Kleene's T Predicate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
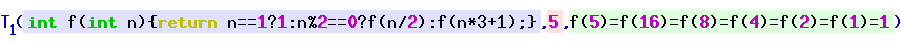 The definition depends on a suitable Gödel numbering that assigns natural numbers to
The definition depends on a suitable Gödel numbering that assigns natural numbers to
computability theory
Computability theory, also known as recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic, computer science, and the theory of computation that originated in the 1930s with the study of computable functions and Turing degrees. The field has since ex ...
, the T predicate, first studied by mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene
Stephen Cole Kleene ( ; January 5, 1909 – January 25, 1994) was an American mathematician. One of the students of Alonzo Church, Kleene, along with Rózsa Péter, Alan Turing, Emil Post, and others, is best known as a founder of the branch of ...
, is a particular set of triples of natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive in ...
s that is used to represent computable function
Computable functions are the basic objects of study in computability theory. Informally, a function is ''computable'' if there is an algorithm that computes the value of the function for every value of its argument. Because of the lack of a precis ...
s within formal theories of arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
. Informally, the ''T'' predicate tells whether a particular computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangibl ...
will halt when run with a particular input, and the corresponding ''U'' function is used to obtain the results of the computation if the program does halt. As with the smn theorem, the original notation used by Kleene has become standard terminology for the concept.The predicate described here was presented in (Kleene 1943) and (Kleene 1952), and this is what is usually called "Kleene's ''T'' predicate". (Kleene 1967) uses the letter ''T'' to describe a different predicate related to computable functions, but which cannot be used to obtain Kleene's normal form theorem.
Definition
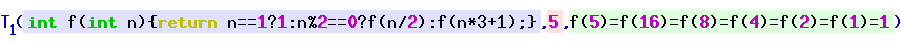 The definition depends on a suitable Gödel numbering that assigns natural numbers to
The definition depends on a suitable Gödel numbering that assigns natural numbers to computable function
Computable functions are the basic objects of study in computability theory. Informally, a function is ''computable'' if there is an algorithm that computes the value of the function for every value of its argument. Because of the lack of a precis ...
s (given as Turing machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algori ...
s). This numbering must be sufficiently effective that, given an index of a computable function and an input to the function, it is possible to effectively simulate the computation of the function on that input. The predicate is obtained by formalizing this simulation.
The ternary relation takes three natural numbers as arguments. is true if encodes a computation history of the computable function with index when run with input , and the program halts as the last step of this computation history. That is,
* first asks whether is the Gödel number of a finite sequence of complete configurations of the Turing machine with index , running a computation on input .
* If so, then asks if this sequence begins with the starting state of the computation and each successive element of the sequence corresponds to a single step of the Turing machine.
* If it does, finally asks whether the sequence ends with the machine in a halting state.
If all three of these questions have a positive answer, then is true, otherwise, it is false.
The predicate is primitive recursive in the sense that there is a primitive recursive function that, given inputs for the predicate, correctly determines the truth value of the predicate on those inputs.
There is a corresponding primitive recursive function such that if is true then returns the output of the function with index on input .
Because Kleene's formalism attaches a number of inputs to each function, the predicate can only be used for functions that take one input. There are additional predicates for functions with multiple inputs; the relation
:
is true if encodes a halting computation of the function with index on the inputs .
Like , all functions are primitive recursive.
Because of this, any theory of arithmetic that is able to represent every primitive recursive function is able to represent and . Examples of such arithmetical theories include Robinson arithmetic and stronger theories such as Peano arithmetic.
Normal form theorem
The predicates can be used to obtain Kleene's normal form theorem for computable functions (Soare 1987, p. 15; Kleene 1943, p. 52—53). This states there exists a fixedprimitive recursive function
In computability theory, a primitive recursive function is, roughly speaking, a function that can be computed by a computer program whose loops are all "for" loops (that is, an upper bound of the number of iterations of every loop is fixed befor ...
such that a function is computable if and only if there is a number such that for all one has
:,
where ''μ'' is the ''μ'' operator ( is the smallest natural number for which is true) and is true if both sides are undefined or if both are defined and they are equal. By the theorem, the definition of every general recursive function
In mathematical logic and computer science, a general recursive function, partial recursive function, or μ-recursive function is a partial function from natural numbers to natural numbers that is "computable" in an intuitive sense – as well as i ...
''f'' can be rewritten into a normal form such that the ''μ'' operator is used only once, viz. immediately below the topmost , which is independent of the computable function .
Arithmetical hierarchy
In addition to encoding computability, the ''T'' predicate can be used to generate complete sets in thearithmetical hierarchy
In mathematical logic, the arithmetical hierarchy, arithmetic hierarchy or Kleene–Mostowski hierarchy (after mathematicians Stephen Cole Kleene and Andrzej Mostowski) classifies certain sets based on the complexity of formulas that define th ...
. In particular, the set
:
which is of the same Turing degree
In computer science and mathematical logic the Turing degree (named after Alan Turing) or degree of unsolvability of a set of natural numbers measures the level of algorithmic unsolvability of the set.
Overview
The concept of Turing degree is fund ...
as the halting problem
In computability theory (computer science), computability theory, the halting problem is the problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running, or continue to run for ...
, is a complete unary relation (Soare 1987, pp. 28, 41). More generally, the set
:
is a -complete (''n''+1)-ary predicate. Thus, once a representation of the ''T''''n'' predicate is obtained in a theory of arithmetic, a representation of a -complete predicate can be obtained from it.
This construction can be extended higher in the arithmetical hierarchy, as in Post's theorem (compare Hinman 2005, p. 397). For example, if a set is complete then the set
:
is complete.
Notes
References
* Peter Hinman, 2005, ''Fundamentals of Mathematical Logic'', A K Peters. * Reprinted in ''The Undecidable'', Martin Davis, ed., 1965, pp. 255–287. * —, 1952, ''Introduction to Metamathematics'', North-Holland. Reprinted by Ishi press, 2009, . * —, 1967. ''Mathematical Logic,'' John Wiley. Reprinted by Dover, 2001, . * Robert I. Soare, 1987, ''Recursively enumerable sets and degrees,'' Perspectives in Mathematical Logic, Springer. {{isbn, 0-387-15299-7 Computability theory