King’s College Chapel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
King's College Chapel is the

 Henry VI planned a university counterpart to
Henry VI planned a university counterpart to
 This large wooden screen, which separates the
This large wooden screen, which separates the
chapel
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christianity, Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their o ...
of King's College in the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
. It is considered one of the finest examples of late Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-ce ...
English architecture
The architecture of England is the architecture of the historic Kingdom of England up to 1707, and of England since then, but is deemed to include buildings created under English influence or by English architects in other parts of the world, p ...
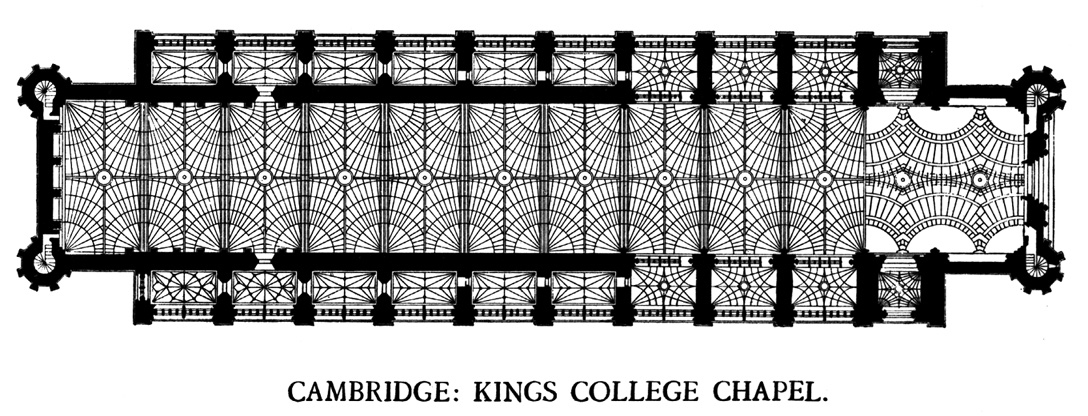
and features the world's largest fan vault
A fan vault is a form of vault used in the Gothic style, in which the ribs are all of the same curve and spaced equidistantly, in a manner resembling a fan. The initiation and propagation of this design element is strongly associated with E ...
. The Chapel was built in phases by a succession of kings of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
from 1446 to 1515, a period which spanned the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
and three subsequent decades. The Chapel's large stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ...
windows were completed by 1531, and its early Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
rood screen
The rood screen (also choir screen, chancel screen, or jubé) is a common feature in late medieval church architecture. It is typically an ornate partition between the chancel and nave, of more or less open tracery constructed of wood, stone, o ...
was erected in 1532–36. The Chapel is an active house of worship, and home of the King's College Choir. It is a landmark and a commonly used symbol of the city of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
.
Construction

 Henry VI planned a university counterpart to
Henry VI planned a university counterpart to Eton College
Eton College ( ) is a Public school (United Kingdom), public school providing boarding school, boarding education for boys aged 13–18, in the small town of Eton, Berkshire, Eton, in Berkshire, in the United Kingdom. It has educated Prime Mini ...
(whose Chapel
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christianity, Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their o ...
is very similar, but not on the scale intended by Henry). The King decided the dimensions of the Chapel. Reginald Ely
Reginald Ely or Reynold of Ely (fl. 1438–1471) was an English master mason and architect working in Gothic architecture in the Kingdom of England in the 15th century.
was most likely the architect and worked on the site since 1446. Two years earlier Reginald was charged with sourcing craftsmen for the Chapel's construction. He continued to work on the site until building was interrupted in 1461, having probably designed the elevations
The elevation of a geographic ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
. The original plans called for lierne Lierne may refer to:
Places
*Lierne Municipality, a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway
* Lierne National Park, a national park in Trøndelag county, Norway
Other
*Lierne (vault)
In Gothic architecture, a lierne is a tertiary rib connecti ...
vaulting, and the piers Piers may refer to:
* Pier, a raised structure over a body of water
* Pier (architecture), an architectural support
* Piers (name), a given name and surname (including lists of people with the name)
* Piers baronets, two titles, in the baronetages ...
of the choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
were built to conform with them. Ultimately, a complex fan vault
A fan vault is a form of vault used in the Gothic style, in which the ribs are all of the same curve and spaced equidistantly, in a manner resembling a fan. The initiation and propagation of this design element is strongly associated with E ...
was constructed instead. Reginald probably designed the window tracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support th ...
at the extreme east of the church's north side: the east window of the easternmost side chapel, which unlike the Perpendicular style of the others is in ''curvilinear'' Gothic style. The priest and later bishop Nicholas Close
Nicholas Close (died 1452) was an English priest.
Close is widely regarded as having been born in Westmorland, in Birkbeck Fells, but may have been of Flemish descent. He was educated at King's College, Cambridge, being elected a fellow in 1443 ...
(or Cloos) was recorded as the "surveyor", having been the curate
A curate () is a person who is invested with the ''care'' or ''cure'' () of souls of a parish. In this sense, ''curate'' means a parish priest; but in English-speaking countries the term ''curate'' is commonly used to describe clergy who are as ...
of St John Zachary, a church demolished to make way for the Chapel.
The first stone of the Chapel was laid, by Henry himself, on the Feast of St James the Apostle, 25 July 1446, the College having been begun in 1441. By the end of the reign of Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
(1485), despite the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
, five bays had been completed and a timber roof erected. Henry VII visited in 1506, paying for the work to resume and even leaving money so that the work could continue after his death. In 1515, under Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, the building was complete but the great windows had yet to be made.
The Chapel features the world's largest fan vault, constructed between 1512 and 1515 by master mason John Wastell
John Wastell ( – 1518) was an English gothic architect and master mason responsible for the fan vaulted ceiling and other features of King's College Chapel, Cambridge, the crossing tower (Bell Harry Tower) of Canterbury Cathedral, and sections ...
. It also features fine medieval stained glass.
Above the altar is ''The Adoration of the Magi
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
'' by Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens ( ; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens' highly charged compositions reference erudite aspects of clas ...
, painted in 1634 for the Convent of the White Nuns at Louvain
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the sub-municipalities of ...
in Belgium. The painting was installed in the Chapel in 1968 amid national controversy; this involved the lowering of the Sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred space, sacred place, such as a shrine, protected by ecclesiastical immunity. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This seconda ...
floor leading up to the High Altar. It had been believed that gradations were created in 1774 by James Essex
James Essex (1722–1784) was an English builder and architect who mostly worked in Cambridge, where he was born. He designed portions of many colleges of the University of Cambridge, and carried out major restorations of the cathedrals at Ely an ...
, when Essex had in fact ''lowered'' the floor by 5 1/2 inches, but at the demolition of these steps, it was found that the floor instead rested on Tudor brick arches.
During the removal of these Tudor steps, built at the Founder's specific request that the high altar should be 3 ft above the choir floor, human remains in intact lead coffins with brass plaques were discovered, dating from the 15th to 18th centuries, and were disinterred.
The eventual installation of the Rubens was also not without problems: once seen beneath the east window, a conflict was felt between the picture's swirling colours and those of the stained glass. The Rubens was also a similar shape to the window, which "dwarfed it and made it look rather like a dependent postage stamp". Plain shutters were proposed, one on each side, to give it a triptych
A triptych ( ) is a work of art (usually a panel painting) that is divided into three sections, or three carved panels that are hinged together and can be folded shut or displayed open. It is therefore a type of polyptych, the term for all m ...
shape (although the picture was never part of a triptych) and lend it independence of form, which is how one sees the Rubens today. The installation was designed by architect Sir Martyn Beckett, who was "philosophical about the furore this inevitably occasioned - which quickly became acceptance of a solution to a difficult problem."
Many religious sites suffered damage during the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
as Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
sought to remove or deface iconography they considered inappropriate. Although Parliamentarian troops stationed in Cambridge used the chapel as a training ground, the building was largely untouched. Some sources suggest that Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
, who had studied at Cambridge, ordered its protection. Near the altar, on the north and south walls, there is still graffiti left by the soldiers. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, most of the chapel's stained glass was placed in storage as a precautionary measure, but the chapel again avoided damage.
Great windows
The windows of King's College Chapel are some of the finest in the world from their era. There are 12 large windows on each side of the Chapel, and larger windows at the east and west ends. With the exception of the west window, they are byFlemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
hands and date from 1515 to 1531. Barnard Flower Barnard Flower (died July or August 1517) was a Flemish glazier. He was King's Glazier to Henry VII and Henry VIII from 1505 to 1517, the first non-Englishman to hold this office.
Flower came to work in England in the late 15th century. By 1496 ...
, the first non-Englishman appointed as the King's Glazier, completed four windows. Galyon Hone
Galyon Hone (died 1552) was a glazier from Bruges who worked for Henry VIII of England at Hampton Court and in other houses making stained glass windows. His work involved replacing the heraldry and ciphers of Henry VIII's wives in windows when th ...
and three partners (two English and one Flemish) are responsible for the east window and 16 others between 1526 and 1531. The final four were made by Francis Williamson and Symon Symondes. The one modern window is that in the west wall, which was donated by King's alumnus Francis Stacey and is by the Clayton and Bell
Clayton and Bell was one of the most prolific and proficient British workshops of stained-glass windows during the latter half of the 19th century and early 20th century. The partners were John Richard Clayton (1827–1913) and Alfred Bell (1832� ...
company and dates from 1879.
Rood screen
 This large wooden screen, which separates the
This large wooden screen, which separates the ante-chapel
The ante-chapel is that portion of a chapel which lies on the western side of the choir screen.
In some of the colleges at Oxford and Cambridge the ante-chapel is carried north and south across the west end of the chapel, constituting a western ...
from the choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
and supports the organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
, was erected in 1532–36 by Henry VIII in celebration of his marriage to Anne Boleyn
Anne Boleyn (; 1501 or 1507 – 19 May 1536) was List of English royal consorts, Queen of England from 1533 to 1536, as the Wives of Henry VIII, second wife of King Henry VIII. The circumstances of her marriage and execution, by beheading ...
. The screen is an example of early Renaissance architecture: a striking contrast to the Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-ce ...
Chapel; Sir Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (195 ...
said it is "the most exquisite piece of Italian decoration surviving in England".
Current use
The Chapel is actively used as a place of worship and also for some concerts and college events. Notable college events include the annual King's College Music Society May Week Concert, held on the Monday ofMay Week
May Week is the name used in the University of Cambridge to refer to a period at the end of the academic year. Originally May Week took place in the week during May before year-end exams began. Nowadays, May Week takes place in June after exa ...
. The event is popular with students, alumni, and visitors to the city.
The Chapel is noted for its splendid acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
. The world-famous Choir of King's College, Cambridge
The Choir of King's College, Cambridge is an English Anglican choir. It was created by Henry VI of England, King Henry VI, who founded King's College, Cambridge, in 1441, to provide daily singing in his King's College Chapel, Cambridge, Chapel, ...
, consists of choral scholars, organ scholars (male students at the college), and choristers (boys educated at the nearby King's College School
King's College School, also known as Wimbledon, KCS, King's and KCS Wimbledon, is a Private schools in the United Kingdom, private Public school (United Kingdom), public school in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, southwest London, England. The s ...
). From 1982 until shortly before his death on 22 November 2019 the director of music for the choir was Sir Stephen Cleobury
Sir Stephen John Cleobury ( ; 31 December 1948 – 22 November 2019)Daniel Hyde. The choir sings services on most days in term-time, and also performs concerts and makes recordings and broadcasts.
The
File:20130808 Kings College Chapel 01.jpg, Side view of the Chapel from inside the college
King's College Chapel, Cambridge, South Entrance by Henry Fox Talbot, cropped.png, King's College Chapel, Cambridge, South Entrance, by
King's College: the Chapel
{{Authority control Chapels of Colleges of the University of Cambridge Grade I listed churches in Cambridgeshire Grade I listed buildings in Cambridge
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
has broadcast the Choir's Nine Lessons and Carols
Nine Lessons and Carols, also known as the Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols and Service of Nine Lessons and Carols, is a service of Christian worship traditionally celebrated on or near Christmas Eve in Anglican churches. The story of the f ...
from the chapel on Christmas Eve
Christmas Eve is the evening or entire day before Christmas, the festival commemorating nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus. Christmas Day is observance of Christmas by country, observed around the world, and Christma ...
, during which a solo treble sings the first verse of ''Once in Royal David's City
Once in Royal David's City is a Christmas carol originally written as a poem by Cecil Frances Alexander. The carol was first published in 1848 in her hymnbook ''Hymns for Little Children''. A year later, the English organist Henry Gauntlett d ...
''. There is also a chapel choir of male and female students, King's Voices
King's Voices is an English choir, and is the mixed-voice chapel choir of King's College, Cambridge. It is a resident choir to the college's chapel, alongside the Choir of King's College, Cambridge.
Foundation and role in college
The choir was ...
, which sings Evensong
Evensong is a church service traditionally held near sunset focused on singing psalms and other biblical canticles. It is loosely based on the canonical hours of vespers and compline. Old English speakers translated the Latin word as , which ...
on Mondays during term-time.
The chapel is widely seen as a symbol of Cambridge (for example in the logo of Cambridge City Council
Cambridge City Council is the local authority for Cambridge, a non-metropolitan district with city status in the United Kingdom, city status in Cambridgeshire, England. The council has been under Labour Party (UK), Labour majority control since ...
).
Dean of the Chapel
The Dean of the Chapel is responsible to the College Council and the Governing Body for the conduct of services within the Chapel. King's College Chapel, like other Cambridge colleges, is not formally part of the structure of the Church of England, but the Dean is customarily licensed by theBishop of Ely
The Bishop of Ely is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Ely in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese roughly covers the county of Cambridgeshire (with the exception of the Soke of Peterborough), together with ...
. Both he and the Chaplain take a regular part in chapel services: each is normally present at services six days a week during Full Term
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception usually occurs following vaginal intercourse, but can also ...
, and each preaches once or twice a term. The Chapel is run by a Chapel Committee chaired by the Dean. A Use of Choirs Committee, also chaired by the Dean, organises the engagements of the Chapel choir.
The current Chaplain is Revd Mary Kells, who has been in the post since September 2021. She was preceded in the post by Revd Ayla Lepine (2020–2021). Revd Tom McLean served as Interim Chaplain in 2020. He followed the Revd Andrew Hammond, who held the role of Chaplain from 2015 to 2019, after the Revd Richard Lloyd Morgan who served from 2003 to 2014.
Recent deans
Source: * 1890 to 1893 – The Revd Dr. Alfred Hands Cooke * 1894 to 1918 – The Revd Dr. Alan England Brooke * 1918 to 1941 – The Very RevdEric Milner-White
Eric Milner Milner-White, (23 April 1884 – 15 June 1963) was a British Anglican priest, academic, and decorated military chaplain. He was a founder of the Oratory of the Good Shepherd, an Anglican dispersed community, and served as its super ...
* 1942 to 1948 – The Rt Revd Archibald Rollo Graham Campbell
* 1949 to 1956 – The Revd Ivor Erskine St Clair Ramsay
Ivor Erskine St Clair Ramsay (1 November 1902 – 22 January 1956) was a Scottish Anglican priest in the middle part of the 20th century.
He was born on 1 November 1902 and educated at Ardvreck School, Uppingham School and Glasgow Universit ...
* 1956 to 1966 – The Revd Dr. Alexander Roper Vidler
* 1966 to 1970 – The Very Revd Dr. David Lawrence Edwards
* 1970 to 1981 – The Very Revd Michael Stanley Till
* 1981 to 1991 – The Very Revd John Henry Drury
* 1991 to 2001 – The Revd Canon Prof. George Pattison
George Linsley Pattison (born 1950) is a retired English theologian and Anglican priest. His last post prior to retirement was as Professor of Divinity at the University of Glasgow. He was previously Lady Margaret Professor of Divinity at the Uni ...
* January to September 2002 – The Revd Canon Martin Shaw (temporary Dean)
* 2002 to 2004 – The Revd Prof. Christopher John Ryan
* 2005 to 2009 – The Revd Ian Malcolm Thompson
* 2010 to 2014 – The Revd Dr. Jeremy Morris
* 2014 to present – The Revd Dr. Stephen Cherry
Gallery
Henry Fox Talbot
William Henry Fox Talbot (; 11 February 180017 September 1877) was an English scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer who invented the salted paper and calotype processes, precursors to photographic processes of the later 19th and 20th c ...
,
File:King's College Chapel Vault.jpg, The vault of King's College Chapel
File:Thomas Malton - Cambridge University, Kings College Chapel - B1977.14.11895 - Yale Center for British Art.jpg, Landscape painting of the Chapel by Thomas Malton
__NOTOC__
Thomas Malton (1748 – 7 March 1804; also known as Thomas Malton the Younger), was an English painter of topography, topographical and architectural views, and an engraver. J. M. W. Turner and Thomas Girtin were amongst his pupils. ...
, dated 1798
File:Kings College Chapel, Cambridge interior by Loggan 1690 - RIBA 16020.jpg, Engraving of the interior of the Chapel by David Loggan
David Loggan (1634–1692) was an English baroque engraver, draughtsman, and painter.
Life
He was baptised on 27 August 1634 in Danzig, then a semi-autonomous city (granted by the Danzig law) within Polish Prussia (''Prusy Królewskie'') ...
, published 1690
File:Cambridge KingsCollege Towers.jpg, The Chapel's towers
File:Kings chapel roof.jpg, The Chapel's roof
Bibliography
* Warrior, Josephine. ''A Guide to King's College Chapel''. Photography and design byTim Rawle
Tim Rawle is an English architectural photographer and writer. He is best known for his photographs of buildings in Cambridge, England.
Biography
Tim Rawle was born in Ashford, Kent. After studying fine art and graphic design at St Martin's ...
(Cambridge 1994, reprinted 1997, 2001, 2003, 2007, 2014)
References
External links
King's College: the Chapel
{{Authority control Chapels of Colleges of the University of Cambridge Grade I listed churches in Cambridgeshire Grade I listed buildings in Cambridge
Chapel
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christianity, Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their o ...
Religious buildings and structures completed in 1515
Tudor architecture