Labile affect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pseudobulbar affect (PBA), or emotional incontinence, is a type of affect disorder connected to neurological conditions. It is characterized by brief, intense, uncontrollable episodes of crying or laughing. The affect is triggered by emotionally trivial or neutral stimuli, that not necessarily relate to the emotional state.
PBA is a consequence of another neurologic disorder or
 PBA may often be misdiagnosed as
PBA may often be misdiagnosed as
"Pseudobulbar affect and stroke"
on the National Stroke Association website {{Medical resources , ICD10 = {{ICD10, F48.8 , ICD10CM = {{ICD10CM, F48.2 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 310.81 , ICDO = , OMIM = , DiseasesDB = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , MeshID = Symptoms and signs of mental disorders
brain injury
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
. Patients may find themselves crying uncontrollably at something that is only slightly sad, being unable to stop themselves for several minutes. Episodes may also be mood-incongruent: a patient may laugh uncontrollably when angry or frustrated, for example. Sometimes, the episodes may switch between emotional states, resulting in the patient crying uncontrollably before dissolving into fits of laughter.
PBA is a severe disruption of momentary emotional expression rather than the persistent, excessive, and pervasive disturbances characteristic of mood disorders. Thus, it is to be distinguished from emotional lability as it occurs with depression. PBA, emotional lability, and irritability are subsumed under the term emotional dyscontrol.
Signs and symptoms
The cardinal feature of the disorder is a pathologically lowered threshold for exhibiting the behavioral response of laughter, crying, anger or all of the above. An affected individual exhibits episodes of laughter, crying, anger or a combination of these without an apparent motivating stimulus or in response to stimuli that would not have elicited such an emotional response before the onset of their underlying neurologic disorder. In some patients, the emotional response is exaggerated in intensity but is provoked by a stimulus with an emotional valence congruent with the character of the emotional display. For example, a sad stimulus provokes a pathologically exaggerated weeping response instead of a sigh, which the patient normally would have exhibited in that particular instance. However, in some other patients, the character of the emotional display can be incongruent with, and even contradictory to, the emotional valence of the provoking stimulus or may be incited by a stimulus with no clear valence. For example, a patient may laugh in response to sad news or cry in response to stimuli with no emotional undertone, or, once provoked, the episodes may switch from laughing to crying or vice versa. The symptoms of PBA can be severe, with persistent and unremitting episodes. Characteristics include: * The onset can be sudden and unpredictable, and has been described by some patients as coming on like a seizure; * The outbursts have a typical duration of a few seconds to several minutes; and, * The outbursts may happen several times a day. Many people with neurologic disorders exhibit uncontrollable episodes of laughing, crying, or anger that are either exaggerated or contradictory to the context in which they occur. Where patients have significant cognitive deficits (e.g., Alzheimer's) it can be unclear whether it is true PBA as opposed to a grosser form of emotional dysregulation, but patients with intact cognition often report the symptom as disturbing. Patients report that their episodes are at best only partially amenable to voluntary control, and unless they experience a severe change of mental status, as intraumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
they often have insight into their problem and judge their emotional displays as inappropriate and out of character. The clinical effect of PBA can be severe, with unremitting and persistent symptoms that can be disabling to patients, and may significantly affect quality of life for caregivers.
Differential diagnosis
 PBA may often be misdiagnosed as
PBA may often be misdiagnosed as clinical depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
or bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
; however, many clear distinctions exist for differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to di ...
.
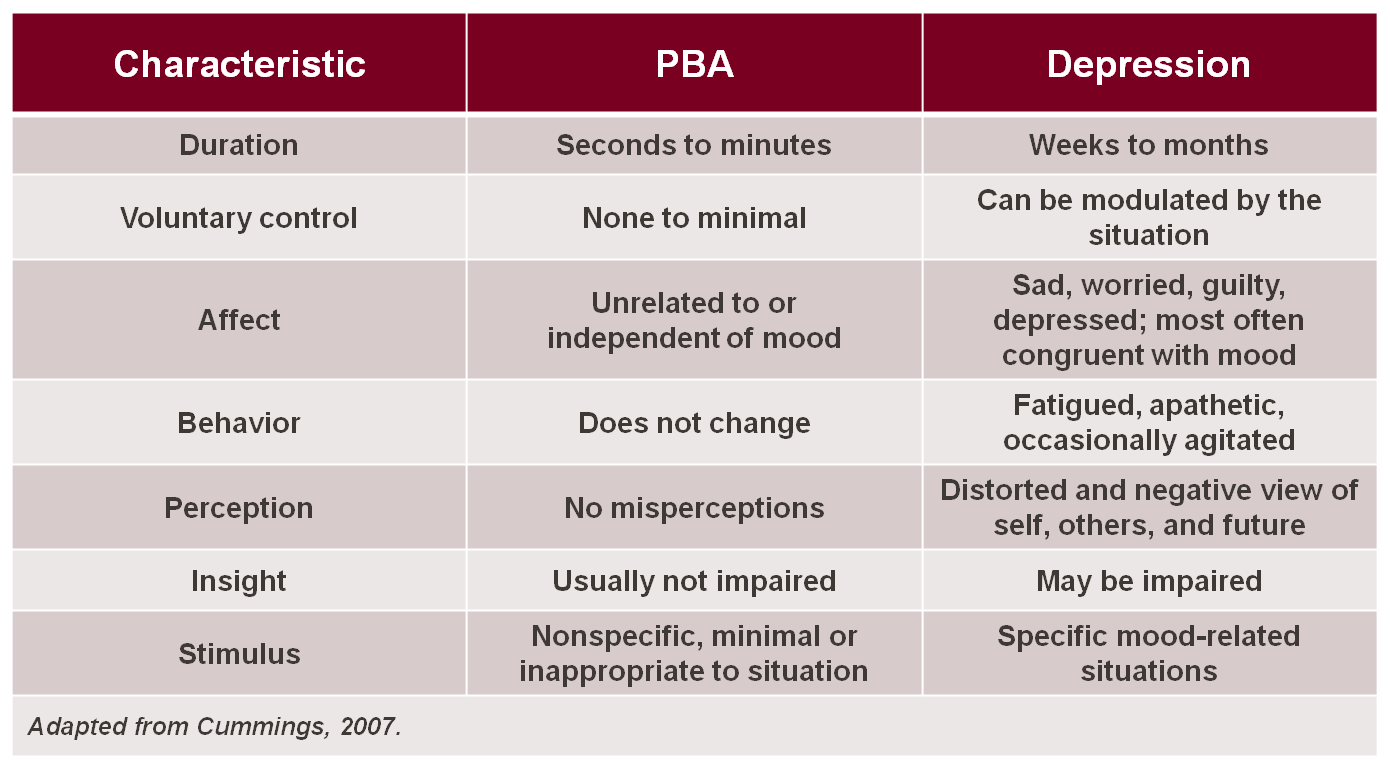
In depressive and bipolar disorders, crying, anger or laughter are typically indicative of mood, whereas the pathological displays of crying which occur in PBA are often in contrast to the underlying mood, or greatly in excess of the mood or eliciting stimulus. In addition, a key to differentiating depression from PBA is duration: PBA episodes are sudden, occurring in an episodic manner, while crying in depression is a more sustained presentation and closely relates to the underlying mood state. The level of control that one has over the crying, anger or other emotional displays in PBA is minimal or nonexistent, whereas for those with depression, the emotional expression (typically crying) can be modulated by the situation. Similarly, the trigger for episodes of crying in patients with PBA may be nonspecific, minimal or inappropriate to the situation, but in depression the stimulus is specific to the mood-related condition. These differences are outlined in the adjacent Table.
In some cases, depressed mood and PBA may co-exist. Since depression is one of the most common emotional changes in patients with neurodegenerative disease or post-stroke sequelae, it is often comorbid with PBA. Comorbidity implies that depression is distinct from PBA and is not necessary for, nor does it exclude, a diagnosis of PBA.
Causes
The specific pathophysiology involved in this frequently debilitating condition is still under investigation; the primary pathogenic mechanisms of PBA remain controversial. One hypothesis, established by early researchers such as Wilson and Oppenheim, placed emphasis on the role of the corticobulbar pathways in modulating emotional expression in a top-down model, and theorized that PBA occurs when bilateral lesions in the descendingcorticobulbar tract
The corticobulbar (or corticonuclear) tract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the Medullary pyramids (brainstem), medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblonga ...
cause failure of voluntary control of emotion, which leads to the disinhibition, or release, of laughing/crying centers in the brainstem. Other theories implicate the prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, ...
.
Secondary condition
PBA is a condition that occurs secondary to neurological disease or brain injury, and is thought to result from disruptions ofneural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
that control the generation and regulation of motor output of emotions. PBA is most commonly observed in people with neurologic injuries such as traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
(TBI) and stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, and neurologic diseases such as dementias including Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
(ADHD), multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
(MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
(ALS), and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
(PD). It has been reported as a symptom of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
, Graves' disease
Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter or Basedow's disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyro ...
, or hypothyroidism in combination with depression.
PBA has also been observed in association with a variety of other brain disorders, including brain tumors, Wilson's disease, syphilitic pseudobulbar palsy, and various encephalitides. Rarer conditions associated with PBA include gelastic epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
, dacrystic epilepsy, central pontine myelinolysis, olivopontinocerebellar atrophy, lipid storage diseases, chemical exposure (e.g., nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
and insecticides
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, in ...
), '' fou rire prodromique'', and Angelman syndrome
Angelman syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder that affects approximately 1 in 15,000 individuals. AS impairs the function of the nervous system, producing symptoms, such as severe intellectual disability, developmental disability, limited to no ...
.
It is hypothesized that these primary neurologic injuries and diseases affect chemical signaling in the brain, which in turn disrupts the neurologic pathways that control emotional expression.
Stroke
PBA is one of the most frequently reported post-stroke behavioral disorders, with a range of reported prevalence from 28% to 52%. The higher prevalence rates tend to be reported in stroke patients who are older or who have a history of prior stroke. The relationship between post-stroke depression and PBA is complicated, because the depressive syndrome also occurs with high frequency in stroke survivors. Post-stroke patients with PBA are more depressed than post-stroke patients without PBA, and the presence of a depressive syndrome may exacerbate the weeping side of PBA symptoms.Multiple sclerosis
Recent studies suggest that approximately 10% of patients withmultiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
(MS) will experience at least one episode of emotional lability. PBA is generally associated with later stages of the disease (chronic progressive phase). PBA in MS patients is associated with more severe intellectual deterioration, physical disability, and neurological disability.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
A study designed specifically to survey for prevalence found that 49% of patients withamyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
(ALS) also had PBA. PBA does not appear to be associated with duration of ALS. It is a symptom of ALS that many patients are unaware of and do not receive information about from their physician.
Traumatic brain injury
One study of 301 consecutive cases in a clinic setting reported a 5% prevalence. PBA occurred in patients with more severe head injury, and coincided with other neurological features suggestive of pseudobulbar palsy. The Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA) indicates that approximately 80% of survey respondents experience symptoms of PBA. Results from a recent investigation estimate the prevalence of PBA associated with traumatic brain injury to exceed more than 55% of survivors.Consequences
While not as profoundly disabling as the physical symptoms of the most common diseases that cause it (such as ALS), PBA may significantly influence individuals' social functioning and their relationships with others. Such sudden, frequent, extreme, uncontrollable emotional outbursts may lead to social withdrawal and interfere with activities of daily living, social and professional pursuits, and reduce overall healthcare. For example, patients with ALS and MS are often cognitively normal. However, the appearance of uncontrollable emotions is commonly associated with many additional neurological disorders such asParkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, spasticity, stiff muscles, Paresis, weak muscles, and tremors. There may b ...
, autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
, and migraines. This may lead to avoidance of social interactions for the patient, which in turn impairs their coping mechanisms and their careers.
Treatment
Education of patients, families, and caregivers is an important component of the appropriate treatment of PBA. Crying associated with PBA may be incorrectly interpreted as depression; laughter may be embarrassing, anger can be debilitating. It is therefore critical for families and caregivers to recognize the pathological nature of PBA and the reassurance that this is an involuntary syndrome that is manageable. Traditionally,antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s such as sertraline
Sertraline, sold under the brand name Zoloft among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, socia ...
, fluoxetine, citalopram, nortriptyline and amitriptyline have been prescribed with some efficacy.
Medication
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide affects the signals in the brain that trigger the cough reflex. It is used as a cough suppressant, although it can sometimes be used, medicinally, as a pain reliever, and is also used as a recreational drug. Quinidine sulfate affects the way the heart beats, and is generally used in people with certain heart rhythm disorders. It is also used to treat malaria. Quinidine sulfate, as a metabolic inhibitor, "increases plasma levels of dextromethorphan by competitively inhibiting cytochrome P450 2D6, which catalyzes a major biotransformation pathway for dextromethorphan," enabling therapeutic dextromethorphan concentrations. Dextromethorphan/quinidine is a combination of these two generic drugs, and is the first FDA-approved drug for the treatment of PBA, approved on October 29, 2010. In the pivotal multicenter study that led to its approval, the "Objectives... ereto evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of two different doses of AVP-923 extromethorphan/quinidine combination..when compared to placebo." The conditions and results of that study are as follows:Epidemiology
Prevalence estimates place the number of people with PBA between 1.5 and 2 million in the United States alone, which would be less than 1% of the U.S. population even at the high end of the estimate. Some argue that the number is probably higher and that clinicians underdiagnose PBA. However, the prevalence estimate of 2 million is based on an online survey. Self-selected computer-savvy patients in at-risk groups evaluated their own symptoms and submitted their self-diagnoses. No doctor or clinic confirmed the data. Motivation to participate could have been influenced by the presence of symptoms, which would have skewed the results. The actual prevalence could very well be quite a bit lower than estimated.History
'' The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' byCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
was published in 1872. In Chapter VI, "Special Expressions of Man: Suffering and Weeping", Darwin discusses cultural variations in the acceptability of weeping and the wide differences in individual responses to suffering. The chapter contains the following sentence:
Terminology
Historically, there have been a variety of terms used for the disorder, including pseudobulbar affect, pathological laughter and crying, emotional lability, emotionalism, emotional dysregulation, or more recently, involuntary emotional expression disorder. The term ''pseudobulbar'' ('' pseudo-'' + '' bulbar'') came from the idea that the symptoms seemed similar to those caused by a bulbarlesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
(that is, a lesion in the medulla oblongata).
Terms such as forced crying, involuntary crying, pathological emotionality, and emotional incontinence have also been used, although less frequently.
In popular culture
Arthur Fleck, the central character of the 2019 film '' Joker'', displays signs of pseudobulbar affect, which are said to be what Joaquin Phoenix used as inspiration for his character's signature laugh. In the 2019 movie ''Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
'', the character Ki-woo sustains head trauma, and although it is not clearly mentioned that he's affected by pseudobulbar affect, he mentions not being able to stop laughing when thinking about all the events that occur in the movie.
In the 2020 movie '' Naan Sirithal'', the character Gandhi ( Hiphop Tamizha Adhi) suffers from pseudobulbar affect due to all the stress he suffers from various parts of his life gets accumulated and starts to laugh uncontrollably.
In the medical television show ''House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air c ...
'', season 7, episode 8 (" Small Sacrifices"), the character Ramon Silva, played by Kuno Becker displays pseudobulbar affect, with uncontrollable incongruent laughter, while having the Marburg variety of multiple sclerosis.
In season 3, episode 9 of '' The Good Fight'', the character Brenda DeCarlo, an external auditor, displays pseudobulbar affect, with uncontrollable incongruent laughter.
See also
*Affect (psychology)
Affect, in psychology, is the underlying experience of feeling, emotion, attachment theory, attachment, or Mood (psychology), mood. It encompasses a wide range of emotional states and can be positive (e.g., happiness, joy, excitement) or negat ...
* Affect display
References
External links
"Pseudobulbar affect and stroke"
on the National Stroke Association website {{Medical resources , ICD10 = {{ICD10, F48.8 , ICD10CM = {{ICD10CM, F48.2 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 310.81 , ICDO = , OMIM = , DiseasesDB = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , MeshID = Symptoms and signs of mental disorders