labia (genitalia) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
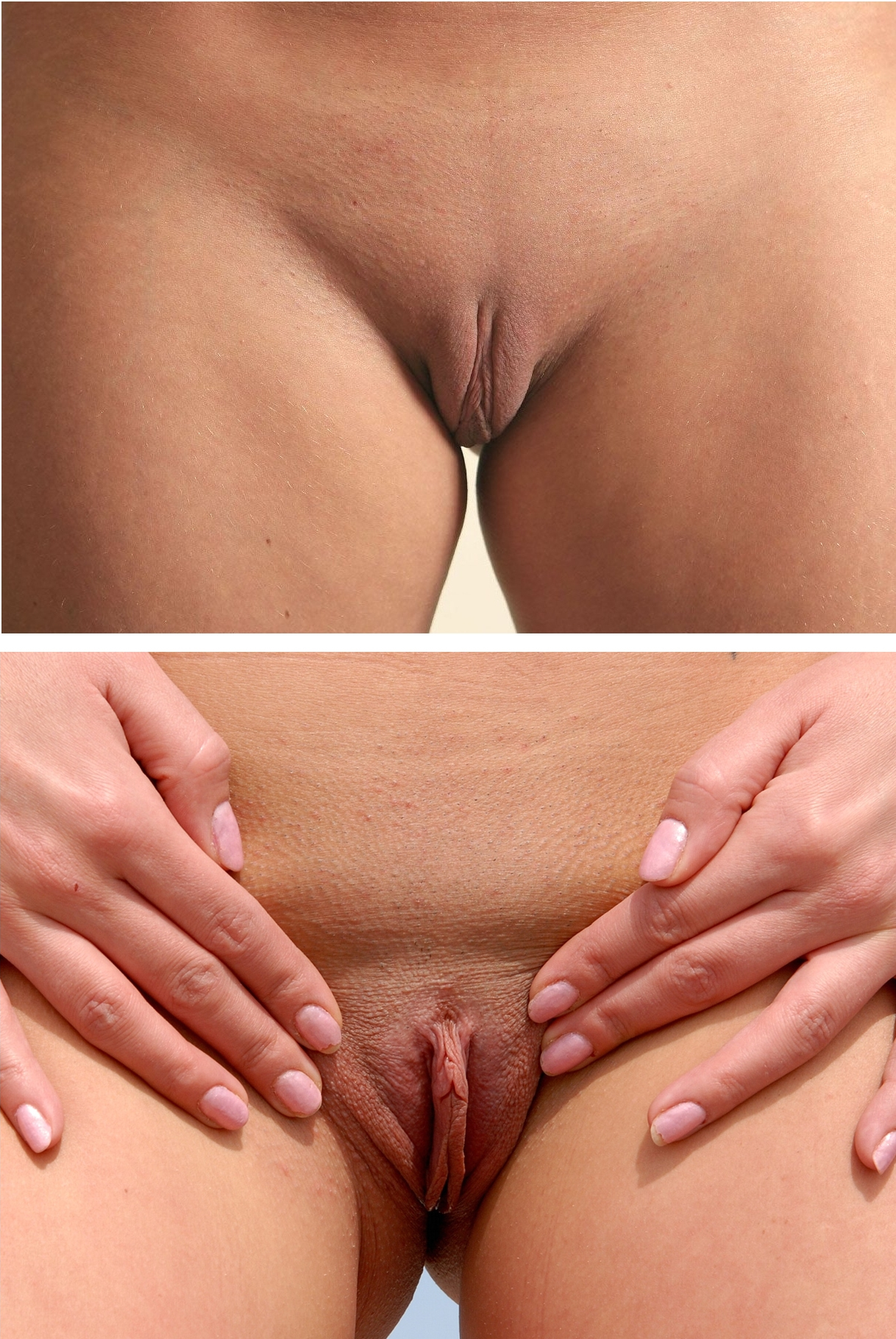 The labia are part of the female
The labia are part of the female
 The
The
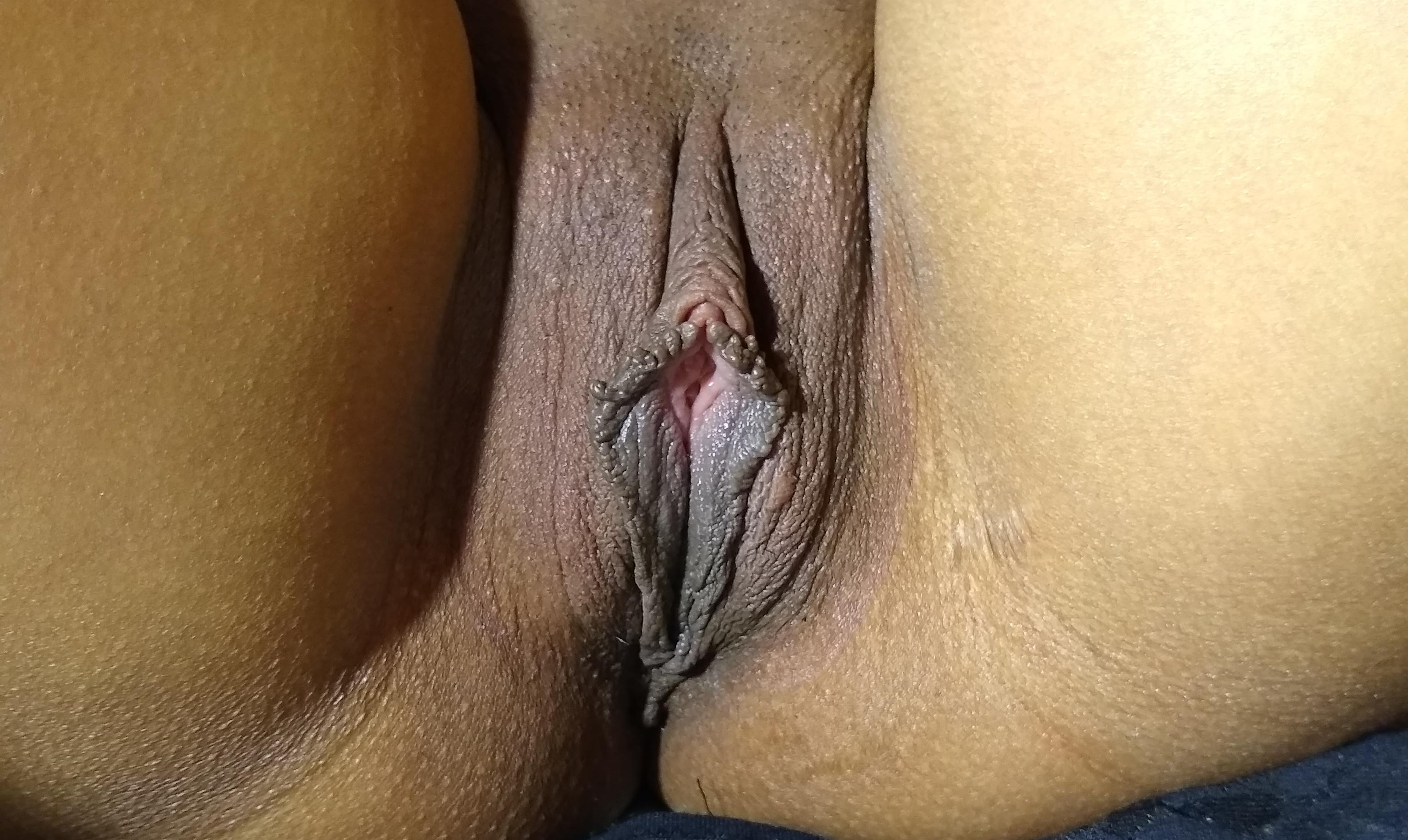 The color, size, length and shape of the inner labia can vary extensively from woman to woman. In some women the ''labia minora'' are almost non-existent, and in others they can be fleshy and protuberant. They can range in color from a light pink to brownish black, and texturally can vary between smooth and very rugose.
The color, size, length and shape of the inner labia can vary extensively from woman to woman. In some women the ''labia minora'' are almost non-existent, and in others they can be fleshy and protuberant. They can range in color from a light pink to brownish black, and texturally can vary between smooth and very rugose.
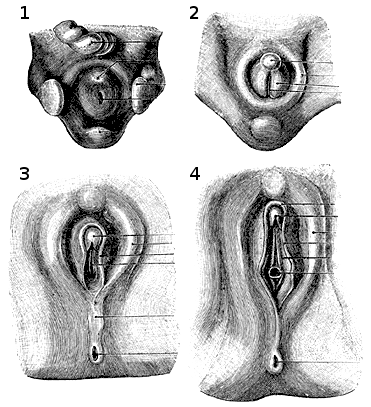 The biological sex of an individual is determined at conception, which is the moment a sperm fertilizes an
The biological sex of an individual is determined at conception, which is the moment a sperm fertilizes an
 The genital tissues are greatly influenced by natural fluctuations in
The genital tissues are greatly influenced by natural fluctuations in  During early childhood, the labia majora look flat and smooth because of decreasing levels of body fat, and the diminished effects of maternal hormones. The labia minora become less prominent.
During
During early childhood, the labia majora look flat and smooth because of decreasing levels of body fat, and the diminished effects of maternal hormones. The labia minora become less prominent.
During
 The labia are one of a woman's
The labia are one of a woman's
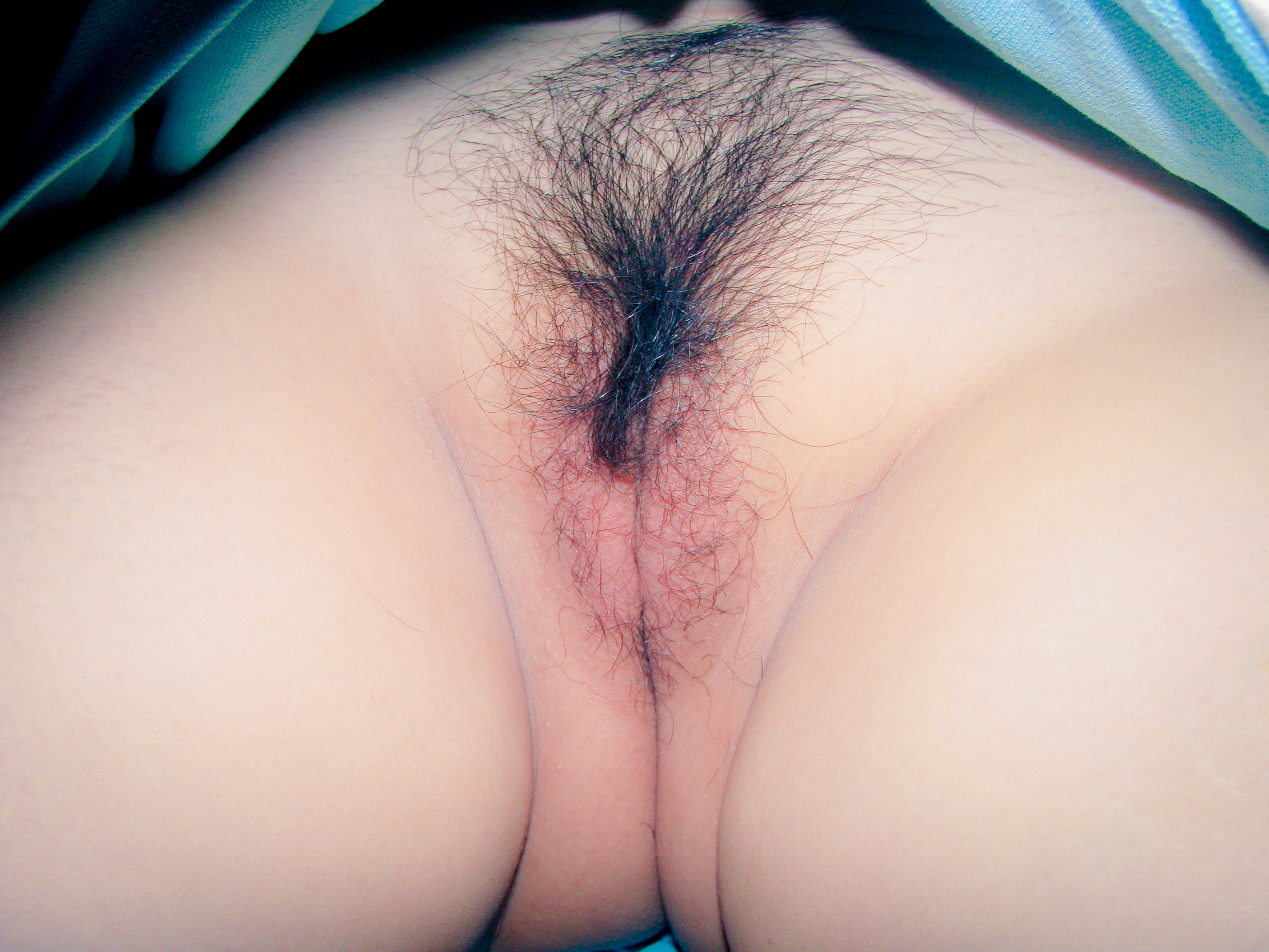 Views on pubic hair differ between people and between cultures. Some women prefer the look or feel of pubic hair, while others may choose to remove some or all of it. Temporary methods of removal include
Views on pubic hair differ between people and between cultures. Some women prefer the look or feel of pubic hair, while others may choose to remove some or all of it. Temporary methods of removal include  Some women are self-conscious about the size, color or asymmetry of their labia. Viewing
Some women are self-conscious about the size, color or asymmetry of their labia. Viewing The Centrefold Project
/ref> Labia piercing is a cosmetic piercing, usually with a special needle under
File:Clitoris_outer_anatomy.gif, Outer anatomy of clitoris.
File:Illu repdt female.jpg, Organs of the female reproductive system.
File:Gray1230.png, Median sagittal section of female pelvis.
File: Hairy vulva of a young woman 2.jpg, Labia majora with pubic hair.
 The labia are part of the female
The labia are part of the female genitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, ...
; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, v ...
. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva.
The labia majo ...
'' (or the outer labia) are larger and thicker, while the ''labia minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', singular: ''labium minus'', 'smaller lip'), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips or nymphae are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening in the vulva, situated be ...
'' are folds of skin between the outer labia. The labia surround and protect the clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the o ...
and the openings of the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hy ...
and the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra c ...
.
Etymology
''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is aLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
-derived term meaning " lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labium'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, v ...
.
Anatomy
 The
The labia majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva.
The labia majo ...
, also commonly called outer labia or outer lips, are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
(fatty) tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, v ...
to form the pudendal cleft
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, v ...
through the middle. The labia majora often have a plump appearance, and are thicker towards the anterior. The anterior junction of the labia majora is called the anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most exist ...
, which is below the mons pubis
In human anatomy, and in mammals in general, the ''mons pubis'' or pubic mound (also known simply as the mons, and known specifically in females as the ''mons Venus'' or ''mons veneris'') is a rounded mass of fatty tissue found over the pubic sy ...
and above the clitoris. To the posterior, the labia majora join at the posterior commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light refle ...
, which is above the perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), inclu ...
and below the frenulum of the labia minora. The grooves between the labia majora and labia minora are known as the interlabial sulci or interlabial folds.
The labia minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', singular: ''labium minus'', 'smaller lip'), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips or nymphae are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening in the vulva, situated be ...
(obsolete: nymphae), also called inner labia or inner lips, are two soft folds of fat-free, hairless skin between the labia majora. They enclose and protect the vulvar vestibule, urethra and vagina. The upper portion of each labium minora splits to join with both the clitoral glans
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the o ...
, and the clitoral hood
In the female human body, the clitoral hood (also called preputium clitoridis and clitoral prepuce) is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external shaft of the clitoris, develops as part of t ...
. The labia minora meet posterially at the frenulum of the labia minora (also known as the fourchette), which is a fold of skin below the vaginal orifice. The fourchette is more prominent in younger women, and often recedes after sexual activity and childbirth.
When standing or with the legs together, the labia majora usually entirely or partially cover the moist, sensitive inner surfaces of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, v ...
, which indirectly protects the vagina and urethra, much like the lips protect the mouth. The outer surface of the labia majora is pigmented skin, and develops pubic hair during puberty. The inner surface of the labia majora is smooth, hairless skin, which resembles a mucous membrane, and is only visible when the labia majora and labia minora are drawn apart.
Both the inner and outer surfaces of the labia majora contain sebaceous glands
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number ...
(oil glands), apocrine sweat glands
An apocrine sweat gland (; from Greek ''apo'' 'away' and ''krinein'' 'to separate') is composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the ...
, and eccrine sweat glands
Eccrine sweat glands (; from Greek ''ekkrinein'' 'secrete'; sometimes called merocrine glands) are the major sweat glands of the human body, found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in palm and soles, then on the head, but much less ...
. The labia majora have fewer superficial nerve endings than the rest of the vulva, but the skin is highly vascularized. The internal surface of the labia minora is a thin moist skin, with the appearance of a mucous membrane. They contain many sebaceous glands, and occasionally have eccrine sweat glands. The labia minora have many sensory nerve endings, and have a core of erectile tissue.
Diversity
 The color, size, length and shape of the inner labia can vary extensively from woman to woman. In some women the ''labia minora'' are almost non-existent, and in others they can be fleshy and protuberant. They can range in color from a light pink to brownish black, and texturally can vary between smooth and very rugose.
The color, size, length and shape of the inner labia can vary extensively from woman to woman. In some women the ''labia minora'' are almost non-existent, and in others they can be fleshy and protuberant. They can range in color from a light pink to brownish black, and texturally can vary between smooth and very rugose.
Embryonic development and homology
 The biological sex of an individual is determined at conception, which is the moment a sperm fertilizes an
The biological sex of an individual is determined at conception, which is the moment a sperm fertilizes an ovum
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete i ...
, creating a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
. The chromosome type contained in the sperm determines the sex of the zygote. A Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or a ...
results in a male, and an X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes ( allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO se ...
results in a female. A male zygote will later grow into an embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
and form testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
, which produce androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s (primarily male hormones), usually causing male genitals to be formed. Female genitals will usually be formed in the absence of significant androgen exposure.
The genitals begin to develop after approximately 4 to 6 weeks of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
. Initially, the external genitals develop the same way regardless of the sex of the embryo, and this period of development is called the ''sexually indifferent'' stage. The embryo develops three distinct external genital structures: a genital tubercle
A genital tubercle or phallic tubercle is a body of tissue present in the development of the reproductive system. It forms in the ventral, caudal region of mammalian embryos of both sexes, and eventually develops into a primordial phallus. In ...
; two urogenital folds
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically ...
, one on either side of the tubercle; and two labioscrotal swellings
The labioscrotal swellings (genital swellings or labioscrotal folds) are paired structures in the human embryo that represent the final stage of development of the caudal end of the external genitals before sexual differentiation. In both males a ...
, each bounding one of the urogenital folds.
Sexual differentiation
Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation; sex determination is the designation for the dev ...
starts on the internal sex organs at about 5 weeks of gestation, resulting in the formation of either testes in males, or ovaries in females. If testes are formed, they begin to secrete androgens that affect the external genital development at about week 8 or 9 of gestation. The urogenital folds form the labia minora in females, or penile shaft in males. The labioscrotal swellings become the labia majora in females, or they fuse to become the scrotum in males. Because the male and female parts develop from the same tissues, this makes them homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
(different versions of the same structure). Sexual differentiation is complete at around 12 weeks of gestation.
Changes over time
hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
levels, which lead to changes in labia size, appearance, and elasticity at various life stages. At birth, the labia minora are well-developed, and the labia majora appear plump due to being exposed to maternal hormones in the womb. The labia majora have the same color as the surrounding skin. Labial adhesion
Labial fusion is a medical condition of the female genital anatomy where the labia minora become fused together. It is generally a pediatric condition.
Presentation
Labial fusion is rarely present at birth, but rather acquired later in infancy, s ...
s can occur between the ages of 3 months and 2 years, and may make the vulva look flat. These adhesions are not usually a cause for concern, and usually disappear without treatment. Treatment options may include estrogen cream, manual separation with local anesthesia, or surgical separation under sedation. During early childhood, the labia majora look flat and smooth because of decreasing levels of body fat, and the diminished effects of maternal hormones. The labia minora become less prominent.
During
During early childhood, the labia majora look flat and smooth because of decreasing levels of body fat, and the diminished effects of maternal hormones. The labia minora become less prominent.
During puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a b ...
, increased hormone levels often significantly change the appearance of the labia. The labia minora become more elastic, prominent, and wrinkled. The labia majora regain fat, and begin growing pubic hair close to the pudendal cleft. Hair is initially sparse and straight, but gradually becomes darker, denser, and curlier as growth spreads outward and upward toward the thighs and mons pubis. At the end of puberty, pubic hair will be coarse, curly, and fairly thick. The patch of pubic hair covering the genitals will eventually often form a triangle shape.
By adulthood, the outer surface of the labia majora may be darker than the surrounding skin, and may have wrinkles similar to those on a male's scrotum. During the reproductive years, if a woman delivers a child, the fourchette will flatten. Pregnancy may cause the labia minora to darken in color.
Later in life, the labia majora once again gradually lose fat, becoming flatter and more wrinkled, and pubic hair turns grey. Following menopause, falling hormone levels cause further changes to the labia. The labia minora atrophy, making them become less elastic, and pubic hair on the labia majora becomes more sparse.
Sexual arousal and response
erogenous zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response, suc ...
s. The labia minora are sexually responsive, and sensitivity varies greatly between women. In some women, they are so sensitive that anything other than light touch may be uncomfortable, whereas stimulation may elicit no sexual response in others. The labia may be sexually stimulated as part of masturbation or with a sex partner
Sexual partners are people who engage in sexual activity together. The sexual partners may be in a committed relationship, either on an exclusive basis or not, or engage in the sexual activity on a casual basis. They may be on intimate terms ...
, such as by fingering or oral sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred to as oral intercourse, is sexual activity involving the stimulation of the genitalia of a person by another person using the mouth (including the lips, tongue, or teeth) and the throat. Cunnilingus is oral sex p ...
. Moving the labia minora can also stimulate the extremely sensitive clitoris.
During sexual arousal, the labia majora swell due to increased blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
flow to the region, and draw back, opening the vulva slightly. The labia minora become engorged with blood, causing them to expand in diameter by two to three times, and darken or redden in color. Because pregnancy and childbirth increase genital vascularity, the inner and outer labia will engorge faster in women who have had children.
After a period of sexual stimulation, the labia minora will become further engorged with blood approximately 30 seconds to 3 minutes before orgasm, causing them to redden further. In women who have had children, the labia majora may also swell significantly during this period, becoming dark red. Continued stimulation can result in an orgasm, and the orgasmic contractions help remove blood trapped in the inner and outer labia, as well as the clitoris and other parts of the vulva, which causes pleasurable orgasmic sensations.
Following orgasm or when a woman is no longer sexually aroused, the labia gradually return to their unaroused state. The labia minora return to their original color within 2 minutes, and engorgement dissipates in about 5 to 10 minutes. The labia majora return to their pre-arousal state in approximately 1 hour.
Society and culture
In many cultures and locations all over the world, the labia, as part of thegenitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, ...
, are considered private, or intimate part
An intimate part, personal part or private part is a place on the human body which is customarily kept covered by clothing in public venues and conventional settings, as a matter of fashion and cultural norms. In several cultures, revealing these p ...
s, whose exposure (especially in public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
) is governed by fairly strict socio-cultural mores
Mores (, sometimes ; , plural form of singular , meaning "manner, custom, usage, or habit") are social norms that are widely observed within a particular society or culture. Mores determine what is considered morally acceptable or unacceptable ...
. In many cases, public exposure is limited, and often prohibited by law.
 Views on pubic hair differ between people and between cultures. Some women prefer the look or feel of pubic hair, while others may choose to remove some or all of it. Temporary methods of removal include
Views on pubic hair differ between people and between cultures. Some women prefer the look or feel of pubic hair, while others may choose to remove some or all of it. Temporary methods of removal include shaving
Shaving is the removal of hair, by using a razor or any other kind of bladed implement, to slice it down—to the level of the skin or otherwise. Shaving is most commonly practiced by men to remove their facial hair and by women to remove the ...
, trimming, waxing
Waxing is the process of hair removal from the root by using a covering of a sticky substance, such as wax, to adhere to body hair, and then removing this covering and pulling out the hair from the follicle. New hair will not grow back in the pr ...
, sugaring and depilatory products while permanent hair removal can be accomplished using electrolysis or laser hair removal. In Korea, pubic hair is considered a sign of fertility, leading some women to have pubic hair transplants.
 Some women are self-conscious about the size, color or asymmetry of their labia. Viewing
Some women are self-conscious about the size, color or asymmetry of their labia. Viewing pornography
Pornography (often shortened to porn or porno) is the portrayal of sexual subject matter for the exclusive purpose of sexual arousal. Primarily intended for adults,
may influence a woman's view of her genitals. Models in pornography frequently have small or non-existent labia minora, and images are often airbrushed, so pornographic images do not depict the full range of natural variations of the vulva. This can lead viewers of pornography to have unrealistic expectations about how the labia should look. Similar to how some women develop self-esteem issues from comparing their faces and bodies to airbrushed models in magazines, women who compare their vulvas to idealized pornographic images may believe their own labia are abnormal. This can have a negative impact on a woman's life, since genital self-consciousness makes it more difficult to enjoy sexual activity, see a gynecologist, or perform a genital self-examination. Developing an awareness for how much the labia truly differ between individuals may help to overcome this self-consciousness.
In several countries in Africa and Asia, the external female genitals are routinely altered or removed for reasons related to ideas about tradition, purity, hygiene and aesthetics. Known as female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found ...
, the procedures include clitoridectomy
Clitoridectomy or clitorectomy is the surgical removal, reduction, or partial removal of the clitoris. It is rarely used as a therapeutic medical procedure, such as when cancer has developed in or spread to the clitoris. It is often performed on ...
and so-called " pharaonic circumcision," whereby the inner and outer labia are removed and the vulva is sewn shut. FGM is mostly outlawed around the world, even in countries where the practice is widespread.
Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty (also known as labioplasty, labia minora reduction, and labial reduction) is a plastic surgery procedure for altering the labia minora (inner labia) and the labia majora (outer labia), the folds of skin surrounding the human vulva. T ...
is a controversial plastic surgery
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes cranio ...
procedure that involves the creation or reshaping of the labia./ref> Labia piercing is a cosmetic piercing, usually with a special needle under
sterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis, a state of being free from biological contaminants
* Sterile (archaeology), a sediment deposit which contains no evidence of human activity
*Sterilization (microbiology), any process that eliminates or ...
conditions, of the inner or outer labia. Jewelry is worn in the resulting opening.
Additional images
See also
* '' Femalia'' * Labia pride *Labia stretching
Labia stretching, also referred to as labia elongation or labia pulling, is the act of lengthening the ''labia minora'' (the inner lips of the female genitals) through manual manipulation (pulling) or physical equipment (such as weights).
* Labiaplasty
Labiaplasty (also known as labioplasty, labia minora reduction, and labial reduction) is a plastic surgery procedure for altering the labia minora (inner labia) and the labia majora (outer labia), the folds of skin surrounding the human vulva. T ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control * Mammal female reproductive system