Lanthanum strontium manganite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
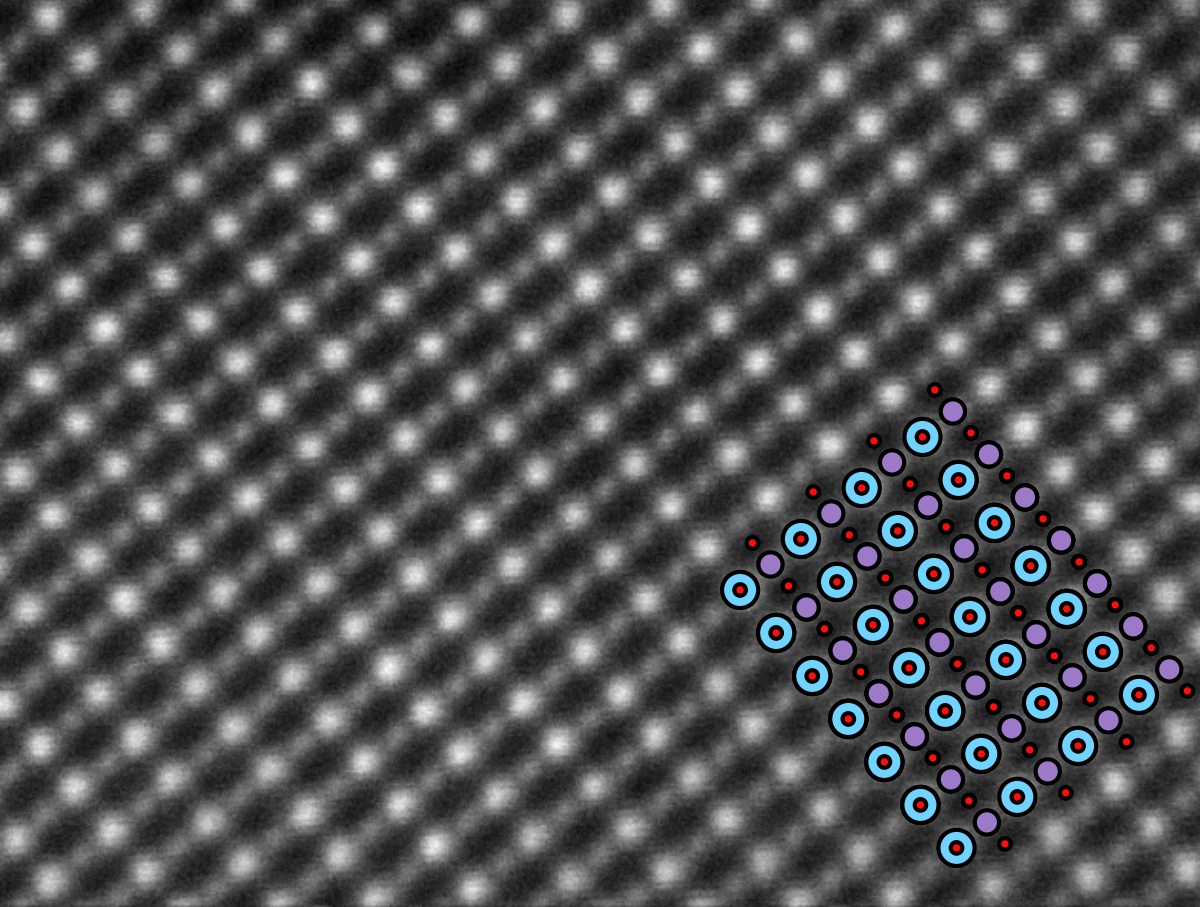 Lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM or LSMO) is an
Lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM or LSMO) is an
 Lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM or LSMO) is an
Lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM or LSMO) is an oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
ceramic material with the general formula La1−xSrxMnO3, where ''x'' describes the doping level.
It has a perovskite
Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as (XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3), known as ...
-based crystal structure, which has the general form ABO3. In the crystal, the 'A' sites are occupied by lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lantha ...
and strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is ex ...
atoms, and the 'B' sites are occupied by the smaller manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
atoms. In other words, the material consists of lanthanum manganite
Lanthanum manganite is an inorganic compound with the formula LaMnO3, often abbreviated as LMO. Lanthanum manganite is formed in the perovskite structure, consisting of oxygen octahedra with a central Mn atom. The cubic perovskite structure is d ...
with some of the lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lantha ...
atoms substitutionally doped with strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is ex ...
atoms. The strontium (valence 2+) doping on lanthanum (valence 3+) introduces extra holes in the valence band and thus increases electronic conductivity.
Depending on the x value in La1−xSrxMnO3, the unit cell of LSMO can be rhombohedral, cubic, or hexagonal. This change in the unit cell is explained on the basis of the Goldschmidt tolerance factor for perovskites. The change in the oxidation state of the Mn cation in LSMO can be readily observed through the position of the XPS peak for the Mn 2p3/2 orbital, and the interesting ferromagnetic ordering obtained when x=0.5 and 0.7 in the La1−xSrxMnO3.
LSM has a rich electronic phase diagram, including a doping-dependent metal-insulator transition, paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
and ferromagnetism
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials ...
. The existence of a Griffith phase has been reported as well.
LSM is black in color and has a density of approximately 6.5 g/cm3. The actual density will vary depending on the processing method and actual stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equal ...
. LSM is primarily an electronic conductor, with transference number close to 1.
This material is commonly used as a cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
material in commercially produced solid oxide fuel cell
A solid oxide fuel cell (or SOFC) is an electrochemical conversion device that produces electricity directly from oxidizing a fuel. Fuel cells are characterized by their electrolyte material; the SOFC has a solid oxide or ceramic electrolyte.
A ...
s (SOFCs) because it has a high electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allow ...
at higher temperatures, and its thermal expansion coefficient
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ...
is well matched with yttria-stabilized zirconia
Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) is a ceramic in which the cubic crystal structure of zirconium dioxide is made stable at room temperature by an addition of yttrium oxide. These oxides are commonly called "zirconia" ( Zr O2) and "yttria" ( Y2 O3 ...
(YSZ), a common material for SOFC electrolytes
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon di ...
.
In research, LSM is one of the perovskite manganites that show the colossal magnetoresistance
Colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) is a property of some materials, mostly manganese-based perovskite oxides, that enables them to dramatically change their electrical resistance in the presence of a magnetic field. The magnetoresistance of conventio ...
(CMR) effect, and is also an observed half-metal
A half-metal is any substance that acts as a conductor to electrons of one spin orientation, but as an insulator or semiconductor to those of the opposite orientation. Although all half-metals are ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic), most ferroma ...
for compositions around ''x''=0.3.
LSM behaves like a half-metal
A half-metal is any substance that acts as a conductor to electrons of one spin orientation, but as an insulator or semiconductor to those of the opposite orientation. Although all half-metals are ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic), most ferroma ...
, suggesting its possible use in spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-sta ...
. It displays a colossal magnetoresistance
Colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) is a property of some materials, mostly manganese-based perovskite oxides, that enables them to dramatically change their electrical resistance in the presence of a magnetic field. The magnetoresistance of conventio ...
effect. Above its Curie temperature
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by induced magnetism. The Cur ...
(about 350 K) Jahn-Teller polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle used in condensed matter physics to understand the interactions between electrons and atoms in a solid material. The polaron concept was proposed by Lev Landau in 1933 and Solomon Pekar in 1946 to describe an electro ...
s are formed; the material's ability to conduct electricity depends on the presence of the polarons.
See also
*Solid oxide fuel cell
A solid oxide fuel cell (or SOFC) is an electrochemical conversion device that produces electricity directly from oxidizing a fuel. Fuel cells are characterized by their electrolyte material; the SOFC has a solid oxide or ceramic electrolyte.
A ...
* magnetic tunnel junction
Tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) is a magnetoresistive effect that occurs in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), which is a component consisting of two ferromagnets separated by a thin insulator. If the insulating layer is thin enough (typically a fe ...
References
Lanthanum compounds Strontium compounds Manganates Ceramic materials Oxides Perovskites {{material-stub