Kitefin shark on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The kitefin shark or seal shark (''Dalatias licha'') is a
 The kitefin shark has a moderately elongated body with a very short, rounded snout. The eyes and
The kitefin shark has a moderately elongated body with a very short, rounded snout. The eyes and
Biological Profiles: Kitefin Shark
Florida Museum of Natural History Ichthyology Department. Retrieved on June 15, 2009. Off the
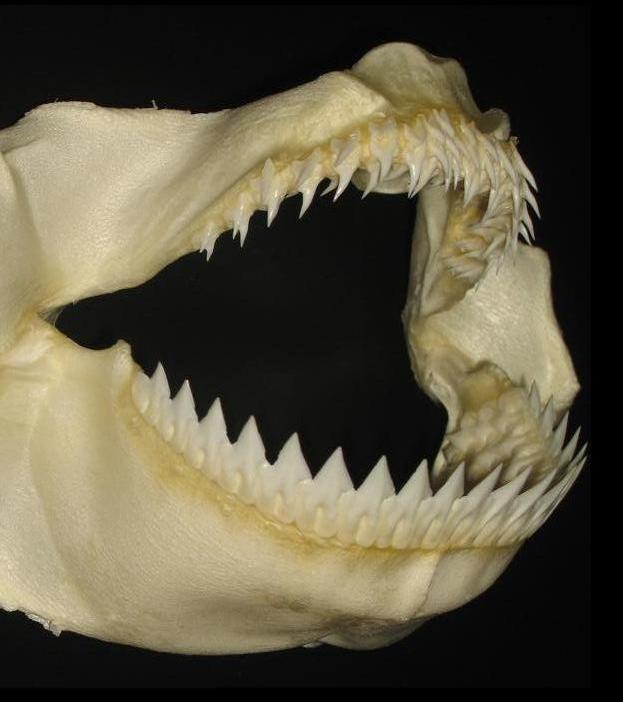 Relatively common where it occurs, kitefin sharks are usually solitary in nature but may form small groups. It is a slow swimmer with a large
Relatively common where it occurs, kitefin sharks are usually solitary in nature but may form small groups. It is a slow swimmer with a large
 The kitefin shark inhabits depths too great for it to be a danger to humans. Its upper teeth have been found lodged in underwater fiberoptic cables. This species has a long history of human exploitation: the meat is consumed in the eastern Atlantic and Japan, and the
The kitefin shark inhabits depths too great for it to be a danger to humans. Its upper teeth have been found lodged in underwater fiberoptic cables. This species has a long history of human exploitation: the meat is consumed in the eastern Atlantic and Japan, and the
Report of the Working Group Elasmobranch Fishes (WGEF), 22–28 June 2007, Galway, Ireland.
ICES CM 2007/ACFM:27. pp. 52–55. Fisheries operating off Portugal and Japan are responsible for most commercial landings of the kitefin shark, generally as
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of squaliform shark in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Dalatiidae
The Dalatiidae are the family of kitefin sharks of the order Squaliformes (the term "kitefin shark" also refers specifically to the species ''Dalatias licha''). Members of this family are small, under long, and are found worldwide. They have cig ...
, and the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
in its genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
. It is found sporadically around the world, usually close to the sea floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
at depths of . With a sizable oil-filled liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
to maintain neutral buoyancy
Neutral buoyancy occurs when an object's average density is equal to the density of the fluid in which it is immersed, resulting in the buoyant force balancing the force of gravity that would otherwise cause the object to sink (if the body's dens ...
, this shark is able to cruise slowly through the water while expending little energy. The kitefin shark, the largest luminous vertebrate on record, has a slender body with a very short, blunt snout, large eyes, and thick lips. Its teeth are highly differentiated between the upper and lower jaws, with the upper teeth small and narrow and the lower teeth large, triangular, and serrated. Its typical length is , though examples as long as have been encountered.
Armed with large teeth and a strong bite, the kitefin shark is a powerful, solitary predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
that takes many different types of prey, ranging from bony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilag ...
es, sharks and rays, to cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s, polychaete worm
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are mad ...
s, siphonophore
Siphonophorae (from Greek ''siphōn'' 'tube' + ''pherein'' 'to bear') is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 specie ...
s, and possibly carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
. It also takes bites out of animals larger than itself, similar to its smaller relative, the cookiecutter shark
The cookiecutter shark (''Isistius brasiliensis''), also called the cigar shark, is a species of small squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae. This shark occurs in warm, oceanic waters worldwide, particularly near islands, and has been reco ...
(''Isistius brasiliensis''). This shark is aplacental viviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ...
and gives birth to 10–14 young. The kitefin shark is fished commercially for its meat, skin, and liver oil, primarily by Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. A fishery targeting this species existed off the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
from the 1970s to the 1990s, but collapsed due to overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
and falling liver oil prices; the rapid depletion of the Azores stock is often cited as an example of the susceptibility of deep-sea sharks to human exploitation. The low reproductive rate of this species renders it susceptible to overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
and, coupled with known population declines, has led it to be assessed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
(IUCN).
Taxonomy
The kitefin shark was originally described as ''Squalus licha'' by French naturalistPierre Joseph Bonnaterre
Abbé Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre (1752, Aveyron – 20 September 1804, Saint-Geniez-d'Olt) was a French zoology, zoologist who contributed sections on cetaceans, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and insects to the ''Tableau encyclopéd ...
, in his 1788 ''Tableau encyclopédique et méthodique des trois regnes de la nature''; the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
from "Le cap Breton" has since been lost. This species was later placed in its own genus, ''Dalatias'', which came from the synonymy
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
of Constantine Rafinesque
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz (; October 22, 1783September 18, 1840) was a French 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ultimat ...
's 1810 ''Dalatias sparophagus'' with ''S. licha''. However, some authorities dispute this on the grounds that ''D. sparophagus'' is a ''nomen dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application.
Zoology
In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...
'', and prefer to use the next available genus name ''Scymnorhinus''. The genus name ''Dalatias'' is derived from the Greek ''dalos'' or ''dalou'', meaning "torch". The specific epithet
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
''licha'' comes from ''liche'', the French name for this shark (from Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
''lecha'', from ''lec'', " glutton"). Additional common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrast ...
s used for the kitefin shark include black shark and darkie Charlie.
Phylogeny and evolution
Cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived char ...
studies have consistently found that the closest relatives of the kitefin shark are the cookiecutter sharks (''Isistius
''Isistius'' is a genus of Squaliformes, dogfish sharks in the family (biology), family Dalatiidae. They are commonly known as cookiecutter sharks. Members of the genus are known for their unusual behaviour and dentition.
Species
*''Isistius br ...
''), with which they share several dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
al, skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, and muscular
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle ...
similarities. ''Dalatias'' and ''Isistius'' are believed to have evolutionarily diverged
Divergent evolution or divergent selection is the accumulation of differences between closely related populations within a species, leading to speciation. Divergent evolution is typically exhibited when two populations become separated by a geog ...
shortly after the transition between the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods (65.5 Ma), as part of a larger adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
of dogfish sharks from the deep sea into relatively shallower habitats.
The oldest fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
teeth that definitively belong to the kitefin shark date to the Middle Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
, such as those recovered from Bortonian
While also using the international geologic time scale, many nations–especially those with isolated and therefore non-standard prehistories–use their own systems of dividing geologic time into epochs and faunal stages. In New Zealand, these epo ...
-stage deposits (43.0–37.0 Ma) in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
. ''Dalatias'' fossil teeth dating to various ages have also been discovered in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, the former USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, Japan, and western India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The fossil material now recognized as belonging to this species were historically described under a multitude of different names.
Description
 The kitefin shark has a moderately elongated body with a very short, rounded snout. The eyes and
The kitefin shark has a moderately elongated body with a very short, rounded snout. The eyes and spiracle Spiracle or spiraculum may refer to:
* Spiracle (arthropods), opening in the exoskeletons of some arthropods
* Spiracle (vertebrates), openings on the surface of some vertebrates
* Spiraculum, a genus of land snails in family Cyclophoridae
Cycl ...
s are large. The lips are thick with pleats or fringes, though are not modified to be suctorial Suctorial pertains to the adaptation for sucking or suction, as possessed by marine parasites such as the Cookiecutter shark, specifically in a specialised lip organ enabling attachment to the host.
Suctorial organs of a different form are possesse ...
. There are 16–21 tooth rows in the upper jaw and 17–20 tooth rows in the lower jaw. The upper teeth are small and spike-shaped, curving slightly towards the corners of the mouth. The lower teeth are very large, knife-shaped, and serrated, with their bases interlocking to form a continuous cutting surface.
The first dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through conv ...
is slightly smaller and shorter-based than the second, and neither has spines. The first dorsal fin originates behind the free rear tip of the pectoral fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as ...
s, while the second originates above the middle of the pelvic fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral surface of fish. The paired pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods.
Structure and function Structure
In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two en ...
bases. The pectoral fins are short and rounded. The caudal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
has a prominent upper lobe with a well-developed notch near the tip, and a barely present lower lobe. The form and arrangement of the fins is similar to the Portuguese dogfish
The Portuguese dogfish (''Centroscymnus coelolepis'') or Portuguese shark, is a species of sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae. This globally distributed species has been reported down to a depth of , making it the deepest-living shark known. ...
(''Centroscymnus coelolepis''), from which this species can be distinguished by the lack of fin spines. The dermal denticle
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as we ...
s are small and flat, with a single horizontal ridge ending in a point.
The coloration is a uniform dark brown or gray, sometimes with faint black spots on the back. The fins have white or translucent trailing edges, and the tip of the caudal fin is black. An long kitefin shark with partial albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
, lacking pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compo ...
on 59% of its body, was caught in the Gulf of Genoa
The Gulf of Genoa (''Golfo di Genova'') is the northernmost part of the Ligurian Sea. This Italian gulf is about wide from the city of Imperia in the west to La Spezia in the east. The largest city on its coast is Genoa, which has an important p ...
in 2003. Unlike in a previous case of an albino Portuguese dogfish, the abnormal coloration of this individual had not diminished its ability to capture prey. Most kitefin sharks are long and weigh ; the maximum reported length is , possibly .
The kitefin shark is the largest known shark that exhibits bioluminesce. The light is generated by photophores
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
that consist of a single photocyte within in a cup-shaped pigmented cell, with lens cells on the surface. The bioluminesence is directed downwards from its front or belly. There are two hypotheses for the use of bioluminesence by ''D. licha''; either it illuminates the sea floor while the shark is searching for prey, or it is used as a counter-illumination
Counter-illumination is a method of active camouflage seen in marine animals such as firefly squid and midshipman fish, and in military prototypes, producing light to match their backgrounds in both brightness and wavelength.
Marine animals of ...
camouflage when approaching prey.
Distribution and habitat
The kitefin shark has an almost circumglobalrange
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
in tropical and warm-temperature waters, consisting of a number of widely separated populations with likely little interchange between them. This shark has not been reported from the eastern Pacific and northern Indian Oceans. In the northern Atlantic, it occurs in the Georges Bank
Georges Bank (formerly known as St. Georges Bank) is a large elevated area of the sea floor between Cape Cod, Massachusetts (United States), and Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia (Canada). It separates the Gulf of Maine from the Atlantic Ocean.
Th ...
and the northern Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, and from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
to Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
, including around the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, in the western and central Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, and off Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
and the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
. In the Indian Ocean, it is found off South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
. In the Pacific, it occurs off Japan, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, and the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
. There is a single record of this species in the southern Atlantic, from off southern Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
.
An offshore, deepwater species, the kitefin shark is most common at a depth of , but has been captured from the surface to as deep as .Bester, C. and Burgess, GBiological Profiles: Kitefin Shark
Florida Museum of Natural History Ichthyology Department. Retrieved on June 15, 2009. Off the
Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
this shark segregates by sex, with females most common around a depth of and males most common around . The kitefin shark inhabits the outer continental shelves and upper continental slopes, and is also found around oceanic islands and seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s. It is the only member of its family that tends to be found close to the sea floor as opposed to in the middle of the water column, though on occasion it has been captured well above the bottom.
Biology and ecology
liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
filled with squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
, a lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
less dense than water, allowing it to maintain neutral buoyancy and hover above the bottom with little effort. Studies off the coast of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and in the Gulf of Genoa have found males outnumbering females by 2:1 and 5:1 respectively; this imbalanced sex ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species devia ...
has not been observed off South Africa and may reflect sampling bias
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population have a lower or higher sampling probability than others. It results in a biased sample of a population (or non-human fa ...
. The kitefin shark is preyed upon by larger fishes and sharks, as well as by sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
s (''Physeter macrocephalus''). Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
data on this species is limited; an examination of two sharks caught off Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
found three nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
lumen. One could be identified as ''Anisakis simplex'' L3, while another may have been a larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
l ''Raphidascaris''.
A powerful and versatile deepwater predator, the short, robust jaws of the kitefin shark give it an enormously strong bite. It feeds mainly on bony fishes (including deepwater smelts, viperfish
A viperfish is any species of marine fish in the genus ''Chauliodus''. Viperfishes are mostly found in the mesopelagic zone and are characterized by long, needle-like teeth and hinged lower jaws. A typical viperfish grows to lengths of . Viperf ...
es, scaly dragonfishes, barracudina
Barracudinas are any member of the marine mesopelagic fish family (biology), family Paralepididae: 50 or so extant species are found almost worldwide in deep waters. Several genera are known only from fossils dating back to the Ypresian epoch.
...
s, greeneye
Greeneyes are deep-sea aulopiform marine fishes in the small family Chlorophthalmidae. Thought to have a circumglobal distribution in tropical and temperate waters, the family contains just 18 species in two genera. The family name Chlorophthalm ...
s, lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represente ...
es, bristlemouth
The Gonostomatidae are a family of mesopelagic marine fish, commonly named bristlemouths, lightfishes, or anglemouths. It is a relatively small family, containing only eight known genera and 32 species. However, bristlemouths make up for their ...
s, cod and other gadids, grenadier
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word '' grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited fr ...
s, deepwater scorpionfish
Deepwater may refer to ocean water in the abyssal zone, hadal zone, or other deep ocean zones.
Deepwater may also refer to:
Entertainment
* Deep Water (Highsmith novel), a 1957 a psychological thriller novel by Patricia Highsmith
* ''Deepwat ...
es, bonito
Bonitos are a tribe of medium-sized, ray-finned predatory fish in the family Scombridae – a family it shares with the mackerel, tuna, and Spanish mackerel tribes, and also the butterfly kingfish. Also called the tribe Sardini, it consists of ...
, snake mackerel
The snake mackerel (''Gempylus serpens'') is the sole species of fish in the monotypic genus ''Gempylus'', belonging to the family Gempylidae (which is also referred to generally as "snake mackerels"). It is found worldwide in tropical and sub ...
s, deepwater cardinalfishes, and sea toad
The sea toads and coffinfishes are a family of deep-sea anglerfishes known as the Chaunacidae.
These are bottom-dwelling fishes found on the continental slopes of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, at depths to at least . There have also ...
s), but also takes a wide variety of other animals, including skate
Skate or Skates may refer to: Fish
*Skate (fish), several genera of fish belonging to the family Rajidae
* Pygmy skates, several genera of fish belonging to the family Gurgesiellidae
* Smooth skates or leg skates, several genera of fish belongin ...
s, smaller sharks (''Galeus
''Galeus'' is a genus of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, commonly known as sawtail catsharks in reference to a distinctive saw-toothed crest of enlarged dermal denticles, found along the upper edges of their caudal fins. They a ...
'', ''Squalus
''Squalus'' is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae. Commonly known as spurdogs, these sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines, teeth in upper and lower jaws similar in size, caudal peduncle with lateral keels; upper pr ...
'', '' Etmopterus'' and ''Centrophorus
''Centrophorus'' is a genus of squaliform sharks. These deep-water sharks, found in temperate and tropical oceans throughout the world, are characterized by grey or brown bodies, large green eyes, and spines on both dorsal fins. These spines gi ...
''), squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting t ...
and octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
, crustaceans (amphipod
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far descr ...
s, isopod
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, an ...
s, shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
and lobster
Lobsters are a family (biology), family (Nephropidae, Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs ...
s), polychaete worms, and siphonophores. Like the related cookiecutter shark, the kitefin shark is also capable of excising chunks of flesh from animals larger than itself, including other sharks and whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s. The presence of fast-swimming fishes in its diet suggests the kitefin shark may scavenge
Scavengers are animals that consume Corpse decomposition, dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a h ...
, or have some other means of capturing faster prey. In the Mediterranean, bony fishes are the most important food year-round, with the second-most important prey being sharks in the winter and spring, crustaceans in the summer, and cephalopods in the fall. Captured males are more likely to have full stomachs than females for unknown reasons.
Reproduction in the kitefin shark is aplacental viviparous, with the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s hatching inside the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uter ...
and being sustained to term by yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
. Adult females have two functional ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
and two functional uteruses; the uterus is not divided into compartments. In the Mediterranean, breeding occurs throughout the year with peaks in spring and fall; females may have a year of rest in between pregnancies. The litter size is 10–16, increasing with female size. The young are born at a length of , varying by geographic location, after a possible gestation period
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it ...
of two years.da Silva, H.M. (1988). "Growth and reproduction of kitefin shark, ''Dalatias licha ''(Bonn 1788) in Azorean waters." ICES, Demersal Fish Committee CM 1988/G:21. pp. 1–16. The males mature sexually at a length of , and the females at a length of . There is no relationship between an individual's size at birth, size at maturity, and maximum size.
Human interactions
 The kitefin shark inhabits depths too great for it to be a danger to humans. Its upper teeth have been found lodged in underwater fiberoptic cables. This species has a long history of human exploitation: the meat is consumed in the eastern Atlantic and Japan, and the
The kitefin shark inhabits depths too great for it to be a danger to humans. Its upper teeth have been found lodged in underwater fiberoptic cables. This species has a long history of human exploitation: the meat is consumed in the eastern Atlantic and Japan, and the offal
Offal (), also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the organs of a butchered animal. The word does not refer to a particular list of edible organs, which varies by culture and region, but usually excludes muscle. Offal may also refe ...
processed into fishmeal
Fish meal is a commercial product made from whole wild-caught fish, bycatch and fish by-products to feed farm animals, e.g., pigs, poultry, and farmed fish.R. D. Miles and F. A. Chapman.FA122: The Benefits of Fish Meal in Aquaculture DietsFisherie ...
. The liver oil is utilized in Portugal, Japan, and South Africa. The skin is made into a type of shagreen
Shagreen is a type of rawhide consisting of rough untanned skin, historically from a horse's or onager's back, or from shark or ray.
Etymology
The word derives from the French ''chagrin'' and is related to Italian ''zigrino'' and Venetian '' ...
useful in the making of furniture and jewelry, and is also favored for the manufacture of "boroso", a Spanish polished leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
. This shark has no commercial value in the western Atlantic.
The continuing expansion of commercial fisheries into the deep sea has raised concerns about the vulnerability of this and other deepwater shark species to overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
, as these sharks have slow growth and reproductive rates. This is exemplified by the rapid stock depletion and collapse of the Azores kitefin shark fishery. This targeted fishery began in the early 1970s for the production of liver oil. In the early 1980s, the fishing fleet was enlarged with the addition of industrial vessels equipped with demersal gillnets, resulting in a fishery peak in 1984 of 937 tons landed. After 1991, kitefin shark catches declined precipitously to under 15 tons annually which, along with a drop in the global price of liver oil, led to the fishery becoming unprofitable by the end of the decade. A population assessment has suggested that the northeastern Atlantic stock had fallen to 50% of the pre-exploitation biomass.ICES. (2007)Report of the Working Group Elasmobranch Fishes (WGEF), 22–28 June 2007, Galway, Ireland.
ICES CM 2007/ACFM:27. pp. 52–55. Fisheries operating off Portugal and Japan are responsible for most commercial landings of the kitefin shark, generally as
bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
in bottom trawl
Bottom trawling is trawling (towing a trawl, which is a fishing net) along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling. Benthic trawling is towing ...
s and on hook-and-line. Portugal reported a kitefin shark bycatch of 282 tons in 2000 and 119 tons in 2003. In other areas of the northeastern Atlantic this shark is rare and reported catches are likely confounded by misidentifications of other species; some are caught by mixed-species gillnet
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is ...
fisheries operating in deep water west of the British Isles, where surveys suggest that kitefin shark numbers may have declined by 94% since the 1970s. In the Mediterranean, this shark is caught incidentally by bottom trawl
Bottom trawling is trawling (towing a trawl, which is a fishing net) along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling. Benthic trawling is towing ...
and gillnet fisheries. Although it is generally discarded alive, many are unable to return to deep water and do not survive. In the Southern Hemisphere, catches by the Australian South East Trawl Fishery are increasing following the relaxation of regulations regarding seafood mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
content; this species is not included under Australian fishery quota
Quota may refer to:
Economics
* Import quota, a trade restriction on the quantity of goods imported into a country
* Market Sharing Quota, an economic system used in Canadian agriculture
* Milk quota, a quota on milk production in Europe
* Indi ...
s. New Zealand kitefin shark catches peaked from 1986 to 1997. In June 2018 the New Zealand Department of Conservation
An environmental ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for the environment and/or natural resources. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of the Environment ...
classified the kitefin shark as "Not Threatened" with the qualifier "Secure Overseas" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System
The New Zealand Threat Classification System is used by the Department of Conservation to assess conservation priorities of species in New Zealand.
The system was developed because the IUCN Red List, a similar conservation status system, had some ...
. The International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
has assessed the kitefin shark as a vulnerable species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, ...
in light of documented population declines.
See also
*List of prehistoric cartilaginous fish
This list of prehistoric cartilaginous fish genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the class chondrichthyes ''and'' are known from the fossil record. This list excludes purely vernacula ...
References
{{Good article Dalatiidae Taxa named by Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre Fish described in 1788 Extant Eocene first appearances