Languages of Palau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an
 Palau was originally settled between the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, most likely from the Philippines or Indonesia.
Palau was originally settled between the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, most likely from the Philippines or Indonesia.
 British traders became regular visitors to Palau in the 18th century (the British East India Company packet ship ''Antelope'' shipwrecked off
British traders became regular visitors to Palau in the 18th century (the British East India Company packet ship ''Antelope'' shipwrecked off
 In international politics, Palau often votes with the United States on
In international politics, Palau often votes with the United States on

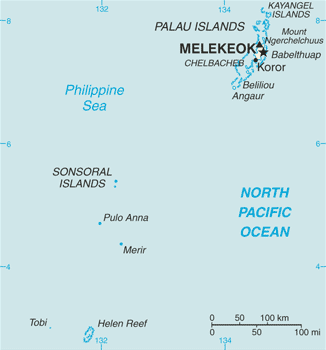 Palau is divided into sixteen states (until 1984 called municipalities). These are listed below with their areas (in square kilometres) and 2012 estimated and 2015 Census populations:
Historically, Palau's Rock Islands have been part of the State of Koror. The Southwestern islands (Sonsorol and Hatohobei States) do not speak Palauan, but the distantly related Sonsorolese-
Palau is divided into sixteen states (until 1984 called municipalities). These are listed below with their areas (in square kilometres) and 2012 estimated and 2015 Census populations:
Historically, Palau's Rock Islands have been part of the State of Koror. The Southwestern islands (Sonsorol and Hatohobei States) do not speak Palauan, but the distantly related Sonsorolese-
 Palau's
Palau's



 Palau has a history of strong environment conservation. For example, Ngerukewid islands and the surrounding area are protected under the Ngerukewid Islands Wildlife Preserve, which was established in 1956.
While much of Palau remains free of environmental degradation, areas of concern include illegal
Palau has a history of strong environment conservation. For example, Ngerukewid islands and the surrounding area are protected under the Ngerukewid Islands Wildlife Preserve, which was established in 1956.
While much of Palau remains free of environmental degradation, areas of concern include illegal
 Palau's
Palau's
 Palau International Airport provides scheduled
Palau International Airport provides scheduled
 Palauan society follows a very strict
Palauan society follows a very strict
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
and microstate in the western Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
. It has a total area of . The most populous island is Koror, home to the country's most populous city of the same name. The capital Ngerulmud
Ngerulmud () is the seat of government of the Republic of Palau, an island nation in the Pacific Ocean. It replaced Koror City, Palau's largest city, as the capital in 2006. The settlement is located in the state of Melekeok on Babeldaob, the ...
is located on the nearby island of Babeldaob
Babeldaob (also Babelthuap) is the largest island in the island nation of the Republic of Palau. It is in the western Caroline Islands, and the second largest island (after Guam) in the Micronesia region of Oceania. Palau's capital, Ngerulmud, i ...
, in Melekeok State
Melekeok is a state of the Republic of Palau located on the central east coast of Babeldaob Island. The seat of government of the country, Ngerulmud, is located in the state. The state consists of long beaches, hills, steep ridges, rivers, and t ...
. Palau shares maritime boundaries
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Bound ...
with international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
to the north, the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
to the east, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
to the south, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
to the northwest.
The country was originally settled approximately 3,000 years ago by migrants from Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
. Palau was first drawn on a European map by the Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
missionary Paul Klein based on a description given by a group of Palauans shipwrecked on the Philippine coast on Samar
Samar ( ) is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided in ...
. Palau islands were made part of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales espa├▒olas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
in 1885. Following Spain's defeat in the SpanishŌĆōAmerican War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
in 1898, the islands were sold to Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1899 under the terms of the GermanŌĆōSpanish Treaty, where they were administered as part of German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the islands were made a part of the Japanese-ruled South Seas Mandate by the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Soci├®t├® des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
, skirmishes, including the major Battle of Peleliu
The Battle of Peleliu, codenamed Operation Stalemate II by the US military, was fought between the United States and Japan during the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign of World War II, from September 15 to November 27, 1944, on the island of ...
, were fought between American and Japanese troops as part of the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign
The Mariana and Palau Islands campaign, also known as Operation Forager, was an offensive launched by United States forces against Imperial Japanese forces in the Mariana Islands and Palau in the Pacific Ocean between June and November 1944 du ...
. Along with other Pacific Islands, Palau was made a part of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
-governed Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the Trus ...
in 1947. Having voted in a referendum against joining the Federated States of Micronesia in 1978, the islands gained full sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
in 1994 under a Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
with the United States.
Politically, Palau is a presidential republic in free association with the United States, which provides defense, funding, and access to social services. Legislative power is concentrated in the bicameral Palau National Congress
Palau has a bicameral legislature, the Palau National Congress (''Olbiil era Kelulau''), consisting of the House of Delegates and the Senate of Palau, which both sit at the capitol complex in Ngerulmud, Melekeok State. The House of Delegates h ...
. Palau's economy is based mainly on tourism, subsistence agriculture and fishing, with a significant portion of gross national product
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign ...
(GNP) derived from foreign aid. The country uses the United States dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
as its official currency. The islands' culture mixes Micronesian, Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n, Asian, and Western elements. Ethnic Palauans, the majority of the population, are of mixed Micronesian, Melanesian, and Austronesia
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
n descent. A smaller proportion of the population is of Japanese descent. The country's two official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s are Palauan (a member of the Austronesian language family) and English, with Japanese, Sonsorolese, and Tobian
Tobian (, literally "the language of Tobi") is the language of Tobi, one of the Southwest Islands of Palau, and the main island of Hatohobei state. Tobian is a Micronesian language spoken by approximately 150 people, about 22 are native speaker ...
recognized as regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
s.
Etymology
The name for the islands in thePalauan language
Palauan () is a Malayo-Polynesian language native to the Republic of Palau, where it is one of the two official languages, alongside English. It is widely used in day-to-day life in the country. Palauan is not closely related to other Malayo-Pol ...
, ''Belau'', derives from the Palauan word for "village", ''beluu'' (thus ultimately from Proto-Austronesian
Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify ...
*''banua''), or from ''aibebelau'' ("indirect replies"), relating to a creation myth. The name "Palau" originated in the Spanish ''Los Palaos'', eventually entering English via the German ''Palau''. An archaic name for the islands in English was the "Pelew Islands". ''Palau'' is unrelated to ''Pulau'', which is a Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
word meaning "island" found in a number of place names in the region.
History
Early history
 Palau was originally settled between the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, most likely from the Philippines or Indonesia.
Palau was originally settled between the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, most likely from the Philippines or Indonesia. Sonsorol
Sonsorol is one of the sixteen states of Palau. The inhabitants speak Sonsorolese, a local Chuukic language, and Palauan.
The islands of the state of Sonsorol, together with the islands of Hatohobei, form the Southwest Islands of Palau.
Hi ...
, part of the Southwest Islands, an island chain approximately from the main island chain of Palau, was sighted by the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
as early as 1522, when the Spanish mission of the ''Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
'', the flagship of Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fern├Żo de Magalh├Żes, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 ŌĆō 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
's voyage of circumnavigation, sighted two small islands around the 5th parallel north
The 5th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 5 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, and South America.
The Pacific Ocean is at its ...
, naming them "San Juan".
After the 16th century
The next recording of the existence of Palau by Europeans came a century later in 1697 when a group of Palauans were shipwrecked on the Philippine island ofSamar
Samar ( ) is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided in ...
to the northwest. They were interviewed by the Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
missionary Paul Klein on 28 December 1696. Klein was able to draw the first known European map of Palau based on the Palauans' representation of their home islands that they made with an arrangement of 87 pebbles on the beach. Klein reported his findings to the Jesuit Superior General in a letter sent in June 1697.
Spanish era
This map and the letter caused a vast interest in the new islands. Another letter written by Fr. Andr├®s Serrano was sent toEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
in 1705, essentially copying the information given by Klein. The letters resulted in three unsuccessful Jesuit attempts to travel to Palau from Spanish Philippines
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
in 1700, 1708 and 1709. The islands were first visited by the Jesuit expedition led by Francisco Padilla on 30 November 1710. The expedition ended with the stranding of the two priests, Jacques Du Beron and Joseph Cortyl, on the coast of Sonsorol, because the mother ship '' Sant├Łsima Trinidad'' was driven to Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘åž»ž¦┘垦┘ł) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
by a storm. Another ship was sent from Guam
Guam (; ch, Gu├źhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
in 1711 to save them only to capsize, causing the death of three more Jesuit priests. The failure of these missions gave Palau the original Spanish name ''Islas Encantadas'' (Enchanted Islands).
Transitions era
Ulong Island
Ulong is a major island and channel of western Palau. It is sometimes called Aulong and originally written Oroolong in English. Ulong is regarded by many as one of the best drift dives in the world.
Geography
Ngerumekaol Pass (also known as Ulon ...
in 1783, leading to Prince Lee Boo
Prince Lee Boo or Lebu (1764 ŌĆō 27 December 1784) was the second son of Abba Thulle (Ibedul), the ruler of Koror in the Pelew Islands, now called Palau. Prince Lee Boo was one of the first people from the Pacific Islands to visit Great Britain. W ...
's visit to London), followed by expanding Spanish influence in the 19th century. Palau, under the name ''Palaos'', was included in the Malolos Congress
The Malolos Congress (also known as the Revolutionary Congress), formally known as the National Assembly, was the legislative body of the Revolutionary Government of the Philippines. Members were chosen in the elections held from June 23 to Septe ...
in 1898, the first revolutionary congress in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, which wanted full independence from colonialists. Palau, at the time, was part of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales espa├▒olas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
headquartered in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. Palau had one appointed member to the Congress, becoming the only group of islands in the entire Caroline Islands granted high representation in a non-colonial Philippine Congress. The Congress also supported the right of Palau to self-determination if ever it wished to pursue such a path. Later in 1899 as part of the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
, Palau was sold by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio espa├▒ol), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarqu├Ła Hisp├Īnica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarqu├Ła Cat├│lica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
to the German Empire as part of German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
in the GermanŌĆōSpanish Treaty (1899). During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Japanese Empire annexed the islands after seizing them from Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1914. Following World War I, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Soci├®t├® des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
formally placed the islands under Japanese administration as part of the South Seas Mandate. In World War II, Palau was used by Japan to support its 1941 invasion of the Philippines, which succeeded in 1942. The invasion overthrew the American-installed Commonwealth government in the Philippines and installed the Japanese-backed Second Philippine Republic
The Second Philippine Republic, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines ( tl, Rep├║blik├Ī ng Pilipinas; es, Rep├║blica de Filipinas; ja, ŃāĢŃéŻŃā¬ŃāöŃā│Õģ▒ÕÆīÕøĮ, ''Firipin-ky┼Źwakoku'') and also known as the Japanese-sponsored Phi ...
in 1943.
United States era
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
, the United States captured Palau from Japan in 1944 after the costly Battle of Peleliu
The Battle of Peleliu, codenamed Operation Stalemate II by the US military, was fought between the United States and Japan during the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign of World War II, from September 15 to November 27, 1944, on the island of ...
, when more than 2,000 Americans and 10,000 Japanese were killed and later the Battle of Angaur
The Battle of Angaur was a major battle of the Pacific campaign in World War II, fought on the island of Angaur in the Palau Islands from 17 SeptemberŌĆö22 October 1944. This battle was part of a larger offensive campaign known as Operation ...
. In 1945ŌĆō1946, the United States re-established control on the Philippines, and managed Palau through the Philippine capital of Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
. By the later half of 1946, however, the Philippines was granted full independence with the formation of the Third Republic of the Philippines
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1Ōüä60 of a ''second'', or 1Ōüä3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hig ...
, shifting the U.S. Far West Pacific capital to Guam
Guam (; ch, Gu├źhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
. Palau passed formally to the United States under United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
auspices in 1947 as part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the Trus ...
established pursuant to Security Council Resolution 21.
Independence
Four of the Trust Territory districts joined together and formed theFederated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
in 1979, but the districts of Palau and the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, ß╣éajeßĖĘ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolep─ün Aor┼Źkin ß╣éajeßĖĘ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
voted against the proposed constitution. Palau, the westernmost cluster of the Carolines, instead opted for independent status in 1978, which was widely supported by the Philippines, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, and Japan. It approved a new constitution and became the Republic of Palau on 1 January 1981. It signed a Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
with the United States in 1982. In the same year, Palau became one of the founding members of the Nauru Agreement
The Nauru Agreement Concerning Cooperation in the Management of Fisheries of Common Interest, or The Nauru Agreement is an Oceania subregional agreement between the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Nauru, Palau, P ...
. After eight referendums and an amendment to the Palauan constitution, the Compact was ratified in 1993. The Compact went into effect on 1 October 1994, making Palau ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' independent, although it had been ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' independent since 25 May 1994, when the trusteeship ended. Formal diplomatic relations with the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
were re-established in the same year, although the two nations already had diplomatic back channels prior to 1994. Palau also became a member of the Pacific Islands Forum, but withdrew in February 2021 after a dispute regarding Henry Puna
Henry Tuakeu Puna (born 29 July 1949) is a Cook Islands politician, and the current secretary-general of the Pacific Islands Forum. He was Prime Minister of the Cook Islands from November 2010 to October 2020. Since 2006 he has been leader of th ...
's election as the Forum's secretary-general.
Legislation making Palau an "offshore" financial center was passed by the U.S. Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
in 1998.
In 2001, Palau passed its first bank regulation
Bank regulation is a form of government regulation which subjects banks to certain requirements, restrictions and guidelines, designed to create market transparency between banking institutions and the individuals and corporations with whom th ...
and anti- money laundering laws.
In 2005, Palau led the Micronesia challenge, which would conserve 30% of near-shore coastal waters and 20% of forest land of participating countries by 2020. In 2009, Palau created the world's first shark sanctuary
A shark sanctuary is an area that forbids commercial fishing operations from targeting and retaining caught sharks, including their fins. The first shark sanctuary was created by Palau in 2009. It was followed by Maldives, Honduras, The Bahamas and ...
, banning commercial shark fishing within its waters. In 2012, the Rock Islands of Palau was declared as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
In 2015, Palau became a member of the Climate Vulnerable Forum
The Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) is a global partnership of countries that are disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. The forum addresses the negative effects of climate change as a result of heightened socioeconomic ...
under the chairmanship of the Philippines, and at the same time, the country officially protected 80% of its water resources, becoming the first country to do so. The protection of its water resources made significant increases in the country's economy in less than two years. In 2017, the nation became the first to establish an eco-promise, known as the ''Palau Pledge'', which are stamped on local and foreign passports. In 2018, Palau and the Philippines began re-connecting their economic and diplomatic relations. The Philippines supported Palau to become an observer state in ASEAN
ASEAN ( , ), officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, militar ...
, as Palau also has Southeast Asian ethnic origins.
In November 2020, Surangel Whipps Jr was elected as the new President of Palau
The president of the Republic of Palau is the head of state and head of government of Palau. The president is directly elected to a four-year term, and can be reelected once in a consecutive manner.
List of presidents
Latest election
...
to succeed President Tommy Remengesau
Thomas Esang "Tommy" Remengesau Jr. (born 28 February 1956) is a Palauan politician; in 2013 he was elected the ninth president of Palau and was re-elected to that office in 2016. Previously he served as the seventh president of the island nat ...
.
Politics and government
Palau is a democratic republic. ThePresident of Palau
The president of the Republic of Palau is the head of state and head of government of Palau. The president is directly elected to a four-year term, and can be reelected once in a consecutive manner.
List of presidents
Latest election
...
is both head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110ŌĆō11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
. Executive power
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state.
In political systems b ...
is exercised by the government, while legislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known a ...
is vested in both the government and the Palau National Congress
Palau has a bicameral legislature, the Palau National Congress (''Olbiil era Kelulau''), consisting of the House of Delegates and the Senate of Palau, which both sit at the capitol complex in Ngerulmud, Melekeok State. The House of Delegates h ...
. The judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
is independent of the executive and the legislature. Palau adopted a constitution in 1981.
The governments of the United States and Palau concluded a Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
in 1986, similar to compacts that the United States had entered into with the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
and the Republic of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, ß╣éajeßĖĘ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolep─ün Aor┼Źkin ß╣éajeßĖĘ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
. The compact entered into force on 1 October 1994, concluding Palau's transition from trusteeship to independence as the last portion of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the Trus ...
to secure its independence pursuant to Security Council Resolution 956.
The Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
between the United States and Palau sets forth the free and voluntary association of their governments. It primarily focuses on the issues of government, economic, security and defense relations. Palau has no independent military, relying on the United States for its defense. Under the compact, the American military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
was granted access to the islands for 50 years. The U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
role is minimal, limited to a handful of Navy Seabees (construction engineers). The U.S. Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, mul ...
patrols in national waters.
Foreign relations
As a sovereign nation, Palau conducts its own foreign relations. Since independence, Palau has established diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including many of its Pacific neighbors, likeMicronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. On 29 November 1994, the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
passed Resolution 963 recommending Palau's admission to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
. The United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assembl├®e g├®n├®rale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
approved admission for Palau pursuant to Resolution 49/63 on 15 December 1994. Palau has since joined several other international organizations. In September 2006, Palau hosted the first Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
-Pacific Allies Summit. Its President has made official visits to other Pacific countries, including Japan.
The United States maintains a diplomatic delegation and an embassy
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually den ...
in Palau, but most aspects of the countries' relationship have to do with Compact-funded projects, which are the responsibility of the U.S. Department of the Interior's Office of Insular Affairs
The Office of Insular Affairs (OIA) is a unit of the United States Department of the Interior that oversees federal administration of several United States insular areas. It is the successor to the Bureau of Insular Affairs of the War Departme ...
. For example, as part of this Compact, Palau was granted zip codes 96939 and 96940, along with regular U.S. Mail
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U. ...
delivery.
United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assembl├®e g├®n├®rale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
resolutions.
Palau has maintained close ties with Japan, which has funded infrastructure projects, including the KororŌĆōBabeldaob Bridge. In 2015, Emperor Akihito
is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 7 January 1989 until his abdication on 30 April 2019. He presided over the Heisei era, ''Heisei'' being an expression of achieving peace worldwide.
B ...
and Empress Michiko
is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who served as the Empress consort of Japan as the wife of Akihito, the 125th Emperor of Japan reigning from 7 January 1989 to 30 April 2019.
Michiko married Crown Prince Akihito and became the Crow ...
visited Peleliu
Peleliu (or Beliliou) is an island in the island nation of Palau. Peleliu, along with two small islands to its northeast, forms one of the sixteen states of Palau. The island is notable as the location of the Battle of Peleliu in World War II.
H ...
to honor the 70th anniversary of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
.
Palau is a member of the Nauru Agreement
The Nauru Agreement Concerning Cooperation in the Management of Fisheries of Common Interest, or The Nauru Agreement is an Oceania subregional agreement between the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Nauru, Palau, P ...
for the Management of Fisheries.
In 1981, Palau voted for the world's first nuclear-free constitution. This constitution banned the use, storage and disposal of nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
, toxic chemical, gas and biological weapon
A biological agent (also called bio-agent, biological threat agent, biological warfare agent, biological weapon, or bioweapon) is a bacterium, virus, protozoan, parasite, fungus, or toxin that can be used purposefully as a weapon in bioterroris ...
s without first being approved by a , or 75 percent, majority in a referendum. This ban delayed Palau's transition to independence, because while negotiating the Compact, the U.S. insisted on the option to operate nuclear propelled vessels and store nuclear weapons within the territory, prompting campaigns for independence and denuclearization. After several referendums that failed to achieve a majority, the people of Palau finally approved the Compact in 1994.
The Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, a neighboring ally of Palau to the west, has expressed its intent to back Palau if ever it wishes to join ASEAN
ASEAN ( , ), officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, militar ...
.
In June 2009, Palau announced that it would accept up to seventeen Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=W├®iw├║'─ør, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
who had previously been detained by the American military at Guantanamo Bay,
with some American compensation for the cost of their upkeep.
Only one of the Uyghurs initially agreed to resettlement, but by the end of October, six of the seventeen had been transferred to Palau.
An aid agreement with the United States, finalized in January 2010, was reported to be unrelated to the Uyghur agreement.
In 2017, Palau signed the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), or the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty, is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons with the ultimate goal being their total elimination. It ...
.
Administrative divisions

 Palau is divided into sixteen states (until 1984 called municipalities). These are listed below with their areas (in square kilometres) and 2012 estimated and 2015 Census populations:
Historically, Palau's Rock Islands have been part of the State of Koror. The Southwestern islands (Sonsorol and Hatohobei States) do not speak Palauan, but the distantly related Sonsorolese-
Palau is divided into sixteen states (until 1984 called municipalities). These are listed below with their areas (in square kilometres) and 2012 estimated and 2015 Census populations:
Historically, Palau's Rock Islands have been part of the State of Koror. The Southwestern islands (Sonsorol and Hatohobei States) do not speak Palauan, but the distantly related Sonsorolese-Tobian
Tobian (, literally "the language of Tobi") is the language of Tobi, one of the Southwest Islands of Palau, and the main island of Hatohobei state. Tobian is a Micronesian language spoken by approximately 150 people, about 22 are native speaker ...
(related to Woleaian
Woleaian is the main language of the island of Woleai and surrounding smaller islands in the state of Yap of the Federated States of Micronesia. Woleaian is a Chuukic language. Within that family, its closest relative is Satawalese, with whic ...
of Woleai atoll, Yap State
Yap State, also known in the Yapese language as Nam nu Wa'ab (lit. "Island of Yap") or simply as Wa'ab, is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). The other states are Kosrae State, Pohnpei State, and Chuuk State.
...
)
Maritime law enforcement
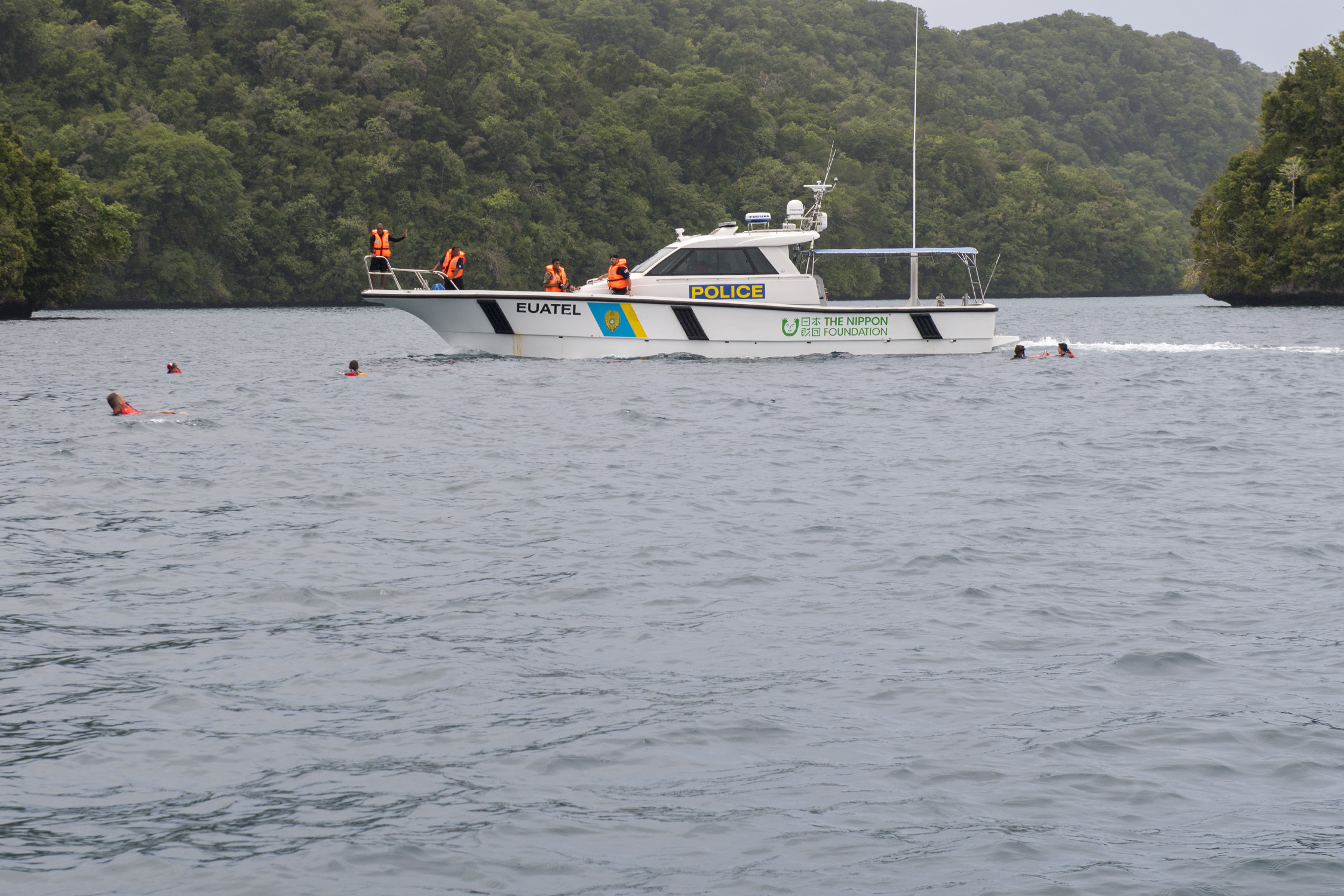
 Palau's
Palau's Division of Marine Law Enforcement
The defense of Palau is the responsibility of the United States, but local police matters are handled by the Palau Police, the national police force. Some of the sixteen states also had separate police departments during the 1980s and 1990s.
Th ...
patrols the nation's exclusive economic zone. They operate two long range patrol boats, the '' Kedam'' and the '' Remeliik II'', to hunt for poachers and unlicensed fishermen. Smaller boats are used for littoral operations. They are based on Koror.
Political future
Palau may now be seen, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, as a key example of the successes of modern state building. It has successfully transitioned peacefully from colonial rule to full admission to the United Nations. Palau has maintained strong foreign relations with its neighbors with its region of Oceania, maintaining membership in the Pacific Island Forum. There have also been pushes for Palau to have observer status to the ASEAN as a demonstration of its growing influence in the region. However, PalauŌĆÖs peaceful transition to fully autonomous sovereign nation is not without debate. Palau is hugely reliant on international aid, as demonstrated by President Surangel Whipps Jr address to the UN General Assembly in 2021. American influence has also led some to contest that there are challenges to its sovereignty with its reliance on the American military under theCompact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
, although not officially designated a de facto protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
or otherwise. American influence has also resulted in huge changes to PalauŌĆÖs society with vast changes to the economy and political processes and as such Palau may not yet be seen as a fully independent state or a fully realised success of modern state-building.
International shipping
Although Palau's ship registry represents less than 0.001% of the world fleet of commercial ships, it contains almost 60% of last-voyage flags in 2019. It suggests that the registry is used by shipping companies to evade end-of-life responsibilities. These responsibilities entail the decommissioning of a ship in such a way that the environmental impact and labor conditions are in order.Geography
Palau's territory consists of an archipelago located in thePacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. Its most populous island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
s are Angaur
, or in Palauan, is an island and state in the island nation of Palau.
History
Angaur was traditionally divided among some eight clans. Traditional features within clan areas represent important symbols giving identity to families, clans an ...
, Babeldaob
Babeldaob (also Babelthuap) is the largest island in the island nation of the Republic of Palau. It is in the western Caroline Islands, and the second largest island (after Guam) in the Micronesia region of Oceania. Palau's capital, Ngerulmud, i ...
, Koror and Peleliu
Peleliu (or Beliliou) is an island in the island nation of Palau. Peleliu, along with two small islands to its northeast, forms one of the sixteen states of Palau. The island is notable as the location of the Battle of Peleliu in World War II.
H ...
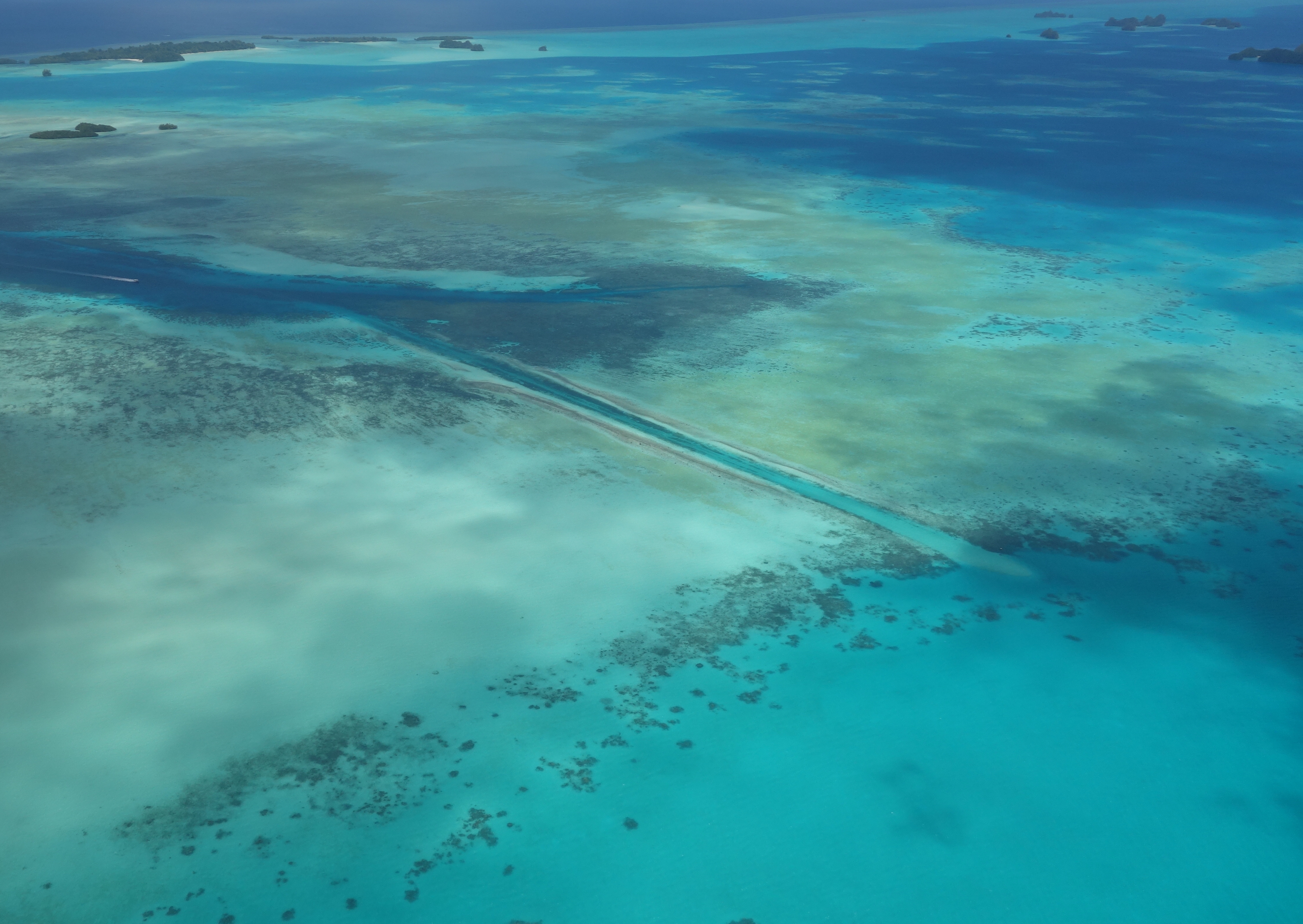
. The latter three lie together within the same barrier reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
, while Angaur is an oceanic island several kilometers to the south. About two-thirds of the population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
lives on Koror.
The coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and ...
atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
of Kayangel
Kayangel (Ngcheangel) is the northernmost state of Palau north of Koror. The land area is about . The population is 54 (2015 census).
History
The state was colonized by Spain from the end of the 16th century until 1899 when the territory was s ...
is north of these islands, while the uninhabited Rock Islands (about 200) are west of the main island group. A remote group of six islands, known as the Southwest Islands, some from the main islands, make up the states of Hatohobei and Sonsorol.
Climate
Palau has atropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southea ...
with an annual mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the '' ari ...
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
of . Rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
is heavy throughout the year
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hou ...
, averaging . The average humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
is 82% and, although rain falls more frequently between June and October, there is still much sunshine.
Palau lies on the edge of the typhoon belt. Tropical disturbances frequently develop near Palau every year, but significant tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depen ...
s are quite rare. Mike
Mike may refer to:
Animals
* Mike (cat), cat and guardian of the British Museum
* Mike the Headless Chicken, chicken that lived for 18 months after his head had been cut off
* Mike (chimpanzee), a chimpanzee featured in several books and docume ...
, Bopha and Haiyan are the only systems that struck Palau as typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180┬░ and 100┬░E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
s on record.
Environment



 Palau has a history of strong environment conservation. For example, Ngerukewid islands and the surrounding area are protected under the Ngerukewid Islands Wildlife Preserve, which was established in 1956.
While much of Palau remains free of environmental degradation, areas of concern include illegal
Palau has a history of strong environment conservation. For example, Ngerukewid islands and the surrounding area are protected under the Ngerukewid Islands Wildlife Preserve, which was established in 1956.
While much of Palau remains free of environmental degradation, areas of concern include illegal dynamite fishing
Blast fishing, fish bombing, dynamite fishing or grenade fishing is a destructive fishing practice using explosives to stun or kill schools of fish for easy collection. This often illegal practice is extremely destructive to the surrounding eco ...
, inadequate solid waste disposal
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal.
This includes the collection, transport, treatment and disposal of waste, together with monitorin ...
facilities in Koror and extensive sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
and coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and ...
dredging in the Palau lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') ...
. As with other Pacific island nations, rising sea level
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1ŌĆō2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryo ...
presents a major environmental threat. However, according to the Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research average carbon dioxide emissions per person were 60 tonnes in 2019, the highest in the world and mostly from transport. Inundation of low-lying areas threatens coastal vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characte ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
, and an already insufficient water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
. Wastewater treatment is a problem, along with the handling of toxic waste
Toxic waste is any unwanted material in all forms that can cause harm (e.g. by being inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the skin). Mostly generated by industry, consumer products like televisions, computers, and phones contain toxic chemi ...
from fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s and biocides.
One species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been list ...
, ''Crocodylus porosus'', is also indigenous to Palau, occurring in varying numbers throughout the mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
s and in parts of the Rock Islands. Although this species is generally considered extremely dangerous, there has only been one fatal human attack, on 28 December 1965, in Palau in modern history. This attack led to a crocodile eradication program and trade in crocodile hides that ran into the 1980s. A management and conservation program running since the 1990s has led to a stabilization of the Palauan crocodile population. In Palau, the largest crocodile measured .
The nation is also vulnerable to earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s, volcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
, and tropical storms
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dependi ...
. Palau already has a problem with inadequate water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
and limited agricultural areas to support its population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
.
On 5 November 2005, President Tommy E. Remengesau, Jr. took the lead on a regional environmental initiative called the Micronesia challenge, which would conserve 30% of near-shore coastal waters and 20% of forest land by 2020. Following Palau, the initiative was joined by the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, ß╣éajeßĖĘ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolep─ün Aor┼Źkin ß╣éajeßĖĘ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
, and the U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected┬Āto a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
of Guam
Guam (; ch, Gu├źhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
and Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mari├źnas; cal, Commonwealth T├®├®l Fal├║w kka Ef├Īng ll├│l Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
. Together, this combined region represents nearly 5% of the marine area of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
and 7% of its coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
.
Palau contains the Palau tropical moist forests terrestrial ecoregion. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 8.09/10, ranking it 27th globally out of 172 countries.
Sanctuary
On 25 September 2009, Palau announced that it would create the world's firstshark sanctuary
A shark sanctuary is an area that forbids commercial fishing operations from targeting and retaining caught sharks, including their fins. The first shark sanctuary was created by Palau in 2009. It was followed by Maldives, Honduras, The Bahamas and ...
. Palau banned all commercial shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
within the waters of its exclusive economic zone (EEZ). The sanctuary protects about of ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
, a similar size to France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
. President Johnson Toribiong announced the sanctuary at a meeting of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
. President Toribiong proposed a worldwide ban on fishing for sharks. In 2012, Palau received the Future Policy Award from World Future Council
The World Future Council (WFC) is a German non-profit foundation with its headquarters in Hamburg. It works to pass on a healthy and sustainable planet with just and peaceful societies to future generations.
FuturePolicy.org
The website f ...
, because "Palau is a global leader in protecting marine ecosystems".
Economy
 Palau's
Palau's economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
consists primarily of tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
, subsistence agriculture and fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
. Tourist activity focuses on scuba diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for " Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chr ...
and snorkeling
Snorkeling ( British and Commonwealth English spelling: snorkelling) is the practice of swimming on or through a body of water while equipped with a diving mask, a shaped breathing tube called a snorkel, and usually swimfins. In cooler waters ...
in the islands' rich marine environment, including its barrier reefs
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
' walls and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
wrecks. In April 2022, Palau launched ''Ol'au Palau'', a responsible tourism program aimed to preserve the country's natural environment and traditional culture. The government is the largest employer, relying heavily on U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
financial assistance. Business and tourist arrivals numbered some 50,000 in fiscal year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
2000ŌĆō2001.
The population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
enjoys a per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
twice that of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
as a whole. Long-term prospects for the key tourist sector have been greatly bolstered by the expansion of air travel
Air travel is a form of travel in vehicles such as airplanes, jet aircraft, helicopters, hot air balloons, blimps, gliders, hang gliders, parachutes, or anything else that can sustain flight.
in the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
, the rising prosperity of leading East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
n countries and the willingness of foreigners to finance infrastructure development.
Air service has at times been spotty. Palau Micronesia Air
Palau Micronesia Air was an airline based in Palau. It operated services under the Air New Zealand air operators certificate. It suspended operations in December 2004.Flight International 12ŌĆō18 April 2005
History
The airline was established ...
, Asian Spirit
Zest Airways, Inc., operated as AirAsia Zest (formerly Asian Spirit and Zest Air), was a low-cost airline based at the Ninoy Aquino International Airport in Pasay, Metro Manila in the Philippines. It operated scheduled domestic and international ...
and Pacific Flier
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
provided service to the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and other destinations at various times during the 2000s, but all suspended service. United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
now provides near-daily service to and from Guam
Guam (; ch, Gu├źhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and once-weekly service to Yap
Yap ( yap, Waqaab) traditionally refers to an island group located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, a part of Yap State. The name "Yap" in recent years has come to also refer to the state within the Federated States of Micr ...
. Also, Korean Air
Korean Air Co., Ltd. (), operating as Korean Air (Korean Air Lines before 1984), is the flag carrier of South Korea and its largest airline based on fleet size, international destinations and international flights.
The present-day Korean Air ...
provides service three times per week to Incheon.
Palau is served by an 80 bed hospital, Belau National Hospital. With some medical specialties, there are no such specialty care in Palau necessitating medical care in Taiwan, Philippines, or Hawaii. There are no dermatologists or ophthalmologists (eye specialists) in Palau. VEGF drugs for diabetic eye diseases cannot be given for eye conditions so laser surgery is done by visiting American ophthalmologists. Belau National Hospital cannot treat certain brain hemorrhages necessitating emergency airlift to Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
.
In November 2006, Pacific Saving Bank officially announced bankruptcy. On 13 December 2006, the ''Palau Horizon
The ''Palau Horizon'' is a newspaper headquartered in Koror, Palau. The newspaper was launched in Palau in 1998 and had a circulation of approximately 8,000 readers in 2008. The newspaper is a sister publication of the larger ''Marianas Variety ...
'' reported that 641 depositors
A deposit account is a bank account maintained by a financial institution in which a customer can deposit and withdraw money. Deposit accounts can be savings accounts, current accounts or any of several other types of accounts explained below.
...
had been affected. Among them, 398 held less than US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
5,000, with the remainder ranging from US$5,000 to US$2 million. On 12 December 79 affected people received compensation. Mr. Toribiong said, "The fund for the payout came from the balance of Palau government's loan from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
." From a total of US$1 million, which originally was for assisting Palau's development, US$955,000 was left at the time of bankruptcy. Toribiong requested the Taiwanese government use the balance to repay its loans. Taiwan agreed to the request. The compensation would include those who held less than US$4,000 in an account.
The income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
has three brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or ' ...
with progressive rates of 9.3 percent, 15 percent, and 19.6 percent respectively. Corporate tax is four percent, and the sales tax is zero. There are no property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inhe ...
es.
Major tourist draws in Palau include Rock Islands Southern Lagoon, a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, and four tentative UNESCO sites, namely, Ouballang ra Ngebedech (Ngebedech Terraces), Imeong Conservation Area, Yapease Quarry Sites, and Tet el Bad (Stone Coffin).
Transportation
direct flight
A direct flight in the aviation industry is any flight between two points by an airline with no change in flight numbers, which may include one or more stops at an intermediate point(s). A stop may either be to get new passengers (or allow some ...
s with Guam
Guam (; ch, Gu├źhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
, and Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the ...
. Palau Pacific Airways
Palau Pacific Airways (PPA) was a charter airline from Palau.
History
The airline launched scheduled charter flights between Hong Kong and its base Koror on 7 November 2014. It is often confused with Palau Airways although they are not assoc ...
also has charter flights to and from Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
and Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
. In addition, the states of Angaur
, or in Palauan, is an island and state in the island nation of Palau.
History
Angaur was traditionally divided among some eight clans. Traditional features within clan areas represent important symbols giving identity to families, clans an ...
and Peleliu
Peleliu (or Beliliou) is an island in the island nation of Palau. Peleliu, along with two small islands to its northeast, forms one of the sixteen states of Palau. The island is notable as the location of the Battle of Peleliu in World War II.
H ...
have regular service to domestic destinations.
Freight, military and cruise ships often call at Malakal Harbor, on Malakal Island
Malakal Island ("Ngemelachel" in Palauan) is an island in the state of Koror, Palau. It is located at 134.45, 7.330278.
One of the tribes in Survivor: Micronesia was named Malakal.
Malakal Island is the site of Koror's port, as well as the ra ...
outside Koror. The country has no railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
s, and of the of highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-acces ...
s, only are paved
Pavement may refer to:
* Pavement (architecture), an outdoor floor or superficial surface covering
* Road surface, the durable surfacing of roads and walkways
** Asphalt concrete, a common form of road surface
* Sidewalk or pavement, a walkway ...
. Driving
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a vehicle, including cars, motorcycles, trucks, buses, and bicycles. Permission to drive on public highways is granted based on a set of conditions being met and drivers are required to f ...
is on the right and the speed limit
Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed - expre ...
is . Taxis
A taxis (; ) is the movement of an organism in response to a stimulus such as light or the presence of food. Taxes are innate behavioural responses. A taxis differs from a tropism (turning response, often growth towards or away from a stim ...
are available in Koror. They are not metered and fare
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various pa ...
s are negotiable. Transportation between islands mostly relies on private boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on inl ...
s and domestic air services. However, there are some state-run boats between islands as a cheaper alternative.
Demographics
The population of Palau is approximately , of whom 73% are native Palauans of mixedMelanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n and Austronesian descent. There are many Asian communities within Palau. Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
form the largest Asian group and second largest ethnic group in the country, dating back to the Spanish colonial period. There are significant numbers of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
and Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
. There are also smaller numbers of Palauans of mixed or full Japanese ancestry. Smaller numbers of Bangladeshi and Nepalese migrant workers and their descendants who came to the islands during the late 1900s can also be found. Most Palauans of Asian origin came during the late 1900s with many Chinese, Bangladeshis and Nepalese coming to Palau as unskilled workers and professionals. There are also small numbers of Europeans and Americans.
Languages
The official languages of Palau are Palauan andEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, except in two states (Sonsorol
Sonsorol is one of the sixteen states of Palau. The inhabitants speak Sonsorolese, a local Chuukic language, and Palauan.
The islands of the state of Sonsorol, together with the islands of Hatohobei, form the Southwest Islands of Palau.
Hi ...
and Hatohobei
Tobi, or Hatohobei ( Tobian), is the southernmost of Palau's sixteen states, consisting of Tobi Island and Helen Reef. The total land area is about 0.88 km┬▓. The population was 25 in 2015. Tobian, English, and Sonsorolese are the offici ...
) where the local languages, Sonsorolese and Tobian
Tobian (, literally "the language of Tobi") is the language of Tobi, one of the Southwest Islands of Palau, and the main island of Hatohobei state. Tobian is a Micronesian language spoken by approximately 150 people, about 22 are native speaker ...
, respectively, along with Palauan, are official. Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
is spoken by some older Palauans and is an official language in the State of Angaur
, or in Palauan, is an island and state in the island nation of Palau.
History
Angaur was traditionally divided among some eight clans. Traditional features within clan areas represent important symbols giving identity to families, clans an ...
. Including second-language speakers, more people speak English than Palauan in Palau. Additionally, a significant portion of the population speak the Filipino language
Filipino (; , ) is an Austronesian language. It is the national language ( / ) of the Philippines, and one of the two official languages of the country, with English. It is a standardized variety of Tagalog based on the native dialect, sp ...
and Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
language.
Religion
According to 2015 estimates 45.3% of the population isRoman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
(due to its shared colonial heritage with the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
), 6.9% Seventh-day Adventist
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
, 34.9% other Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
(due to American administration), 5.7% Modekngei
Modekngei, or ''Ngara Modekngei'' (United Sect), is a monotheistic religious movement founded around 1915 by "Tamadad," a native of the island of Babeldaob, that spread throughout Palau. It rose to political significance between the First and Se ...
and 3.0% Muslim (due to its shared Islamic heritage with southern Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, Rep├║blica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
). In 2009, the small Jewish
Jews ( he, ūÖų░ūöūĢų╝ūōų┤ūÖūØ, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
community sent two cyclists to the 18th Maccabiah Games.
The German and Japanese occupations of Palau both subsidized missionaries to follow the Spanish. Germans sent Roman Catholic and Protestant, Japanese sent Shinto and Buddhist, and Spaniards sent Roman Catholic missionaries as they controlled Palau. Three quarters of the population are Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christ├│s'' (╬¦Žü ...
(mainly Roman Catholics and Protestants), while Modekngei
Modekngei, or ''Ngara Modekngei'' (United Sect), is a monotheistic religious movement founded around 1915 by "Tamadad," a native of the island of Babeldaob, that spread throughout Palau. It rose to political significance between the First and Se ...
(a combination of Christianity, traditional Palauan religion and fortune telling) and the ancient Palauan religion are commonly observed. Japanese rule brought Mahayana Buddhism and Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
to Palau, which were the majority religions among Japanese settlers. However, following Japan's World War II defeat, the remaining Japanese largely converted to Christianity, while the remainder continued to observe Buddhism, but stopped practicing Shinto rites. There are also approximately 400 Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘å, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
in Palau, and recently a few Uyghurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=W├®iw├║'─ør, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghur ...
detained in Guantanamo Bay were allowed to settle in the island nation.
Culture
 Palauan society follows a very strict
Palauan society follows a very strict matrilineal
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline ŌĆō their mother's lineage ŌĆō and which can involve the inheritance ...
system. Matrilineal practices are seen in nearly every aspect of Palauan traditions, especially in funeral, marriage, inheritance and the passing of traditional titles. The system probably had its origins from the Philippine archipelago, which had a similar system until the archipelago was colonized by Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de Espa├▒a.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de Espa├▒a (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
.Evidence?
The cuisine includes local foods such as cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
, yam, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
and pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved; ...
. Western cuisine
European cuisine comprises the cuisines of Europe "European Cuisine."kava; and the chewing of
Republic of Palau National Government
Embassy of the Republic of Palau in Japan
Chief of State and Cabinet Members
Honorary Consulate of the Republic of Palau to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Honorary Consulate-General of Palau to Belgium
Island Times
'
Palau Wave Radio
Pacific Note
Palau
''
Palau
from the University of Colorado at Boulder Libraries (USA) ŌĆō Government Publications *
Palau profile
from the
"Palau"
Ćö''
NOAA's National Weather Service ŌĆō Palau
''The Interesting History of Prince Lee Boo, Brought to England from the Pelew Islands''
ĆöFrom the Collections at the Library of Congress {{Authority control 1994 establishments in Oceania Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Associated states of the United States * Countries in Micronesia Countries in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Former colonies in Oceania Former German colonies Former Japanese colonies Former Spanish colonies German New Guinea Island countries Islands of Oceania Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States South Seas Mandate Spanish East Indies States and territories established in 1994 Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
betel nut
The betel (''Piper betle'') is a vine of the family Piperaceae, which includes pepper and kava. The betel plant is native to Southeast Asia. It is an evergreen, dioecious perennial, with glossy heart-shaped leaves and white catkins. Betel p ...
s.
The traditional government system still influences the nation's affairs, leading the federal government to repeatedly attempt to limit its power. Many of these attempts took the form of amendments to the constitution that were supported by the corporate sector to protect what they deemed should be free economic zones. One such example occurred in early 2010, where the Idid clan, the ruling clan of the Southern Federation, under the leadership of Bilung, the Southern Federation's queen, raised a civil suit against the Koror State Public Lands Authority (KSPLA). The Idid clan laid claim over Malakal Island, a major economic zone and Palau's most important port, citing documents from the German Era. The verdict held that the island belonged to the KSPLA.
Traditional government
The present-day "traditional" government of Palau is a continuation of its predecessors. Traditionally, Palau was hierarchically organized. The lowest level is the village or hamlet, then the chiefdom (now politically referred to as astate
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
) and finally alliances of chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
s. In ancient times, numerous federations divided power, but upon the 17th century introduction of firearms by the British, an imbalance of power occurred.
Palau became divided into northern and southern federations. The Northern Federation is headed by the high chief and chiefess of the ruling clan Uudes of Melekeok state, the Reklai and Ebilreklai. They are commonly referred to as the king and queen of the Northern Federation. This northern federation comprises the states of Kayangel, Ngerchelong, Ngardmau, Ngiwal, Ngaraard, Ngatpang, Ngeremlengui, Melekok, Aimeliik, Ngchesar and Airai. The Southern Federation is likewise represented by the high chief and chiefess of the ruling Idid of Koror state.
The Southern Federation comprises the states of Koror, Peleliu and Angaur. However, fewer and fewer Palauans have knowledge of the concept of federations, and the term is slowly dying out. Federations were established as a way of safeguarding states and hamlets who shared economic, social, and political interests, but with the advent a federal government, safeguards are less meaningful. However, in international relations, the king of Palau is synonymous with the Ibedul of Koror. This is because Koror is the industrial capital of the nation, elevating his position over the Reklai of Melekeok.
It is a misconception that the king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
and queen of Palau, or any chief and his female counterpart for that matter, are married. Traditional leaders and their female counterparts have always been related and unmarried (marrying relatives was a traditional taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclop├”dia Britannica ...
). Usually, a chief and his female counterpart are brother and sister, or close cousins, and have their own spouses.
Newspapers
Palau has several newspapers: * '' Rengel Belau'' (1983ŌĆō1985) * '' Tia Belau'' (1992ŌĆōpresent) * '' Island Times''Sports
Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding t ...
is a popular sport in Palau after its introduction by the Japanese in the 1920s. The Palau national baseball team won the gold medal at the 1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of humanity on Earth, astrophysicist ...
, 1998
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''.
Events January
* January 6 ŌĆō The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently s ...
and 2010 Micronesian Games
The 7th Micronesian Games was held August 1ŌĆō10 in Palau.
Initially, the 7th Games were to be hosted in Majuro, Marshall Islands; however, in April 2008, the organisers announced that the Games could be "scaled down", with a number events cancel ...
, as well as at the 2007 Pacific Games
The 2007 South Pacific Games were held in Apia, Samoa, from 25 August to 8 September 2007. The Games were the thirteenth to be held since the inception of the South Pacific Games in 1963, and included traditional multi-sport event disciplines, su ...
.
Palau also has a national football team, organized by the Palau Football Association
The Palau Football Association is the governing body for association football in Palau. The association is based in the town of Koror. Palau currently is not a member of the Oceania Football Confederation (OFC), the Asian Football Federation (AFC), ...
, but is not a member of FIFA. The Association also organizes the Palau Soccer League
The Palau Soccer League is the highest division of competitive association football in the nation of Palau, founded in 2004 by the Palau Soccer Association. Due to the lack of equipment and facilities, all matches are played in the Palau Track ...
.
On June 20, 2022, left fielder Bligh Madris played his first game for the Pittsburgh Pirates against the Chicago Cubs, thus becoming the first player ever to play in MLB from Palau. He went 3-for-4 with two RBI in his debut.
Education
Primary education is required until the age of 16. Schools include both public and private institutions as well as some fields of study available at Palau Community College. For further undergraduate, graduate and professional programs, students travel abroad to attend tertiary institutions, primarily in the United States of America. Other popular choices among Palauan scholars includeSan Diego State University
San Diego State University (SDSU) is a public research university in San Diego, California. Founded in 1897 as San Diego Normal School, it is the third-oldest university and southernmost in the 23-member California State University (CSU) system ...
, the University of Guam
University of Guam ( ch, Unibetsed├źt Gu├źhan) (U.O.G.) is a public land-grant university in Mangilao, Guam. It is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges and offers thirty-four degree programs at the undergraduate level a ...
, the University of Hawai╩╗i at Hilo
The University of Hawaii at Hilo (UH Hilo) is a public university in Hilo, Hawaii. It is one of ten general campuses of the University of Hawaii system. It was founded as Hilo Center at Lyman Hall of the Hilo Boys School in 1945 and was a bran ...
, the University of the Philippines
The University of the Philippines (UP; fil, Pamantasan ng Pilipinas Unibersidad ng Pilipinas) is a state university system in the Philippines. It is the country's national university, as mandated by Republic Act No. 9500 (UP Charter of 20 ...
, Mindanao State University
Mindanao State University, commonly referred to as MSU Main, is a regional state, coeducational, research higher education institution in the city of Marawi, Philippines. Founded in 1961, it is the flagship and the largest campus of the Mindana ...
, and the University of the South Pacific
The University of the South Pacific (USP) is a public research university with locations spread throughout a dozen countries in Oceania. Established in 1968, the university is organised as an intergovernmental organisation and is owned by the go ...
.
Cuisine
Palau has its own cuisine, for instance, a dessert called ''tama''. Palauan cuisine includes local foods such ascassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
, yam, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
and pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved; ...
. It is also heavily influenced by Japanese, American as well as the Philippines' cuisine, due to the significant presence of Filipino migrant workers. Fruit bat
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera (bats). They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, orŌĆöespecially the genera '' Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''ŌĆöflying foxes. They are the only member of the ...
soup is a commonly referenced Palauan delicacy.
See also
* Index of Palau-related articles * Outline of PalauReferences
Notes
External links
Government
Republic of Palau National Government
Embassy of the Republic of Palau in Japan
Chief of State and Cabinet Members
Honorary Consulate of the Republic of Palau to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Honorary Consulate-General of Palau to Belgium
Local News
*Island Times
'
Palau Wave Radio
Pacific Note
General information
Palau
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Palau
from the University of Colorado at Boulder Libraries (USA) ŌĆō Government Publications *
Palau profile
from the
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
"Palau"
Ćö''
Encyclop├”dia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclop├”dia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclop├”dia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
'' entry
*
NOAA's National Weather Service ŌĆō Palau
''The Interesting History of Prince Lee Boo, Brought to England from the Pelew Islands''
ĆöFrom the Collections at the Library of Congress {{Authority control 1994 establishments in Oceania Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Associated states of the United States * Countries in Micronesia Countries in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Former colonies in Oceania Former German colonies Former Japanese colonies Former Spanish colonies German New Guinea Island countries Islands of Oceania Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States South Seas Mandate Spanish East Indies States and territories established in 1994 Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands