Kinzigtal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kinzig is a
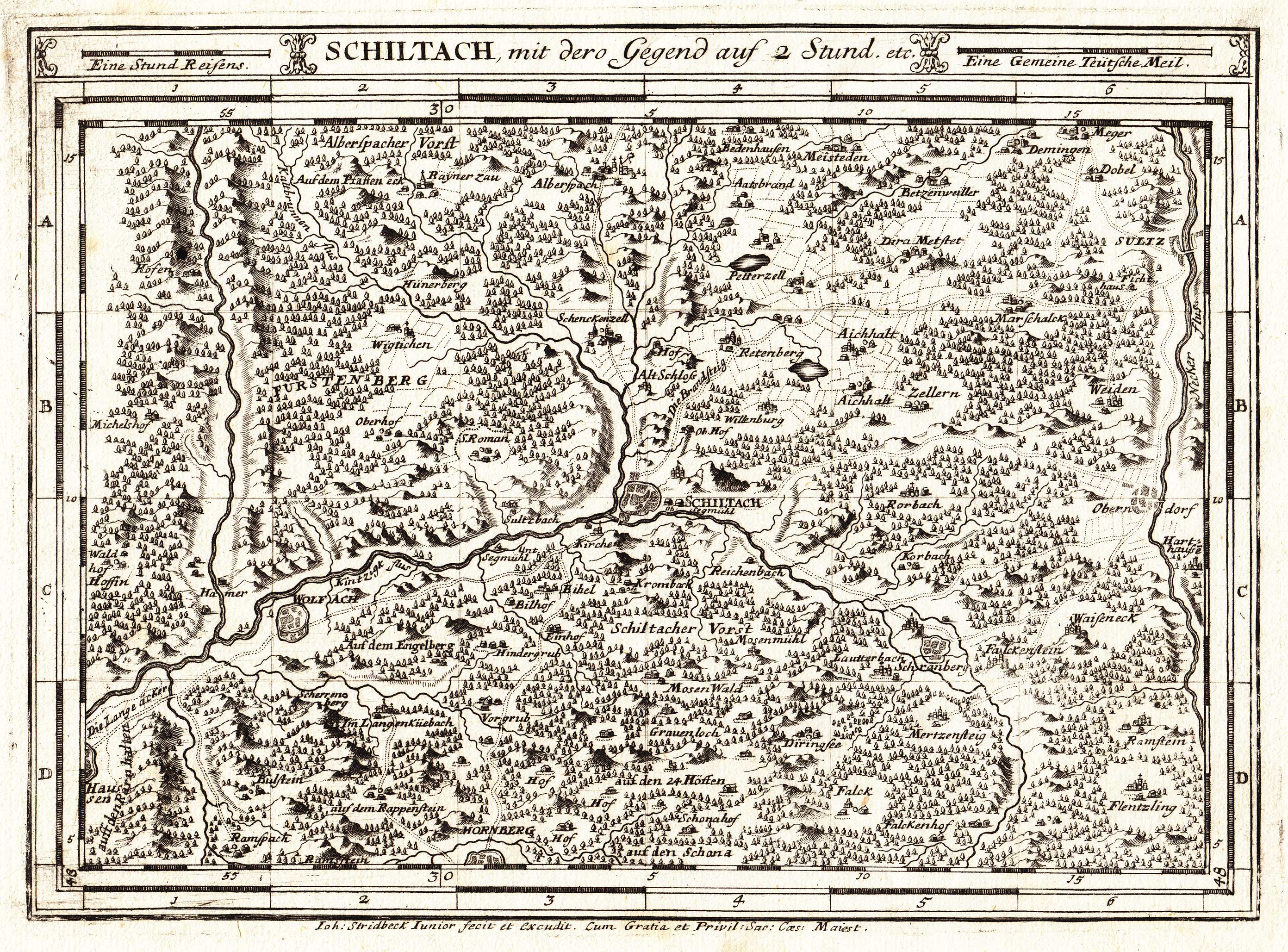 The width, length and the favourable east-west direction of the middle and lower valley of the Kinzig make it important for as a communication route. For example, the
The width, length and the favourable east-west direction of the middle and lower valley of the Kinzig make it important for as a communication route. For example, the
Schenkenburg.jpg, The Schenkenburg near Schenkenzell
Schloss wolfach im winter.jpg, Schloss Wolfach
Klosterkirche und Lorettokapelle.jpg, Abbey church and Loretto Chapel of the Capuchin abbey in Haslach, Feb 2006
GermanyBlackForestCastleHohengeroldseck.jpg, The ruins of Hohengeroldseck
Gengenbach3.JPG, Gengenbach Abbey
Schloss Ortenberg im Mai 2008.jpg, Schloss Ortenberg, May 2008
*
Tourism site of the Kinzig Valley communities
Rafters' Museum Gengenbach
*
*
Information about and images
{{Authority control Rivers of Baden-Württemberg Rivers of the Black Forest Rivers of Germany
river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
in southwestern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, a right tributary of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
.
It runs for 93 km from the Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is t ...
through the Upper Rhine River Plains
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
. The Kinzig valley and secondary valleys constitute the largest system of valleys in the Black Forest. Depending on the definition, the Kinzig is either the border between the Northern and Middle Black Forest or part of the Middle Black Forest. It is located entirely inside the State of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
and its name is supposed to be of Celtic origin. During the last glacial period the Kinzig and the Murg created a common Kinzig-Murg river system.
Course of the river
The origin of the Kinzig is located on the land of the town of Loßburg in the district of Freudenstadt. It runs south, then makes a gradual turn to the west. It leaves the district of Freudenstadt just after it emerges fromAlpirsbach
Alpirsbach () is a town in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest on the Kinzig river, south of Freudenstadt.
Because of the local brewery “Alpirsbacher Klosterbräu“, the monastery ...
, touches the district of Rottweil and continues to spend the largest part of its course in the district of Ortenau. The Kinzig leaves the Black Forest near Offenburg
Offenburg ("open borough" - coat of arms showing open gates; Low Alemmanic: ''Offäburg'') is a city located in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With nearly 60,000 inhabitants (2019), it is the largest city and the administrative capital ...
and flows into the Rhine near Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some municipal servicesfor exa ...
. The upper part the Kinzig is a true mountain river that over time has caused quite a few serious floods. Its middle and lower parts have been squeezed into a straight bed lined with tall levees
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastli ...
. Renaturation is in progress in the area where the Schutter flows into the Kinzig.
Name
In 1099 the river was first mentioned as ''ad Chinzechun, ad aliam Chinzichun'', in 1128 as Kinzicha. In 1539, 1543, 1560, 1620, 1652 and 1654 it was listed as Künzlin, Küntzgen, Kintzg, Kintzgen, Oberkentzgenwüß and Köntzig, respectively. In 1837 it was referred to for the first time as Kinzig. According to Adolf Bach and Bruno Boesch there is some doubt about whether the name Kinzig can really be traced back to the ''ad Chinczechun, ad aliam Chinzichun'' of 1099. Bach points to the usage in the northernBreisgau
The Breisgau () is an area in southwest Germany between the Rhine River and the foothills of the Black Forest. Part of the state of Baden-Württemberg, it centers on the city of Freiburg im Breisgau. The district of Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, ...
where ''Kinzigs'' are described as "paths at the bottom of a canyon through the loess". In Upper Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
and Graubünden rivers with the word Kinzig in their name usually describe a canyon. Some argue that the name developed from the Celtic ''kent'' meaning various kinds of quick movement or from the Lepontic
Lepontic is an ancient Alpine Celtic languageJohn T. Koch (ed.) ''Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia'' ABC-CLIO (2005) that was spoken in parts of Rhaetia and Cisalpine Gaul (now Northern Italy) between 550 and 100 BC. Lepontic is atte ...
word ''Centica (Cinti)'' which means "water".
With all these possibilities in mind, we can return to Adolf Bach and Bruno Boesch, who think these derivations doubtful. In addition, the question remains of how far the Celts or Pre-Celts had settled the Kinzig area, and which settlers had originally given the river its name. While these questions are difficult to answer for pre-historic times, the fact is that the Kinzig only created a small canyon in its upper part. A completely different river with many twists and turns presents itself as it moves towards the Upper Rhine River Plains
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
. At the end of the last ice age it wound its way through the Plains for a long time, on the way absorbing the Murg and only joining the Rhine after it reached the general area of Hockenheim
Hockenheim () is a town in northwest Baden-Württemberg, Germany, about 20 km south of Mannheim and 10 km west of Walldorf. It is located in the Upper Rhine valley on the tourist theme routes "Baden Asparagus Route" () and Bertha Benz M ...
.
Tributaries
In the Black Forest many tributaries empty into the Kinzig, including several longer streams of 20-30 kilometres in length, most coming from the north or south. The following is a list of those over 10 kilometres in length: * Little Kinzig, from the right near the Schenkenzell railway bridge, 20.2 km and 62.9 km². *Schiltach
Schiltach is a town in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Black Forest, on the river Kinzig, 20 km south of Freudenstadt.
Geography
Schiltach lies on the eastern side of the Black Forest ...
, from the left in Schiltach
Schiltach is a town in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Black Forest, on the river Kinzig, 20 km south of Freudenstadt.
Geography
Schiltach lies on the eastern side of the Black Forest ...
, 29.5 km and 115.8 km².
* Wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
, formerly the ''Wolfach'', from the right in Wolfach, 30.8 km and 129.6 km².
* Gutach, from the left near Gutach (Schwarzwaldbahn), 29.3 km and 161.5 km².
* ''Mühlbach'' or Welschensteinachbach, from the left near Steinach, 10.5 km and 24.9 km².
* Erlenbach, from the right near Biberach, 18.9 km (together with the rather larger ''Harmersbach'', the much longer of its two headstreams, the Harmersbach
Harmersbach (below its confluence with the ''Nordrach'': ''Erlenbach'') is a river of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It passes through Zell am Harmersbach, and flows into the Kinzig in Biberach. Until 1806, the Harmersbach valley held the unique ...
and the Nordrach) and 102.9 km².
The largest tributary overall reaches the Kinzig a little before its mouth in the Upper Rhine Plain:
* Schutter, from the left near Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some municipal servicesfor exa ...
, 56.8 km and 338.2 km².
Importance as a transport and trade route
Timber rafting
In the past, the Kinzig was very important fortimber rafting
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest mean ...
. The earliest mention of this trade on the Kinzig dates to the year 1339. The rafting towns of Wolfach and Schiltach
Schiltach is a town in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Black Forest, on the river Kinzig, 20 km south of Freudenstadt.
Geography
Schiltach lies on the eastern side of the Black Forest ...
had their own rafting corporations, which organized timber rafting to the Rhine and on to Holland; these corporations were the so-called ''Schifferschaften'' ("boatmen's associations"). They were given the sole rights of timber export by their respective overlords and ran a lucrative business that helped the towns' prosperity. Sebastian Münster
Sebastian Münster (20 January 1488 – 26 May 1552) was a German cartographer and cosmographer. He also was a Christian Hebraist scholar who taught as a professor at the University of Basel. His well-known work, the highly accurate world map, ' ...
writes in his '' Cosmographia universalis'': ''"The people living by the River Kyntzig, especially around Wolfach, earn a living from the great quantity of construction timber, which the float down the waters of the Kyntzig to Strasburg and into the Rhine, and earn a great deal of money every year."'' Rafting on the Kinzig reached its peak in the 15th and 16th centuries and then again in the 18th century, when the demand for wood began to rise rapidly, as the Netherlands and England began to build their mighty naval and merchant fleets. The rafters could not match the capabilities of the newly introduced railways, however, and the last commercial timber raft
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest mean ...
ran down the Kinzig in 1896. Today, timber rafting festivals, museums in Gengenbach
Gengenbach (; gsw, label=Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic, Gängäbach) is a town in the Ortenaukreis, district of Ortenau, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, and a popular tourist destination on the western edge of the Black Forest, with about 11,0 ...
, Wolfach and Schiltach
Schiltach is a town in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Black Forest, on the river Kinzig, 20 km south of Freudenstadt.
Geography
Schiltach lies on the eastern side of the Black Forest ...
, as well as numerous technical facilities, such as weir
A weir or low head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the river level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
s recall the timber rafting era.
Historical Roman road
 The width, length and the favourable east-west direction of the middle and lower valley of the Kinzig make it important for as a communication route. For example, the
The width, length and the favourable east-west direction of the middle and lower valley of the Kinzig make it important for as a communication route. For example, the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
built a road that passed through the valley: the Kinzig Valley Way (''Kinzigtalstrasse'') is a Roman road which was built under the Emperor, Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
, in 73/74 A.D. from Offenburg
Offenburg ("open borough" - coat of arms showing open gates; Low Alemmanic: ''Offäburg'') is a city located in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With nearly 60,000 inhabitants (2019), it is the largest city and the administrative capital ...
through the valley to the simultaneously founded Roman town of Rottweil (''Arae Flaviae'') and on to Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen ( Alemannic: ''Duttlinga'') is a town in Baden-Württemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, ''Möhringen'' and ''Eßlingen'' are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia ea ...
. It was mainly intended to create a shorter strategic link from Mainz to Augsburg, which had for a long time had to take a long detour via the Rhine Knee
The Rhine knee or Rhine's knee (german: Rheinknie) is the name of several distinctive bends in the course of the river Rhine.
Basel
In Basel, the Rhine changes its westerly direction of flow in an angle of 90 degrees to a northerly direction, alo ...
(''Rheinknie'') at Basle
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), ...
. During the revolt of the Batavi
The Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi, a small but militarily powerful Germanic tribe that inhabited Batavia, on t ...
in 69/70 this detour had proved a problem.
Fauna and flora
Fauna
A regeneration program has been in progress since 2002 to re-introducesalmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Oncorhy ...
into the Kinzig by putting young salmon into the water and removing obstacles. These efforts seem to be successful as in early 2005, for the first time in 50 years, salmon spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: ...
were found in a river in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
.
Flora
The Kinzig valley is the deepest in the inner Black Forest. In the lower Kinzig valley the villages are below 200 metres above sea level. The climate in the valley is therefore milder than in most other areas of the Black Forest. In the lower valley fruit andwine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
are produced; Gengenbach, Ortenberg and Ohlsbach are well-known names of wine-growing villages, some of which are on the Baden Wine Road. The countryside around the Kinzig valley in spring blooms far earlier than the surrounding regions of the Black Forest.
Infrastructure
The width, length and favourable east-west direction in the middle and lower valley make the Kinzig Valley important for infrastructure. TheRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
maintained a road that traversed the valley. The ''Kinzigtalstraße'' was a military road built under Emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
in 73/74 AD from Offenburg
Offenburg ("open borough" - coat of arms showing open gates; Low Alemmanic: ''Offäburg'') is a city located in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With nearly 60,000 inhabitants (2019), it is the largest city and the administrative capital ...
through the Kinzig Valley into the Roman Rottweil (Arae Flaviae) and on to Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen ( Alemannic: ''Duttlinga'') is a town in Baden-Württemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, ''Möhringen'' and ''Eßlingen'' are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia ea ...
. The main purpose of the road was to shorten the strategically important connection between Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
and Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ...
. Until this road was built, the connection took troops via the Rhine bend at Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
and during the revolt of the Batavers in 69/70 AD, this had proved to be a problem. During construction of the road, several Castelles were built. In addition to Rottweil, the rest areas in Offenburg
Offenburg ("open borough" - coat of arms showing open gates; Low Alemmanic: ''Offäburg'') is a city located in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With nearly 60,000 inhabitants (2019), it is the largest city and the administrative capital ...
-Rammersweier, Offenburg-Zunsweier, Waldmössingen, Sulz and Geislingen- Häsenbühl, were augmented by part of the Alb Limes
The Alb Limes (german: Alblimes) is a Roman frontier fortification or ''limes'' of the late 1st century AD in the Swabian Jura, also known as the Swabian Alb. The Alb Limes runs for just under 135 kilometres from Rottweil (Latin: '' Arae Flaviae'') ...
fortifications in Frittlingen, Lautlingen and Burladingen
Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
History
In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Prov ...
-Hausen. All of them were located in Upper Germanic country except for Burladingen which was in Rhaetian territory. The surprising discovery of the fortification in Frittlingen in 1992 only a few kilometers southeast of Rottweil shows that the ''Kinzigtalstraße'' was secured and covered with a tight net of military fortifications. The suggestion that the Kinzig Valley itself was home to another fortification has thus gained credibility. Until then, it was supposed that there must have been one or two more yet to be discovered fortifications merely on the basis that the distance between the known ones in Offenburg and Waldmössingen was very big. Another fortification is assumed in Rottenburg by the end of the 1st century however, it is not clear whether it existed as early as 73/74 AD or not until later in 98 AD.
Roughly at the same time that the ''Kinzigtalstraße'' was built, Roman forts were constructed further north on the right side of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
in places like Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
, Heddernheim
Heddernheim is a quarter of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is part of the '' Ortsbezirk Nord-West'' and is subdivided into the ''Stadtbezirke'' Heddernheim-Ost and Heddernheim-West.
History Antiquity
The Roman town of Nida (Roman town) was situ ...
, Karben, Groß-Gerau
Groß-Gerau () is the district seat of the Groß-Gerau district, lying in the southern Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region in Hesse, Germany, and serving as a hub for the surrounding area. In 1994, the town hosted the 34th Hessentag state festival.
Geogra ...
, Gernsheim
Gernsheim () is a town in Groß-Gerau district and Darmstadt region in Hesse, Germany, lying on the Rhine.
Geography
Location
The ''Schöfferstadt Gernsheim'', as Gernsheim may officially call itself – it was Peter Schöffer's birthplace – ...
, Ladenburg
Ladenburg is a town in northwestern Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It lies on the right bank of the river Neckar, northwest of Heidelberg and east of Mannheim.
The town's history goes back to the Celtic and Roman Ages, when it was called Lopo ...
( Lopodunum), Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914 ...
and Baden-Baden
Baden-Baden () is a spa town in the state of Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, at the north-western border of the Black Forest mountain range on the small river Oos, ten kilometres (six miles) east of the Rhine, the border with Fra ...
(Aquae). Whether these were advanced posts or the Roman border between 73 and 98 AD, (following a generally defined line east of the Rhine), has yet to be determined.
In 98 AD, in the area of present-day southwest Germany, the route between Odenwald and Neckar came under Roman control, making the connection from Mainz to Augsburg shorter yet. As a result, the ''Kinzigtalstraße'' lost superregional significance.
In present-day Germany, the federal highway B 33 runs parallel to the Kinzig from Offenburg until it leaves the Kinzig in the upper valley to follow the Gutach towards Villingen-Schwenningen. From Hausach
Hausach (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Huusä) is a town in the Ortenaukreis, in western Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
History
Hausach was founded in the 13th century, below Husen Castle. In the 14th century, it became a possession of the Coun ...
on towards Freudenstadt
Freudenstadt (Swabian: ''Fraidestadt'') is a town in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is capital of the district Freudenstadt. The closest population centres are Offenburg to the west (approx. 36 km away) and Tübingen to the eas ...
, the federal highway B 294, follows the upper Kinzig.
For the Black Forest Railway (''Schwarzwaldbahn'') train service, the valley is also very important. It runs from Offenburg to Hausach where it turns into the Gutach Valley to continue on to Konstanz
Konstanz (, , locally: ; also written as Constance in English) is a university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the south of Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was th ...
at Lake Constance. In the upper Kinzig Valley, the Kinzig Valley Railway (''Kinzigtalbahn'') provides a connection between Hausach and Freudenstadt.
Towns and villages
(starting at the origin)Castles, abbeys and stately homes
Alpirsbach Abbey
Alpirsbach Abbey (''Kloster Alpirsbach'') is a former Benedictine monastery and later Protestant seminary located at Alpirsbach in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The monastery was established in the late 11th century and possessed considerable free ...
, Alpirsbach
Alpirsbach () is a town in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest on the Kinzig river, south of Freudenstadt.
Because of the local brewery “Alpirsbacher Klosterbräu“, the monastery ...
* Schenkenburg Castle, Schenkenzell
* Schiltach Castle, Schiltach
Schiltach is a town in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the eastern Black Forest, on the river Kinzig, 20 km south of Freudenstadt.
Geography
Schiltach lies on the eastern side of the Black Forest ...
* Willenburg Castle, Schiltach
* Schloss Wolfach, Wolfach
* Husen Castle, Hausach
Hausach (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Huusä) is a town in the Ortenaukreis, in western Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
History
Hausach was founded in the 13th century, below Husen Castle. In the 14th century, it became a possession of the Coun ...
* Haslach Abbey, Haslach
* Hohengeroldseck Castle, between Seelbach and Biberach (Baden)
* Gengenbach Abbey, Gengenbach
Gengenbach (; gsw, label=Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic, Gängäbach) is a town in the Ortenaukreis, district of Ortenau, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, and a popular tourist destination on the western edge of the Black Forest, with about 11,0 ...
* Schloss Ortenberg
''Schloss'' (; pl. ''Schlösser''), formerly written ''Schloß'', is the German language, German term for a building similar to a château, palace, or manor house.
Related terms appear in several Germanic languages. In the Scandinavian langu ...
, Ortenberg (Baden)
See also
* Mother KinzigReferences
Sources
* Emil Imm (ed.) - Land um Kinzig und Rench, Rombach-Verlag (1974) * Kurt Klein - Leben am Fluss, Schwarzwald-Verlag (2002) * STALF, A. (1932): Korrektion und Unterhaltung der Kinzig. Die Ortenau 19. pp 124–144. * NEUWERCK, A. (1986): Der Lachsfang in der Kinzig. Die Ortenau 66. pp 499–525. * Bach, Adolf, Deutsche Namenkunde, Bd. II/2, Heidelberg 1981 * Bahlow, Hans, Deutschlands geographische Namenwelt, Frankfurt 1985, p. 263 * Boesch, Bruno,Kleine Schriften
' is a German phrase ("short writings" or "minor works"; la, Opuscula) often used as a title for a collection of articles and essays written by a single scholar over the course of a career. "Collected Papers" is an English equivalent. These short ...
zur Namenforschung, Heidelberg 1981
* Buck, M. R., Oberdeutsches Flurnamenbuch, Stuttgart 1880, p. 130
* Keinath, Walther, Orts- und Flurnamen in Württemberg, Stuttgart 1951
* Krahe, Hans, Unsere ältesten Flussnamen, Wiesbaden 1964
* Obermüller, Wilhelm, Deutsch – Keltisches Wörterbuch, 1872, Reprint-Druck, Vaduz 1993, Bd. II, pp 178f
* Springer, Otto, Die Flussnamen Württembergs und Badens, Stuttgart 1930, pp 53, 60
* Traub, Ludwig, Württembergische Flußnamen aus vorgeschichtlicher Zeit in ihrer Bedeutung für die einheimische Frühgeschichte, in: Württembergische Vierteljahrshefte für Landesgeschichte, XXXIV. Jahrgang, 1928, Stuttgart 1929, p. 16
External links
Tourism site of the Kinzig Valley communities
Rafters' Museum Gengenbach
*
*
Information about and images
{{Authority control Rivers of Baden-Württemberg Rivers of the Black Forest Rivers of Germany