Lens Luxation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
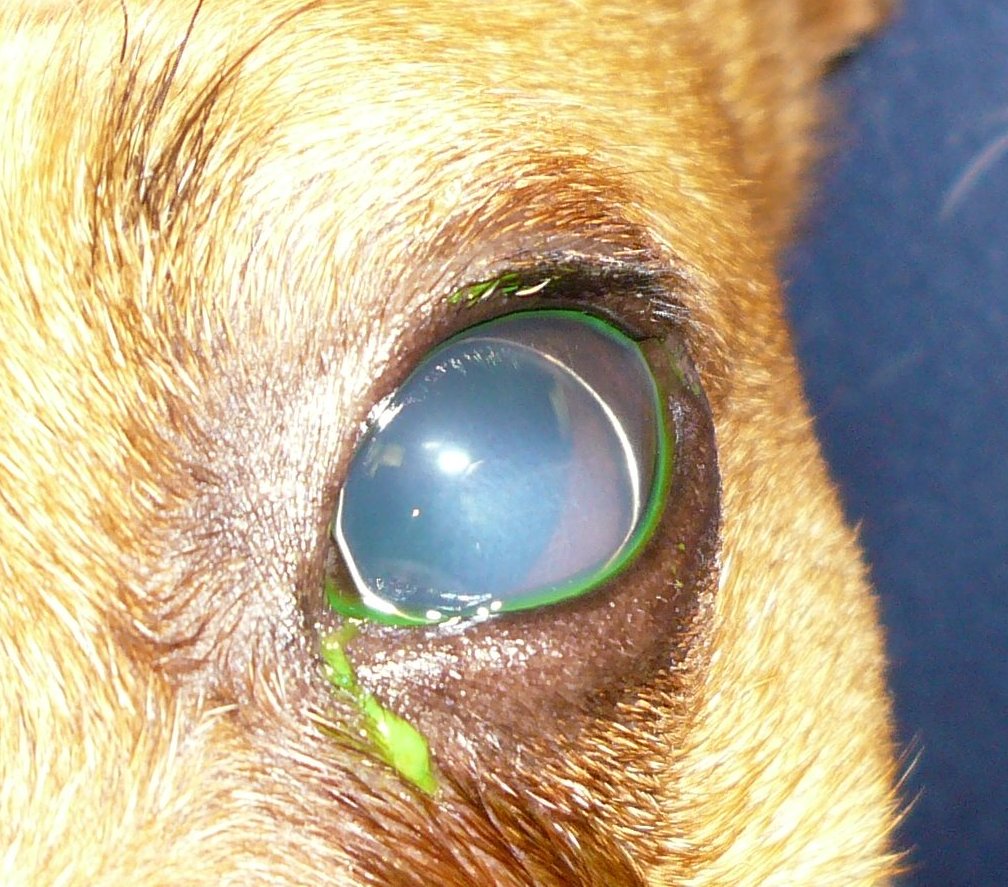
 Ectopia lentis is a displacement or malposition of the eye's
Ectopia lentis is a displacement or malposition of the eye's
"Ectopia Lentis"
eMedicine.com. November 24, 2004. More common: * Marfan syndrome (upward and outward) *
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on ADAMTSL4-Related Eye Disorders, Autosomal Recessive Isolated Ectopia Lentis, Ectopia Lentis et Pupillae
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of eye, ear, face and neck Dog diseases Cat diseases Congenital disorders of eyes Disorders of lens
crystalline lens
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. By changing shape, it functions to change the focal length of the eye so that it ca ...
from its normal location. A partial dislocation of a lens is termed lens subluxation or subluxated lens; a complete dislocation of a lens is termed lens luxation or luxated lens.
Ectopia lentis in dogs and cats
Although observed in humans and cats, ectopia lentis is most commonly seen indog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Do ...
s. Ciliary zonules normally hold the lens in place. Abnormal development of these zonules can lead to primary ectopia lentis, usually a bilateral condition. Luxation can also be a secondary condition, caused by trauma, cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble ...
formation (decrease in lens diameter may stretch and break the zonules), or glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
(enlargement of the globe stretches the zonules). Steroid administration weakens the zonules and can lead to luxation, as well. Lens luxation in cats can occur secondary to anterior uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and in ...
(inflammation of the inside of the eye).
Anterior lens luxation
With anterior lens luxation, the lens pushes into theiris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
or actually enters the anterior chamber
The anterior chamber ( AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Hyphema, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood f ...
of the eye. This can cause glaucoma, uveitis, or damage to the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
. Uveitis (inflammation of the eye) causes the pupil to constrict (miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil.Farlex medical dictionary
citing: ...
) and trap the lens in the anterior chamber, leading to an obstruction of outflow of citing: ...
aqueous humour
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the poster ...
and subsequent increase in ocular pressure (glaucoma). Better prognosis is valued in lens replacement surgery (retained vision and normal intraocular pressure) when it is performed before the onset of secondary glaucoma Secondary glaucoma is a collection of progressive optic nerve disorders associated with a rise in intraocular pressure (IOP) which results in the loss of vision. In clinical settings, it is defined as the occurrence of IOP above 21 mmHg requiring t ...
. Glaucoma secondary to anterior lens luxation is less common in cats than dogs due to their naturally deeper anterior chamber and the liquification of the vitreous humour
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor ...
secondary to chronic inflammation. Anterior lens luxation is considered to be an ophthalmological emergency.
Posterior lens luxation
With posterior lens luxation, the lens falls back into the vitreous humour and lies on the floor of the eye. This type causes fewer problems than anterior lens luxation, although glaucoma or ocular inflammation may occur. Surgery is used to treat dogs with significant symptoms. Removal of the lens before it moves to the anterior chamber may prevent secondary glaucoma.Lens subluxation
Lens subluxation is also seen in dogs and is characterized by a partial displacement of the lens. It can be recognized by trembling of the iris (iridodonesis Iridodonesis () is the vibration or agitated motion of the iris with eye movement. This may be caused by lens subluxation, the incomplete or partial dislocation of the lens; or by aphakia, the absence of a lens. The term originated from irido- ( la, ...
) or lens (phacodonesis Phacodonesis (; ) is the tremulousness or vibration of the lens with eye movement. This is often due to lens subluxation
Ectopia lentis is a displacement or malposition of the eye's crystalline lens from its normal location. A partial dislocatio ...
) and the presence of an aphakic crescent (an area of the pupil where the lens is absent). Other signs of lens subluxation include mild conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
l redness, vitreous humour degeneration, prolapse of the vitreous into the anterior chamber, and an increase or decrease of anterior chamber depth. Removal of the lens before it completely luxates into the anterior chamber may prevent secondary glaucoma. Extreme degree of luxation of lens is called "lenticele" in which lens comes out of the eyeball and becomes trapped under the Tenon's capsule or conjunctiva. A nonsurgical alternative treatment involves the use of a miotic to constrict the pupil and prevent the lens from luxating into the anterior chamber.
Breed predisposition
Terrier breeds are predisposed to lens luxation, and it is probably inherited in theSealyham Terrier
The Sealyham Terrier ( cy, Daeargi Sealyham) is a rare Welsh breed of small to medium-sized terrier that originated in Wales as a working dog. It is principally a white-bodied, rough-coated breed, developed in the mid-to-late-19th century by ...
, Jack Russell Terrier
The Jack Russell Terrier is a small terrier that has its origins in fox hunting in England. It is principally white-bodied and smooth, rough or broken-coated and can be any colour.
Small tan and white terriers that technically belong to ot ...
, Wirehaired Fox Terrier, Rat Terrier
The Rat Terrier is an American dog breed with a background as a farm dog and hunting companion. They share much ancestry with the small hunting dogs known as feists. Common throughout family farms in the 1920s and 1930s, they are now recognize ...
, Teddy Roosevelt Terrier
The Teddy Roosevelt Terrier is a small to medium-sized American hunting terrier. It is lower-set, with shorter legs, and is more muscular with heavier bone density than the related American Rat Terrier. Much diversity exists in the history of ...
, Tibetan Terrier
The Tibetan Terrier is a medium-sized breed of dog that originated in Tibet.American Kennel Club (2013). '' Get to know the Tibetan Terrier.'' Retrieved from http://www.akc.org/breeds/tibetan_terrier/index.cfm Despite its name, it is not a membe ...
, Miniature Bull Terrier
The English Miniature Bull Terrier is a breed with origins in the extinct English White Terrier, the Dalmatian and the Bulldog. The first existence is documented in 1872 in ''The Dogs of British Island''.
Description Appearance
Miniature Bul ...
, Shar Pei
The Shar Pei (Cantonese: ''shā pèih'' or Mandarin: 沙皮 ''shā pí'') is a dog breed from
southern China. Traditionally kept as a property guardian, the Shar Pei was driven to the brink of extinction in the 20th century. The breed is known ...
, and Border Collie
The Border Collie is a Scottish breed of herding dog of medium size. Widely considered to be the most intelligent dog breed, they are descended from landrace sheepdogs once found all over the British Isles, but became standardised in the Ang ...
. The mode of inheritance in the Tibetan Terrier and Shar Pei is likely autosomal recessive. Labrador Retrievers and Australian Cattle Dogs are also predisposed.
Systemic associations in humans
In humans, a number of systemic conditions are associated with ectopia lentis:Eifrig CW, Eifrig DE"Ectopia Lentis"
eMedicine.com. November 24, 2004. More common: * Marfan syndrome (upward and outward) *
Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria or HCU is an inherited disorder of the metabolism of the amino acid methionine due to a deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase or methionine synthase. It is an inherited autosomal recessive trait, which means a child needs to i ...
(downward and inwards)
*Weill–Marchesani syndrome
Weill–Marchesani syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by short stature; an unusually short, broad head (brachycephaly) and other facial abnormalities; hand defects, including unusually short fingers (brachydactyly); and distinctive ...
* Sulfite oxidase deficiency
*Molybdenum cofactor deficiency
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency is a rare human disease in which the absence of molybdopterin – and consequently its molybdenum complex, commonly called molybdenum cofactor – leads to accumulation of toxic levels of sulphite and neurological da ...
*Hyperlysinemia
Hyperlysinemia is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by an abnormal increase of lysine in the blood, but appears to be benign. It is caused by mutations in ''AASS'', which encodes α-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase.
Hyper ...
Less common:
* Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
* Crouzon disease
* Refsum syndrome
* Kniest syndrome
* Mandibulofacial dysostosis
*Sturge–Weber syndrome
Sturge–Weber syndrome, sometimes referred to as encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis, is a rare congenital neurological and skin disorder. It is one of the phakomatoses and is often associated with port-wine stains of the face, glaucoma, seizures, ...
* Conradi syndrome
* Pfaundler syndrome
*Pierre Robin syndrome
Pierre Robin sequence (; abbreviated PRS) is a congenital defect observed in humans which is characterized by facial abnormalities. The three main features are micrognathia (abnormally small mandible), which causes glossoptosis (downwardly displa ...
* Wildervanck syndrome
*Sprengel deformity
Sprengel's deformity (also known as high scapula or congenital high scapula) is a rare congenital skeletal abnormality where a person has one shoulder blade that sits higher on the back than the other. The deformity is due to a failure in early f ...
See also
*List of systemic diseases with ocular manifestations
An ocular manifestation of a systemic disease is an eye condition that directly or indirectly results from a disease process in another part of the body. There are many diseases known to cause ocular or visual changes. Diabetes, for example, is th ...
References
External links
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on ADAMTSL4-Related Eye Disorders, Autosomal Recessive Isolated Ectopia Lentis, Ectopia Lentis et Pupillae
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of eye, ear, face and neck Dog diseases Cat diseases Congenital disorders of eyes Disorders of lens