Land Management In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet
 The earliest material found in the Solar System is dated to (billion years ago); therefore, the Earth itself must have been formed by
The earliest material found in the Solar System is dated to (billion years ago); therefore, the Earth itself must have been formed by
 Terrain refers to an area of land and its features, or landforms. It affects travel, mapmaking, ecosystems, and surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can influence climate and weather patterns. The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands.
Elevation is defined as the vertical distance between an object and sea level, while altitude is defined as the vertical distance from an object to Earth's surface. The elevation of Earth's land surface varies from the low point of −418 m (−1,371 ft) at the Dead Sea, to a maximum altitude of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at the top of Mount Everest. The mean height of land above sea level is about 797 m (2,615 ft), with 98.9% of dry land situated above sea level.
Topographic relief, Relief refers to the difference in elevation within a landscape; for example, flat terrain would have "low relief", while terrain with a large elevation difference between the highest and lowest points would be deemed "high relief". Most land has relatively low relief. The change in elevation between two points of the terrain is called a slope or gradient. A topographic map is a form of terrain cartography which depicts terrain in terms of its elevation, slope, and the orientation of its landforms. It has prominent contour lines, which connect points of similar elevation, while perpendicular slope lines point in the direction of the steepest slope. Hypsometric tints are colors placed between contour lines to indicate elevation relative to sea level.
A difference between uplands, or highlands, and lowlands is drawn in several earth science fields. In river ecology, "Upland and lowland, upland" rivers are fast-moving and colder than "lowland" rivers, encouraging different species of fish and other aquatic wildlife to live in these habitats. For example, nutrients are more present in slow-moving lowland rivers, encouraging different species of macrophytes to grow there. The term "upland" is also used in wetland ecology, where "upland" plants indicate an area that is not a wetland. In addition, the term moorland refers to upland shrubland biomes with acidic soils, while heathlands are lowland shrublands with acidic soils.
Terrain refers to an area of land and its features, or landforms. It affects travel, mapmaking, ecosystems, and surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can influence climate and weather patterns. The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands.
Elevation is defined as the vertical distance between an object and sea level, while altitude is defined as the vertical distance from an object to Earth's surface. The elevation of Earth's land surface varies from the low point of −418 m (−1,371 ft) at the Dead Sea, to a maximum altitude of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at the top of Mount Everest. The mean height of land above sea level is about 797 m (2,615 ft), with 98.9% of dry land situated above sea level.
Topographic relief, Relief refers to the difference in elevation within a landscape; for example, flat terrain would have "low relief", while terrain with a large elevation difference between the highest and lowest points would be deemed "high relief". Most land has relatively low relief. The change in elevation between two points of the terrain is called a slope or gradient. A topographic map is a form of terrain cartography which depicts terrain in terms of its elevation, slope, and the orientation of its landforms. It has prominent contour lines, which connect points of similar elevation, while perpendicular slope lines point in the direction of the steepest slope. Hypsometric tints are colors placed between contour lines to indicate elevation relative to sea level.
A difference between uplands, or highlands, and lowlands is drawn in several earth science fields. In river ecology, "Upland and lowland, upland" rivers are fast-moving and colder than "lowland" rivers, encouraging different species of fish and other aquatic wildlife to live in these habitats. For example, nutrients are more present in slow-moving lowland rivers, encouraging different species of macrophytes to grow there. The term "upland" is also used in wetland ecology, where "upland" plants indicate an area that is not a wetland. In addition, the term moorland refers to upland shrubland biomes with acidic soils, while heathlands are lowland shrublands with acidic soils.
 Earth's land interacts with and influences its climate heavily, since the land's surface heats up and cools down faster than air or water. Latitude, elevation, topography, reflectivity, and land use all have varying effects on climate. The latitude of the land will influence how much solar irradiance, solar radiation reaches its surface. High latitudes receive less solar radiation than low latitudes. The land's topography is important in creating and transforming airflow and
Earth's land interacts with and influences its climate heavily, since the land's surface heats up and cools down faster than air or water. Latitude, elevation, topography, reflectivity, and land use all have varying effects on climate. The latitude of the land will influence how much solar irradiance, solar radiation reaches its surface. High latitudes receive less solar radiation than low latitudes. The land's topography is important in creating and transforming airflow and
 The area where land meets the ocean or another large body of water like a lake is called a coast or, alternatively, a "coastline". When land is in contact with bodies of water, the land is likely weathered and eroded. The weathering of a coastline may be impacted by the tides, caused by changes in gravitational forces on larger bodies of water. The precise length of Earth's coastline is indeterminable due to the coastline paradox.
Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of
The area where land meets the ocean or another large body of water like a lake is called a coast or, alternatively, a "coastline". When land is in contact with bodies of water, the land is likely weathered and eroded. The weathering of a coastline may be impacted by the tides, caused by changes in gravitational forces on larger bodies of water. The precise length of Earth's coastline is indeterminable due to the coastline paradox.
Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of
 Any highly elevated part of Earth's crust may be called a mountain. Mountains are formed from a number of orogeny events; for example, where a plate at a convergent plate boundary pushes one plate above the other, mountains could be formed by either collisional events, such that Earth's crust is pushed upwards, or subductional events, where Earth's crust is pushed into the mantle, causing the crust to melt into diapirs that bubble back to the surface and re-mineralize as dome mountains. The line of mountains in a mountain range are usually formed from the same orogeny events, and their study is important to historical geology.
A plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side, creating steep Cliff, cliffs or Escarpment, escarpments. Both volcanic activity such as the upwelling of magma and extrusion of lava, or erosion of mountains caused from water, glaciers, or aeolian processes, can create plateaus. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones -- buttes are smaller ones with less extrusive and more intrusive igneous rock, while plateaus or highlands are the widest, and mesas are a general-sized plateau with horizontal bedrock strata.
Any highly elevated part of Earth's crust may be called a mountain. Mountains are formed from a number of orogeny events; for example, where a plate at a convergent plate boundary pushes one plate above the other, mountains could be formed by either collisional events, such that Earth's crust is pushed upwards, or subductional events, where Earth's crust is pushed into the mantle, causing the crust to melt into diapirs that bubble back to the surface and re-mineralize as dome mountains. The line of mountains in a mountain range are usually formed from the same orogeny events, and their study is important to historical geology.
A plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side, creating steep Cliff, cliffs or Escarpment, escarpments. Both volcanic activity such as the upwelling of magma and extrusion of lava, or erosion of mountains caused from water, glaciers, or aeolian processes, can create plateaus. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones -- buttes are smaller ones with less extrusive and more intrusive igneous rock, while plateaus or highlands are the widest, and mesas are a general-sized plateau with horizontal bedrock strata.
 Wide, flat areas of land are called Plain, plains, which cover more than one-third of Earth's land area. When they occur as lowered areas between mountains, they can create Valley, valleys, Canyon, canyons, gorges, and ravines. A plateau can be thought of as an elevated plain. Plains are known to have fertile soils and be important for agriculture due to their flatness supporting grasses suitable for livestock and facilitating the harvest of crops. Floodplain, Floodplains provided agricultural land for the some of the Cradle of civilization, earliest civilizations. Erosion is often a main driver for the creation of plains and valleys, with Rift valley, rift valleys being a noticeable exception. Fjord, Fjords are glacial valleys that can be thousands of meters deep, opening out to the sea.
Wide, flat areas of land are called Plain, plains, which cover more than one-third of Earth's land area. When they occur as lowered areas between mountains, they can create Valley, valleys, Canyon, canyons, gorges, and ravines. A plateau can be thought of as an elevated plain. Plains are known to have fertile soils and be important for agriculture due to their flatness supporting grasses suitable for livestock and facilitating the harvest of crops. Floodplain, Floodplains provided agricultural land for the some of the Cradle of civilization, earliest civilizations. Erosion is often a main driver for the creation of plains and valleys, with Rift valley, rift valleys being a noticeable exception. Fjord, Fjords are glacial valleys that can be thousands of meters deep, opening out to the sea.
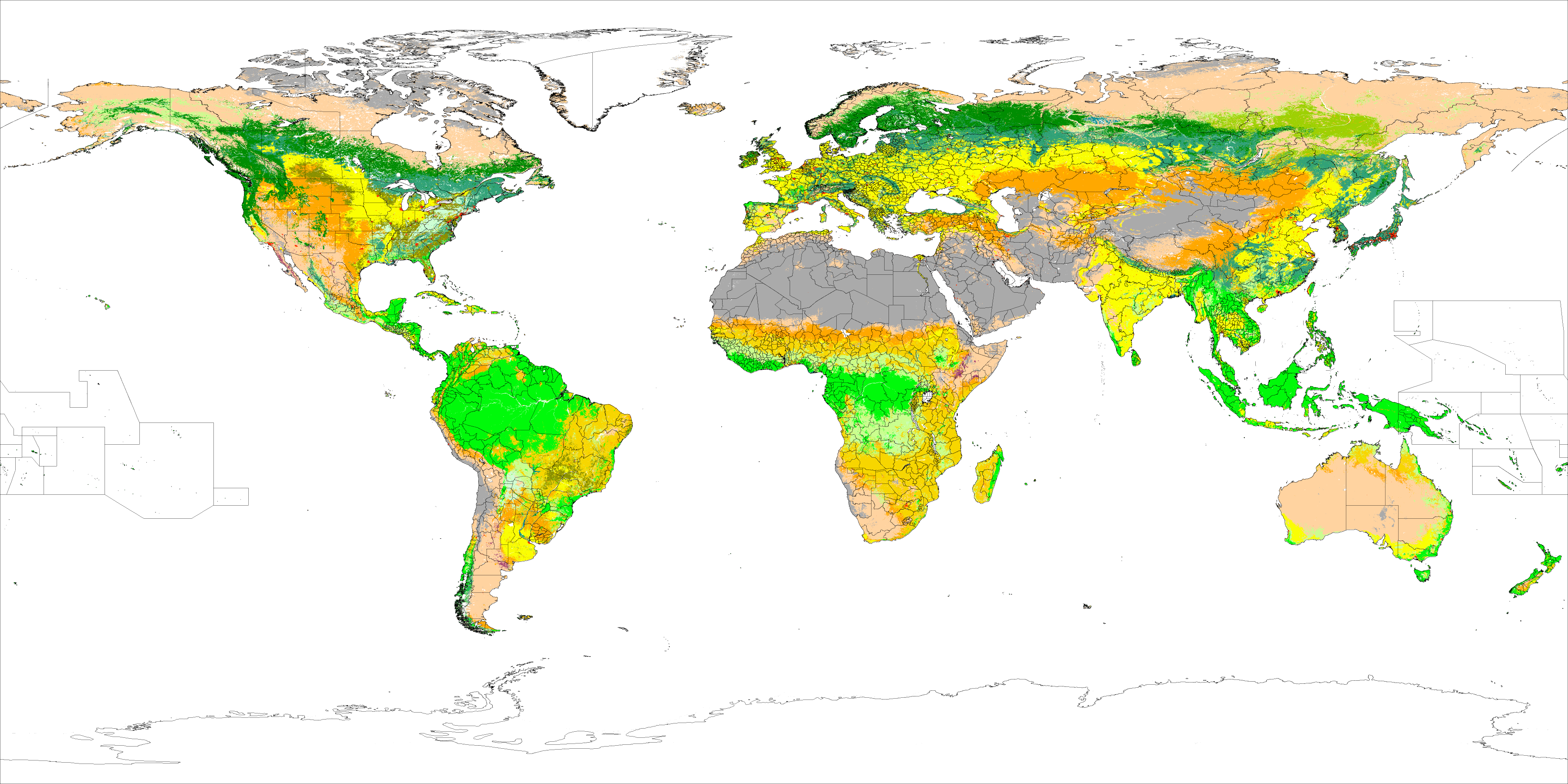 Land cover refers to the material physically present on the land surface, for example, woody crops, herbaceous crops, barren land, and shrub-covered areas. Artificial surfaces (including cities) account for about a third of a percent of all land. Land use refers to human allocation of land for various purposes, including farming, ranching, and recreation (e.g. national parks); worldwide, there are an estimated of cropland, and of pastureland.
Land cover change detection using remote sensing and geospatial data provides baseline information for assessing the climate change impacts on habitats and biodiversity, as well as natural resources, in the target areas. Land cover change detection and mapping is a key component of interdisciplinary land change science, which uses it to determine the consequences of land change on climate. Land change modeling is used to predict and analyze changes in land cover and use.
Land cover refers to the material physically present on the land surface, for example, woody crops, herbaceous crops, barren land, and shrub-covered areas. Artificial surfaces (including cities) account for about a third of a percent of all land. Land use refers to human allocation of land for various purposes, including farming, ranching, and recreation (e.g. national parks); worldwide, there are an estimated of cropland, and of pastureland.
Land cover change detection using remote sensing and geospatial data provides baseline information for assessing the climate change impacts on habitats and biodiversity, as well as natural resources, in the target areas. Land cover change detection and mapping is a key component of interdisciplinary land change science, which uses it to determine the consequences of land change on climate. Land change modeling is used to predict and analyze changes in land cover and use.
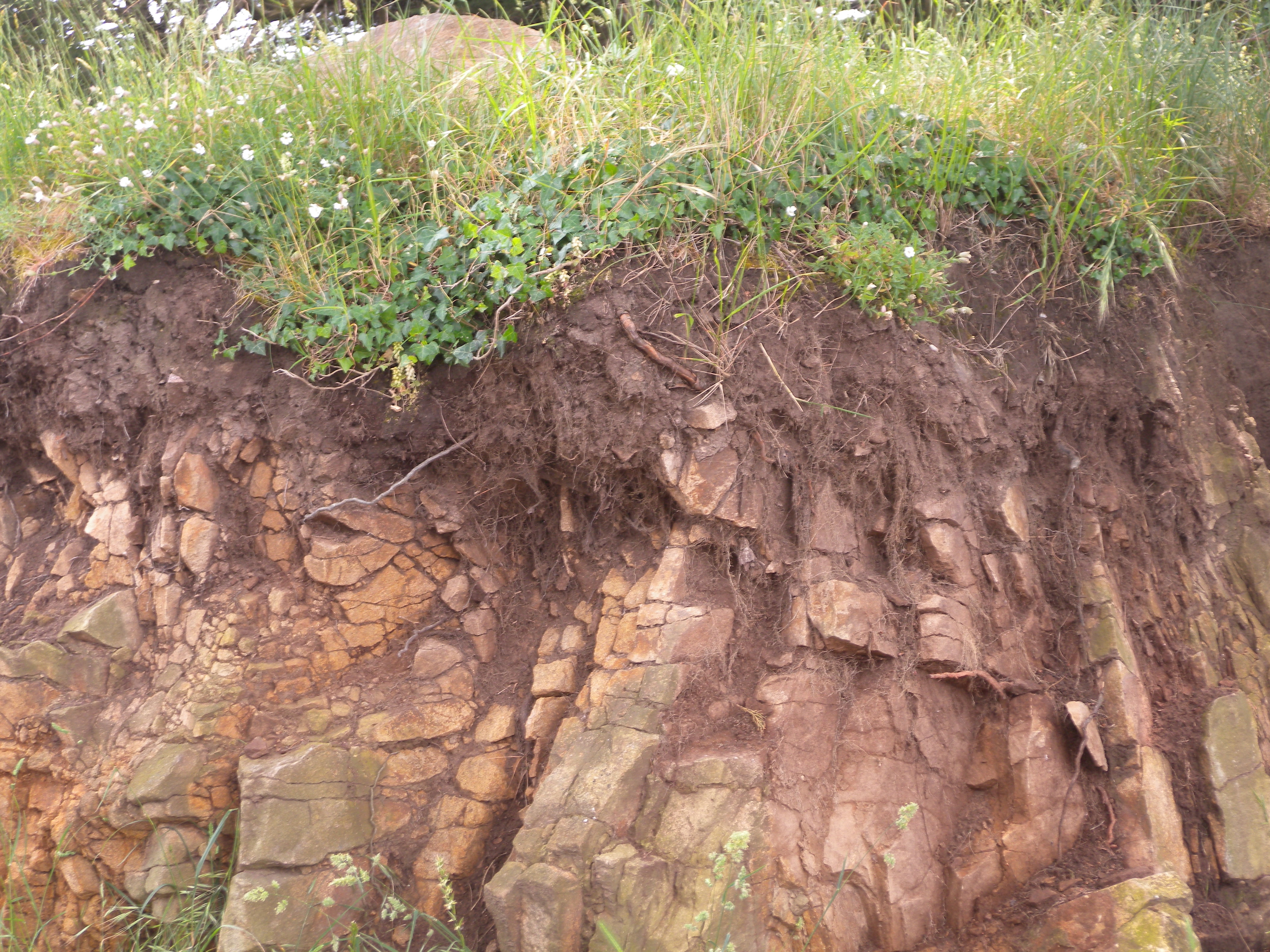 Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a Porosity, porous phase that holds Soil gas, gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-State of matter, state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, Terrain, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering and erosion.
Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, Soil ecology, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Soil acts as an engineering medium, a habitat for soil organisms, a recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes, a regulator of water quality, a modifier of Atmospheric chemistry, atmospheric composition, and a medium for plant growth, making it a critically important provider of ecosystem services. Since soil has a tremendous range of available Ecological niche, niches and habitats, it contains a prominent part of the Earth's genetic diversity. A gram of soil can contain billions of organisms, belonging to thousands of species, mostly microbial and largely still unexplored.
Soil is a major component of the Earth's ecosystem. The world's ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollution. With respect to Earth's
Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a Porosity, porous phase that holds Soil gas, gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-State of matter, state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, Terrain, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering and erosion.
Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, Soil ecology, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Soil acts as an engineering medium, a habitat for soil organisms, a recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes, a regulator of water quality, a modifier of Atmospheric chemistry, atmospheric composition, and a medium for plant growth, making it a critically important provider of ecosystem services. Since soil has a tremendous range of available Ecological niche, niches and habitats, it contains a prominent part of the Earth's genetic diversity. A gram of soil can contain billions of organisms, belonging to thousands of species, mostly microbial and largely still unexplored.
Soil is a major component of the Earth's ecosystem. The world's ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollution. With respect to Earth's

 * A desert is a barren area of landscape where little
* A desert is a barren area of landscape where little
 Many humans see land as a source of "spirituality, inspiration, and beauty." Many also derive a sense of belonging from land, especially if it also belonged to their ancestors. Various religions teach about a connection between humans and the land (such as veneration of Bhumi (goddess), Bhumi, a personification of the Earth in Hinduism, and the obligation to protect land as Hima (environmental protection), hima in Islam), and in almost every Indigenous peoples, Indigenous group there are Etiology, etiological stories about the land they live on. For Indigenous peoples, connection to the land is an important part of their identity and culture, and some religious groups consider a particular area of land to be Sacredness, sacred, such as the Holy Land in the Abrahamic religions.
Creation myths in many religions involve stories of the creation of the world by a supernatural deity or deities, including accounts wherein the land is separated from the oceans and the air. The Earth itself has often been personified as a deity, in particular a goddess. In many cultures, the mother goddess is also portrayed as a Fertility god, fertility deity. To the Aztecs, Earth was called ''Tonantzin''—"our mother"; to the Incas, Earth was called ''Pachamama''—"mother earth". The Chinese Earth goddess Hou Tu is similar to Gaia (mythology), Gaia, the Greek goddess personifying the Earth. In Norse mythology, the Earth giantess Jörð was the mother of Thor and the daughter of Annar. Ancient Egyptian religion, Ancient Egyptian mythology is different from that of other cultures because Earth (Geb) is male and the sky (Nut (goddess), Nut) is female.
Ancient Near Eastern cultures conceived of the world as a flat disk of land surrounded by ocean. The Pyramid Texts and Coffin Texts reveal that the ancient Egyptians believed Nu (mythology), Nun (the ocean) was a circular body surrounding ''nbwt'' (a term meaning "dry lands" or "islands"). The Hebrew Bible, drawing on other Near Eastern ideas, Biblical cosmology#Earth, depicts the Earth as a flat disc floating on water, with another expanse of water above it. A similar model is found in the Homeric account of the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods."
The spherical form of the Earth was suggested by early Greek philosophers, a belief espoused by Pythagoras. Contrary to popular belief, most educated people in the Middle Ages did not believe the Earth was flat: this misconception is often called the "Myth of the Flat Earth". As evidenced by thinkers such as Thomas Aquinas, the European belief in a spherical Earth was widespread by this point in time. Prior to Magellan expedition, circumnavigation of the planet and the introduction of space flight, belief in a spherical Earth was based on observations of the secondary effects of the Earth's shape and parallels drawn with the shape of other planets.
Many humans see land as a source of "spirituality, inspiration, and beauty." Many also derive a sense of belonging from land, especially if it also belonged to their ancestors. Various religions teach about a connection between humans and the land (such as veneration of Bhumi (goddess), Bhumi, a personification of the Earth in Hinduism, and the obligation to protect land as Hima (environmental protection), hima in Islam), and in almost every Indigenous peoples, Indigenous group there are Etiology, etiological stories about the land they live on. For Indigenous peoples, connection to the land is an important part of their identity and culture, and some religious groups consider a particular area of land to be Sacredness, sacred, such as the Holy Land in the Abrahamic religions.
Creation myths in many religions involve stories of the creation of the world by a supernatural deity or deities, including accounts wherein the land is separated from the oceans and the air. The Earth itself has often been personified as a deity, in particular a goddess. In many cultures, the mother goddess is also portrayed as a Fertility god, fertility deity. To the Aztecs, Earth was called ''Tonantzin''—"our mother"; to the Incas, Earth was called ''Pachamama''—"mother earth". The Chinese Earth goddess Hou Tu is similar to Gaia (mythology), Gaia, the Greek goddess personifying the Earth. In Norse mythology, the Earth giantess Jörð was the mother of Thor and the daughter of Annar. Ancient Egyptian religion, Ancient Egyptian mythology is different from that of other cultures because Earth (Geb) is male and the sky (Nut (goddess), Nut) is female.
Ancient Near Eastern cultures conceived of the world as a flat disk of land surrounded by ocean. The Pyramid Texts and Coffin Texts reveal that the ancient Egyptians believed Nu (mythology), Nun (the ocean) was a circular body surrounding ''nbwt'' (a term meaning "dry lands" or "islands"). The Hebrew Bible, drawing on other Near Eastern ideas, Biblical cosmology#Earth, depicts the Earth as a flat disc floating on water, with another expanse of water above it. A similar model is found in the Homeric account of the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods."
The spherical form of the Earth was suggested by early Greek philosophers, a belief espoused by Pythagoras. Contrary to popular belief, most educated people in the Middle Ages did not believe the Earth was flat: this misconception is often called the "Myth of the Flat Earth". As evidenced by thinkers such as Thomas Aquinas, the European belief in a spherical Earth was widespread by this point in time. Prior to Magellan expedition, circumnavigation of the planet and the introduction of space flight, belief in a spherical Earth was based on observations of the secondary effects of the Earth's shape and parallels drawn with the shape of other planets.
 For more than 10,000 years, humans have engaged in activities on land such as hunting, foraging, Controlled burn, controlled burning, Deforestation, land clearing, and
For more than 10,000 years, humans have engaged in activities on land such as hunting, foraging, Controlled burn, controlled burning, Deforestation, land clearing, and
 Borders are geographical boundaries imposed either by geographic features (
Borders are geographical boundaries imposed either by geographic features (
 Terrestrial biodiversity loss refers to the worldwide extinction of various land-based species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in certain habitats. Biodiversity loss is caused by many human activities. Agriculture can cause biodiversity loss as land is converted for agricultural use at a very high rate, particularly in the tropics, which directly causes habitat loss. The use of pesticides and herbicides can also negatively impact the health of local species. Ecosystems can also be divided and degraded by infrastructure development outside of urban areas.
Biodiversity loss can sometimes be reversed through ecological restoration or ecological resilience, such as through the restoration of abandoned agricultural areas; however, it may also be permanent (e.g. through land loss). The planet's ecosystem is quite sensitive: occasionally, minor changes from a healthy Equilibrium point, equilibrium can have dramatic influence on a food web or food chain, up to and including the coextinction of that entire food chain. Biodiversity loss leads to reduced ecosystem services, and can eventually threaten food security. Earth is currently undergoing its Holocene extinction, sixth mass extinction (the ''Holocene extinction'') as a result of human activities which push beyond the planetary boundaries. So far, this extinction has proven irreversible.
Terrestrial biodiversity loss refers to the worldwide extinction of various land-based species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in certain habitats. Biodiversity loss is caused by many human activities. Agriculture can cause biodiversity loss as land is converted for agricultural use at a very high rate, particularly in the tropics, which directly causes habitat loss. The use of pesticides and herbicides can also negatively impact the health of local species. Ecosystems can also be divided and degraded by infrastructure development outside of urban areas.
Biodiversity loss can sometimes be reversed through ecological restoration or ecological resilience, such as through the restoration of abandoned agricultural areas; however, it may also be permanent (e.g. through land loss). The planet's ecosystem is quite sensitive: occasionally, minor changes from a healthy Equilibrium point, equilibrium can have dramatic influence on a food web or food chain, up to and including the coextinction of that entire food chain. Biodiversity loss leads to reduced ecosystem services, and can eventually threaten food security. Earth is currently undergoing its Holocene extinction, sixth mass extinction (the ''Holocene extinction'') as a result of human activities which push beyond the planetary boundaries. So far, this extinction has proven irreversible.
PhysicalGeography.net educational website
{{Authority control Physical geography Geography terminology Geomorphology
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
that is not submerged by the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
or other bodies of water
A body of water or waterbody (often spelled water body) is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as p ...
. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
and various islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
. Earth's land surface is almost entirely covered by regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestria ...
, a layer of rock, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
, and minerals that forms the outer part of the crust. Land plays important roles in Earth's climate system
Earth's climate system is a complex system having five interacting components: the atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), the cryosphere (ice and permafrost), the lithosphere (earth's upper rocky layer) and the biosphere (living things). '' ...
and is involved in the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as ...
, nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biologi ...
, and water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
. One-third of land is covered in trees, 15% is used for crops, and 10% is covered in permanent snow and glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
.
Land terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word ...
varies greatly and consists of mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, glaciers, and other landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
s. In physical geology, the land is divided into two major categories: mountain ranges
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
and relatively flat interiors called craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s. Both are formed over millions of years through plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
. A major part of Earth's water cycle, stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...
s shape the landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the ...
, carved rocks, transport sediments, and replenish groundwater. At high elevations or latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s, snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
is compacted and recrystallized over hundreds or thousands of years to form glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s, which can be so heavy that they warp the Earth's crust. About 30 percent of land has a dry climate, due to losing more water through evaporation than it gains from precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. Since warm air rises, this generates winds, though the Earth's rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
and uneven sun distribution also play a part.
Land is commonly defined as the solid, dry surface of Earth. The word ''land'' may also collectively refer to land cover
Land cover is the physical material at the surface of Earth. Land covers include grass, asphalt, trees, bare ground, water, etc. Earth cover is the expression used by ecologist Frederick Edward Clements that has its closest modern equivalent being ...
, rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
, shallow lakes
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
, natural resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
, non-marine fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
and flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
(biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
), the lower portions of the atmosphere (troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From ...
), groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
reserves, and the physical results of human activity on land, such as architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. Even though saturated land, or mud
A MUD (; originally multi-user dungeon, with later variants multi-user dimension and multi-user domain) is a Multiplayer video game, multiplayer Time-keeping systems in games#Real-time, real-time virtual world, usually Text-based game, text-bas ...
, is common away from the ocean, to anyone in a body of water the shoreline
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
is referred to as where dry land begins.
Though modern terrestrial plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s and animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s evolved from aquatic creatures, Earth's first cellular life likely originated on land. Survival on land depends on fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
from rivers, streams, lakes, and glaciers, which constitutes only three percent of the water on Earth. The vast majority of human activity throughout history has occurred in land areas that are habitable
Habitability refers to the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws it is said to be habitable. In extreme e ...
and support agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and various natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
s. In recent decades, scientists and policymakers have emphasized the need to manage
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activities o ...
land and its biosphere more sustainably, notably by restoring degraded soil, preserving biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, protecting endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
, and addressing climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
.
Etymology
The word "land" is derived from theOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, meaning 'ground, soil', and 'definite portion of the earth's surface, home region of a person or a people, territory marked by political boundaries'. It evolved from the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
and from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
'land, open land, heath'. The word has many cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
s in other languages, such as non, land, ofs, land, got, land, german: Land, sga, land, wlm, llan 'an open space', cy, llan 'enclosure, church', br, lann 'heath', cu, ledina 'wasteland, heath', and cs, lada 'fallow land'. Etymological
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
evidence within Gothic usage suggests that the original meaning of ''land'' was 'a definite portion of the earth's surface owned by an individual or home of a nation.' The meaning was extended to 'solid surface of the earth'. The original meaning is now associated with "country".
A country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
or nation may be referred to as the motherland
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethni ...
, fatherland
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethn ...
, or homeland
A homeland is a place where a cultural, national, or racial identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethni ...
of its people. Many countries and other places have names incorporating the suffix -land
The suffix -land which can be found in several countries' name and country subdivisions indicates a toponymy—a Terrestrial ecoregion, land. The word came via Germanic languages, Germanic "wikt:land, land."
Below is the list of places that ends ...
(e.g. England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
). The equivalent suffix ''-stan
The suffix -stan ( fa, ـستان, translit=''stân'' after a vowel; ''estân'' or ''istân'' after a consonant), has the meaning of "a place abounding in" or "a place where anything abounds" in the Persian language. It appears in the names of ...
'' from Indo-Iranian, ultimately derived from the Proto-Indo-Iranian
Proto-Indo-Iranian, also Proto-Indo-Iranic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Indo-Iranian/Indo-Iranic branch of Indo-European. Its speakers, the hypothetical Proto-Indo-Iranians, are assumed to have lived in the late 3rd millennium B ...
, is also present in many country and location names, such as Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and others throughout Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. The suffix is also used more generally, as in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
() "place of sand, desert", () "place of flowers, garden", () "graveyard, cemetery", and ''Hindustân
''Hindūstān'' ( , from ''Hindus#Etymology, Hindū'' and -stan, ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian language, Persian-language name for the Indian subcont ...
'' () "land of the Indo
Indo may refer to:
* Indo-, a prefix indicating India or the Indian Subcontinent
* Indonesia, a country in Asia
** INDO LINES, callsign of Indonesian Airlines
** Indo people, people of mixed European and Indonesian ancestry
** Indo cuisine, fusion ...
people".
Physical science
The study of land and its history in general is calledgeography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
. Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proces ...
is the study of minerals, and petrology
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together ...
is the study of rocks. Soil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to th ...
is the study of soils, encompassing the sub-disciplines of pedology
Pedology (from Greek: πέδον, ''pedon'', "soil"; and λόγος, ''logos'', "study") is a discipline within soil science which focuses on understanding and characterizing soil formation, evolution, and the theoretical frameworks for modeling ...
, which focuses on soil formation, and edaphology
Edaphology (from Greek , ''edaphos'', "ground",, '' -logia'') is concerned with the influence of soils on living beings, particularly plants.
It is one of two main divisions of soil science, the other being pedology. Edaphology includes the study ...
, which focuses on the relationship between soil and life.
Formation
 The earliest material found in the Solar System is dated to (billion years ago); therefore, the Earth itself must have been formed by
The earliest material found in the Solar System is dated to (billion years ago); therefore, the Earth itself must have been formed by accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
around this time. The formation and evolution of the Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a ...
bodies occurred in tandem with the Sun. In theory, a solar nebula
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a ...
partitions a volume out of a molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen ...
by gravitational collapse, which begins to spin and flatten into a circumstellar disc
A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reser ...
, out of which the planets then grow (in tandem with the star). A nebula contains gas, ice grains and dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes ...
(including primordial nuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
s). In nebular theory
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbiting t ...
, planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System a ...
s commence forming as particulate
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
matter accrues by cohesive clumping and then by gravity. The assembly of the primordial Earth proceeded for 10–. By , the primordial Earth had formed.
Earth's atmosphere and oceans were formed by volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
activity and outgassing
Outgassing (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality) is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation (which a ...
that included water vapour
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
. The origin of the world's oceans
The origin of water on Earth is the subject of a body of research in the fields of planetary science, astronomy, and astrobiology. Earth is unique among the rocky planets in the Solar System in that it is the only planet known to have oceans ...
was condensation augmented by water and ice delivered by asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s, proto-planets, and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
s. In this model, atmospheric "greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
es" kept the oceans from freezing while the newly forming Sun was only at 70% luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a st ...
. By , the Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
was established, which helped prevent the atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sola ...
. The atmosphere and oceans of the Earth continuously shape the land by eroding and transporting solids on the surface.
Earth's crust formed when molten outer layer of the planet Earth cooled to form a solid mass as the accumulated water vapour began to act in the atmosphere. Once land became capable of supporting life, biodiversity evolved over hundreds of million years, expanding continually except when punctuated by mass extinctions.
The two models that explain land mass propose either a steady growth to the present-day forms or, more likely, a rapid growth early in Earth history followed by a long-term steady continental area. Continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
s are formed by plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
, a process ultimately driven by the continuous loss of heat from the Earth's interior. On time scales
Time scale may refer to:
*Time standard, a specification of either the rate at which time passes, points in time, or both
*A duration or quantity of time:
**Orders of magnitude (time) as a power of 10 in seconds;
**A specific unit of time
* Geolog ...
lasting hundreds of millions of years, the supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
s have formed and broken apart three times. Roughly (million years ago), one of the earliest known supercontinents, Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probably ...
, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600–, then finally Pangaea, which also broke apart .
Landmasses
A continuous area of land surrounded by an ocean is called a landmass. Although it is most often written as one word to distinguish it from the usage "land mass"—the measure of land area—it may also be written as two words. There are four major continuous landmasses on Earth: Afro-Eurasia, the Americas, Antarctica, and Australia (continent), Australia, which are then divided into continents. Up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these continents are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia.Terrain
 Terrain refers to an area of land and its features, or landforms. It affects travel, mapmaking, ecosystems, and surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can influence climate and weather patterns. The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands.
Elevation is defined as the vertical distance between an object and sea level, while altitude is defined as the vertical distance from an object to Earth's surface. The elevation of Earth's land surface varies from the low point of −418 m (−1,371 ft) at the Dead Sea, to a maximum altitude of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at the top of Mount Everest. The mean height of land above sea level is about 797 m (2,615 ft), with 98.9% of dry land situated above sea level.
Topographic relief, Relief refers to the difference in elevation within a landscape; for example, flat terrain would have "low relief", while terrain with a large elevation difference between the highest and lowest points would be deemed "high relief". Most land has relatively low relief. The change in elevation between two points of the terrain is called a slope or gradient. A topographic map is a form of terrain cartography which depicts terrain in terms of its elevation, slope, and the orientation of its landforms. It has prominent contour lines, which connect points of similar elevation, while perpendicular slope lines point in the direction of the steepest slope. Hypsometric tints are colors placed between contour lines to indicate elevation relative to sea level.
A difference between uplands, or highlands, and lowlands is drawn in several earth science fields. In river ecology, "Upland and lowland, upland" rivers are fast-moving and colder than "lowland" rivers, encouraging different species of fish and other aquatic wildlife to live in these habitats. For example, nutrients are more present in slow-moving lowland rivers, encouraging different species of macrophytes to grow there. The term "upland" is also used in wetland ecology, where "upland" plants indicate an area that is not a wetland. In addition, the term moorland refers to upland shrubland biomes with acidic soils, while heathlands are lowland shrublands with acidic soils.
Terrain refers to an area of land and its features, or landforms. It affects travel, mapmaking, ecosystems, and surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can influence climate and weather patterns. The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands.
Elevation is defined as the vertical distance between an object and sea level, while altitude is defined as the vertical distance from an object to Earth's surface. The elevation of Earth's land surface varies from the low point of −418 m (−1,371 ft) at the Dead Sea, to a maximum altitude of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at the top of Mount Everest. The mean height of land above sea level is about 797 m (2,615 ft), with 98.9% of dry land situated above sea level.
Topographic relief, Relief refers to the difference in elevation within a landscape; for example, flat terrain would have "low relief", while terrain with a large elevation difference between the highest and lowest points would be deemed "high relief". Most land has relatively low relief. The change in elevation between two points of the terrain is called a slope or gradient. A topographic map is a form of terrain cartography which depicts terrain in terms of its elevation, slope, and the orientation of its landforms. It has prominent contour lines, which connect points of similar elevation, while perpendicular slope lines point in the direction of the steepest slope. Hypsometric tints are colors placed between contour lines to indicate elevation relative to sea level.
A difference between uplands, or highlands, and lowlands is drawn in several earth science fields. In river ecology, "Upland and lowland, upland" rivers are fast-moving and colder than "lowland" rivers, encouraging different species of fish and other aquatic wildlife to live in these habitats. For example, nutrients are more present in slow-moving lowland rivers, encouraging different species of macrophytes to grow there. The term "upland" is also used in wetland ecology, where "upland" plants indicate an area that is not a wetland. In addition, the term moorland refers to upland shrubland biomes with acidic soils, while heathlands are lowland shrublands with acidic soils.
Geomorphology
Geomorphology refers to the study of the natural processes that shape land's surface, creating landforms. Erosion and tectonics, Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, flooding, weathering, glaciation, the growth of coral reefs, and meteorite impacts are among the processes that constantly reshape Earth's surface over geological time. Erosion transports one part of land to another via natural processes, such as Aeolian processes, wind, water, ice, and Mass wasting, gravity. In contrast, weathering wears away rock and other solid land without transporting the land somewhere else. Natural erosional processes usually take a long time to cause noticeable changes in the landscape—for example, the Grand Canyon was created over the past 70 million years by the Colorado river, which scientists estimate continues to erode the canyon at a rate of 0.3 meters (1 foot) every 200 years. However, humans have caused erosion to be 10-40 times faster than normal, causing half the topsoil of the surface of Earth's land to be lost within the past 150 years. Plate tectonics refers to the theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into "tectonic plates" that move over the mantle. This results in continental drift, with continents moving relative to each other. The scientist Alfred Wegener first hypothesized the theory of continental drift in 1912. More researchers gradually developed his idea throughout the 20th century into the widely accepted theory of plate tectonics of today. Several key characteristics define modern understanding of plate tectonics. The place where two tectonic plates meet is called a plate boundary, with different geological phenomena occurring across different kinds of boundaries. For example, at divergent plate boundaries, seafloor spreading is usually seen, in contrast with the subduction zones of Convergent plate boundary, convergent or Transform fault, transform plate boundaries. Earthquakes and volcanic activity are common in all types of boundaries. Volcanic activity refers to any rupture in Earth's surface where magma escapes, therefore becoming lava. The Ring of Fire, containing two-thirds of the world's volcanos, and over 70% of Earth's Seismology, seismological activity, comprises plate boundaries surrounding the Pacific Ocean.Climate
 Earth's land interacts with and influences its climate heavily, since the land's surface heats up and cools down faster than air or water. Latitude, elevation, topography, reflectivity, and land use all have varying effects on climate. The latitude of the land will influence how much solar irradiance, solar radiation reaches its surface. High latitudes receive less solar radiation than low latitudes. The land's topography is important in creating and transforming airflow and
Earth's land interacts with and influences its climate heavily, since the land's surface heats up and cools down faster than air or water. Latitude, elevation, topography, reflectivity, and land use all have varying effects on climate. The latitude of the land will influence how much solar irradiance, solar radiation reaches its surface. High latitudes receive less solar radiation than low latitudes. The land's topography is important in creating and transforming airflow and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. Large landforms, such as mountain ranges, can divert wind energy and make Fluid parcel, air parcels less dense and therefore able to hold less heat. As air rises, this cooling effect causes condensation and precipitation.
Different types of land cover will influence the land's albedo, a measure of the solar radiation that is reflected, rather than absorbed and transferred to Earth. Vegetation has a relatively low albedo, meaning that vegetated surfaces are good absorbers of the sun's energy. Forests have an albedo of 10–15 percent while grasslands have an albedo of 15–20 percent. In comparison, sandy deserts have an albedo of 25–40 percent.
Land use by humans also plays a role in the regional and global climate. Densely populated cities are warmer and create urban heat islands that have effects on the precipitation, cloud cover, and temperature of the region.
Features
A landform is a natural or manmade land feature. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in thelandscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the ...
is known as topography. Landforms include Hill, hills, Mountain, mountains, Canyon, canyons, and Valley, valleys, as well as shoreline
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
features such as Bay, bays and Peninsula, peninsulas.
Coasts and islands
 The area where land meets the ocean or another large body of water like a lake is called a coast or, alternatively, a "coastline". When land is in contact with bodies of water, the land is likely weathered and eroded. The weathering of a coastline may be impacted by the tides, caused by changes in gravitational forces on larger bodies of water. The precise length of Earth's coastline is indeterminable due to the coastline paradox.
Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of
The area where land meets the ocean or another large body of water like a lake is called a coast or, alternatively, a "coastline". When land is in contact with bodies of water, the land is likely weathered and eroded. The weathering of a coastline may be impacted by the tides, caused by changes in gravitational forces on larger bodies of water. The precise length of Earth's coastline is indeterminable due to the coastline paradox.
Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
. On land, they harbour important ecosystems such as freshwater or estuarine wetlands, which are important for bird populations and other terrestrial animals. In wave-protected areas they harbor Salt marsh, saltmarshes, mangroves or Seagrass meadow, seagrasses, all of which can provide nursery habitat for finfish, shellfish, and other aquatic species. Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of Sessility (motility), sessile animals (e.g. mussels, starfish, barnacles) and various kinds of seaweeds. Along Tropics, tropical coasts with clear, nutrient-poor water, coral reefs can often be found between depths of 1–50 meters (3.3–164.0 feet).
According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 150 km (93 mi) of the sea. Because of their importance in society and high concentration of population, the coast is important for major parts of the global food and economic system, and they provide many ecosystem services to humankind. For example, important human activities happen in Port, port cities. Coastal fisheries (commercial, recreational, and subsistence) and aquaculture are major economic activities and create jobs, livelihoods, and protein for the majority of coastal human populations. Other coastal spaces like beaches and seaside resorts generate large revenues through tourism. Marine coastal ecosystems can also provide protection against sea level rise and tsunamis. In many countries, mangroves are the primary source of wood for fuel (e.g. charcoal) and building material. Coastal ecosystems like mangroves and seagrasses have a much higher capacity for carbon sequestration than many terrestrial ecosystems, and as such can play a critical role in the near future to help Climate change mitigation, mitigate climate change effects by uptake of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric anthropogenic carbon dioxide.
An Isolated system, isolated land habitat surrounded by water is an island, while a chain of islands is an archipelago. The smaller the island, the larger the percentage of its land area will be adjacent to the water, and subsequently will be coast or beach. Islands can be formed by a variety of processes. The Hawaiian islands, for example, even though they are not near a plate boundary, formed from Hotspot (geology), isolated volcanic activity. Atolls are ring-shaped islands made of coral, created when subsidence causes an island to sink beneath the ocean surface and leaves a ring of reefs around it.
Mountains and plateaus
 Any highly elevated part of Earth's crust may be called a mountain. Mountains are formed from a number of orogeny events; for example, where a plate at a convergent plate boundary pushes one plate above the other, mountains could be formed by either collisional events, such that Earth's crust is pushed upwards, or subductional events, where Earth's crust is pushed into the mantle, causing the crust to melt into diapirs that bubble back to the surface and re-mineralize as dome mountains. The line of mountains in a mountain range are usually formed from the same orogeny events, and their study is important to historical geology.
A plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side, creating steep Cliff, cliffs or Escarpment, escarpments. Both volcanic activity such as the upwelling of magma and extrusion of lava, or erosion of mountains caused from water, glaciers, or aeolian processes, can create plateaus. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones -- buttes are smaller ones with less extrusive and more intrusive igneous rock, while plateaus or highlands are the widest, and mesas are a general-sized plateau with horizontal bedrock strata.
Any highly elevated part of Earth's crust may be called a mountain. Mountains are formed from a number of orogeny events; for example, where a plate at a convergent plate boundary pushes one plate above the other, mountains could be formed by either collisional events, such that Earth's crust is pushed upwards, or subductional events, where Earth's crust is pushed into the mantle, causing the crust to melt into diapirs that bubble back to the surface and re-mineralize as dome mountains. The line of mountains in a mountain range are usually formed from the same orogeny events, and their study is important to historical geology.
A plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side, creating steep Cliff, cliffs or Escarpment, escarpments. Both volcanic activity such as the upwelling of magma and extrusion of lava, or erosion of mountains caused from water, glaciers, or aeolian processes, can create plateaus. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones -- buttes are smaller ones with less extrusive and more intrusive igneous rock, while plateaus or highlands are the widest, and mesas are a general-sized plateau with horizontal bedrock strata.
Plains and valleys
Caves and craters
Any natural void in the ground which can be entered by a human can be considered a cave. They have been important to humans as a place of Shelter (building), shelter since the dawn of humanity. Crater, Craters are depressions in the ground, but unlike caves, they do not provide shelter or extend Subterranea (geography), underground. They are many kinds of craters, such as impact craters, volcanic calderas, and isostatic depressions, such as the one in Greenland. Karst processes can create both solution caves, the most frequent cave type, and craters, as seen in karst Sinkhole, sinkholes.Layers
The pedosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's continental surface and is composed of soil and subject to Pedogenesis, soil formation processes. Below it, the lithosphere encompasses both Earth's crust and the uppermost layer of the Earth's mantle, mantle. The lithosphere rests, or "floats", on top of the mantle below it via isostasy. Above the solid ground, thetroposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From ...
and humans' use of land can be considered layers of the land.
Land cover
 Land cover refers to the material physically present on the land surface, for example, woody crops, herbaceous crops, barren land, and shrub-covered areas. Artificial surfaces (including cities) account for about a third of a percent of all land. Land use refers to human allocation of land for various purposes, including farming, ranching, and recreation (e.g. national parks); worldwide, there are an estimated of cropland, and of pastureland.
Land cover change detection using remote sensing and geospatial data provides baseline information for assessing the climate change impacts on habitats and biodiversity, as well as natural resources, in the target areas. Land cover change detection and mapping is a key component of interdisciplinary land change science, which uses it to determine the consequences of land change on climate. Land change modeling is used to predict and analyze changes in land cover and use.
Land cover refers to the material physically present on the land surface, for example, woody crops, herbaceous crops, barren land, and shrub-covered areas. Artificial surfaces (including cities) account for about a third of a percent of all land. Land use refers to human allocation of land for various purposes, including farming, ranching, and recreation (e.g. national parks); worldwide, there are an estimated of cropland, and of pastureland.
Land cover change detection using remote sensing and geospatial data provides baseline information for assessing the climate change impacts on habitats and biodiversity, as well as natural resources, in the target areas. Land cover change detection and mapping is a key component of interdisciplinary land change science, which uses it to determine the consequences of land change on climate. Land change modeling is used to predict and analyze changes in land cover and use.
Soil
 Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a Porosity, porous phase that holds Soil gas, gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-State of matter, state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, Terrain, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering and erosion.
Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, Soil ecology, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Soil acts as an engineering medium, a habitat for soil organisms, a recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes, a regulator of water quality, a modifier of Atmospheric chemistry, atmospheric composition, and a medium for plant growth, making it a critically important provider of ecosystem services. Since soil has a tremendous range of available Ecological niche, niches and habitats, it contains a prominent part of the Earth's genetic diversity. A gram of soil can contain billions of organisms, belonging to thousands of species, mostly microbial and largely still unexplored.
Soil is a major component of the Earth's ecosystem. The world's ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollution. With respect to Earth's
Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a Porosity, porous phase that holds Soil gas, gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three-State of matter, state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, Terrain, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering and erosion.
Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, Soil ecology, soil ecologists regard soil as an ecosystem. Soil acts as an engineering medium, a habitat for soil organisms, a recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes, a regulator of water quality, a modifier of Atmospheric chemistry, atmospheric composition, and a medium for plant growth, making it a critically important provider of ecosystem services. Since soil has a tremendous range of available Ecological niche, niches and habitats, it contains a prominent part of the Earth's genetic diversity. A gram of soil can contain billions of organisms, belonging to thousands of species, mostly microbial and largely still unexplored.
Soil is a major component of the Earth's ecosystem. The world's ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollution. With respect to Earth's carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as ...
, soil acts as an important Carbon sink, carbon reservoir, and it is potentially one of the most reactive to human disturbance and climate change. As the planet warms, it has been predicted that soils will add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere due to increased Soil biology, biological activity at higher temperatures, a positive feedback (amplification). This prediction has, however, been questioned on consideration of more recent knowledge on soil carbon turnover.
Continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of Igneous rock, igneous, Sedimentary rock, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as Continental shelf, continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicate and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''Sima (geology), sima'' which is richer in Talc, magnesium silicate. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The composition of land is not uniform across the Earth, varying between locations and between Stratum, strata within the same location. The most prominent components of upper continental crust include silicon dioxide, aluminium oxide, and magnesium. The continental crust consists of lower density material such as the igneous rocks granite and andesite. Less common is basalt, a denser volcanic rock that is the primary constituent of the ocean floors. Sedimentary rock is formed from the accumulation of sediment that becomes buried and Diagenesis, compacted together. Nearly 75% of the continental surfaces are covered by sedimentary rocks, although they form about 5% of the crust. The most abundant silicate minerals on Earth's surface include quartz, feldspars, amphibole, mica, pyroxene and olivine. Common carbonate minerals include calcite (found in limestone) and Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. The rock that makes up land is thicker than oceanic crust, and it is far more varied in terms of composition. About 31% of this continental crust is submerged in shallow water, forming continental shelves.Life science
Land provides many Ecosystem service, ecosystem services, such as mitigating climate change, regulating water supply through drainage basins and river systems, and supporting food production. Land resources are finite, which has led to regulations intended to safeguard these ecosystem services, and a set of practices called sustainable land management.Land biomes
A biome is an area "characterized by its vegetation, soil, climate, and wildlife." There are five major types of biomes on land: grasslands, forests, deserts, tundras, and freshwater. Other types of biomes include shrublands, wetlands, and polar ice caps. An ecosystem refers to the interaction between organisms within a particular environment, and a habitat refers to the environment where a given species or population of organisms lives. Biomes may span more than one continent, and contain a variety of ecosystems and habitats.
 * A desert is a barren area of landscape where little
* A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of Earth's land surface is arid or Semi-arid climate, semi-arid. This includes much of the Polar regions of Earth, polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by their average temperature, by the causes of desertification, or by their geographical location.
* Tundra is a biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian language, Russian () from the Kildin Sámi language, Kildin Sámi word () meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". There are three regions and associated types of tundra: Arctic tundra alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra.
* A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Many definitions of "forest" are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as: "land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a Canopy (biology), canopy cover of more than 10 per cent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use."
* Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found, along with variable proportions of legumes like clover and other Herbaceous plant, herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica and are found in most ecoregions of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. Furthermore, grasslands are one of the largest biomes on earth and dominate the landscape worldwide. There are different types of grasslands: natural grasslands, semi-natural grasslands, and agricultural grasslands.
Fauna and flora
Land plants evolved from green algae, and are called embryophytes. They include trees, shrubs, grass, moss, and flowers. Most plants are vascular plants, meaning that their tissues distribute water and minerals throughout the plant. Through photosynthesis, most plants nourish themselves from sunlight and water, breathing in carbon dioxide and breathing out oxygen. Between 20 and 50% of oxygen is produced by land vegetation. Unlike plants, terrestrial animals are not a Monophyly, monophyletic group—that is, a group including all terrestrial animals does not encompass all lineages from a common ancestor. This is because there are organisms, such as the whale, that evolved from terrestrial mammals Evolution of cetaceans, back to an aquatic lifestyle. Many megafauna of the past, such as the dinosaurs, have become extinct due to extinction events, e.g. the Quaternary extinction event.Humans and land
Land is "deeply intertwined with human development." Humans depend on land for subsistence, and can develop strong symbolic attachments to it. Access to land can determine "survival and wealth," particularly in developing countries, giving rise to complex power relationships in production and consumption. Most of the world's philosophies and religions recognize a human duty of Stewardship (theology), stewardship towards land and nature.Culture
 Many humans see land as a source of "spirituality, inspiration, and beauty." Many also derive a sense of belonging from land, especially if it also belonged to their ancestors. Various religions teach about a connection between humans and the land (such as veneration of Bhumi (goddess), Bhumi, a personification of the Earth in Hinduism, and the obligation to protect land as Hima (environmental protection), hima in Islam), and in almost every Indigenous peoples, Indigenous group there are Etiology, etiological stories about the land they live on. For Indigenous peoples, connection to the land is an important part of their identity and culture, and some religious groups consider a particular area of land to be Sacredness, sacred, such as the Holy Land in the Abrahamic religions.
Creation myths in many religions involve stories of the creation of the world by a supernatural deity or deities, including accounts wherein the land is separated from the oceans and the air. The Earth itself has often been personified as a deity, in particular a goddess. In many cultures, the mother goddess is also portrayed as a Fertility god, fertility deity. To the Aztecs, Earth was called ''Tonantzin''—"our mother"; to the Incas, Earth was called ''Pachamama''—"mother earth". The Chinese Earth goddess Hou Tu is similar to Gaia (mythology), Gaia, the Greek goddess personifying the Earth. In Norse mythology, the Earth giantess Jörð was the mother of Thor and the daughter of Annar. Ancient Egyptian religion, Ancient Egyptian mythology is different from that of other cultures because Earth (Geb) is male and the sky (Nut (goddess), Nut) is female.
Ancient Near Eastern cultures conceived of the world as a flat disk of land surrounded by ocean. The Pyramid Texts and Coffin Texts reveal that the ancient Egyptians believed Nu (mythology), Nun (the ocean) was a circular body surrounding ''nbwt'' (a term meaning "dry lands" or "islands"). The Hebrew Bible, drawing on other Near Eastern ideas, Biblical cosmology#Earth, depicts the Earth as a flat disc floating on water, with another expanse of water above it. A similar model is found in the Homeric account of the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods."
The spherical form of the Earth was suggested by early Greek philosophers, a belief espoused by Pythagoras. Contrary to popular belief, most educated people in the Middle Ages did not believe the Earth was flat: this misconception is often called the "Myth of the Flat Earth". As evidenced by thinkers such as Thomas Aquinas, the European belief in a spherical Earth was widespread by this point in time. Prior to Magellan expedition, circumnavigation of the planet and the introduction of space flight, belief in a spherical Earth was based on observations of the secondary effects of the Earth's shape and parallels drawn with the shape of other planets.
Many humans see land as a source of "spirituality, inspiration, and beauty." Many also derive a sense of belonging from land, especially if it also belonged to their ancestors. Various religions teach about a connection between humans and the land (such as veneration of Bhumi (goddess), Bhumi, a personification of the Earth in Hinduism, and the obligation to protect land as Hima (environmental protection), hima in Islam), and in almost every Indigenous peoples, Indigenous group there are Etiology, etiological stories about the land they live on. For Indigenous peoples, connection to the land is an important part of their identity and culture, and some religious groups consider a particular area of land to be Sacredness, sacred, such as the Holy Land in the Abrahamic religions.
Creation myths in many religions involve stories of the creation of the world by a supernatural deity or deities, including accounts wherein the land is separated from the oceans and the air. The Earth itself has often been personified as a deity, in particular a goddess. In many cultures, the mother goddess is also portrayed as a Fertility god, fertility deity. To the Aztecs, Earth was called ''Tonantzin''—"our mother"; to the Incas, Earth was called ''Pachamama''—"mother earth". The Chinese Earth goddess Hou Tu is similar to Gaia (mythology), Gaia, the Greek goddess personifying the Earth. In Norse mythology, the Earth giantess Jörð was the mother of Thor and the daughter of Annar. Ancient Egyptian religion, Ancient Egyptian mythology is different from that of other cultures because Earth (Geb) is male and the sky (Nut (goddess), Nut) is female.
Ancient Near Eastern cultures conceived of the world as a flat disk of land surrounded by ocean. The Pyramid Texts and Coffin Texts reveal that the ancient Egyptians believed Nu (mythology), Nun (the ocean) was a circular body surrounding ''nbwt'' (a term meaning "dry lands" or "islands"). The Hebrew Bible, drawing on other Near Eastern ideas, Biblical cosmology#Earth, depicts the Earth as a flat disc floating on water, with another expanse of water above it. A similar model is found in the Homeric account of the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods."
The spherical form of the Earth was suggested by early Greek philosophers, a belief espoused by Pythagoras. Contrary to popular belief, most educated people in the Middle Ages did not believe the Earth was flat: this misconception is often called the "Myth of the Flat Earth". As evidenced by thinkers such as Thomas Aquinas, the European belief in a spherical Earth was widespread by this point in time. Prior to Magellan expedition, circumnavigation of the planet and the introduction of space flight, belief in a spherical Earth was based on observations of the secondary effects of the Earth's shape and parallels drawn with the shape of other planets.
Travel
Humans have commonly traveled for business, pleasure, discovery, and adventure, all made easier in recent human history as a result of technologies like cars, trains, Airplane, planes, and ships. Land navigation is an aspect of travel and refers to progressing through unfamiliar terrain using navigational tools like maps with references to terrain, a compass, or satellite navigation. Navigation on land is often facilitated by reference to landmarks – enduring and recognizable natural or artificial features that stand out from their nearby environment and are often visible from long distances. Natural landmarks can be characteristic features, such as mountains or plateaus, with examples including Table Mountain in South Africa, Mount Ararat in Turkey, the Grand Canyon in the United States, Uluru in Australia, and Mount Fuji in Japan. Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of divergence, and one of convergence. The former saw humans moving out of Africa, settling in new lands, and developing distinct cultures in relative isolation. Early explorers settled in Europe and Asia; 14,000 years ago, some crossed the Settlement of the Americas, Ice Age land bridge from Siberia to Alaska and moved southbound to settle in the Americas. For the most part, these cultures were ignorant of each other's existence. The second period, occurring over roughly the last 10,000 years, saw increased cross-cultural exchange through trade and exploration, marking a new era of cultural intermingling.Trade
Human trade has occurred since the prehistoric era. Peter Watson (business writer), Peter Watson dates the History of international trade, history of long-distance commerce from c. 150,000 years ago.#Watson2005, Watson (2005), Introduction. Major trade routes throughout history have existed on land, such as the Silk Road which linked East Asia with Europe and the Amber Road which was used to transfer amber from Northern Europe to the Mediterranean Sea. The Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages led trade to collapse in the West, but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China, and Southeast Asia. During the Middle Ages, Central Asia was the economic centre of the world, and luxury goods were commonly traded in Europe. Physical money (either barter or precious metals) was dangerous to carry over a long distance. To address this, a burgeoning banking industry enabled the shift to movable wealth or capital, making it far easier and safer to trade across long distances. After the Age of Sail, international trade mostly occurred along sea routes, notably to prevent intermediary countries from being able to control trade routes and the flow of goods. In economics, Land (economics), ''land'' refers to a factor of production. It can be leased in exchange for Renting, rent, and use of its various raw material resources (trees, oil, metals).Land use
 For more than 10,000 years, humans have engaged in activities on land such as hunting, foraging, Controlled burn, controlled burning, Deforestation, land clearing, and
For more than 10,000 years, humans have engaged in activities on land such as hunting, foraging, Controlled burn, controlled burning, Deforestation, land clearing, and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. Beginning with the Neolithic Revolution and the spread of agriculture around the world, human land use has significantly altered terrestrial ecosystems, with an essentially global transformation of Earth's landscape by 3000 years ago. From around 1750, human land use has increased at an accelerating rate due to the Industrial Revolution, which created a greater demand for natural resources and caused rapid population growth.
Agriculture includes both crops, crop farming and animal husbandry. A third of Earth's land surface is used for agriculture, with estimated of cropland and of pastureland. This has had significant impacts on Earth's ecosystems. When land is cleared to make way for agriculture, native flora and fauna are replaced with newly introduced crops and livestock. Excessively high agricultural land use is driven by poor management practices (which lead to lower food yields, necessitating more land use), food demand, Food loss and waste, food waste, and Environmental impact of meat production#Grazing and land use, diets high in meat.
Urbanization has led to greater population growth in urban areas in the last century. Although urban areas make up less than 3 percent of Earth's land area, the global population shifted from a majority living in rural areas to a majority living in urban areas in 2007. People living in urban areas depend on food produced in rural areas outside of their cities, which creates greater demand for agriculture and drives land use change well beyond city boundaries. Urbanization also displaces agricultural land because it mainly takes place on the most fertile land. Urban expansion in Peri-urbanisation, peri-urban areas fragments agricultural and natural lands, forcing agriculture to move to less fertile land elsewhere. Because this land is less fertile, more land is needed for the same output, which increases the total agricultural land use.
Another form of land use is mining, whereby minerals are extracted from the ground using a variety of methods. Evidence of mining activity dates back to around 3000 BCE in Ancient Egypt. Important minerals include iron ore, mined for use as a raw material, coal, mined for Fossil fuel, energy production, and gemstones, mined for use in jewellery and currency.
Law
The phrase "Law of the land, the law of the land" first appeared in 1215 in the Magna Carta, inspiring its later usage in the United States Constitution. The idea of common land also originated with medieval English law, and refers collective ownership of land, treating it as a common good. In environmental science, economics, and game theory, the tragedy of the commons refers to individuals' use of common spaces for their own gain, deteriorating the land overall by taking more than their fair share and not cooperating with others. The idea of common land suggests public ownership; but there is still some land that can be privatized as property for an individual, such as a landlord or king. In the developed world, land is expected to be privately owned by an individual with legal Title (property), title, but in the developing world the right to use land is often divided, with the rights to land resources being given to different people at different times for the same area of land. Beginning in the late 20th century, the international community has begun to recognise Indigenous land rights in law, for example, the Treaty of Waitangi for Māori people, Māori people, the 2008 Greenlandic self-government referendum, Act on Greenland Self-Government for Inuit people, and the Indigenous Peoples Rights Act in the Philippines.Geopolitics
ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s, mountain ranges, rivers) or by Polity, political entities (governments, states, or subnational entities). Political borders can be established through warfare, colonization, or mutual agreements between the political entities that reside in those areas; the creation of these agreements is called boundary delimitation.
Many wars and other conflicts have occurred in efforts by participants to expand the land under their control, or to assert control of a specific area of considered to hold strategic, historical, or cultural significance. The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous land empire in human history, history through war and conquest.
In the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States, a concept of manifest destiny was developed by various groups, asserting that American settlers were destined to expand across North America. This concept was used to justify military action against the indigenous peoples of North America and Indigenous peoples of Mexico, of Mexico.
The aggression of Nazi Germany in World War II was motivated in part by the concept of ''Lebensraum'' ("living space"), which had first became a geopolitical goal of German Empire, Imperial Germany in World War I (1914–1918) originally, as the core element of the of territorial expansion. The most extreme form of this ideology was supported by the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Lebensraum was one of the leading motivations Nazi Germany had in initiating World War II, and it would continue this policy until the end of World War II.
Environmental issues
Land degradation is "the reduction or loss of the biological or economic productivity and complexity" of land as a result of human activity. Land degradation is driven by many different activities, including agriculture, urbanization, energy production, and mining. Humans have altered more than three-quarters of ice-free land through habitation and other use, fundamentally changing ecosystems. Human activity is a major factor in the Holocene extinction, and human-caused climate change is causing Sea level rise, rising sea levels and ecosystem loss. Environmental scientists study land's ecosystems, natural resources,biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
(fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
and flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
), troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From ...
, and the impact of human activity on these. Their recommendations have led to international action to prevent biodiversity loss and desertification, and encourage sustainable forest management, forest and waste management, waste management. The conservation movement lobbies for the protection of endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
and the protection of natural areas, such as parks. International frameworks have focused on analyzing how humans can meet their needs while using land more efficiently and preserving its natural resources, notably under the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals framework.
Soil degradation
Human land use can cause soil to degrade, both in quality and in quantity. Soil degradation can be caused by agrochemicals (such as fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides), infrastructure development, and mining among other activities. There are several different processes that lead to soil degradation. Physical processes, such as Soil erosion, erosion, Soil sealing, sealing, and Soil crust#Physical soil crusts, crusting, lead to the structural breakdown of the soil. This means water cannot penetrate the soil surface, causing surface runoff. Chemical processes, such as Soil salinity, salinization, Soil acidification, acidification, and toxication, lead to chemical imbalances in the soil. Salinization in particular is detrimental, as it makes land less productive for agriculture and affects at least 20% of all irrigated lands. Deliberate disruption of soil in the form of tillage can also alter biological processes in the soil, which leads to excessive Mineralization (soil science), mineralization and the loss of nutrients. Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which fertile areas become increasingly arid as a result of natural processes or human activities, resulting in loss of biological productivity. This spread of arid areas can be influenced by a variety of human factors, such as deforestation, improper land management, overgrazing, anthropogenicclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
, and overexploitation of soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
. Throughout geological history, desertification has occurred naturally, though in recent times it is greatly accelerated by human activity.
Pollution
Ground pollution includes litter. Some landfills, such as the Apex landfill, Apex Regional landfill in Las Vegas, can be thousands of acres in size. Water pollution on land is the contamination of non-oceanic hydrological surface and underground water features such aslakes
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
, ponds, rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
, streams, wetlands, aquifers, reservoirs, and groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
as a result of human activities. It may be caused by toxic substances (e.g., oil, metals, plastics, pesticides, persistent organic pollutants, industrial waste products), stressful conditions (e.g., changes of pH, Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxia or anoxia, increased temperatures, excessive turbidity, unpleasant taste or odor, and changes of salinity), or Pathogen, pathogenic organisms.
Biodiversity loss
Resource depletion
Although humans have used land for itsnatural resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
since ancient times, demand for resources such as timber, minerals, and energy has grown exponentially since the Industrial Revolution due to population growth. When a natural resource is depleted to the point of diminishing returns, it is considered the overexploitation of that resource. Some natural resources, such as timber, are considered renewable, because with sustainable practices they replenish to their previous levels. Fossil fuels such as coal are not considered renewable, as they take millions of years to form, with the current supply of coal expected to peak in the middle of the 21st century. Economic materialism, or consumerism, has influenced destructive patterns of modern resource usage, in contrast with pre-industrial usage.
See also
* Solid earthNotes
References
Sources
* *External links
PhysicalGeography.net educational website
{{Authority control Physical geography Geography terminology Geomorphology