Lavochkin La-200 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lavochkin La-200 (a.k.a. Aircraft 200) was a two-seater,
Ugolok Neba
(also photos and drawings) {{Lavochkin aircraft Abandoned military aircraft projects of the Soviet Union
swept wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigate ...
ed, night
Night (also described as night time, unconventionally spelled as "nite") is the period of ambient darkness from sunset to sunrise during each 24-hour day, when the Sun is below the horizon. The exact time when night begins and ends depends o ...
/all-weather jet interceptor
Interceptor may refer to:
Vehicles
* Interceptor aircraft (or simply "interceptor"), a type of point defense fighter aircraft designed specifically to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft
* Ford Crown Victoria Police Interceptor, a police car
* ...
designed and manufactured by the Soviet Union's Lavochkin Design Bureau from 1948.
Design and development
In response to a requirement for a high performancenight
Night (also described as night time, unconventionally spelled as "nite") is the period of ambient darkness from sunset to sunrise during each 24-hour day, when the Sun is below the horizon. The exact time when night begins and ends depends o ...
and all-weather interceptor, Lavochkin (OKB-310), Sukhoi
The JSC Sukhoi Company (russian: ПАО «Компания „Сухой“», ) is a Russian aircraft manufacturer (formerly Soviet), headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, that designs both civilian and milita ...
( OKB-134) and Mikoyan-Gurevich (OKB-155) design bureau
OKB is a transliteration of the Russian initials of "" – , meaning 'experiment and design bureau'. During the Soviet era, OKBs were closed institutions working on design and prototyping of advanced technology, usually for military applications. ...
developed the La-200, Su-15
The Sukhoi Su-15 (NATO reporting name: Flagon) is a twinjet supersonic interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union. It entered service in 1965 and remained one of the front-line designs into the 1990s. The Su-15 was designed to replace t ...
, and I-320 (where the I stands for ''Istrebitel'', or "Fighter") respectively. A key component of the three competing aircraft, was the "Toriy" ("Thorium") centimetre waveband NII-17 radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
at Tikhomirnov NIIP - (NIIP for ''Nauchno-Issledovatel'skiy Institut Priborostroyeniya'', or "Research
Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular att ...
Institute
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes can ...
of Instrument Engineering
Instrumentation a collective term for measuring instruments that are used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
Instrumentation can refer to ...
"), which was capable of detecting a Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Fl ...
bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
at a range of .
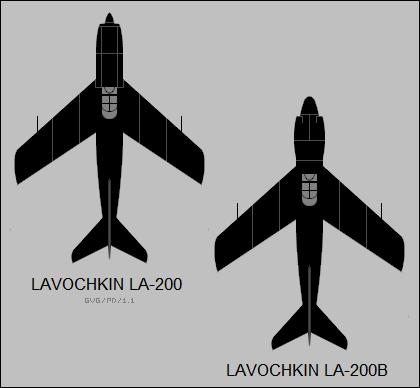
The La-200 was an all-metal, two seater, twin-engined jet aircraft, with a tricycle undercarriage
Tricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or ''landing gear'', arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle ge ...
and mid set wings with 40° sweep
Sweep or swept may refer to:
Cleaning
* Sweep, the action of using a brush to clean
* Chimney sweep, a worker who clears ash and soot from chimneys
* Street sweeper, a person's occupation, or a machine that cleans streets
* Swept quartz, a cleani ...
at 1/4 chord. The two Klimov
The JSC Klimov (or Joint Stock Company Klimov) presently manufactures internationally certified gas turbine engines, main gearboxes and accessory drive gearboxes for transport aircraft.
Originally established as ''Kirill Klimov Experimental De ...
RD-45F centrifugal flow turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and ...
engines were to be fitted in tandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which a team of machines, animals or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction.
The original use of the term in English was in ''tandem harness'', which is used for two ...
inside the front and rear fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
with the air intake
An intake (also inlet) is an opening, structure or system through which a fluid is admitted to a space or machine as a consequence of a pressure differential between the outside and the inside. The pressure difference may be generated on the ins ...
at the extreme nose. The forward engine exhausted under the centre fuselage and the rear engine exhausted at the end of the rear fuselage. Access to the engines for maintenance
Maintenance may refer to:
Biological science
* Maintenance of an organism
* Maintenance respiration
Non-technical maintenance
* Alimony, also called ''maintenance'' in British English
* Champerty and maintenance, two related legal doctrine ...
and removal was gained by removing the forward fuselage forward of the nose undercarriage
Undercarriage is the part of a moving vehicle that is underneath the main body of the vehicle. The term originally applied to this part of a horse-drawn carriage, and usage has since broadened to include:
*The landing gear of an aircraft.
*The ch ...
and the rear fuselage forward of the fin
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. Fin ...
.
The main and nose undercarriages were housed entirely within the fuselage. The nose undercarriage rotated 90° to lie flat under the forward engine, and the twin wheeled main undercarriage legs, with long travel levered suspension, retracted into the centre fuselage above the forward jet pipe and astride the fuel tank and intake trunking for the rear engine.
The swept wings were of constant chord with 2/3 span flaps, 1/3 span aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around ...
s, and wing fence
Wing fences, also known as boundary layer fences and potential fences are fixed aerodynamic devices attached to aircraft wings. Often seen on swept-wing aircraft, wing fences are flat plates fixed to the upper surfaces parallel to the wing ch ...
s at approximately 1/4 and 1/2 span. The tail unit comprised a sharply swept broad chord tapered fin with a sharply swept tapered tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabiliser, is a small lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplane ...
at 2/3 fin length. The swept wings maximised the speed performance but imposed a higher wing loading
In aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft in straight, level flight is partly determined by its wing loading. An aircraft or animal with a ...
than specified by the Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
, thus the RD-45F engines were replaced with Klimov VK-1
The Klimov VK-1 was the first Soviet jet engine to see significant production. It was developed by and first produced by the GAZ 116 works. Derived from the Rolls-Royce Nene, the engine was also built under licence in China as the Wopen WP-5.
...
engines, (up-rated RD-45F's).
The "Toriy" radar was initially fitted in an ogival radome
A radome (a portmanteau of radar and dome) is a structural, weatherproof enclosure that protects a radar antenna (radio), antenna. The radome is constructed of material transparent to radio waves. Radomes protect the antenna from weather and ...
in the centre of the air intake.
Operational history
The La-200 incorporated many innovative systems, including powered flying controls, high capacityhydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counter ...
and pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
systems, high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant spec ...
AC electrical power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions of ...
system and a comprehensive avionics
Avionics (a blend word, blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, ...
suite. OKB-301 carried out extensive ground tests, allowing problems revealed in the tests to be addressed before the first flight.
For initial tests the aircraft was fitted with dual controls in the side by side cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a Pilot in command, pilot controls the aircraft.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the ...
. Flight trials were relatively successful, but revealed a tendency to drop the starboard
Port and starboard are nautical terms for watercraft and aircraft, referring respectively to the left and right sides of the vessel, when aboard and facing the bow (front).
Vessels with bilateral symmetry have left and right halves which are ...
wing at high speeds (known colloquially as ''val'ozhka''). Other problems included vibrations of the rear fuselage with the rear engine throttled back and the front engine at maximum power, the twin mainwheels proved troublesome as well as unreliable radio and very poor performance from the radar.
To help cure the problems the starboard wing incidence was increased by 1° 30', and the twin mainwheels were replaced by single wheel units. Spill doors were fitted to the rear fuselage, arranged to open automatically when the rear engine was throttled back. The flaps and wings were stiffened, and separate aileron hydraulic actuators were installed in the wings rather than a single actuator behind the cockpit seats. Cooling air was provided for the radio which was located close to the front engine jetpipe. To address the failings of the radar, it was decided to replace it with the Korshun -(Kite) radar also developed by NII-17. The single antenna was moved to the top lip of a redesigned air intake.
By the spring of 1951 Aircraft 200 was the only one of the three competitors to survive and pass State acceptance trials. Production was provisionally ordered as the La-17, but the production directive was not endorsed so production was abandoned.
While other OKB's were designing the next generation of all-weather interceptors, OKB-301 was tasked with fitting the new Sokol (Falcon) radar into the La-200. The result was Aircraft 200B, with a new fuselage nose housing the radar behind a large radome with three air intakes surrounding the radome. By mid 1953 the radar was working adequately but Aircraft 200B's performance was no longer good enough and further work was abandoned.
Variants
* - 200 with Toriy (Thorium) radar * - 200 with Korshun (Kite) radar * - La-17 the proposed production version of the 200 with Korshun radar was not produced but designation re-used later for a target drone. * - 200B with Sokol (Falcon) radarSpecifications (La-200B)

See also
References
* Gunston, Bill. ''The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995''. London:Osprey, 1995. . *Gordon,Yefim. ''Lavochkin's Last Jets''. Midland Publishing. Hinkley. 2007.External links
Ugolok Neba
(also photos and drawings) {{Lavochkin aircraft Abandoned military aircraft projects of the Soviet Union
200
__NOTOC__
Year 200 ( CC) was a leap year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 953 '' Ab ur ...
1940s Soviet fighter aircraft
Twinjets
Mid-wing aircraft
Aircraft first flown in 1949