Kiel, Germany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern
 The capital of the county (later duchy) of
The capital of the county (later duchy) of
 From 1773 to 1864, the town belonged to the king of
From 1773 to 1864, the town belonged to the king of
. Accessed 4 May 2007 There were several bombing raids of the port area during the period 20 February – 20 April 1945 which successfully eliminated many
 Kiel has about 40 districts, but there is no standard division. The districts are traditionally grouped into 30 boroughs (Stadtteil
Kiel has about 40 districts, but there is no standard division. The districts are traditionally grouped into 30 boroughs (Stadtteil
Another, more recent structure summarizes the districts in 18 political districts (Ortsteil
The city has 25 electoral districts. The biggest districts, by population, are Wik (20,100), Gaarden-Ost (19,200) and Mettenhof (19,900). Gaarden, located at the southern end of the fjord, is a traditional working-class district that used to be home to mainly shipyard workers. Mettenhof is a large housing estate (satellite town) that was built in the 1960s and 1970s on the western outskirts of the city. The city districts of Düsternbrook, Schreventeich, Ravensberg and Blücherplatz, north of the city centre, are popular places to live with many 19th century buildings, villas and tree-lined streets. The government offices, ministries and parliament of the state of
 The oldest building in the city is the 13th century '' St. Nikolai, Kiel, Church of St. Nicholas'', which has a sculpture by
The oldest building in the city is the 13th century '' St. Nikolai, Kiel, Church of St. Nicholas'', which has a sculpture by
, City of Kiel webpage, in German Particularly intriguing is the history of the carnival in Kiel. The Schifffahrtsmuseum is in the former fish market building in the harbour. Laboe is home to the
File:Willy Lucas - Die Holstenstraße in Kiel 1917.jpg, Holstenstraße Kiel 1917, by Willy Lucas
File:Ubena von Bremen Kiel2007.jpg, Historic ships at
City of Kiel
 The Kiel city council governs the city alongside the Mayor. The results of the city council election on 6 May 2018 were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left,
The Kiel city council governs the city alongside the Mayor. The results of the city council election on 6 May 2018 were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left,
City of Kiel

 Kiel's economy is dominated by the service sector, transport and maritime industries. Kiel is also one of the major ports of the
Kiel's economy is dominated by the service sector, transport and maritime industries. Kiel is also one of the major ports of the
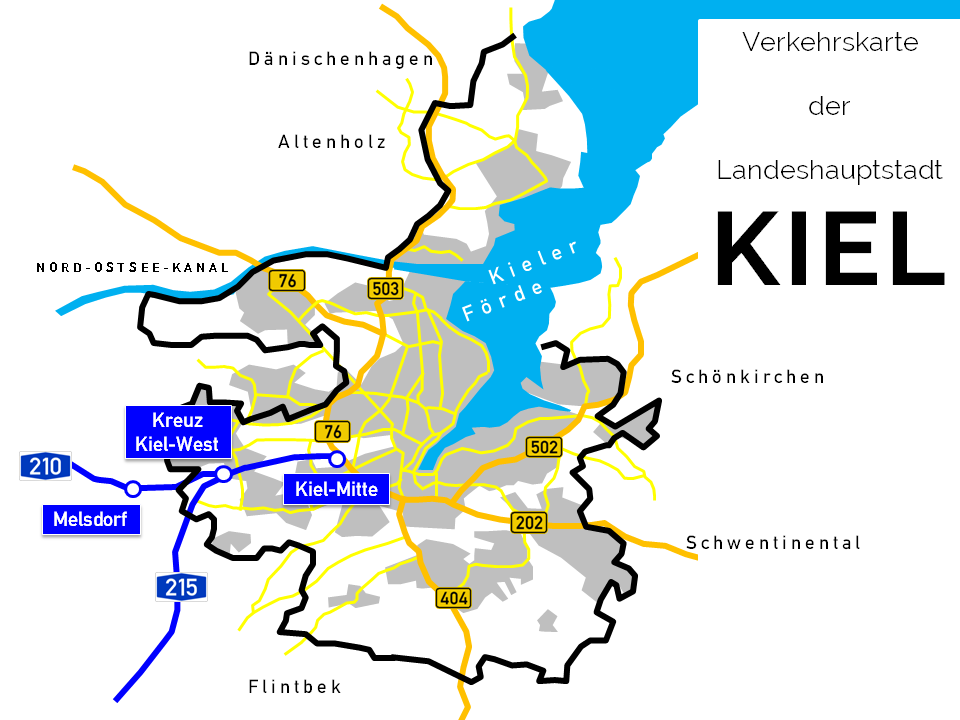 Kiel is situated near an important pan-European motorway, the A7, which connects northern Europe with central and southern Europe.
The central railway station,
Kiel is situated near an important pan-European motorway, the A7, which connects northern Europe with central and southern Europe.
The central railway station,
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
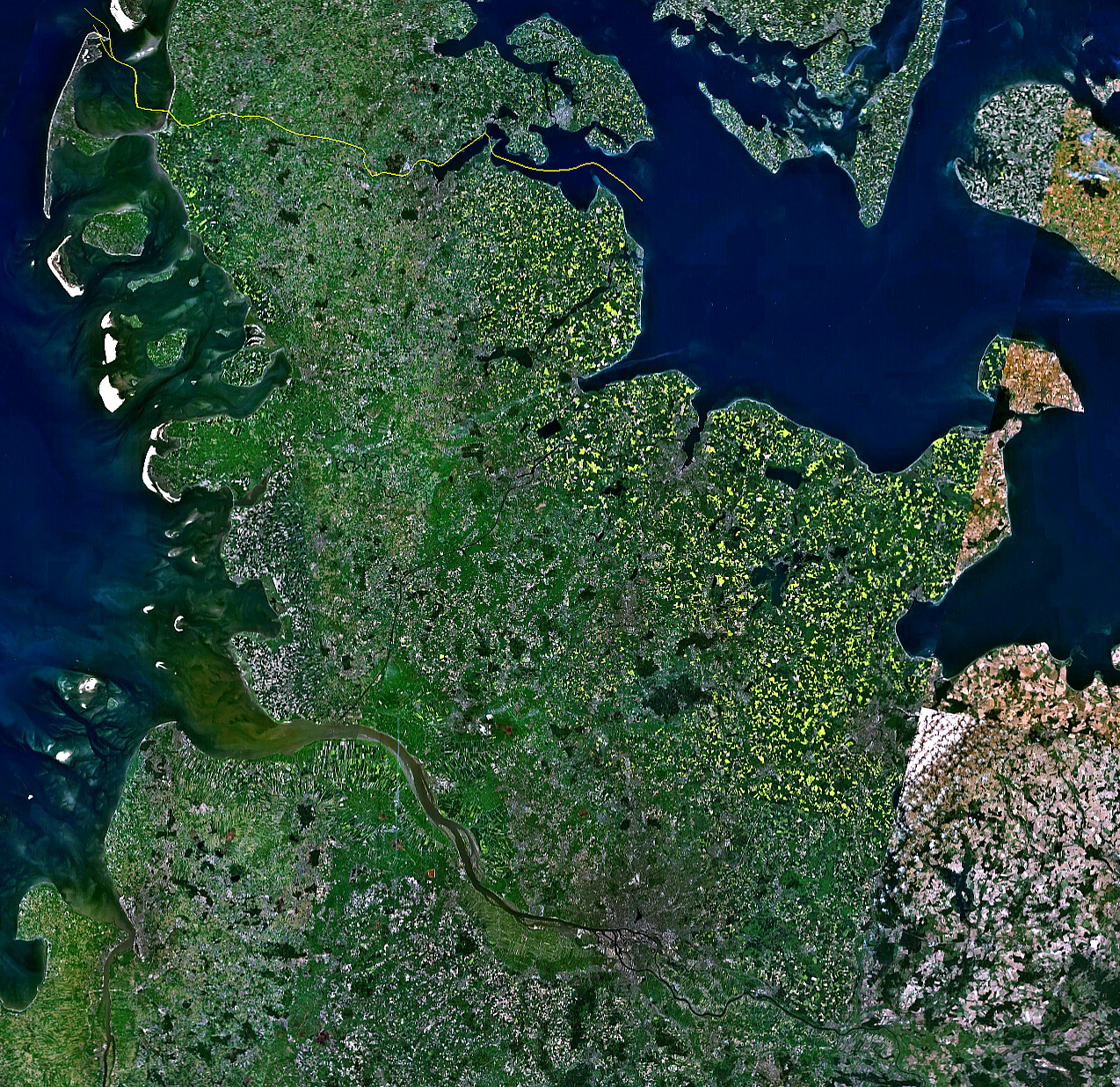
. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. It is located on the Kieler Förde
Kieler Förde is an inlet of the Baltic Sea, approximately long, on the eastern side of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Formed by glacier, glacial movement during the Last Glacial Period, last ice age, it divides Danish Wold peninsula from Wagri ...
inlet of the Bay of Kiel
The Bay of Kiel or Kiel Bay (, ; ) is a bay in the southwestern Baltic Sea, off the shores of Schleswig-Holstein in Germany and the islands of Denmark. It is connected with the Bay of Mecklenburg in the east, the Little Belt in the northwest, ...
and lies in the southeast of the Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
Peninsula, on the mouth of the Schwentine
The Schwentine is a river in the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is approximately long and rises on the hill of Bungsberg, the highest point in the state, near the village of Kasseedorf in Ostholstein. It then runs from its source t ...
River, approximately northeast of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
. The world's busiest artificial waterway, the Kiel Canal
The Kiel Canal (, until 1948 called in German the ) is a fresh water canal that links the North Sea () to the Baltic Sea (). It runs through the Germany, German states of Germany, state of Schleswig-Holstein, from Brunsbüttel to the Holtenau di ...
, has a terminus in Kiel's Holtenau
Holtenau (; Danish: Holtenå) is a district of Kiel, on the southeastern part of the Danish Wahld. It was historically part of the Duchy of Schleswig, and has cultural influences from both Germany and Denmark.
The district is located at the mouth ...
district. This canal connects the Baltic to the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
, with its other end in Brunsbüttel
Brunsbüttel (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Bruunsbüddel'') is a town in the district of Dithmarschen, in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany that lies at the mouth of the Elbe river, near the North Sea. It is the location of the western entrance to t ...
. Most of Kiel is part of Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
. The boroughs north of the Schwentine
The Schwentine is a river in the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is approximately long and rises on the hill of Bungsberg, the highest point in the state, near the village of Kasseedorf in Ostholstein. It then runs from its source t ...
also belong to Wagria
WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of Holstein in the German state of Schleswig- ...
, while those north of the Kiel Canal
The Kiel Canal (, until 1948 called in German the ) is a fresh water canal that links the North Sea () to the Baltic Sea (). It runs through the Germany, German states of Germany, state of Schleswig-Holstein, from Brunsbüttel to the Holtenau di ...
are historically part of Southern Schleswig
Southern Schleswig ( or ', ; ) is the southern half of the former Duchy of Schleswig in Germany on the Jutland Peninsula. The geographical area today covers the large area between the Eider river in the south and the Flensburg Fjord in the no ...
.
Kiel is one of Germany's major maritime centres, known for a variety of international sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
events, including the annual Kiel Week
The Kiel Week () or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is considered to be one of the largest sailing events globally, and also the largest summer festivals in Northern Europe, ...
, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. Kiel is also known for the Kiel Mutiny
The Kiel mutiny () was a revolt by sailors of the German High Seas Fleet against the Seekriegsleitung, maritime military command in Kiel. The mutiny broke out on 3 November 1918 when some of the ships' crews refused to sail out from Wilhelmshav ...
, when sailors refused orders to prepare to engage the British Navy in the last weeks of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, sparking the German Revolution
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, which led to the abdication of the Kaiser
Kaiser ( ; ) is the title historically used by German and Austrian emperors. In German, the title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (). In English, the word ''kaiser'' is mainly applied to the emperors ...
and the formation of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
. The Olympic sailing competitions of the 1936
Events January–February
* January 20 – The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII, following the death of his father, George V, at Sandringham House.
* January 28 – Death and state funer ...
and the 1972 Summer Olympics
The 1972 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XX Olympiad () and officially branded as Munich 1972 (; ), were an international multi-sport event held in Munich, West Germany, from 26 August to 11 September 1972. It was the ...
were held in the Bay of Kiel
The Bay of Kiel or Kiel Bay (, ; ) is a bay in the southwestern Baltic Sea, off the shores of Schleswig-Holstein in Germany and the islands of Denmark. It is connected with the Bay of Mecklenburg in the east, the Little Belt in the northwest, ...
.
Kiel has also been one of the traditional homes of the German Navy
The German Navy (, ) is part of the unified (Federal Defense), the German Armed Forces. The German Navy was originally known as the ''Bundesmarine'' (Federal Navy) from 1956 to 1995, when ''Deutsche Marine'' (German Navy) became the official ...
's Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
fleet, and continues to be a major high-tech shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other Watercraft, floating vessels. In modern times, it normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation th ...
centre. The University of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel, (, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a public research university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in 1665 as the ''Academia Holsator ...
, founded in 1665, is home to the GEOMAR – Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel. Kiel is an important sea transport hub, with passenger ferries to Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
and other countries. Moreover, today the Port of Kiel
__NOTOC__
The Port of Kiel () is a port for passenger and cargo shipping located in Kiel, Germany. It occupies the inner part of the Baltic Sea inlet Kieler Förde and includes the approach to the locks at the eastern end of Kiel Canal.
Harbours ...
is a popular destination for cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
s touring the Baltic Sea.
Kiel's recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
began in the 13th century. Before then, in the eighth century, it was a Danish village. Until 1864 it was administered by Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
. In 1866 the city was annexed by Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
and in 1871 it became part of Germany.
Kiel was one of the founding cities of the original European Green Capital Award
The European Green Capital Award (EGCA) is an award given by the European Commission each year to a European city based on its environmental record. The award was launched on 22 May 2008, with the first award being given to Stockholm for the y ...
in 2006. In 2005 Kiel's GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
per capita was €
The euro sign () is the currency sign used for the euro, the official currency of the eurozone. The design was presented to the public by the European Commission on 12 December 1996. It consists of a stylized letter E (or epsilon), crossed by t ...
35,618, which is well above Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
's national average, and 159% of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's average.
History
Middle Ages
The city of Kiel was founded in 1233 as ''Holstenstadt tom Kyle'' by CountAdolf IV of Holstein
Adolf IV (before 1205 – 8 July 1261) was a Count of Schauenburg (1225–1238) and of Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein, Holstein (1227–1238), of the House of Schaumburg. Adolf was the eldest son of Adolf III of Holstein, Adolf III of Scha ...
, and granted Lübeck city rights
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and the second-largest city in the state of Schle ...
in 1242 by Adolf's eldest son, John I John I may refer to:
People
Religious figures
* John I (bishop of Jerusalem)
* John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople
* John I of Antioch (died 441)
* Pope John I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope from 496 to 505
* Pope John I, P ...
of Schauenburg. As a part of Holstein, Kiel belonged to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
and was situated only a few kilometres south of the Danish border.
 The capital of the county (later duchy) of
The capital of the county (later duchy) of Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
, Kiel was a member of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
from 1284 until it was expelled in 1518 for harbouring pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
. The ''Kieler Umschlag'' (trade fair
A trade show, also known as trade fair, trade exhibition, or trade exposition, is an exhibition organized so that companies in a specific Industry (economics), industry can showcase and demonstrate their latest Product (business), products and se ...
), first held in 1431, became the central market for goods and money in the Duchy of Holstein. It began to decline and ceased in 1900.
Modern times
TheUniversity of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel, (, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a public research university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in 1665 as the ''Academia Holsator ...
was founded on 29 September 1665 by Christian Albert, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp () is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, also known as Ducal Holstein, that were ruled by the dukes of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, a side ...
. A number of important scholars, including Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; ; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th ce ...
, Felix Jacoby
Felix Jacoby (; 19 March 1876 – 10 November 1959) was a German classicist and philologist. He is best known among classicists for his highly important work '' Fragmente der griechischen Historiker'', a collection of text fragments of ancient ...
, Hans Geiger
Johannes Wilhelm Geiger ( , ; ; 30 September 1882 – 24 September 1945) was a German nuclear physicist. He is known as the inventor of the Geiger counter, a device used to detect ionizing radiation, and for carrying out the Rutherford scatt ...
and Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (; ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quantum, quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial con ...
, studied or taught there.
 From 1773 to 1864, the town belonged to the king of
From 1773 to 1864, the town belonged to the king of Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
. However, because the king ruled Holstein as a fief of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
only through a personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
, the town was not incorporated as part of Denmark proper. Even though the empire was abolished in 1806, the Danish king continued to rule Kiel only through his position as Duke of Holstein, which became a member of the German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
in 1815. When Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been di ...
and Holstein rebelled against Denmark in 1848 (the First Schleswig War
The First Schleswig War (), also known as the Schleswig-Holstein uprising () and the Three Years' War (), was a military conflict in southern Denmark and northern Germany rooted in the Schleswig–Holstein question: who should control the Du ...
), Kiel became the capital of Schleswig-Holstein until the Danish victory in 1850.
During the Second Schleswig War
The Second Schleswig War (; or German Danish War), also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War, was the second military conflict over the Schleswig–Holstein question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 Februar ...
in 1864, Kiel and the rest of the duchies of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been di ...
and Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
were conquered by a German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
alliance of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
and the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
. After the war, Kiel was briefly administered by both the Austrians and the Prussians, but the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War (German: ''Preußisch-Österreichischer Krieg''), also known by many other names,Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Second War of Unification, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), ''Deutsc ...
in 1866 led to the formation of the Province of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein ( ) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia (from 1868 to 1918) and the Free State of Prussia (from 1918 to 1946).
History
It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, which had been conquere ...
and the annexation of Kiel by Prussia in 1867. On 24 March 1865 King William I William I may refer to:
Kings
* William the Conqueror (–1087), also known as William I, King of England
* William I of Sicily (died 1166)
* William I of Scotland (died 1214), known as William the Lion
* William I of the Netherlands and Luxembour ...
based Prussia's Baltic Sea fleet in Kiel instead of Danzig (Gdańsk). The Imperial shipyard Kiel was established in 1867 in the town.
When William I of Prussia became Emperor William I William I may refer to:
Kings
* William the Conqueror (–1087), also known as William I, King of England
* William I of Sicily (died 1166)
* William I of Scotland (died 1214), known as William the Lion
* William I of the Netherlands and Luxembour ...
of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871, he designated Kiel and Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsha ...
as ''Reichskriegshäfen'' ("Imperial War Harbours"). The Kiel Yacht Club
Kieler Yacht-Club (''Kiel Yacht Club'') is one of the oldest yacht clubs in Germany. It is located in the harbor city of Kiel.
This club is well known for some of the yacht racing events it organizes. The main one is the yearly Kieler Woche (Kie ...
was established in 1887 with Prince Henry of Prussia as its patron. Emperor Wilhelm II became its commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (India), in India
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ' ...
in 1891.
Because of its new role as Germany's main naval base, Kiel very quickly increased in size in the following years, from 18,770 in 1864 to about 200,000 in 1910. Much of the old town centre and other surroundings were levelled and redeveloped to provide for the growing city. The Kiel tramway network, opened in 1881, had been enlarged to 10 lines, with a total route length of , before the end of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
.
Kiel was the site of the sailors' mutiny which led to the German Revolution
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
in late 1918. Just before the end of the First World War, the German fleet stationed at Kiel was ordered to sail out for a last great battle with the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
. The sailors, who thought of it as a suicide mission which would have no effect on the outcome of the war, decided they had nothing to lose and refused to obey orders. They took over Kiel and then spread out to other north German ports, sparking the revolution which led to the abolition of the monarchy and the creation of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Kiel remained one of the major naval bases and shipbuilding centres of the German Reich. There was also a slave
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
labour camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see British and American spelling differences, spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are unfree labour, forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have ...
for the local industry. Owing to its status as a naval port and production site for submarines, Kiel was heavily bombed by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
during this period. The bombing destroyed more than 80% of the remaining old town, 72% of the central residential areas, and 83% of the industrial areas. During the RAF bombing of 23/24 July 1944, Luftwaffe fighters tried to intercept the spoof (i.e. decoy) force instead of the main force attacking Kiel, and there was no water for three days; trains and buses did not run for eight days and there was no gas available for cooking for three weeks.Campaign Diary: July 44. Accessed 4 May 2007 There were several bombing raids of the port area during the period 20 February – 20 April 1945 which successfully eliminated many
U-boats
U-boats are naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the First and Second World Wars. The term is an anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Na ...
, and the few large warships (cruisers Hipper, Scheer, and Köln
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
) still afloat at that time. It and its port, and the canal were seized by a British T-Force
T-Force was the operational arm of a joint US Army–British Army mission to secure German scientific and industrial technology before it could be destroyed by retreating German forces or looters during the final stages of the Second World War a ...
led by Major Tony Hibbert
Anthony James Hibbert (born 20 February 1981) is an English former professional footballer.
Originally a midfielder, Hibbert converted to play at right-back. He spent his entire professional career with Everton, having joined the club in 1991. ...
on 5 May 1945.
Like other heavily bombed German cities, the city was rebuilt after the war. In 1946, Kiel was named the seat of government for Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
, and it officially became the state's capital in 1952.
Today, Kiel is once again an important maritime centre of Germany, with high-tech shipbuilding, submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
construction and one of the world's largest ocean research centers, the GEOMAR. Regular ferries to Scandinavia and Lithuania, as well as the largest sailing event in the world called the Kiel Week
The Kiel Week () or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is considered to be one of the largest sailing events globally, and also the largest summer festivals in Northern Europe, ...
(Kieler Woche) in German and The Kiel Regatta in English. The ''Kieler Umschlag'' is another festival, which has been taking place again since 1975. Kiel is also home to a large service sector and a number of research institutions including the University of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel, (, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a public research university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in 1665 as the ''Academia Holsator ...
, which is the oldest, largest, and most prestigious university in the state.
Geography
Climate
Kiel has anoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: ''Cfb''; Trewartha: ''Dolk''). Located on the Baltic Sea coast, the temperature fluctuates less than inland, with warm winters and cool summers throughout the year. The average temperature ranges from in winter to in summer. Days with a temperature above are rare, with an average of only 2.8 days per year.
The Kiel weather station has recorded the following extreme values:
* Highest Temperature on 20 July 2022.
* Warmest Minimum on 1 August 1994.
* Coldest Maximum on 12 February 1940.
* Lowest Temperature on 13 February 1940.
* Highest Daily Precipitation on 27 August 1989.
* Wettest Month in August 2011.
* Wettest Year in 2002.
* Driest Year in 1959.
* Longest annual sunshine: 2,115.3 hours in 1959.
* Shortest annual sunshine: 1,299.4 hours in 1987.
Note
Districts
Another, more recent structure summarizes the districts in 18 political districts (Ortsteil
The city has 25 electoral districts. The biggest districts, by population, are Wik (20,100), Gaarden-Ost (19,200) and Mettenhof (19,900). Gaarden, located at the southern end of the fjord, is a traditional working-class district that used to be home to mainly shipyard workers. Mettenhof is a large housing estate (satellite town) that was built in the 1960s and 1970s on the western outskirts of the city. The city districts of Düsternbrook, Schreventeich, Ravensberg and Blücherplatz, north of the city centre, are popular places to live with many 19th century buildings, villas and tree-lined streets. The government offices, ministries and parliament of the state of
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
are also mainly based in these neighbourhoods, particularly Düsternbrook. In contrast to the heavy bomb damage inflicted on the central parts of the city during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, most of the residential areas were not severely damaged. Hence, Kiel's more modern-style inner city and Kiel's more historic/elaborate residential areas stand in architectural contrast to one another.
There are plans for large-scale improvement and building efforts for the inner city, providing better pavements, better access to and view of the waterfront, and a generally more attractive feel to the place. These plans, most notably the "Kleiner Kiel Kanal", a restoration of a historic canal that was filled in to make place for road infrastructure, are to be implemented in the next few years.
Main sights
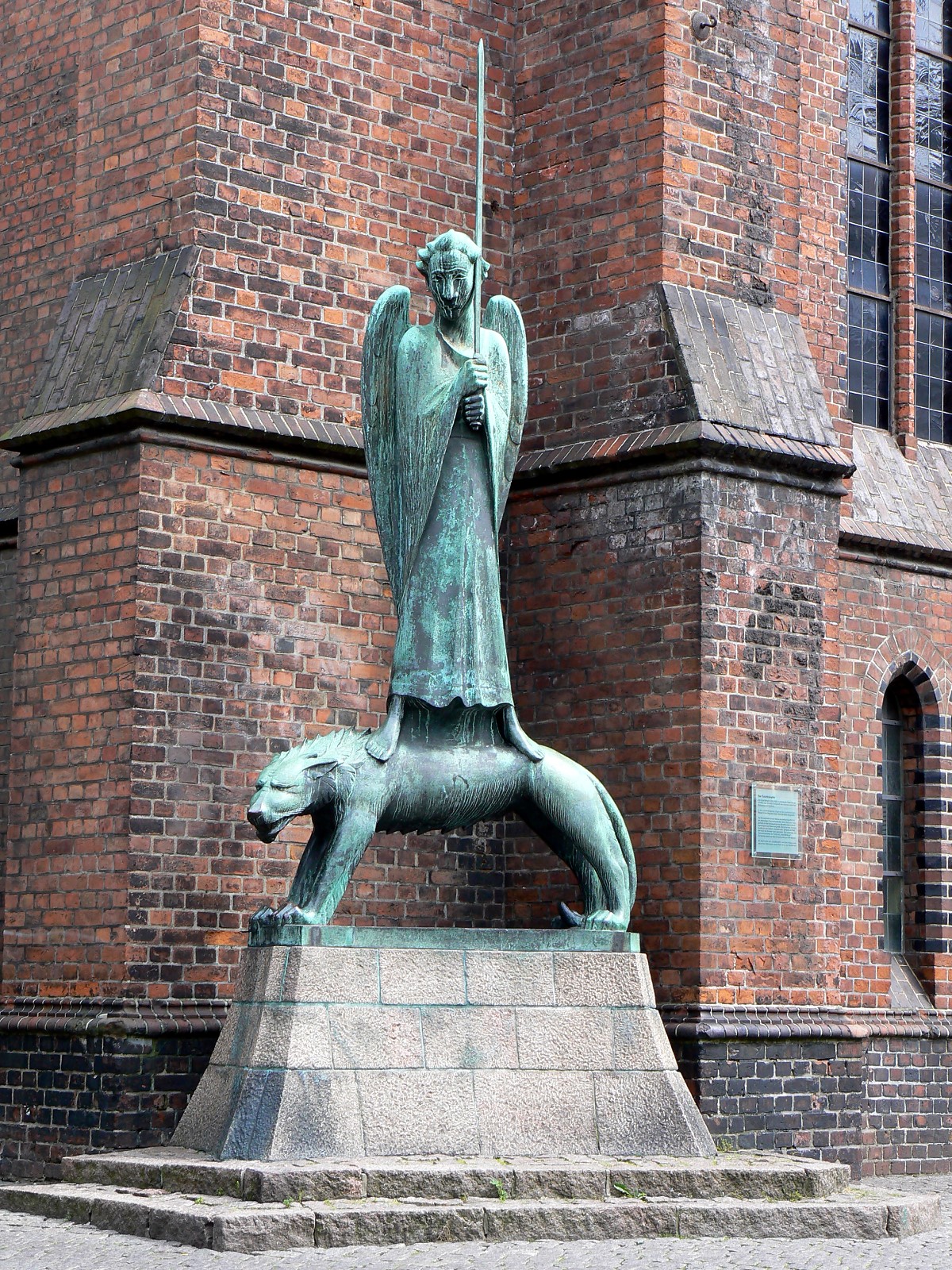
 The oldest building in the city is the 13th century '' St. Nikolai, Kiel, Church of St. Nicholas'', which has a sculpture by
The oldest building in the city is the 13th century '' St. Nikolai, Kiel, Church of St. Nicholas'', which has a sculpture by Ernst Barlach
Ernst Heinrich Barlach (2 January 1870 – 24 October 1938) was a German Expressionism, expressionist sculptor, medallist, printmaker and writer. Although he was a supporter of the war in the years leading to World War I, his participation in th ...
in front of it called ''Geistkämpfer''.
Kiel is Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
's largest city, and therefore Kiel's shopping district is a major attraction, and will see further improvement and renovation efforts in the upcoming years. Kiel's Holstenstraße (Holsten Street) is one of the longest shopping streets in Germany. The Rathaus
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
(Town Hall), which was built in 1911, has an operating paternoster lift
A paternoster (, , or ) or paternoster lift is a passenger elevator, consisting of a chain of open compartments, each usually designed for two people, that move slowly in a loop up and down inside a building without stopping. Passengers can s ...
and the design of its tower was based on one in Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
. The square in front of it is bordered by a lake and the Opernhaus Kiel
Opernhaus Kiel (Kiel Opera House) is the major venue for opera, ballet, and orchestral performances in Kiel, and home to Theater Kiel. It is a Grade II listed building.
History
After an architectural competition, the Kiel City Council commis ...
(Kiel Opera House). There are also a number of lakes and parks in the city centre, such as Schrevenpark. There are two botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens. is ...
s, the Old Botanical Garden and the Botanischer Garten der Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (or New Botanical Garden).
As Kiel is situated near the sea, the beaches to the north of Kiel, such as Strande, Kiel-Schilksee
Schilksee () is a town on the Danish Wahld peninsula in the Kieler Förde. In 1959, the town was incorporated into the city of Kiel, therefore today sometimes named as Kiel-Schilksee ().
The town is a popular vacation destination because of its b ...
, Möltenort and Laboe
Laboe () is a municipality in the district of Plön, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the Baltic Sea coast, approximately 10 km northeast of Kiel. The Laboe Naval Memorial is located within the municipality, as is the U-boa ...
, are also popular places to visit in spring and summer.
Kiel Week
The Kiel Week () or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is considered to be one of the largest sailing events globally, and also the largest summer festivals in Northern Europe, ...
, also known in English as the Kiel Regatta, is the largest sailing event in the world and takes place every year in the last full week in June. Many thousands of boats and ships of all kinds and eras take part in the parade. Kiel Week is also a festival, ''Volksfest
A ( ; German for "people's festival")Cognate of "folk festival" in English is a large event in German-speaking countries which usually combines a beer festival or wine festival and a travelling funfair. Attractions may include amusement rides, g ...
'' and fair as well as a maritime event. There are a number of yachting and sailing clubs in picturesque settings.
Kiel also features a number of museums, including zoological, geological, historical, fine art, industrial and military museums. Notable is the Stadt- und Schifffahrtsmuseum Warleberger Hof (City and Maritime Museum), which belongs to the association '' Museen am Meer''. In addition to preserving architecture from the 16th century and historic rooms with painted stucco ceilings, it displays urban and cultural exhibits of the 19th and 20th centuries."Kieler Stadtmuseum Warleberger Hof", City of Kiel webpage, in German Particularly intriguing is the history of the carnival in Kiel. The Schifffahrtsmuseum is in the former fish market building in the harbour. Laboe is home to the
Laboe Naval Memorial
The Laboe Naval Memorial (a.k.a. ''Laboe Tower,'' German: ''Marine-Ehrenmal Laboe'') is a memorial located in Laboe, near Kiel, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Started in 1927 and completed in 1936, the monument originally commemorated the World ...
and the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
submarine , which are both popular tourist sites.
Kiel Week
The Kiel Week () or Kiel Regatta is an annual sailing event in Kiel, the capital of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is considered to be one of the largest sailing events globally, and also the largest summer festivals in Northern Europe, ...
File:Alter Botanischer Garten Kiel Pavillon.jpg, Old Botanical Garden, Kiel
File:U995 Laboe.jpg, U995 Laboe
File:Warleberger Hof Wappen Kiel2008.jpg, Warleberger Hof
File:Kiel Holtenau Leuchtturm.jpg, Lighthouse in Kiel-Holtenau
File:Opernhaus Kiel msu2017-9209.jpg, Opera House
File:Kiel Wasserturm.jpg, Water tower in Kiel-Ravensberg
Population
Kiel has a population of 250,412. In 1946, when Kiel became the capital ofSchleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
, its population was about 214,000. Kiel is Germany's largest coastal city and its only state capital located on the sea. In the 1950s Kiel, with its marine port, attracted members of the navy. Kiel had its highest peak of population in 1973 at 273,000. The population declined since then. Many people moved away from this city and Kiel became very poor and had a big problems with unemployed people at that time. Kiel is now a city with universities and active marine stations which attracts many young students and marines to Kiel.
Politics
City Council
The City Council is the municipal representative body of Kiel. Its composition is determined by citizens in elections held every five years. Since the last election on May 14, 2023, in whichAlliance 90/The Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (, ), often simply referred to as Greens (, ), is a Green (politics), green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of the Greens (formed in West Germany in 1980) and Alliance 90 (formed in East Ger ...
became the strongest party in Kiel for the first time, the city has been governed by a green-red coalition. This coalition, formed by the Greens and the SPD
The Social Democratic Party of Germany ( , SPD ) is a social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany. Saskia Esken has been the party's leader since the 2019 leadership election together wi ...
, holds 25 of the 49 seats in the Kiel City Council and operates under a cooperation agreement from 2023 to 2028.
Mayor
The current mayor of Kiel is Ulf Kämpfer of theSocial Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Form ...
(SPD). Kämpfer has stated that he will not run for a third five year term. His current term ends in 2026. The results of the 29 October 2019 election were as follows.:
! colspan=2, Candidate
! Party
! Votes
! %
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Ulf Kämpfer
, align=left, Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Form ...
, 48,033
, 65.8
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Andreas Ellendt
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union
, 14,776
, 20.3
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Björn Thoroe
, align=left, The Left
, 6,643
, 9.1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Florian Wrobel
, align=left, Die PARTEI
(''Party for Labour, Rule of Law, Animal Protection, Promotion of Elites and Grassroots Democratic Initiative''), or Die PARTEI (''The PARTY''), is a German political party. It was founded in 2004 by the editors of the German satirical magazine ...
, 3,513
, 4.8
, -
! colspan=3, Valid votes
! 72,965
! 99.3
, -
! colspan=3, Invalid votes
! 500
! 0.7
, -
! colspan=3, Total
! 73,465
! 100.0
, -
! colspan=3, Electorate/voter turnout
! 193,653
! 37.9
, -
, colspan=7, SourceCity of Kiel
2018 City Council election
Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Form ...
(SPD)
, 26,617
, 29.9
, 5.8
, 18
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, 20,987
, 23.5
, 6.2
, 14
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (, ), often simply referred to as Greens (, ), is a Green (politics), green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of the Greens (formed in West Germany in 1980) and Alliance 90 (formed in East Ger ...
(Grüne)
, 18,215
, 20.4
, 2.8
, 12
, 3
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, The Left (Die Linke)
, 6,437
, 7.2
, 3.8
, 4
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, 5,764
, 6.5
, 2.6
, 4
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alternative for Germany
Alternative for Germany (, AfD, ) is a Far-right politics in Germany (1945–present), far-right,Far-right:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Right-wing populism, right-wing populist and National conservatism, national-conservative p ...
(AfD)
, 5,293
, 5.9
, New
, 3
, New
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, South Schleswig Voters' Association
The South Schleswig Voters' AssociationOther translations include ''South Schleswig Voter Alliance'', ''South Schleswig Voters' Committee'', ''South Schleswig Voter Federation'', ''South Schleswig Voters Group'', ''South Schleswig Voters League'', ...
(SSW)
, 2,521
, 2.8
, 0.6
, 2
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Die PARTEI
(''Party for Labour, Rule of Law, Animal Protection, Promotion of Elites and Grassroots Democratic Initiative''), or Die PARTEI (''The PARTY''), is a German political party. It was founded in 2004 by the editors of the German satirical magazine ...
, 2,278
, 2.6
, New
, 2
, New
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Pirate Party Germany
The Pirate Party Germany (), commonly known as Pirates (), is a political party in Germany founded in September 2006 at c-base. It states general agreement with the Swedish Piratpartiet as a party of the information society; it is part of the i ...
(Piraten)
, 1,011
, 1.1
, 1.9
, 1
, 1
, -
, colspan=7 bgcolor=lightgrey,
, -
,
, align=left, Independent
, 36
, 0.0
, New
, 0
, New
, -
! colspan=2, Valid votes
! 89,159
! 99.1
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Invalid votes
! 766
! 0.9
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 89,925
! 100.0
!
! 59
! 6
, -
! colspan=2, Electorate/voter turnout
! 196,334
! 45.8
! 8.7
!
!
, -
, colspan=7, SourceCity of Kiel
Culture

Sports
There are a number of sports venues in Kiel, most notably the Wunderino Arena (formerly known as Baltic Sea Hall or ''Ostseehalle''), which is the home ground of one of the most successfulteam handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball, Olympic handball or indoor handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a Handball goalkeeper, goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands ...
clubs in the world and multiple German champion, THW Kiel
THW Kiel is a professional handball club from Kiel, Germany. Currently, they compete in the Handball-Bundesliga and are the record champion with 23 titles.
2007 and 2012 were the most successful years in the club's history, as THW completed t ...
. Holstein Kiel
Kieler Sportvereinigung Holstein von 1900 e.V., commonly known as Holstein Kiel () or KSV Holstein, is a German association football and sports club based in the city of Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein. From the 1900s through the 1960s, the club was o ...
, an association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
club, which plays at Holstein-Stadion, plays in the Bundesliga
The Bundesliga (; ), sometimes referred to as the Fußball-Bundesliga () or 1. Bundesliga (), is a professional association football league in Germany and the highest level of the German football league system. The Bundesliga comprises 18 teams ...
in the 2024–2025 season for the first time in the club's history.
Education and scientific research
TheUniversity of Kiel
Kiel University, officially the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel, (, abbreviated CAU, known informally as Christiana Albertina) is a public research university in the city of Kiel, Germany. It was founded in 1665 as the ''Academia Holsator ...
(German: Christian-Albrechts-Universität) was founded by Duke Christian Albrecht in 1665. It is the only full university of Schleswig-Holstein, with about 27.000 students. Partly linked to the University Kiel are other independent research facilities such as the German National Library of Economics
The National Library of Economics (, "ZBW – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics", formerly: ''Deutsche Zentralbibliothek für Wirtschaftswissenschaften'') is the world's largest research infrastructure for economic literature, online as ...
– Leibniz Informationcenter for Economy, the Kiel Institute for the World Economy
The Kiel Institute for the World Economy (, or IfW Kiel) is an independent, non-profit economic research institute and think tank based in Kiel, Germany. In 2017, it was ranked as one of the top 50 most influential think tanks in the world and w ...
, the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel
The GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), formerly known as the ''Leibniz Institute of Marine Sciences'' ( German: ''Leibniz-Institut für Meereswissenschaften'', IFM-GEOMAR), is a research institute in Kiel, Germany. It wa ...
and the research institute of the Bundeswehr
The (, ''Federal Defence'') are the armed forces of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. The is divided into a military part (armed forces or ''Streitkräfte'') and a civil part, the military part consists of the four armed forces: Germ ...
for water sound and geophysics. Besides these there are other educational institutions such as the Fachhochschule Kiel (founded in 1969) and the Muthesius School of Arts (founded in 1907). The projects Murmann School of Global Management and Economics and Multimedia Campus Kiel were ultimately unsuccessful. The Wirtschaftsakademie Schleswig-Holstein offers besides advanced training at the Berufsakademie dual study courses for economists, business information specialists and industrial engineers.
Noteworthy as departmental research institute is the federal institute for dairy research which was merged into the Max-Rubner-Institut together with other institutions in 2004. The state capital Kiel is a corporative sponsoring member of the Max Planck Society
The Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science (; abbreviated MPG) is a formally independent non-governmental and non-profit association of German research institutes. Founded in 1911 as the Kaiser Wilhelm Society, it was renamed to the M ...
.
The ARGE-SH, the oldest research institution of the republic of Germany, has its headquarters in Kiel.
There are twelve gymnasiums
A gym, short for gymnasium (: gymnasiums or gymnasia), is an indoor venue for exercise and sports. The word is derived from the ancient Greek term " gymnasion". They are commonly found in athletic and fitness centres, and as activity and learn ...
in Kiel, of which the Kieler Gelehrtenschule, founded in 1320 as a humanistic gymnasium, is the oldest. Other secondary schools include the Gymnasium Elmschenhagen and the Max-Planck-Schule with a focus on natural sciences. There are many comprehensive schools – partially with secondary schools – all over the city area, as well as private schools.
BZ am NOK (Berufsbildungszentrum am Nord-Ostsee-Kanal)is a vocational training center provides education and training in over 40 professions. It includes dual training programs, vocational schools, technical colleges, and vocational grammar schools.
Economy and infrastructure
German Navy
The German Navy (, ) is part of the unified (Federal Defense), the German Armed Forces. The German Navy was originally known as the ''Bundesmarine'' (Federal Navy) from 1956 to 1995, when ''Deutsche Marine'' (German Navy) became the official ...
, and a leading centre of German high-tech military and civil shipbuilding. Kiel is the home of Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft
Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft GmbH (often abbreviated HDW) is a German shipbuilding company, headquartered in Kiel. It is part of the ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS) group, owned by ThyssenKrupp. The Howaldtswerke shipyard was founded in Kiel i ...
, a shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes m ...
founded in 1838 famed for its construction of submarines
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or info ...
. HDW built the first German submarine ''Brandtaucher
''Brandtaucher'' ( German for ''Fire-diver'') was a submersible designed by the Bavarian inventor and engineer Wilhelm Bauer and built by Schweffel & Howaldt in Kiel for Schleswig-Holstein's Flotilla (part of the '' Reichsflotte'') in 1850. ...
'' in 1850, and is today a subsidiary of ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
TKMS –officially branded as ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems until June 2025– is a group and holding company of providers of naval vessels, surface ships and submarines. It was founded when large industrial conglomerate ThyssenKrupp acquired Howal ...
, the leading German group of shipyards.
Statistics
In 2005, the GDP per person was €35,618, which is well above the national average ofGermany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and 159% of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
average.
Notable companies
Some of the most notable companies having branches or their headquarters in Kiel are: Ferry operators *DFDS Seaways
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions (DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) in ...
* Stena Line
Stena Line is a Swedish Shipping line, shipping line company and one of the world's largest ferry operators. It services Denmark, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland and Sweden. Stena Line is a ...
* Color Line
Military contractors
* Raytheon
Raytheon is a business unit of RTX Corporation and is a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. Founded in 1922, it merged in 2020 with Unite ...
* Rheinmetall
Rheinmetall AG () is a German automotive and arms manufacturer, headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. The group was promoted to the DAX, Germany's leading stock market index, in March 2023. It is the largest German and fifth largest Europe ...
* ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
TKMS –officially branded as ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems until June 2025– is a group and holding company of providers of naval vessels, surface ships and submarines. It was founded when large industrial conglomerate ThyssenKrupp acquired Howal ...
(through their subsidiary Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft
Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft GmbH (often abbreviated HDW) is a German shipbuilding company, headquartered in Kiel. It is part of the ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS) group, owned by ThyssenKrupp. The Howaldtswerke shipyard was founded in Kiel i ...
)
Engineering and industrial machinery
* Heidelberger Druckmaschinen
Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG (), sometimes referred to as Heidelberg or Heideldruck for short, is a German precision mechanical engineering company with registered offices in Heidelberg (Baden-Württemberg) and headquarters in nearby Wiesloch-W ...
* Voith
The Voith Group is a global technology company. With its broad portfolio of systems, products, services and digital applications, Voith trades in the markets of energy, paper, raw materials and transport. Founded in 1867, Voith today has aroun ...
* Vossloh
Vossloh AG is a rail technology company based in Werdohl in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The SDAX-listed group achieved sales of around €930 million in 2016 and, , had more than 4,000 employees.
Vossloh can trace its origins ...
* Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc., also known as Cat, is an American construction, mining and other engineering equipment manufacturer. The company is the world's largest manufacturer of construction equipment.
In 2018, Caterpillar was ranked number 73 on the ' ...
(through their subsidiary MaK)
Others
* LaserSoft Imaging
LaserSoft Imaging AG is a software developer designing image processing software such as SilverFast for scanners and large format printers. The company's headquarters is located in Kiel, Germany, north of Hamburg, and another office in Saras ...
* Schenker AG
Schenker AG (trading as DB Schenker) is a subsidiary of Danish logistics company DSV. The company was previously owned by German rail operator Deutsche Bahn, which acquired the subsidiary back in 2002. It comprises divisions for air, land, sea fr ...
* HSH Nordbank
Hamburg Commercial Bank (formerly HSH Nordbank) is a commercial bank in northern Europe with headquarters in Hamburg as well as Kiel, Germany. It is active in corporate and private banking. Considered to be the world’s largest provider of maritim ...
Kiel is also home to several insurances and banks, most notably the HSH Nordbank
Hamburg Commercial Bank (formerly HSH Nordbank) is a commercial bank in northern Europe with headquarters in Hamburg as well as Kiel, Germany. It is active in corporate and private banking. Considered to be the world’s largest provider of maritim ...
, Provinzial NordWest, Förde Sparkasse, Kieler Volksbank eG and Evangelischen Bank eG.
There is also an active startup scene in Kiel with startup accelerator StarterKitchen and startups like SciEngines GmbH, Real-Eyes, myBoo, SealMedia, Cliplister, Druckpreis.DE, promotionbasis.de, Yoosello, GetAnEdge, Flowy Apps, fraguru, lokalportal, PianoMotion and ubique art.
Kiel is home to several media companies, including a branch of the Norddeutscher Rundfunk
(; "North German Broadcasting"), commonly shortened to NDR (), is a public broadcasting, public radio and television broadcaster, based in Hamburg. In addition to the city-state of Hamburg, NDR broadcasts for the German states of Lower Saxony, ...
producing one radio channel and several local programmes in Kiel, a station of the British Forces Broadcasting Service
The British Forces Broadcasting Service (BFBS) provides radio and television programmes for His Majesty's Armed Forces, and their dependents worldwide. Editorial control is independent of the Ministry of Defence and the armed forces themsel ...
, the daily newspaper ''Kieler Nachrichten
The ''Kieler Nachrichten'' (literally "Kiel News") or ''KN'' is the only German language, German-language newspaper published in Kiel, Germany. It is published by "Kieler Zeitung Verlags und Druckerei KG-GmbH & Co.", a subdivision of Axel Springe ...
'' and several smaller local radio channels and magazines.
Transport
 Kiel is situated near an important pan-European motorway, the A7, which connects northern Europe with central and southern Europe.
The central railway station,
Kiel is situated near an important pan-European motorway, the A7, which connects northern Europe with central and southern Europe.
The central railway station, Kiel Hauptbahnhof
Kiel Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in the northern German city of Kiel. It consists of eight rail tracks and is a central hub for regional and long-distance passenger transport. There are regular connections to other cities in Schleswi ...
, has hourly trains to Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
, Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
, Flensburg
Flensburg (; Danish language, Danish and ; ; ) is an independent city, independent town in the far north of the Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. After Kiel and Lübeck, it is the third-largest city in Schleswig-Holstein.
Flensburg's ...
, and Husum
Husum (, ) is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of the annual i ...
. The ''Intercity Express
Intercity Express (commonly known as ICE () and running under this category) is a high-speed rail system in Germany. It also serves destinations in Austria, France, Belgium, Switzerland and the Netherlands as part of cross-border services. It ...
'' (ICE) connects Kiel with Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
. There are 8 regional railway stations within the city proper, which are connected with each other, the main railway station Kiel Hbf and other stations by regional trains, which can be used within the boundaries of the city with a normal bus ticket.
The city's bus service is provided by local company KVG. Autokraft and Verkehrsbetriebe Kreis Plön providing regional bus service, and the Schlepp- und Fährgesellschaft Kiel provides public transport on the fjord with ferries.
The Port of Kiel
__NOTOC__
The Port of Kiel () is a port for passenger and cargo shipping located in Kiel, Germany. It occupies the inner part of the Baltic Sea inlet Kieler Förde and includes the approach to the locks at the eastern end of Kiel Canal.
Harbours ...
is a significant port for passenger and cargo shipping from Germany to Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
, the Baltic States
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Passenger ferries operate to and from Gothenburg
Gothenburg ( ; ) is the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, second-largest city in Sweden, after the capital Stockholm, and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries. Situated by the Kattegat on the west coast of Sweden, it is the gub ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
(Stena Line
Stena Line is a Swedish Shipping line, shipping line company and one of the world's largest ferry operators. It services Denmark, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland and Sweden. Stena Line is a ...
, 13 hours, daily), Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022 ...
in Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
( Color Line, 19 hours, daily), and Klaipėda
Klaipėda ( ; ) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the List of cities in Lithuania, third-largest city in Lithuania, the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, fifth-largest city in the Baltic States, and the capi ...
in Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
(DFDS Lisco
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions ( DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) i ...
, 21 hours, 6 times per week). Cargo ferries operate from and to Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(DFDS Lisco
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions ( DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) i ...
, twice a week), and Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(NSA, once a week).
The nearest international airport is Hamburg Airport
Hamburg Airport () , is a major international airport in Hamburg, the second-largest city in Germany. Since November 2016 the airport has been named after the former German chancellor Helmut Schmidt. It is located north of the city centre in t ...
, which is situated approximately to the south of Kiel. There is a shuttle bus service (''KIELIUS'') operating between Hamburg Airport and Kiel central railway station. There is also an airport at Lübeck.
Notable people
Twin towns – sister cities
Kiel is twinned with: *Aarhus
Aarhus (, , ; officially spelled Århus from 1948 until 1 January 2011) is the second-largest city in Denmark and the seat of Aarhus municipality, Aarhus Municipality. It is located on the eastern shore of Jutland in the Kattegat sea and app ...
, Denmark (2019)
* Antakya
Antakya (), Turkish form of Antioch, is a municipality and the capital Districts of Turkey, district of Hatay Province, Turkey. Its area is . Prior to the devastating 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes, 2023 earthquakes, its population was recorded ...
, Turkey (2012)
* Brest, France (1964)
* Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
, United Kingdom (1947)
* Gdynia
Gdynia is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With an estimated population of 257,000, it is the List of cities in Poland, 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in the Pomeranian Voivodeship after Gdańsk ...
, Poland (1985)
* Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad,. known as Königsberg; ; . until 1946, is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, an Enclave and exclave, exclave of Russia between Lithuania and Poland ( west of the bulk of Russia), located on the Prego ...
, Russia (1992)
* Kherson
Kherson (Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and , , ) is a port city in southern Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located by the Black Sea and on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, Kherson is the home to a major ship-bui ...
, Ukraine (2024)
* Moshi Rural District
Moshi is one of the seven administrative districts of the Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. The district covers an area of . The District is bordered to the north by the Rombo District, to the west by the Hai District, to the east by the Mwanga D ...
, Tanzania (2009)
* Samsun
Samsun is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and a major Black Sea port. The urban area recorded a population of 738,692 in 2022. The city is the capital of Samsun Province which has a population of ...
, Turkey (2010)
* San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, USA (2017)
* Sovetsk, Russia (1992)
* Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish language, Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German language, German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklen ...
, Germany (1987)
* Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
, Estonia (1986)
* Vaasa
Vaasa (; , ), formerly (1855-1917) known as Nikolaistad (; ),Kiel, Wisconsin
* Steenbek-Projensdorf
Official tourism
Official website of the association museen am meer
{{Authority control 1233 establishments in Europe Cities in Schleswig-Holstein German state capitals Members of the Hanseatic League Populated coastal places in Germany (Baltic Sea) Populated places established in the 13th century Port cities and towns in Germany Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Urban districts of Schleswig-Holstein
References
External links
*Official tourism
Official website of the association museen am meer
{{Authority control 1233 establishments in Europe Cities in Schleswig-Holstein German state capitals Members of the Hanseatic League Populated coastal places in Germany (Baltic Sea) Populated places established in the 13th century Port cities and towns in Germany Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea Urban districts of Schleswig-Holstein