Khanate Of Kokand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Khanate of Kokand ( fa, ; ''Khānneshin-e Khoqand'', chg, ''Khoqand Khānligi'') was a
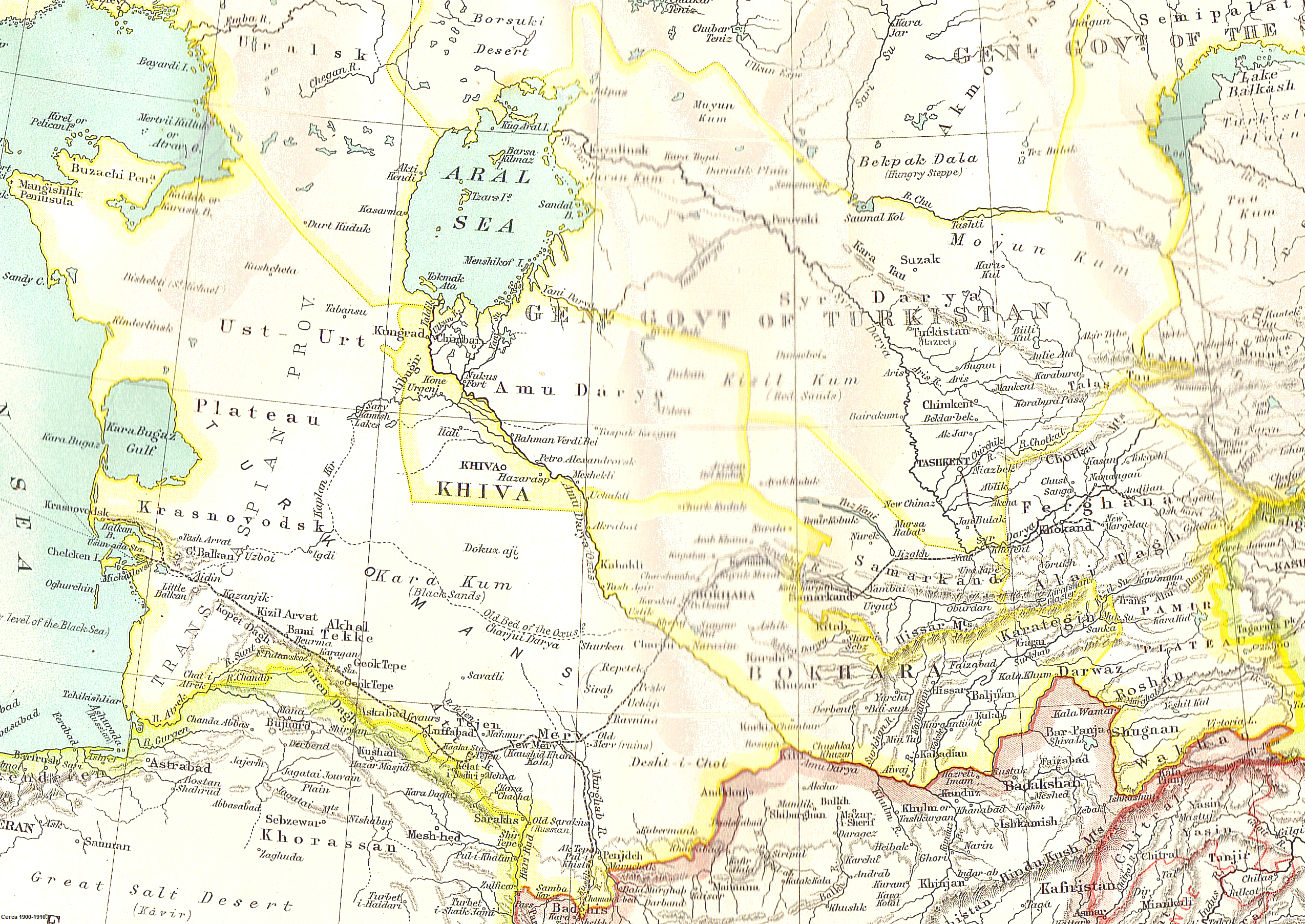
 Sources:Levi, The Rise and Fall of Khoqand, 1709 - 1876, p. XIX.
Sources:Levi, The Rise and Fall of Khoqand, 1709 - 1876, p. XIX.
"Imitation of Timurids and Pseudo-Legitimation: On the origins of a manuscript anthology of poems dedicated to the Kokand ruler Muhammad Ali Khan (1822–1842)"
GSAA Online Working Paper No. 5. *Erkinov, Aftandil S. "Les timourides, modeles de legitimite et les recueils poetiques de Kokand". Ecrit et culture en Asie centrale et dans le monde Turko-iranien, XIVe-XIXe siècles // Writing and Culture in Central Asia and in the Turko-Iranian World, 14th-19th Centuries. F.Richard, M.Szuppe (eds.), ahiers de Studia Iranica. 40 Paris: AAEI, 2009. * *Golden, Peter B. (2011), Central Asia in World History, Oxford University Press. * *Howorth, Sir Henry Hoyle. History of the Mongols: From the 9th to the 19th Century, Volume 2, Issue 2, pp. 795–801,816-845. https://archive.org/details/p2historyofmongo02howouoft/page/784/mode/2up * *"The Muslim World"; Part III, "The Last Great Muslim Empires": Translation and Adaptations by F.R.C. Bagley. (Originally published 1969). Brill Academic Publishers, . *Nalivkine, V. P. Histoire du Khanat de Khokand. Trad. A.Dozon. Paris, 1889. *Nalivkine, V. P. "Kratkaia istoria kokandskogo khanstva". Istoria Srednei Azii. A.I.Buldakov, S.A.Shumov, A.R.Andreev (eds.). Moskva, 2003. * OʻzME. Birinchi jild. Tashkent, 2000. *Roy, Olivier. (2007). "The New Central Asia: Geopolitics and the Birth of Nations". I.B.Tauris. * *Vakhidov, Sh.Kh. XIX-ХХ asr bāshlarida Qoqān khānligida tarikhnavislikning rivājlanishi. arikh fanlari doktori dissertatsiyasi. Tāshkent, 1998.
Uzbek tourist site
unesco site
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kokand, Khanate of Historical Turkic states Turkic dynasties 1709 establishments in Asia Subdivisions of the Russian Empire 1876 disestablishments Former monarchies
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
n polity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of ...
in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand
Kokand ( uz, Qo‘qon/Қўқон/قوقان, ; russian: Кока́нд; fa, خوقند, Xuqand; Chagatai: خوقند, ''Xuqand''; ky, Кокон, Kokon; tg, Хӯқанд, Xöqand) is a city in Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan, at the so ...
between 1709 and 1876. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
.
History
TheKhanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mo ...
of Kokand was established in 1709 when the Shaybanid
The Shibanids or Shaybanids ( fa, سلسله شیبانیان) or more accurately the Abu'l-Khayrid-Shibanids were a Persianized''Introduction: The Turko-Persian tradition'', Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective, ed. Robert L. ...
emir Shahrukh, of the Ming Tribe of Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
, declared independence from the Khanate of Bukhara
The Khanate of Bukhara (or Khanate of Bukhoro) ( fa, , Khānāt-e Bokhārā; ) was an Uzbek state in Central Asia from 1500 to 1785, founded by the Abu'l-Khayrid dynasty, a branch of the Shaybanids. From 1533 to 1540, Bukhara briefly became its ...
, establishing a state in the eastern part of the Fergana Valley. He built a citadel as his capital in the small town of Kokand
Kokand ( uz, Qo‘qon/Қўқон/قوقان, ; russian: Кока́нд; fa, خوقند, Xuqand; Chagatai: خوقند, ''Xuqand''; ky, Кокон, Kokon; tg, Хӯқанд, Xöqand) is a city in Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan, at the so ...
, thus starting the Khanate of Kokand. His son, Abdul Kahrim Bey, and grandson, Narbuta Bey, enlarged the citadel, but both were forced to submit as a protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its in ...
, and pay tribute to, the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
between 1774 and 1798.Starr.
Narbuta Bey’s son Alim
Alim (''ʿAlīm'' , also anglicized as ''Aleem'') is one of the Names of God in Islam, meaning "''All-knowing one''". It is also used as a personal name, as a short form of Abdul Alim, "''Servant of the All-Knowing''":
Given name
* Alim ad-Din ...
was both ruthless and efficient. He hired a mercenary army of Ghalcha highlanders, and conquered the western half of the Fergana Valley, including Khujand and Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
. He was assassinated by his brother Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
in 1811. Umar's son, Mohammed Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and activist. Nicknamed "The Greatest", he is regarded as one of the most significant sports figures of the 20th century, ...
(Madali Khan), ascended to the throne in 1822 at the age of 12. During his reign, the Khanate of Kokand reached its greatest territorial extent. The Kokand Khanate also housed the Khojas
The Khojas ( sd}; gu, ખોજા, hi, ख़ोजा) are a mainly Nizari Isma'ili Shia community of people originating in Gujarat, India.
Derived from the Persian Khwaja, a term of honor, the word Khoja is used to refer to Lohana Rajput ...
of Kashgar like Jahangir Khoja
Jahanghir Khoja, Jāhangīr Khwāja or Jihangir Khoja (, جهانگير خوجة; ; 1788 – 1828), was a member of the influential East Turkestan Afaqi khoja clan, who managed to wrest Kashgaria from the Qing Empire's power for a few years ...
. In 1841, the British officer Captain Arthur Conolly failed to persuade the various khanates to put aside their differences, in an attempt to counter the growing penetration of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
into the area. In November 1841, Captain Conolly left Kokand for Bukhara
Bukhara ( Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and the city ...
in an ill-fated attempt to rescue fellow officer Colonel Charles Stoddart, and both were executed on 24 June 1842 by the order of Emir Nasrullah Khan of Bukhara.
Following this, Madali Khan, who had received Conolly in Kokand, and who had also sought an alliance with Russia, lost the trust of Nasrullah. The Emir, encouraged by the conspiratorial efforts of several influential figures in Kokand (including the commander in chief of its army), invaded the Khanate in 1842. Shortly thereafter he executed Madali Khan, his brother, and Omar Khan's widow, the famed poet Nodira. Madali Khan's cousin, Shir Ali, was installed as the Khan of Kokand in June 1842. Over the next two decades, the khanate was weakened by a bitter civil war, which was further exacerbated by Bukharan and Russian incursions. During this period, the Kyrgyz tribes also broke away, forming the under the leadership of Ormon Khan. Shir Ali's son, Khudayar Khan, ruled from 1844 to 1858, from 1862 to 1863, and from 1865 to 1875. In the meantime, Russia was continuing its advance; on 29 June 1865 Tashkent was taken by the Russian troops of General Chernyayev; the loss of Khujand followed in 1867.
Shortly before the fall of Tashkent, Kokand’s best-known son, Yakub Beg
Muhammad Yaqub Bek (محمد یعقوب بیگ; uz, Яъқуб-бек, ''Ya’qub-bek''; ; 182030 May 1877) was a Khoqandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria) during his invasion of Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He held the title of Atalik Ghazi ("C ...
, former lord of Tashkent, was sent by the then Khan of Kokand, Alimqul, to Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
, where the Hui Muslims were in revolt against the Chinese. When Alimqul was killed in 1865 during the battle with Russia for Tashkent, many Kokandian soldiers fled to join Yaqub Beg, helping him establish his dominion throughout the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
, which lasted until 1877, when Qing reconquered the region.
In 1868, a treaty turned Kokand into a Russian vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back t ...
. The now powerless Khudayar Khan spent his energies improving his lavish palace. Western visitors were impressed by the city of 80,000 people, which contained some 600 mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s and 15 madrasah
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
s. Insurrections against Russian rule and Khudayar’s oppressive taxes forced him into exile in 1875. He was succeeded by his son, Nasruddin Khan, whose anti-Russian stance provoked the annexation of Kokand (after six months of fierce fighting) by Generals Konstantin von Kaufman and Mikhail Skobelev
Mikhail Dmitriyevich Skobelev (russian: Михаил Дмитриевич Скобелев; 29 September 1843 – 7 July 1882), a Russian general, became famous for his conquest of Central Asia and for his heroism during the Russo-Turkish War ...
. In January 1876, Tsar Alexander II stated that he had been forced to "... yield to the wishes of the Kokandi people to become Russian subjects." The Khanate of Kokand was declared abolished, and incorporated into the Fergana Oblast of Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan (russian: Русский Туркестан, Russkiy Turkestan) was the western part of Turkestan within the Russian Empire’s Central Asian territories, and was administered as a Krai or Governor-Generalship. It comprised the ...
.
Rulers of Kokand (1709-1876)

 Sources:Levi, The Rise and Fall of Khoqand, 1709 - 1876, p. XIX.
Sources:Levi, The Rise and Fall of Khoqand, 1709 - 1876, p. XIX.
See also
*List of Turkic dynasties and countries
The following is a list of dynasties, states or empires which are Turkic-speaking, of Turkic origins, or both. There are currently six recognised Turkic sovereign states. Additionally, there are six federal subjects of Russia in which a Turkic ...
* List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
* Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
* Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
* Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramau ...
* Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
* Khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except fo ...
Notes
Citations
References
*Beisembiev, T. K. Kokandskaia istoriografiia : Issledovanie po istochnikovedeniiu Srednei Azii XVIII-XIX vekov. Almaty, TOO "PrintS", 2009.. *Beisembiev, T. K. "Annotated indices to the Kokand Chronicles". Tokyo: Research Institute for Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies. Studia Culturae Islamica. № 91, 2008.. *Beisembiev, T. K. "The Life of Alimqul: A Native Chronicle of Nineteenth Century Central Asia". Published 2003. Routledge . *Beisembiev, T. K. "Ta'rikh-i SHakhrukhi" kak istoricheskii istochnik. Alma Ata: Nauka, 1987. *Beisembiev, T. K. "Legenda o proiskhozhdenii kokandskikh khanov kak istochnik po istorii ideologii v Srednei Azii (na materialakh sochinenii kokandskoi istoriografii)". Kazakhstan, Srednjaja i Tsentralnaia Azia v XVI-XVIII vv. Alma-ata, 1983. * *Dubavitski, Victor and Bababekov, Khaydarbek, in S. Frederick Starr, ed., Ferghana Valley: The Heart of Central Asia. *Erkinov, Aftandil S"Imitation of Timurids and Pseudo-Legitimation: On the origins of a manuscript anthology of poems dedicated to the Kokand ruler Muhammad Ali Khan (1822–1842)"
GSAA Online Working Paper No. 5. *Erkinov, Aftandil S. "Les timourides, modeles de legitimite et les recueils poetiques de Kokand". Ecrit et culture en Asie centrale et dans le monde Turko-iranien, XIVe-XIXe siècles // Writing and Culture in Central Asia and in the Turko-Iranian World, 14th-19th Centuries. F.Richard, M.Szuppe (eds.), ahiers de Studia Iranica. 40 Paris: AAEI, 2009. * *Golden, Peter B. (2011), Central Asia in World History, Oxford University Press. * *Howorth, Sir Henry Hoyle. History of the Mongols: From the 9th to the 19th Century, Volume 2, Issue 2, pp. 795–801,816-845. https://archive.org/details/p2historyofmongo02howouoft/page/784/mode/2up * *"The Muslim World"; Part III, "The Last Great Muslim Empires": Translation and Adaptations by F.R.C. Bagley. (Originally published 1969). Brill Academic Publishers, . *Nalivkine, V. P. Histoire du Khanat de Khokand. Trad. A.Dozon. Paris, 1889. *Nalivkine, V. P. "Kratkaia istoria kokandskogo khanstva". Istoria Srednei Azii. A.I.Buldakov, S.A.Shumov, A.R.Andreev (eds.). Moskva, 2003. * OʻzME. Birinchi jild. Tashkent, 2000. *Roy, Olivier. (2007). "The New Central Asia: Geopolitics and the Birth of Nations". I.B.Tauris. * *Vakhidov, Sh.Kh. XIX-ХХ asr bāshlarida Qoqān khānligida tarikhnavislikning rivājlanishi. arikh fanlari doktori dissertatsiyasi. Tāshkent, 1998.
External links
Uzbek tourist site
unesco site
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kokand, Khanate of Historical Turkic states Turkic dynasties 1709 establishments in Asia Subdivisions of the Russian Empire 1876 disestablishments Former monarchies