Leopard (heraldry) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The leopard in
 *
*
heraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch ...
is traditionally depicted the same as a lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
, but in a walking position
Position often refers to:
* Position (geometry), the spatial location (rather than orientation) of an entity
* Position, a job or occupation
Position may also refer to:
Games and recreation
* Position (poker), location relative to the dealer
* ...
with its head turned to full face, thus it is also known as a lion passant guardant in some texts, though leopards more naturally depicted make some appearances in modern heraldry. ''The Oxford Guide to Heraldry'' makes little mention of leopards but glosses ''leopard'' as a "term used in medieval heraldry for ''lion passant guardant''. Now used for the natural beast." Another name for this beast is the ounce.
Early heraldic leopards
The typical heraldic leopard differs from the naturalleopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
(''Panthera pardus'') in that it has no spots and often has a mane, but is generally similar in appearance to a heraldic lion, other than its attitude
Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), an individual's predisposed state of mind regarding a value
* Metaphysics of presence
* Propositional attitude, a relational mental state connecting a person to a pro ...
. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, ...
were thought to be a crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
between a lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
and a pard.
Arthur Charles Fox-Davies
Arthur Charles Fox-Davies (28 February 1871 – 19 May 1928) was a British expert on heraldry. His ''Complete Guide to Heraldry'', published in 1909, has become a standard work on heraldry in England. A barrister by profession, Fox-Davies worke ...
wrote in 1909 that the distinction between lions (which were constantly rampant
In heraldry, the term attitude describes the ''position'' in which a figure (animal or human) is emblazoned as a charge, a supporter, or as a crest. The attitude of an heraldic figure always precedes any reference to the tincture of the figure ...
) and leopards (which were necessarily walking) originated in French heraldry
French heraldry is the use of heraldic symbols in France. Although it had a considerable history, existing from the 11th century, such formality has largely died out in France, as far as regulated personal heraldry is concerned. Civic heraldry on ...
and was brought into English heraldry
English heraldry is the form of coats of arms and other heraldic bearings and insignia used in England. It lies within the so-called Gallo-British tradition. Coats of arms in England are regulated and granted to individuals by the English kings ...
along with so much else of English language and custom deriving from French traditions. But "the use of the term ''leopard'' in heraldry to signify a certain position for the lion never received any extensive sanction, and has long since become obsolete in British armory," though the distinction is still observed in French blazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct the appropriate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The vis ...
.
Fox-Davies further notes that the lions depicted in the royal arms of England
The royal arms of England are the Coat of arms, arms first adopted in a fixed form at the start of the age of heraldry (circa 1200) as Armorial of the House of Plantagenet, personal arms by the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet kings who ruled ...
, though passant guardant, have never represented anything other than ''lions'', also pointing out that another ancient (if controversial) rule distinguishing leopards from lions dictated that while several leopards could appear on one shield, there could not be more than one lion on the shield (with the apparent exception of two lions combatant); multiple rampant lions on one shield were called ''lioncels''.Fox-Davies (1909), p. 174.
Countries with leopards in their coats of arms
One leopard
*Coat of arms of Fiji
The coat of arms of Fiji is the heraldic device consisting of a shield divided quarterly by Cross of St. George and charged with a gold lion at the top, supported by two Fijian warriors, one on each side, and topped with a canoe as the crest. A ...
*Coat of arms of Ghana
The coat of arms of Ghana was designed by Ghanaian artist Nii Amon Kotei and was introduced on 4 March 1957.
Description
*The first quarter, on the upper left shows a sword used by chiefs, and a staff, used by the linguist (known as an ''okyeam ...
Two leopards
* Coat of arms of the principality of Hohenlohe *Coat of arms of Normandy
The flag and coat of arms of Normandy are symbols of Normandy, a region in north-western France.
Normandy
The traditional provincial flag, ''gules, two lions passant or'', is used in both former regions of France: Lower Normandy and Upper Norman ...
Three leopards
*Coat of arms of Canada
The Arms of Canada (french: Armoiries du Canada, links=no), also known as the Royal Coat of Arms of Canada (french: armoiries royales du Canada, links=no) or formally as the Arms of His Majesty the King in Right of Canada (french: Armoiries de Sa M ...
*Coat of arms of Denmark
The coat of arms of Denmark ( da, Danmarks rigsvåben) has a lesser and a greater version.
The state coat of arms () consists of three pale blue lion (heraldry), lions attitude (heraldry)#Passant, passant wearing crown (heraldic charge), crowns ...
(12th century - 1819. After that changed to lions.)
*Coat of arms of Estonia
The coat of arms of Estonia is a golden shield which includes a picture of three left-facing blue lions with red tongues in the middle, with golden oak branches placed on both sides of the shield. The insignia derive(s) from the coat of arms of ...
*Coat of arms of England
The royal arms of England are the arms first adopted in a fixed form at the start of the age of heraldry (circa 1200) as personal arms by the Plantagenet kings who ruled England from 1154. In the popular mind they have come to symbolise the n ...
*Coat of arms of Jersey
The coat of arms of Jersey is the heraldic device consisting of a shield charged with three gold leopards on a red field. Utilised unofficially before the 20th century, its status as the coat of arms of the Bailiwick of Jersey was formalized in ...
*Coat of arms of Guernsey
The coat of arms of Guernsey is the official symbol of the Channel Island of Guernsey. It is very similar to the arms of Normandy, Jersey and England.
Seal of Guernsey
The Seal of Guernsey closely follows the Coat of Arms, it originates from 12 ...
Leopard's heads
 *
*Coat of arms of Dalmatia
The coat of arms of Dalmatia is the heraldic symbol used for the historical region of Dalmatia on the eastern coast of Adriatic Sea. It is also featured on the ''crest'' of the coat of arms of Croatia.
History
The arms first appeared in 14th cent ...
, until 1526 the official arms of Croatia and was later used by Kingdom of Dalmatia
The Kingdom of Dalmatia ( hr, Kraljevina Dalmacija; german: Königreich Dalmatien; it, Regno di Dalmazia) was a crown land of the Austrian Empire (1815–1867) and the Cisleithanian half of Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). It encompassed the entir ...
in Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
; it is now part of Coat of arms of Croatia
The coat of arms of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Grb Republike Hrvatske) consists of one main shield and five smaller shields which form a crown over the main shield. The main coat of arms is a checkerboard (chequy) that consists of 13 red an ...
.
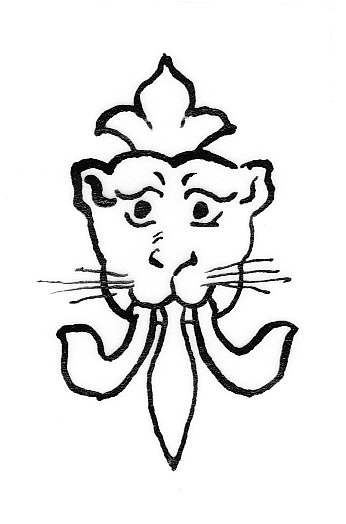
*A leopard's face is frequently shown Jessant-de-lys
Jessant-de-lys is a heraldic term denoting a fleur-de-lys issuing out of any object. It is most frequently seen in conjunction with a leopard's face, meaning in heraldic language the face of a lion.
Description
Charles Boutell (1863) described t ...
, as in the 13th century arms of Cantilupe displayed by Thomas de Cantilupe
Thomas de Cantilupe (25 August 1282; also spelled ''Cantelow, Cantelou, Canteloupe'', Latinised to ''de Cantilupo'') was Lord Chancellor of England and Bishop of Hereford. He was canonised in 1320 by Pope John XXII.
Origins
Thomas was the third ...
and his nephew William de Cantilupe.
Natural leopards
*Coat of arms of Benin
The coat of arms or national seal of Benin, originally introduced in 1964,'':de:Wappen Benins, Wappen Benins'' (German Wikipedia) was readopted in 1990 after being replaced in 1975.
At the top of the emblem is the national crest that consists ...
*Arms of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The arms of the Democratic Republic of the Congo has changed several times since 1997. The current one was introduced in 2006 and depicts a leopard head, surrounded by an elephant tusk to the left and a spear to the right. Below are the three wor ...
(formerly Zaire
Zaire (, ), officially the Republic of Zaire (french: République du Zaïre, link=no, ), was a Congolese state from 1971 to 1997 in Central Africa that was previously and is now again known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zaire was, ...
)
*Coat of arms of Gabon
The coat of arms of Gabon was designed by the Swiss heraldist and vexillologist Louis Mühlemann, one of the founding members of the FIAV and the designer of the coat of arms of the Republic of Congo. It has been in use since 15 July 1963.
Of ...
(black panther
A black panther is the melanistic colour variant of the leopard (''Panthera pardus'') and the jaguar (''Panthera onca''). Black panthers of both species have excess black pigments, but their typical rosettes are also present. They have been d ...
)
*Coat of arms of Malawi
The coat of arms of Malawi is based on the earlier heraldic arms of Nyasaland. It is supported by a lion and a leopard, above a scroll reading "Unity and Freedom". A rising sun in a black field, like in the lower field in the shield, is also prese ...
*Coat of arms of Somalia
The coat of arms of Somalia was adopted on October 10, 1956 and features a golden framed shield of the Somali flag supported by two Cheetah standing on spears. The Cheetah is a common animal seen in Somalia. Cheetah are a common motif in Somali c ...
See also
*Lion (heraldry)
The lion is a common charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, royalty, strength, stateliness and valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Christia ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Leopard (Heraldry) Felids in heraldry