Kauwukah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kawfakha' ( ar, كوفخة) was a
119
/ref> In 1882, the PEF's ''
4
The village had an elementary school and some small shops. The villagers obtained water for domestic use from two
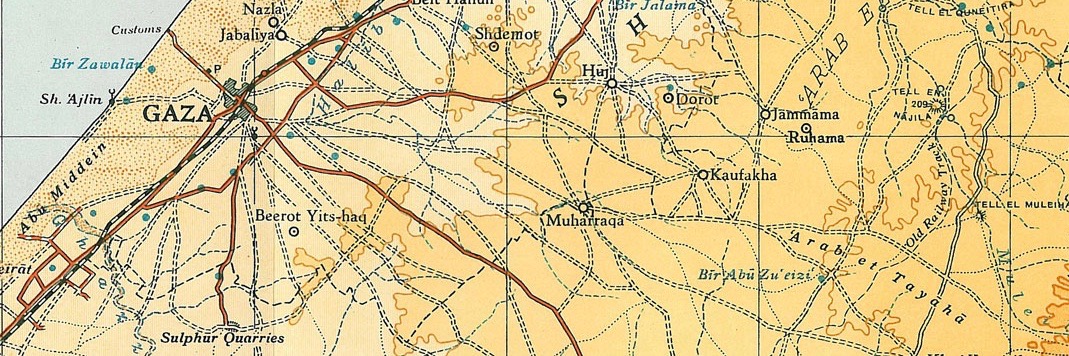 In the 1945 statistics Kawfakha had a population of 500 Muslims, with a total of 8,569
In the 1945 statistics Kawfakha had a population of 500 Muslims, with a total of 8,569
195
6.
Palestine Remembered - Kawfakha
Kawfakha
IAAWikimedia commons
from the
Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
village located east of Gaza that was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
.
Location
The village stood on a stretch of sandy, rolling land in the northernNegev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
. A network of secondary roads linked it to the highways between Gaza and Julis
Julis ( ar, جولس ''Jūlis'', he, ג'וּלִס ''G'ulis'') is a Druze village and local council in the Northern District of Israel. In it had a population of .
Etymology
According to local legend, the name is derived from "Julius," the na ...
, which ran parallel to the coastal highway.Khalidi, 1992, p. 119
History
Ceramics from theByzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
era have been found here.
Ottoman era
In 1838, in the late Ottoman era, ''el-Kaufakhah'' was noted as a place "in ruins or deserted."Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p.119
/ref> In 1882, the PEF's ''
Survey of Western Palestine
The PEF Survey of Palestine was a series of surveys carried out by the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) between 1872 and 1877 for the Survey of Western Palestine and in 1880 for the Survey of Eastern Palestine. The survey was carried out after the ...
'' (SWP) noted at ''Khurbet el Kofkhah'': "a large site. Rubble cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
s, a marble capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
, with acanthus leaves. Scattered stones and pottery."
Kawfakwa was founded in the late nineteenth century by Gaza city residents who came to cultivate the surrounding land. In its center was a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
that was well known in the region, built in the reign of the Ottoman sultan Abd al-Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to ...
(1876–1909).
British mandate era
In the1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divisi ...
, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, ''Kufakha'' had a population of 203 Muslims, increasing in the 1931 census to 317, still all Muslims, in 56 houses.Mills, 1932, p4
The village had an elementary school and some small shops. The villagers obtained water for domestic use from two
wells
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
*Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wells ...
inside the village. The land on the northern side of the village was planted with fruit trees, such as apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also ...
s, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
s, almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
s, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
s and fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
s. On the other sides of the village grain was grown.

 In the 1945 statistics Kawfakha had a population of 500 Muslims, with a total of 8,569
In the 1945 statistics Kawfakha had a population of 500 Muslims, with a total of 8,569 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; tr, dönüm; he, דונם), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount ...
s of land, according to an official land and population survey. Of this, a total of 97 dunums
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; tr, dönüm; he, דונם), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount ...
was irrigated or used for orchards, and 7,768 dunums (of public land) were allotted to cereals, while 41 dunams were built-up, public land.
1948 and after
During the1948 Arab-Israeli War
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
, the villagers of Kawfakha repeatedly asked to surrender, accept Jewish rule and be allowed to stay, all to no avail. Kawfakha, together with al-Muharraqa
Al-Muharraqa ( ar, المحرّقة) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located east of Gaza city. The village laid on rolling terrain on the southern coastal plain of Palestine, on a bend in the ''wadi''. It had an eleva ...
, was raided by the Palmach
The Palmach (Hebrew: , acronym for , ''Plugot Maḥatz'', "Strike Companies") was the elite fighting force of the Haganah, the underground army of the Yishuv (Jewish community) during the period of the British Mandate for Palestine. The Palmach ...
's Negev Brigade
The 12th Negev Brigade ( he, חטיבת הנגב, ''Hativat HaNegev'') is an Israeli reserve infantry brigade under the Sinai Division, that originally served in the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
History
Founding and organization
The brigade was fou ...
on May 27–28, and the inhabitants of both villages were expelled or driven out. On May 30, a ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' correspondent reported that the two villages had been captured.
Following the war the area was incorporated into the State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and the moshav
A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 an ...
of Nir Akiva
Nir Akiva ( he, נִיר עֲקִיבָא, ''lit.'' Akiva's Meadow) is a moshav in southern Israel. Located in the north-western Negev near Netivot and Nir Moshe and covering 1,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Merhavim Regional C ...
was established in 1953 on village lands, southwest of the village site.Khalidi, 1992, p. 120
According to Khalidi, by 1992 the village remaining structures on the village land were:
"Only the mosque remains, and it is used as a storehouse for animal fodder and as a horse stable. It is a stone structure with arched entrances and windows on all sides; its roof is topped by three shallow domes. The site, which contains piles of rubble and is overgrown with cactuses and other desert plants, has been fenced in and serves as a pasture. There is a citrus grove west of it, and grain is grown by Israeli farmers on part of the surrounding land."The village mosque was inspected in 1994, and found to be built of
ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruv ...
stones (approximately 0.2m x 0.4 m) with the corners emphasised by a slight offset. At the north-west corner there was a thick square minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ...
10–15 meters high with chamfered corners. There are three doorways on the north side, two of which lead into the prayer hall, whilst the east door leads into a separate room. At the time of the inspection, the mosque was used as a storehouse for a nearby farm ("Avi´s Ranch").Petersen, 2001, pp195
6.
See also
* Depopulated Palestinian locations in IsraelReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Palestine Remembered - Kawfakha
Kawfakha
Zochrot
Zochrot ( he, זוכרות; "Remembering"; ar, ذاكرات; "Memories") is an Israeli nonprofit organization founded in 2002. Based in Tel Aviv, its aim is to promote awareness of the Palestinian ''Nakba'' ("Catastrophe"), including the 1948 Pa ...
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 20IAA
from the
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center () is a leading Palestinian arts and culture organization that aims to create a pluralistic, critical liberating culture through research, query, and participation, and that provides an open space for the community ...
{{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War
Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
District of Gaza