Kingdom Of Navarre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western
Navarra
in the Auñamendi Entziklopedia (click on "NAVARRA – NAFARROA (NOMBRE Y EMBLEMAS)") of Latin appears in Eginhard's chronicle of the feats of Charles the Great. Other Royal Frankish Annals give ''nabarros''. There are two proposed etymologies for the name of //: * Basque (declined absolutive
 The kingdom originated in the southern side of the western Pyrenees, in the flatlands around the city of
The kingdom originated in the southern side of the western Pyrenees, in the flatlands around the city of  The Franks renewed their attempts to control the region and in 806 took Navarre under their protection. Following a truce between the Frankish kingdom and Córdoba, in 812
The Franks renewed their attempts to control the region and in 806 took Navarre under their protection. Following a truce between the Frankish kingdom and Córdoba, in 812
 After taking the political power from Fortún Garcés, Sancho Garcés (905–925), son of Dadilde, sister of Raymond I, Count of Pallars and Ribagorza, proclaimed himself king, terminating the alliance with the Emirate of Córdoba and expanding its domains through the course of the River Ega all the way south to the
After taking the political power from Fortún Garcés, Sancho Garcés (905–925), son of Dadilde, sister of Raymond I, Count of Pallars and Ribagorza, proclaimed himself king, terminating the alliance with the Emirate of Córdoba and expanding its domains through the course of the River Ega all the way south to the  In the year 1011 Sancho III married Muniadona of Castile, daughter of the Count of Castile Sancho García. In 1016 the County of Castile and the Kingdom of Navarre made a pact on their future expansion: Pamplona would expand towards the south and east, the eastern region of Soria and the
In the year 1011 Sancho III married Muniadona of Castile, daughter of the Count of Castile Sancho García. In 1016 the County of Castile and the Kingdom of Navarre made a pact on their future expansion: Pamplona would expand towards the south and east, the eastern region of Soria and the
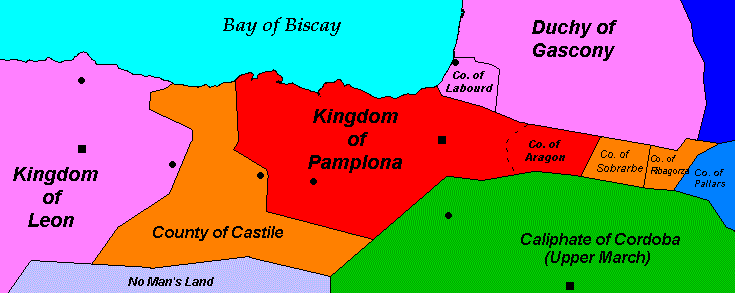 At its greatest extent the Kingdom of Navarre included all the modern Spanish province; the northern slope of the western Pyrenees the Spaniards called the ''ultra puertos'' ("country beyond the mountain passes") or French Navarre; the Basque provinces of Spain and France; the Bureba, the valley between the Basque mountains and the Montes de Oca to the north of
At its greatest extent the Kingdom of Navarre included all the modern Spanish province; the northern slope of the western Pyrenees the Spaniards called the ''ultra puertos'' ("country beyond the mountain passes") or French Navarre; the Basque provinces of Spain and France; the Bureba, the valley between the Basque mountains and the Montes de Oca to the north of
 García Sánchez III (1035–1054) soon found himself struggling for supremacy against his ambitious brothers, especially Ferdinand. García had supported the armed conflict between Ferdinand and his brother-in-law
García Sánchez III (1035–1054) soon found himself struggling for supremacy against his ambitious brothers, especially Ferdinand. García had supported the armed conflict between Ferdinand and his brother-in-law
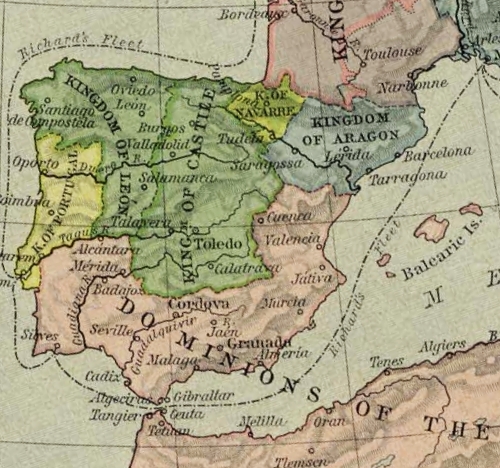 ''The Restorer'' and
''The Restorer'' and  In 1199 Alfonso VIII of Castile, son of Sancho III of Castile and Blanche of Navarre, was determined to take over coastal Navarre, a strategic region that would allow Castile much easier access to European wool markets and would isolate Navarre as well. He launched a massive expedition against Navarre. Sancho the Strong was abroad in
In 1199 Alfonso VIII of Castile, son of Sancho III of Castile and Blanche of Navarre, was determined to take over coastal Navarre, a strategic region that would allow Castile much easier access to European wool markets and would isolate Navarre as well. He launched a massive expedition against Navarre. Sancho the Strong was abroad in
 In spite of the treaties, Ferdinand the Catholic did not relinquish his long-cherished designs on Navarre. In 1506, the 53-year-old widower remarried, to Germaine of Foix (aged 16), daughter of Catherine's uncle John of Foix, who had attempted to claim Navarre over his under-age nephew and niece. However, their infant son died shortly after birth, ending hopes of a possible inheritance of Navarre. Ferdinand kept intervening directly or indirectly in the internal affairs of Navarre by means of the Beaumont party. In 1508, the Navarrese royal troops finally suppressed a rebellion of the count of Lerin after a long standoff. In a letter to the rebellious count, the king of Aragon insisted that while he may take over one stronghold or another, he should use "''theft, deceit and bargain''" instead of violence (23 July 1509).
When Navarre refused to join one of many Holy Leagues against France and declared itself neutral, Ferdinand asked the Pope to excommunicate Albret, which would have legitimised an attack. The Pope was reluctant to label the Crown of Navarre as schismatic explicitly in a first bull against the French and the Navarrese (21 July 1512), but Ferdinand's pressure bore fruit when a (second) bull named Catherine and John III "heretic" (18 February 1513). On 18 July 1512, Fadrique Álvarez de Toledo, 2nd Duke of Alba, Don Fadrique de Toledo was sent to invade Navarre in the context of the second phase of the War of the League of Cambrai.
Unable to face the powerful Castilian-Aragonese army, Jean d'Albret fled to Béarn (Orthez, Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau, Tarbes). Pamplona, Estella, Olite, Sanguesa, and Tudela were captured by September. The Agramont party sided with Queen Catherine while most, but not all, of the Beaumont party lords supported the occupiers. In October 1512, the legitimate King John III returned with an army recruited north of the Pyrenees and attacked Pamplona without success. By the end of December the Castilians were in St-Jean-Pied-de-Port.
After this failure, the Navarrese ''Cortes'' (Parliament) had no option but pledge loyalty to King Ferdinand of Aragon. In 1513, the first Castilian viceroy took a formal oath to respect Navarrese institutions and law ('' fueros''). The Spanish Inquisition was extended into Navarre. The Jews had already been forced into conversion or exile by the Alhambra Decree in Castile and Aragon, and now the Jewish community of Navarre and the Muslims of Tudela suffered its persecution.
In spite of the treaties, Ferdinand the Catholic did not relinquish his long-cherished designs on Navarre. In 1506, the 53-year-old widower remarried, to Germaine of Foix (aged 16), daughter of Catherine's uncle John of Foix, who had attempted to claim Navarre over his under-age nephew and niece. However, their infant son died shortly after birth, ending hopes of a possible inheritance of Navarre. Ferdinand kept intervening directly or indirectly in the internal affairs of Navarre by means of the Beaumont party. In 1508, the Navarrese royal troops finally suppressed a rebellion of the count of Lerin after a long standoff. In a letter to the rebellious count, the king of Aragon insisted that while he may take over one stronghold or another, he should use "''theft, deceit and bargain''" instead of violence (23 July 1509).
When Navarre refused to join one of many Holy Leagues against France and declared itself neutral, Ferdinand asked the Pope to excommunicate Albret, which would have legitimised an attack. The Pope was reluctant to label the Crown of Navarre as schismatic explicitly in a first bull against the French and the Navarrese (21 July 1512), but Ferdinand's pressure bore fruit when a (second) bull named Catherine and John III "heretic" (18 February 1513). On 18 July 1512, Fadrique Álvarez de Toledo, 2nd Duke of Alba, Don Fadrique de Toledo was sent to invade Navarre in the context of the second phase of the War of the League of Cambrai.
Unable to face the powerful Castilian-Aragonese army, Jean d'Albret fled to Béarn (Orthez, Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau, Tarbes). Pamplona, Estella, Olite, Sanguesa, and Tudela were captured by September. The Agramont party sided with Queen Catherine while most, but not all, of the Beaumont party lords supported the occupiers. In October 1512, the legitimate King John III returned with an army recruited north of the Pyrenees and attacked Pamplona without success. By the end of December the Castilians were in St-Jean-Pied-de-Port.
After this failure, the Navarrese ''Cortes'' (Parliament) had no option but pledge loyalty to King Ferdinand of Aragon. In 1513, the first Castilian viceroy took a formal oath to respect Navarrese institutions and law ('' fueros''). The Spanish Inquisition was extended into Navarre. The Jews had already been forced into conversion or exile by the Alhambra Decree in Castile and Aragon, and now the Jewish community of Navarre and the Muslims of Tudela suffered its persecution.

 There were two more attempts at liberation in 1516 and 1521, both supported by popular rebellion, especially the second one. It was in 1521 that the Navarrese came closest to regaining their independence. As a liberation army commanded by André de Foix, General Asparros approached Pamplona, the citizens rose in revolt and besieged the military governor, Ignatius Loyola, Iñigo de Loyola, in his newly built castle. Tudela and other cities also declared their loyalty to the House of Albret. While at first distracted due to only recently overcoming the Revolt of the Comuneros, the Navarrese-Béarnese army managed to liberate all the Kingdom, but shortly thereafter Asparros faced a large Castilian army at the Battle of Esquiroz, Battle of Noáin on 30 June 1521. Asparros was captured, and the army completely defeated.
There were two more attempts at liberation in 1516 and 1521, both supported by popular rebellion, especially the second one. It was in 1521 that the Navarrese came closest to regaining their independence. As a liberation army commanded by André de Foix, General Asparros approached Pamplona, the citizens rose in revolt and besieged the military governor, Ignatius Loyola, Iñigo de Loyola, in his newly built castle. Tudela and other cities also declared their loyalty to the House of Albret. While at first distracted due to only recently overcoming the Revolt of the Comuneros, the Navarrese-Béarnese army managed to liberate all the Kingdom, but shortly thereafter Asparros faced a large Castilian army at the Battle of Esquiroz, Battle of Noáin on 30 June 1521. Asparros was captured, and the army completely defeated.
 As the Kingdom of Navarre was originally organized, it was divided into ''merindades'', districts governed by a ''merino'' ("mayorino", a sheriff), the representative of the king. They were the "Ultrapuertos" (French Navarre), Pamplona, Estella,
As the Kingdom of Navarre was originally organized, it was divided into ''merindades'', districts governed by a ''merino'' ("mayorino", a sheriff), the representative of the king. They were the "Ultrapuertos" (French Navarre), Pamplona, Estella,
File:COA Navarre escarbuncles.svg, Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Navarre during the reign of Sancho VI of Navarre, Sancho VI
File:Sign of Sancho VII of Navarre.svg, Sign of Sancho VII of Navarre, Sancho VII
File:Seal of Sancho VII of Navarre.svg, Seal of Sancho VII
(reverse) File:Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Navarre.svg, Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Navarre, 1234–1580 File:Former Royal Badge of Navarre.svg, Royal Badge of the Medieval Monarchs of Navarre File:EstandNavarra.png, Standard of the Medieval Monarchs of Navarre since 1212
Medieval History of Navarre
Genealogy {{Authority control Kingdom of Navarre, Basque history Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula, Navarre Former kingdoms, Navarre Former monarchies of Europe, Navarre, Kingdom of Christian states, Navarre Medieval Spain Spanish Renaissance Early Modern history of Spain States and territories established in the 820s States and territories disestablished in 1841 824 establishments 9th-century establishments in Spain 1841 disestablishments in Spain 9th-century establishments in Europe 1841 disestablishments in Europe
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
, alongside the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
between present-day Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
The medieval state took form around the city of Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
during the first centuries of the Iberian Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
. The kingdom has its origins in the conflict in the buffer region between the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
and the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba that controlled most of the Iberian Peninsula. The city of Pamplona (; ), had been the main city of the indigenous Vasconic
The Vasconic languages (from Latin 'Basque') are a putative family of languages that includes Basque and the extinct Aquitanian language. The extinct Iberian language is sometimes putatively included.
The concept of the Vasconic languages is o ...
population and was located amid a predominantly Basque-speaking area. In an event traditionally dated to 824, Íñigo Arista
Íñigo Arista ( eu, Eneko, ar, ونّقه, ''Wannaqo'', c. 790 – 851 or 852) was a Basque leader, considered the first king of Pamplona. He is thought to have risen to prominence after the defeat of local Frankish partisans at the Battle of ...
was elected or declared ruler of the area around Pamplona in opposition to Frankish expansion into the region, originally as vassal to the Córdoba Emirate. This polity evolved into the Kingdom of Pamplona. In the first quarter of the 10th century, the Kingdom was able to briefly break its vassalage under Córdoba and expand militarily, but again found itself dominated by Córdoba until the early 11th century. A series of partitions and dynastic changes led to a diminution of its territory and to periods of rule by the kings of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
(1054–1134) and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
(1285–1328).
In the 15th century, another dynastic dispute over control by the king of Aragon led to internal divisions and the eventual conquest of the southern part of the kingdom by Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia fro ...
in 1512 (permanently annexed in 1524). It was annexed by the Courts of Castile to the Crown of Castile in 1515. The remaining northern part of the kingdom was once again joined with France by personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
in 1589 when King Henry III of Navarre inherited the French throne as Henry IV of France
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monar ...
, and in 1620 it was merged into the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
. The monarchs of this unified state took the title "King of France and Navarre" until its fall in the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, and again during the Bourbon Restoration Bourbon Restoration may refer to:
France under the House of Bourbon:
* Bourbon Restoration in France (1814, after the French revolution and Napoleonic era, until 1830; interrupted by the Hundred Days in 1815)
Spain under the Spanish Bourbons:
* Ab ...
from 1814 until 1830 (with a brief interregnum in 1815).
Today, the ancient Kingdom of Navarre comprise the Spanish autonomous communities of Navarre, and and the French community of .
Etymology
There are similar earlier toponyms but the first documentation Bernardo Estornés Lasa's Spanish article oNavarra
in the Auñamendi Entziklopedia (click on "NAVARRA – NAFARROA (NOMBRE Y EMBLEMAS)") of Latin appears in Eginhard's chronicle of the feats of Charles the Great. Other Royal Frankish Annals give ''nabarros''. There are two proposed etymologies for the name of //: * Basque (declined absolutive
singular
Singular may refer to:
* Singular, the grammatical number that denotes a unit quantity, as opposed to the plural and other forms
* Singular homology
* SINGULAR, an open source Computer Algebra System (CAS)
* Singular or sounder, a group of boar ...
): "brownish", "multicolor", which would be a contrast with the green mountain lands north of the original County of Navarre.
* Basque , Castilian ("valley", "plain", present across Spain) + Basque ("people", "land").
The linguist Joan Coromines considers ''naba'' as not clearly Basque in origin but as part of a wider pre-Roman substrate.
Early historic background
Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
. According to Roman geographers such as Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
and Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, these regions were inhabited by the Vascones
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides wi ...
and other related Vasconic-Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region '' Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such ...
an tribes, a pre-Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
group of peoples who inhabited the southern slopes of the western Pyrenees and part of the shore of the Bay of Biscay. These tribes spoke an archaic version of the Basque language, usually known by linguistics as Proto-Basque
Proto-Basque ( eu, aitzineuskara; es, protoeuskera, protovasco; french: proto-basque), or Pre-Basque, is the reconstructed predecessor of the Basque language before the Roman conquests in the Western Pyrenees.
Background
The first linguist w ...
, as well as some other related languages, such as the Aquitanian language
The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine (approximately between the Pyrenees and the Garonne, in the region later known as Gascony) and in the areas sout ...
. The Romans took full control of the area by 74 BC, but unlike their northern neighbors, the Aquitanians, and other tribes from the Iberian Peninsula, the Vascones negotiated their status within the Roman Empire. The region first was part of the Roman province of Hispania Citerior
Hispania Citerior (English: "Hither Iberia", or "Nearer Iberia") was a Roman province in Hispania during the Roman Republic. It was on the eastern coast of Iberia down to the town of Cartago Nova, today's Cartagena in the autonomous community of ...
, then of the Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
. It would be under the jurisdiction of the of Caesaraugusta (modern Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Province of Zaragoza, Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Ara ...
).
The Roman empire influenced the area in urbanization, language, infrastructure, commerce, and industry. During the Sertorian War, Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
would command the foundation of a city in Vasconic territory, giving origin to ''Pompaelo'', modern-day Pamplona, founded on a previously existent Vasconic town. Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
of the Vascones led to their eventual adoption of forms of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
that would evolve into the Navarro-Aragonese language, though the Basque language would remain widely spoken, especially in rural and mountainous areas.
After the decline of the Western Roman Empire, the Vascones were slow to be incorporated into the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
, which was in a civil war that provided the opportunity for the Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
. The Basque leadership probably joined in the appeal that, in the hope of stability, brought the Muslim conquerors. By 718, Pamplona had formed a pact that allowed a wide degree of autonomy in exchange for military and political subjugation, along with the payment of tribute to Córdoba. Burial ornamentation shows strong contacts with the Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaul ...
France and the Gascons of Aquitaine, but also items with Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
ic inscriptions, while a Muslim cemetery in Pamplona, the use of which spanned several generations, suggests the presence of a Muslim garrison in the decades following the Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
invasion.
The origin and foundation of the Kingdom of Pamplona is intrinsically related to the southern expansion of the Frankish kingdom under the Merovingians and their successors, the Carolingians. About 601, the Duchy of Vasconia () was established by the Merovingians, based around Roman Novempopulania and extending from the southern branch of the river Garonne
The Garonne (, also , ; Occitan, Catalan, Basque, and es, Garona, ; la, Garumna
or ) is a river of southwest France and northern Spain. It flows from the central Spanish Pyrenees to the Gironde estuary at the French port of Bordeaux – ...
to the northern side of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
. The first documented Duke of Vasconia was Genial
Genial (Latin ''Genialis'' or ''Genealis'') was the Duke of Gascony ('' Vasconia'') in the early seventh century. He is mentioned in the ''Chronicle of Fredegar''.
Genial was probably a Frank or a Gallo-Roman when Theuderic II and Theudebert II ...
, who would hold that position until 627.
The Duchy of Vasconia then became a frontier territory with varying levels of autonomy granted by the Merovingian monarchs. The suppression of the Duchy of Vasconia as well as the Duchy of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine ( oc, Ducat d'Aquitània, ; french: Duché d'Aquitaine, ) was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, flu ...
by the Carolingians would lead to a rebellion, led by Lupo II of Gascony. Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
launched a punitive War in Aquitaine (760–768) that put down the uprising and resulted in the division of the Duchy into several counties, ruled from Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
. Similarly, across the eastern Pyrenees the Marca Hispánica was established next to the Marca Gothica, a Frankish attempt at creating buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between t ...
s between the Carolingian empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
and the Emirate of Córdoba
The Emirate of Córdoba ( ar, إمارة قرطبة, ) was a medieval Islamic kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. Its founding in the mid-eighth century would mark the beginning of seven hundred years of Muslim rule in what is now Spain and Po ...
.
The Franks under Charlemagne extended their influence and control southward, occupying several regions of the north and east of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. It is unclear how solidly the Franks exercised control over Pamplona. In 778, Charlemagne was invited by rebellious Muslim lords on the Upper March
The Upper March (in ar, الثغر الأعلى, ''aṯ-Tagr al-A'la''; in Spanish: ''Marca Superior'') was an administrative and military division in northeast Al-Andalus, roughly corresponding to the Ebro valley and adjacent Mediterranean coa ...
of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
to lead an expedition south with the intention of taking the city of Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Province of Zaragoza, Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Ara ...
from the Emirate of Córdoba. However, the expedition was a failure, and the Frankish army was forced to withdraw. During their retreat, they destroyed the city walls of Pamplona to weaken the city and avoid a possible rebellion, reminiscent of the approach the Carolingians had used elsewhere against Christian cities that seemed content to live under Córdoban control.
However, while moving through the Pyrenees on 15 August 778, the rearguard of the Frankish army, led by Roland was attacked by the Basque tribes in a confrontation that came to be known as the Battle of Roncevaux Pass
The Battle of Roncevaux Pass ( French and English spelling, ''Roncesvalles'' in Spanish, ''Orreaga'' in Basque) in 778 saw a large force of Basques ambush a part of Charlemagne's army in Roncevaux Pass, a high mountain pass in the Pyrenees on ...
. Roland was killed and the rearguard scattered. As a response to the attempted Frankish seizure of Zaragoza, the Córdoban emir retook the city of Pamplona and its surrounding lands. In 781 two local Basque lords, ''Ibn Balask'' ("son of Velasco"), and ''Mothmin al-Akra'' ("Jimeno ''the Strong''") were defeated and forced to submit. The next mention of Pamplona is in 799, when Mutarrif ibn Musa, thought to have been a governor of the city and a member of the muwallad Banu Qasi
The Banu Qasi, Banu Kasi, Beni Casi ( ar, بني قسي or بنو قسي, meaning "sons" or "heirs of Cassius"), Banu Musa, or al-Qasawi were a Muladí (local convert) dynasty that in the 9th century ruled the Upper March, a frontier te ...
family, was killed there by a pro-Frankish faction.
During this period, Basque territory extended on the west to somewhere around the headwaters of the Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
river. Equally Einhart's ''Vita Karoli Magni'' pinpoints the source of the Ebro in the land of the Navarrese. However, this western region fell under the influence of the Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of ...
.
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
went to Pamplona, likely to establish there a county that would prove short-lived. However, continued rebellion in Gascony rendered Frankish control south of the Pyrenees tenuous, and the Emirate was able to reclaim the region following victory in the 816 Battle of Pancorbo, in which they defeated and killed the "enemy of Allah", ''Balask al-Yalaski'' (Velasco the Gascon), along with the uncle of Alfonso II of Asturias, Garcia ibn Lubb ('son of Lupus'), Sancho, the 'premier knight of Pamplona', and the pagan warrior ''Ṣaltān''. North of the Pyrenees in the same year, Louis the Pious removed Seguin as Duke of Vasconia, which initiated a rebellion,
led by Garcia Jiménez, who was killed in 818. Louis's son Pepin, then King of Aquitaine, stamped out the Vasconic revolt in Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part ...
then hunted the chieftains who had taken refuge in southern Vasconia, i.e., Pamplona and Navarre, no longer controlled by the Franks. He sent an army led by the counts Aeblus Aeblus, Ebalus, or Ebles was a Frankish count in Gascony early in the ninth century.
With Aznar Sánchez, he led a large expedition across the Pyrenees to re-establish control over Navarre. After accomplishing their goals and entering Pamplona w ...
and Aznar Sanchez (the latter being appointed lord, but not duke, of Vasconia by Pepin after suppressing the uprising in the Duchy), accomplishing their goals with no resistance in Pamplona (which still lacked walls after the 778 destruction). On the way back, however, they were ambushed and defeated in Roncevaux by a force probably composed both of Basques and the Córdoba-allied muwallad Banu Qasi
The Banu Qasi, Banu Kasi, Beni Casi ( ar, بني قسي or بنو قسي, meaning "sons" or "heirs of Cassius"), Banu Musa, or al-Qasawi were a Muladí (local convert) dynasty that in the 9th century ruled the Upper March, a frontier te ...
.
Nascent state and kingdom
Establishment by Iñigo Arista
Out of the pattern of competing Frankish and Córdoban interests, the Basque chieftainÍñigo Arista
Íñigo Arista ( eu, Eneko, ar, ونّقه, ''Wannaqo'', c. 790 – 851 or 852) was a Basque leader, considered the first king of Pamplona. He is thought to have risen to prominence after the defeat of local Frankish partisans at the Battle of ...
took power. Tradition tells he was elected as king of Pamplona in 824, giving rise to a dynasty of kings in Pamplona that would last for eighty years. However, the region around Pamplona continued to fall within the sphere of influence of Córdoba, presumably as part of its broader frontier region, the Upper March
The Upper March (in ar, الثغر الأعلى, ''aṯ-Tagr al-A'la''; in Spanish: ''Marca Superior'') was an administrative and military division in northeast Al-Andalus, roughly corresponding to the Ebro valley and adjacent Mediterranean coa ...
, ruled by Íñigo's half-brother, Musa ibn Musa al-Qasawi. The city was allowed to remain Christian and have its own administration but had to pay the traditional taxes to the Emirate, including the ''jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Islamic law. The jizya tax has been understood in ...
'' assessed on non-Muslims living under their control. Íñigo Arista is mentioned in Arab records as ''sâhib'' (lord) or ''amîr'' of the Vascones (''bashkunish'') and not as ''malik'' (king) or ''tâgiya'' (tyrant) used for the kings of Asturias and France, indicating the lower status of these ''ulûj'' (barbarians, not accepting Islam) within the Córdoba sphere. In 841, in concert with Musa ibn Musa, Íñigo rebelled. Although Musa was eventually forced to submit, Íñigo was still in rebellion at the time of his death in 851/2.
Pamplona and Navarre are distinguished in Carolingian chronicles. Pamplona is cited in 778 as a Navarrese stronghold, which may be due to their lack of information about the Basque territory. The chronicles did distinguish between Navarre and its main town in 806 (''"In Hispania, vero Navarrensis et Pampelonensis"''), while the ''Chronicle of Fontenelle'' refers to "''Induonis et Mitionis, ducum Navarrorum''" (Induo �ñigo Aristaand Mitio erhaps Jimeno dukes of the Navarrese). However, Arab chroniclers make no such distinctions, and just refer to the ''Baskunisi'', a transliteration of ''Vascones
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides wi ...
'', since a big majority of the population was Basque. The primitive Navarre may have comprised the valleys of Goñi, Gesalaz, Lana, Allin, Deierri, Berrueza and Mañeru, which later formed the ''merindad'' of Estella.
The role of Pamplona as a focus coordinating both rebellion against and accommodation with Córdoba seen under Íñigo would continue under his son, García Íñiguez (851/2–882), who formed alliances with Asturias, Gascons, Aragonese and with families in Zaragoza opposed to Musa ibn Musa. This established a pattern of raids and counter-raids, capturing slaves and treasure, as well as full military campaigns that would restore full Córdoban control with renewed oaths of fidelity. His son Fortún Garcés (882-905) spent two decades in Córdoban captivity before succeeding in Pamplona as vassal of the Emirate. Neither of these kings would make significant territorial expansion. This period of a fractious, but in the end subservient, Navarre came to an end amidst a period when generalized rebellion within the Emirate prevented them from being able to suppress the inertial forces in the western Pyrenees. The ineffectual Fortún was forced to abdicate in favor of a new dynasty from the vehemently anti-Muslim east of Navarre, the founders of which took a less accommodationist view. With this change, al-Andalus sources shift to calling the Pamplona rulers 'tyrants', as with the independent kings of Asturias: Pamplona had passed out of the Córdoban sphere.
Jiménez rule
Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
and taking the regions of Nájera and Calahorra, which caused the decline of the Banu Qasi
The Banu Qasi, Banu Kasi, Beni Casi ( ar, بني قسي or بنو قسي, meaning "sons" or "heirs of Cassius"), Banu Musa, or al-Qasawi were a Muladí (local convert) dynasty that in the 9th century ruled the Upper March, a frontier te ...
family, who ruled these lands. As a response, Abd-ar-Rahman III undertook two expeditions to these lands, earning a victory at the Battle of Valdejunquera, after which the Emirate retook the lands south of the river Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
, and by 924 attacked Pamplona. The daughter of Sancho Garcés, Sancha, was married to the King of Leon Ordoño II, establishing an alliance with the Leonese kingdom and ensuring the Calahorra region. The valleys of the river Aragón and river Gállego all the way down to Sobrarbe
Sobrarbe is one of the comarcas of Aragon, Spain. It is located in the northern part of the province of Huesca, part of the autonomous community of Aragon in Spain. Many of its people speak the Aragonese language locally known as ''fabla''.
T ...
also ended up under control of Pamplona, and to the west the lands of the kingdom reached the counties of Álava and Castile, which were under control of the Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of ...
. The kingdom had at this time an extent of about 15,000 km. The Chronicle of Albelda (last updated in 976) outlines the extent in 905 of the Kingdom of Pamplona for the first time. It extended to Nájera and ''Arba'' (arguably Araba). Some historians believe that this suggests that it included the Western Basque Country as well:
After the death of Sancho Garcés, the crown passed to his brother, Jimeno Garcés Jimeno (also Gimeno, Ximeno, Chemene, Exemeno) is a given name derived from ''Ximen'',OMAECHEVARRIA, Ignacio, "Nombres propios y apellidos en el País Vasco y sus contornos". ''Homenaje a D. Julio de Urquijo'', volume II, pages 153-175. a variant of ...
(925–931), joined by Sancho's underage son, García Sánchez (931–970), in his last year. García continued to rule under the tutelage of his mother, Sancho's widow Toda Aznarez, who also engineered several political marriages with the other Christian kingdoms and counties of northern Iberia. Oneca was married to Alfonso IV of León and her sister Urraca to Ramiro II of León, while other daughters of Sancho were married to counts of Castile, Álava
Álava ( in Spanish) or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álav ...
and Bigorre
Bigorre ({{IPA-fr, biɡɔʁ; Gascon: ''Bigòrra'') is a region in southwest France, historically an independent county and later a French province, located in the upper watershed of the Adour, on the northern slopes of the Pyrenees, part of th ...
. The marriage of the Pamplonese king García Sánchez with Andregoto Galíndez, daughter of Galindo Aznárez II, Count of Aragon linked the eastern county to the Kingdom. In 934, he invited Abd-ar-Rahman III to intervene in the kingdom in order to emancipate himself from his mother, and this began a period of tributary status by Pamplona and frequent punitive campaigns from Córdoba.
García Sánchez's heir, Sancho II (970–994), set up his half brother, Ramiro Garcés of Viguera, to rule in the short-lived Kingdom of Viguera. The ''Historia General de Navarra'' by Jaime del Burgo says that on the occasion of the donation of the villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became ...
of Alastue by the king of Pamplona to the monastery of San Juan de la Peña in 987, he styled himself "King of Navarre", the first time that title had been used. In many places he appears as the first King of Navarre and in others the third; however, he was at least the seventh king of Pamplona
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state to ...
.
During the late 10th century, Almanzor, the ruler of Al Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mu ...
, frequently led raids against the Christian kingdoms, and attacked the Pamplonese lands on at least nine occasions. In 966, clashes between the Islamic factions and the Kingdom resulted in the loss of Calahorra and the valley of the river Cidacos. Sancho II, while allied with Castilian militias, suffered a grave defeat in the Battle of Torrevicente. Sancho II was forced to hand over one of his daughters and one of his sons as tokens of peace. After the death of Sancho II and during the reign of García Sánchez II, Pamplona was attacked by the Caliphate on several occasions, being completely destroyed in 999, the King himself killed during a raid in the year 1000.
After the death of García Sánchez II, the crown passed to Sancho III, just eight years old at the time, and probably completely controlled by the Caliphate. During the first years of his reign the Kingdom was ruled by his cousins Sancho and García of Viguera until the year 1004, when Sancho III would become ruling king, mentored by his mother Jimena Fernández. The links with Castile became stronger through marriages. The death of Almanzor in 1002 and his successor Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan in 1008 caused the decline of the Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ( ar, خلافة قرطبة; transliterated ''Khilāfat Qurṭuba''), also known as the Cordoban Caliphate was an Islamic state ruled by the Umayyad dynasty from 929 to 1031. Its territory comprised Iberia and part ...
and the progress of the County of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; es, Reino de Castilla, la, Regnum Castellae) was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th cen ...
south, while Pamplona, led by Sancho Garcés III, strengthen the position of his kingdom on the borderlands of the Taifa of Zaragoza, controlling the territories of Loarre
Loarre is a municipality in the province of Huesca, Spain. As of 2010, it had a population of 371 inhabitants.
See also
* Loarre Castle
The Castle of Loarre is a Romanesque Castle and Abbey located near the town of the same name, Huesca P ...
, Funes, Sos
is a Morse code distress signal (), used internationally, that was originally established for maritime use. In formal notation is written with an overscore line, to indicate that the Morse code equivalents for the individual letters of "SOS" ...
, Uncastillo
Uncastillo ( Aragonese: Uncastiello) is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Aragon, eastern Spain. At the 2010 census,Instituto Nacional de Estadística (Spain) it had a population of 781.
Along with Sos d'o Rei Catolico, Exeya d'os C ...
, Arlas, Caparroso
Caparroso is a town and municipality located in the province and autonomous community of Navarre, in the north of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_mo ...
and Boltaña
Boltaña (in Aragonese: ''Boltanya'') is a municipality located in the province of Huesca, Aragon, Spain. According to the 2004 census ( INE), the municipality has a population of 870 inhabitants.
Boltaña is the economic development capital of ...
.
Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
valley, including territories that were at the time part of Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Province of Zaragoza, Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Ara ...
. Thus, the Kingdom of Pamplona comprised a territory of 15,000 km2 between Pamplona, Nájera and Aragón with vassals of Pamplonese and Aragonese origin.
The assassination of Count García Sánchez of Castile in 1028 allowed Sancho to appoint his younger son Ferdinand as count. He also exerted a protectorate over the Duchy of Gascony. He seized the country of the Pisuerga and the Cea, which belonged to the Kingdom of León, and marched armies to the heart of that kingdom, forcing king Bermudo III of León
Bermudo III or Vermudo III (c. 1015– 4 September 1037) was the king of León from 1028 until his death. He was a son of Alfonso V of León by his first wife Elvira Menéndez, and was the last scion of Peter of Cantabria to rule in the Leones ...
to flee to a Galician refuge. Sancho thereby effectively ruled the north of Iberia from the boundaries of Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
to those of the count of Barcelona.
By the time of the death of Sancho III in 1035, the Kingdom had reached its greatest historical extent. Sancho III wrote a problematic will, in which he divided his territory into three kingdoms.
Ecclesiastical affairs
In this period of independence, the ecclesiastical affairs of the country reached a high state of development. Sancho the Great was brought up at Leyre, which was also for a short time the capital of the Diocese of Pamplona. Beside this see, there existed the Bishopric of Oca, which was united in 1079 to the Diocese of Burgos. In 1035 Sancho III re-established the See of Palencia, which had been laid waste at the time of the Moorish invasion. When, in 1045, the city of Calahorra was wrested from the Moors, under whose dominion it had been for more than three hundred years, a see was also founded there, which in the same year absorbed the Diocese of Najera and, in 1088, the Diocese of Alava, the jurisdiction of which covered about the same ground as that of the present Diocese of Vitoria. The See of Pamplona owed its re-establishment to Sancho III, who for this purpose convened a synod at Leyre in 1022 and one at Pamplona in 1023. These synods likewise instituted a reform of ecclesiastical life, with the above-named convent as a centre.Dismemberment
Division of Sancho's domains
 At its greatest extent the Kingdom of Navarre included all the modern Spanish province; the northern slope of the western Pyrenees the Spaniards called the ''ultra puertos'' ("country beyond the mountain passes") or French Navarre; the Basque provinces of Spain and France; the Bureba, the valley between the Basque mountains and the Montes de Oca to the north of
At its greatest extent the Kingdom of Navarre included all the modern Spanish province; the northern slope of the western Pyrenees the Spaniards called the ''ultra puertos'' ("country beyond the mountain passes") or French Navarre; the Basque provinces of Spain and France; the Bureba, the valley between the Basque mountains and the Montes de Oca to the north of Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence o ...
; and the Rioja and Tarazona in the upper valley of the Ebro. On his death, Sancho divided his possessions among his four sons. Sancho the Great's realm was never again united (until Ferdinand the Catholic): Castile was permanently joined to Leon, whereas Aragon enlarged its territory, joining Catalonia through a marriage.
Following the traditional succession customs, the first-born son of Sancho III, García Sánchez III, received the title and lands of the Kingdom of Pamplona, which included the territory of Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
, Nájera and parts of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
. The rest of the territory was given to his widow Muniadona to split among all the legitimate sons: thus García Sánchez III also received the territory to the northeast from the County of Castile (La Bureba
La Bureba is a ''comarca'' located in the northeast of the Province of Burgos in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. It is bounded on the north by Las Merindades, east by the Comarca del Ebro, south-east by the Montes de Oca and ...
, Montes de Oca) and the County of Álava. Ferdinand received the rest of the County of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; es, Reino de Castilla, la, Regnum Castellae) was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th cen ...
and the lands between the Pisuerga and the Cea. Another son of Sancho, Gonzalo, received the counties of Sobrarbe
Sobrarbe is one of the comarcas of Aragon, Spain. It is located in the northern part of the province of Huesca, part of the autonomous community of Aragon in Spain. Many of its people speak the Aragonese language locally known as ''fabla''.
T ...
and Ribargoza as vassal of his eldest brother, García. Lands in Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
were allotted to Sancho's bastard son Ramiro.
Partition and union with Aragon
Bermudo III of León
Bermudo III or Vermudo III (c. 1015– 4 September 1037) was the king of León from 1028 until his death. He was a son of Alfonso V of León by his first wife Elvira Menéndez, and was the last scion of Peter of Cantabria to rule in the Leones ...
, who was ultimately killed in the Battle of Tamarón (1037). This allowed Ferdinand to unite his Castilian county with the new-won crown of León as king Ferdinand I. For several years a mutual collaboration between the two kingdoms took place. The relationship between García and his step-brother Ramiro was better. The latter had acquired all of Aragon, Ribagorza and Sobrarbe on the sudden death of his brother Gonzalo, forming what would become the Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon ...
. García and Ramiro's alliance with Ramon Berenguer, the Count of Barcelona, was effective to keep the Muslim Taifa of Zaragoza at bay. After the capture of Calahorra in 1044, a period peace followed on the southern border and trade was established with Zaragoza.
The relationship between García and Ferdinand deteriorated with time, the two disputing the lands on the Pamplonese-Castilian border, and ended violently in September 1054 at the Battle of Atapuerca
The Battle of Atapuerca was fought on 1 September 1054 at the site of Piedrahita ("standing stone") in the valley of Atapuerca between two brothers, King García Sánchez III of Navarre and King Ferdinand I of Castile.
The Castilians won and Ki ...
, in which García was killed, and Ferdinand took from Pamplona the lands in La Bureba
La Bureba is a ''comarca'' located in the northeast of the Province of Burgos in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. It is bounded on the north by Las Merindades, east by the Comarca del Ebro, south-east by the Montes de Oca and ...
and the Tirón River.
García was succeeded by Sancho IV (1054–1076) ''of Peñalén'', whom Ferdinand had recognised as king of Pamplona immediately after the death of his father. He was fourteen years old at the time, and under the regency of his mother Estefanía and his uncles Ferdinand and Ramiro. After the death of his mother in 1058, Sancho IV lost the support of the local nobility, and the relations between them worsened after he became allied with Ahmad al-Muqtadir
Ahmad ibn Sulayman al-Muqtadir (or just Moctadir; ar, أبو جعفر أحمد "المقتدر بالله" بن سليمان, ''Abu Ja'far Ahmad al-Muqtadir bi-Llah ibn Sulayman'') was a member of the Banu Hud family who ruled the Islamic taifa ...
, ruler of Zaragoza. On 4 June 1076, a conspiracy involving Sancho IV's brother Ramón and sister Ermesinda ended with the murder of the king. The neighboring kingdoms and the nobility probably had a part in the plot.
The dynastic crisis resulting from Sancho's assassination worked to the benefit of the Castilian and Aragonese monarchs. Alfonso VI of León and Castile took control of La Rioja, the Lordship of Biscay, the County of Álava, the County of Durango and part of Gipuzkoa
Gipuzkoa (, , ; es, Guipúzcoa ; french: Guipuscoa) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the autonomous community of the Basque Country. Its capital city is Donostia-San Sebastián. Gipuzkoa shares borders with the French de ...
. Sancho Ramírez, successor to his father, Ramiro of Aragon, took control of the rest of the territory and was recognised as king by the Pamplonese nobility. The land around the city of Pamplona, the core of the original kingdom, became known as the County of Navarre, and was recognised by Alfonso VI as a vassal state of the kingdom of León and Castile. Sancho Ramírez began in 1084 a renewed military expansion of the southern lands controlled by Muslim forces. That year, the city of Arguedas, from which the Bardenas region could be controlled, was taken. After the death of Sancho Ramírez in 1094, he was succeeded by Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
, who resumed the expansion of the territory, taking the cities of Sádaba in 1096 and Milagro in 1098, while threatening Tudela Tudela may refer to:
*Tudela, Navarre, a town and municipality in northern Spain
** Benjamin of Tudela Medieval Jewish traveller
** William of Tudela, Medieval troubadour who wrote the first part of the ''Song of the Albigensian Crusade''
** Ba ...
.
Alfonso the Battler
Alfonso I (''c''. 1073/10747 September 1134), called the Battler or the Warrior ( es, el Batallador), was King of Aragon and Navarre from 1104 until his death in 1134. He was the second son of King Sancho Ramírez and successor of his brother P ...
(1104–1134), brother of Peter I, secured for the country its greatest territorial expansion. He wrested Tudela Tudela may refer to:
*Tudela, Navarre, a town and municipality in northern Spain
** Benjamin of Tudela Medieval Jewish traveller
** William of Tudela, Medieval troubadour who wrote the first part of the ''Song of the Albigensian Crusade''
** Ba ...
from the Moors (1114), re-conquered the entire country of Bureba, which Navarre had lost in 1042, and advanced into the current Province of Burgos. He also annexed Labourd
Labourd ( eu, Lapurdi; la, Lapurdum; Gascon: ''Labord'') is a former French province and part of the present-day Pyrénées Atlantiques ''département''. It is one of the traditional Basque provinces, and identified as one of the territorial c ...
, with its strategic port of Bayonne
Bayonne (; eu, Baiona ; oc, label= Gascon, Baiona ; es, Bayona) is a city in Southwestern France near the Spanish border. It is a commune and one of two subprefectures in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine r ...
, but lost its coastal half to the English soon after. The remainder has been part of Navarre since then and eventually came to be known as Lower Navarre. Toward the south, he moved the Islamic border to the Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
river, with Rioja, Nájera, Logroño, Calahorra, and Alfaro added to his domain.
In 1118, the city of Zaragoza
Zaragoza, also known in English as Saragossa,''Encyclopædia Britannica'"Zaragoza (conventional Saragossa)" is the capital city of the Province of Zaragoza, Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Ara ...
was taken by the Aragonese forces, and on 25 February 1119 the city of Tudela was taken and incorporated into Pamplona.
The 1127 Peace of Támara delimited the territorial domains of the Castilian and Aragonese realms, the latter including Pamplona. The lands of Biscay
Biscay (; eu, Bizkaia ; es, Vizcaya ) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilbao. ...
, Álava
Álava ( in Spanish) or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álav ...
, Gipuzkoa
Gipuzkoa (, , ; es, Guipúzcoa ; french: Guipuscoa) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the autonomous community of the Basque Country. Its capital city is Donostia-San Sebastián. Gipuzkoa shares borders with the French de ...
, Belorado
Belorado is a village and municipality in Spain, belonging to the Province of Burgos, in the autonomous community of Castile-Leon. It has a population of approximately 2,100 inhabitants. It is also known for being a city in the Way of Saint J ...
, Soria and San Esteban de Gormaz went back to the Pamplonese kingdom.
Restoration and the loss of western Navarre
The status quo between Aragon and Castile stood until the 1134 death of Alfonso. Being childless, he willed his realm to the military orders, particularly theTemplars
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
. This decision was rejected by the courts (parliaments) of both Aragon and Navarre, which then chose separate kings.
García Ramírez, known as ''the Restorer'', is the first King of Navarre to use such a title. He was Lord of Monzón, a grandson of Rodrigo Diaz de Vivar, El Cid, and a descendant by illegitimate line of king García Sánchez III. Sancho Garcia, known as Sancho VI "the Wise" (1150–1194), a patron of learning, as well as an accomplished statesman, fortified Navarre within and without, granted charters (fueros) to a number of towns, and was never defeated in battle. He was the first king to issue royal documents entitling him ''rex Navarrae'' or ''rex Navarrorum'', appealing to a wider power base, defined as politico-juridical by Urzainqui (a "populus"), beyond Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
and the customary ''rex Pampilonensium''. As attested in the charters of San Sebastián and Vitoria-Gasteiz (1181), the natives are called ''Navarri'', as well as in another contemporary document at least, where those living to the north of Peralta are defined as Navarrese.
 ''The Restorer'' and
''The Restorer'' and Sancho the Wise
Sancho Garcés VI ( eu, Antso VI.a; 21 April 1132 - 27 June 1194), called the Wise ( eu, Jakituna, es, el Sabio) was King of Navarre from 1150 until his death in 1194. He was the first monarch to officially drop the title of ''King of Pamplona'' ...
were faced with an ever-increasing intervention of Castile in Navarre. In 1170, Alfonso VIII of Castile
Alfonso VIII (11 November 11555 October 1214), called the Noble (''El Noble'') or the one of Las Navas (''el de las Navas''), was King of Castile from 1158 to his death and King of Toledo. After having suffered a great defeat with his own army a ...
and Eleanor
Eleanor () is a feminine given name, originally from an Old French adaptation of the Old Provençal name ''Aliénor''. It is the name of a number of women of royalty and nobility in western Europe during the High Middle Ages.
The name was intro ...
, daughter of Henry II Plantagenet, married, with the Castilian king claiming Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part ...
as part of the dowry. It turned out a much needed pretext for the invasion of Navarre during the following years (1173–1176), with a special focus on Navarre's coastal districts, coveted by Castile in order to become a maritime power. In 1177, the dispute was submitted to arbitration by Henry II of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin kin ...
. The Navarrese made their point on a number of claims, namely "the proven will of the locals" (''fide naturalium hominum suorum exhibita''), the assassination of the King Sancho Garces IV of Navarre by the Castilians (''per violentiam fuit expulsus'', 1076), as well as law and custom, while the Castilians made their case by citing the Castilian takeover following the death of Sancho Garces IV, the dynastic links of Alfonso with Navarre, and the conquest of Toledo. Henry did not dare issue a verdict based entirely on the legal grounds as presented by both sides, instead deciding to refer them back to the boundaries held by both kingdoms at the start of their reigns in 1158, besides agreeing to a truce of seven years. It thus confirmed the permanent loss of the Bureba and Rioja areas for the Navarrese. However, soon, Castile breached the compromise, starting a renewed effort to harass Navarre both in the diplomatic and military arenas.
The rich dowry of Berengaria, daughter of Sancho VI the Wise and Blanche of Castile, made her a desirable catch for Richard I of England
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Duke of Aquitaine, Aquitaine and Duchy of Gascony, Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Co ...
. His mother, Eleanor of Aquitaine
Eleanor ( – 1 April 1204; french: Aliénor d'Aquitaine, ) was Queen of France from 1137 to 1152 as the wife of King Louis VII, List of English royal consorts, Queen of England from 1154 to 1189 as the wife of Henry II of England, King Henry I ...
, crossed the Pyrenean passes to escort Berengaria to Sicily, eventually to wed Richard in Cyprus, on 12 May 1191. She remains the only Queen of England who never set foot in England during her reign. The reign of Sancho the Wise's successor, the last king of the male line of Sancho the Great and the kings of Pamplona, Sancho VII the Strong (''Sancho el Fuerte'') (1194–1234), was more troubled. He appropriated the revenues of churches and convents, granting them instead important privileges; in 1198 he presented to the See of Pamplona his palaces and possessions there; this gift was confirmed by Pope Innocent III on 29 January 1199.
Tlemcen
Tlemcen (; ar, تلمسان, translit=Tilimsān) is the second-largest city in northwestern Algeria after Oran, and capital of the Tlemcen Province. The city has developed leather, carpet, and textile industries, which it exports through the p ...
(modern Algeria) seeking support to counter the Castilian push, by opening a second front. Pope Celestine III
Pope Celestine III ( la, Caelestinus III; c. 1106 – 8 January 1198), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 30 March or 10 April 1191 to his death in 1198. He had a tense relationship with several monarchs, ...
intervened to frustrate the alliance.
The towns of Vitoria and Treviño
Treviño (in Basque: Trebiñu) is the capital of the municipality Condado de Treviño, province of Burgos, in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. The Condado de Treviño and the geographically smaller La Puebla de Arganzón ma ...
resisted the Castilian assault but the Bishop of Pamplona was sent to inform them that no reinforcements would arrive. After nine months of siege, Vitoria surrendered, but Treviño did not, having to be conquered by force of arms. By 1200 the conquest of western Navarre was complete. Castile allowed these territories (with the exceptions of Treviño and Oñati, which were directly ruled from Castile) the right to keep their traditional customs and laws (''viz.'', Navarrese law), which came to be known as fueros. Alava was made a county, Biscay a lordship and Gipuzkoa just a province. In 1207, an arrangement in Guadalajara between both kings sealed a 5-year truce over the occupied territories; still Castile kept a '' fait accompli'' policy.
Sancho the Strong would join in the battle of Las Navas de Tolosa (1212), where he added his small force to the Christian alliance that was victorious over the Caliph Muhammand An-Nasir. He suffered from a varicose ulcer in his leg that led him to retire to Tudela, where he died in 1234. His elder sister Berengaria, Queen of England, had died childless some years earlier. His deceased younger sister Blanca, countess of Champagne, had left a son, Theobald IV of Champagne. Thus the Kingdom of Navarre, though the crown was still claimed by the kings of Aragon, passed by marriage to the House of Champagne, firstly to the heirs of Blanca, who were simultaneously counts of Champagne and Brie, with the support of the Navarrese Parliament (''Cortes'').
Navarre in the Late Middle Ages
Rule by Champagne and France
Theobald I made of his court a centre where the poetry of the troubadours that had developed at the court of the counts of Champagne was welcomed and fostered; his reign was peaceful. His son, King Theobald II (1253–70), married Isabella, daughter of KingLouis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the d ...
, and accompanied his saintly father-in-law upon his crusade to Tunis. On the homeward journey, he died at Trapani in Sicily, and was succeeded by his brother, King Henry I, who had already assumed the reins of government during his absence, but ruled for only three years (1271–74). His daughter, Queen Joan I, ascended as a minor and the country was once again invaded from all sides. The queen and her mother, Blanche of Artois, sought refuge at the court of King Philip III of France. His son, the future King Philip IV of France, had become engaged to the young sovereign and married her in 1284. From 1276, the time of the negotiations for this marriage, Navarre effectively passed into French control, though not without the French suppression of native resistance in the 1276-1277 War of the Navarreria.
The Kingdom of Navarre remained in personal union with the Kingdom of France until the death of Charles IV of France, King Charles I (Charles IV of France) in 1328. He was succeeded by his niece, Joan II of Navarre, Queen Joanna II, daughter of Louis X of France, King Louis I (Louis X of France), and nephew-in-law, Philip III of Navarre, King Philip III. Joanna waived all claim to the throne of France and accepted as compensation for the counties of Champagne and Brie those of Angoumois, Angoulême, County of Longueville, Longueville, and List of Counts of Mortain, Mortain.
King Philip III devoted himself to the improvement of the laws of the country, and joined King Alfonso XI of Castile in battle against the Moors of 1343. After the death of his mother (1349), Charles II of Navarre, King Charles II assumed the reins of government (1349–87). He played an important part in the Hundred Years' War and in the French civil unrest of the time, and on account of his deceit and cruelty he received the epithet of 'the Bad'. He gained and lost possessions in Normandy and, later in his reign, the Navarrese Company acquired island possessions in Greece.
His eldest son, on the other hand, Charles III of Navarre, King Charles III, 'the Noble', once more returned the land to peaceful and happy government (1387–1425). He reformed the government, built canals, and made the tributaries of the Ebro flowing through Navarre navigable. As he outlived his legitimate sons, he was succeeded by his daughter, Blanche I of Navarre, Queen Blanche I (1425–1441), and son-in-law, John II of Aragon, King John II (1398–1479).
Navarre under the Foix and Albret dynasties
After Queen Blanche I of Navarre's death in 1441, Navarre was mired in continued disputes over royal succession. King John II was ruling in Aragon in the name of his brother, Alfonso V of Aragon. He left his son, Charles, Prince of Viana, with merely the rank of governor, whereas Queen Blanche I had intended him to succeed her, as was the custom. In 1450, John II himself came back to Navarre, and, urged on by his ambitious second wife Juana Enriquez, endeavoured to obtain the succession for their son Ferdinand the Catholic, Ferdinand. Mirroring inter-clan disputes during the bloody War of the Bands in the rest of the Basque territories, in 1451 Navarre split in two confederacies, the Agramonts and the Beaumonts, over royal succession, with ramifications both within and outside Navarre. In the violent Navarrese Civil War (1451–1455), civil war that broke out, the Agramonts sided with John II of Aragon, John II, and the Beaumonts — named after their leader, the chancellor, John of Beaumont — espoused the cause of Charles, Prince of Viana.Monreal, G./Jimeno, R. The fights involved the high aristocracy and their junior branches, who carried on the feuds of their senior lines and thrived on weak, often absent, royal authority. The unhappy prince Charles was defeated by his father at Aibar in 1451, and held prisoner for two years, during which he wrote his famous ''Chronicle of Navarre'', a major source for the period. After his release, Charles sought the assistance of King Charles VII of France and his uncle Alfonso V (who resided in Naples), but in vain. In 1460 he was again imprisoned at the instigation of his stepmother, but the History of Catalonia#The Crown of Aragon, Catalans rose in revolt at this injustice, and he was again liberated and named governor of Catalonia. He died in 1461, poisoned by his stepmother Juana Enríquez without being able to retake the reins of Navarre. He had named as heir his next sister, Blanche II of Navarre, Queen Blanche II, but she was immediately imprisoned by John II and died in 1464. While this episode of the civil war came to an end, it inaugurated a period of instability including on-off periods of struggle and uprisings all the way to the Spanish conquest (1512). On Charles' demise in 1461, Eleanor of Navarre, Countess of Foix and Béarn, was proclaimed Princess of Viana, but the instability took a toll. The south-western tip of Navarre—the Sonsierra (Oyón-Oion, Oyon, Laguardia, Álava, Laguardia, in present-day Álava), and Los Arcos—was occupied by Henry IV of Castile. Castile's eventual annexation of this territory in 1463 was upheld by the French king Louis XI in Bayonne on 23 April 1463.Monreal, G./Jimeno, R. John II continued to rule as king up to 1479, when Queen Eleanor succeeded him for only 15 days and then died; she left the crown to her grandson, Francis Phoebus of Navarre, Francis Phoebus, but this inaugurated another period of instability. Eleanor's 13-year-old granddaughter Catherine I of Navarre succeeded her brother Francis Phoebus in accordance with his will (1483). As a minor she remained under the guardianship of her mother, Magdalena of Valois, and was sought by Ferdinand the Catholic as a bride. However, another claimant to the throne was stubbornly trying to stop her, John of Foix, Viscount of Narbonne, brother-in-law of the future King Louis XII of France. Invoking the French Salic Law, he called himself King of Navarre and sent diplomats to Ferdinand II. Pressure built on Catherine's regent Magdalena of Valois who, intent on saving their French possessions, eventually decided to marry the young Queen to the 7-year-old John of Albret, despite the Parliament of Navarre's preference for John of Aragon, son of Ferdinand and Isabella. The Beaumont party rose up, while the Agramonts split over the marriage. Ferdinand II of Aragon in turn reconsidered his diplomatic policy on Navarre. The crown of Navarre fell back on their default policy of diplomacy, and signed the Treaty of Valencia on 21 March 1488, whereby trade was restored between Navarre and the Aragon-Castile tandem. Still, Ferdinand did not recognize Catherine and installed Castilian troops in Navarre, banning French troops in both the kingdom and the principality of Béarn. Ferdinand also pushed for the introduction of the coercive cross-border tribunal, the Inquisition, which the Navarrese hated, but, under pressure from the Aragonese monarch, the doors of Navarre (Tudela) finally opened to the Church institution between 1486 and 1488, pushed by the Aragonese monarch's threats. Still, in 1510 the authorities of Tudela decreed the expulsion of the monk "calling himself inquisitor." Catherine and John III also lacked French royal support: both Charles VIII of France, Charles VIII and Louis XII of France pushed hard to have John of Foix declared king. Finally, following a short period of peace with Ferdinand after a treaty was signed, in January 1494 the coronation of the royal family took place in Pamplona. The monarchs Catherine I and John III swore an oath to respect the liberties of Navarre, and the proclamation was celebrated with a week-long festival, while the ceremony was not attended by the Aragonese bishops with jurisdiction in Navarre. During this period, the realm of Navarre-Beárn was defined by Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Maximilian I's diplomat Müntzer as a nation like Switzerland.Urzainqui, T./Esarte, P./Et al. In the same treaty, Ferdinand renounced war on Navarre or Béarn from Castile, but the attempt to restore royal authority and patrimony met with the resistance of the defiant count of Lerin, Louis of Beaumont, whose estates were confiscated. Catherine and John III's guardian Magdalena of Valois died in 1495 and John's father Alain I of Albret signed another treaty with Ferdinand, whereby the count of Lerín should abandon Navarre, receiving in compensation real estate and various enclaves in the recently conquered Granada. In exchange, Alain made an array of painful concessions: Ferdinand received the count of Lerín's patrimony and gained control of important fortresses across Navarre, including the right to keep a garrison in Olite at the heart of the kingdom. Also, Queen Catherine's 1-year-old daughter Magdalena was to be sent to Castile to be raised, with a plan on a future marriage — she would die young in Castile (1504). Following developments in France, the whole treaty was reverted in 1500 and another compromise was reached with Ferdinand, ensuring peace for another 4 years.Spanish conquest
 In spite of the treaties, Ferdinand the Catholic did not relinquish his long-cherished designs on Navarre. In 1506, the 53-year-old widower remarried, to Germaine of Foix (aged 16), daughter of Catherine's uncle John of Foix, who had attempted to claim Navarre over his under-age nephew and niece. However, their infant son died shortly after birth, ending hopes of a possible inheritance of Navarre. Ferdinand kept intervening directly or indirectly in the internal affairs of Navarre by means of the Beaumont party. In 1508, the Navarrese royal troops finally suppressed a rebellion of the count of Lerin after a long standoff. In a letter to the rebellious count, the king of Aragon insisted that while he may take over one stronghold or another, he should use "''theft, deceit and bargain''" instead of violence (23 July 1509).
When Navarre refused to join one of many Holy Leagues against France and declared itself neutral, Ferdinand asked the Pope to excommunicate Albret, which would have legitimised an attack. The Pope was reluctant to label the Crown of Navarre as schismatic explicitly in a first bull against the French and the Navarrese (21 July 1512), but Ferdinand's pressure bore fruit when a (second) bull named Catherine and John III "heretic" (18 February 1513). On 18 July 1512, Fadrique Álvarez de Toledo, 2nd Duke of Alba, Don Fadrique de Toledo was sent to invade Navarre in the context of the second phase of the War of the League of Cambrai.
Unable to face the powerful Castilian-Aragonese army, Jean d'Albret fled to Béarn (Orthez, Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau, Tarbes). Pamplona, Estella, Olite, Sanguesa, and Tudela were captured by September. The Agramont party sided with Queen Catherine while most, but not all, of the Beaumont party lords supported the occupiers. In October 1512, the legitimate King John III returned with an army recruited north of the Pyrenees and attacked Pamplona without success. By the end of December the Castilians were in St-Jean-Pied-de-Port.
After this failure, the Navarrese ''Cortes'' (Parliament) had no option but pledge loyalty to King Ferdinand of Aragon. In 1513, the first Castilian viceroy took a formal oath to respect Navarrese institutions and law ('' fueros''). The Spanish Inquisition was extended into Navarre. The Jews had already been forced into conversion or exile by the Alhambra Decree in Castile and Aragon, and now the Jewish community of Navarre and the Muslims of Tudela suffered its persecution.
In spite of the treaties, Ferdinand the Catholic did not relinquish his long-cherished designs on Navarre. In 1506, the 53-year-old widower remarried, to Germaine of Foix (aged 16), daughter of Catherine's uncle John of Foix, who had attempted to claim Navarre over his under-age nephew and niece. However, their infant son died shortly after birth, ending hopes of a possible inheritance of Navarre. Ferdinand kept intervening directly or indirectly in the internal affairs of Navarre by means of the Beaumont party. In 1508, the Navarrese royal troops finally suppressed a rebellion of the count of Lerin after a long standoff. In a letter to the rebellious count, the king of Aragon insisted that while he may take over one stronghold or another, he should use "''theft, deceit and bargain''" instead of violence (23 July 1509).
When Navarre refused to join one of many Holy Leagues against France and declared itself neutral, Ferdinand asked the Pope to excommunicate Albret, which would have legitimised an attack. The Pope was reluctant to label the Crown of Navarre as schismatic explicitly in a first bull against the French and the Navarrese (21 July 1512), but Ferdinand's pressure bore fruit when a (second) bull named Catherine and John III "heretic" (18 February 1513). On 18 July 1512, Fadrique Álvarez de Toledo, 2nd Duke of Alba, Don Fadrique de Toledo was sent to invade Navarre in the context of the second phase of the War of the League of Cambrai.
Unable to face the powerful Castilian-Aragonese army, Jean d'Albret fled to Béarn (Orthez, Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau, Tarbes). Pamplona, Estella, Olite, Sanguesa, and Tudela were captured by September. The Agramont party sided with Queen Catherine while most, but not all, of the Beaumont party lords supported the occupiers. In October 1512, the legitimate King John III returned with an army recruited north of the Pyrenees and attacked Pamplona without success. By the end of December the Castilians were in St-Jean-Pied-de-Port.
After this failure, the Navarrese ''Cortes'' (Parliament) had no option but pledge loyalty to King Ferdinand of Aragon. In 1513, the first Castilian viceroy took a formal oath to respect Navarrese institutions and law ('' fueros''). The Spanish Inquisition was extended into Navarre. The Jews had already been forced into conversion or exile by the Alhambra Decree in Castile and Aragon, and now the Jewish community of Navarre and the Muslims of Tudela suffered its persecution.
 There were two more attempts at liberation in 1516 and 1521, both supported by popular rebellion, especially the second one. It was in 1521 that the Navarrese came closest to regaining their independence. As a liberation army commanded by André de Foix, General Asparros approached Pamplona, the citizens rose in revolt and besieged the military governor, Ignatius Loyola, Iñigo de Loyola, in his newly built castle. Tudela and other cities also declared their loyalty to the House of Albret. While at first distracted due to only recently overcoming the Revolt of the Comuneros, the Navarrese-Béarnese army managed to liberate all the Kingdom, but shortly thereafter Asparros faced a large Castilian army at the Battle of Esquiroz, Battle of Noáin on 30 June 1521. Asparros was captured, and the army completely defeated.
There were two more attempts at liberation in 1516 and 1521, both supported by popular rebellion, especially the second one. It was in 1521 that the Navarrese came closest to regaining their independence. As a liberation army commanded by André de Foix, General Asparros approached Pamplona, the citizens rose in revolt and besieged the military governor, Ignatius Loyola, Iñigo de Loyola, in his newly built castle. Tudela and other cities also declared their loyalty to the House of Albret. While at first distracted due to only recently overcoming the Revolt of the Comuneros, the Navarrese-Béarnese army managed to liberate all the Kingdom, but shortly thereafter Asparros faced a large Castilian army at the Battle of Esquiroz, Battle of Noáin on 30 June 1521. Asparros was captured, and the army completely defeated.
Independent Navarre north of the Pyrenees
A small portion of Navarre north of the Pyrenees, Lower Navarre, along with the neighbouring Viscounty of Béarn, Principality of Béarn survived as an independent kingdom which passed by inheritance. Navarre received from Henry II of Navarre, King Henry II, the son of Queen Catherine and King John III, Estates of Navarre, a representative assembly, the clergy being represented by the bishops of Bayonne and Dax, Landes, Dax, their vicars-general, the parish priest of St-Jean-Pied-de-Port, and the priors of Saint-Palais, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Saint-Palais, Utziat and Harambels (Haranbeltz). Jeanne d'Albret, Jeanne III converted to Calvinism in 1560, and thereupon commissioned a translation of the New Testament into Basque; one of the first books published in this language. Jeanne also declared Calvinism to be the official religion of Navarre. She and her son, Henry IV of France, Henry III, led the Huguenot party in the French Wars of Religion. In 1589, Henry became the sole rightful claimant to the crown of France, though he was not recognized as such by many of his subjects until his conversion to Catholicism four years later. WhenLabourd
Labourd ( eu, Lapurdi; la, Lapurdum; Gascon: ''Labord'') is a former French province and part of the present-day Pyrénées Atlantiques ''département''. It is one of the traditional Basque provinces, and identified as one of the territorial c ...
and Upper Navarre were shaken by the Basque witch trials between 1609 and 1613, many sought refuge in Lower Navarre. The last independent king of Navarre, Henry III (reigned 1572–1610), succeeded to the throne of France as Henry IV of France, Henry IV in 1589, founding the Bourbon dynasty. Between 1620 and 1624, Lower Navarre and Béarn were incorporated into France proper by Henry's son, Louis XIII of France, Louis XIII of France (Louis II of Navarre). The Parliament of Navarre and Béarn, Parliament of Navarre, seated at Pau, was also created by merging the Royal Council of Navarre and the sovereign Council of Béarn.
The 1659 Treaty of the Pyrenees put an end to the litigation over the definite French-Spanish borders and to any French-Navarrese dynastic claim over Spanish Navarre. The title of King of Navarre continued to be used by the Kings of France until the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
in 1792, and was revived again during the French Restoration, Restoration, 1814–30. Since the rest of Navarre was in Spanish hands, the kings of Spain would also use the title of King of Navarre, and continue to do so. During the Estates General of 1789, 1789 Estates-General, the Estates of Navarre sent Étienne Polverel to Paris to defend the idiosyncrasy and independence of Navarre in the face of the planned homogenizing administrative layout of France.
The crown and the kingdom: A constitutional foundation
Tudela Tudela may refer to:
*Tudela, Navarre, a town and municipality in northern Spain
** Benjamin of Tudela Medieval Jewish traveller
** William of Tudela, Medieval troubadour who wrote the first part of the ''Song of the Albigensian Crusade''
** Ba ...
and Sangüesa. In 1407 the ''merindad'' of Olite was added. The Parliament, Cortes of Navarre began as the king's council of churchmen and nobles, but in the course of the 14th century the burgesses were added. Their presence was due to the fact that the king had need of their co-operation to raise money by grants and aids, a development that was being paralleled in England.
The Cortes henceforth consisted of the churchmen, the nobles and the representatives of twenty-seven (later thirty-eight) "good towns"—towns which were free of a feudal lord, and, therefore, held directly by the king. The independence of the burgesses was better secured in Navarre than in other parliaments of Spain by the constitutional rule which required the consent of a majority of ''each order'' to every act of the Cortes. Thus the burgesses could not be outvoted by the nobles and the Church, as they could be elsewhere. Even in the 18th century the Navarrese successfully resisted Bourbon attempts to establish custom houses on the French frontier, dividing French from Spanish Navarre.
The institutions of Navarre which maintained their autonomy until the 19th century included the Cortes (''The Three States'', precursor to the Parliament of Navarre), Royal Council, Supreme Court and ''Diputacion del Reino''. Similar institutions existed in the Crown of Aragon (in Aragon, Catalonia and Valencia) until the 18th century. The Spanish monarch was represented by a viceroy, who could object to the decisions made in the Navarrese context.
During that period Navarre enjoyed a special status within the Spanish monarchy; it had its own parliament, cortes, taxation system, and separate customs laws.
Later history and the end of the ''fueros''
By the War of the Pyrenees and the Peninsular War, Navarre was in a deep crisis over the Spanish royal authority, involving the Spanish prime minister Manuel Godoy, who bitterly opposed the Basque charters and their autonomy, and maintained high duty exactions on the Ebro customs against the Navarrese, and the Basques as a whole. The only way out the Navarrese found was an increased trade with France, which in turn spurred the importation of bourgeois, modern ideas. However, the progressive, enlightened bourgeois circles strong in Pamplona—and other Basque towns and cities like San Sebastián, Donostia—were eventually quelled during the above wars. After the French defeat, the only source of support for Navarrese self-government was Ferdinand VII. The king wielded the flag of the ancient régime, as opposed to the liberal Constitution of Cádiz (1812), which ignored the Navarrese and Basque ''fueros'' and any different identities in Spain, or the "Spains", as it was considered before the 19th century. During the Napoleonic wars, many in Navarre took to the bush to avoid tax exactions and the military abuses over property and people during their expeditions, be they French, English, or Spanish. These parties sowed the seeds of the later militias of the Carlist Wars acting under different banners, Carlists most often, but also pro-''fueros'' liberals. However, once the local, urban based enlightened bourgeois were suppressed by the Spanish authorities and bristled at despotic French rule during the occupation, the most staunchly Catholic rose to prominence in Navarre, coming under strong clerical influence. This, and the resentment felt at the loss of their autonomy when they were incorporated into Spain in 1833, account for the strong support given by many Navarrese to the Carlist cause. In 1833, Navarre and the whole Basque people, Basque region in Spain became the chief stronghold of the Carlists, but in 1837 a Spanish Liberal, centralist constitution was proclaimed in Madrid, and Isabella II of Spain, Isabella II recognized as queen. Following the Convention of Vergara, August 31, 1839, armistice putting an end to the First Carlist War, Navarre remained in a shaky state. Its separate status was acknowledged on the Act promulgated in October that year, but after arrival of Baldomero Espartero and the anti-''fueros'' Progressives to office in Madrid, talks with Navarrese Liberal negotiators led to a near-assimilation of Navarre with the Spanish province. Navarre was not a kingdom any more, but another Spanish province. In exchange for giving up self-government, the Navarrese were compensated with the ''Compromise Act'' () in 1841, a set of tax, administrative and other prerogatives, conjuring an idea of 'compromise between two equal sides', and not a granted charter.Province of Spain
Following the 1839–1841 treaties, conflict with Madrid's central government over Navarre's agreed administrative and fiscal idiosyncrasies contributed to the Third Carlist War (1872–76), largely centred in the Southern Basque Country, Basque districts. Myriad parties and factions emerged in Navarre demanding different degrees of restoration of native institutions and laws. Catholicism and traditionalism became major driving forces behind Navarrese politics. The Church in Navarre became a mainstay of the reactionary Spanish Nationalist uprising against the 2nd Spanish Republic (1936). The figure of progressives and inconvenient dissidents exterminated across Navarre is estimated at around 3,000 in the period immediately after the successful military uprising (July 1936). As a reward for its support in the Spanish Civil War, Franco allowed Navarre, as it happened with Álava, to maintain Fueros of Navarre, some prerogatives reminiscent of the ancient Navarrese liberties. Navarre's specific status during Franco's regime led to the present-day Chartered Community of Navarre during the Spanish transition to democracy (the so-called ''Amejoramiento'', 1982).Territory today
The territory formerly known as Navarre now belongs to two nations, Spain and France, depending on whether it lies south or north of the Western Pyrenees. The Basque language is still spoken in most of the provinces. Today, Navarre is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain and Lower Navarre, Basse-Navarre is part of France's Pyrénées-Atlantiques département. Other former Navarrese territories belong now to several autonomous communities of Spain: Basque Country (autonomous community), the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country, La Rioja (autonomous community), La Rioja, Aragon, and Castile and León.Historical symbols
(reverse) File:Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Navarre.svg, Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Navarre, 1234–1580 File:Former Royal Badge of Navarre.svg, Royal Badge of the Medieval Monarchs of Navarre File:EstandNavarra.png, Standard of the Medieval Monarchs of Navarre since 1212
See also
* Chartered Community of Navarra, Navarre (modern) * List of Navarrese monarchs * Kings of Navarre family tree * Court officials of the Kingdom of Navarre * Basque Country (historical territory) * Fuero#Basque and Pyrenean fueros, Basque and Pyrenean Fueros * History of the Basque people * History of Pamplona *Vascones
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides wi ...
* , a historic novel mixing history and legend about the origins of monarchy in Navarre.
Historic languages of the Kingdom of Navarre (824–1841):
* Basque language, Basque, natural language in most of the realm except for the southern plains (Ribera), 824–1841
* Navarro-Aragonese, natural language along the Ebro, in the south-east, some boroughs, and status language, 10–15th century
* Occitan language#Occitan in Spain, Occitan, natural language in some boroughs, status language, 11–14th century
* Castilian language, natural language in southern and increasingly central areas and many urban centres substituting Basque, status language, 15th century – 1841
* Gascon dialect, Gascon, written language in Lower Navarre and limited geographical and social contexts, 1305–1790
* Andalusian Arabic, Arabic, language of the Mudéjar, Muslim communities remaining in southern areas after Reconquista, the conquest of Tudela in 1118, as well as Sunni Islam, Muslim liturgy language, 824–14th century and 824–early 16th century respectively
* French language, French, status language increasingly replacing Gascon (Béarnese) in administration and politics, 1624–1790
* Erromintxela language, Erromintxela, language used by the native Romani people, Romani communities especially in hilly areas, 15th century – 1841
* Hebrew, religious and written language in Jewish communities located in certain urban centres, 10th century – 1512
* Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Christian Catholic liturgy language and formal language in written scripts increasingly replaced by other Romance languages, 824–1841
Notes
References
Sources
* Ariqita y Lasa, ''Colección de documentos para la historia de Navarra'' (Pamplona, 1900) * Joxe Azurmendi, Azurmendi, Joxe: "Die Bedeutung der Sprache in Renaissance und Reformation und die Entstehung der baskischen Literatur im religiösen und politischen Konfliktgebiet zwischen Spanien und Frankreich" In: Wolfgang W. Moelleken (Herausgeber), Peter J. Weber (Herausgeber): ''Neue Forschungsarbeiten zur Kontaktlinguistik'', Bonn: Dümmler, 1997. * Bascle de Lagreze, ''La Navarre française'' (Paris, 1881) * Blade, ''Les Vascons espagnols'' (Agen, 1891) * Pierre Boissonade, ''Histoire de la reunion de la Navarre à la Castille'' (Paris, 1893) * Chappuys, ''Histoire du royaume de Navarre'' (Paris, 1590; 1616) * * * Favyn, ''Histoire de Navarre'' (Paris, 1612) * Ferreras'', La Historia de España'' (Madrid, 1700–27) * * Galland, ''Memoires sur la Navarre'' (Paris, 1648) * Jaurgain, ''La Vasconie'' (Pau, 1898) * * de Marca, ''Histoire de Béarn'' (Paris, 1640) * * * * * * * * Moret, ''Investigationes históricas del reino de Navarra'' (Pamplona, 1655) * Oihenart, ''Notitia utriusque Vasconiae'' (Paris, 1656) * Risco, ''La Vasconia en España Sagrada'', XXXII (Madrid, 1779) * Ruano Prieto, ''Anexión del Reino de Navarra en tiempo del Rey Católico'' (Madrid, 1899) * * Sorauren, Mikel. ''Historia de Navarra, el estado vasco''. Pamiela, 1999. * * * * Yanguas y Miranda, José, ''Annales del reino de Navarra'' (5 vols., Pamplona, 1684–95; 12 vols., Tolosa, 1890–92) * Yanguas y Miranda, José, ''Crónica de los reyes de Navarra'' (Pamplona, 1843) * Yanguas y Miranda, José, ''Diccionario de las antigüedades de Nayanna'' (Pamplona, 1840–43) * Yanguas y Miranda, José, ''Historia compendiada del reino de Navarra'' (S. Sebastián, 1832)External links
Medieval History of Navarre
Genealogy {{Authority control Kingdom of Navarre, Basque history Former countries on the Iberian Peninsula, Navarre Former kingdoms, Navarre Former monarchies of Europe, Navarre, Kingdom of Christian states, Navarre Medieval Spain Spanish Renaissance Early Modern history of Spain States and territories established in the 820s States and territories disestablished in 1841 824 establishments 9th-century establishments in Spain 1841 disestablishments in Spain 9th-century establishments in Europe 1841 disestablishments in Europe