Kelvin Clip on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Four-terminal sensing (4T sensing), 4-wire sensing, or 4-point probes method is an
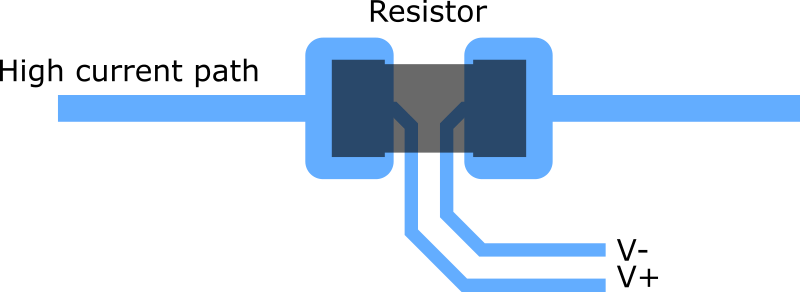 When a Kelvin connection is used, current is supplied via a pair of force connections (current leads). These generate a voltage drop across the impedance to be measured according to
When a Kelvin connection is used, current is supplied via a pair of force connections (current leads). These generate a voltage drop across the impedance to be measured according to
''DC Metering Circuits''
chapter fro
free ebook an
''Lessons In Electric Circuits''
series.
Four-Point Techniques for Measuring Electrical Conductivity and Resistivity
Explanatory Video about Four Wire Resistance Measurement in Energy Systems using Kelvin Clamps
Scientific techniques Impedance measurements
electrical impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.
Quantitatively, the impedance of a two-terminal circuit element is the ratio of the comp ...
measuring technique that uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge t ...
-sensing electrodes to make more accurate measurements than the simpler and more usual two-terminal (2T) sensing. Four-terminal sensing is used in some ohmmeter
An analog ohmmeter
An ohmmeter is an electrical instrument that measures electrical resistance (the opposition offered by a circuit or component to the flow of electric current). Multimeters also function as ohmmeters when in resistance-measu ...
s and impedance analyzer
An impedance analyzer is a type of electronic test equipment used to measure complex electrical impedance as a function of test frequency.
Impedance is an important parameter used to characterize electronic components, electronic circuits, and ...
s, and in wiring for strain gauge
A strain gauge (also spelled strain gage) is a device used to measure strain on an object. Invented by Edward E. Simmons and Arthur C. Ruge in 1938, the most common type of strain gauge consists of an insulating flexible backing which supports ...
s and resistance thermometer
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructi ...
s. Four-point probes are also used to measure sheet resistance
Sheet resistance, is a measure of resistance of thin films that are uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these ...
of thin film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many a ...
s (particularly semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
thin films).
Separation of current and voltage electrodes eliminates the lead and contact resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is described ...
from the measurement. This is an advantage for precise measurement of low resistance values. For example, an LCR bridge instruction manual recommends the four-terminal technique for accurate measurement of resistance below 100 ohms.Manual for the Racal-Dana Databridge 9343M: "If the resistance value is low, less than 100 ohms, make a four-terminal connection..."
Four-terminal sensing is also known as Kelvin sensing, after William Thomson, Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
, who invented the Kelvin bridge in 1861 to measure very low resistances using four-terminal sensing. Each two-wire connection can be called a Kelvin connection. A pair of contacts that is designed to connect a force-and-sense pair to a single terminal or lead simultaneously is called a Kelvin contact. A clip, often a crocodile clip
Alligator clip
A crocodile clip or alligator clip is a plier-like spring-tensioned metal clip with elongated, serrated jaws that is used for creating a temporary electrical connection. This simple mechanical device gets its name from the re ...
, that connects a force-and-sense pair (typically one to each jaw) is called a Kelvin clip.
Operating principle
 When a Kelvin connection is used, current is supplied via a pair of force connections (current leads). These generate a voltage drop across the impedance to be measured according to
When a Kelvin connection is used, current is supplied via a pair of force connections (current leads). These generate a voltage drop across the impedance to be measured according to Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equatio ...
''V''=''IR''. A pair of sense connections (voltage leads) are made immediately adjacent to the target impedance, so that they do not include the voltage drop in the force leads or contacts. Since almost no current flows to the measuring instrument, the voltage drop in the sense leads is negligible.
It is usual to arrange the sense wires as the inside pair, while the force wires are the outside pair. If the force and sense connections are exchanged, accuracy can be affected, because more of the lead resistance is included in the measurement. The force wires may have to carry a large current when measuring very small resistances, and must be of adequate gauge; the sense wires can be of a small gauge.
The technique is commonly used in low-voltage power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a r ...
, where it is called remote sensing, to measure the voltage delivered to the load independent of the voltage drop in the supply wires.
It is common to provide 4-wire connections to current-sensing shunt resistors of low resistance operating at high current.
3-wire sensing
A variant uses three wires, with separate load and sense leads at one end, and a common wire on the other. Voltage drop in the common wire is compensated for by assuming that it is the same as in the load wire, of the same gauge and length. This technique is widely used inresistance thermometer
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructi ...
s, also known as resistance temperature detectors or RTDs. It is not as accurate as 4-wire sensing but can remove most of the error caused by cable resistance and is accurate enough for most applications.
Another example is in the ATX power supply standard, which includes a remote sense wire connected to the 3.3 V supply line at connector pin 13, but no sense connection for the ground wires.
See also
*Electrode array
An electrode array is a configuration of electrodes used for measuring either an electric current or voltage. Some electrode arrays can operate in a bidirectional fashion, in that they can also be used to provide a stimulating pattern of electric c ...
** Wenner array configuration
** Schlumberger array configuration
* Electrical measurements
Electrical measurements are the methods, devices and calculations used to measure electrical quantities. Measurement of electrical quantities may be done to measure electrical parameters of a system. Using transducers, physical properties such as t ...
References
External links
*{{Commons category inline, Four-terminal sensing''DC Metering Circuits''
chapter fro
free ebook an
''Lessons In Electric Circuits''
series.
Four-Point Techniques for Measuring Electrical Conductivity and Resistivity
Explanatory Video about Four Wire Resistance Measurement in Energy Systems using Kelvin Clamps
Scientific techniques Impedance measurements