Krestovsky island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Krestovsky Island (russian: Крестовский остров) is a 3.4 km2 island in
Krestovsky Island (russian: Крестовский остров) is a 3.4 km2 island in
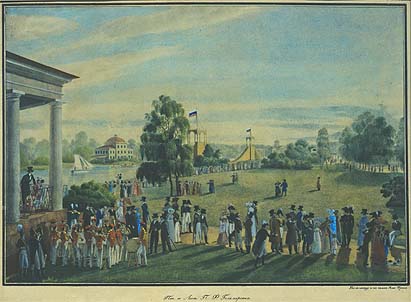 On Krestovsky island, many "first" Russian sports venues and activities were launched with Belosselsky-Belozersky active support. The Krestovsky tennis club "Lawn Tennis Club", (with the main efforts undertaken by the resident Scotsman Arthur MacPherson, whose sons were some of the first Russian tennis champions with George Vasilievich Bray, who is considered to have been the first Russian Champion. George was also the Treasurer of the Krestovsky Lawn Tennis Club; See the note at the bottom of this paragraph for more information) Belosselsky horse polo grounds, as well as a yacht club and a rowing club were launched here in late 19th century along with a clay pigeon shooting range; memoirs by well known socialites of the late 1900s (i.e. princess Orbeliani) mention also a basic golf links on the island; all prior to the 1917 Revolution.
The island was always a center for sports and recreation for the St. Petersburg residents. Prior to the revolution, it was also a unique gathering place and venue for the "high-society" active in sports, the military officers and foreign diplomats, who participated in the horse polo events organized by the Belosselsky-Belozerskys. As this sport was known to be a preferred sport of Englishmen at the time, the elder prince Belosselsky-Belozersky, Constantine Esperovich, became known as the "Angloman" for his keen interest in promoting this sport. His elder son, prince Sergei Constantinovich was one of the first Russian international players of polo and took part regularly in the annual events in England and France at Rugby, Paris Bagatelle, Deauville, Biarritz, Pau, etc. He organized many horse polo competitions on their Krestovsky island estate polo grounds, including international team events. Well known visiting and resident international players of the time included British Ambassador
On Krestovsky island, many "first" Russian sports venues and activities were launched with Belosselsky-Belozersky active support. The Krestovsky tennis club "Lawn Tennis Club", (with the main efforts undertaken by the resident Scotsman Arthur MacPherson, whose sons were some of the first Russian tennis champions with George Vasilievich Bray, who is considered to have been the first Russian Champion. George was also the Treasurer of the Krestovsky Lawn Tennis Club; See the note at the bottom of this paragraph for more information) Belosselsky horse polo grounds, as well as a yacht club and a rowing club were launched here in late 19th century along with a clay pigeon shooting range; memoirs by well known socialites of the late 1900s (i.e. princess Orbeliani) mention also a basic golf links on the island; all prior to the 1917 Revolution.
The island was always a center for sports and recreation for the St. Petersburg residents. Prior to the revolution, it was also a unique gathering place and venue for the "high-society" active in sports, the military officers and foreign diplomats, who participated in the horse polo events organized by the Belosselsky-Belozerskys. As this sport was known to be a preferred sport of Englishmen at the time, the elder prince Belosselsky-Belozersky, Constantine Esperovich, became known as the "Angloman" for his keen interest in promoting this sport. His elder son, prince Sergei Constantinovich was one of the first Russian international players of polo and took part regularly in the annual events in England and France at Rugby, Paris Bagatelle, Deauville, Biarritz, Pau, etc. He organized many horse polo competitions on their Krestovsky island estate polo grounds, including international team events. Well known visiting and resident international players of the time included British Ambassador  For sailing, the Krestovsky island was an ideal venue as it was here that the first Russian yacht clubs, "The Nevsky Flot" was launched by no other than Peter the Great in 1718. The club is still active, although it has undergone several episodes of transformations, but is located on the Martynova Embankment at the North shore of Krestovsky Island.
During the Soviet times, as well, the Krestovsky island was the base of many of the most successful sport and rowing clubs; among other, Energia and Krasnoe Znamia. Some fourteen Olympic champions came from this tradition. Founded in 1889 and active still on Krestovsky Island during the early 1990s as Znamia, the club produced Olympic rowing champions Y. Tsykalov, V. Boreiko, O.Golovanov, and A. Klepikov, as well as three-time Olympic kayaking/canoeing champion L. Pinaeva. In addition the club produced several World and European champions. A tradition started after WWII by the Krestovsky rowers is still alive today. The autumn meet in rowing they started became an international competition and continues as such today-every first Sunday of October.
The island was also home to the Leningrad division of the "people's' committee on internal affairs (NKVD)" sports and football club "Dinamo". Dinamo's athletic fields and grounds as well as clubhouse in the "functional" architectural style of the 1930s is the area due east of the Belosselsky-Belozelsky rebuilt manor-house. These cover still a large area despite recent encroaching business and apartment/housing projects.
Today, Krestovsky island continues its tradition as a base for sports and recreation and is still the home to half a dozen tennis clubs, several boating and rowing clubs as well as the site of the new stadium of Zenit, officially known today as "Gazprom Stadion" replacing the Kirov stadium, which was built after the Second World War and which survived until the 1990s at the western spit of the island.
Many contemporary Russian tennis players have come from the Krestovsky island tennis tradition of Russian champions, started by the Scot MacPherson, his sons as well as
For sailing, the Krestovsky island was an ideal venue as it was here that the first Russian yacht clubs, "The Nevsky Flot" was launched by no other than Peter the Great in 1718. The club is still active, although it has undergone several episodes of transformations, but is located on the Martynova Embankment at the North shore of Krestovsky Island.
During the Soviet times, as well, the Krestovsky island was the base of many of the most successful sport and rowing clubs; among other, Energia and Krasnoe Znamia. Some fourteen Olympic champions came from this tradition. Founded in 1889 and active still on Krestovsky Island during the early 1990s as Znamia, the club produced Olympic rowing champions Y. Tsykalov, V. Boreiko, O.Golovanov, and A. Klepikov, as well as three-time Olympic kayaking/canoeing champion L. Pinaeva. In addition the club produced several World and European champions. A tradition started after WWII by the Krestovsky rowers is still alive today. The autumn meet in rowing they started became an international competition and continues as such today-every first Sunday of October.
The island was also home to the Leningrad division of the "people's' committee on internal affairs (NKVD)" sports and football club "Dinamo". Dinamo's athletic fields and grounds as well as clubhouse in the "functional" architectural style of the 1930s is the area due east of the Belosselsky-Belozelsky rebuilt manor-house. These cover still a large area despite recent encroaching business and apartment/housing projects.
Today, Krestovsky island continues its tradition as a base for sports and recreation and is still the home to half a dozen tennis clubs, several boating and rowing clubs as well as the site of the new stadium of Zenit, officially known today as "Gazprom Stadion" replacing the Kirov stadium, which was built after the Second World War and which survived until the 1990s at the western spit of the island.
Many contemporary Russian tennis players have come from the Krestovsky island tennis tradition of Russian champions, started by the Scot MacPherson, his sons as well as
 There was a duel between Prince Nikolai Yusupov, Count Sumarakoff-Elston, and Count Arvid Manteuffel, over Marina von Hayden, the latter's wife. Yusupov had caused a great open scandal by having an affair with the wife of the Imperial Horse Guards' officer. It seems
There was a duel between Prince Nikolai Yusupov, Count Sumarakoff-Elston, and Count Arvid Manteuffel, over Marina von Hayden, the latter's wife. Yusupov had caused a great open scandal by having an affair with the wife of the Imperial Horse Guards' officer. It seems
 On 1 January 1917 (
On 1 January 1917 (
Krestovsky Island
@ ''Encyclopaedia of Saint Petersburg'' {{Authority control Islands of Saint Petersburg River islands of Russia
 Krestovsky Island (russian: Крестовский остров) is a 3.4 km2 island in
Krestovsky Island (russian: Крестовский остров) is a 3.4 km2 island in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, between several tributaries of the Neva
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it ...
: the Srednyaya Nevka, the Malaya Nevka
The Little Nevka or Malaya Nevka (russian: Ма́лая Не́вка) is the southern distributary of the Great Nevka. The Great Nevka splits into Little Nevka (the southern armlet) and Middle Nevka (the northern armlet) near the Kamenny Isla ...
and the Krestovka. The island is served by the Krestovsky Ostrov
Krestovsky Ostrov (russian: Крестовский остров) is a station on the Frunzensko-Primorskaya Line of Saint Petersburg Metro, opened on September 3, 1999. It should have been opened earlier but the opening was postponed due to delays ...
station of Saint Petersburg Metro
The Saint Petersburg Metro (russian: links=no, Петербургский метрополитен, Peterburgskiy metropoliten) is a rapid transit system in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Construction began in early 1941, but was put on hold due to Wor ...
. Until recently, the western part of the island was occupied by the Maritime Victory Park
Maritime Victory Park (russian: Приморский парк Победы) is a municipal park on Krestovsky Island in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It was opened in 1945 to commemorate the Allied victory over Nazi Germany
in World War II. Today, it ...
, where the international Goodwill Games
The Goodwill Games were an international sports competition created by Ted Turner in reaction to the political troubles surrounding the Olympic Games of the 1980s. In 1979, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan caused the United States and other ...
of sports and athletics competition took place in 1994, which was the first large scale post-Soviet Union international event in Russia. A new stadium, Gazprom Arena
Krestovsky Stadium, known as Gazprom Arena for sponsorship reasons (russian: «Газпром Арена»), is a retractable roof stadium with a retractable pitch in the western portion of Krestovsky Island in Saint Petersburg, Russia, which s ...
, is located where Kirov Stadium
Kirov may refer to:
* Sergei Kirov (1886–1934), Soviet Bolshevik leader in Leningrad after whom all other entries are named
* Kirov (surname)
Places Armenia
*Amrakits or Kirov
*Taperakan or Kirov
Azerbaijan
* Kirov, Baku
* Kirov, Lankaran
* Kir ...
was. The stadium serves as home for FC Zenit Saint Petersburg
Football Club Zenit (russian: link=no, Футбольный клуб «Зенит» ), also known as Zenit Saint Petersburg or simply Zenit, is a Russian professional association football, football club based in Saint Petersburg. Founded in ...
.
Meanwhile, the eastern part of this beautiful St Petersburg island, has seen slow but steady urbanization since the early 1900s, which has slowly changed its parkland nature. Recently there has been even more pressure from today's "nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal naming conventions, conventions of everyday speech to the i ...
" to locate top-end housing projects and high-prestige homes here - a long-time tendency that also continues today, since historically the island was always owned by families who were close to and favourites of the Tzars/"powers-to-be" and who served them well.
History
The history of Krestovsky island and its near past up to the early 1900s is closely tied with the owners of the island, the Belosselsky-Belozersky family, and the way they developed and used the island. In the 19th through early 20th centuries the island belonged to theBelosselsky-Belozersky family
The Belosselsky-Belozersky princely and Rurikid family is an aristocratic Russian family that descends in a direct male line from the Earliest Kievan Rus rulers and later of the medieval sovereigns of the Principality of Beloozero.
Origins
The f ...
. Aided by the infusion of wealth from the fortune of his second wife Anna Grigorievna (ne'e Kozitskaya and the wealth through her mother's Myasnikov family from Siberian mining and metals fortunes) Prince Alexander Mikhailovich Belosselsky-Belozersky acquired the island in 1803. Previously it had belonged to the courtier Count Cyril Razumovsky and his family. During the mid-1800s the Belosselskys reconstructed the original Razumovsky stone manor house, which was located at the southern shore of the island using the well-known architect A.I. Stackenschneider for the works. This house served the family as their summer retreat for years to come.
In the 1880s after having sold their famous Beloselsky-Belozersky Palace
Beloselsky Belozersky Palace (Russian: Дворе́ц Белосе́льских-Белозе́рских; also known before the Revolution as the Palace of the Grand Duchess Elizabeth Fyodorovna, the Sergei Palace, and the Dmitry Palace) is a Ne ...
(the pink palace at No. 41 Nevsky Prospect
Nevsky Prospect ( rus, Не́вский проспе́кт, r=Nevsky Prospekt, p=ˈnʲɛfskʲɪj prɐˈspʲɛkt) is the main street (high street) in the federal city of St. Petersburg in Russia. It takes its name from the Alexander Nevsky La ...
at the Anichkov Bridge
The Anichkov Bridge (Russian: ''Аничков мост'', ''Anichkov Most'') is the oldest and most famous bridge across the Fontanka River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The current bridge, built in 1841-42 and reconstructed in 1906-08, combines ...
) to Grand Duke Sergei Alexandrovich Romanov (Nicholas II's uncle) the Belosselsky-Belozersky family moved to live on their Krestovsky island and the estate at the southern side of the island, now year-round. They reconstructed the original Stackenschneider designed manorial building into a small palace (using the contemporary court architect Rastrelli Rastrelli may refer to the following persons:
* Antonio Rastrelli (politician) (1927–2019), Italian politician
* Antonio Rastrelli (born 1945), Italian Olympic swimmer
* Carlo Bartolomeo Rastrelli (1675–1744), Italian sculptor who emigra ...
for its design). Popularly, this building was known as the "Datcha of the Belosselskys".
Many street names on Krestovsky island today still remind of and reflect the Belosselsky-Belozersky family having owned and occupied the Krestovsky island: e.g. ''Olgina'', ''Eleninskaya'', ''Esperova'', ''Konstantinova'' streets have survived the change of times and herald the names of some of the Belosselsky-Belozersky immediate family members who lived on the island at the end of the Tsarist period until the 1917 Russian Revolution (Olga's street, Elena's street, Esper's street, Konstantin's street, respectively). Prior to the Revolution the main north to south street leading to the Belosselsky-Belozersky manor house was named ''Belosselsky Prospect'' (the Belosselsky avenue/view). After the Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, the street name was changed to ''Riukhina'' street (which runs South towards the edge of Malaya Nevka
The Little Nevka or Malaya Nevka (russian: Ма́лая Не́вка) is the southern distributary of the Great Nevka. The Great Nevka splits into Little Nevka (the southern armlet) and Middle Nevka (the northern armlet) near the Kamenny Isla ...
from the new Metro station on the island). The St Petersburg city council has approved and implemented, at the end of June 2011, the renaming of the lane one street over to the East and South of the Riukhina to "Belosselsky Pereulok" (the Belosselsky Lane), bringing back a relevant piece of the Krestovsky history and improving the awareness of this important period of the islands history.
However, the ''Alexandrovskiy'' avenue (avenue named for the first Belosselsky owner of the island, Prince Alexander Mikhailovich Belosselsky), ''Nadezhdinskaya'' (wife of Constantine Esperovich), ''Sergievskaya'', ''Andrievskaya'' (sons of Sergei Konstantinovich), ''Mariinsky,'' (daughter of Konstantin Esperovich) as well as the ''Nikolayevsky'' and ''Vladimirsky'' streets (named for the Tsar and the Romanov Grand Duke respectively under whom some Belosselskys served as aide de camp during the last years of the Tsarist era), these all have been victims of urbanisation and disappeared under apartment blocks and Dynamo sports facilities built in the 1950s and since.
Two interesting streets and their names ''Yuriyuzanskaya'' and ''Vyazova'' still remain, reflecting two of the three main areas of metals and mining and the ironworks in the Urals, which were properties in Bashkiria/Bashkortostan (between Ufa and Cheliabinsk) owned by the Belosselsky family, (these also as a legacy of the marriage of Alexander Mikhailovich Belosselsky-Belozersky to Anna Grigorievna Kozitsky and her inheritance from Myasnikovs) and from where they drew some of their enormous wealth still during the end of the 19th century. The third such street, ''Katavskaya'' street, does not exist any longer. ''Katavskaya'' street was named for the ironworks of Ust-Katav and Katav-Ivanovsk, which were major producers of metals and metallurgy for the Belosselskys' enterprises. This street used to run parallel to the Belosselsky Prospect, immediately east of it and on the southern side of ''Morskoy'' prospect and has since the 1950s building of apartment "massifs" (blocks) been overtaken by these and "Dinamo" club's sporting venues and fields. The current ''Dinamo Prospect'' has replaced the former ''Alexandrovskii Prospect'' as the avenue leading from the ''Krestovsky Most'' (Bridge) in the eastern bridge-led entry to the island toward the Belosselsky-Belozersky summer palace/manor house, formerly the main conduit to the manor house but now blocked by the Dinamo sports fields and other adjacent constructed buildings.
Finally, the ''Novorossiskaya'' street, which also was overtaken by these same buildings and sports fields, ran parallel to the ''Katavskaya'' street to its east. This street was named in honor of Sergei Constantinovich being the commander of His Majesty's Third Dragoons of Novorossiisk Dragoons' Regiment. The same fate has fallen to the southwestern embankment of the island, which was named ''Amerikanskaya ulitsa'' (American street) in honor of the nationality of Sergey Constantinovich' wife Suzy Belosselsky-Belozersky ne'e Susan Tucker-Whittier (daughter of `nj7US Army General Charles Whittier).
Early sports venue for tennis, polo, sailing, rowing and others
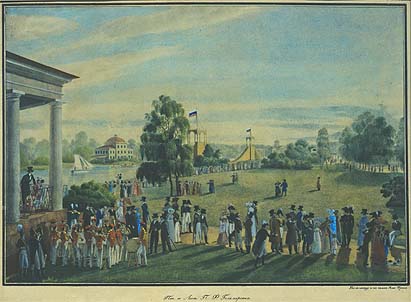 On Krestovsky island, many "first" Russian sports venues and activities were launched with Belosselsky-Belozersky active support. The Krestovsky tennis club "Lawn Tennis Club", (with the main efforts undertaken by the resident Scotsman Arthur MacPherson, whose sons were some of the first Russian tennis champions with George Vasilievich Bray, who is considered to have been the first Russian Champion. George was also the Treasurer of the Krestovsky Lawn Tennis Club; See the note at the bottom of this paragraph for more information) Belosselsky horse polo grounds, as well as a yacht club and a rowing club were launched here in late 19th century along with a clay pigeon shooting range; memoirs by well known socialites of the late 1900s (i.e. princess Orbeliani) mention also a basic golf links on the island; all prior to the 1917 Revolution.
The island was always a center for sports and recreation for the St. Petersburg residents. Prior to the revolution, it was also a unique gathering place and venue for the "high-society" active in sports, the military officers and foreign diplomats, who participated in the horse polo events organized by the Belosselsky-Belozerskys. As this sport was known to be a preferred sport of Englishmen at the time, the elder prince Belosselsky-Belozersky, Constantine Esperovich, became known as the "Angloman" for his keen interest in promoting this sport. His elder son, prince Sergei Constantinovich was one of the first Russian international players of polo and took part regularly in the annual events in England and France at Rugby, Paris Bagatelle, Deauville, Biarritz, Pau, etc. He organized many horse polo competitions on their Krestovsky island estate polo grounds, including international team events. Well known visiting and resident international players of the time included British Ambassador
On Krestovsky island, many "first" Russian sports venues and activities were launched with Belosselsky-Belozersky active support. The Krestovsky tennis club "Lawn Tennis Club", (with the main efforts undertaken by the resident Scotsman Arthur MacPherson, whose sons were some of the first Russian tennis champions with George Vasilievich Bray, who is considered to have been the first Russian Champion. George was also the Treasurer of the Krestovsky Lawn Tennis Club; See the note at the bottom of this paragraph for more information) Belosselsky horse polo grounds, as well as a yacht club and a rowing club were launched here in late 19th century along with a clay pigeon shooting range; memoirs by well known socialites of the late 1900s (i.e. princess Orbeliani) mention also a basic golf links on the island; all prior to the 1917 Revolution.
The island was always a center for sports and recreation for the St. Petersburg residents. Prior to the revolution, it was also a unique gathering place and venue for the "high-society" active in sports, the military officers and foreign diplomats, who participated in the horse polo events organized by the Belosselsky-Belozerskys. As this sport was known to be a preferred sport of Englishmen at the time, the elder prince Belosselsky-Belozersky, Constantine Esperovich, became known as the "Angloman" for his keen interest in promoting this sport. His elder son, prince Sergei Constantinovich was one of the first Russian international players of polo and took part regularly in the annual events in England and France at Rugby, Paris Bagatelle, Deauville, Biarritz, Pau, etc. He organized many horse polo competitions on their Krestovsky island estate polo grounds, including international team events. Well known visiting and resident international players of the time included British Ambassador Charles Hardinge
Charles Hardinge, 1st Baron Hardinge of Penshurst, (20 June 1858 – 2 August 1944) was a British diplomat and statesman who served as Viceroy and Governor-General of India from 1910 to 1916.
Background and education
Hardinge was the second ...
, 1st Baron Hardinge of Penshurst (later Viceroy of India), British embassy secretaries Beaumont, Sperling, American Ambassador George von L. Meyer
George von Lengerke Meyer (June 24, 1858 – March 9, 1918) was a Massachusetts businessman and politician who served in the Massachusetts House of Representatives, as United States ambassador to Italy and Russia, as United States Postmaster Gener ...
and Chargé d'Affaires Spencer Eddy were among the company of the first local Russian players, who in addition to the Belosselskys, were Grand Duke Boris Vladimirovich of Russia
Grand Duke Boris Vladimirovich of Russia (russian: Борис Владимирович; 24 November 1877 – 9 November 1943) was a son of Grand Duke Vladimir Alexandrovich of Russia, a grandson of Tsar Alexander II of Russia and a first cousin ...
, Grand Duke Dmitri Pavlovich of Russia
Grand Duke Dmitri Pavlovich of Russia (russian: Великий Князь Дмитрий Павлович; 18 September 1891 – 5 March 1942) was a son of Grand Duke Paul Alexandrovich of Russia, a grandson of Tsar Alexander II of Russia and a ...
, Prince Michael Cantacuzène-Speranski, Count Kinsky, Messrs. Mouravi and Grabovski. A special frequent player was Sergei Constantinovich's fellow general, later a Finnish Marshal, Carl Gustaf Mannerheim
Carl Gustaf Mannerheim may refer to:
* Carl Gustaf Mannerheim (naturalist)
Count Carl Gustaf Mannerheim (10 August 1797 – 9 October 1854) was a Finnish entomologist and governor of the Viipuri province in the Grand Duchy of Finland.
Caree ...
, who also was part of the inauguration competition of the Krestovsky polo field, in the summer of 1897.
Sergei Constantinovich was also a founder and sponsor of an early St. Petersburg athletics club named "Sport", which was located on Krestovsky island. His activities led to him being invited to become a Russian representative to the International Olympic Committee (IOC). This made him the second all-time Russian and 28th overall representative to this venerable and still very active key international sports body. Prince Sergei acceded the IOC together with count Ribaupierre, after Major-General A.D. Butovsky and before prince Troubetzkoy. In capacity of the IOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
member, prince Sergei participated in the organizational committee of the 1900 Paris Olympic games and took part in equestrian events.
The younger son of prince Constantin, prince Esper Constantinovich Beloselsky-Belozersky was an avid sailor and won an Olympic bronze medal in sailing (10 meter class) for Russia in the 1912 Stockholm Olympics as helmsman of the "Gallia II".  For sailing, the Krestovsky island was an ideal venue as it was here that the first Russian yacht clubs, "The Nevsky Flot" was launched by no other than Peter the Great in 1718. The club is still active, although it has undergone several episodes of transformations, but is located on the Martynova Embankment at the North shore of Krestovsky Island.
During the Soviet times, as well, the Krestovsky island was the base of many of the most successful sport and rowing clubs; among other, Energia and Krasnoe Znamia. Some fourteen Olympic champions came from this tradition. Founded in 1889 and active still on Krestovsky Island during the early 1990s as Znamia, the club produced Olympic rowing champions Y. Tsykalov, V. Boreiko, O.Golovanov, and A. Klepikov, as well as three-time Olympic kayaking/canoeing champion L. Pinaeva. In addition the club produced several World and European champions. A tradition started after WWII by the Krestovsky rowers is still alive today. The autumn meet in rowing they started became an international competition and continues as such today-every first Sunday of October.
The island was also home to the Leningrad division of the "people's' committee on internal affairs (NKVD)" sports and football club "Dinamo". Dinamo's athletic fields and grounds as well as clubhouse in the "functional" architectural style of the 1930s is the area due east of the Belosselsky-Belozelsky rebuilt manor-house. These cover still a large area despite recent encroaching business and apartment/housing projects.
Today, Krestovsky island continues its tradition as a base for sports and recreation and is still the home to half a dozen tennis clubs, several boating and rowing clubs as well as the site of the new stadium of Zenit, officially known today as "Gazprom Stadion" replacing the Kirov stadium, which was built after the Second World War and which survived until the 1990s at the western spit of the island.
Many contemporary Russian tennis players have come from the Krestovsky island tennis tradition of Russian champions, started by the Scot MacPherson, his sons as well as
For sailing, the Krestovsky island was an ideal venue as it was here that the first Russian yacht clubs, "The Nevsky Flot" was launched by no other than Peter the Great in 1718. The club is still active, although it has undergone several episodes of transformations, but is located on the Martynova Embankment at the North shore of Krestovsky Island.
During the Soviet times, as well, the Krestovsky island was the base of many of the most successful sport and rowing clubs; among other, Energia and Krasnoe Znamia. Some fourteen Olympic champions came from this tradition. Founded in 1889 and active still on Krestovsky Island during the early 1990s as Znamia, the club produced Olympic rowing champions Y. Tsykalov, V. Boreiko, O.Golovanov, and A. Klepikov, as well as three-time Olympic kayaking/canoeing champion L. Pinaeva. In addition the club produced several World and European champions. A tradition started after WWII by the Krestovsky rowers is still alive today. The autumn meet in rowing they started became an international competition and continues as such today-every first Sunday of October.
The island was also home to the Leningrad division of the "people's' committee on internal affairs (NKVD)" sports and football club "Dinamo". Dinamo's athletic fields and grounds as well as clubhouse in the "functional" architectural style of the 1930s is the area due east of the Belosselsky-Belozelsky rebuilt manor-house. These cover still a large area despite recent encroaching business and apartment/housing projects.
Today, Krestovsky island continues its tradition as a base for sports and recreation and is still the home to half a dozen tennis clubs, several boating and rowing clubs as well as the site of the new stadium of Zenit, officially known today as "Gazprom Stadion" replacing the Kirov stadium, which was built after the Second World War and which survived until the 1990s at the western spit of the island.
Many contemporary Russian tennis players have come from the Krestovsky island tennis tradition of Russian champions, started by the Scot MacPherson, his sons as well as Mikhail Sumarokov-Elston
Count Mikhail Nikolayevich Sumarokov-Elston ( rus, Михаил Николаевич Сумароков-Эльстон, p=mʲɪxɐˈil nʲɪkɐˈlaɪvʲɪtɕ sʊmɐˈrokəf ˈelʲstən french: link=no, Michel de Soumarokoff-Elston; 1893 or 18943 ...
and George Bray in the late 19th century. The best known was Swetlana Kuznetsova
Although the island has changed significantly since the Russian Revolution in terms of its land use, even more so during the past decades, there is still the dominant presence of sports on Krestovsky.
Belosselsky-Belozersky residence
Today, the Belosselsky-Belozersky residence on Krestovsky island has been reconstructed at the same location where it stood until the late 1950s (the original structure was badly damaged during the nearly 900-day siege of Leningrad, from shelling during World War II; it was repaired and used for various purposes, but was demolished finally around 1956). The rebuilt "Datcha" is true to the original architectural drawings but boasts all modern conveniences indoors, such as elevators, etc. It has been put on the market for sale recently. Meanwhile, the only original structures which remain of the Belosselsky-Belozersky era to these days are some horse stables on the now Riukhina street, present Belosselsky Pereulok/Lane and the still beautiful landscaped park with a small pond and walkways around it adjacent on the north-western and western side of the area where the Belosselsky-Belozersky house stood and now stands again. There is also the unique "accent" piece of the estate remaining by the edge of the water, of theMalaya Nevka
The Little Nevka or Malaya Nevka (russian: Ма́лая Не́вка) is the southern distributary of the Great Nevka. The Great Nevka splits into Little Nevka (the southern armlet) and Middle Nevka (the northern armlet) near the Kamenny Isla ...
, due south of the property (and the rebuilt house). This is a beautiful dark rose colored granite stone structure, holding a bench circular steps enveloping the structure and leading to the water's edge, forming a landing for boats and offering a calm venue to view the Southern exposure from the estate. The structure, sitting under the shade of oak and linden trees, was draped with a beautiful wrought iron and bronze balustrade (original design of this beautiful structure was by a Swiss architect).
Duel on Krestovsky Island
 There was a duel between Prince Nikolai Yusupov, Count Sumarakoff-Elston, and Count Arvid Manteuffel, over Marina von Hayden, the latter's wife. Yusupov had caused a great open scandal by having an affair with the wife of the Imperial Horse Guards' officer. It seems
There was a duel between Prince Nikolai Yusupov, Count Sumarakoff-Elston, and Count Arvid Manteuffel, over Marina von Hayden, the latter's wife. Yusupov had caused a great open scandal by having an affair with the wife of the Imperial Horse Guards' officer. It seems Felix Yusupov
Prince Felix Felixovich Yusupov, Count Sumarokov-Elston (russian: Князь Фе́ликс Фе́ликсович Юсу́пов, Граф Сумаро́ков-Эльстон, Knyaz' Féliks Féliksovich Yusúpov, Graf Sumarókov-El'ston; – ...
, his younger brother, had organized their first meeting.
The deadly encounter took place at dawn on July 5, 1908, when Count Manteuffel and Prince Yusupov met in a duel on the Krestovsky park land grounds of the estate owned by Belosselsky-Belozersky family
The Belosselsky-Belozersky princely and Rurikid family is an aristocratic Russian family that descends in a direct male line from the Earliest Kievan Rus rulers and later of the medieval sovereigns of the Principality of Beloozero.
Origins
The f ...
, at the time Constantin Esperovich.
The parties and their seconds met as agreed at dawn on the 5th of July 1908. Nikolai Yusupov was mortally wounded by the second round of shots and died.
Rasputin
 On 1 January 1917 (
On 1 January 1917 (Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, this is the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries between 158 ...
) the corpse of Grigory Rasputin
Grigori Yefimovich Rasputin (; rus, links=no, Григорий Ефимович Распутин ; – ) was a Russian mystic and self-proclaimed holy man who befriended the family of Nicholas II, the last Emperor of Russia, thus ga ...
was found close to the Bolshoy Petrovsky Bridge
The Great or Bolshoi Petrovsky bridge is a bridge across Little Nevka in St. Petersburg, Russia, connecting Petrovsky Island with Krestovsky Island and passing over a small nameless islet on Little Nevka. It is very near the mouth of the river ...
, off Krestovsky Island. From Maurice Paleologue Maurice may refer to:
People
*Saint Maurice (died 287), Roman legionary and Christian martyr
*Maurice (emperor) or Flavius Mauricius Tiberius Augustus (539–602), Byzantine emperor
* Maurice (bishop of London) (died 1107), Lord Chancellor and L ...
's diary who was the last French Ambassador to Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
(the description is often questioned as being a historically correct description of the event...).
References
Sources
*"Dvorets Belosselsky-Belozersky", Maria Petrovna Zeliadt, Beloje i Zarnoje, St Petersburg 1996. *Letter of V.N. Soloviev, Director of Teaching-Sports Center "Znamia", 18.02.1992, No. 13. licensed under "Leningrad oblast counsel of professional unions", where solicitation made for reconstruction of Belosselsky-Belozersky "datcha" according to drawings from year 1954 (at an estimated cost of 150-200 million roubles (of 1992 value)). Letter also lists "Znamia" center as one of the oldest for Russian rowing sports (100 years in 1989) and the referenced champions from the club (refers to letter act No 5/1807 of 25.04.1990 and letter of management of "Gosinspektia" regarding conservation of "pamietnikow" (monuments/memorials) No 7/721 of 14.03. 1990). *(In Russian) "Dacha Belosselskikh-Belozerskikh na Krestovskom Ostrove, Istoricheskaya Spravka", Sostavitel, Zorina A.M., Sankt Peterburg, 1991. (Describes Krestovsky island and history of the ownership of Krestovsky island, the buildings, etc.). *(In Russian) "Kirovskie ostrova" (Kirov Islands), H.D. Sintsov, Leningrad 1937. *(In Russian) "Parki Pobedi" (Victory Parks), V.I. Markov, Leningrad, 1956 and 1962. *(In Russian) "Nevskii ostrova" (Neva river islands), V.A. Vitjazev, Leningrad, 1986. *"Квартальный надзиратель", St. Petersburg, 2005, 2007; Article, ("Усадьба Белосельских-Белозерских станет отелем"). *"POLO", von Heinrich Hasperg jr., Chevalier Verlag, 2010, Beatrice Tiple, Aachen. Reprint of 1907 original, (Neu editierter Nachdruck der Ausgabe 1907, erschienen bei Grethlein & Co.). Printed in Germany. . *"MODERN POLO" by CAPTAIN E. D. MILLER, D.S.O, edited by M. H. HAYES, (F.R.C.V.S.) author of "Points of the Horse", "Illustrated Horse-breaking", "Veterinary Notes for Horse Owners", "Riding and Hunting", etc. SECOND EDITION, REVISED AND ENLARGED. LONDON : HURST AND BLACKETT, LIMITED, NEW YORK : CHARLES SCRIBNER'S SONS, 1902 (References to early Russian polo; Belosselsky polo grounds at Krestovsky, Sergei Konstantinovich Belosselsky as an international player; Belosselsky polo pony by the name of "Negress"). *"In the Name of Russia", Russia Abroad Publishing House, New York 1965. *"Memoirs of Prince Sergei Sergeivich Belosselsky-Belozersky", Sergei Sergeivich Belosselsky-Belozersky, edited by Marvin Lyons; Jacques Ferrand, Paris 1989. *"Killed in a Duel", Article in "New York Times", Published: July 6, 1908. *"His brother's keeper" by Gretchen Haskin, Part 2, Originally published in Atlantis Magazine, volume 2, issue 4, 2000. (Recounts and annotates the information regarding the duel between Manteuffel and Sumarakoff-Elston). *"THE 1900 OLYMPIC GAMES", by Bill Mallon; (RESULTS OF THE EARLY MODERN OLYMPICS), Jefferson, North Carolina, and London. . McFarland & Company, Inc., Publishers (references to Sergei Sergeievich Belosselsky participation into 1900 Paris Olympic Games' organisational committee as representative of Russia to the IOC). *"Guide to the Great Siberian Railway", Ministry of Ways and Communication. Edited by A.I. Dmitriev-Mamonov and A.F. Zdziarsky,(English translation by Miss L. Kukol-Yasnopolsky; Revised by John Marshall). St. Petersburg, Artistic Printing Society, 1900 (pp. 100–101 ref. Belosselsky-Belozersky metal, ironworks of Ust-Katav, Vyazovaya, Katav-Ivanovsk and Yuriuzan).External links
Krestovsky Island
@ ''Encyclopaedia of Saint Petersburg'' {{Authority control Islands of Saint Petersburg River islands of Russia