Kingdom of Naples on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the
 When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using as a pretext the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited in 1481 on the will of Charles IV of Anjou, nephew and heir of King René who had no surviving son. This began the
When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using as a pretext the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited in 1481 on the will of Charles IV of Anjou, nephew and heir of King René who had no surviving son. This began the  The kingdom continued to be disputed between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and never genuinely endangered Spanish control.
The French finally abandoned their claims to Naples by the
The kingdom continued to be disputed between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and never genuinely endangered Spanish control.
The French finally abandoned their claims to Naples by the
 After the
After the
 Ferdinand's decision to ally with the
Ferdinand's decision to ally with the
File:Flag of the Kingdom of Naples.svg, 1282–1442
Angevin flag of Naples File:Bandera de Nápoles - Trastámara.svg, 1442–1516
Flag changed after Alfonso I of the House of Trastámara became King. Flag of Cross of Burgundy.svg, The kingdom adopted the flag of the
Flag changed after Charles VI became King. File:Flag of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies (1738).svg, 1738–1806; 1815–1816
Flag changed after Charles VII became King of Naples. Flag was reinstated as the flag of Naples after the
Flag of Naples changed after
Flag of Naples changed after Joachim Murat became king. File:Flag of the Kingdom of Naples (1811).svg, 1811–1815
Flag of Naples changed
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302), when the island of Sicily revolted and was conquered by the Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
, becoming a separate kingdom also called the Kingdom of Sicily. In 1816, it reunified with the island of Sicily to form the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
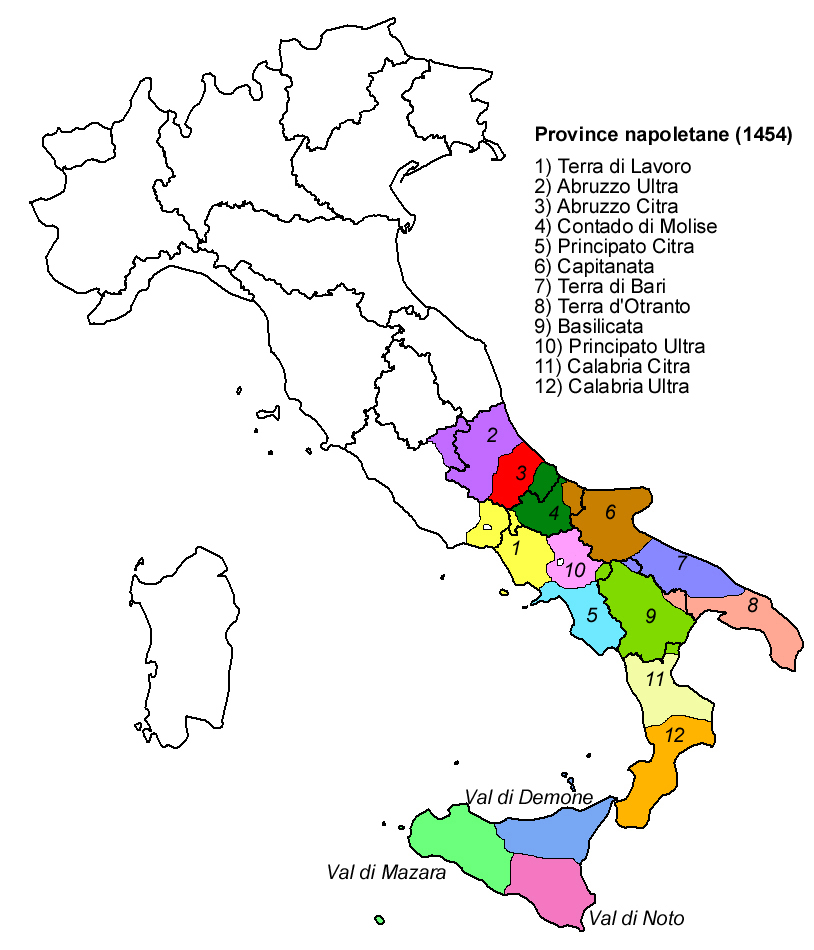
The territory of the Kingdom of Naples corresponded to the current Italian regions of Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
, Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata
it, Lucano (man) it, Lucana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
...
, Abruzzo
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1 ...
, Molise
it, Molisano (man) it, Molisana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 ...
and also included some areas of today's southern and eastern Lazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
.
Nomenclature
The term "Kingdom of Naples" is in near-universal use among historians, but it was not used officially by the government. Since the Angevins remained in power on the Italian peninsula, they kept the original name of the Kingdom of Sicily (). At the end of the War of the Vespers, the Peace of Caltabellotta (1302) provided that the name of the kingdom would be Kingdom of Sicily had become known colloquially as the Kingdom of Naples ( or ). In the late Middle Ages, it was common to distinguish the two Sicilies by noting its location relative to the rest of Italy and the , i.e., the Strait of Messina. The peninsular kingdom was known as Sicily or ('on this side of Faro'), and the island kingdom was known as Sicily or (on the other side of Faro). When both kingdoms came under the rule of Alfonso the Magnanimous in 1442, this usage became official, although Ferdinand I (1458–94) preferred the simple title King of Sicily ().Eleni Sakellariou, ''Southern Italy in the Late Middle Ages: Demographic, Institutional and Economic Change in the Kingdom of Naples, c.1440–c.1530'' (Brill, 2012), pp. 63–64. In the 18th century, the Neapolitan intellectual Giuseppe Maria Galanti argued that Apulia was the true "national" name of the kingdom. By the time of Alfonso the Magnanimous, the two kingdoms were sufficiently distinct that they were no longer seen as divisions of a single kingdom. Despite being repeatedly inpersonal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
, they remained administratively separate. In 1816, the two kingdoms finally merged to form the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
History
Background
Naples, which was the capital of the Duchy of Naples since the7th century
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Mu ...
, surrendered to Roger II of Sicily in 1137, and was annexed to the Kingdom of Sicily. The Normans were the first to bring political unity to southern Italy in the centuries after the failure of the Byzantine effort to reconquer Italy. The Normans established a kingdom that included southern mainland Italy and the island of Sicily, which was primarily ruled from Palermo. The title of ''King of Sicily'' was established by the Antipope Anacletus II as early as 1130 and subsequently legitimized, in 1139, by Pope Innocent II. Since the royal titles over the State had been assigned to the Normans by Innocent II, the popes, in particular Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
and Pope Innocent IV, claimed the feudal rights of the Church State
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from ...
over the Kingdom. After Constance, Queen of Sicily
Constance I ( it, Costanza; 2 November 1154 – 27 November 1198) was reigning Queen of Sicily from 1194–98, jointly with her spouse from 1194 to 1197, and with her infant son Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1198, as the heiress of th ...
married Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, the region was inherited by their son Frederick II, as King of Sicily. The region that later became the separate Kingdom of Naples under the Angevins formed part of the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily and Apulia.
Angevin dynasty
Following the rebellion in 1282, King Charles I of Sicily (Charles of Anjou) was forced to leave the island ofSicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
by Peter III of Aragon
Peter III of Aragon ( November 1285) was King of Aragon, King of Valencia (as ), and Count of Barcelona (as ) from 1276 to his death. At the invitation of some rebels, he conquered the Kingdom of Sicily and became King of Sicily in 1282, pre ...
's troops. Charles, however, maintained his possessions on the mainland, customarily known as the "Kingdom of Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
", after its capital city.
Charles and his Angevin successors maintained a claim to Sicily, warring against the Aragonese until 1373, when Queen Joan I of Naples formally renounced the claim by the Treaty of Villeneuve. Joan's reign was contested by Louis the Great, the Angevin King of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, who captured the kingdom several times (1348–1352).
Queen Joan I also played a part in the ultimate demise of the first Kingdom of Naples. As she was childless, she adopted Louis I, Duke of Anjou, as her heir, in spite of the claims of her cousin, the Prince of Durazzo, effectively setting up a junior Angevin line in competition with the senior line. This led to Joan I's murder at the hands of the Prince of Durazzo in 1382, and his seizing of the throne as Charles III of Naples.
The two competing Angevin lines contested each other for the possession of the Kingdom of Naples over the following decades. In 1389 Louis II of Anjou son of Louis I managed to seize the throne from Ladislas of Naples son of Charles III, but was expelled by Ladislas in 1399. Charles III's daughter Joan II (r. 1414–1435) adopted Alfonso V of Aragon
Alfonso the Magnanimous (139627 June 1458) was King of Aragon and King of Sicily (as Alfonso V) and the ruler of the Crown of Aragon from 1416 and King of Naples (as Alfonso I) from 1442 until his death. He was involved with struggles to the ...
(whom she later repudiated) and Louis III of Anjou as heirs alternately, finally settling succession on Louis' brother René of Anjou of the junior Angevin line, and he succeeded her in 1435.
René of Anjou temporarily united the claims of junior and senior Angevin lines. In 1442, however, Alfonso V conquered the Kingdom of Naples and unified Sicily and Naples once again as dependencies of Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
. At his death in 1458, the War of the Neapolitan Succession (1458–1462) erupted, after which the kingdom was again separated and Naples was inherited by Ferrante, Alfonso's illegitimate son.
Aragonese dynasty
 When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using as a pretext the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited in 1481 on the will of Charles IV of Anjou, nephew and heir of King René who had no surviving son. This began the
When Ferrante died in 1494, Charles VIII of France invaded Italy, using as a pretext the Angevin claim to the throne of Naples, which his father had inherited in 1481 on the will of Charles IV of Anjou, nephew and heir of King René who had no surviving son. This began the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
.
Charles VIII expelled Alfonso II of Naples from Naples in 1495, but was soon forced to withdraw due to the support of Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia fro ...
for his cousin, Alfonso II's son Ferrantino. Ferrantino was restored to the throne but died in 1496 and was succeeded by his uncle, Frederick IV.
Charles VIII's successor, Louis XII reiterated the French claim. In 1501, he occupied Naples and partitioned the kingdom with Ferdinand of Aragon, who abandoned his cousin King Frederick. However, disputes over ownership of key Neapolitan territories made the deal quickly fall through, and Aragon and France resumed their war over the kingdom in 1502. The Spanish troops occupying Calabria and Apulia, led by Gonzalo Fernandez de Cordova, invaded and expelled all Frenchmen from the area. The resulting Aragonese victory left Ferdinand in full control of the kingdom by 1504.
The peace treaties that continued were never definitive, but they established at least that the title of King of Naples was reserved for Ferdinand's grandson, the future Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Ferdinand nevertheless continued in possession of the kingdom, being considered the legitimate heir of his uncle Alfonso I of Naples and also to the former Kingdom of Sicily (''Regnum Utriusque Siciliae'').
 The kingdom continued to be disputed between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and never genuinely endangered Spanish control.
The French finally abandoned their claims to Naples by the
The kingdom continued to be disputed between France and Spain for the next several decades, but French efforts to gain control of it became feebler as the decades went on, and never genuinely endangered Spanish control.
The French finally abandoned their claims to Naples by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pe ...
in 1559. In the Treaty of London (1557), five cities on the coast of Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
were designated the ''Stato dei Presidi'' ( State of the Presidi), and part of the Kingdom of Naples.
As the most populous holding of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
outside of Castile itself (with 3 million inhabitants in 1600), Naples remained an important source of economic and military power for the Spanish. Heavy taxation was levied upon the kingdom to pay for Spain's wars, especially after 1580. Beyond dispatching troops to fight the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Ref ...
in the Low Countries, Naples also disbursed a third of the military expenditures accruing to Lombardy and paid for the Spanish garrisons in Tuscany. This all costed them 800,000 ducats annually, or about a third of the kingdom's revenues; moreover, the public debt also had a military origin, and interest payments on it devoured 40 percent of all tax income. Naples was rich enough to redeem the debt and pay an attractive ten percent in full to lenders. While the soldiers of Naples were under the command of the Spanish viceroy, Neapolitan nobles enjoyed ascendancy in the assemblies and committees that financed and administered the army.
The kingdom suffered a heavy burden from the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659)
The Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659) was fought between France and Spain, with the participation of a changing list of allies through the war. The first phase, beginning in May 1635 and ending with the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, is considered ...
. From 1631 to 1636 alone, Naples sent 53,500 soldiers and 3.5 million scudi to support the Spanish king. This was actually more than was raised in the same time by Castile, which had a population twice the size. Naples provided and paid for 10,000 troops and 1,000 horses annually from 1630 to 1643, on top of a 1 million ducat annual subsidy for the war effort and more funds and soldiers for the kingdom's garrisons and navy. The kingdom was increasingly forced to revert to borrowing to finance the war as it went on, which it could do due to its good credit. From 1612 to 1646, Neapolitan taxes tripled and the public debt quintupled, and 57 percent of the kingdom's revenue was devoted to interest payments. Spain's wars crushed the Neapolitan economy. Furthermore, 90 percent of taxes were collected by state creditors, meaning the state paid an effective interest rate of 70 percent annually on the money it borrowed to fight the war. The kingdom started selling state assets to anyone willing to buy them, which usually ended up being barons; these assets included prisons, forests, buildings, and even royal fortresses, as well as titles.Hanlon 1997, pp. 119-120.
Spanish rule under the Habsburgs and Bourbons
 After the
After the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
in the early 18th century, possession of the kingdom again changed hands. Under the terms of the Treaty of Rastatt in 1714, Naples was given to Charles VI, the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. He also gained control of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
in 1720, but Austrian rule did not last long. Both Naples and Sicily were conquered by a Spanish army during the War of the Polish Succession in 1734, and Charles, Duke of Parma, a younger son of King Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724, and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign of 45 years is the longest in the history of the Spanish mo ...
, the first member of the French House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
to rule in Spain, was installed as King of Naples and Sicily from 1735. When Charles inherited the Spanish throne from his older half-brother in 1759, he left Naples and Sicily to his younger son, Ferdinand IV. Despite the two Kingdoms being in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
under the Habsburg and Bourbon dynasties, they remained constitutionally separate.
Being a member of the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
, Ferdinand IV was a natural opponent of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
and Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
. On 29 November 1798, he effectively started the War of the Second Coalition by briefly occupying Rome, but was expelled from it by French Revolutionary forces within the year and safely returned home. Soon afterwards, on 23 December 1798, Ferdinand fled Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
to Palermo, Sicily as a French army closed in. In January 1799, the French armies installed a Parthenopaean Republic, but this proved short-lived, and a peasant counter-revolution inspired by the clergy allowed Ferdinand to return to his capital. However, in 1801 Ferdinand was compelled to make important concessions to the French by the Treaty of Florence, which reinforced France's position as the dominant power in mainland Italy.
Napoleonic kingdom
Third Coalition
The War of the Third Coalition)
* In French historiography, it is known as the Austrian campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Autriche de 1805) or the German campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Allemagne de 1805) was a European conflict spanni ...
against Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1805 proved more damaging. In 1806, following decisive victories over the allied armies at Austerlitz and over the Neapolitans at Campo Tenese, Napoleon installed his brother, Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the m ...
as King of Naples, he conferred the title "Prince of Naples" to be hereditary on his children and grandchildren. When Joseph was sent off to Spain two years later, he was replaced by Napoleon's sister Caroline
Caroline may refer to:
People
*Caroline (given name), a feminine given name
* J. C. Caroline (born 1933), American college and National Football League player
* Jordan Caroline (born 1996), American (men's) basketball player
Places Antarctica
* ...
and his brother-in-law Marshal Joachim Murat, as ''King of the Two Sicilies''.
Meanwhile, Ferdinand had fled to Sicily, where he retained his throne, despite successive attempts by Murat to invade the island. The British would defend Sicily for the remainder of the war but despite the Kingdom of Sicily nominally being part of the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth Coalitions against Napoleon, Ferdinand and the British were unable to ever challenge French control of the Italian mainland.
After Napoleon's defeat in 1814, Murat reached an agreement with Austria and was allowed to retain the throne of Naples, despite the lobbying efforts of Ferdinand and his supporters. However, with most of the other powers, particularly Britain, hostile towards him and dependent on the uncertain support of Austria, Murat's position became less and less secure. Therefore, when Napoleon returned to France for the Hundred Days in 1815, Murat once again sided with him. Realising the Austrians would soon attempt to remove him, Murat gave the Rimini Proclamation
The Rimini Proclamation was a proclamation on 30 March 1815 by Joachim Murat, who had been made king of Naples by Napoleon I. Murat had just declared war on Austria and used the proclamation to call on Italians to revolt against their Austria ...
hoping to save his kingdom by allying himself with Italian nationalists.
The ensuing Neapolitan War
The Neapolitan War, also known as the Austro-Neapolitan War, was a conflict between the Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples and the Austrian Empire. It started on 15 March 1815 when King Joachim Murat declared war on Austria and ended on 20 May 1815 ...
between Murat and the Austrians was short, ending with a decisive victory for the Austrian forces at the Battle of Tolentino
The Battle of Tolentino was fought from 2–3 May 1815 near Tolentino, Kingdom of Naples in what is now Marche, Italy: it was the decisive battle in the Neapolitan War, fought by the Napoleonic King of Naples Joachim Murat to keep the throne aft ...
. Murat was forced to flee, and Ferdinand IV of Sicily was restored to the throne of Naples. Murat would attempt to regain his throne but was quickly captured and executed by firing squad in Pizzo, Calabria. The next year, 1816, finally saw the formal union of the Kingdom of Naples with the Kingdom of Sicily into the new Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Flags
Angevin flag of Naples File:Bandera de Nápoles - Trastámara.svg, 1442–1516
Flag changed after Alfonso I of the House of Trastámara became King. Flag of Cross of Burgundy.svg, The kingdom adopted the flag of the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
when the Habsburg Charles V became King of Naples in 1516.
File:Banner of the Holy Roman Emperor (after 1400).svg, 1714–1738Flag changed after Charles VI became King. File:Flag of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies (1738).svg, 1738–1806; 1815–1816
Flag changed after Charles VII became King of Naples. Flag was reinstated as the flag of Naples after the
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
.
File:Flag_of_Kingdom_of_Naples_(1806-1808).svg, 1806–1808Flag of Naples changed after
Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic ...
became king.
File:Flag of the Kingdom of Naples (1808).svg, 1808–1811Flag of Naples changed after Joachim Murat became king. File:Flag of the Kingdom of Naples (1811).svg, 1811–1815
Flag of Naples changed
See also
* History of Naples * List of monarchs of NaplesReferences
Sources
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom Of Naples History of NaplesNaples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
1282 establishments in Europe
13th-century establishments in Italy
Italian Renaissance
1816 disestablishments in Italy
1816 disestablishments in Europe
States and territories disestablished in 1816
Early Modern period
Former monarchies of Europe
Former countries