Kenyan Constitutional Referendum, 2010 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A constitutional referendum was held in
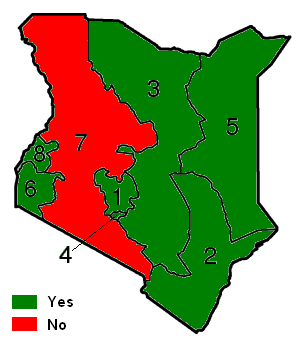 The result was a victory for the "Yes" campaign, with 69% in favour and 31% against on a turnout of 72.2%. Most areas of the country voted in favour of the Constitution, with the notable exception of the
The result was a victory for the "Yes" campaign, with 69% in favour and 31% against on a turnout of 72.2%. Most areas of the country voted in favour of the Constitution, with the notable exception of the
Kenya president ratifies new constitution
BBC News, 27 August 2010
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
on 4 August 2010. Voters were asked whether they approved of a proposed new constitution, which had been passed by the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the rep ...
on 1 April 2010. The new constitution was seen as a vital step to avoid a repetition of the violent outbursts after the 2007 general elections.
The result was a victory for the "Yes" campaign, with 68.6% of voters approving the constitution. The "No" campaign's main spokesman, Higher Education Minister William Ruto
William Kipchirchir Samoei Arap Ruto (born 21 December 1966) is a Kenyan politician who is serving as the fifth and current president of Kenya since 13 September 2022. Prior to becoming president, he served as the 11th deputy president of Ken ...
, conceded defeat. The new constitution came into force on 27 August.
Background
The 1963 constitution was replaced by a new constitution in 1969. This was amended on several occasions, including a 1982 amendment that led to a coup attempt. The amendment saw the addition of a section 2A to the constitution, making Kenya a single-party state under PresidentDaniel arap Moi
Daniel Toroitich arap Moi ( ; 2 September 1924 – 4 February 2020) was a Kenyan politician who served as the second president of Kenya from 1978 to 2002. He was the country's longest-serving president. Moi previously served as the third vice ...
. Following protests in the late 1980s, section 2A was repealed in 1991, establishing the multi-party state, and the Constitution has existed unmodified since then. Although this was seen as a step forward, the country retained a reputation for corruption and many Kenyans desired a completely revised document. This came a step closer to reality in 1998 when a law was passed in parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
calling for a review of the constitution. However, little was done to effect this during the remaining years of Moi's administration.
In the run-up to his victory in the 2002 general elections, President Mwai Kibaki made constitutional reform and the anti-corruption drive a key priority. Despite promises to conduct a review early in the parliament, the new government continued to drag its feet. This was due mainly to the presence of senior officials from the previous regime, whose defection had been vital to Kibaki's election success, but who were ultimately unwilling to risk upsetting the status quo.Firestone, p33 Eventually, in 2004, a proposed new constitution known as the Bomas draft was released. This proposed wide-reaching changes to the structure of government, including the transfer of some powers from the President to a newly created post of Prime Minister. Fearing the loss of power, senior government figures watered down the Bomas draft, leading to widespread opposition, civil unrest and the resignation of several senior members of Kibaki's coalition. The revised document was presented to the people in the November 2005 constitutional referendum, and was defeated.
Following the referendum, politicians that had campaigned against the draft united to form a new party in opposition, known as the Orange Democratic Movement
The Orange Democratic Movement (ODM) is a centre-left political party in Kenya. It is the successor of a grassroots people's movement which was formed during the 2005 Kenyan constitutional referendum campaign. This movement separated in Augu ...
, after the symbol of an orange, which had been present on the referendum ballot papers to signify a "no" vote. Despite splits, the party appeared to be in a strong position going into the 2007 presidential election, but was ultimately defeated in controversial circumstances, leading to the violence of the 2007–2008 Kenyan crisis. The peace deal that ended the crisis mandated that the constitutional question be revisited, which led in November 2009 to a new draft. After minor modifications and the passage of the draft through parliament, the referendum date was set for 4 August 2010.
Question
The referendum question was announced on 13 May 2010: Voter's choices in response to this question were "Yes" or "No". To reduce confusion and make it easier for understanding, the law required that each response was accompanied by a visual symbol to ensure voters were aware of which choice they were making. The symbols chosen for this referendum were colours: green for "Yes" and red for "No". To be passed, the referendum required a simple majority overall and at least 25% of votes in five of Kenya's eight provinces.Campaign
Most senior figures in the coalition government were supporters of the "Yes" campaign, including President Mwai Kibaki, Prime MinisterRaila Odinga
Raila Amolo Odinga (born 7 January 1945) is a Kenyan politician, former Member of Parliament (MP) for Langata and businessman who served as the Prime Minister of Kenya from 2008 to 2013. He is assumed to be the Leader of Opposition in Kenya sin ...
, Vice-President Kalonzo Musyoka and both deputy Prime Ministers, Musalia Mudavadi
Wycliffe Musalia Mudavadi (born 21 September 1960) is a Kenyan politician and land economist who is currently serving as the Prime Cabinet Secretary of Kenya. Until October 2022, he was also the party leader of the Amani National Congress (ANC ...
and Uhuru Kenyatta
Uhuru Muigai Kenyatta (born 26 October 1961) is a Kenyan politician who served as the fourth president of Kenya from 2013 to 2022.
Kenyatta was chosen by Daniel Arap Moi as his preferred successor, but Kenyatta was defeated by opposition le ...
. The notable exceptions to this were Minister for Higher Education, William Ruto
William Kipchirchir Samoei Arap Ruto (born 21 December 1966) is a Kenyan politician who is serving as the fifth and current president of Kenya since 13 September 2022. Prior to becoming president, he served as the 11th deputy president of Ken ...
and Minister for Information, Samuel Poghisio, who led the "No" campaign along with former president Daniel arap Moi
Daniel Toroitich arap Moi ( ; 2 September 1924 – 4 February 2020) was a Kenyan politician who served as the second president of Kenya from 1978 to 2002. He was the country's longest-serving president. Moi previously served as the third vice ...
. These politicians felt the new law would not be good for Kenyans, arguing that the President would still retain excessive powers and that the provisions on land ownership were anti-capitalist.
The other major source of opposition to the constitution came from the Christian churches
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for ...
, who feared it would lead to the legalisation of abortion, due to a clause permitting abortion for maternal health reasons. The other clause considered contentious by the church was the inclusion of Kadhi courts for settling some civil issues relating to Muslim citizens. Although these courts have been present since pre-colonial times, they were not previously enshrined in the Constitution.
Conduct
The run-up to the referendum was largely peaceful, although there were isolated incidents of violence, such as when six people were killed and many more injured in June 2010, in a bomb attack on a rally for the "No" campaign inNairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper h ...
. The Uchaguzi organisation was established to monitor the referendum.
The vote took place amid tight security to avoid a repeat of the previous elections' aftermath. There were particular worries in the Rift Valley Province
Rift Valley Province ( sw, Mkoa wa Bonde la Ufa) of Kenya, bordering Uganda, was one of Kenya's eight provinces, before the Kenyan general election, 2013.
Rift Valley Province was the largest and one of the most economically important provinces i ...
, where tensions between Kalenjin Kalenjin may refer to:
* Kalenjin people
The Kalenjin are a group of tribes designated as Highland Nilotes and are descended from Maliri people ''(thus related to Daasanach of Ethiopia.)'' The Kalenjin are cousins with Datooga people of Tan ...
and Kikuyu Kikuyu or Gikuyu (Gĩkũyũ) mostly refers to an ethnic group in Kenya or its associated language.
It may also refer to:
* Kikuyu people, a majority ethnic group in Kenya
*Kikuyu language, the language of Kikuyu people
*Kikuyu, Kenya, a town in Cent ...
populations had caused the worst of the 2007 violence. The vote eventually passed off peacefully, with no reports of violence.
Opinion polls
Opinion polls taken between April and July 2010 showed a consistent lead for the "Yes" campaign, with support ranging between 49% and 64%, compared to a range of 17% — 22% for the "No" campaign.Results
 The result was a victory for the "Yes" campaign, with 69% in favour and 31% against on a turnout of 72.2%. Most areas of the country voted in favour of the Constitution, with the notable exception of the
The result was a victory for the "Yes" campaign, with 69% in favour and 31% against on a turnout of 72.2%. Most areas of the country voted in favour of the Constitution, with the notable exception of the Rift Valley Province
Rift Valley Province ( sw, Mkoa wa Bonde la Ufa) of Kenya, bordering Uganda, was one of Kenya's eight provinces, before the Kenyan general election, 2013.
Rift Valley Province was the largest and one of the most economically important provinces i ...
, where the majority of voters followed the advice of local leaders William Ruto and Daniel arap Moi in voting against. The only area that failed to vote overwhelmingly as predicted was the Ukambani area of the lower Eastern Province, where the "Yes" camp recorded only a very narrow victory despite support from local leaders Kalonzo Musyoka and Charity Ngilu
Charity Kaluki Ngilu (born 28 January 1952) is a Kenyan politician and the second governor elected for Kitui County. She unsuccessfully vied to be President of the Republic of Kenya in 1997. She served as Minister for Health from 2003 until 200 ...
.
By province
Reactions
The result was generally welcomed by the international community, with messages of congratulations to the government and people of Kenya from, amongst others, US PresidentBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
, former UN Secretary General Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (; 8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founde ...
and the leaders of other African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
nations.
Aftermath
As required by the law mandating the referendum, the new Constitution was formally promulgated in a ceremony on 27 August 2010 by President Kibaki. This historic occasion was attended by foreign leaders and dignitaries from Africa and all over the world.BBC News, 27 August 2010
References
{{Kenya topics 2010 2010 in Kenya 2010 referendums Constitutional referendums