Knights Of The Golden Circle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
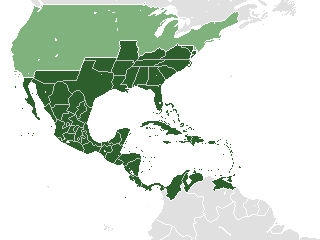
 The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a
The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a
 Hounded by creditors, Bickley left Cincinnati in the late 1850s and traveled through the East and South, promoting an armed expedition to Mexico. The group's original goal was to provide a force to colonize the northern part of Mexico and the
Hounded by creditors, Bickley left Cincinnati in the late 1850s and traveled through the East and South, promoting an armed expedition to Mexico. The group's original goal was to provide a force to colonize the northern part of Mexico and the
''An Authentic Exposition of the “K.G.C.” “Knights of the Golden Circle,” or, A History of Secession from 1834 to 1861, by A Member of the Order'' (Indianapolis, Indiana: C. O. Perrine, Publisher, 1861).
* Donald S. Frazier, ''Blood & Treasure: Confederate Empire in the Southwest'' (College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 1996). * Warren Getler and Bob Brewer, ''Rebel Gold: One Man’s Quest to Crack the Code Behind the Secret Treasure of the Confederacy'' (New York: Simon & Schuster, 2004). * Dion Haco, ed., ''The Private Journal and Diary of John H. Surratt, The Conspirator'' (New York: Frederic A. Brady, Publisher, 1866). * James D. Horan, ''Confederate Agent: A Discovery in History'' (New York: Crown Publishers, Inc., 1954). * Jesse Lee James, ''Jesse James and the Lost Cause'' (New York: Pageant Press, 1961). * Jack Myers, ''Knights' Gold'' (CreateSpace Independent Publishing, 2016).
Sons of Liberty (American Civil War)
– Ohio History Central
Joseph Holt, ''Report of the Judge Advocate General on “The Order of American Knights,” alias "The Sons of Liberty." A Western Conspiracy in aid of the Southern Rebellion'' (Washington, D.C.: Union Congressional Committee, 1864).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Knights Of The Golden Circle 1854 establishments in Ohio 1860 in Central America 1860s in Central America 1860s in politics 1860s in the Caribbean 19th century in Central America 19th century in the Caribbean American Civil War political groups American proslavery activists Bleeding Kansas California in the American Civil War Expansion of slavery in the United States History of United States expansionism Indiana in the American Civil War James–Younger Gang Ohio in the American Civil War Pennsylvania in the American Civil War Political history of the United States Proposed countries Proposed states and territories of the United States Secret societies in the United States Slavery in the United States Texas in the American Civil War 1863 disestablishments in Ohio

 The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a
The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a secret society
A secret society is a club or an organization whose activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
founded in 1854 by American George W. L. Bickley, the objective of which was to create a new country, known as the Golden Circle ( es, Círculo Dorado), where slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
would be legal. The country would have been centered in Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
and would have consisted of the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
and a "golden circle" of territories in Mexico (which was to be divided into 25 new slave states), Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, northern parts of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
, and Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, and most other islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
, about in diameter.
Originally, the KGC advocated that the new territories should be annexed by the United States, in order to vastly increase the number of slave states and thus the power of the slave-holding Southern upper classes. In response to the increased anti-slavery agitation that followed the Dred Scott decision
''Dred Scott v. Sandford'', 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, enslaved or free; th ...
(1857) the Knights changed their position: the Southern United States should secede, forming their own confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
, and then invade and annex the area of the Golden Circle to vastly expand the power of the South. In the United States, the new country's northern border would roughly coincide with the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, also called the Mason and Dixon line or Mason's and Dixon's line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (part of Virginia ...
, and within it were included such cities as Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
, and Panama City
Panama City ( es, Ciudad de Panamá, links=no; ), also known as Panama (or Panamá in Spanish), is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is locat ...
.
The KGC's proposal grew out of previous unsuccessful proposals to annex Cuba (Ostend Manifesto
The Ostend Manifesto, also known as the Ostend Circular, was a document written in 1854 that described the rationale for the United States to purchase Cuba from Spain while implying that the U.S. should declare war if Spain refused. Cuba's annex ...
), parts of Central America (Filibuster War
The Filibuster War or Walker affair was a military conflict between filibustering multinational troops stationed in Nicaragua and a coalition of Central American armies. An American mercenary William Walker invaded Nicaragua in 1855 with a sma ...
), and all of Mexico ( All of Mexico Movement). In Cuba, the issue was complicated by the desire of many in the colony for independence from Spain. Mexico and Central America had no interest in being part of the United States.
As abolitionism in the United States
In the United States, abolitionism, the movement that sought to end slavery in the country, was active from the late colonial era until the American Civil War, the end of which brought about the abolition of American slavery through the Thi ...
grew in opposition to slavery, the KGC members proposed a separate confederation of slave states, with U.S. states south of the Mason-Dixon line to secede and to align with other slave states to be formed from the "golden circle". In either case, the goal was to increase the power of the Southern slave-holding upper class to such a degree that it could never be dislodged.Woodward, Colin. ''American Nations: A History of the Eleven Rival Regional Cultures of North America.'' New York: Penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
, 2017, p. 207.
During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, some Southern sympathizers in the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
or Northern states, such as Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, and Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
, were accused of belonging to the Knights of the Golden Circle, and in some cases, such as that of Lambdin P. Milligan, they were imprisoned for their activities.
Although nominally a secret society, the existence of the Knights of the Golden Circle was not, in fact, a secret.
Background
European colonialism and dependence on slavery had declined more rapidly in some countries than others. The Spanish possessions ofCuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
and the Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom Pe ...
continued to depend on slavery, as did the Southern United States. In the years prior to the American Civil War, the rise of support for abolition of slavery was one of several divisive issues in the United States. The slave population there had continued to grow due to natural increase even after the ban on international trade. It was concentrated in the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, on large plantations devoted to the commodity crops of cotton and sugar cane, but it was the basis of agricultural and other labor throughout the southern states.
Early history
George W. L. Bickley, a doctor, editor, and adventurer who lived inCincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line wit ...
, founded the association, organizing the first ''castle,'' or local branch, in Cincinnati in 1854. Membership increased slowly until 1859 and reached its height in 1860. The membership, scattered from New York to California and into Latin America, was never large. Records of the KGC convention held in 1860 state that the organization "originated at Lexington, Kentucky, on the fourth day of July 1854, by five gentlemen who came together on a call made by Gen. George Bickley".
Some Knights of the Golden Circle active in northern states, such as Illinois, were accused of anti-Union activities after the Civil War began in 1861.
 Hounded by creditors, Bickley left Cincinnati in the late 1850s and traveled through the East and South, promoting an armed expedition to Mexico. The group's original goal was to provide a force to colonize the northern part of Mexico and the
Hounded by creditors, Bickley left Cincinnati in the late 1850s and traveled through the East and South, promoting an armed expedition to Mexico. The group's original goal was to provide a force to colonize the northern part of Mexico and the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
. This would extend pro-slavery interests. In August 1861 ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' described the order as a successor to the Order of the Lone Star, which had been organized for the purpose of conquering Cuba and Nicaragua, succeeding in the latter cause in 1856 under William Walker before being driven out by a coalition of neighboring states. At that time the order's prime objective was said to be to raise an army of 16,000 men to conquer and "Southernize" Mexico, which meant making slavery, not legal in Mexico, again legal, while supporting the "Knights of the Columbian Star"—those in the KGC's highest level of membership—for public office.
Plans to seize Lincoln and inaugurate Breckinridge as president
Several members of President James Buchanan's administration were members of the order, as well as Virginia's secessionist Senator James M. Mason. The Secretary of War, John Floyd and of Treasury,Howell Cobb
Howell Cobb (September 7, 1815 – October 9, 1868) was an American and later Confederate political figure. A southern Democrat, Cobb was a five-term member of the United States House of Representatives and the speaker of the House from 184 ...
, were members of the circle, in addition to Vice President John Breckenridge. Floyd received instructions from the Order to "seize Navy-yards, Forts, etc. while KGC members were still Cabinet officers and Senators". The plan was to prevent Lincoln from reaching Washington by capturing him in Baltimore. Then they would occupy the District of Columbia, and install Breckinridge as president instead of Lincoln. Floyd used his position as Secretary of War to move munitions and men to the South towards the end of Buchanan's presidency. His plot was discovered, and led to greater distrust of secret societies and Copperheads in general. This distrust was the result of a confirmed plot to overthrow the federal government, rather than general discontent.
Robert Barnwell Rhett
Robert Barnwell Rhett (born Robert Barnwell Smith; December 21, 1800September 14, 1876) was an American politician who served as a deputy from South Carolina to the Provisional Confederate States Congress from 1861 to 1862, a member of the US H ...
, who has been called "the father of secession", said a few days after Lincoln's election:
Civil War
Southwest
In 1859, futureConfederate States Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
brigadier general Elkanah Greer established KGC castles in East Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
and Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
.Hudson, Linda S. "The Knights of the Golden Circle in Texas, 1858–1861: An Analysis of the First (Military) Degree Knights", p. 53, in Howell, Kenneth W., ed. ''The Seventh Star of the Confederacy: Texas during the Civil War''. University of North Texas Press: Denton, Texas, 2009. . Although a Unionist, United States Senator
The United States Senate is the Upper house, upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives being the Lower house, lower chamber. Together they compose the national Bica ...
Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two i ...
introduced a resolution in the U.S. Senate in 1858 for the "United States to declare and maintain an efficient protectorate over the States of Mexico, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, and San Salvador." This measure, which supported the goal of the KGC, failed to be adopted. In the spring of 1860, Elkanah Greer had become general and grand commander of 4,000 Military Knights in the KGC's Texas division of 21 castles. The Texas KGC supported President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
James Buchanan's policy of, and draft treaty for, protecting routes for U.S commerce across Mexico, which also failed to be approved by the U.S. Senate.Hudson, 2009, p. 54.
With the election of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
as President of the United States, the Texas KGC changed its emphasis from a plan to expand U.S. territory into Mexico in order to focus its efforts on providing support for the Southern States' secession from the Union. On February 15, 1861, Ben McCulloch
Brigadier general, Brigadier-General Benjamin McCulloch (November 11, 1811 – March 7, 1862) was a soldier in the Texas Revolution, a Texas Ranger Division, Texas Ranger, a Major general (United States), major-general in the Texas militia and t ...
, United States Marshal
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforcem ...
and former Texas Ranger, began marching toward the Federal arsenal at San Antonio, Texas
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
, with a cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
force of about 550 men, about 150 of whom were Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) from six castles. As volunteers continued to join McCulloch the following day, United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
Brevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'état-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
David E. Twiggs
David Emanuel Twiggs (February 14, 1790 – July 15, 1862), born in Georgia, was a career army officer, serving during the War of 1812, the Black Hawk War, and Mexican–American War.
As commander of the U.S. Army's Department of Texas when the ...
surrendered the arsenal peacefully to the secessionists. Twiggs was appointed a major general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
in the Confederate States Army on May 22, 1861.
KGC members also figured prominently among those who, in 1861, joined Lt. Col. John Robert Baylor in his temporarily successful takeover of southern New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of ''Santa Fe de Nuevo México ...
. In May 1861, members of the KGC and the Confederate Rangers attacked a building which housed a pro-Union newspaper, the ''Alamo Express,'' owned by J. P. Newcomb, and burned it down. Other KGC members followed Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Henry Hopkins Sibley
Henry Hopkins Sibley (May 25, 1816 – August 23, 1886) was a career officer in the United States Army, who commanded a Confederate cavalry brigade in the Civil War.
In 1862, he attempted to forge a supply route from California, in defiance ...
on the 1862 New Mexico Campaign, which sought to bring the New Mexico Territory into the Confederate fold. Both Baylor and Trevanion Teel, Sibley's captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
of artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
, had been among the KGC members who rode with Ben McCulloch.
North
In early 1862,Radical Republicans
The Radical Republicans (later also known as " Stalwarts") were a faction within the Republican Party, originating from the party's founding in 1854, some 6 years before the Civil War, until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Reco ...
in the Senate, aided by Secretary of State William H. Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senate, United States Senat ...
, suggested that former president Franklin Pierce
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. He was a northern Democrat who believed that the abolitionist movement was a fundamental threat to the nation's unity ...
, who was greatly critical of the Lincoln administration's war policies, was an active member of the Knights of the Golden Circle. In an angry letter to Seward, Pierce denied that he knew anything about the KGC, and demanded that his letter be made public. California Senator Milton Latham
Milton Slocum Latham (May 23, 1827 – March 4, 1882) was an American politician, who served as the sixth governor of California and as a U.S. Representative and U.S. Senator. Latham holds the distinction of having the shortest governorship in ...
subsequently did so when he entered the entire PierceSeward correspondence into the '' Congressional Globe''.
Appealing to the Confederacy's friends in both the North and the border states, the Order spread to Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
as well as the southern parts of such Union states as Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, and Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
. It became strongest among Copperheads, who were Democrats who wanted to end the Civil War via settlement with the South. Some supported slavery and others were worried about the power of the federal government. In the summer of 1863, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
authorized a military draft
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day und ...
, which the administration soon put into operation. Leaders of the Democratic Party opposed to Abraham Lincoln's administration denounced the draft and other wartime measures, such as the arrest of seditious persons and the president's temporary suspension of the writ of ''habeas corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a recourse in law through which a person can report an unlawful detention or imprisonment to a court and request that the court order the custodian of the person, usually a prison official, t ...
.''
During the 1863 Gettysburg Campaign, scam artists in south-central Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
sold Pennsylvania Dutch
The Pennsylvania Dutch ( Pennsylvania Dutch: ), also known as Pennsylvania Germans, are a cultural group formed by German immigrants who settled in Pennsylvania during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. They emigrated primarily from German-spe ...
farmers $1 paper tickets purported to be from the Knights of the Golden Circle. Along with a series of secret hand gestures, these tickets were supposed to protect the horses and other possessions of ticket holders from seizure by invading Confederate soldiers. When Confederate Maj. Gen. Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was a Virginia lawyer and politician who became a Confederate general during the American Civil War. Trained at the United States Military Academy, Early resigned his U.S. Army commissio ...
's infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine i ...
division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
passed through York County, Pennsylvania
York County ( Pennsylvania Dutch: Yarrick Kaundi) is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 456,438. Its county seat is York. The county was created on August 19, 1749, from part of Lancaster ...
, they took what they needed anyway. They often paid with Confederate States dollar
The Confederate States dollar was first issued just before the outbreak of the American Civil War by the newly formed Confederacy. It was not backed by hard assets, but simply by a promise to pay the bearer after the war, on the prospect of Sou ...
s or with drafts on the Confederate government. The Confederate cavalry
The American Civil War saw cavalry tactics move largely away from the offensive towards the defensive, with the emphasis on screening, raiding, and reconnaissance. Development of the rifled musket had also rendered the cavalry charge bot ...
commander J.E.B. Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a United States Army officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials of ...
also reported the alleged KGC tickets when documenting the campaign.
That same year, Asbury Harpending
Asbury Harpending (September 14, 1839 – January 26, 1923) was an adventurer and financier in San Francisco, California, Mexico, and New York City.
Early life
Harpending was born in Hopkinsville in Christian County in southwestern Kentucky. At th ...
and California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
members of the Knights of the Golden Circle in San Francisco outfitted the schooner '' J. M. Chapman'' as a Confederate privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
in San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
, with the object of raiding commerce on the Pacific Coast and capturing gold shipments to the East Coast. Their attempt was detected and they were seized on the night of their intended departure.
In late 1863, the KGC reorganized as the Order of American Knights. In 1864, it became the Order of the Sons of Liberty, with the Ohio politician Clement L. Vallandigham
Clement Laird Vallandigham ( ; July 29, 1820 – June 17, 1871) was an American politician and leader of the Copperhead (politics), Copperhead faction of anti-war History of the United States Democratic Party, Democrats during the American Civil ...
, most prominent of the Copperheads, as its supreme commander. In most areas only a minority of its membership was radical enough to discourage enlistments, resist the draft, and shield deserters. The KGC held numerous peace meetings. A few agitators, some of them encouraged by Southern money, talked of a revolt in the Old Northwest
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
, with the goal of ending the war.
Survival conspiracy theory
The ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the Un ...
'' noted that one theory, among many, on the origin of the Saddle Ridge Hoard of gold coins is that it was cached by the KGC, which "some believe buried millions in ill-gotten gold across a dozen states to finance a second Civil War".
Alleged members
* George W. L. Bickley *John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838 – April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who assassinated United States President Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the prominent 19th-century Booth th ...
* Confederados
''Os Confederados'' () is the Brazilian name for Confederate expatriates who fled the Southern United States during Reconstruction and their Brazilian descendants. They were enticed to Brazil by offers of cheap land from Emperor Dom Pedro II, ...
(some)
* Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
* Nathan Bedford Forrest
Nathan Bedford Forrest (July 13, 1821October 29, 1877) was a prominent Confederate Army general during the American Civil War and the first Grand Wizard of the Ku Klux Klan from 1867 to 1869. Before the war, Forrest amassed substantial wealt ...
* Jesse James
Jesse Woodson James (September 5, 1847April 3, 1882) was an American outlaw, bank and train robber, guerrilla and leader of the James–Younger Gang. Raised in the " Little Dixie" area of Western Missouri, James and his family maintained stro ...
* Thomas Lubbock
* Lambdin P. Milligan
* Buckner Stith Morris
Buckner Stith Morris (August 19, 1800 – December 16, 1879) served as Mayor of Chicago, Illinois (1838–1839) for the Whig Party.
Morris married Evelina Barker in Kentucky in 1832 and the couple moved to Chicago in 1834 where Morris establis ...
* Samuel Mudd
Samuel Alexander Mudd Sr. (December 20, 1833 – January 10, 1883) was an American physician who was imprisoned for conspiring with John Wilkes Booth concerning the assassination of Abraham Lincoln.
Mudd worked as a doctor and tobacco fa ...
* John Surratt
John Harrison Surratt Jr. (April 13, 1844 – April 21, 1916) was an American Confederate spy who was accused of plotting with John Wilkes Booth to kidnap U.S. President Abraham Lincoln; he was also suspected of involvement in the Abraham Linc ...
In popular culture
* In November 1950 theanthology
In book publishing, an anthology is a collection of literary works chosen by the compiler; it may be a collection of plays, poems, short stories, songs or excerpts by different authors.
In genre fiction, the term ''anthology'' typically categ ...
radio drama
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance: a play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has been ...
''Destination Freedom
''Destination Freedom'' was a weekly radio program produced by WMAQ in Chicago from 1948 to 1950 that presented biographical histories of prominent African-Americans such as George Washington Carver, Satchel Paige, Frederick Douglass, Harriet Tu ...
'' recapped the early history of the Knights in an episode entitled "The Golden Circle".
* The alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, altern ...
novel ''Bring the Jubilee
''Bring the Jubilee'' is a 1953 novel of alternate history by American writer Ward Moore.
The point of divergence occurs in July 1863 when the Confederate States of America wins the Battle of Gettysburg and subsequently declares victory in ...
'' (1958) by Ward Moore
Joseph Ward Moore (August 10, 1903 – January 29, 1978) was an American science fiction writer. According to ''The Encyclopedia of Science Fiction'', "he contributed only infrequently to the field, uteach of his books became something of a clas ...
and the similarly themed movie '' C.S.A.: The Confederate States of America'' explore the results of a Southern victory in the Civil War. Both works posit the Golden Circle as a plan enacted after the war. Both also have the Confederacy take over all of South America rather than the northern portion of the continent. However, in the former, the Confederacy annexes both Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
, and in the latter the Confederacy also annexes all of the continental United States.
* In the Southern Victory Series
The ''Southern Victory'' series or Timeline-191 is a series of eleven alternate history novels by author Harry Turtledove, beginning with ''How Few Remain'' (1997) and published over a decade. The period addressed in the series begins during th ...
by Harry Turtledove
Harry Norman Turtledove (born June 14, 1949) is an American author who is best known for his work in the genres of alternate history, historical fiction, fantasy, science fiction, and mystery fiction. He is a student of history and completed ...
, the Confederacy's post-war territorial expansion into Latin America amounts only to the purchase of Cuba from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the purchase of Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is d ...
and Chihuahua from the Mexican Empire Mexican Empire may refer to:
* First Mexican Empire, the regime under Agustín de Iturbide (Agustín I) from 1821 to 1823
* Second Mexican Empire
The Second Mexican Empire (), officially the Mexican Empire (), was a constitutional monarchy est ...
for the purposes of constructing a transcontinental railway and establishing a Confederate naval presence in the Pacific. Following the Confederacy's defeat in the Second Great War, Cuba, Sonora and Chihuahua along with the rest of the CSA are annexed to the United States.
* ''The Night of the Iron Tyrants'' (1990–1991), written by the novelist Mark Ellis and drawn by Darryl Banks
Darryl Banks is an American comic book artist. He worked on one of the first painted comic books, ''Cyberpunk'', and teamed with the writer Mark Ellis (American author), Mark Ellis to revamp the long-running ''Justice Machine, The Justice Machin ...
, is a four-part comic book
A comic book, also called comicbook, comic magazine or (in the United Kingdom and Ireland) simply comic, is a publication that consists of comics art in the form of sequential juxtaposed panels that represent individual scenes. Panels are of ...
miniseries
A miniseries or mini-series is a television series that tells a story in a predetermined, limited number of episodes. "Limited series" is another more recent US term which is sometimes used interchangeably. , the popularity of miniseries format h ...
based on ''The Wild Wild West
''The Wild Wild West'' is an American Western, espionage, and science fiction television series that ran on the CBS television network for four seasons from September 17, 1965, to April 11, 1969. Two satirical comedy television film sequels w ...
'' television series. It features the Knights of the Golden Circle in an assassination plot against President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
and Dom Pedro II of Brazil during the Philadelphia Centennial Exposition
The Centennial International Exhibition of 1876, the first official World's Fair to be held in the United States, was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from May 10 to November 10, 1876, to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the signing of the ...
of 1876.
* The KGC are the villains of the graphic novel ''Batman
Batman is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by artist Bob Kane and writer Bill Finger, and debuted in Detective Comics 27, the 27th issue of the comic book ''Detective Comics'' on ...
: Detective No. 27'' (2003) by Michael Uslan
Michael E. Uslan (; born June 2, 1951) is an American lawyer and film producer. Uslan has also dabbled in writing and teaching, he is known for being the first instructor to teach an accredited course on comic book folklore at any university.
Ear ...
and Peter Snejbjerg
Peter Snejbjerg is a Danish comic book artist. He was educated at the Kolding Kunsthåndværkerskole from 1983 to 1987. Some of his major works include the DC Comics title Starman, and various Vertigo titles. He has also drawn several issues o ...
.
* The KGC are portrayed as conspirators in the Lincoln assassination
On April 14, 1865, Abraham Lincoln, the 16th president of the United States, was assassinated by well-known stage actor John Wilkes Booth, while attending the play ''Our American Cousin'' at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C.
Shot in the hea ...
in the Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
movie '' National Treasure: Book of Secrets'' (2007).
* In the William Martin novel ''The Lincoln Letter'' (2012), the KGC are a group of conspirators in Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
, during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
* The KGC and their potential involvement in President Lincoln's assassination are discussed in an episode of the History Channel
History (formerly The History Channel from January 1, 1995 to February 15, 2008, stylized as HISTORY) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by A&E Networks, a joint venture between Hearst Communications and the Disney ...
series ''America Unearthed
''America Unearthed'' was an American entertainment television series, the first original series to air on the A&E Networks channel H2. The show premiered on December 21, 2012, and was produced by Committee Films of Minneapolis, Minnesota. The p ...
''.
* The KGC are the antagonists in a story which is featured in the Atomic Robo
''Atomic Robo'' is an American comic book series created by ''8-Bit Theater'' writer Brian Clevinger and artist Scott Wegener, depicting the adventures of the eponymous character, a self-aware robot built by Nikola Tesla. The series is split i ...
web comic.
* The KGC are referenced during a discussion concerning a potential assassination plot in the PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcasting, public broadcaster and Non-commercial activity, non-commercial, Terrestrial television, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly fu ...
television series ''Mercy Street
"Mercy Street" is a song written by English musician Peter Gabriel from his 1986 album '' So''.
Background and recording
The song was inspired by the personal and confessional works of the American poet Anne Sexton, who wrote a play titled '' ...
''.
* The KGC are the subject of a historical fiction novel by Steve Berry which is entitled ''The Lost Order'', released April 4, 2017.
See also
* Adams-Onís Treaty * All of Mexico Movement *American imperialism
American imperialism refers to the expansion of American political, economic, cultural, and media influence beyond the boundaries of the United States. Depending on the commentator, it may include imperialism through outright military conquest ...
* Antebellum South
In History of the Southern United States, the history of the Southern United States, the Antebellum Period (from la, ante bellum, lit=Status quo ante bellum, before the war) spanned the Treaty of Ghent, end of the War of 1812 to the start of ...
* Judah P. Benjamin
Judah Philip Benjamin, QC (August 6, 1811 – May 6, 1884) was a United States senator from Louisiana, a Cabinet officer of the Confederate States and, after his escape to the United Kingdom at the end of the American Civil War, an English ba ...
* Camp Douglas Conspiracy
* Confederados
''Os Confederados'' () is the Brazilian name for Confederate expatriates who fled the Southern United States during Reconstruction and their Brazilian descendants. They were enticed to Brazil by offers of cheap land from Emperor Dom Pedro II, ...
* Confederate colonies
Confederate colonies were made up of Confederate refugees who were displaced or fled their homes during or immediately after the American Civil War. They migrated to various countries, but especially Brazil, where slavery remained legal, and to a ...
* Filibuster (military)
A filibuster (from the Spanish ''filibustero''), also known as a freebooter, is someone who engages in an unauthorized military expedition into a foreign country or territory to foster or support a political revolution or secession. The term is ...
* Linconia
Linconia was the name of a proposed Central American colony suggested by Republican United States Senator Samuel Pomeroy of Kansas in 1862, after U.S. President Abraham Lincoln asked the Senator and United States Secretary of the Interior Caleb ...
* Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
* Republic of Sonora
The Republic of Baja California and Sonora or more simply known as the Republic of Sonora was a short-lived, unrecognized federal republic ruled by filibuster William Walker in 1854. It was based in Baja California and also claimed (but never ...
* Republic of Yucatán
The Republic of Yucatán ( es, República de Yucatán) was a sovereign state during two periods of the nineteenth century. The first Republic of Yucatán, founded May 29, 1823, willingly joined the Mexican federation as the Federated Republic ...
* Second Mexican Empire
The Second Mexican Empire (), officially the Mexican Empire (), was a constitutional monarchy established in Mexico by Mexican monarchists in conjunction with the Second French Empire. The period is sometimes referred to as the Second French i ...
* Slave Power
* Slavery in the United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Sl ...
* Walker affair
The Filibuster War or Walker affair was a military conflict between filibustering multinational troops stationed in Nicaragua and a coalition of Central American armies. An American mercenary William Walker invaded Nicaragua in 1855 with a sma ...
References
Notes Bibliography * * * * * (currently published under the title of Rebel Gold ) * * * * * * * Further reading *''An Authentic Exposition of the “K.G.C.” “Knights of the Golden Circle,” or, A History of Secession from 1834 to 1861, by A Member of the Order'' (Indianapolis, Indiana: C. O. Perrine, Publisher, 1861).
* Donald S. Frazier, ''Blood & Treasure: Confederate Empire in the Southwest'' (College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 1996). * Warren Getler and Bob Brewer, ''Rebel Gold: One Man’s Quest to Crack the Code Behind the Secret Treasure of the Confederacy'' (New York: Simon & Schuster, 2004). * Dion Haco, ed., ''The Private Journal and Diary of John H. Surratt, The Conspirator'' (New York: Frederic A. Brady, Publisher, 1866). * James D. Horan, ''Confederate Agent: A Discovery in History'' (New York: Crown Publishers, Inc., 1954). * Jesse Lee James, ''Jesse James and the Lost Cause'' (New York: Pageant Press, 1961). * Jack Myers, ''Knights' Gold'' (CreateSpace Independent Publishing, 2016).
External links
Sons of Liberty (American Civil War)
– Ohio History Central
Joseph Holt, ''Report of the Judge Advocate General on “The Order of American Knights,” alias "The Sons of Liberty." A Western Conspiracy in aid of the Southern Rebellion'' (Washington, D.C.: Union Congressional Committee, 1864).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Knights Of The Golden Circle 1854 establishments in Ohio 1860 in Central America 1860s in Central America 1860s in politics 1860s in the Caribbean 19th century in Central America 19th century in the Caribbean American Civil War political groups American proslavery activists Bleeding Kansas California in the American Civil War Expansion of slavery in the United States History of United States expansionism Indiana in the American Civil War James–Younger Gang Ohio in the American Civil War Pennsylvania in the American Civil War Political history of the United States Proposed countries Proposed states and territories of the United States Secret societies in the United States Slavery in the United States Texas in the American Civil War 1863 disestablishments in Ohio