Khanate of Khiva on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a


 After the capital was moved to Khiva,
After the capital was moved to Khiva,  Before 1505,
Before 1505,

 Russians made five attacks on Khiva. Around 1602 some free
Russians made five attacks on Khiva. Around 1602 some free
 After the 1917
After the 1917
 Data on the Khivan Khans is sparse and sometimes contradictory, especially for the minor khans. Names and dates from Bregel/Muniz which probably gives the best modern scholarship. Short biographies are from Howarth's 1880 book which is old but has biographies of most of the khans. RU: is data from the Russian Wikipedia when nothing could be found in English or there was a major contradiction. RU: has sources in local languages.
Data on the Khivan Khans is sparse and sometimes contradictory, especially for the minor khans. Names and dates from Bregel/Muniz which probably gives the best modern scholarship. Short biographies are from Howarth's 1880 book which is old but has biographies of most of the khans. RU: is data from the Russian Wikipedia when nothing could be found in English or there was a major contradiction. RU: has sources in local languages.
 *
*
History of the Mongols
From the 9th to the 19th Century, By Sir
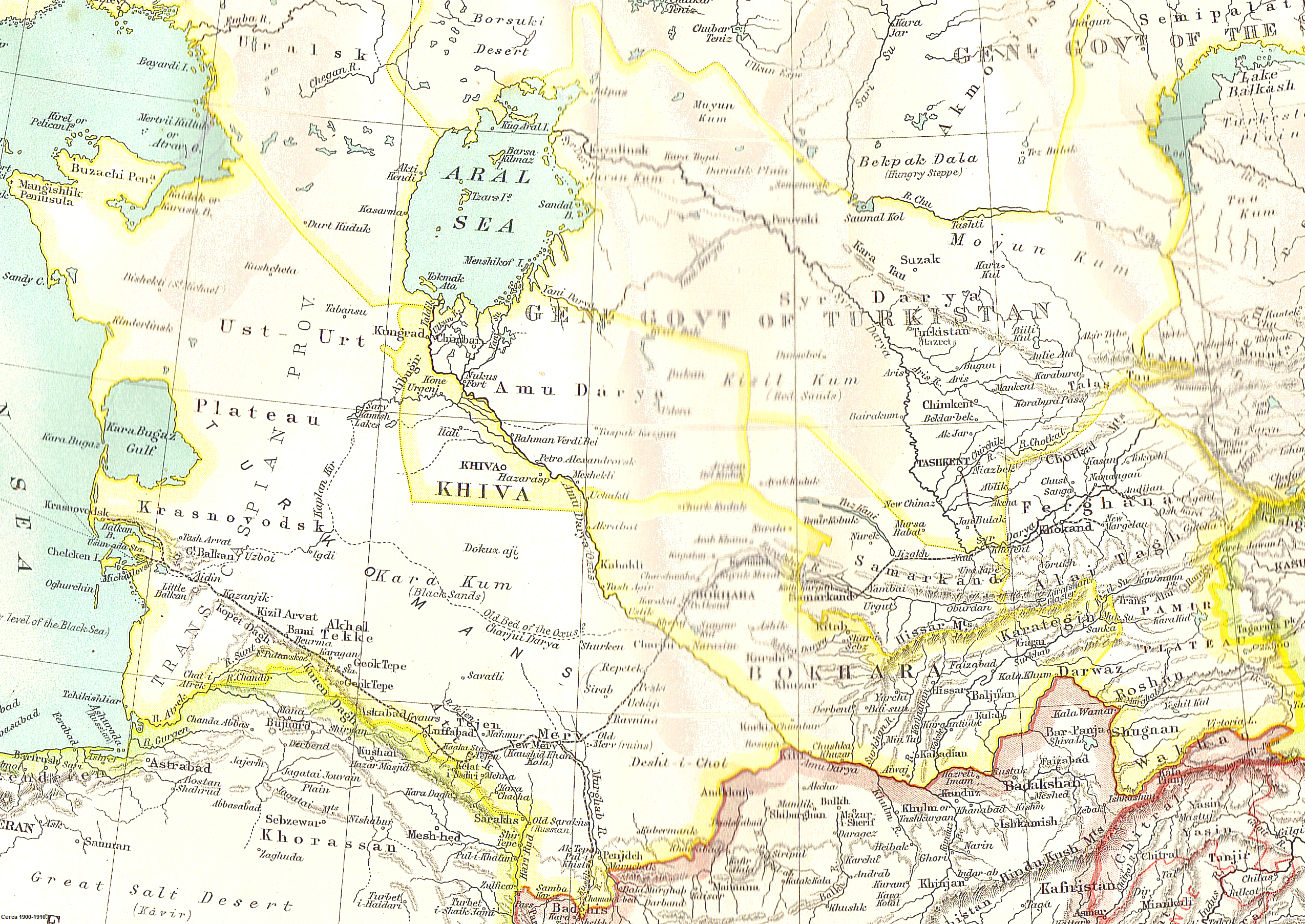
"Russian Invasion (the end of the XIX century)"Map of the Khanates of Bukhara, Khiva, and Khokand and Part of Russian Turkistan
from 1875 by
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
n polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except for a period of Afsharid
Afsharid Iran ( fa, ایران افشاری), also referred as the Afsharid Empire was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, ruling Iran (Persia). The state was ruled by the ...
occupation by Nader Shah between 1740 and 1746. Centred in the irrigated plains of the lower Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
, south of the Aral Sea, with the capital in the city of Khiva, the country was ruled by a Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually ...
tribe, the Khongirads, who came from Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
. It covered present western Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
, southwestern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
and much of Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
before Russian arrival at the second half of the 19th century.
In 1873, the Khanate of Khiva was much reduced in size and became a Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
. The other regional protectorate that lasted until the Revolution was the Emirate of Bukhara. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, Khiva had a revolution too, and in 1920 the Khanate was replaced by the Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic ( uz, Хоразм Халқ Совет Республикаси; rus, Хорезмская Народная Советская Республика, r=Khorezmskaya Narodnaya Sovetskaya Respublika) was the st ...
. In 1924, the area was formally incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and today is largely a part of Karakalpakstan
Karakalpakstan, / officially the Republic of Karakalpakstan, / is an autonomous republic of Uzbekistan. It occupies the whole northwestern part of Uzbekistan. The capital is Nukus (' / ). The Republic of Karakalpakstan has an area of , and ...
, Xorazm Region
Xorazm Region (, خارەزم ۋىلايەتى, ) or Khorezm Region as it is still more commonly known, is a viloyat (region) of Uzbekistan located in the northwest of the country in the lower reaches of the Amu Darya River. It borders with Tu ...
in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
, and Daşoguz Region of Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
.
History
Early history
SeeKhwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
, the local name of the region.
After 1500


 After the capital was moved to Khiva,
After the capital was moved to Khiva, Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
came to be called the Khanate of Khiva (the state had always referred to itself as Khwarazm, the Khanate of Khiva as a name was popularized by Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
historians in honor of its capital, Khiva). Some time around 1600, the Daryaliq or west branch of the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
dried up causing the capital to be moved south to Khiva from Konye-Urgench
Konye-Urgench ( tk, Köneürgenç / Көнеүргенч; fa, کهنه گرگانج, ''Kuhna Gurgānj'', literally "Old Gurgānj"), also known as Old Urgench or Urganj, is a city of about 30,000 inhabitants in north Turkmenistan, just south fro ...
. Although based in the Oxus delta, the Khanate usually controlled most of what is now Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
. The population consisted of agriculturalists along the river, the Turkic Sart
Sart is a name for the settled inhabitants of Central Asia which has had shifting meanings over the centuries.
Origin
There are several theories about the origin of the term. It may be derived from the Sanskrit ''sārthavāha'' "merchant, t ...
s, and nomads or semi-nomads away from the river. It is overall arbitrary to anachronistically project modern ethnic and national identifications, largely based on Soviet national delimitation policies, on pre-modern societies. The settled population was composed by aristocratic and peasants bound to the land. During the mid 1600s there were many Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
slaves who had been captured by Turkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-weste ...
and a few Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
slaves alongside other Turkic slaves. Before and during this period, the settled area was increasingly infiltrated by Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
from the north, with their Turkic dialects evolving into what is now the Uzbek language
Uzbek (''Oʻzbekcha, Oʻzbek tili or Ўзбекча, Ўзбек тили''), formerly known as ''Turki'' or ''Western Turki'', is a Turkic language spoken by Uzbeks. It is the official, and national language of Uzbekistan. Uzbek is spoken as ...
while the original Iranian Khwarezmian language died out. The swampy area of the lower delta was increasingly populated by Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; kaa, Qaraqalpaqlar, Қарақалпақлар, قاراقلپقلر), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reach ...
and there were Kazakh nomads on the northern border. The Turkmen nomads paid taxes to the Khan and were a large part of his army but often revolted. Since the heart of the Khanate was surrounded by semi-desert the only easy military approach was along the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
. This led to many wars with the Khanate of Bukhara further up the river (1538–40, 1593, 1655, 1656, 1662, 1684, 1689, 1694, 1806, and others).
 Before 1505,
Before 1505, Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
was nominally dependent on the Timurid Timurid refers to those descended from Timur (Tamerlane), a 14th-century conqueror:
* Timurid dynasty, a dynasty of Turco-Mongol lineage descended from Timur who established empires in Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
** Timurid Empire of C ...
Sultan Husayn Mirza Bayqara who was based in Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
. From 1488 Muhammad Shaybani
Muhammad Shaybani Khan ( uz, Muhammad Shayboniy, also known as Abul-Fath Shaybani Khan or Shayabak Khan or Shahi Beg Khan, originally named "Shibägh", which means " wormwood" or "obsidian") (c. 1451 – 2 December 1510), was an Uzbek leader ...
built a large but short-lived empire in southern Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, taking Khwarazm in 1505. At nearly the same time, Shah Ismail I
Ismail I ( fa, اسماعیل, Esmāʿīl, ; July 17, 1487 – May 23, 1524), also known as Shah Ismail (), was the founder of the Safavid dynasty of Safavid Iran, Iran, ruling as its King of Kings (''Shahanshah'') from 1501 to 1524. His re ...
was building a powerful Shiite
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
state in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The two necessarily clashed and in 1510 Muhammad was killed and Khwarazm soon occupied. The Shah's religion provoked resistance and in 1511 his garrison was expelled and power passed to Ilbars, who founded the long-lived Arabshahid dynasty.
Around 1540 and 1593, the Khans were driven out by the Bukharans. In both cases they fled to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and soon returned. In 1558, Anthony Jenkinson
Anthony Jenkinson (1529 – 1610/1611) was born at Market Harborough, Leicestershire. He was one of the first Englishmen to explore Muscovy and present-day Russia. Jenkinson was a traveller and explorer on behalf of the Muscovy Company ...
visited Old Urgench
Konye-Urgench ( tk, Köneürgenç / Көнеүргенч; fa, کهنه گرگانج, ''Kuhna Gurgānj'', literally "Old Gurgānj"), also known as Old Urgench or Urganj, is a city of about 30,000 inhabitants in north Turkmenistan, just south fro ...
and was not impressed. Following Arap Munhammad (1602–23), who moved the capital to Khiva, there was a period of disorder, including an invasion by the Kalmyks, who left laden with plunder. Disorder was ended by Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur (1643–1663) who twice defeated the Kalmyks and wrote a history of Central Asia. His son Anusha (1663–1685) presided over a period of urban growth until he was deposed and blinded. From 1695, Khiva was for some years a vassal of Bukhara which appointed two khans. Shir Gazi Khan (1714–1727), who was killed by slaves, is said to have been the last proper Arabshahid. Khan Ilbars (1728–40) was a Shibanid ruler, son of Shakhniyaz khanŠir-Moḥammad Mirāb Munes and Moḥammad-Reżā Mirāb Āgahi, Ferdaws al-eqbāl, ed., tr., and annotated by Yuri Bregel as Firdaws al-iqbal: History of Khorezm, 2 vols., Leiden, 1988–99. p. 162,62,567–68 who unwisely killed some Persian ambassadors. In a repeat of the Shah Ismail
Ismail I ( fa, اسماعیل, Esmāʿīl, ; July 17, 1487 – May 23, 1524), also known as Shah Ismail (), was the founder of the Safavid dynasty of Iran, ruling as its King of Kings (''Shahanshah'') from 1501 to 1524. His reign is often c ...
story, Nadir Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian ...
conquered Khiva, beheaded Ilbars and freed some 12,000–20,000 slaves. Next year the Persian garrison was slaughtered, but the rebellion was quickly suppressed. Persian pretensions ended with Nadir's murder in 1747. After 1746, the Qongrat tribe became increasingly powerful and appointed puppet khans. Their power was formalized as the Qongrat dynasty by Iltuzar Khan in 1804. Khiva flourished under Muhammad Rahim Khan (1806–1825) and Allah Quli Khan (1825–1840) and then declined. After Muhammad Amin Khan was killed trying to retake Sarakhs
Sarakhs ( fa, سرخس, Saraxs, also Romanized as Serakhs) is a city in Sarakhs County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. Sarakhs was once a stopping point along the Silk Road, and in its 11th century heyday had many libraries. Much of the origina ...
on March 19, 1855, there was a long Turkmen rebellion (1855–1867). In the first two years of the rebellion, two or three Khans were killed by Turkmens.
Russian Empire period
 Russians made five attacks on Khiva. Around 1602 some free
Russians made five attacks on Khiva. Around 1602 some free Ural Cossacks
The Ural Cossack Host was a cossack host formed from the Ural Cossacks – those Eurasian cossacks settled by the Ural River. Their alternative name, Yaik Cossacks, comes from the old name of the river.
They were also known by the names:
*Rus ...
unsuccessfully raided Khwarazm. In 1717 Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky attacked Khiva from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. After he won the battle, Shir Ghazi Khan (1715–1728) made a treaty and suggested that the Russians disperse so that they could be better fed. After they dispersed they were all killed or enslaved, only a few surviving to tell the tale. In 1801 an army was sent toward Khiva but was recalled when Paul I Paul I may refer to:
*Paul of Samosata (200–275), Bishop of Antioch
* Paul I of Constantinople (died c. 350), Archbishop of Constantinople
*Pope Paul I (700–767)
*Paul I Šubić of Bribir (c. 1245–1312), Ban of Croatia and Lord of Bosnia
*Pau ...
was murdered. In the Khivan campaign of 1839 Perovsky tried an attack from Orenburg. The weather was unusually cold and he was forced to turn back after losing many men and most of his camels. Khiva was finally conquered by the Khivan campaign of 1873
In the Russo–Khivan War of 1873, Russia conquered the Khanate of Khiva, and it became a Russian protectorate.
Background
Twice before, Russia had failed to subjugate Khiva. In 1717, Prince Bekovitch-Cherkassky marched from the Caspian and f ...
. The Russians installed Sayyid Muhammad Rahim Bahadur Khan II as the vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
ruler of the region.
The conquest of Khiva was part of the Russian conquest of Turkestan
The partially successful Territorial evolution of Russia, conquest of Central Asia by the Russian Empire took place in the second half of the nineteenth century. The land that became Russian Turkestan and later Soviet Central Asia is now divide ...
. British attempts to deal with this were called the Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empi ...
. One of the reasons for the 1839 attack was the increasing number of Russian slaves held at Khiva. To remove this pretext Britain launched its own effort to free the slaves. Major Todd, the senior British political officer stationed in Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd ...
(in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
) dispatched Captain James Abbott, disguised as an Afghan, on 24 December 1839, for Khiva. Abbott arrived in late January 1840 and, although the Khan was suspicious of his identity, he succeeded in talking the Khan into allowing him to carry a letter for the Tsar regarding the slaves. He left on 7 March 1840, for Fort Alexandrovsk, and was subsequently betrayed by his guide, robbed, then released when the bandits realized the origin and destination of his letter. His superiors in Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd ...
, not knowing of his fate, sent another officer, Lieutenant Richmond Shakespear
Sir Richmond Campbell Shakespear, CB (11 May 1812 – 16 December 1861) was an Indian-born British Indian Army officer. He helped to influence the Khan of Khiva to abolish the capture and selling of Russian slaves in Khiva. This likely foresta ...
, after him. Shakespear had more success than Abbott: he convinced the khan to free all Russian subjects under his control, and also to make the ownership of Russian slaves a crime punishable by death. The freed slaves and Shakespear arrived in Fort Alexandrovsk on 15 August 1840, and Russia lost its primary motive for the conquest of Khiva, for the time being.
A permanent Russian presence on the Aral Sea began in 1848 with the building of Fort Aralsk at the mouth of the Syr Darya. The Empire's military superiority was such that Khiva and the other Central Asian principalities, Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and Kokand, had no chance of repelling the Russian advance, despite years of fighting. In 1873, after Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
conquered the great cities of Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
and Samarkand, General Von Kaufman launched an attack on Khiva consisting of 13,000 infantry and cavalry. The city of Khiva fell on 10 June 1873 and, on 12 August 1873, a peace treaty was signed that established Khiva as a quasi-independent Russian protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
. After the conquest of what is now Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
(1884) the protectorates of Khiva and Bukhara were surrounded by Russian territory.
The first significant settlement of Europeans in the Khanate was a group of Mennonites
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
who migrated to Khiva in 1882. The German-speaking Mennonites had come from the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
region and the Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhzhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today, the central village, known as Molochansk, has a population less than 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna ...
colony under the leadership of Claas Epp Jr. The Mennonites played an important role in modernizing the Khanate in the decades prior to the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
by introducing photography, resulting in the development of Uzbek photography and filmmaking, more efficient methods for cotton harvesting, electrical generators, and other technological innovations.
Civil war and Soviet Republic
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
seizure of power in the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
, anti-monarchists and Turkmen tribesmen joined forces with the Bolsheviks at the end of 1919 to depose the khan. By early February 1920, the Khivan army under Junaid Khan Junaid Khan may refer to:
* Junaid Khan (de facto ruler of Khiva), political leader in the Khanate of Khiva and the Basmachi movement
*Junaid Khan (cricketer), Pakistani cricketer
*Junaid Khan (actor)
Junaid Khan (born as Junaid Khan Niazi 2 ...
was completely defeated. On 2 February 1920, Khiva's last Kungrad khan, Sayid Abdullah
Sayid Abdullah (1873–1933) was the last Khan of Khiva of the Khongirad (Qungrat) dynasty, from 1 October 1918 until 1 February 1920. His father was Muhammad Rahim Khan II.
Sayid Abdullah had no real power (titular ruler), because the Khanate ...
, abdicated and a short-lived Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic ( uz, Хоразм Халқ Совет Республикаси; rus, Хорезмская Народная Советская Республика, r=Khorezmskaya Narodnaya Sovetskaya Respublika) was the st ...
(later the Khorezm SSR) was created out of the territory of the old Khanate of Khiva, before it was finally incorporated into the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in 1924, with the former khanate divided between the new Turkmen SSR
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish des ...
and Uzbek SSR
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Уз ...
. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in 1991, these became Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
respectively. Today, the area that was the khanate has a mixed population of Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
, Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; kaa, Qaraqalpaqlar, Қарақалпақлар, قاراقلپقلر), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reach ...
, Turkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-weste ...
, and Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also parts o ...
.
Khans of Khiva (1511–1920)
 Data on the Khivan Khans is sparse and sometimes contradictory, especially for the minor khans. Names and dates from Bregel/Muniz which probably gives the best modern scholarship. Short biographies are from Howarth's 1880 book which is old but has biographies of most of the khans. RU: is data from the Russian Wikipedia when nothing could be found in English or there was a major contradiction. RU: has sources in local languages.
Data on the Khivan Khans is sparse and sometimes contradictory, especially for the minor khans. Names and dates from Bregel/Muniz which probably gives the best modern scholarship. Short biographies are from Howarth's 1880 book which is old but has biographies of most of the khans. RU: is data from the Russian Wikipedia when nothing could be found in English or there was a major contradiction. RU: has sources in local languages.
Arabshahid dynasty (Yadigarid Shibanid dynasty, 1511–1804)
*X: According to Howorth, the ancestors of Ilbars were Arabshah, Haji Tuli, Timur Sheikh, Yadigar Khan, Bereke, Ilbars. Arabshah's brother was Ibrahim Oghlan, ancestor of the khans of Bukhara. *Ilbars I (1511–1518) 1. Enthroned by locals, fought several months to drive thePersians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
out, brought in Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
in numbers to raid Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
.
*Sultan Haji (1518–1519) 2. Nephew of Ilbars I, had a short reign; real power in the hands of his cousin Sultan Ghazi.
*Hasan Quli (1519–1524, ru:1519) 3. cousin of Ilbar I, killed by Ilbars' sons after 4-month siege of Urganch.
*Sufyan (1529–1535, ru:1519–22) 4. 'Sofian Khan', second cousin of Ilbars, fought Turkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-weste ...
on lower Uzboy River
The Uzboy (sometimes rendered Uzboj) was a distributary of the Amu Darya which flowed through the northwestern part of the Karakum Desert of Turkmenistan until the 17th century, when it abruptly dried up, eliminating the agricultural population t ...
, which then had water.
*Bujugha (1524–1529, ru:1522–26) 5. brother of Sufyan, raided Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, concluded a marriage alliance with Tahmasp I
Tahmasp I ( fa, طهماسب, translit=Ṭahmāsb or ; 22 February 1514 – 14 May 1576) was the second shah of Safavid Iran from 1524 to 1576. He was the eldest son of Ismail I and his principal consort, Tajlu Khanum. Ascending the throne after ...
using Sufyan's daughter. Dates from Bregel/Muniz reverse 4 and 5.
*Avniq (1535–1538, ru:1526–38) 6. 'Avaneq', brother of Sufyan, blood feud with Ilbars' family and others led to an invasion by Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and his death. Bukharans held Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
until they were driven out by his son, Din Muhammed.
*Qal (1539–1549, ru:1541–47) 7. 'Khal Khan', son of Avniq, prosperous reign.
*Aqatay (1549–1557, ru:1547–57) 8. 'Akatai', brother of Sufyan, fought the sons of several of his brothers, defeated and impaled.
*Dust Muhammad (1557–1558) 9. 'Dost Khan', son of 5, fought his brother Ish and both were killed.
*Haji Muhammad I (1558–1602) 10. son of 8, fought Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, which conquered Khiva, 3 years in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, regained homeland, driven out, retook it. Visit of Anthony Jenkinson
Anthony Jenkinson (1529 – 1610/1611) was born at Market Harborough, Leicestershire. He was one of the first Englishmen to explore Muscovy and present-day Russia. Jenkinson was a traveller and explorer on behalf of the Muscovy Company ...
.
*Arab Muhammad I (1602–1623, ru:1603–21) 11. son of 10, Ural Cossack raid defeated, two Kalmyk raids, weak, two sons rebelled, blinded, later killed.
*Isfandiyar (1623–1643) 12. son of 11, killed his rebellious brothers, pro- Turkmen, anti- Uzbek.
* Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur (1643–1663) 13. son of 11, khan after defeating Turkmen-Bukharan faction, fought Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and Kalmyks, wrote the Genealogy of Turkmens, an important historical source.
*Anusha (1663–1685) 14. son of 13, took Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
ru: has Samarqand, Howorth says 'the city' implying Bukhara. and lost it, three more failures at Bukhara, overthrown and blinded by son Erenk.
*X: Between Anusha and Sher Gazi (1685–1714) Bregel and Howorth diverge, as do entries in the Russian Wikipedia. Howorth has A. Muhammed Erenk, failed attack on Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, poisoned, B. Shah Niaz (1687-after 1700) appointed by Bukhara, letter to czar in 1700. C. Arab Muhammed, letter from Czar in 1703. D. Haji Muhammed Behadur envoy to czar in 1714, E. Yadiger (−1714), F. Arank, a Karakalpak, father of Shir Gazi.
*Khudaydad (1685–1687) ru: 1686–89, son of Anusha, enthroned at 15, killed.
*Muhammad Awrang I (1687–1694) ru:1689–94, son of Anusha, killed by fall from horse.
*Chuchaq (1694–1697) ru: calls him 'Jochi Khan', descendant of Haji Muhammad I.
*Vali (1697–1698)ru: descendant of Haji Mukhammad, could not maintain stability and was removed.
*Ishaq Agha Shah Niyaz (1698–1701) ru: son of Jochi/Chuchaq. Howorth has Shah Niyaz appointed by Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
in 1687.
*Awrang II (1701–1702)
*ru only:Shakhbakht Khan (1702–03) son of Shah Niyaz, overthrown.
*ru only:Sayyid Ali Khan (1703) son of Shah Niyaz, reign lasted several days.
*Musa (1702–1712) ru:1703–04, son of Jochi/Chucaq, fled to Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
.
*Yadigar I (1712–1713) ru:1704–14, son of Haji Muhammad I, followed by Sher Ghazi.
*Awrang III (c. 1713 – c. 1714).
*Haji Muhammad II (c. 1714) envoy to czar in 1714, grandson of Abul Ghazi.
*Shir Ghazi (1714–1727) from Bukhara, defeated Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky, fought rival state on lower delta under Timur Sultan, visited by Florio Beneveni, minor slave rebellion. ru:killed by slaves in same year as Howorth's slave rebellion, descendant of Sultan Gazi (see Sultan Haji).
*Sarigh Ayghir (1727)
*Ilbars II (1728–1740), son of Shakhniyaz khanrejected threat from Nadir Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian ...
, surrendered to him, executed by Nadir because he had killed Nadir's envoys. Nadir freed many slaves.
*Tahir (1740–1742) cousin of Bukharan khan, appointed by Nadir Shah, killed when Nadir's army was elsewhere.
*Nurali I (1742) Kazakh, son of Abul Khair Khan
Mirza Abū'l-Khair Mūhammed Khan bin Qājı Abdūllah Sultan ( kk, Мырза Әбілқайыр Мұхаммед хан бин Қажы Абдұллаh Сұлтан, , romanized: ''Myrza Äbılqaiyr Mūhammed Han bin Qajy Abdūllah Sūltan''), ...
, helped expel Nadir's garrison, fled to steppe before Persian army returned. ru: expelled by Persians.
*Abu Muhammad (1742) son of Ilbars, appointed by returning Persians
*Abu al-Ghazi II Muhammad (1742–1747) resisted returning Persians?
*Ghaib (Kaip Khan
AIP may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Action International Pictures
* Afghan Islamic Press
* AIP Records, a record label
* American International Pictures, an independent film production/distribution company, now a subsidiary of MGM
...
) (1747–1758) a Kazakh, enemy of Nurali, driven out, later khan of Little Horde.
*X Between Kaip and 1804 Howorth cannot identify khans. He says that they were titular rulers and often exiled after a few years. Real power was in the hands of Inaks or hereditary prime ministers who were also chiefs on the Qungrat
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: ᠬᠣᠩᠭᠢᠷᠠᠳ; Хонгирад; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (Qoŋğırat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
tribe in the lower delta. He lists these Inaks: A. Ishmed bi; B. Muhammed Amin (1755–1782) son of A; C. Ivaz, (?–1804), son of B, Dr Blankenagel (1793) could not cure his brother's blindness but left account; D. Iltazar, son of C, after six months expelled last Arabshahid khan.
*Abdullah Qara Beg (1758)
*Timur Ghazi (1758–1764)
*Tawke (1764–1766)
*Shah Ghazi (1766–1768)
*Abu al-Ghazi III (1768–1769) ru: son of Kaip, later khan of Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; kaa, Qaraqalpaqlar, Қарақалпақлар, قاراقلپقلر), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reach ...
, later on lower Syr Darya, died in poverty in 1815.
*Nurali II (1769)
*Jahangir (1769–1770) ru: son of Kaip.
*Bölekey (1770) ru: a Kazakh from lower Syr Darya, expelled above and soon driven out himself.
*Aqim (first time, 1770–1771)
*Abd al-Aziz (c. 1771)
*Artuq Ghazi (c. 1772)
*Abdullah (c. 1772)
*Aqim (second time, c. 1772 – c. 1773)
*Yadigar II (first time, c. 1773–1775)
*Abu'l Fayz (1775–1779)
*Yadigar II (second time, 1779–1781)
*Pulad Ghazi (1781–1783)
*Yadigar II (third time, 1783–1790)
*Abu al-Ghazi IV (1790–1802) visit of Russian Dr. Blankenagel in 1793.
*Abu al-Ghazi V ibn Gha'ib (1802–1804)
Qungrat dynasty (1804–1920)
Qungrat Inaks *Ishmed bi: Howorth only, information from Muraviev who visited in 1820 *Muhammed Amin Biy: ru: 1763–1790, slowly restored relative peace, defeatedTurkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-weste ...
in 1770 and Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
in 1782.
*Avaz or Ivaz: ru: 1790–1804, son of above, relative peace and stability, in 1793 rebellion in lower delta suppressed, but area somewhat independent for about 20 years, in 1793 Russian Dr. Blankenagle was unable to cure his brother's blindness, but left report. According to Howorth, the brother, Fazil bi was 'always consulted' by Avaz and his father.
*Eltuzar (1804): son of above, made himself khan after a few months.
Qungrat Khans
*Iltazar Inaq ibn Iwaz Inaq Biy (1804–1806) Inak, exiled last khan, said he would find another, collected army and had himself made khan, attacked Yomuds towards Asterabad
Gorgan ( fa, گرگان ; also romanized as ''Gorgān'', ''Gurgān'', and ''Gurgan''), formerly Esterabad ( ; also romanized as ''Astarābād'', ''Asterabad'', and ''Esterābād''), is the capital city of Golestan Province, Iran. It lies appro ...
, then allied with them, attacked Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, defeated, fled across the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
in a boat, so many people piled onto it that it sank and he was drowned.
*Muhammad Rahim Bahadur I. (1806–1825) son of above, said to be cruel but strong measures restored order, conquered lower delta (ru:1811), subjugated tribes, fought Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, visited by Muraviev (1820) who left report. Munis
A municipal bond, commonly known as a muni, is a Bond (finance), bond issued by state or local governments, or entities they create such as authorities and special districts. In the United States, interest income received by holders of municipal ...
wrote history of Khiva used by Bregel.
*Allah Quli Bahadur (1825–1842) son of above, c 1832 took Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
and Serakhs
Sarahs (, also written Saraghs, Serahs, Sarakhs, Saragt, or Serakhs, the last a backformation of russian: Серахс) is an oasis city in Ahal Province, Turkmenistan, and the administrative center of Sarahs district ( tk, Sarahs etraby). It is ...
, Alexander Burnes met his army there, 1839 Russian invasion defeated by cold weather, c1840 visited by James Abbott, Richmond Shakespear
Sir Richmond Campbell Shakespear, CB (11 May 1812 – 16 December 1861) was an Indian-born British Indian Army officer. He helped to influence the Khan of Khiva to abolish the capture and selling of Russian slaves in Khiva. This likely foresta ...
and Arthur Conolly
Arthur Conolly (2 July 1807, London – 17 June 1842, Bukhara) was a British intelligence officer, explorer and writer. He was a captain of the 6th Bengal Light Cavalry in the service of the British East India Company. He participated in many r ...
.
*Muhammad Rahim Quli (1842–1846) son of above, fought tribes south of Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
, brother defeated Bukharan invasion.
*Abu al-Ghazi Muhammad Amin Bahadur (1846– 19 March 1855) brother of above, took Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
, garrison expelled, retaken, fought Tekes, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
built forts on the Syr Darya, but Khivans only raided the surrounding areas, campaigned south of Merv, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
intervened, captured and beheaded because he unwisely pitched his tent on the edge of the camp.
*Abdullah (1855) grandson of Ittazar's second son (ru:son of Muhammad Amin), enthroned by defeated army, soon killed by Turkmen rebels.
* (1855–1856) brother of above, fought same rebels, assassinated by rebel ally who pretended to pay homage.
* (1856) Apparently Howorth's Sayid Mahmud, an opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
addict who abdicated in favor of his younger brother below.
* (1856 – September 1864) son of second Qungrat
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: ᠬᠣᠩᠭᠢᠷᠠᠳ; Хонгирад; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (Qoŋğırat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
khan, civil war, famine and plague, Ignatiev mission(1858), Arminius Vambery's visit (1863).
* (Feruz Khan) (10 September 1864 – September 1910) son of above, conquered by Russia in 1873, Khiva became a Russian protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
.
* Isfandiyar Jurji Bahadur (September 1910 – 1 October 1918) son of the above. Following
''Following'' is a 1998 independent neo-noir crime thriller film written, produced, edited and directed by Christopher Nolan. It tells the story of a young man who follows strangers around the streets of London and is drawn into a criminal unde ...
the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
, lost the country to Junaid Khan Junaid Khan may refer to:
* Junaid Khan (de facto ruler of Khiva), political leader in the Khanate of Khiva and the Basmachi movement
*Junaid Khan (cricketer), Pakistani cricketer
*Junaid Khan (actor)
Junaid Khan (born as Junaid Khan Niazi 2 ...
of the Turkmen Yomut
The Yomut or Yomud is a Turkmen tribe that lives in Western and Central Asia, including Gorgan, Iran; Turkmenbashi, Turkmenistan; the eastern Caspian shores; Khiva, Uzbekistan; and Dashoguz, Turkmenistan.
The Yomut carpet is a type of rug t ...
tribe and was executed by him.
 *
*Sayid Abdullah
Sayid Abdullah (1873–1933) was the last Khan of Khiva of the Khongirad (Qungrat) dynasty, from 1 October 1918 until 1 February 1920. His father was Muhammad Rahim Khan II.
Sayid Abdullah had no real power (titular ruler), because the Khanate ...
(1 October 1918 – 1 February 1920) brother of the above. Real power in hands of Junaid Khan.
See also
* Khiva *Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic ( uz, Хоразм Халқ Совет Республикаси; rus, Хорезмская Народная Советская Республика, r=Khorezmskaya Narodnaya Sovetskaya Respublika) was the st ...
*Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
*List of Sunni dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
*Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
*Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
*Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramaut) ...
* List of Turkic dynasties and countries
Notes and sources
*M Annanepesov and H. N. Bababekov, "The Khanates of Khiva and Kokand", in ''History of Civilizations in Central Asia'', Volume V, pp63–71, 2008 *Frederick Burnaby
Colonel Frederick Gustavus Burnaby (3 March 1842 – 17 January 1885) was a British Army intelligence officer. Burnaby's adventurous spirit, pioneering achievements, and swashbuckling courage earned an affection in the minds of Victorian imper ...
, ''A Ride to Khiva: Travels and Adventures in Central Asia'' (1876)History of the Mongols
From the 9th to the 19th Century, By Sir
Henry Hoyle Howorth
Sir Henry Hoyle Howorth (1 July 1842 – 15 July 1923) was a British Conservative politician, barrister and amateur historian and geologist.''Obituary: Sir Henry Howorth, A Life of Wide Interests, Politics, Science, and Art'', The Times, ...
(biographies of the Khans)
External links
"Russian Invasion (the end of the XIX century)"
from 1875 by
Eugene Schuyler
Eugene Schuyler (February 26, 1840 – July 16, 1890) was a nineteenth-century American scholar, writer, explorer and diplomat. Schuyler was one of the first three Americans to earn a Ph.D. from an American university; and the first American tra ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Khiva
States and territories established in 1511
States and territories disestablished in 1920
Turkic dynasties
Central Asia in the Russian Empire
Lists of khans
Former Russian protectorates
Historical Turkic states
Former monarchies