kynodesme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A kynodesmē (, English translation: "dog tie") was a cord or string or sometimes a
A kynodesmē (, English translation: "dog tie") was a cord or string or sometimes a
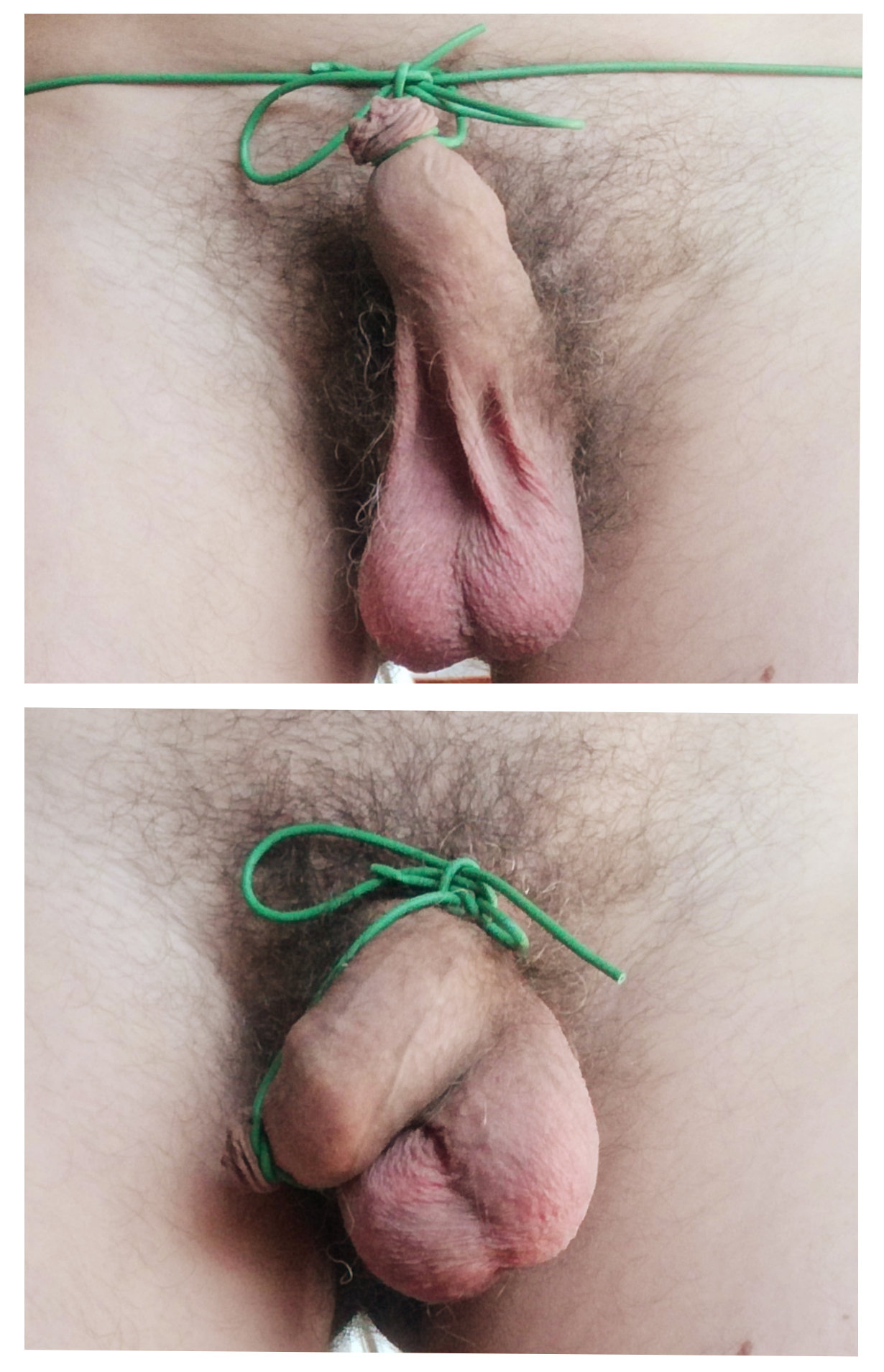 The public exposure of the penis head was regarded by the Greeks as dishonourable and shameful, something only seen in slaves and
The public exposure of the penis head was regarded by the Greeks as dishonourable and shameful, something only seen in slaves and
The Ideal Prepuce in Ancient Greece and Rome: Male Genital Aesthetics and Their Relation to ''Lipodermos'', Circumcision, Foreskin Restoration, and the ''Kynodesme''
''Bulletin of the History of Medicine'' 2001; 75:375–405. * * Ancient Greece Sport in ancient Greece Human penis Minimalist clothing Greek clothing {{AncientGreek-lang-stub
 A kynodesmē (, English translation: "dog tie") was a cord or string or sometimes a
A kynodesmē (, English translation: "dog tie") was a cord or string or sometimes a leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
strip that was worn primarily by athletes in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscan civiliza ...
to prevent the exposure of the glans penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual p ...
in public (considered to be ill-mannered) and to restrict untethered movement of the penis during sporting competition. It was tied tightly around the ''akroposthion,'' the most distal, tubular portion of the foreskin
In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the g ...
that extends beyond the glans. As depicted in Ancient Greek art the kynodesme was worn by some athletes, actors, poets, symposiasts and komasts. It was worn temporarily while in public and could be taken off and put back on at will. The remaining length of cord could either be attached to a waist band to pull the penis upward and expose the scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
, or tied around the base of the penis and scrotum so that the penis appeared to curl upwards.
Purpose
 The public exposure of the penis head was regarded by the Greeks as dishonourable and shameful, something only seen in slaves and
The public exposure of the penis head was regarded by the Greeks as dishonourable and shameful, something only seen in slaves and barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less c ...
. Modesty and decency demanded that men who showed themselves naked in a public setting, such as athletes or actors, must conceal their glans.
The usage of the kynodesme might have also helped to naturally elongate the foreskin, which was seen as desirable.Frederick M. Hodges, ''The Ideal Prepuce in Ancient Greece and Rome: Male Genital Aesthetics and Their Relation to Lipodermos, Circumcision, Foreskin Restoration, and the Kynodesme''. Bulletin of the History of Medicine, volume 57, p. 375-405
In Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman medical practice, the uncontrolled dispersing of semen was thought to weaken men, and was particularly thought to affect the quality of the masculine voice. In ancient Rome, this form of non-surgical infibulation
Infibulation is the ritual removal of the external female genitalia and the suturing of the vulva, a practice found mainly in northeastern Africa, particularly in Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan. The World Health Organization refer ...
might thus be used by singers as a regimen for preserving the voice.Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and ...
6.82, Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ), was a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century CE. He is the author of the collection of satirical poems known as the ''Satires''. The details of Juvenal's life ...
6.73, 379; J.P. Sullivan, ''Martial, the Unexpected Classic'' (Cambridge University Press, 1991), p. 189; Peter Schäfer, ''Judeophobia: Attitudes toward the Jews in the Ancient World'' (Harvard University Press, 1997), p. 101; Peter J. Ucko, "Penis Sheaths: A Comparative Study," in ''Material Culture: Critical Concepts in the Social Sciences'' (Routledge, 2004), p. 260.
In art
It is first alluded to in literature in the 5th century BC, in the partially preservedsatyr play
The satyr play is a form of Attic theatre performance related to both comedy and tragedy. It preserves theatrical elements of dialogue, actors speaking verse, a chorus that dances and sings, masks and costumes. Its relationship to tragedy is stro ...
''Theoroi '' by Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, Αἰσχύλος ; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek ...
. There is earlier evidence from the images of athletes on Ancient Greek pottery. The Kynodesme was also used by the Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
who called it a ''ligatura praeputii''. The Romans however preferred to use a ring known as a fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
, rather than a band, to conceal the glans.
See also
*Codpiece
A codpiece () is a triangular piece that attached to the front of men's hose, covering the fly. It may be held in place by ties or buttons. It was an important fashion item of European clothing during the 15th–16th centuries. In the modern era ...
(from Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
: ''cod'', meaning "scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
") – a covering flap or pouch that attaches to the front of men's trousers
Trousers (British English), slacks, or pants are an item of clothing worn from the waist to anywhere between the knees and the ankles, covering both legs separately (rather than with cloth extending across both legs as in robes, skirts, and dr ...
, enclosing the genital
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
area
* Koteka
The koteka, also referred to as a horim or penis gourd, is a penis sheath traditionally worn by native male inhabitants of some (mainly highland) ethnic groups in New Guinea, Indonesia to cover their penises. The koteka is normally made from a ...
– a penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do n ...
sheath traditionally worn by native male inhabitants of some ethnic groups in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
to cover their genitals
* Namba
is a district of Osaka, Japan. It is located in Chūō and Naniwa wards. Namba is regarded as the center of so-called ''Minami'' ("South") area of Osaka. Its name is one of variations on the former name of Osaka, '' Naniwa''. Namba is be ...
– a traditional penis sheath from Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of no ...
* A penile fibula is a ring, attached with a pin through the foreskin to fasten it above the glans penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual p ...
References
Sources
* Hodges FMThe Ideal Prepuce in Ancient Greece and Rome: Male Genital Aesthetics and Their Relation to ''Lipodermos'', Circumcision, Foreskin Restoration, and the ''Kynodesme''
''Bulletin of the History of Medicine'' 2001; 75:375–405. * * Ancient Greece Sport in ancient Greece Human penis Minimalist clothing Greek clothing {{AncientGreek-lang-stub