Kondratieff waves on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In economics, Kondratiev waves (also called supercycles, great surges, long waves, K-waves or the long economic cycle) are hypothesized cycle-like phenomena in the modern
Nikolai Dmitriyevich Kondratiev
''Encyclopedia of Russian History'', 2004, at
Kondratiev, Nikolai (1892–1938)
''Encyclopedia of Modern Europe: Europe Since 1914: Encyclopedia of the Age of War and Reconstruction'',
 Some argue that this logic can be extended. The custom of classifying periods of human development by its dominating general purpose technology has surely been borrowed from historians, starting with the
Some argue that this logic can be extended. The custom of classifying periods of human development by its dominating general purpose technology has surely been borrowed from historians, starting with the
 Long wave theory is not accepted by many academic economists. However, it is important for innovation-based, development and
Long wave theory is not accepted by many academic economists. However, it is important for innovation-based, development and
Kondratieff Waves
almanac *Nefiodow, Leo A. (2014). ''Health: The Economic Growth Engine of the 21st Century''
HealthManagement.org Vol 14 Issue 4/2014
* Béla Sipos: „Empirical research of long-term cycles”. STATISZTIKAI SZEMLE tatistical Survey75: 1. ksz. pp. 119–128., Bp., 1997. *Béla Sipos „Analysis of long-term tendencies in the world economy and Hungary”. STATISZTIKAI SZEMLE tatistical Survey80: Klnsz pp. 86–102. 2002. *Béla Sipos: Empirical Research and Forecasting Based on Hungarian and World Economic Data Series. The Long-Wave Debate. Selected Papers from an IIASA (International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis) International Meeting on Long-Term Fluctuations in Economic Growth: Their Causes and Consequences, Held in Weimar, GDR, June 10–14, 1985. Springer Verlag. 1987.
"Kondratieff waves"
on faculty.Washington.edu (The Evolutionary World Politics Homepage).
"Kondratieff theory explained"
on Kondratyev.com (Kondratyev Theory Letters).
by
world economy
The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system, which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumpt ...
. The phenomenon is closely connected with the technology life cycle
The technology life-cycle (TLC) describes the commercial gain of a product through the expense of research and development phase, and the financial return during its "vital life". Some technologies, such as steel, paper or cement manufacturing, ...
.
It is stated that the period of a wave ranges from forty to sixty years, the cycles consist of alternating intervals of high sectoral growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
and intervals of relatively slow growth.See, e.g.
Long wave theory is not accepted by most academic economists. Among economists who accept it, there is a lack of agreement about both the cause of the waves and the start and end years of particular waves. Among critics of the theory, the consensus is that it involves recognizing patterns that may not exist (apophenia
Apophenia () is the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things. The term (German: ' from the Greek verb ''ἀποφαίνειν'' (apophaínein)) was coined by psychiatrist Klaus Conrad in his 1958 publication on the ...
).
History of concept
The Soviet economistNikolai Kondratiev
Nikolai Dmitriyevich Kondratiev (; also Kondratieff; Russian: Никола́й Дми́триевич Кондра́тьев; 4 March 1892 – 17 September 1938) was a Russian Soviet economist and proponent of the New Economic Policy (NEP) best ...
(also written Kondratieff or Kondratyev) was the first to bring these observations to international attention in his book ''The Major Economic Cycles'' (1925) alongside other works written in the same decade.Vincent BarnettNikolai Dmitriyevich Kondratiev
''Encyclopedia of Russian History'', 2004, at
Encyclopedia.com
Encyclopedia.com (also known as HighBeam Encyclopedia) is an online encyclopedia. It aggregates information from other published dictionaries, encyclopedias and reference works including pictures and videos.
History
The website was launched by ...
.Erik BuystKondratiev, Nikolai (1892–1938)
''Encyclopedia of Modern Europe: Europe Since 1914: Encyclopedia of the Age of War and Reconstruction'',
Gale Publishing
Gale is a global provider of research and digital learning resources. The company is based in Farmington Hills, Michigan, west of Detroit. It has been a division of Cengage since 2007.
The company, formerly known as Gale Research and the Gale Gro ...
, January 1, 2006. In 1939, Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at H ...
suggested naming the cycles "Kondratieff waves" in his honor. The underlying idea is closely linked to organic composition of capital
The organic composition of capital (OCC) is a concept created by Karl Marx in his theory of capitalism, which was simultaneously his critique of the political economy of his time. It is derived from his more basic concepts of 'value composition o ...
.
Two Dutch economists, Jacob van Gelderen and Salomon de Wolff, had previously argued for the existence of 50- to 60-year cycles in 1913 and 1924, respectively.
Since the inception of the theory, various studies have expanded the range of possible cycles, finding longer or shorter cycles in the data. The Marxist scholar Ernest Mandel
Ernest Ezra Mandel (; also known by various pseudonyms such as Ernest Germain, Pierre Gousset, Henri Vallin, Walter (5 April 1923 – 20 July 1995), was a Belgian Marxian economist, Trotskyist activist and theorist, and Holocaust survivor. He f ...
revived interest in long-wave theory with his 1964 essay predicting the end of the long boom after five years and in his Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist, and was one of the most influential economists of his time. His book '' Principles of Economics'' (1890) was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years. I ...
lectures in 1979. However, in Mandel's theory long waves are the result of the normal business cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examin ...
and noneconomic factors, such as wars.
In 1996, George Modelski and William R. Thompson published a book documenting K-Waves dating back to 930 AD in China. Separately, Michael Snyder wrote: "economic cycle theories have enabled some analysts to correctly predict the timing of recessions, stock market peaks and stock market crashes over the past couple of decades".
The historian Eric Hobsbawm
Eric John Ernest Hobsbawm (; 9 June 1917 – 1 October 2012) was a British historian of the rise of industrial capitalism, socialism and nationalism. A life-long Marxist, his socio-political convictions influenced the character of his work. ...
also wrote of the theory: "That good predictions have proved possible on the basis of Kondratiev Long Waves—this is not very common in economics—has convinced many historians and even some economists that there is something in them, even if we don't know what".Hobsbawm (1999), pp. 87f.
US economist Anwar Shaikh analyses the movement of the general price level - prices expressed in gold - in the US and the UK since 1890 and identifies three long cycles with troughs ca. in 1895, 1939 and 1982. With this model 2018 was another trough between the third and a possible future fourth cycle.
Characteristics of the cycle
Kondratiev identified three phases in the cycle, namely expansion, stagnation andrecession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
. More common today is the division into four periods with a turning point ( collapse) between expansion and stagnation.
Writing in the 1920s, Kondratiev proposed to apply the theory to the 19th century:
* 1790–1849, with a turning point in 1815.
* 1850–1896, with a turning point in 1873.
* Kondratiev supposed that in 1896 a new cycle had started.
The long cycle supposedly affects all sectors of an economy. Kondratiev focused on price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in th ...
s and interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
s, seeing the ascendant phase as characterized by an increase in prices and low interest rates while the other phase consists of a decrease in prices and high interest rates. Subsequent analysis concentrated on output.
Explanations of the cycle
Cause and effect
Kondratiev waves present both causes and effects of common events that have recurred in capitalistic economies throughout history. Although Kondratiev himself made little differentiation between cause and effect, understanding the cause and effect of Kondratiev waves is a useful discussion and academic tool. The causes documented by Kondratiev waves primarily include inequity, opportunity and social freedoms. Often, much more discussion is made of the notable effects of these causes as well. Effects are both good and bad and include, to name just a few, technological advance, birthrates, populism and revolution—and revolution's contributing causes which can include racism, religious and political intolerance, failed freedoms and opportunity, incarceration rates, terrorism, etc. When inequity is low and opportunity is easily available, peaceful, moral decisions are preferred and Aristotle's "Good Life" is possible (Americans call the good life "the American Dream"). Opportunity created the simple inspiration and genius of theMayflower Compact
The Mayflower Compact, originally titled Agreement Between the Settlers of New Plymouth, was the first governing document of Plymouth Colony. It was written by the men aboard the ''Mayflower,'' consisting of separatist Puritans, adventurers, ...
, for example. Post-World War II and the post-California gold rush 1850s exemplify times of great opportunity and low inequity, and both resulted in unprecedented technological and industrial advances. On the other hand, 1893's global economic panics were not met with sufficient wealth-distributing government policies internationally, and a dozen major revolutions resulted, which some argue were significant causes of World War I. Few would argue against the assertion that World War II began in response to the economic strictures of World War I's Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
and the failure to create government policy that supported economic opportunity during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The Financial contagion, ...
.
Technological innovation theory
According to the innovation theory, these waves arise from the bunching of basicinnovations
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entit ...
that launch technological revolution
A technological revolution is a period in which one or more technologies is replaced by another novel technology in a short amount of time. It is an era of accelerated technological progress characterized by new innovations whose rapid applic ...
s that in turn create leading industrial or commercial
Commercial may refer to:
* a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television)
** Radio advertisement
** Television advertisement
* (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and s ...
sectors. Kondratiev's ideas were taken up by Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at H ...
in the 1930s. The theory hypothesized the existence of very long-run macroeconomic
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
and price cycles, originally estimated to last 50–54 years.
In recent decades there has been considerable progress in historical economics and the history of technology, and numerous investigations of the relationship between technological innovation and economic cycles. Some of the works involving long cycle research and technology include Mensch (1979), Tylecote (1991), the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) (Marchetti, Ayres), Freeman
Freeman, free men, or variant, may refer to:
* a member of the Third Estate in medieval society (commoners), see estates of the realm
* Freeman, an apprentice who has been granted freedom of the company, was a rank within Livery companies
* Free ...
and Louçã (2001), Andrey Korotayev and Carlota Perez
Carlota Perez ( es, Carlota Pérez; born September 20, 1939, in Caracas) is a British-Venezuelan scholar specialized in technology and socio-economic development. She researches the concept of Techno-Economic Paradigm Shifts and the theory of gre ...
.
Perez (2002) places the phases on a logistic or ''S'' curve, with the following labels: the beginning of a technological era as irruption, the ascent as frenzy, the rapid build out as synergy and the completion as maturity.
Demographic theory
Because people have fairly typical spending patterns through their life cycle, such as spending on schooling, marriage, first car purchase, first home purchase, upgrade home purchase, maximum earnings period, maximum retirement savings and retirement, demographic anomalies such as baby booms and busts exert a rather predictable influence on the economy over a long time period. TheEasterlin hypothesis The Easterlin hypothesis (Easterlin 1961, 1969, 1973) states that the positive relationship between income and fertility is dependent on relative income. It is considered the first viable and a still leading explanation for mid-twentieth century ba ...
deals with the post-war baby-boom. Harry Dent has written extensively on demographics and economic cycles. Tylecote (1991) devoted a chapter to demographics and the long cycle.
Land speculation
Georgists such asMason Gaffney
Merrill Mason Gaffney (October 18, 1923 – July 16, 2020) was an American economist and a major critic of Neoclassical economics from a Georgist point of view. Gaffney first read Henry George's masterwork ''Progress and Poverty'' as a high school ...
, Fred Foldvary and Fred Harrison argue that land speculation is the driving force behind the boom and bust cycle. Land is a finite resource which is necessary for all production and they claim that because exclusive usage rights are traded around, this creates speculative bubbles which can be exacerbated by overzealous borrowing and lending. As early as 1997, a number of Georgists predicted that the next crash would come in 2008.
Debt deflation
Debt deflation is a theory ofeconomic cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by exami ...
s which holds that recessions and depressions are due to the overall level of debt shrinking (deflating). Hence, the credit cycle The credit cycle is the expansion and contraction of access to credit over time. Some economists, including Barry Eichengreen, Hyman Minsky, and other Post-Keynesian economists, and some members of the Austrian school, regard credit cycles as the fu ...
is the cause of the economic cycle.
The theory was developed by Irving Fisher
Irving Fisher (February 27, 1867 – April 29, 1947) was an American economist, statistician, inventor, eugenicist and progressive social campaigner. He was one of the earliest American neoclassical economists, though his later work on debt d ...
following the Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange coll ...
and the ensuing Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The Financial contagion, ...
. Debt deflation was largely ignored in favor of the ideas of John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes, ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in ...
in Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ...
, but it has enjoyed a resurgence of interest since the 1980s, both in mainstream economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to ...
and in the heterodox
In religion, heterodoxy (from Ancient Greek: , "other, another, different" + , "popular belief") means "any opinions or doctrines at variance with an official or orthodox position". Under this definition, heterodoxy is similar to unorthodoxy, wh ...
school of post-Keynesian economics
Post-Keynesian economics is a school of economic thought with its origins in '' The General Theory'' of John Maynard Keynes, with subsequent development influenced to a large degree by Michał Kalecki, Joan Robinson, Nicholas Kaldor, Sidney ...
and has subsequently been developed by such post-Keynesian economists as Hyman Minsky
Hyman Philip Minsky (September 23, 1919 – October 24, 1996) was an American economist, a professor of economics at Washington University in St. Louis, and a distinguished scholar at the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College. His research a ...
and Steve Keen
Steve Keen (born 28 March 1953) is an Australian economist and author. He considers himself a post-Keynesian, criticising neoclassical economics as inconsistent, unscientific and empirically unsupported. The major influences on Keen's thinking ...
.
Modern modifications of Kondratiev theory
Inequity appears to be the most obvious driver of Kondratiev waves, and yet some researches have presented a technological and credit cycle explanation as well. There are several modern timing versions of the cycle although most are based on either of two causes: one on technology and the other on thecredit cycle The credit cycle is the expansion and contraction of access to credit over time. Some economists, including Barry Eichengreen, Hyman Minsky, and other Post-Keynesian economists, and some members of the Austrian school, regard credit cycles as the fu ...
.
Additionally, there are several versions of the technological cycles and they are best interpreted using diffusion curves of leading industries. For example, railways only started in the 1830s, with steady growth for the next 45 years. It was after Bessemer steel was introduced that railroads had their highest growth rates. However, this period is usually labeled the age of steel. Measured by value added, the leading industry in the U.S. from 1880 to 1920 was machinery, followed by iron and steel.
Any influence of technology during the cycle that began in the Industrial Revolution pertains mainly to England. The U.S. was a commodity producer and was more influenced by agricultural commodity prices. There was a commodity price cycle based on increasing consumption causing tight supplies and rising prices. That allowed new land to the west to be purchased and after four or five years to be cleared and be in production, driving down prices and causing a depression as in 1819 and 1839.
By the 1850s, the U.S. was becoming industrialized.
The technological cycles can be labeled as follows:
* Industrial Revolution (1771)
* Age of Steam and Railways (1829)
* Age of Steel and Heavy Engineering (1875)
* Age of Oil, Electricity, the Automobile and Mass Production (1908)
* Age of Information and Telecommunications (1971)
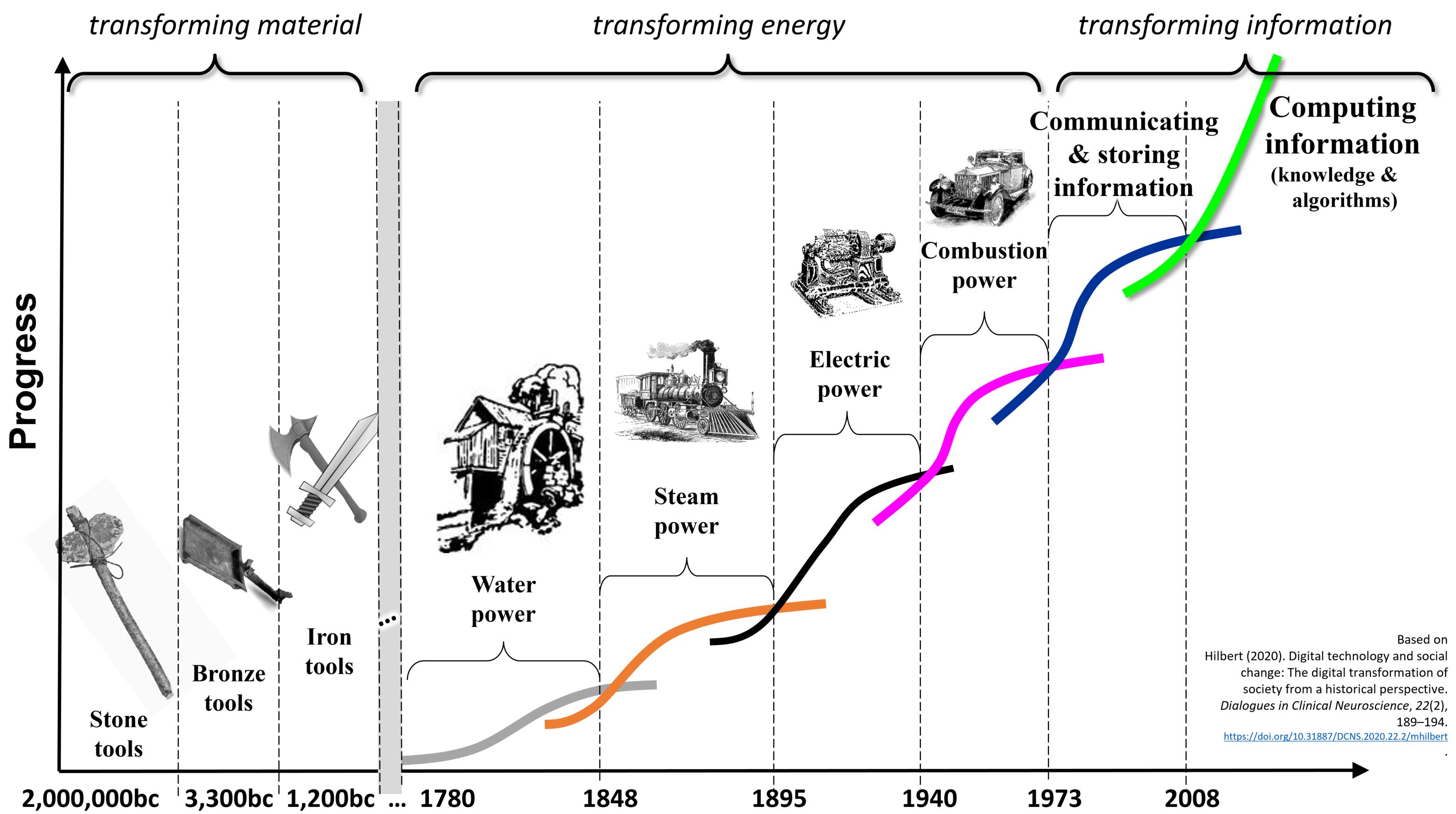
 Some argue that this logic can be extended. The custom of classifying periods of human development by its dominating general purpose technology has surely been borrowed from historians, starting with the
Some argue that this logic can be extended. The custom of classifying periods of human development by its dominating general purpose technology has surely been borrowed from historians, starting with the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with th ...
. Including those, authors distinguish three different long-term metaparadigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm () is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field.
Etymology
''Paradigm'' comes ...
s, each with different long waves. The first focused on the transformation of material, including stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
, bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
, and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in fro ...
. The second, often referred to as industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
s, was dedicated to the transformation of energy, including water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
, steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. ...
, electric, and combustion power. Finally, the most recent metaparadigm aims at transforming information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random, ...
. It started out with the proliferation of communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqu ...
and stored data and has now entered the age of algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing c ...
, which aims at creating automated processes to convert the existing information into actionable knowledge.
Several papers on the relationship between technology and the economy were written by researchers at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an independent international research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna, in Austria. Through its research programs and initiatives, the institute conducts policy-o ...
(IIASA). A concise version of Kondratiev cycles can be found in the work of Robert Ayres (1989) in which he gives a historical overview of the relationships of the most significant technologies. Cesare Marchetti published on Kondretiev waves and on the diffusion of innovations. Arnulf Grübler's book (1990) gives a detailed account of the diffusion of infrastructures including canals, railroads, highways and airlines, with findings that the principal infrastructures have midpoints spaced in time corresponding to 55-year K wavelengths, with railroads and highways taking almost a century to complete. Grübler devotes a chapter to the long economic wave. In 1996, Giancarlo Pallavicini published the ratio between the long Kondratiev wave and information technology and communication.
Korotayev et al. recently employed spectral analysis and claimed that it confirmed the presence of Kondratiev waves in the world GDP dynamics at an acceptable level of statistical significance. Korotayev et al. also detected shorter business cycles, dating the Kuznets to about 17 years and calling it the third harmonic of the Kondratiev, meaning that there are three Kuznets cycles per Kondratiev.
Leo A. Nefiodow shows that the fifth Kondratieff ended with the global economic crisis of 2000–2003 while the new, sixth Kondratieff started simultaneously. According to Leo A. Nefiodow, the carrier of this new long cycle will be health in a holistic sense—including its physical, psychological, mental, social, ecological and spiritual aspects; the basic innovations of the sixth Kondratieff are "psychosocial health" and "biotechnology".
More recently, the physicist and systems scientist Tessaleno Devezas advanced a causal model for the long wave phenomenon based on a generation-learning model and a nonlinear dynamic behaviour of information systems. In both works, a complete theory is presented containing not only the explanation for the existence of K-Waves, but also and for the first time an explanation for the timing of a K-Wave (≈60 years = two generations).
A specific modification of the theory of Kondratieff cycles was developed by Daniel Šmihula. Šmihula identified six long-waves within modern society and the capitalist economy, each of which was initiated by a specific technological revolution:
# Wave of the Financial-agricultural revolution (1600–1780)
# Wave of the Industrial revolution (1780–1880)
# Wave of the Technical revolution (1880–1940)
# Wave of the Scientific-technical revolution (1940–1985)
# Wave of the Information and telecommunications revolution (1985–2015)
# Hypothetical wave of the post-informational technological revolution (Internet of things/renewable energy transition
The energy transition is the process of downshifting fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon energy sources. More generally, an energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding ...
?) (2015–2035?)
Unlike Kondratieff and Schumpeter, Šmihula believed that each new cycle is shorter than its predecessor. His main stress is put on technological progress and new technologies as decisive factors of any long-time economic development. Each of these waves has its innovation phase which is described as a technological revolution and an application phase in which the number of revolutionary innovations falls and attention focuses on exploiting and extending existing innovations. As soon as an innovation or a series of innovations becomes available, it becomes more efficient to invest in its adoption, extension and use than in creating new innovations. Each wave of technological innovations can be characterized by the area in which the most revolutionary changes took place ("leading sectors").
Every wave of innovations lasts approximately until the profits from the new innovation or sector fall to the level of other, older, more traditional sectors. It is a situation when the new technology, which originally increased a capacity to utilize new sources from nature, reached its limits and it is not possible to overcome this limit without an application of another new technology.
For the end of an application phase of any wave there are typical an economic crisis and economic stagnation
Economic stagnation is a prolonged period of slow economic growth (traditionally measured in terms of the GDP growth), usually accompanied by high unemployment. Under some definitions, "slow" means significantly slower than potential growth as e ...
. The financial crisis of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fi ...
is a result of the coming end of the "wave of the Information and telecommunications technological revolution". Some authors have started to predict what the sixth wave might be, such as James Bradfield Moody and Bianca Nogrady who forecast that it will be driven by resource efficiency and clean technology
Clean technology, in short cleantech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Cle ...
. On the other hand, Šmihula himself considers the waves of technological innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed enti ...
s during the modern age (after 1600 AD) only as a part of a much longer "chain" of technological revolutions going back to the pre-modern era. It means he believes that we can find long economic cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by exami ...
s (analogical to Kondratiev cycles in modern economy) dependent on technological revolutions even in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and the Ancient era
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
.
Criticism of Kondratiev theory
 Long wave theory is not accepted by many academic economists. However, it is important for innovation-based, development and
Long wave theory is not accepted by many academic economists. However, it is important for innovation-based, development and evolutionary economics
Evolutionary economics is part of mainstream economics as well as a heterodox school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Much like mainstream economics, it stresses complex interdependencies, competition, growth, stru ...
. Yet, among economists who accept it, there has been no formal universal agreement about the standards that should be used universally to place start and the end years for each wave. Agreement of start and end years can be +1 to 3 years for each 40- to 65-year cycle.
Health economist and biostatistician Andreas J. W. Goldschmidt searched for patterns and proposed that there is a phase shift and overlap of the so-called Kondratiev cycles of IT and health (shown in the figure). He argued that historical growth phases in combination with key technologies does not necessarily imply the existence of regular cycles in general. Goldschmidt is of the opinion that different fundamental innovations and their economic stimuli do not exclude each other as they mostly vary in length and their benefit is not applicable to all participants in a market.
See also
*Business cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examin ...
s
* Clustering illusion
The clustering illusion is the tendency to erroneously consider the inevitable "streaks" or "clusters" arising in small samples from random distributions to be non-random. The illusion is caused by a human tendency to underpredict the amount of v ...
* Grand supercycle (Ralph Nelson Elliott
Ralph Nelson Elliott (28 July 1871 – 15 January 1948) was an American accountant and author, whose study of stock market data led him to develop the Wave Principle, a description of the cyclical nature of trader psychology and a form of technic ...
's wave theory)
* Joshua S. Goldstein
* Kuznets swing
The Kuznets swing (or Kuznets cycle) is a claimed medium-range economic wave with a period of 15–25 years identified in 1930 by Simon Kuznets. Kuznets connected these waves with demographic processes, in particular with immigrant inflows/outflows ...
* Market trend
A market trend is a perceived tendency of financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as ''secular'' for long time-frames, ''primary'' for medium time-frames, and ''secondary'' for short time-fra ...
s
* Martin A. Armstrong
* Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The First ...
* Smihula waves
* Spending wave
* Technological revolution
A technological revolution is a period in which one or more technologies is replaced by another novel technology in a short amount of time. It is an era of accelerated technological progress characterized by new innovations whose rapid applic ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * Grinin, L., Korotayev, A. and Tausch A. (2016) ''Economic Cycles, Crises, and the Global Periphery''. Springer International Publishing, Heidelberg, New York, Dordrecht, London, ; https://www.springer.com/de/book/9783319412603 * * * With contributions bySamir Amin
Samir Amin ( ar, سمير أمين) (3 September 1931 – 12 August 2018) was an Egyptian-French Marxian economist, political scientist and world-systems analyst. He is noted for his introduction of the term Eurocentrism in 1988 and considered ...
, Christopher Chase Dunn, Andre Gunder Frank
Andre Gunder Frank (February 24, 1929 – April 25, 2005) was a German- American sociologist and economic historian who promoted dependency theory after 1970 and world-systems theory after 1984. He employed some Marxian concepts on politic ...
, Immanuel Wallerstein
Immanuel Maurice Wallerstein (; September 28, 1930 – August 31, 2019) was an American sociologist and economic historian. He is perhaps best known for his development of the general approach in sociology which led to the emergence of his wor ...
.
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Weekly Column from 11.09.2007 predicting a major turning-point between 2007 and 2009 and the start of a Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The Financial contagion, ...
.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* This book provides the history of the many ups and downs of the economies.
*
Kondratieff Waves
almanac *Nefiodow, Leo A. (2014). ''Health: The Economic Growth Engine of the 21st Century''
HealthManagement.org Vol 14 Issue 4/2014
* Béla Sipos: „Empirical research of long-term cycles”. STATISZTIKAI SZEMLE tatistical Survey75: 1. ksz. pp. 119–128., Bp., 1997. *Béla Sipos „Analysis of long-term tendencies in the world economy and Hungary”. STATISZTIKAI SZEMLE tatistical Survey80: Klnsz pp. 86–102. 2002. *Béla Sipos: Empirical Research and Forecasting Based on Hungarian and World Economic Data Series. The Long-Wave Debate. Selected Papers from an IIASA (International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis) International Meeting on Long-Term Fluctuations in Economic Growth: Their Causes and Consequences, Held in Weimar, GDR, June 10–14, 1985. Springer Verlag. 1987.
External links
"Kondratieff waves"
on faculty.Washington.edu (The Evolutionary World Politics Homepage).
"Kondratieff theory explained"
on Kondratyev.com (Kondratyev Theory Letters).
by
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School, economic historian, political theorist, and activist. Rothbard was a central figure in the 20th-century American libertarian ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kondratiev Wave
Business cycle theories
1925 in economics
Soviet inventions