Kyiv Culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
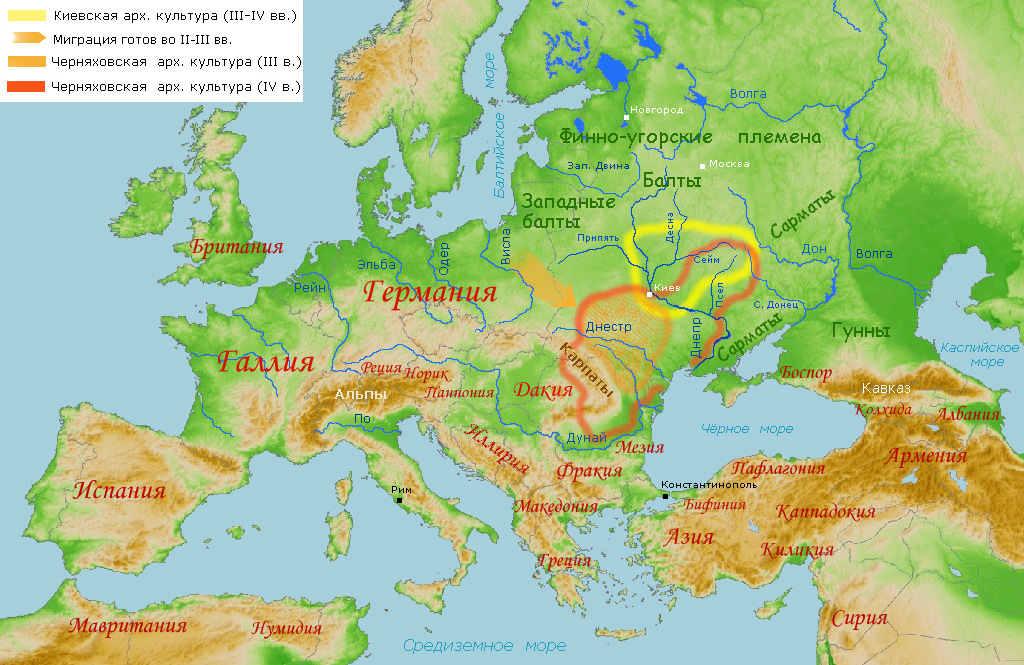 The Kyiv culture or Kiev culture is an
The Kyiv culture or Kiev culture is an Buko, Andrzej (2008). ''The Archeology of Early Medieval Poland. Discoveries-Hypotheses-Interpretations''. Brill.
There is, however, a substantial disagreement in the scientific community over the identity of the Kyiv culture's predecessors, with some historians and archaeologists tracing it directly from the
 The Kyiv culture or Kiev culture is an
The Kyiv culture or Kiev culture is an archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
dating from about the 3rd to 5th centuries, named after Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, the capital of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. It is widely considered to be the first identifiable Slavic archaeological culture. It was contemporaneous to (and located mostly just to the north of) the Chernyakhov culture
The Chernyakhov culture, Cherniakhiv culture or Sântana de Mureș—Chernyakhov culture was an archaeological culture that flourished between the 2nd and 5th centuries CE in a wide area of Eastern Europe, specifically in what is now Ukraine, Rom ...
.
Settlements are found mostly along river banks, frequently either on high cliffs or right by the edge of rivers. The dwellings are overwhelmingly of the semi-subterranean type (common among earlier Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
and Germanic and later among Slavic cultures), often square (about four by four meters), with an open hearth in a corner. Most villages consist of just a handful of dwellings. There is very little evidence of the division of labor, although in one case a village belonging to the Kiev culture was preparing thin strips of antlers to be further reworked into the well-known Gothic antler combs, in a nearby Chernyakhov culture village.
The descendants of the Kyiv culture — the Prague-Korchak, Penkovka and Kolochin cultures — established in the 5th century in Eastern Europe.There is, however, a substantial disagreement in the scientific community over the identity of the Kyiv culture's predecessors, with some historians and archaeologists tracing it directly from the
Milograd culture
The Milograd culture (also spelled Mylohrad, also known as Pidhirtsi culture on Ukrainian territory) is an archaeological culture, lasting from about the 7th century BC to the 1st century AD. Geographically, it corresponds to present day souther ...
, others, from the Chernoles culture
Chernoles culture or Black Forest cultureEllen D. Reeder, Esther Jacobson, Scythian gold: treasures from ancient Ukraine. San Antonio Museum of Art - 1999 - p. 352 (Чорноліська культура) is an Iron Age archaeological unit dati ...
(the Scythian farmers of Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
) through the Zarubintsy culture
The Zarubintsy or Zarubinets culture was a culture that, from the 3rd century BC until the 1st century AD, flourished in the area north of the Black Sea along the upper and middle Dnieper and Pripyat Rivers, stretching west towards the Southern B ...
, still others through both the Przeworsk culture
The Przeworsk culture () was an Iron Age material culture in the region of what is now Poland, that dates from the 3rd century BC to the 5th century AD. It takes its name from the town Przeworsk, near the village where the first artifacts wer ...
and the Zarubintsy culture.
References
{{reflist Archaeological cultures of Eastern Europe Iron Age cultures of Europe Archaeological cultures in Ukraine Archaeological cultures in Belarus Archaeological cultures in Russia Slavic archaeological cultures Goths Migration Period