express Entry points system. *Setting aside a minimum of $1 billion to support provinces or territories who implement a ban on handguns across their jurisdiction.Provincial parties
Each province and one territory in Canada has its own Liberal Party; however, only those inNew Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic Canad ...
, Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native En ...
, and Prince Edward Island are politically and organizationally affiliated with the federal Liberal Party. While other provincial Liberal parties may align ideologically with the federal party, they operate as completely separate entities. Those provincial parties have separate policies, finances, memberships, constituency associations, executives, conventions and offices.
Electoral performance
Party leadership
To date, only seven Liberal leaders never served as Prime Minister, three of whom were interim leaders.Leaders
Presidents
* Vincent Massey 1932–1935 *Norman Platt Lambert
Norman Platt Lambert (January 7, 1885 – November 4, 1965) was a Canadian journalist and Senator.
Born in Mount Forest, Ontario, he received a Bachelor of Arts degree from the University of Toronto in 1909. After graduating, he started as ...
1936–1941
* ''vacant'' 1941–1943
* Norman Alexander McLarty
Norman Alexander McLarty, (February 18, 1889 – September 6, 1945) was a Canadian politician.
Born in St. Thomas, Ontario, he was first elected to the House of Commons of Canada representing the riding of Essex West in the 1935 federal ...
1943 (acting)
* Wishart McLea Robertson
Wishart McLea Robertson, (February 15, 1891 – August 16, 1967) was a politician in Nova Scotia, Canada.
Robertson's paternal grandfather, Robert Robertson, was a member of Nova Scotia House of Assembly from 1854 until 1878. His father, ...
1943–1945
* James Gordon Fogo
James Gordon Fogo, (July 9, 1896 – July 6, 1952) was a Canadian lawyer and senator.
Born in Halifax, Nova Scotia, the son of Adam Fogo and Alice Hanway, he studied law at Dalhousie University and served as an officer in the Canadian Army ...
1946–1952
* Duncan Kenneth MacTavish
Duncan Kenneth MacTavish (August 3, 1899 – November 15, 1963) was a Canadian Senator.
MacTavish was a millionaire and one of Canada's leading corporate lawyers."Still Seek Reason for Crash in which Senator MacTavish Died", ''Globe and Mail'', N ...
1952–1958
* Bruce Matthews 1958–1961
* John Joseph Connolly 1961–1964
* John Lang Nichol
John Lang Nichol, (January 7, 1924 – February 24, 2020) was a Canadian politician who served as a senator from 1966 to 1973.
Born in Vancouver, British Columbia, he was president of the Liberal Federation of Canada for two terms from 1964 unt ...
1964–1968
* Richard Stanbury
Richard James Hardy Stanbury (May 2, 1923 – July 21, 2014) was a Canadian lawyer and politician. Stanbury was a Senator from February 1968 to May 1998 who also served as president of the Liberal Party of Canada from 1968 to 1973.
Before his a ...
1968–1973
* Gildas Molgat 1973–1976
* Alasdair Graham
Alasdair Bernard Graham (May 21, 1929 – April 22, 2015) was a Canadian politician, journalist and businessman.
Political career
Graham attempted to win a seat in the House of Commons of Canada in the 1958 election from Nova Scotia, but was ...
1976–1980
* Norman MacLeod 1980–1982
* Iona Campagnolo 1982–1986
* J. J. Michel Robert
J.J. Michel Robert, (born January 29, 1938) is a Canadian jurist and former politician from Quebec.
Robert served as president of the Young Liberals of Canada from 1963 to 1965, and was a member of the 1982 to 1985 Royal Commission on the Ec ...
1986–1990
* Don Johnston 1990–1994
* Dan Hays 1994–1998
* Stephen LeDrew 1998–2003
* Michael Eizenga
Michael Eizenga (born July 7, 1956) is a Canadian lawyer who served as president of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2003 to 2006.
Biography
Eizenga was born in London, Ontario.
Education and teaching career
Eizenga earned his B.A. (Hons.) at Hu ...
2003–2006
* Marie Poulin
Marie-Paule Charette-Poulin (born June 21, 1945) was a Canadian senator until resigning in April 2015 and was the president of the Liberal Party of Canada from 2006 to 2008. She is married to international portrait artist Bernard Poulin.
Educat ...
2006–2008
* Doug Ferguson 2008–2009
* Alfred Apps 2009–2012
* Mike Crawley 2012–2014
* Anna Gainey 2014–2018
* Suzanne Cowan 2018–present
See also
*Liberal Party of Canada leadership elections
The first three leaders of the Liberal Party of Canada were not chosen at a leadership convention. Alexander Mackenzie (March 1873 – April 1880) and Edward Blake (May 1880 – June 1887) were chosen by the party caucus. Wilfrid Laurier ( ...
* Liberalism in Canada
* List of political parties in Canada
* Senate Liberal Caucus
* Trudeauism
Notes
References
Further reading
* Bickerton, James, and Alain G. Gagnon. ''Canadian Politics'' (5th ed. 2009), 415pp; university textbook * Bliss, Michael. ''Right Honourable Men: The Descent of Canadian Politics from Macdonald to Mulroney'' (1994), essays on Prime Ministers * Carty, R. Kenneth. ''Big Tent Politics: The Liberal Party’s Long Mastery of Canada’s Public Life'' (2015) * Clarkson, Stephen. ''The Big Red Machine: How the Liberal Party Dominates Canadian Politics'' (2005) * Cohen, Andrew, and J. L. Granatstein, eds. ''Trudeau's Shadow: the life and legacy of Pierre Elliott Trudeau'' (1999). * Gagnon, Alain G., and Brian Tanguay. ''Canadian Parties in Transition'' (3rd ed. 2007), 574pp; university textbook * Granatstein, J.L. ''Mackenzie King: His Life and World'' (1977). * Hillmer, Norman, and Steven Azzi. "Canada's Best Prime Ministers"''Maclean's'' June 20, 2011 online
* Jeffrey, Brooke. ''Divided Loyalties: The Liberal Party of Canada, 1984–2008'' (2010
excerpt and text search
* Jeffrey, Brooke. ''Road to Redemption: The Liberal Party of Canada, 2006-2019'' (2020) * Koop, Royce. "Professionalism, Sociability and the Liberal Party in the Constituencies." ''Canadian Journal of Political Science'' (2010) 43#04 pp: 893–913. * * McCall, Christina. ''Grits: an intimate portrait of the Liberal Party'' (Macmillan of Canada, 1982) *
Neatby, H. Blair
Herbert Blair Neatby (1924–2018) was a Canadian historian. Born on 11 December 1924 in Renown, Saskatchewan, he graduated from the University of Saskatchewan in 1950 and pursued graduate study at the University of Oxford and the University of T ...
. ''Laurier and a Liberal Quebec: A Study in Political Management'' (1973)
* Whitaker, Reginald. ''The Government Party: Organizing and Financing the Liberal Party of Canada, 1930–1958'' (1977)
*
* Wearing, Joseph. ''The L-Shaped Party: The Liberal Party of Canada, 1958–1980'' (McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 1981)
External links
*Liberal Party of Canada - Canadian Political Parties and Political Interest Groups
- Web Archive created by the University of Toronto Libraries
The Liberal Party of Canada Constitution
Canadian Encyclopedia entry on the Liberal Party
Liberal Party of Canada fonds
at
Library and Archives Canada
Library and Archives Canada (LAC; french: Bibliothèque et Archives Canada) is the federal institution, tasked with acquiring, preserving, and providing accessibility to the documentary heritage of Canada. The national archive and library is t ...
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Liberal Party Of Canada
1867 establishments in Canada
Federal political parties in Canada
Liberal International
Liberal parties in Canada
Political parties established in 1867
Centrist parties in Canada
Centre-left parties
Social liberal parties
Abortion-rights organizations in Canada