L'Aquila on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
L'Aquila ( ; ; ) is a city and ''
 Negotiations for the succession of Edmund, son of
Negotiations for the succession of Edmund, son of 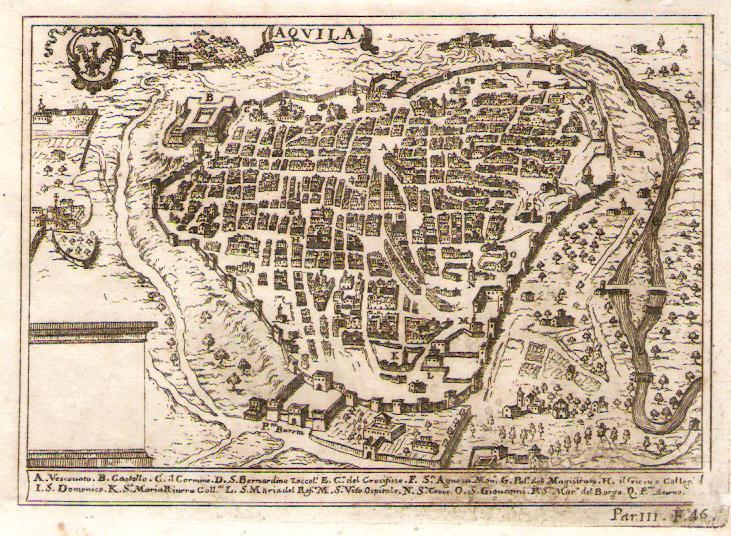
 Although less than an hour-and-a-half drive from Rome, and popular with Romans for summer hiking and winter skiing in surrounding mountains, the city is sparsely visited by tourists. Among the sights are:
Although less than an hour-and-a-half drive from Rome, and popular with Romans for summer hiking and winter skiing in surrounding mountains, the city is sparsely visited by tourists. Among the sights are:

Luigi Serra, ''Aquila''
Book, 1929, 142pp , one section translated into English
Gran Sasso
Images, news
Spanish Fortress
The fountain of 99 spoutsThe images 9 years later 2009 Earthquake (2018)
June 29, 2007 {{DEFAULTSORT:L'aquila Cities and towns in Abruzzo Populated places destroyed by earthquakes Populated places established in the 13th century
comune
A (; : , ) is an administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions () and provinces (). The can also have the City status in Italy, titl ...
'' in central Italy. It is the capital city of the Province of L'Aquila
The province of L'Aquila () is the largest, most mountainous and least densely populated Provinces of Italy, province of the Abruzzo region of Italy. It comprises about half the landmass of Abruzzo and occupies the western part of the region. It ...
and the Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, ; ; , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; ), historically also known as Abruzzi, is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy with an area of 10,763 square km (4,156 sq mi) and a population of 1.3 million. It is divided into four ...
region in Italy. , it has a population of 69,902. Laid out within medieval walls on a hill in the wide valley of the Aterno river, it is surrounded by the Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ...
, with the Gran Sasso d'Italia to the north-east.
L'Aquila sits on a hillside in the middle of a narrow valley; the tall snow-capped mountains of the Gran Sasso massif flank the town. A maze of narrow streets, lined with Baroque and Renaissance buildings and churches, open onto elegant piazzas. Home to the University of L'Aquila, it is a lively college town
A college town or university town is a town or city whose character is dominated by a college or university and their associated culture, often characterised by the student population making up 20 percent of the population of the community, bu ...
and, as such, has many cultural institutions: a repertory theatre
A repertory theatre, also called repertory, rep, true rep or stock, which are also called producing theatres, is a theatre in which a resident company presents works from a specified repertoire, usually in alternation or rotation.
United Kingdom ...
, a symphony orchestra, a fine art academy, a state conservatory and a film institute. There are several ski resorts in the surrounding province ( Campo Imperatore, Ovindoli, Pescasseroli, Roccaraso, Scanno).
Geography
Close to the highest of the Apenninesummits
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous.
The term (mountain top) is generally used only for ...
, L'Aquila, with an elevation of , is situated in the valley of the Aterno-Pescara, between four mountain peaks above .
The mountains block the city off from the warm humid air currents of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, giving rise to a climate that is dry and cooler than most of central Italy
Central Italy ( or ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first-level NUTS region with code ITI, and a European Parliament constituency. It has 11,704,312 inhabita ...
. It's a common saying among locals that the city enjoys 11 cold months a year and one cool one ("Undici misi de friddu e unu de friscu").
L'Aquila is approximately east-northeast of Rome, with which it is connected by an autostrada through the mountains.
History
Middle Ages
The city's construction was begun byFrederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman ...
and King of Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, out of several already existing villages (ninety-nine, according to local tradition; see Amiternum
Amiternum was an ancient Sabine city, then Roman city and later bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see in the central Abruzzo region of modern Italy, located from L'Aquila. Amiternum was the birthplace of the historian Sallust (86 BC).
Histo ...
), as a bulwark against the power of the papacy. The name of Aquila means "Eagle" in Italian. Construction was completed in 1254 under Frederick's son, Conrad IV of Germany. The name was switched to Aquila degli Abruzzi in 1861, and L'Aquila in 1939. After the death of Conrad, the city was destroyed by his brother Manfred in 1259, but soon rebuilt by Charles I of Anjou, his successor as king of Sicily. The walls were completed in 1316.
It quickly became the second city of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
. It was an autonomous city, ruled by a diarchy
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally spelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate. is a form of government charac ...
composed of the City Council (which had varying names and composition over the centuries) and the King's Captain. It fell initially under the lordship of Niccolò dell'Isola, appointed by the people as the People's Knight, but he was then killed when he became a tyrant. Later, it fell under Pietro "Lalle" Camponeschi, Count of Montorio, who became the third side of a new triarchy, with the Council and the King's Captain. Camponeschi, who was also Great Chancellor of the kingdom of Naples, became too powerful, and was killed by order of Prince Louis
Louis may refer to:
People
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
Other uses
* Louis (coin), a French coin
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
...
of Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
. His descendants fought with the Pretatti family for power for several generations, but never again attained the power of their ancestor. The last, and the one true "lord" of L'Aquila, was Ludovico Franchi, who challenged the power of the pope by giving refuge to Alfonso I d'Este, former duke of Ferrara
Ferrara (; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Emilia-Romagna, Northern Italy, capital of the province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main ...
, and the children of Giampaolo Baglioni, deposed lord of Perugia
Perugia ( , ; ; ) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. It has 162,467 ...
. In the end, however, the Aquilans had him deposed and imprisoned by the king of Naples
The following is a list of rulers of the Kingdom of Naples, from its first Sicilian Vespers, separation from the Kingdom of Sicily to its merger with the same into the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Kingdom of Naples (1282–1501)
House of Anjou
...
.
The power of L'Aquila was based on the close connection between the city and its mother-villages, which had established the city as a federation, each of them building a borough and considering it as a part of the mother-village. The Fountain of the 99 Spouts (''Fontana delle 99 Cannelle''), was given its name to celebrate the ancient origin of the town. The City Council was originally composed of the Mayors of the villages, and the city had no legal existence until King Charles II of Naples appointed a "Camerlengo", responsible for city tributes (previously paid separately by each of its mother-villages). Later, the Camerlengo also took political power, as President of the City Council.
From its beginnings the city constituted an important market for the surrounding countryside, which provided it with a regular supply of food: from the fertile valleys came the precious saffron; the surrounding mountain pastures provided summer grazing for numerous transhumant
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower ...
flocks of sheep, which in turn supplied abundant raw materials for export and, to a lesser extent, small local industries, which in time brought craftsmen and merchants from outside the area.
Within a few decades L'Aquila became a crossroads in communications between cities within and beyond the Kingdom, thanks to the so-called "via degli Abruzzi", which ran from Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
to Naples by way of Perugia
Perugia ( , ; ; ) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. It has 162,467 ...
, Rieti, L'Aquila, Sulmona, Isernia, Venafro, Teano and Capua
Capua ( ; ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, located on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etruscan ''Capeva''. The ...
.
 Negotiations for the succession of Edmund, son of
Negotiations for the succession of Edmund, son of Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of John, King of England, King John and Isabella of Ang ...
, to the throne of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
involved L'Aquila in the web of interests linking the Roman Curia
The Roman Curia () comprises the administrative institutions of the Holy See and the central body through which the affairs of the Catholic Church are conducted. The Roman Curia is the institution of which the Roman Pontiff ordinarily makes use ...
to the English court. On 23 December 1256 Pope Alexander IV elevated the churches of Saints Massimo and Giorgio to the status of cathedrals as a reward to the citizens of L'Aquila for their opposition to King Manfred who, in July 1259, had the city razed to the ground in an attempt to destroy the negotiations. On 29 August 1294 the hermit
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions.
Description
In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Chr ...
Pietro del Morrone was consecrated as pope Celestine V
Pope Celestine V (; 1209/1210 or 1215 – 19 May 1296), born Pietro Angelerio (according to some sources ''Angelario'', ''Angelieri'', ''Angelliero'', or ''Angeleri''), also known as Pietro da Morrone, Peter of Morrone, and Peter Celestine, was ...
in the church of Santa Maria di Collemaggio, in commemoration of which the new pope decreed the annual religious rite of the Pardon (nowadays known as Celestinian Forgiveness, ''Perdonanza Celestiniana''), still observed today in the city on 28 and 29 August: it is the immediate ancestor of the Jubilee Year.
The pontificate of Celestine V gave a new impulse to building development, as can be seen from the city statutes. In 1311, moreover, King Robert of Anjou granted privileges which had a decisive influence on the development of trade. These privileges protected all activities related to sheep-farming, exempting them from customs duties on imports and exports. This was the period in which merchants from Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
(Scale, Bonaccorsi) and Rieti purchased houses in the city. Hence the conditions for radical political renewal: in 1355 the trade guilds of leather-workers, metal-workers, merchants and learned men were brought into the government of the city, and these together with the Camerario and the Cinque constituted the new Camera Aquilana. Eleven years earlier, in 1344, the King had granted the city its own mint.
In the middle of the 14th century the city was struck by plague epidemics (1348, 1363) and earthquakes (1349). Reconstruction began soon, however. In the 14th–15th century Jewish families came to live in the city, while the generals of the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
Order chose the city as the seat of the Order's general chapters (1376, 1408, 1411, 1450, 1452, 1495). Bernardino of Siena, of the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
order of the Observance, visited L'Aquila twice, the first time to preach in the presence of King René of Naples, and in 1444, on his second visit, he died in the city. In 1481 Adam of Rottweil, a pupil and collaborator of Johann Gutenberg, obtained permission to establish a printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
in L'Aquila.
The Osservanti branch of the Franciscan order had a decisive influence on L'Aquila. As a result of initiatives by Friar Giovanni da Capistrano and Friar Giacomo della Marca, Lombard masters undertook, in the relatively underdeveloped north-east of the city, an imposing series of buildings centring on the hospital of Saint Salvatore (1446) and the convent and the Basilica of San Bernardino. The construction work was long and difficult, mainly because of the earthquake of 1461, which caused the buildings to collapse, and the translation of the body of San Bernardino did not take place until 14 May 1472. The whole city suffered serious damage on the occasion of the earthquake, and two years went by before repairs on the churches and convents began.
In a strategy finalised to increasing their political and economic autonomy, the Aquilani took a series of political gambles, siding sometimes with the Roman Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, sometimes with the Kingdom of Naples. When the Pope excommunicated Joanna II, Queen of Naples, appointing Louis III of Anjou as heir to the crown in her stead, L'Aquila sided with the Angevines. Joanna hired the condottiero
Condottieri (; singular: ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian military leaders active during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The term originally referred specifically to commanders of mercenary companies, derived from the ...
Braccio da Montone. In exchange for his services, Braccio obtained the lordship of Teramo, as well as the fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
doms of Capua and Foggia: he started a 13-month-long siege of L'Aquila, that resisted bravely. Facing Braccio, at the head of the Angevin army was Muzio Attendolo Sforza and his son Francesco
Francesco, the Italian language, Italian (and original) version of the personal name "Francis (given name), Francis", is one of the List of most popular given names, most common given name among males in Italy. Notable persons with that name inclu ...
. The final clash between the two contenders was just below the walls of Aquila, near the hamlet today called Bazzano. In the battle fought on 2 June 1424, Braccio, mortally wounded in the neck, was made prisoner and transported to Aquila, where he died three days later, on 5 June 1424. The Pope had him buried in deconsecrated earth. The citizens of L'Aquila honoured the bravery of their enemy Braccio by dedicating one of the main streets of the city to his name.

Modern era
This period of freedom and prosperity ended in the 16th century, when Spanish viceroy Philibert van Oranje partially destroyed L'Aquila and established Spanishfeudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
in its countryside. The city, separated from its roots, never developed again. Ancient privileges were revoked. L'Aquila was again destroyed by an earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
in 1703. Successive earthquakes have repeatedly damaged the city's large cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
, and destroyed the original dome of the Basilica of San Bernardino, designed along the lines of the dome of Santa Maria del Fiore in Florence. The city was also sacked two times by French troops in 1799.
L'Aquila, like so much of Italy, is a city of political contrasts. In the 1970s a novel by Alberto Moravia
Alberto Pincherle (; 28 November 1907 – 26 September 1990), known by his pseudonym Alberto Moravia ( , ), was an Italian novelist and journalist. His novels explored matters of modern sexuality, social alienation and existentialism. Moravia i ...
was seized because it was considered obscene, a local Catholic Archbishop protested the nudity of a centuries-old statue of a young man, and a group of local reactionaries even asked for the seizure of the £50 coin because it showed a naked man. In October 2003, however, a liberal judge in l'Aquila ordered the small town of Ofena to remove a crucifix from its elementary school so as not to offend the religious sensibilities of two young Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
students. After a national outcry, the judge's decision was overturned. In May 2007 Massimo Cialente, a physician and medical researcher, was elected mayor of L'Aquila with a centre-left
Centre-left politics is the range of left-wing political ideologies that lean closer to the political centre. Ideologies commonly associated with it include social democracy, social liberalism, progressivism, and green politics. Ideas commo ...
coalition.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes mark the history of L'Aquila, as the city is partly built on an ancient lake-bed which amplifies seismic activity. On 3 December 1315 the city was struck by an earthquake which seriously damaged the San Francesco Church. Another earthquake struck on 9 September 1349, killing about 800 people. Other earthquakes struck in 1452, then on 26 November 1461, and again in 1501 and 1646. On 3 February 1703 a major earthquake struck the town. More than 3,000 people died and almost all the churches collapsed; Rocca Calascio, the highest fortress in Europe was also ruined by this event, yet the town survived. L'Aquila was then repopulated by decision ofPope Clement XI
Pope Clement XI (; ; ; 23 July 1649 – 19 March 1721), born Giovanni Francesco Albani, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 23 November 1700 to his death in March 1721.
Clement XI was a patron of the arts an ...
. The town was rocked by earthquake again in 1706. On 26 June 1958 an earthquake of 5.0 magnitude struck the town.
On 6 April 2009, at 01:32 GMT (03:32 CEST) an earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
of 6.3 magnitude struck central Italy with its epicentre near L'Aquila, at . Initial reports said the earthquake caused damage to between 3,000 and 10,000 buildings in L'Aquila. Several buildings also collapsed. 308 people were killed by the earthquake, and approximately 1,500 people were injured. Twenty of the victims were children. Around 65,000 people were made homeless. There were many students trapped in a partially collapsed dormitory. The 6 April earthquake was felt throughout Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, ; ; , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; ), historically also known as Abruzzi, is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy with an area of 10,763 square km (4,156 sq mi) and a population of 1.3 million. It is divided into four ...
; as far away as Rome, other parts of Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
, Marche, Molise
Molise ( , ; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. Until 1963, it formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Ital ...
, Umbria
Umbria ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region of central Italy. It includes Lake Trasimeno and Cascata delle Marmore, Marmore Falls, and is crossed by the Tiber. It is the only landlocked region on the Italian Peninsula, Apennine Peninsula. The re ...
, and Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
.
G8 summit
Because of the 2009 earthquake, the Berlusconi government decided to move that year's G8 summit from its scheduled Sardinian host of La Maddalena to L'Aquila, so that disaster funds would be distributed to the affected region and to show solidarity with the city's inhabitants. World leaders converged on L'Aquila on 8 July and many of them were given tours of the devastated city by the host Prime Minister.Demographics
Climate
L'Aquila has anoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: Cfb), influenced by its high altitude.
Main sights
Religious buildings
* L'Aquila Cathedral: main church dedicated to Saint Maximus of Aveia (San Massimo), was built in the 13th century, but razed after the 1703 earthquake. The most recent façade dated from the 19th century, but the earthquake of 2009 and subsequent aftershocks collapsed parts of thetransept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque a ...
and possibly more of the cathedral.
* Basilica of San Bernardino (1472): church has a fine Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
façade by Nicola Filotesio (commonly called Cola dell'Amatrice), and contains the monumental tomb of the saint (1480), decorated with sculptures, and executed by Silvestro Ariscola.
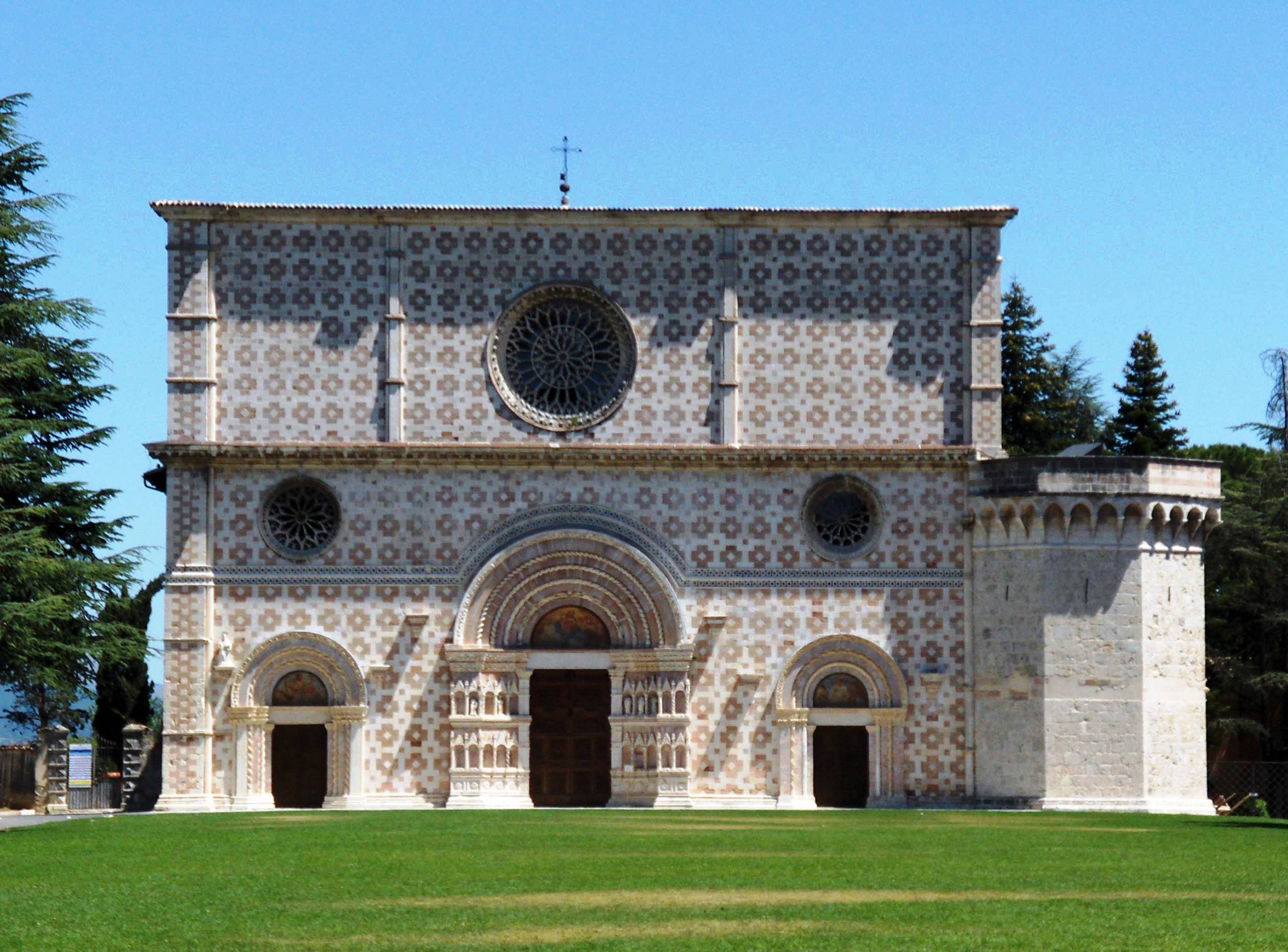
* Santa Maria di Collemaggio: church just outside the town, has a very fine, but simple, Romanesque façade (1270–1280) in red and white marble, with three decorated portals and a rose-window above each. The two side doors are also fine. The interior contains the mausoleum of Pope Celestine V
Pope Celestine V (; 1209/1210 or 1215 – 19 May 1296), born Pietro Angelerio (according to some sources ''Angelario'', ''Angelieri'', ''Angelliero'', or ''Angeleri''), also known as Pietro da Morrone, Peter of Morrone, and Peter Celestine, was ...
erected in 1517.
* Santa Giusta: Romanesque façade with Gothic rose window
* San Silvestro: 14th-century Romanesque façade with Gothic rose window
* Chiesa dei Santi Marciano e Nicandro: a 13th century church
Secular buildings
* Spanish fort (''Forte Spagnolo''): massive castle in the highest part of the town, erected in 1534 by the Spanish viceroy Don Pedro de Toledo. In 2016, home to the National Museum of Abruzzo. *''Fontana Luminosa'' ("Luminous Fountain"): a 1930s sculpture of two women bearing large jars. *''Fontana delle novantanove cannelle'' (1272): a fountain with ninety-nine jets distributed along three walls. The source of the fountain is still unknown. *''L'Aquila cemetery'': includes grave ofKarl Heinrich Ulrichs
Karl Heinrich Ulrichs (28 August 1825 – 14 July 1895) was a German lawyer, jurist, journalist, and writer. He is today regarded as a pioneer of sexology and the modern LGBT rights movement, gay rights movement. Ulrichs has been described as ...
, 19th‑century German gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Not ...
pioneer who lived in L'Aquila; every year, gay people from all over the world meet at the cemetery to honour his memory.
* Palace of Nobles
*''Roman ruins of Amiternum
Amiternum was an ancient Sabine city, then Roman city and later bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see in the central Abruzzo region of modern Italy, located from L'Aquila. Amiternum was the birthplace of the historian Sallust (86 BC).
Histo ...
'': ruins of an Ancient Roman city
Also nearby are several ski resort
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area–a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In North Am ...
s like Gran Sasso d'Italia, the highest of the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ...
where in its valley the movie '' The Name of the Rose'' was filmed in the end of the 1980s. The town also contains some fine palaces: the municipality has a museum, with a collection of Roman inscriptions and some illuminated service books. The Palazzi Dragonetti and Persichetti contain private collections of pictures.
Culture
Cinematographic activities
The first step of L'Aquila in the cinematographic activities was the Cineforum Primo Piano founded by Gabriele Lucci in the middle of the 1970s. As a work of Lucci, in 1981 saw the establishment of l'Istituto Cinematografico dell'Aquila, an institute for the production and diffusion of the cinematographic culture in Italia and abroad. The Teatro Stabile d'Abruzzo is based in the city and was formed in 2000.Sport
The city is the home of five-time Italian championsL'Aquila Rugby
L'Aquila Rugby 1936 was an Italy, Italian rugby union club based in L'Aquila, the capital of Abruzzo.
The official colours of the club were black and green, the colours of the city of L'Aquila. The club went into liquidation and disbanded in 2018. ...
. The football squad, L'Aquila Calcio, played 3 times in serie B
The Serie B (), officially known as Serie BKT for sponsorship reasons, is the second-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie A. It has been operating for over ninety years since the 1929–30 season. It had b ...
.
''Frazioni''
The following is a list of the ''frazioni'' in the ''comune'' of L'Aquila: Aquilio, Aragno, Arischia,Assergi
Assergi is a frazione of the comune of L'Aquila, located about from the capital. With a population of just over 500, it is situated at an altitude of approximately 1,000 meters, below the western slope of the Gran Sasso d'Italia, Gran Sasso in a s ...
, Bagno, Bazzano, Camarda, Cansatessa, Casaline, Cermone, Cese di Preturo, Civita di Bagno, Colle di Preturo, Colle di Sassa, Colle Roio – Poggio di Roio, Collebrincioni, Collefracido di Sassa, Collemare di Sassa, Coppito, Filetto, Foce di Sassa, Forcelle, Genzano di Sassa, Gignano, Monticchio, Onna, Paganica, Pagliare di Sassa, Pescomaggiore, Pettino, Pianola, Pile, Pizzutillo, Poggio di Roio, Poggio Santa Maria, Pozza di Preturo, Pratelle, Preturo, Ripa, Roio Piano, San Giacomo Alto, San Giuliano, San Gregorio, San Leonardo, San Marco Di Preturo, San Martino di Sassa, Santa Rufina di Roio, Sant'Angelo, Sant'Elia, Santi, San Vittorino, Sassa, Tempera, Torretta, Vallesindola, Vasche.
International relations
L'Aquila is twinned with: *Baalbek
Baalbek (; ; ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In 1998, the city had a population of 82,608. Most of the population consists of S ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
* Bernalda
Bernalda (Neapolitan language, Metapontino: or ) is a town and municipality () in the province of Matera, in the southern Italy, Italian region of Basilicata. The nearby village of Metaponto is the site of the ancient city of Metapontum.
Until ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Bistrița, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
* Cuenca, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
* Foggia
Foggia (, ; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) of Apulia, in Southern Italy, capital of the province of Foggia. In 2013, its population was 153,143. Foggia is the main city of a plain called Tavoliere delle Puglie, Tavoliere, also know ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Haining
() is a county-level city in Zhejiang Province, China, and under the jurisdiction of Jiaxing. It is in the south side of Yangtze River Delta, and in the north of Zhejiang. It is to the southwest of central Shanghai, and east of Hangzhou, the p ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
* Hobart
Hobart ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the island state of Tasmania, Australia. Located in Tasmania's south-east on the estuary of the River Derwent, it is the southernmost capital city in Australia. Despite containing nearly hal ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
* Rottweil
Rottweil (; Alemannic: ''Rautweil'') is a town in southwest Germany in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Rottweil was a free imperial city for nearly 600 years.
Located between the Black Forest and the Swabian Alps, Rottweil has over 25,000 ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
* San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
* Sant'Angelo d'Alife, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Siena
Siena ( , ; traditionally spelled Sienna in English; ) is a city in Tuscany, in central Italy, and the capital of the province of Siena. It is the twelfth most populated city in the region by number of inhabitants, with a population of 52,991 ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
* York, Toronto
York is a district and former city within Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is located northwest of Old Toronto, southwest of North York and east of the Humber River (Ontario), Humber River.
Originally formed as York Township, it encompassed th ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
* Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra (; ''Green Mountain''; ) is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (). The region is closely associated with vineyards and holds an annual Zielona Góra Wine Fest, Wine Fest. Zie ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
Transport
L'Aquila railway station, on theTerni–Sulmona railway
The Terni–Sulmona railway is a regional railway line in central Italy, managed by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana. It links three regions, Umbria, Lazio and Abruzzo, and three Provinces of Italy, provincial capitals: Terni, Rieti and L'Aquila. Togeth ...
, is the main train station of the city, with trains to Terni, Rieti and Sulmona
Sulmona (; ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of L'Aquila, in the Italy, Italian region of Abruzzo. It is located in the Valle Peligna, a plain once occupied by a lake that disappeared in prehistoric times. In the ancient era, it was ...
.
Notable people
* Mariangelo Accorso, (Aquila, 1489 – Aquila, 1546), Humanist * Amico Agnifili, ( Rocca di Mezzo, 1398 – Aquila, 1476), Cardinal * Antonia of Florence (1402–1472), saint * Corrado Bafile (1903–2005), Cardinal * Bernardino da Siena, ( Massa Marittima, 1380 – Aquila, 1444), saint. * Braccio da Montone, (Perugia
Perugia ( , ; ; ) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. It has 162,467 ...
, 1368 – Aquila, 1424), condottiero
Condottieri (; singular: ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian military leaders active during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The term originally referred specifically to commanders of mercenary companies, derived from the ...
* Giovanbattista Branconio dell'Aquila, (Aquila, 1473 – 1522), papal protonotary, friend of Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino (; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), now generally known in English as Raphael ( , ), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of paintings by Raphael, His work is admired for its cl ...
* Buccio di Ranallo, (Aquila 1294 – Aquila 1363), epic poet, historian, Count of Pettino
* Raffaele Cappelli (1848–1921)
* John of Capistrano, ( Capestrano, 1386 – Ilok, 1456), saint
* Celestine V Celestine is a given name and a surname.
People Given name
* Pope Celestine I (died 432)
* Pope Celestine II (died 1144)
* Pope Celestine III (c. 1106–1198)
* Pope Celestine IV (died 1241)
* Pope Celestine V (1215–1296)
* Antipop ...
, (?, 1215 – Fumone, 1296), saint
* Pompeo Cesura, (Aquila, ? – Rome, 1571), painter
* Appius Claudius Caecus
Appius Claudius Caecus ( 312–279 BC) was a statesman and writer from the Roman Republic. He is best known for two major building projects: the Appian Way (Latin: Via Appia), the first major Roman road, and the first Roman aqueduct, aqueduc ...
, (Amiternum
Amiternum was an ancient Sabine city, then Roman city and later bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see in the central Abruzzo region of modern Italy, located from L'Aquila. Amiternum was the birthplace of the historian Sallust (86 BC).
Histo ...
, 350 a.C. – ?, 271 a.C.), Roman Politician
* Marco Dall'Aquila (c.1480-after 1538), lutenist and composer
* Nazzareno De Angelis (1881–1962), opera singer
* Nicola Di Francia (born 1985), footballer
* Carlo Franchi (1938–2021), racing driver
* Nestore Leoni (1862–1947), painter
* Mario Magnotta (1942–2009), janitor and internet phenomena
* Lorenzo Natali, (Florence, 1922 – Rome, 1989), vice-president of the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
.
* Paul Piccone (1940–2004), founder and editor of TELOS.
* Roberto Ruscitti (b. 1941), composer
* Sallustius (4th century), historian
* Karl Heinrich Ulrichs
Karl Heinrich Ulrichs (28 August 1825 – 14 July 1895) was a German lawyer, jurist, journalist, and writer. He is today regarded as a pioneer of sexology and the modern LGBT rights movement, gay rights movement. Ulrichs has been described as ...
(1825–1895), writer
* Trebisonda Valla, (Bologna 1916 – L'Aquila 2006), Olympic gold medal
* Amleto Vespa (1888–1940), spy for Japan
* Bruno Vespa (b. 1944), journalist
* Claudia Romani (b. 1982), modelù
* Ferdinando Bologna (1925–2019), Art historian
* Vittorio d'Arienzo (b.1975), Product Global Leader
See also
* Orazio di Santis * Santa Giusta (Bazzano, L'Aquila) * 2009 L'Aquila earthquake * L'Aquila CathedralReferences
Sources
* *External links
*Luigi Serra, ''Aquila''
Book, 1929, 142pp , one section translated into English
Gran Sasso
Images, news
Spanish Fortress
The fountain of 99 spouts
June 29, 2007 {{DEFAULTSORT:L'aquila Cities and towns in Abruzzo Populated places destroyed by earthquakes Populated places established in the 13th century