Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a
transcontinental country
This is a list of countries with territory that straddles more than one continent, known as transcontinental states or intercontinental states.
Contiguous transcontinental countries are states that have one continuous or immediately-adjacent ...
located mainly in
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and partly in
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
. It borders
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
to
the north and west,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
to
the east,
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
to
the southeast,
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
to
the south, and
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
to
the southwest, with a coastline along the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. Its capital is
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022.
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost
Muslim-majority country by land area, and the
ninth-largest country in the world. It has a population of 19 million people, and
one of the lowest population densities in the world, at fewer than 6 people per square kilometre (15 people per square mile).
The country dominates Central Asia economically and politically, generating 60 percent of the region's
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often ...
, primarily through its oil and gas industry; it also has vast mineral resources.
Officially, it is a democratic, secular,
unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
, constitutional republic with a diverse cultural heritage, and has the highest
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
ranking in the region. Kazakhstan is a member state of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, the
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
(CIS), the
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian politics, political, economy, economic and security organization. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geography, geographic scope and world population, population, c ...
, the
Eurasian Economic Union
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of some post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The Treaty on the Eurasian Econo ...
, the
Collective Security Treaty Organization
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics ...
, the
Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
, the
Organization of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
, the
Organization of Turkic States
The Organization of Turkic States (OTS), formerly called the Turkic Council or the Cooperation Council of Turkic Speaking States, is an international organization comprising prominent independent Turkic countries: Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzs ...
, and the
International Organization of Turkic Culture
The International Organization of Turkic Culture tr, Uluslararası Türk Kültürü Teşkilatı or TURKSOY is an international cultural organization of countries with Turkic populations, speaking languages belonging to the Turkic language fami ...
.
The territory of Kazakhstan has historically been inhabited by nomadic groups and empires. In antiquity, the ancient
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
nomadic
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
inhabited the land, and the
Achaemenid Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
expanded towards the southern territory of the modern country.
Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many
Turkic states
The following is a list of dynasties, states or empires which are Turkic-speaking, of Turkic origins, or both. There are currently six recognised Turkic sovereign states. Additionally, there are six federal subjects of Russia in which a Turkic l ...
such as the
First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bumin ...
and the
Second Turkic Khaganate
The Second Turkic Khaganate ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰃𐰠, Türük el, State of the Turks, , known as ''Turk Bilge Qaghan country'' ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰝:𐰋𐰃𐰠𐰏𐰀:𐰴𐰍𐰣:𐰃𐰠𐰭𐰀, Türük Bilgä Qaγan eli) in Bai ...
, have inhabited the country from as early as the 6th century. In the 13th century, the territory was subjugated by the
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
under
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
. In the 15th century, as a result of disintegration of
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
, the
Kazakh Khanate
The Kazakh Khanate ( kk, Қазақ Хандығы, , ), in eastern sources known as Ulus of the Kazakhs, Ulus of Jochi, Yurt of Urus, was a Kazakh state in Central Asia, successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, ...
was established on much of the lands that would later form the territory of modern Kazakhstan.
By the 18th century, Kazakh Khanate disintegrated into three ''
jüz
A ''zhuz'' ( kz, ٴجۇز , Жүз, translit=Jüz, , also translated as "horde") is one of the three main territorial and tribal divisions in the Kypchak Plain area that covers much of the contemporary Kazakhstan. It represents the main tribal di ...
'' which were absorbed and conquered by the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
; by the mid-19th century, the Russians nominally ruled all of Kazakhstan as part of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and liberated all of the slaves that the Kazakhs had captured in 1859. Following the
1917 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
and subsequent outbreak of the
Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
, the territory of Kazakhstan was reorganized several times. In 1936, it was established as the
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
within the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. Kazakhstan was the last of the
Soviet republics
The Republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Union Republics ( rus, Сою́зные Респу́блики, r=Soyúznye Respúbliki) were national-based administrative units of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( ...
to declare independence during the
dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
from 1988 to 1991. Human rights organizations have described the
Kazakh government
The Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan ( kk, Қазақстан Республикасының Үкіметі, tr, ''Qazaqstan Respublikasynyñ Ükımetı'') oversees a presidential republic. The President of Kazakhstan, currently Kassym- ...
as authoritarian, and regularly describe
Kazakhstan's human rights situation as poor.
Etymology
The English word ''Kazakh'', meaning a member of the Kazakh people, derives from . The native name is . It might originate from the Turkic word verb ''qaz-'', 'to wander', reflecting the Kazakhs'
nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
culture.
The term '
Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
' is of the same origin.
The
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
suffix means "land" or "place of", so ''Kazakhstan'' () can be literally translated as "land of the wanderers".
In
Turko-Persian
The composite Turko-Persian, Turco-Persian
''Turko-Persia in historical perspective'', Cambridge University Press, ...
sources, the term ''Özbek-Qazaq'' first appeared during the middle of the 16th century, in the ''Tarikh-i-Rashidi'' by
Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat
Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat Beg (Persian: میرزا محمد حیدر دولت بیگ c. 1499/1500 – 1551) was a Chagatai Turco-Mongol military general, governor of Kashmir, and a historical writer, He was a Turkic speaking Dughlat prince w ...
, a
Chagatayid prince of
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
. In this manuscript, the author locates Kazakh in the eastern part of ''
Desht-i Qipchaq
The name Cumania originated as the Latin exonym for the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, which was a tribal confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries. The confederation was dominated by two T ...
''. According to
Vasily Bartold
Vasily Vladimirovich Bartold (russian: Васи́лий Влади́мирович Барто́льд.; 1869–1930), who published in the West under his German baptism name, Wilhelm Barthold, was a Russian orientalist who specialized in the his ...
, the Kazakhs likely began using that name during the 15th century.
Though ''Kazakh'' traditionally referred only to
ethnic Kazakhs, including those living in China, Russia, Turkey, Uzbekistan and other neighbouring countries, the term is increasingly being used to refer to any inhabitant of Kazakhstan, including residents of other ethnicities.
History
Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
era. The
Botai culture
The Botai culture is an archaeological culture (c. 3700–3100 BC) of prehistoric northern Central Asia. It was named after the settlement of Botai in today's northern Kazakhstan. The Botai culture has two other large sites: Krasnyi ...
(3700–3100 BC) is credited with the first domestication of horses. The Botai population derived most of their ancestry from a deeply European-related population known as
Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to the ...
s, while also displaying some
Ancient East Asian admixture.
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal ...
developed during the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
, as the region's climate and terrain are best suited to a nomadic lifestyle. The population was
Caucasoid
The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid or Europid, Europoid) is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The ''Caucasian race'' was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, de ...
during the
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
and
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
period.
The Kazakh territory was a key constituent of the Eurasian trading
Steppe Route
The Steppe Route was an ancient overland route through the Eurasian Steppe that was an active precursor of the Silk Road. Silk and horses were traded as key commodities; secondary trade included furs, weapons, musical instruments, precious stones ...
, the ancestor of the terrestrial
Silk Roads
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
. Archaeologists believe that humans first
domesticated the horse (i.e., ponies) in the region's vast steppes. During recent prehistoric times, Central Asia was inhabited by groups such as the possibly Indo-European
Afanasievo culture
The Afanasievo culture, or Afanasevo culture (Afanasevan culture) (russian: Афанасьевская культура ''Afanas'yevskaya'' kul'tura), is the earliest known archaeological culture of south Siberia, occupying the Minusinsk Basin a ...
, later early Indo-Iranian cultures such as
Andronovo
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
,
[: "Archaeologists are now generally agreed that the Andronovo culture of the Central Steppe region in the second millennium BC is to be equated with the Indo-Iranians."] and later Indo-Iranians such as the
Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
and
Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translati ...
.
[ "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin"][ "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism."] Other groups included the nomadic
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
and the Persian
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
in the southern territory of the modern country. The Andronovo and
Srubnaya culture
The Srubnaya culture (russian: Срубная культура, Srubnaya kul'tura, ua, Зрубна культура, Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1850–1450 BC cultureParpola, Asko, (2012)"Format ...
s, precursors to the peoples of the
Scythian cultures
The Scytho-Siberian world was an archaeological horizon which flourished across the entire Eurasian Steppe during the Iron Age from approximately the 9th century BC to the 2nd century AD. It included the Scythian, Sauromatia ...
, were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the
Yamnaya
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archa ...
Steppe herders and peoples of the Central European Middle Neolithic.
In 329 BC,
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
and his
Macedonian army fought in the
Battle of Jaxartes
The Battle of Jaxartes was fought in 329 BC by Alexander the Great and his Hellenic (Greek) army against the Saka at the River Jaxartes, now known as the Syr Darya River. The site of the battle straddles the modern borders of Uzbekistan, Tajiki ...
against the
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
along the Jaxartes River, now known as the
Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
along the southern border of modern Kazakhstan.
Cuman-Kipchak and Golden Horde

The main
migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
of
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
occurred between the 5th and 11th centuries when they spread across most of Central Asia. The Turkic peoples slowly replaced and assimilated the previous
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
-speaking locals, turning the population of Central Asia from largely
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
, into primarily of East Asian descent.
The
first Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bumin ...
was founded by
Bumin
Bumin Qaghan ( otk, 𐰉𐰆𐰢𐰣:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Bumïn qaγan, also known as Illig Qaghan (Chinese: 伊利可汗, Pinyin: Yīlì Kèhán, Wade–Giles: i-li k'o-han) or Yamï Qaghan ( otk, 𐰖𐰢𐰃:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Yаmï qaγan, died 552 AD ...
in 552 on the Mongolian Plateau and quickly spread west toward the Caspian Sea. The
Göktürks
The Göktürks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Türük Bodun; ; ) were a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and ...
drove before them various peoples:
Xionites
Xionites, Chionites, or Chionitae (Middle Persian: ''Xiyōn'' or ''Hiyōn''; Avestan: ''Xiiaona''; Sogdian ''xwn''; Pahlavi ''Xyon'') were a nomadic people in the Central Asian regions of Transoxiana and Bactria.
The Xionites appear to be syno ...
,
Uar
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ar, الجمهورية العربية المتحدة, al-Jumhūrīyah al-'Arabīyah al-Muttaḥidah) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 until 1971. It was initially a political union between Eg ...
,
Oghurs and others. These seem to have merged into the
Avars and
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
. Within 35 years the
eastern half and the
Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
were independent. The Western Khaganate reached its peak in the early 7th century.
The
Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian language, Russian Exonym and endonym, exonym ), were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confede ...
entered the steppes of modern-day Kazakhstan around the early 11th century, where they later joined with the
Kipchak and established the vast Cuman-Kipchak confederation. While ancient cities
Taraz
Taraz ( kz, Тараз, تاراز, translit=Taraz ; known to Europeans as Talas) is a city and the administrative center of Jambyl Region in Kazakhstan, located on the Talas (river), Talas (Taraz) River in the south of the country near the borde ...
(Aulie-Ata) and
Hazrat-e Turkestan
Turkistan ( kz, Түркістан, ''Türkıstan'') is a city and the administrative center of Turkistan Region of Kazakhstan, near the Syr Darya river. It is situated north-west of Shymkent on the Trans-Aral Railway between Kyzylorda to the ...
had long served as important way-stations along the
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
connecting Asia and Europe, true political consolidation began only with the Mongol rule of the early 13th century. Under the
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, the first strictly structured administrative districts (Ulus) were established. After the
division of the Mongol Empire
The division of the Mongol Empire began when Möngke Khan died in 1259 in the siege of Diaoyu Castle with no declared successor, precipitating infighting between members of the Tolui family line for the title of khagan that escalated into the T ...
in 1259, the land that would become modern-day Kazakhstan was ruled by the
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
, also known as the Ulus of Jochi. During the Golden Horde period, a
Turco-Mongol tradition
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually ...
emerged among the ruling elite wherein
Turkicised descendants of
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
followed
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and continued to reign over the lands.
Kazakh Khanate
In 1465, the
Kazakh Khanate
The Kazakh Khanate ( kk, Қазақ Хандығы, , ), in eastern sources known as Ulus of the Kazakhs, Ulus of Jochi, Yurt of Urus, was a Kazakh state in Central Asia, successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, ...
emerged as a result of the dissolution of the
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
. Established by
Janibek Khan
Abū Saʿīd Janibek Bahadur Khan bin Barak Sultan (, , ), otherwise known by his shortened regal name Janibek Khan, was a co-founder and second Khan of the Kazakh Khanate from 1473 to 1480. He was a son of Barak, Khan of the Golden Horde from ...
and
Kerei Khan
Kerei Khan (, ) ( 1424, White Horde - 1473/ 4, Kazakh Khanate) was a co-founder and the first Khan of the Kazakh Khanate from c. 1465 to 1473.
History
There are currently two versions how the first dynasty of the Kazakh khans originated. Accordin ...
, it continued to be ruled by the
Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually ...
clan of Tore (
Jochi
Jochi Khan ( Mongolian: mn, Зүчи, ; kk, Жошы, Joşy جوشى; ; crh, Cuçi, Джучи, جوچى; also spelled Juchi; Djochi, and Jöchi c. 1182– February 1227) was a Mongol army commander who was the eldest son of Temüjin (aka G ...
d dynasty).
Throughout this period, traditional
nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
ic life and a livestock-based economy continued to dominate the
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
. In the 15th century, a distinct
Kazakh identity began to emerge among the
Turkic tribes. This was followed by the
Kazakh War of Independence
The Kazakh War of Independence (1468–1500) was a conflict fought in Central Asia between the Kazakh Khanate and the Uzbek Khanate, which attempted to maintain its control over most of modern-day Kazakhstan, which at the time was under Uzbek ...
, where the Khanate gained its sovereignty from the
Shaybanids
The Shibanids or Shaybanids ( fa, سلسله شیبانیان) or more accurately the Abu'l-Khayrid-Shibanids were a Persianized''Introduction: The Turko-Persian tradition'', Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective, ed. Robert L. ...
. The process was consolidated by the mid-16th century with the appearance of the Kazakh
language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
, culture, and economy.

Nevertheless, the region was the focus of ever-increasing disputes between the native Kazakh
emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
s and the neighbouring
Persian-speaking peoples to the south. At its height, the Khanate would rule parts of Central Asia and control
Cumania
The name Cumania originated as the Latin exonym for the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, which was a tribal confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries. The confederation was dominated by two Tur ...
. The Kazakh Khanate's territories would expand deep into Central Asia. By the early 17th century, the Kazakh Khanate was struggling with the impact of tribal rivalries, which had effectively divided the population into the Great, Middle and Little (or Small) hordes (''
jüz
A ''zhuz'' ( kz, ٴجۇز , Жүз, translit=Jüz, , also translated as "horde") is one of the three main territorial and tribal divisions in the Kypchak Plain area that covers much of the contemporary Kazakhstan. It represents the main tribal di ...
''). Political disunion, tribal rivalries, and the diminishing importance of overland trade routes between east and west weakened the Kazakh Khanate. The
Khiva Khanate
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except for ...
used this opportunity and annexed the
Mangyshlak Peninsula
Mangyshlak or Mangghyshlaq Peninsula ( kk, Маңғыстау түбегі, translit=Mañğystau tübegı; russian: Полуостров Мангышла́к, translit=Poluostrov Mangyshlák) is a large peninsula located in western Kazakhstan. It ...
. Uzbek rule there lasted two centuries until the Russian arrival.
During the 17th century, the Kazakhs fought the
Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
Histor ...
, a federation of western
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
tribes, including the
Dzungar
Dzungar may refer to:
*Dzungar people, Oirat tribes in the Dzungar Khanate
*Dzungar Khanate, a historical empire
* Jungar Banner, an administrative division of China
*Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin () is one of the largest sedimentary basins in ...
. The beginning of the 18th century marked the zenith of the Kazakh Khanate. During this period the Little Horde participated in the 1723–1730
war against the Dzungar Khanate, following their "Great Disaster" invasion of Kazakh territory. Under the leadership of
Abul Khair Khan
Mirza Abū'l-Khair Mūhammed Khan bin Qājı Abdūllah Sultan ( kk, Мырза Әбілқайыр Мұхаммед хан бин Қажы Абдұллаh Сұлтан, , romanized: ''Myrza Äbılqaiyr Mūhammed Han bin Qajy Abdūllah Sūltan''), ...
, the Kazakhs won major victories over the Dzungar at the Bulanty River in 1726 and at the
Battle of Añyraqai
The Battle of Añyraqai was a legendary battle that took place during the Kazakh-Dzungar Wars from December 1729 until January 1730. There are not many records about the Kazakh-Dzungar Wars because the Kazakh people did not have a written tra ...
in 1729.
Ablai Khan
Wāli-ūllah Abū'l-Mansūr Khan ( kk, Уәлиұллаh Әбілмансұр хан, , romanized: ''Uäliūllah Äbılmansūr Han''), better known as Abylai Khan or Ablai Khan (May 23, 1711 — May 23, 1781) was a Kazakh khan of the Middle jüz ...
participated in the most significant battles against the Dzungar from the 1720s to the 1750s, for which he was declared a "''batyr''" ("hero") by the people. The Kazakhs suffered from the frequent raids against them by the Volga
Kalmyks
The Kalmyks ( Kalmyk: Хальмгуд, ''Xaľmgud'', Mongolian: Халимагууд, ''Halimaguud''; russian: Калмыки, translit=Kalmyki, archaically anglicised as ''Calmucks'') are a Mongolic ethnic group living mainly in Russia, w ...
. The
Kokand Khanate
The Khanate of Kokand ( fa, ; ''Khānneshin-e Khoqand'', chg, ''Khoqand Khānligi'') was a Central Asian polity in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand between 1709 and 1876. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan, Kyr ...
used the weakness of Kazakh jüzs after Dzungar and Kalmyk raids and conquered present Southeastern Kazakhstan, including
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
, the formal capital in the first quarter of the 19th century. Also, the
Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the lan ...
ruled
Shymkent
Shymkent (; Шымкент, Şymkent), known until 1993 as Chimkent ( uz, Çımkent, چىمكېنت; Yañalif: Çimkent ()); russian: Чимкент, translit=Chimkent (), is a city in Kazakhstan. It is near the border with Uzbekistan. It is one ...
before the Russians gained dominance.
Russian Kazakhstan
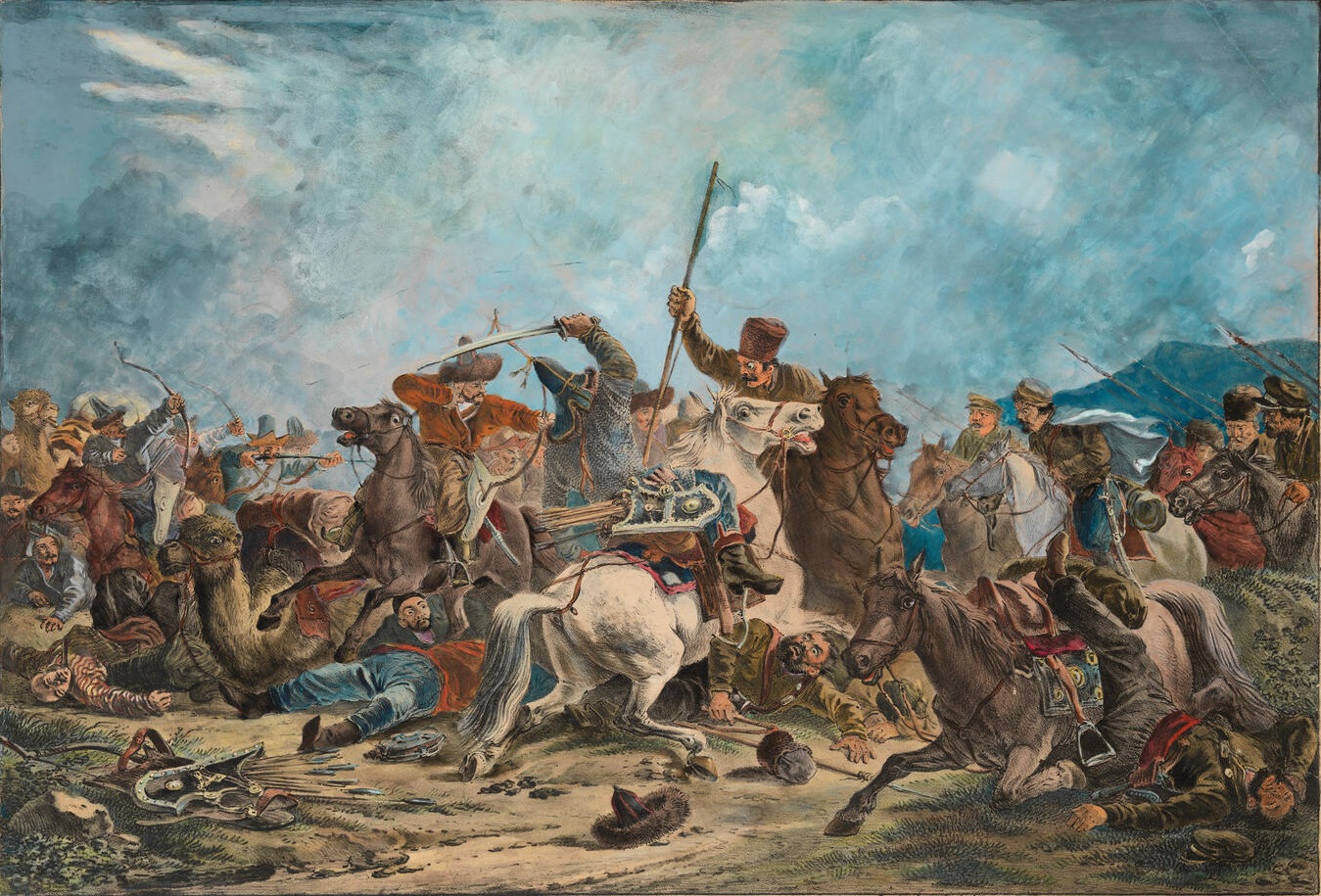

In the first half of the 18th century, the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
constructed the Irtysh line, a series of forty-six forts and ninety-six redoubts, including
Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk ...
(1716),
Semipalatinsk
Semey ( kk, Семей, Semei, سەمەي; cyrl, Семей ), until 2007 known as Semipalatinsk (russian: Семипала́тинск) and in 1917–1920 as Alash-kala ( kk, Алаш-қала, ''Alaş-qala''), is a city in eastern Kazakhst ...
(1718),
Pavlodar
Pavlodar ( ; ) is a city in northeastern Kazakhstan and the capital of Pavlodar Region. It is located 450 km northeast of the national capital Astana and 405 km southeast of the Russian city of Omsk along the Irtysh River. , the cit ...
(1720),
Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the Kazakhstan-Russia bor ...
(1743) and
Petropavl
Petropavl ( kk, Петропавл, Petropavl ) or Petropavlovsk () is a city on the Ishim River in northern Kazakhstan close to the border with Russia. It is the capital of the North Kazakhstan Region. Population: 218,956. The city is also kno ...
ovsk (1752), to prevent Kazakh and Oirat raids into Russian territory. In the late 18th century the Kazakhs took advantage of
Pugachev's Rebellion
Pugachev's Rebellion (, ''Vosstaniye Pugachyova''; also called the Peasants' War 1773–1775 or Cossack Rebellion) of 1773–1775 was the principal revolt in a series of popular rebellions that took place in the Russian Empire after Catherine ...
, which was centred on the Volga area, to raid Russian and
Volga German
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov a ...
settlements. In the 19th century, the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
began to expand its influence into Central Asia. The "
Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empi ...
" period is generally regarded as running from approximately 1813 to the
Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907
The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 (russian: Англо-Русская Конвенция 1907 г., translit=Anglo-Russkaya Konventsiya 1907 g.), or Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet (; ...
. The
tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
s effectively ruled over most of the territory belonging to what is now the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The Russian Empire introduced a system of administration and built military garrisons and barracks in its effort to establish a presence in Central Asia in the so-called "Great Game" for dominance in the area against the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, which was extending its influence from the south in India and Southeast Asia. Russia built its first outpost,
Orsk
Orsk (russian: Орск) is the second largest city in Orenburg Oblast, Russia, located on the steppe about southeast of the southern tip of the Ural Mountains. The city straddles the Ural River. Population: It lies adjacent to the Kazakhstan– ...
, in 1735. Russia introduced the Russian language in all schools and governmental organisations.
Russia's efforts to impose its system aroused the resentment of the
Kazakh people
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also parts o ...
, and, by the 1860s, some Kazakhs resisted its rule. Russia had disrupted the traditional nomadic lifestyle and livestock-based economy, and people were suffering from hunger and starvation, with some Kazakh tribes being decimated. The Kazakh national movement, which began in the late 19th century, sought to preserve the native language and identity by resisting the attempts of the Russian Empire to assimilate and stifle Kazakh culture.
From the 1890s onward, ever-larger numbers of settlers from the Russian Empire began
colonizing the territory of present-day Kazakhstan, in particular, the province of
Semirechye
Zhetysu, or Jeti-Suu ( kk, , Жетісу, pronounced ; ky, ''Jeti-Suu'', (), meaning "seven rivers"; also transcribed ''Zhetisu'', ''Jetisuw'', ''Jetysu'', ''Jeti-su'', ''Jity-su'', ''Жетысу'',, United States National Geospatial-I ...
. The number of settlers rose still further once the
Trans-Aral Railway
The broad gauge Trans-Aral Railway (also known as the Tashkent Railway) was built in 1906 connecting Kinel and Tashkent, then both in the Russian Empire. For the first part of the 20th century it was the only railway connection between European R ...
from
Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the Kazakhstan-Russia bor ...
to
Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
was completed in 1906. A specially created Migration Department (Переселенческое Управление) in
St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
oversaw and encouraged the migration to expand Russian influence in the area. During the 19th century, about 400,000 Russians immigrated to Kazakhstan, and about one million Slavs, Germans, Jews, and others immigrated to the region during the first third of the 20th century.
Vasile Balabanov
Vasily Vasilyevich Balabanov (russian: link=no, Василий Васильевич Балабанов; 30 January 1873 – 27 January 1947) was a former governor of Turkestan in Imperial Russia, a governor of Semirechye, an SR and a commissa ...
was the administrator responsible for the resettlement during much of this time.
The competition for land and water that ensued between the Kazakhs and the newcomers caused great resentment against colonial rule during the final years of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. The most serious uprising, the
Central Asian revolt
The Basmachi movement (russian: Басмачество, ''Basmachestvo'', derived from Uzbek: "Basmachi" meaning "bandits") was an uprising against Russian Imperial and Soviet rule by the Muslim peoples of Central Asia.
The movement's roots l ...
, occurred in 1916. The Kazakhs attacked Russian and
Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
settlers and military garrisons. The revolt resulted in a series of clashes and in brutal massacres committed by both sides. Both sides resisted the communist government until late 1919.
Kazakh SSR


Following the
collapse of central government in
Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in November 1917, the Kazakhs (then in Russia officially referred to as "Kirghiz") experienced a brief period of
autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
(the
Alash Autonomy
The Alash Autonomy ( kk, Алаш Автономиясы; Alaş Avtonomiasy, italic=no, ; russian: Алашская автономия, italic=no, ) was a Kazakh provisional government, or proto-state, located mainly in Central Asia, and partly ...
) before eventually succumbing to the
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s′ rule. On 26 August 1920, the
Kirghiz Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic within the
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
(RSFSR) was established. The Kirghiz ASSR included the territory of present-day Kazakhstan, but its administrative centre was the mainly Russian-populated town of
Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the Kazakhstan-Russia bor ...
. In June 1925, the Kirghiz ASSR was renamed the
Kazak ASSR
The Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (russian: Казахская Автономная Социалистическая Советская Республика; kk, Qazaq Aptonom Sotsijalistik Sovettik Respublikasь), abbreviated as K ...
and its administrative centre was transferred to the town of
Kyzylorda
Kyzylorda ( kk, Қызылорда, translit=Qyzylorda, ), formerly known as Kzyl-Orda (russian: Кзыл-Орда), Ak-Mechet (Ак-Мечеть), Perovsk (Перовск), and Fort-Perovsky (Форт-Перовский), is a city in south-cen ...
, and in April 1927 to
Alma-Ata
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936 as an autonomous republic as part of t ...
.
Soviet repression of the traditional elite, along with forced
collectivisation
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
in the late 1920s and 1930s, brought
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
and high fatalities, leading to unrest (see also:
Famine in Kazakhstan of 1932–33). During the 1930s, some members of the Kazakh intelligentsia were executed – as part of the
policies of political reprisals pursued by the Soviet government in Moscow.
On 5 December 1936, the
Kazakh Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (russian: Казахская Автономная Социалистическая Советская Республика; kk, Qazaq Aptonom Sotsijalistik Sovettik Respublikasь), abbreviated as K ...
(whose territory by then corresponded to that of modern Kazakhstan) was detached from the
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
(RSFSR) and made the
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
, a full
union republic
The Republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Union Republics ( rus, Сою́зные Респу́блики, r=Soyúznye Respúbliki) were National delimitation in the Soviet Union, national-based administrative units of ...
of the USSR, one of eleven such republics at the time, along with the
Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kirghiz SSR; ky, Кыргыз Советтик Социалисттик Республикасы, Kyrgyz Sovettik Sotsialisttik Respublikasy, ky, Кыргыз ССР, Kyrgyz SSR, russian: Киргизск ...
.
The republic was one of the destinations for exiled and convicted persons, as well as for mass resettlements, or deportations affected by the central USSR authorities during the 1930s and 1940s, such as approximately 400,000
Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
deported from the
in September–October 1941, and then later the
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
and
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace
...
. Deportees and prisoners were interned in some of the biggest
Soviet labour camps (the Gulag), including
ALZhIR camp outside Astana, which was reserved for the wives of men considered "enemies of the people". Many moved due to the policy of
population transfer in the Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
and others were forced into
involuntary settlements in the Soviet Union
Forced settlements in the Soviet Union were the result of population transfers and were performed in a series of operations organized according to social class or nationality of the deported. Resettling of "enemy classes" such as prosperous p ...
.

The Eastern Front (World War II), Soviet-German War (1941–1945) led to an increase in industrialisation and mineral extraction in support of the war effort. At the time of Joseph Stalin's death in 1953, however, Kazakhstan still had an overwhelmingly agricultural economy. In 1953, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev initiated the Virgin Lands Campaign designed to turn the traditional pasturelands of Kazakhstan into a major grain-producing region for the Soviet Union. The Virgin Lands policy brought mixed results. However, along with later modernisations under Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev (in power 1964–1982), it accelerated the development of the agricultural sector, which remains the source of livelihood for a large percentage of Kazakhstan's population. Because of the decades of privation, war and resettlement, by 1959 the Kazakhs had become a minority in the country, making up 30 percent of the population. Ethnic Russians accounted for 43 percent.
In 1947, the USSR government, as part of its Soviet atomic bomb project, atomic bomb project, founded an Semipalatinsk Test Site, atomic bomb test site near the north-eastern town of
Semipalatinsk
Semey ( kk, Семей, Semei, سەمەي; cyrl, Семей ), until 2007 known as Semipalatinsk (russian: Семипала́тинск) and in 1917–1920 as Alash-kala ( kk, Алаш-қала, ''Alaş-qala''), is a city in eastern Kazakhst ...
, where the RDS-1, first Soviet nuclear bomb test was conducted in 1949. Hundreds of nuclear tests were conducted until 1989 with adverse consequences for the nation's environment and population. The Anti-nuclear movement in Kazakhstan became a major political force in the late 1980s.
In December 1986, mass demonstrations by young ethnic Kazakhs, later called the Jeltoqsan riot, took place in Almaty to protest the replacement of the General Secretary, First Secretary of the Communist Party of Kazakhstan, Communist Party of the Kazakh SSR Dinmukhamed Konayev with Gennady Kolbin from the Russian SFSR. Governmental troops suppressed the unrest, several people were killed, and many demonstrators were jailed. In the waning days of Soviet rule, discontent continued to grow and found expression under Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev's policy of ''glasnost'' ("openness").
Independence

On 25 October 1990, Kazakhstan declared its sovereignty on its territory as a republic within the Soviet Union. Following the August 1991 aborted 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, coup attempt in Moscow, Kazakhstan declared Kazakhstani Independence Day, independence on 16 December 1991, thus becoming the last Soviet republic to declare independence. Ten days later, the Soviet Union itself dissolution of the Soviet Union, ceased to exist.
Kazakhstan's communist-era leader, Nursultan Nazarbayev, became the country's first President. Nazarbayev ruled in an authoritarian manner. An emphasis was placed on converting the country's economy to a market economy while political reforms lagged behind economic advances. By 2006, Kazakhstan was generating 60 percent of the GDP of Central Asia, primarily through its oil industry.
In 1997, the government moved the capital to
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
, renamed Nur-Sultan on 23 March 2019, from
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
, Kazakhstan's largest city, where it had been established under the Soviet Union.
In March 2019, Nazarbayev resigned 29 years after taking office. However, he continued to lead the influential security council and held the formal title Leader of the Nation. Kassym-Jomart Tokayev succeeded Nazarbayev as the President of Kazakhstan. His first official act was to rename the capital after his predecessor. In June 2019, the new president, Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, won Kazakhstan's presidential 2019 Kazakh presidential election, election.
In January 2022, the country plunged into 2022 Kazakhstan unrest, political unrest following a spike in fuel prices. In consequence, President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev took over as head of the powerful Security Council, removing his predecessor Nursultan Nazarbayev from the post. In September 2022, the name of the country's capital was changed back to Astana from Nur-Sultan.
Geography

As it extends across both sides of the Ural River, considered the dividing line separating Europe and Asia, Kazakhstan is one of only two Landlocked country, landlocked countries in the world that transcontinental countries, has territory in two continents (the other is Azerbaijan).
With an area of equivalent in size to Western EuropeKazakhstan is the ninth-largest country and largest landlocked country in the world. While it was part of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, Kazakhstan lost some of its territory to China's Xinjiang province, and some to Uzbekistan's Karakalpakstan autonomous republic during Soviet years.

It shares borders of with Russia, with
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
, with China, with
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
, and with
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
. Major cities include
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
,
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
, Karagandy,
Shymkent
Shymkent (; Шымкент, Şymkent), known until 1993 as Chimkent ( uz, Çımkent, چىمكېنت; Yañalif: Çimkent ()); russian: Чимкент, translit=Chimkent (), is a city in Kazakhstan. It is near the border with Uzbekistan. It is one ...
, Atyrau, and Oskemen. It lies between latitudes 40th parallel north, 40° and 56th parallel north, 56° N, and longitudes 46th meridian east, 46° and 88th meridian east, 88° E. While located primarily in Asia, a small portion of Kazakhstan is also located west of the Urals in Eastern Europe.
Kazakhstan's terrain extends west to east from the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
to the Altay Mountains and north to south from the plains of Siberia, Western Siberia to the oases and deserts of Central Asia. The Kazakh Steppe (plain), with an area of around , occupies one-third of the country and is the world's largest dry
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
region. The steppe is characterised by large areas of grasslands and sandy regions. Major seas, lakes and rivers include Lake Balkhash, Lake Zaysan, the Charyn Canyon, Charyn River and gorge, the Ili River, Ili, Irtysh River, Irtysh, Ishim River, Ishim, Ural River, Ural and
Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
rivers, and the Aral Sea until it largely dried up in one of the world's worst environmental disasters.
The Charyn Canyon is long, cutting through a red sandstone plateau and stretching along the Charyn River gorge in northern Tian Shan ("Heavenly Mountains", east of Almaty) at . The steep canyon slopes, columns and arches rise to heights of between . The inaccessibility of the canyon provided a safe haven for a rare ash tree, ''Fraxinus sogdiana'', which survived the Last Glacial Period, Ice Age there and has now also grown in some other areas. Bigach crater, at , is a Pliocene or Miocene asteroid impact crater, in diameter and estimated to be 5±3 million years old.
Kazakhstan's
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
region is also home to the Mynzhylky mountain plateau.
Natural resources

Kazakhstan has an abundant supply of accessible mineral and fossil fuel resources. Development of petroleum, natural gas, and mineral extractions has attracted most of the over $40 billion in foreign investment in Kazakhstan since 1993 and accounts for some 57 percent of the nation's industrial output (or approximately 13 percent of gross domestic product). According to some estimates,
[Mineral Wealth](_blank)
homestead.com Kazakhstan has the second largest uranium, chromium, lead, and zinc reserves; the third largest manganese reserves; the fifth largest copper reserves; and ranks in the top ten for coal, iron, and gold. It is also an exporter of diamonds. Perhaps most significant for economic development, Kazakhstan also has the 11th largest proven reserves of both petroleum and natural gas.
In total, there are 160 deposits with over of petroleum. Oil explorations have shown that the deposits on the Caspian sea, Caspian shore are only a small part of a much larger deposit. It is said that of oil and of gas could be found in that area. Overall the estimate of Kazakhstan's oil deposits is . However, there are only three Oil refinery, refineries within the country, situated in Atirau, Atyrau,
Pavlodar
Pavlodar ( ; ) is a city in northeastern Kazakhstan and the capital of Pavlodar Region. It is located 450 km northeast of the national capital Astana and 405 km southeast of the Russian city of Omsk along the Irtysh River. , the cit ...
, and
Shymkent
Shymkent (; Шымкент, Şymkent), known until 1993 as Chimkent ( uz, Çımkent, چىمكېنت; Yañalif: Çimkent ()); russian: Чимкент, translit=Chimkent (), is a city in Kazakhstan. It is near the border with Uzbekistan. It is one ...
. These are not capable of processing the total crude output, so much of it is exported to Russia. According to the US Energy Information Administration, Kazakhstan was producing approximately of oil per day in 2009.
Kazakhstan also possesses large deposits of phosphorite. Two of the largest deposits include the Karatau basin with 650 million tonnes of P
2O
5 and the Chilisai deposit of the :ru:Актобинский фосфоритоносный бассейн, Aqtobe phosphorite basin located in northwestern Kazakhstan, with resources of 500–800million tonnes of 9 percent ore.
On 17 October 2013, the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) accepted Kazakhstan as "EITI Compliant", meaning that the country has a basic and functional process to ensure the regular disclosure of natural resource revenues.
Climate

Kazakhstan has an "extreme" continental climate, with hot summers and very cold winters. Indeed, Astana is the second coldest capital city in the world after Ulaanbaatar. Precipitation (meteorology), Precipitation varies between arid and semi-arid conditions, the winter being particularly dry.
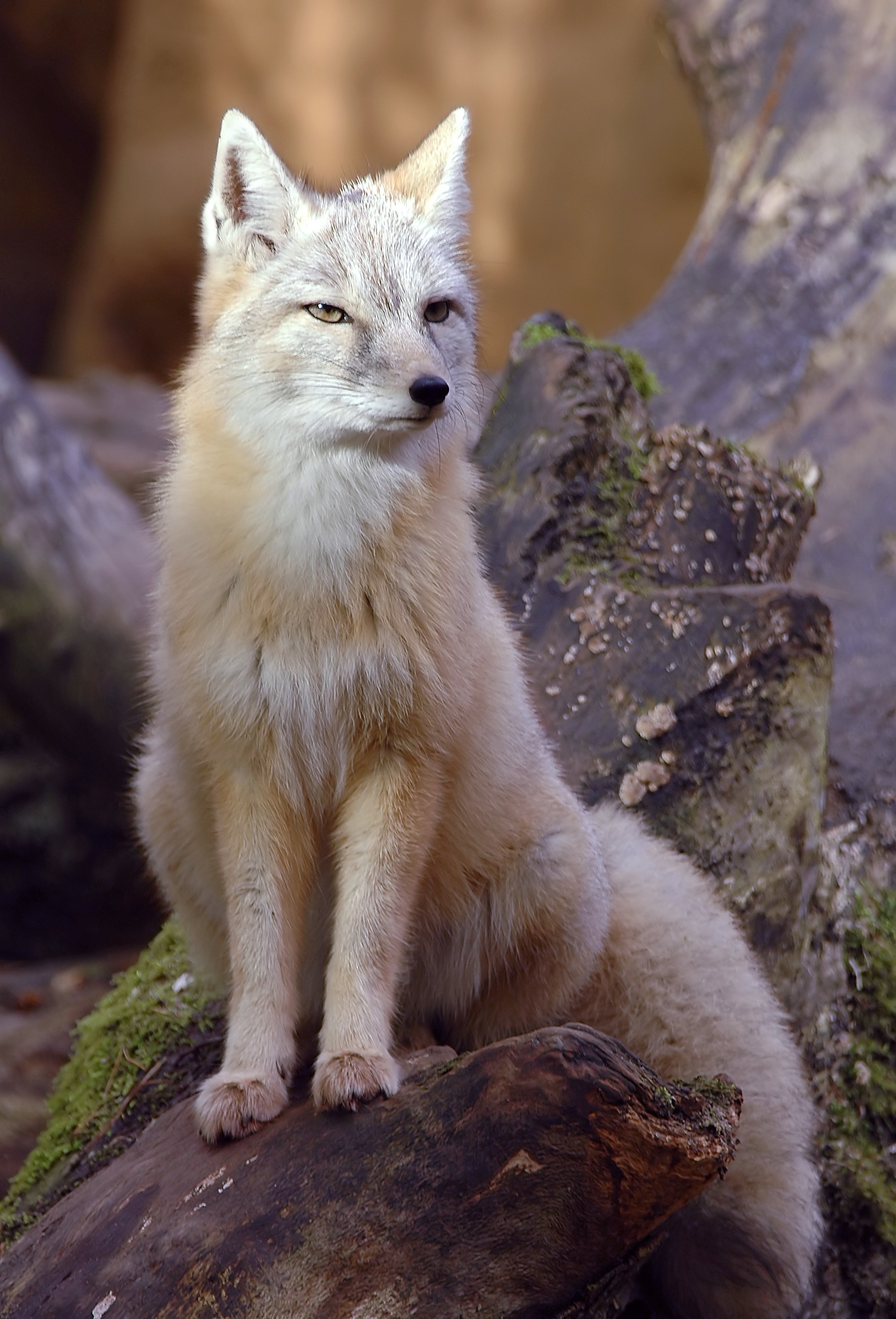
Wildlife

There are ten List of protected areas of Kazakhstan, nature reserves and ten List of national parks of Kazakhstan, national parks in Kazakhstan that provide safe haven for many rare and endangered plants and animals. Common plants are ''Astragalus'', ''Gagea'', ''Allium'', ''Carex'' and ''Oxytropis''; endangered plant species include native wild apple (''Malus sieversii''), wild grape (''Vitis vinifera'') and several wild tulip species (e.g., ''Tulipa greigii'') and rare onion species ''Allium karataviense'', also ''Iris willmottiana'' and ''Tulipa kaufmanniana''. Kazakhstan had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.23/10, ranking it 26th globally out of 172 countries.
Common mammals include the wolf, red fox, corsac fox, moose, argali (the largest species of sheep), Eurasian lynx, Pallas's cat, and snow leopards, several of which are protected.
Kazakhstan's Red Book of Protected Species lists 125 vertebrates including many birds and mammals, and 404 plants including fungi, algae and lichens.
Government and politics
Political system
Officially, Kazakhstan is a democratic, secular, constitutional unitary republic; Nursultan Nazarbayev led the country from 1991 to 2019. He was succeeded by Kassym-Jomart Tokayev.
The president may veto legislation that has been passed by the Parliament of Kazakhstan, parliament and is also the commander in chief of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan, armed forces. The prime minister chairs the cabinet of ministers and serves as Kazakhstan's head of government. There are three deputy prime ministers and sixteen ministers in the cabinet.
Kazakhstan has a bicameral parliament composed of the ''Majilis'' (the lower house) and Senate of Kazakhstan, senate (the upper house). Single-mandate districts popularly elect 107 seats in the ''Majilis''; there also are ten members elected by party-list vote. The senate has 48 members. Two senators are selected by each of the elected assemblies (mäslihats) of Kazakhstan's sixteen principal Administrative divisions of Kazakhstan, administrative divisions (fourteen regions plus the cities of Astana, Almaty, and Shymkent). The president appoints the remaining fifteen senators. ''Majilis'' deputies and the government both have the right of legislative initiative, though the government proposes most legislation considered by the parliament.
In 2020, Freedom House rated Kazakhstan as a "consolidated authoritarian regime", stating that freedom of speech is not respected and "Kazakhstan’s electoral laws do not provide for free and fair elections."
Political reforms
Reforms have begun to be implemented after the election of Kassym-Jomart Tokayev in June 2019. Tokayev supports a culture of opposition, public assembly, and loosening rules on forming political parties.
In June 2019, on the initiative of the President of Kazakhstan, Kassym-Jomart Tokayev the National Council of Public Trust have been established as a platform in which wider society can discuss different views and strengthen the national conversation regarding government policies and reforms.
[ ] Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
. In July 2019, the President of Kazakhstan announced a concept of a ‘listening state’ that quickly and efficiently responds to all constructive requests of the country's citizens. A law will be passed to allow representatives from other parties to hold Chair positions on some Parliamentary committees, to foster alternative views and opinions. The minimum membership threshold needed to register a political party will be reduced from 40,000 to 20,000 members.
Special places for peaceful rallies in central areas will be allocated and a new draft law outlining the rights and obligations of organisers, participants and observers will be passed.
In an effort to increase public safety, President Tokayev has strengthened the penalties for those who commit crimes against individuals.
On 17 September 2022, Tokayev signed a decree that limits presidential tenure to one term of seven years. He furthermore announced the preparation of a new reform package to “decentralize” and “distribute” power between government institutions, such as ministries and regional heads. The reform package also seeks to modify the electoral system and increase the decision-making authorities of Kazakhstan’s regions.
The powers of the parliament were expanded at the expense of those of the president, whose relative are now also barred from holding government positions, while the Constitutional Court was restored and the death penalty abolished.
Elections

Elections in Kazakhstan, Elections to the Majilis in September 2004, yielded a lower house dominated by the pro-government Nur-Otan, Otan Party, headed by President Nazarbayev. Two other parties considered sympathetic to the president, including the agrarian-industrial bloc AIST and the Asar Party, founded by President Nazarbayev's daughter, won most of the remaining seats. The opposition parties which were officially registered and competed in the elections won a single seat. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe was monitoring the election, which it said fell short of international standards.

On 4 December 2005, Nursultan Nazarbayev was re-elected in an apparent landslide victory. The electoral commission announced that he had won over 90% of the vote. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) concluded the election did not meet international standards despite some improvements in the administration of the election.
On 17 August 2007, elections to the lower house of parliament were held and a coalition led by the ruling Nur-Otan party, which included the Asar Party, the Civil Party of Kazakhstan, and the Agrarian Party of Kazakhstan, Agrarian Party, won every seat with 88% of the vote. None of the opposition parties has reached the benchmark 7% level of the seats. Opposition parties made accusations of serious irregularities in the election.

In 2010, president Nazarbayev rejected a call from supporters to hold a referendum to keep him in office until 2020. He insisted on presidential elections for a five-year term. In a vote held on 3 April 2011, president Nazarbayev received 95.54% of the vote with 89.9% of registered voters participating. In March 2011, Nazarbayev outlined the progress made toward democracy by Kazakhstan. , Kazakhstan was reported on the Democracy Index by ''The Economist'' as an authoritarian regime.
On 26 April 2015, the fifth presidential election was held in Kazakhstan.
Nursultan Nazarbayev was re-elected with 97.7% of votes.
On 19 March 2019, Nazarbayev announced his resignation from the presidency. Kazakhstan's senate speaker Kassym-Jomart Tokayev became acting president after Nursultan Nazarbayev's resignation. Later, Tokayev won the 2019 Kazakh presidential election, 2019 presidential election that was held on 9 June.
Administrative divisions
Kazakhstan is divided into seventeen Regions of Kazakhstan, regions ( kk, облыстар, ; russian: link=no, области, ) plus three cities (Almaty, Astana and Shymkent) which are independent of the region in which they are situated. The regions are subdivided into 177 Districts of Kazakhstan, districts ( kk, аудандар, ; russian: link=no, районы, ).
The districts are further subdivided into rural districts at the lowest level of administration, which include all rural settlements and villages without an associated municipal government.
The cities of
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
and
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
have status "state importance" and do not belong to any region. The city of Baikonur has a special status because it is being leased until 2050 to Russia for the Baikonur cosmodrome.
[Kazakhstan](_blank)
. ''CIA World Factbook''. In June 2018 the city of
Shymkent
Shymkent (; Шымкент, Şymkent), known until 1993 as Chimkent ( uz, Çımkent, چىمكېنت; Yañalif: Çimkent ()); russian: Чимкент, translit=Chimkent (), is a city in Kazakhstan. It is near the border with Uzbekistan. It is one ...
became a "city of republican significance".
Each region is headed by an Akim, äkim (regional governor) appointed by the president. District ''äkimi'' are appointed by regional ''akim''s. Kazakhstan's government relocated its capital from Almaty, established under the Soviet Union, to Astana on 10 December 1997.
Municipal divisions
Municipalities exist at each level of administrative division in Kazakhstan. Cities of republican, regional, and district significance are designated as urban inhabited localities; all others are designated rural.
At the highest level are the cities of Almaty and Astana, which are classified as ''cities of republican significance'' on the administrative level equal to that of a region.
At the intermediate level are ''cities of regional significance'' on the administrative level equal to that of a district. Cities of these two levels may be divided into city districts.
At the lowest level are ''cities of district significance'', and over two-thousand ''villages and rural settlements'' () on the administrative level equal to that of rural districts.
Urban centres
Foreign relations

Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Economic Cooperation Organization and the
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian politics, political, economy, economic and security organization. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geography, geographic scope and world population, population, c ...
. The nations of Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan established the Eurasian Economic Community in 2000, to revive earlier efforts to harmonise trade tariffs and to create a free trade zone under a customs union. On 1 December 2007, it was announced that Kazakhstan had been chosen to chair the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe for the year 2010. Kazakhstan was elected a member of the UN Human Rights Council for the first time on 12 November 2012.
Kazakhstan is also a member of the United Nations, Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council, Turkic Council, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). It is an active participant in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, North Atlantic Treaty Organisation Partnership for Peace program.
In 1999, Kazakhstan had applied for observer status at the Council of Europe Parliamentary Assembly. The official response of the Assembly was that because Kazakhstan is partially located in Europe, it could apply for full membership, but that it would not be granted any status whatsoever at the council until its democracy and human rights records improved.
Since independence in 1991, Kazakhstan has pursued what is known as the "multivector foreign policy" ( kk, көпвекторлы сыртқы саясат), seeking equally good relations with its two large neighbours, Russia and China, as well as with the United States and the rest of the Western world. Russia leases approximately of territory enclosing the Baikonur Cosmodrome space launch site in south central Kazakhstan, where the first man was launched into space as well as Soviet space shuttle Buran (spacecraft), Buran and the well-known space station Mir.
On 11 April 2010, presidents Nazarbayev and Barack Obama, Obama met at the Nuclear Security Summit in Washington, D.C., and discussed strengthening the strategic partnership between the United States and Kazakhstan. They pledged to intensify bilateral co-operation to promote nuclear safety and non-proliferation, regional stability in Central Asia, economic prosperity, and universal values.
In April 2011, Obama called Nazarbayev and discussed many cooperative efforts regarding nuclear security, including securing nuclear material from the BN-350 reactor. They reviewed progress on meeting goals that the two presidents established during their bilateral meeting at the Nuclear Security Summit in 2010. Since 2014 the Kazakhstani government has been bidding for a non-permanent member seat on the UN Security Council for 2017–2018.
On 28 June 2016 Kazakhstan was elected as a non-permanent member to serve on the UN Security Council for a two-year term.
Kazakhstan has supported UN peacekeeping missions in Haiti, Western Sahara, and Côte d'Ivoire.
In March 2014, the Ministry of Defense chose 20 Kazakhstani military men as observers for the UN peacekeeping missions. The military personnel, ranking from captain to colonel, had to go through specialised UN training; they had to be fluent in English and skilled in using specialised military vehicles.
In 2014, Kazakhstan gave Ukraine humanitarian aid during the conflict with Russian-backed rebels. In October 2014, Kazakhstan donated $30,000 to the International Committee of the Red Cross's humanitarian effort in Ukraine. In January 2015, to help the humanitarian crisis, Kazakhstan sent $400,000 of aid to Novorossiya (confederation), Ukraine's southeastern regions.
President Nazarbayev said of the war in Ukraine, "The fratricidal war has brought true devastation to eastern Ukraine, and it is a common task to stop the war there, strengthen Ukraine's independence and secure territorial integrity of Ukraine."
Experts believe that no matter how the Ukraine crisis develops, Kazakhstan's relations with the European Union will remain normal.
It is believed that Nazarbayev's mediation is positively received by both Russia and Ukraine.
Kazakhstan's Ministry of Foreign Affairs released a statement on 26 January 2015: "We are firmly convinced that there is no alternative to peace negotiations as a way to resolve the crisis in south-eastern Ukraine."
In 2018, Kazakhstan signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.

On 6 March 2020, the Concept of the Foreign Policy of Kazakhstan for 2020–2030 was announced. The document outlines the following main points:
* An open, predictable and consistent foreign policy of the country, which is progressive in nature and maintains its endurance by continuing the course of the First President – the country at a new stage of development;
* Protection of human rights, development of humanitarian diplomacy and environmental protection;
* Promotion of the country's economic interests in the international arena, including the implementation of state policy to attract investment;
* Maintaining international peace and security;
* Development of regional and multilateral diplomacy, which primarily involves strengthening mutually beneficial ties with key partners – Russia, China, the United States, Central Asian states and the EU countries, as well as through multilateral structures – the United Nations, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, the Commonwealth of Independent States, and others.

Kazakhstan's memberships of international organisations include:
*
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
(CIS)
*
Collective Security Treaty Organization
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics ...
(CSTO)
*
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian politics, political, economy, economic and security organization. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geography, geographic scope and world population, population, c ...
* Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council
* Individual Partnership Action Plan, with NATO, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Moldova, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro
* Turkic Council and the TÜRKSOY community. (The national language, Kazakh language, Kazakh, is related to the other Turkic languages, with which it shares cultural and Turkic peoples, historical ties)
* United Nations
* Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE)
* UNESCO, where Kazakhstan is a member of its World Heritage Committee
* Nuclear Suppliers Group as a participating government
*
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
* Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
Based on these principles, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Kazakhstan has increasingly pursued an independent foreign policy, defined by its own foreign policy objectives and ambitions through which the country attempts to balance its relations with "all the major powers and an equally principled aversion towards excessive dependence in any field upon any one of them, while also opening the country up economically to all who are willing to invest there."
Military


Most of Kazakhstan's military was inherited from the Soviet Armed Forces' Turkestan Military District. These units became the core of Kazakhstan's new military. It acquired all the units of the 40th Army (Soviet Union), 40th Army (the former 32nd Army) and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land-force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments, and a large amount of equipment that had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. Since the late 20th century, the Kazakhstan Army has focused on expanding the number of its armoured units. Since 1990, armoured units have expanded from 500 to 1,613 in 2005.
The Kazakh air force is composed mostly of Soviet-era planes, including 41 MiG-29s, 44 MiG-31s, 37 Su-24s and 60 Su-27s. A small naval force is maintained on the Caspian Sea.
Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq to assist the History of Iraq (2003–2011), US post-invasion mission in Iraq. During the second Iraq War, Kazakhstani troops dismantled 4 million mines and other explosives, helped provide medical care to more than 5,000 coalition members and civilians, and purified of water.
Kazakhstan's National Security Committee of the Republic of Kazakhstan, National Security Committee (UQK) was established on 13 June 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, Border Guard, several Commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau). The latter is considered the most important part of KNB. Its director is Nurtai Abykayev.
Since 2002, the joint tactical peacekeeping exercise "Steppe Eagle" has been hosted by the Kazakhstan government. "Steppe Eagle" focuses on building coalitions and gives participating nations the opportunity to work together. During the Steppe Eagle exercises, the KAZBAT peacekeeping battalion operates within a multinational force under a unified command within multidisciplinary peacekeeping operations, with NATO and the U.S. Military.
In December 2013, Kazakhstan announced it will send officers to support United Nations Peacekeeping forces in Haiti, Western Sahara, Ivory Coast and Liberia.
Human rights
The Economist Intelligence Unit has consistently ranked Kazakhstan as an "authoritarian regime" in its Democracy Index, ranking it 128th out of 167 countries for 2020.
Kazakhstan was ranked 122th out of 180 countries in Reporters Without Borders' Press Freedom Index for 2022; previously it ranked 155th for 2021.
Kazakhstan's human rights situation has been described as poor by independent observers. In its 2015 report of human rights in the country, Human Rights Watch said that "Kazakhstan heavily restricts freedom of assembly, speech, and religion."
[Human Rights Watch]
World Report 2015: Kazakhstan
, accessed October 2015. It has also described the government as authoritarian. In 2014, authorities closed newspapers, jailed or fined dozens of people after peaceful but unsanctioned protests, and fined or detained worshipers for practising religion outside state controls. Government critics, including opposition leader Vladimir Kozlov (politician), Vladimir Kozlov, remained in detention after unfair trials. In mid-2014, Kazakhstan adopted new criminal, criminal executive, criminal procedural, and administrative codes, and a new law on trade unions, which contain articles restricting fundamental freedoms and are incompatible with international standards. Torture remains common in places of detention." However, Kazakhstan has achieved significant progress in reducing the prison population. The 2016 Human Rights Watch report commented that Kazakhstan "took few meaningful steps to tackle a worsening human rights record in 2015, maintaining a focus on economic development over political reform." Some critics of the government have been COVID-19 misinformation#Efforts to combat misinformation, arrested for allegedly spreading false information about the COVID-19 pandemic in Kazakhstan. Various police reforms, like creation of local police service and zero-tolerance policing, aimed at bringing police closer to local communities have not improved cooperation between police and ordinary citizens.
According to a U.S. government report released in 2014, in Kazakhstan:
The law does not require police to inform detainees that they have the right to an attorney, and police did not do so. Human rights observers alleged that law enforcement officials dissuaded detainees from seeing an attorney, gathered evidence through preliminary questioning before a detainee's attorney arrived, and in some cases used corrupt defense attorneys to gather evidence. [...]["Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2013: Kazakhstan"](_blank)
, released by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
Kazakhstan's global rank in the World Justice Project's 2015 Rule of Law Index was 65 out of 102; the country scored well on "Order and Security" (global rank 32/102), and poorly on "Constraints on Government Powers" (global rank 93/102), "Open Government" (85/102) and "Fundamental Rights" (84/102, with a downward trend marking a deterioration in conditions).
The ABA Rule of Law Initiative of the American Bar Association has programs to train justice sector professionals in Kazakhstan.
Kazakhstan's Supreme Court has taken steps to modernise and to increase transparency and oversight over the country's legal system. With funding from the US Agency for International Development, the ABA Rule of Law Initiative began a new program in April 2012 to strengthen the independence and accountability of Kazakhstan's judiciary.
In an effort to increase transparency in the criminal justice and court system, and improve human rights, Kazakhstan intended to digitise all investigative, prosecutorial and court records by 2018.
Many criminal cases are closed before trial on the basis of reconciliation between the defendant and the victim because they simplify the work of the law-enforcement officers, release the defendant from punishment, and pay little regard to the victim's rights.
Homosexuality has been legal in Kazakhstan since 1997, although it is still socially unacceptable in most areas. Discrimination against LGBT rights in Kazakhstan, LGBT people in Kazakhstan is widespread.
Economy

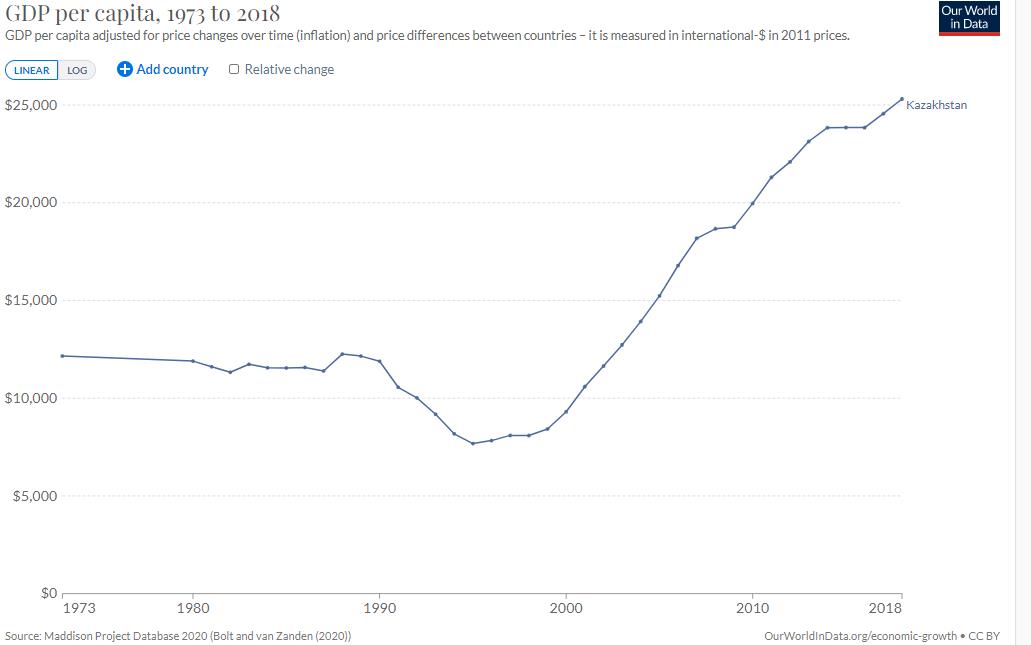

Kazakhstan's economy, supported by rising oil output and prices, grew at an average of 8 percent per year until 2013, before suffering a slowdown in 2014 and 2015.
Kazakhstan was the first former Soviet Republic to repay all of its debt to the International Monetary Fund, 7 years ahead of schedule.
Kazakhstan has a GDP of $179.332 billion and an annual growth rate of 4.5 percent. Per capita, Kazakhstan's GDP stands at $9,686.
Kazakhstan's increased role in global trade and central positioning on the Belt and Road Initiative, new Silk Road gave the country the potential to open its markets to billions of people.
Kazakhstan joined the World Trade Organization in 2015.
Buoyed by high world crude oil prices, GDP growth figures were between 8.9 percent and 13.5 percent from 2000 to 2007 before decreasing to 1 to 3 percent in 2008 and 2009, and then rising again from 2010. Other major exports of Kazakhstan include wheat, textiles, and livestock. Kazakhstan is a leading exporter of uranium.
Kazakhstan's economy grew by 4.6 percent in 2014.
The country experienced a slowdown in economic growth from 2014 sparked by falling oil prices and the effects of the Ukrainian crisis. The country devalued its currency by 19 percent in February 2014. Another 22 percent devaluation occurred in August 2015.
Kazakhstan's government continued to follow a conservative fiscal policy by controlling budget spending and accumulating oil revenue savings in its Oil Fund – Samruk-Kazyna. The global financial crisis forced Kazakhstan to increase its public borrowing to support the economy. Public debt increased to 13.4 per cent in 2013 from 8.7 per cent in 2008. Between 2012 and 2013, the government achieved an overall fiscal surplus of 4.5 per cent.
Since 2002, Kazakhstan has sought to manage strong inflows of foreign currency without sparking inflation. Inflation has not been under strict control, however, registering 6.6 percent in 2002, 6.8 percent in 2003, and 6.4 percent in 2004.
In March 2002, the US Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce granted Kazakhstan market economy status under Trade Act of 2002, US trade law. This change in status recognised substantive market economy reforms in the areas of currency convertibility, wage rate determination, openness to foreign investment, and government control over the means of production and allocation of resources.
Kazakhstan weathered the global financial crisis by combining fiscal relaxation with monetary stabilisation. In 2009, the government introduced large-scale support measures such as the recapitalisation of banks and support for the real estate and agricultural sectors, as well as for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The total value of the stimulus programs amounted to $21 billion, or 20 per cent of the country's GDP, with $4 billion going to stabilise the financial sector.
During the global economic crisis, Kazakhstan's economy contracted by 1.2 percent in 2009, while the annual growth rate subsequently increased to 7.5 percent and 5 percent in 2011 and 2012, respectively.

In September 2002, Kazakhstan became the first country in the CIS to receive an investment grade credit rating from a major international credit rating agency. By late December 2003, Kazakhstan's gross foreign debt was about $22.9 billion. Total governmental debt was $4.2 billion, 14 percent of GDP. There has been a reduction in the ratio of debt to GDP. The ratio of total governmental debt to GDP was 21.7 percent in 2000, 17.5 percent in 2001, and 15.4 percent in 2002. In 2019, it rose to 19.2 percent.
Economic growth, combined with earlier tax reform, tax and financial sector reforms, has dramatically improved government finance from the 1999 budget deficit level of 3.5 percent of GDP to a deficit of 1.2 percent of GDP in 2003. Government revenues grew from 19.8 percent of GDP in 1999 to 22.6 percent of GDP in 2001, but decreased to 16.2 percent of GDP in 2003. In 2000, Kazakhstan adopted a new tax code in an effort to consolidate these gains.
On 29 November 2003, the Law on Changes to Tax Code which reduced Tax rates around the world, tax rates was adopted. The value added tax fell from 16% to 15%, the social tax, payable by all employers, from 21 percent to 20 percent, and the personal income tax, from 30 percent to 20 percent. On 7 July 2006, the personal income tax was reduced even further to a flat rate of 5 percent for personal income in the form of dividends and 10 percent for other personal income. Kazakhstan furthered its reforms by adopting a new land code on 20 June 2003, and a new customs code on 5 April 2003.

Energy has been the leading economic sector. Production of crude oil and natural gas condensate from the oil and gas basins of Kazakhstan amounted to in 2012 up from in 2003. Kazakhstan raised oil and gas condensate exports to 44.3 million tons in 2003, 13 percent higher than in 2002. Gas production in Kazakhstan in 2003, amounted to , up 22.7 percent compared to 2002, including natural gas production of . Kazakhstan holds about of proven recoverable oil reserves and of gas. Kazakhstan is the 19th largest oil-producing nation in the world. Kazakhstan's oil exports in 2003, were valued at more than $7 billion, representing 65 percent of overall exports and 24 percent of the GDP. Major oil and gas fields and recoverable oil reserves are Tengiz Field, Tengiz with ; Karachaganak Field, Karachaganak with and of natural gas; and Kashagan Field, Kashagan with 7 to .
KazMunayGas (KMG), the national oil and gas company, was created in 2002 to represent the interests of the state in the oil and gas industry. The Tengiz Field was jointly developed in 1993 as a 40-year Tengizchevroil venture between Chevron Texaco (50 percent), US ExxonMobil (25 percent), KazMunayGas (20 percent), and LukArco (5 percent). The Karachaganak Field, Karachaganak natural gas and gas condensate field is being developed by BG Group, BG, Agip, ChevronTexaco, and Lukoil.
Also China, Chinese oil companies are involved in Kazakhstan's oil industry.
Kazakhstan instituted a pension reform program in 1998. By January 2012, the pension assets were about $17 billion (KZT 2.5 trillion). There are 11 saving pension funds in the country. The State Accumulating Pension Fund, the only state-owned fund, was Privatization, privatised in 2006. The country's unified financial regulatory agency oversees and regulates pension funds. The growing demand of pension funds for investment outlets triggered the development of the debt Security (finance), securities market. Pension fund capital is being invested almost exclusively in corporate and government Bond (finance), bonds, including the government of Kazakhstan Eurobonds. The government of Kazakhstan was studying a project to create a unified national pension fund and transfer all the accounts from the private pension funds into it.
The National Bank of Kazakhstan, Kazakh National Bank introduced deposit insurance in a campaign to strengthen the banking sector. Several major foreign banks had branches in Kazakhstan, including Royal Bank of Scotland, RBS, Citibank, and HSBC. Kookmin and UniCredit both entered Kazakhstan's financial services market through acquisitions and Equity (finance), stake-building.
According to the 2010–11 World Economic Forum in Global Competitiveness Report, Kazakhstan was ranked 72nd in the world in economic competitiveness. One year later, the Global Competitiveness Report ranked Kazakhstan 50th in most competitive markets.
In 2012, Kazakhstan attracted $14 billion of foreign direct investment inflows into the country at a 7 percent growth rate. In 2018, $24 billion of FDI was directed into Kazakhstan, a significant increase since 2012.

Kazakhstan climbed to 41st on the 2018 Economic Freedom Index published by ''The Wall Street Journal'' and The Heritage Foundation.
Kazakhstan's economy grew at an average of 8 percent per year over the past decade on the back of hydrocarbon exports.
Despite the lingering uncertainty of the global economy, Kazakhstan's economy has been stable. GDP growth in January–September 2013 was 5.7 percent, according to preliminary calculations of the Ministry Economy and Budget Planning.
From January to September 2014 Kazakhstan's GDP grew at 4 percent.
According to the results from the first half of the year, the current account surplus is $6.6 billion, a figure two times higher than that of the first half of 2013.
According to the Chairman of the National Bank of Kazakhstan, Kairat Kelimbetov, the increase was caused by a trade surplus of 17.4 per cent, or approximately US$22.6 billion.
The overall inflation rate for 2014 is forecasted at 7.4 percent.
China is one of the main economic and trade partners of Kazakhstan. In 2013, China launched the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in which Kazakhstan functions as a transit hub.
Foreign trade
Kazakhstan's foreign trade turnover in 2018 was $93.5 billion, which is 19.7 percent more compared to 2017. Export in 2018 reached $67 billion (up 25.7 percent in comparison to 2017) and import was $32.5 billion (up 9.9 percent in comparison to 2017). Exports accounted for 40.1 percent of Kazakhstan's gross domestic product (GDP) in 2018. Kazakhstan exports 800 products to 120 countries.
Agriculture
Agriculture in Kazakhstan, Agriculture accounts for approximately 5 percent of Kazakhstan's GDP.
Grain, potatoes, grapes, vegetables, melons and livestock are the most important agricultural commodities. Agricultural land occupies more than . The available agricultural land consists of of arable land and of pasture and hay land. Over 80 percent of the country's total area is classified as agricultural land, including almost 70 percent occupied by pasture. Its arable land has the second highest availability per inhabitant (1.5 hectares).
Chief livestock products are dairy products, leather, meat, and wool. The country's major crops include wheat, barley, cotton, and rice. Wheat exports, a major source of hard currency, rank among the leading commodities in Kazakhstan's export trade. In 2003 Kazakhstan harvested 17.6 million tons of grain in gross, 2.8% higher compared to 2002. Kazakhstani agriculture still has many environmental problems from mismanagement during its years in the Soviet Union. Some Kazakh wine is produced in the mountains to the east of Almaty.
Kazakhstan is thought to be one of the places that the apple originated, particularly the wild ancestor of ''Malus domestica'', ''Malus sieversii''. It has no common name in English, but is known in its native Kazakhstan as ''alma''. The region where it is thought to originate is called ''Almaty'': "rich with apple". This tree is still found wild in the mountains of Central Asia, in southern Kazakhstan,
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
, Tajikistan and Xinjiang in China.
Infrastructure

Railways provide 68 percent of all cargo and passenger traffic to over 57 percent of the country. There are in common carrier service, excluding industrial lines.
of gauge, electrified, in 2012.
Most cities are connected by railroad; high-speed trains go from
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
(the southernmost city) to
Petropavl
Petropavl ( kk, Петропавл, Petropavl ) or Petropavlovsk () is a city on the Ishim River in northern Kazakhstan close to the border with Russia. It is the capital of the North Kazakhstan Region. Population: 218,956. The city is also kno ...
(the northernmost city) in about 18 hours.
Kazakhstan Temir Zholy (KTZ) is the national railway company. KTZ cooperates with French locomotive manufacturer Alstom in developing Kazakhstan's railway infrastructure. Alstom has more than 600 staff and two joint ventures with KTZ and its subsidiary in Kazakhstan. In July 2017, Alstom opened its first locomotive repairing centre in Kazakhstan. It is the only repairing centre in Central Asia and the Caucasus.
As the Kazakhstani rail system was designed during the Soviet era, rail routes reflected the goals of Soviet planning. This has caused anomalies such as the route from Oral, Kazakhstan, Oral to Aktobe now passes briefly through Russian territory.
Astana Nurly Zhol railway station, the most modern railway station in Kazakhstan, was opened in Astana on 31 May 2017. The opening of the station coincided with the start of the Expo 2017 international exhibition. According to Kazakhstan Railways (KTZ), the 120,000m
2 station was expected to be used by 54 trains and would have the capacity to handle 35,000 passengers a day.
There is a small rapid transit, metro system in
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
. Second and third metro lines were planned for the future. The second line would intersect with the first line at Alatau (Almaty Metro), Alatau and Zhibek Zholy (Almaty Metro), Zhibek Zholy stations.
In May 2011, the construction of the second phase of the Almaty Metro line 1 began. The general contractor is Almatymetrokurylys. More than of tunnels on the extension project have been excavated. The extension includes five new stations and will connect the downtown area of Almaty with Kalkaman in the suburbs. Its length will be .
The construction is divided into 3 phases. The first phase (the current phase) will be the addition of two stations: Sairan and Moscow, a length of .
For more details see: Almaty Metro.There was a tram system of 10 lines which operated from 1937 to 2015.
The Astana Metro system has been under construction, but was abandoned at one point in 2013. In May 2015, an agreement was signed for the project to be resumed. There is an tram network, which began service in 1965 with, as of 2012, 20 regular and three special routes.
Pavlodar
Pavlodar ( ; ) is a city in northeastern Kazakhstan and the capital of Pavlodar Region. It is located 450 km northeast of the national capital Astana and 405 km southeast of the Russian city of Omsk along the Irtysh River. , the cit ...
The Khorgos Gateway dry port is one of Kazakhstan's primary dry ports for handling trans-Eurasian trains, which travel more than between China and Europe. The Khorgos Gateway dry port is surrounded by Khorgos Eastern Gate SEZ which officially commenced operations in December 2016.
In 2009 the European Commission blacklisted all Kazakh air carriers with a sole exception of Air Astana. Thereafter, Kazakhstan took measures to modernise and revamp its air safety oversight. In 2016 the European air safety authorities removed all Kazakh airlines from the blacklist, saying there was "sufficient evidence of compliance" with international standards by Kazakh Airlines and the Civil Aviation Committee.
Tourism
Kazakhstan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-largest country by area and the largest landlocked country in the world. As of 2014, tourism accounted for 0.3 percent of Kazakhstan's GDP, but the government had plans to increase it to 3 percent by 2020.
According to the World Economic Forum's Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report of 2017, travel and tourism industry GDP in Kazakhstan was $3.08 billion or only 1.6 percent of total GDP. The WEF ranked Kazakhstan 80th in its 2019 report.
In 2017, Kazakhstan ranked 43rd in the number of tourist arrivals. In 2014, The Guardian described tourism in Kazakhstan as, "hugely underdeveloped", despite the country's mountain, lake and desert landscapes.
Factors hampering an increase in tourism were said to include high prices, "shabby infrastructure," "poor service" and the difficulties of travel in a large underdeveloped country.
Even for Kazakhs, going for holiday abroad may have cost only half the price of taking a holiday in Kazakhstan.
The Kazakh Government, long characterised as authoritarian with a history of human rights abuses and suppression of political opposition,
in 2015 issued a "Tourism Industry Development Plan 2020." It aimed to establish five tourism clusters in Kazakhstan:
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
city,
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
city, East Kazakhstan Region, East Kazakhstan, South Kazakhstan Region, South Kazakhstan, and West Kazakhstan Region, West Kazakhstan Oblasts. It also sought investment of $4 billion and the creation of 300,000 new jobs in the tourism industry by 2020.
Kazakhstan has offered a permanent visa-free regime for up to 90 days to citizens of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova,
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. ...
, Mongolia, Russia and Ukraine, and for up to 30 days to citizens of Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador, Serbia, South Korea, Tajikistan, Turkey, UAE and
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
. It also established a visa-free regime for citizens of 54 countries, including the European Union and OECD#Member countries, OECD member states, the United States, U.S., Japan, Mexico, Australia and New Zealand.
Green economy

Kazakhstan launched the Green Economy Plan in 2013. It committed Kazakhstan to meet 50 percent of its energy needs from alternative and renewable sources by 2050. The green economy was projected to increase GDP by 3 percent and create some 500,000 jobs. The government set prices for energy produced from renewable sources. The price of 1 kilowatt-hour for energy produced by wind power plants was set at 22.68 tenge ($0.12), for 1 kilowatt-hour produced by small hydro-power plants 16.71 tenges ($0.09), and from biogas plants 32.23 tenges ($0.18).
Foreign direct investment
Kazakhstan has attracted $330 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI) from more than 120 countries since its independence. In 2015, the U.S. State Department said Kazakhstan was widely considered to have the best investment climate in the region.
In 2014,
President Nazarbayev signed into law tax concessions to promote foreign direct investment which included a 10-year exemption from corporation tax, an eight-year exemption from property tax, and a 10-year freeze on most other taxes.
Other incentives include a refund on capital investments of up to 30 percent once a production facility is in operation.
In 2014, the European Bank of Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and Kazakhstan created the partnership for Re-Energizing the Reform Process in Kazakhstan to work with international financial institutions to channel US$2.7 billion provided by the Kazakh government into important sectors of Kazakhstan's economy.
As of May 2014, Kazakhstan had attracted $190 billion in gross foreign investments since its independence in 1991 and it led the CIS countries in terms of FDI attracted per capita.
One of the factors that attract foreign direct investments is country's political stability.
The OECD 2017 Investment Policy Review noted that "great strides" had been made to open up opportunities to foreign investors and improve policy to attract FDI.
Banking
The banking industry of Kazakhstan went through a boom-and-bust cycle in the early 21st century. After several years of rapid expansion in the mid-2000s, the banking industry collapsed in 2008. Several large banking groups, including BTA Bank J.S.C. and Alliance Bank, defaulted soon thereafter. The industry shrank and was restructured, with system-wide loans dropping from 59 percent of GDP in 2007 to 39 percent in 2011. Although the Russian and Kazakhstani banking systems share some common features, there are key differences: Banks in Kazakhstan experienced a lengthy period of political stability and economic growth, which helped push Kazakhstan's banking system to a higher level of development. Banking technology and personnel qualifications were stronger in Kazakhstan. On the negative side, past stability in Kazakhstan arose from the concentration of virtually all political power in the hands of a single individual – the key factor in any assessment of system or country risk.
Bond market
In October 2014, Kazakhstan introduced its first overseas dollar bonds in 14 years.
Kazakhstan issued $2.5 billion of 10- and 30-year bonds on 5 October 2014, in what was the nation's first dollar-denominated overseas sale since 2000.
Kazakhstan sold $1.5 billion of 10-year dollar bonds to yield 1.5 percentage points above midswaps and $1 billion of 30-year debt at two percentage points over midswaps.
The country drew bids for $11 billion.
Housing market

The housing market of Kazakhstan grew after 2010. In 2013, the total housing area in Kazakhstan amounted to . Urban areas contained 62.5 per cent of the country's housing stock. The housing stock rose over the year to 32.7 million sq. ft., nearly an 11 percent increase. Between 2012 and 2013, the living area per Kazakh citizen rose from . The UN's recommended standard for housing stands at per person. Kazakhstan was projected to reach the UN standards by 2019 or 2020.
"Nurly Jol" economic policy
On 11 November 2014, the President of Kazakhstan Nursultan Nazarbayev delivered an unexpected state-of-the-nation address in Astana at an extended session of the Political Council of the Nur Otan party, introducing a "Nurly Jol" (Bright Path), a new economic policy that implies massive state investment in infrastructure over the next several years.
The "Nurly Zhol" policy is accepted as preventive measures needed to help steer the economy towards sustainable growth in the context of the modern global economic and geopolitical challenges, such as the 25 percent-reduction in the oil price, reciprocal sanctions between the West and Russia over Ukraine, etc.
The policy embraces all aspects of economic growth, including finances, industry and social welfare, but especially emphasises investments into the development of infrastructure and construction works.
Given recent decreases in revenues from the export of raw materials, funds will be used from Kazakhstan's National Fund.
Economic competitiveness
In the 2020 Doing Business Report by the World Bank, Kazakhstan ranked 25th globally and as the number one best country globally for protecting minority investors’ rights. Kazakhstan achieved its goal of entering the top 50 most competitive countries in 2013 and has maintained its position in the 2014–2015 World Economic Forum Global Competitiveness Report that was published at the beginning of September 2014.
Kazakhstan is ahead of other states in the CIS in almost all of the report's pillars of competitiveness, including institutions, infrastructure, macroeconomic environment, higher education and training, goods market efficiency, labour market development, financial market development, technological readiness, market size, business sophistication and innovation, lagging behind only in the category of health and primary education.
The Global Competitiveness Index gives a score from 1 to 7 in each of these pillars, and Kazakhstan earned an overall score of 4.4.
Corruption
In 2005, the World Bank listed Kazakhstan as a corruption hotspot, on a par with Angola, Bolivia, Kenya, Libya and Pakistan. In 2012, Kazakhstan ranked low in an index of the least corrupt countries
[OECD Investment Policy Reviews](_blank)
, P112, OECD, 2012 and the World Economic Forum listed corruption as the biggest problem in doing business in the country.
A 2017 OECD report on Kazakhstan indicated that Kazakhstan has reformed laws with regard to the civil service, judiciary, instruments to prevent corruption, access to information, and prosecuting corruption.
Kazakhstan has implemented anticorruption reforms that have been recognised by organizations like Transparency International.
In 2011 Switzerland confiscated US$48 million in Kazakhstani assets from Swiss bank accounts, as a result of a bribery investigation in the United States.
US officials believed the funds represented bribes paid by American officials to Kazakhstani officials in exchange for oil or prospecting rights in Kazakhstan. Proceedings eventually involved US$84 million in the US and another US$60 million in Switzerland.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Kazakh Anti-Corruption Agency signed a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in February 2015.
Science and technology

Research remains largely concentrated in Kazakhstan's largest city and former capital, Almaty, home to 52 percent of research personnel. Public research is largely confined to institutes, with universities making only a token contribution. Research institutes receive their funding from national research councils under the umbrella of the Ministry of Education and Science. Their output, however, tends to be disconnected from market needs. In the business sector, few industrial enterprises conduct research themselves.
One of the most ambitious targets of the State Programme for Accelerated Industrial and Innovative Development adopted in 2010 is to raise the country's level of expenditure on research and development to 1 percent of GDP by 2015. By 2013, this ratio stood at 0.18 percent of GDP. It will be difficult to reach the target as long as economic growth remains strong. Since 2005, the economy has grown faster (by 6 percent in 2013) than gross domestic expenditure on research and development, which only progressed from PPP$598 million to PPP$714 million between 2005 and 2013.
Innovation expenditure more than doubled in Kazakhstan between 2010 and 2011, representing KZT 235 billion (''circa'' US$1.6 billion), or around 1.1 percent of GDP. Some 11 percent of the total was spent on research and development. This compares with about 40 to 70 percent of innovation expenditure in developed countries. This augmentation was due to a sharp rise in product design and the introduction of new services and production methods over this period, to the detriment of the acquisition of machinery and equipment, which has traditionally made up the bulk of Kazakhstan's innovation expenditure. Training costs represented just 2 percent of innovation expenditure, a much lower share than in developed countries.
Kazakhstan was ranked 79th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021.
In December 2012, President Nursultan Nazarbayev announced the ''Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy'' with the slogan "Strong Business, Strong State." This pragmatic strategy proposes sweeping socio-economic and political reforms to hoist Kazakhstan among the top 30 economies by 2050. In this document, Kazakhstan gives itself 15 years to evolve into a knowledge economy. New sectors are to be created during each five-year plan. The first of these, covering the years 2010–2014, focused on developing industrial capacity in car manufacturing, aircraft engineering and the production of locomotives, passenger and cargo railroad cars. During the second five-year plan to 2019, the goal is to develop export markets for these products. To enable Kazakhstan to enter the world market of geological exploration, the country intends to increase the efficiency of traditional extractive sectors such as oil and gas. It also intends to develop rare earth metals, given their importance for electronics, laser technology, communication and medical equipment. The second five-year plan coincides with the development of the ''Business 2020'' roadmap for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which makes provision for the allocation of grants to SMEs in the regions and for microcredit. The government and the National Chamber of Entrepreneurs also plan to develop an effective mechanism to help start-ups.

During subsequent five-year plans to 2050, new industries will be established in fields such as mobile, multi-media, nano- and space technologies, robotics, genetic engineering and alternative energy. Food processing enterprises will be developed with an eye to turning the country into a major regional exporter of beef, dairy and other agricultural products. Low-return, water-intensive crop varieties will be replaced with vegetable, oil and fodder products. As part of the shift to a "green economy" by 2030, 15% of acreage will be cultivated with water-saving technologies. Experimental agrarian and innovational clusters will be established and drought-resistant genetically modified crops developed.
The Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy fixes a target of devoting 3 percent of GDP to research and development by 2050 to allow for the development of new high-tech sectors.
The Digital Kazakhstan program was launched in 2018 to boost the country's economic growth through the implementation of digital technologies. Kazakhstan's digitization efforts generated 800 billion tenges (US$1.97 billion) in two years. The program helped create 120,000 jobs and attracted 32.8 billion tenges (US$80.7 million) of investment into the country.
Around 82 percent of all public services became automated as part of the Digital Kazakhstan program.
Demographics


The US Census Bureau International Database lists the population of Kazakhstan as 18.9 million (May 2019), while United Nations sources such as give an estimate of . Official estimates put the population of Kazakhstan at 18.711 million as of May 2020.
In 2013, Kazakhstan's population rose to 17,280,000 with a 1.7 percent growth rate over the past year according to the Kazakhstan Statistics Agency.
The 2009 population estimate is 6.8 percent higher than the population reported in the last census from January 1999. The decline in population that began after 1989 has been arrested and possibly reversed. Men and women make up 48.3 and 51.7 percent of the population, respectively.
Ethnic groups
As of 2021, ethnic Kazakhs are 70.4 percent of the population and ethnic Russians in Kazakhstan, Russians are 15.5 percent.
Other groups include Tatars (1.1 percent), Ukrainians (2.0 percent), Uzbeks (3.2 percent), Germans (1.2 percent), Uyghur people, Uyghurs (1.5 percent), Azerbaijanis, Dungans, Turkic peoples, Turks, Koreans, Poles in the former Soviet Union, Poles, and Lithuanians. Some minorities such as Ukrainians, Koreans,
Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
(0.9 percent), Chechens, Meskhetian Turks, and Russian political opponents of the regime, had been Population transfer in the Soviet Union, deported to Kazakhstan in the 1930s and 1940s by Josef Stalin. Some of the largest Soviet labour camps (Gulag) existed in the country.

Significant Russian immigration was also connected with the Virgin Lands Campaign and Soviet space program during the Nikita Khrushchev, Khrushchev era. In 1989, ethnic Russians were 37.8 percent of the population and Kazakhs held a majority in only 7 of the 20 regions of the country. Before 1991 there were about 1 million Germans of Kazakhstan, Germans in Kazakhstan, mostly descendants of the
Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
deported to Kazakhstan during World War II. After the
dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, most of them emigrated to Germany. Most members of the smaller Pontian Greek minority have emigrated to Greece. In the late 1930s thousands of Koreans in the Soviet Union were Deportation of Koreans in the Soviet Union, deported to Central Asia. These people are now known as Koryo-saram.
The 1990s were marked by the emigration of many of the country's Russians, Ukrainians in Kazakhstan, Ukrainians and
Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
, a process that began in the 1970s. This has made indigenous Kazakhs the largest ethnic group. Additional factors in the increase in the Kazakhstani population are higher birthrates and Oralman, immigration of ethnic Kazakhs from China, Mongolia, and Russia.
Languages
Kazakhstan is officially a bilingual country. Kazakh language, Kazakh (part of the Kipchak family of Turkic languages) is spoken natively by 64.4 percent of the population and has the status of "state language". Russian is spoken by most Kazakhs, has equal status to Kazakh as an "official language", and is used routinely in business, government, and inter-ethnic communication.
The government announced in January 2015 that the Latin alphabet will replace Cyrillic as the writing system for the Kazakh language by 2025.
[Kazakh language to be converted to Latin alphabet – MCS RK](_blank)
. Inform.kz (30 January 2015). Retrieved 28 September 2015. Other minority languages spoken in Kazakhstan include Uzbek language, Uzbek, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, Uyghur language, Uyghur, Kyrgyz language, Kyrgyz, and Tatar language, Tatar. English, as well as Turkish, have gained popularity among younger people since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Education across Kazakhstan is conducted in either Kazakh, Russian, or both. In Nazarbayev's resignation speech of 2019, he projected that the people of Kazakhstan in the future will speak three languages (Kazakh, Russian and English).
Religion


According to the 2021 census, 69.3% of the population is Islam in Kazakhstan, Muslim; 17.2% is Christianity in Kazakhstan, Christian; 0.2% follows Religion in Kazakhstan, other religions (mostly Buddhism in Kazakhstan, Buddhist and History of the Jews in Kazakhstan, Jewish), and 13.3% are Irreligion, irreligious or chose not to answer.
According to its Constitution, Kazakhstan is a secular state.
Religious freedoms are guaranteed by Article 39 of Kazakhstan's Constitution. Article 39 states: "Human rights and freedoms shall not be restricted in any way." Article 14 prohibits "discrimination on religious basis" and Article 19 ensures that everyone has the "right to determine and indicate or not to indicate his/her ethnic, party and religious affiliation." The Constitutional Council affirmed these rights in a 2009 declaration, which stated that a proposed law limiting the rights of certain individuals to practice their religion was declared unconstitutional.
Islam in Kazakhstan, Islam is the largest religion in Kazakhstan, followed by Eastern Orthodoxy in Kazakhstan, Eastern Orthodox Christianity. After decades of Religion in the Soviet Union, religious suppression by the Soviet Union, the coming of independence witnessed a surge in the expression of ethnic identity, partly through religion. The free practice of Religion, religious beliefs and the establishment of full freedom of religion led to an increase of religious activity. Hundreds of mosques, churches, and other religious structures were built in the span of a few years, with the number of religious associations rising from 670 in 1990 to 4,170 today.
Some figures show that non-denominational Muslims form the majority, while others indicate that most Muslims in the country are Sunni Islam, Sunnis following the Hanafi school. These include ethnic Kazakhs, who constitute about 70% of the population, as well as ethnic Uzbeks, Uighurs, and Tatars.
[Kazakhstan – International Religious Freedom Report 2008](_blank)
U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 7 September 2009. Less than 1% are part of the Sunni Shafi`i school (primarily Chechens). There are also some Ahmadiyya, Ahmadi Muslims. There are a total of 2,300 mosques,
[Religious Situation Review in Kazakhstan](_blank)
Congress of World Religions. Retrieved 7 September 2009. all of them are affiliated with the "Spiritual Association of Muslims of Kazakhstan", headed by a supreme mufti. Unaffiliated mosques are forcefully closed. Eid al-Adha is recognised as a national holiday.
One quarter of the population is Russian Orthodox, including ethnic Russians, Ukrainians and Belarusians.
Other Christian groups include Catholic Church in Kazakhstan, Roman Catholics, Greek Catholics, and Protestants.
There are a total of 258 Orthodox churches, 93 Catholic churches (9 Greek Catholic), and over 500 Protestant churches and prayer houses. The Russian Orthodox Christmas is recognised as a national holiday in Kazakhstan.
Other religious groups include Judaism, the Baháʼí Faith in Kazakhstan, Baháʼí Faith, Hinduism in Kazakhstan, Hinduism, Buddhism in Central Asia, Buddhism, and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
According to the 2009 Census data, there are very few Christians outside the Slavic and Germanic ethnic groups.
Education

Education is universal and mandatory through to the Secondary education, secondary level and the List of countries by literacy rate, adult literacy rate is 99.5%.
On average, these statistics are equal to both women and men in Kazakhstan.
Education consists of three main phases: primary education (forms 1–4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and vocational education. Vocational Education usually lasts three or four years.
(Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education.) These levels can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g., primary school, then secondary school). Recently, several secondary schools, specialised schools, magnet schools, Gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, Lyceum#Lyceums in today's education, lyceums and linguistic and technical gymnasiums have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and vocational schools.
At present, there are List of universities in Kazakhstan, universities, Academy, academies and institutes, College or university school of music, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. There are three main levels: basic higher education that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to the award of the Bachelor's degree; specialised higher education after which students are awarded the Specialist's Diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education which leads to the master's degree. Postgraduate education leads to the ''Kandidat Nauk'' ("Candidate of Sciences") and the Doctor of Sciences (PhD). With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed.
Over 2,500 students in Kazakhstan have applied for student loans totalling about $9 million. The largest number of student loans come from Almaty, Astana and Kyzylorda.
The training and skills development programs in Kazakhstan are also supported by international organisations. For example, on 30 March 2015, the World Banks' Group of Executive Directors approved a $100 million loan for the Skills and Job project in Kazakhstan.
The project aims to provide training to unemployed, unproductively self-employed, and employees in need of training.
Culture

Before the Russian colonisation, the Kazakhs had a highly developed culture based on their nomadic pastoral economy.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was introduced into the region with the arrival of the Arabs in the 8th century. It initially took hold in the southern parts of Turkestan and spread northward. The Samanids helped the religion take root through zealous missionary work. The
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
further propagated Islam amongst the tribes in the region during the 14th century.

Kazakhstan is home to a large number of prominent contributors to literature, science and philosophy: Abay Qunanbayuli, Mukhtar Auezov, Gabit Musirepov, Kanysh Satpayev, Mukhtar Shakhanov, Saken Seyfullin, Jambyl Jabayev, among many others.
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry in Kazakhstan and it is joining the international tourism networking. In 2010, Kazakhstan joined The Region Initiative (TRI) which is a Tri-regional Umbrella of Tourism-related organisations. TRI is functioning as a link between three regions: South Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe. Armenia, Bangladesh, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkey, and Ukraine are now partners, and Kazakhstan is linked with other South Asian, Eastern European, and Central Asian countries in the tourism market.
Literature
Kazakh literature is defined as "the body of literature, both oral literature, oral and written, produced in the Kazakh language by the Kazakh people of Central Asia".
Kazakh literature expands from the current territory of Kazakhstan, also including the era of
Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
, Kazakh recognised territory under the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and the
Kazakh Khanate
The Kazakh Khanate ( kk, Қазақ Хандығы, , ), in eastern sources known as Ulus of the Kazakhs, Ulus of Jochi, Yurt of Urus, was a Kazakh state in Central Asia, successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, ...
. There is some overlap with several complementary themes, including the literature of Turkic tribes that inhabited Kazakhstan over the course of its history and literature written by ethnic Kazakhs.

According to Chinese written sources from the 6th–8th centuries CE, the Turkic tribes of Kazakhstan had an oral poetry tradition. These came from earlier periods and were primarily transmitted by bards: professional storytellers and musical performers.
Traces of this tradition are shown on Old Turkic alphabet, Orkhon script stone carvings dated 5th–7th centuries CE that describe rule of Kultegin and Bilge, two early Turkic rulers ("kagans"). Amongst the Kazakhs, the bard was a primarily, though not exclusively, male profession. Since at least the 17th century, Kazakh bards could be divided into two main categories: the zhıraws (zhiraus, žyraus), who passed on the works of others, usually not creating and adding their own original work; and the aqyns (akyns), who improvised or created their own poems, stories or songs.
There were several types of works, such as didactic ''termes'', elegiac ''tolgaws'', and epic (genre), epic ''zhırs''.
Although the origins of such tales are often unknown, most of them were associated with bards of the recent or more distant past, who supposedly created them or passed them on, by the time most Kazakh poetry and prose was first written down in the second half of the 19th century.
There are clear stylistic differences between works first created in the 19th century, and works dating from earlier periods but not documented before the 19th century, such as those attributed to such 16th- and 17th-century bards as Er Shoban and Dosmombet Zhıraw (also known as Dospambet Žyrau; he appeared to have been literate, and reportedly visited Constantinople), and even to such 15th-century bards as Shalkiz and Asan Qayghı.
Other notable bards include Kaztugan Žyrau, Žiembet Žyrau, Axtamberdy Žyrau, and Buxar Žyrau Kalkamanuly, who was an advisor to
Ablai Khan
Wāli-ūllah Abū'l-Mansūr Khan ( kk, Уәлиұллаh Әбілмансұр хан, , romanized: ''Uäliūllah Äbılmansūr Han''), better known as Abylai Khan or Ablai Khan (May 23, 1711 — May 23, 1781) was a Kazakh khan of the Middle jüz ...
, and whose works have been preserved by Mäšhür Žüsip Köpeev.
''Er Targhın'' and ''Alpamysh, Alpamıs'' are two of the most famous examples of Kazakh literature to be recorded in the 19th century.
The ''Book of Dede Korkut'' and Oguz Name (a story of an ancient Turkic king Oghuz Khan) are the most well-known Turkic heroic legends. Initially created around the 9th century CE, they were passed on through generations in oral form. The legendary tales were recorded by Turkish authors in 14–16th centuries C.E.
The preeminent role in the development of modern literary Kazakh belongs to Abai Qunanbaiuly ( kk, Абай Құнанбайұлы, sometimes Russified to Abay Kunanbayev, Абай Кунанбаев) (1845–1904), whose writings did much to preserve Kazakh folk culture. Abai's major work is ''The Book of Words'' ( kk, қара сөздері, Qara sözderi), a philosophical treatise and collection of poems where he criticises Russian colonial policies and encourages other Kazakhs to embrace education and literacy. The literary magazines ''Ay Qap'' (published between 1911 and 1915 in Arabic script) and ''Qazaq'' (published between 1913 and 1918) played an important role in the development of the intellectual and political life among early 20th-century Kazakhs.
Music

The modern state of Kazakhstan is home to the Kazakh State Kurmangazy Orchestra of Folk Instruments, the Kazakh State Philharmonic Orchestra, the Kazakh National Opera and the Kazakh State Chamber Orchestra. The folk instrument orchestra was named after Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly, a famous composer and dombra player from the 19th century. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1931, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed.
The Foundation Asyl Mura is archiving and publishing historical recordings of great samples of Kazakh music both traditional and classical. The leading conservatoire is in Almaty, the Qurmanghazy Conservatoire. It competes with the national conservatoire in Astana, Kazakhstan's capital.
When referring to traditional Kazakh music, authentic folklore must be separated from "folklorism". The latter denotes music executed by academically trained performers who aim at preserving the traditional music for coming generations. As far as can be reconstructed, the music of Kazakhstan from the period before a strong Russian influence consists of instrumental music and vocal music. Instrumental music, with the pieces ("Küy") being performed by soloists. Text is often seen in the background (or "program") for the music, as a lot of Küy titles refer to stories. Vocal music, either as part of a ceremony such as a wedding (mainly performed by women), or as part of a feast. Here we might divide into subgenres: epic singing, containing not only historical facts, but as well the tribe's genealogy, love songs, and didactic verses; and as a special form the composition of two or more singers in public (Aitys), of dialogue character and usually unexpectedly frankly in content.

The Russian influence on the music life in Kazakhstan can be seen in two spheres: first, the introduction of musical academic institutions such as concert houses with opera stages, and conservatories, where European music was performed and taught, and second, by trying to incorporate Kazakh traditional music into these academic structures. Controlled first by the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and then the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, Kazakhstan's folk and classical traditions became connected with ethnic Russian music and Western European music. Prior to the 20th century, Kazakh folk music was collected and studied by ethnography, ethnographic research teams including composers, music critics and musicology, musicologists. In the first part of the 19th century, Kazakh music was transcribed in linear musical notation, notation. Some composers of this era set Kazakh folk songs to Russian-style European classical music.
The Kazakhs themselves, however, did not write their own music in notation until 1931. Later, as part of the Soviet Union, Kazakh folk culture was encouraged in a sanitised manner designed to avoid political and social unrest. The result was a bland derivative of real Kazakh folk music. In 1920, Aleksandr Zatayevich, a Russian official, created major works of art music with melodies and other elements of Kazakh folk music. Beginning in 1928 and accelerating in the 1930s, he also adapted traditional Kazakh instruments for use in Russian-style ensembles, such as by increasing the number of frets and strings (music), strings. Soon, these styles of modern orchestral playing became the only way for musicians to officially play; Kazakh folk was turned into patriotic, professional and socialist endeavours.
The current situation could be described as the effort to rediscover traditional music as it had been practised before the heavy influence of European musical styles. Contemporary musicians performing in traditional folk music are trained professionals (Rauchan Orazbaeva, Ramazan Stamgazi).
Another very challenging aspect arises from the young composers' generation, and the rock and jazz musicians, as they aim to incorporate their traditional heritage into the music they learned from the western cultures, thus forming a new stage of "ethnic contemporary classics", respectively ethnic rock or jazz music that sounds distinctly Kazakh. For the classical sector outstanding: Aqtoty Raimkulova, Turan ensemble; for jazz: "Magic of Nomads"; for rock: Roksonaki, Urker, Ulytau, Alda span.
Fine arts
In Kazakhstan, the fine arts, in the classical sense, have their origins in the second half of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. It was largely influenced by Russian artists, such as Vasily Vereshchagin and Nikolai Khludov, who intensively travelled in Central Asia. Khludov had a particular influence on the development of the local school of painting, becoming the teacher of many local artists. The most famous of these is Abilkhan Kasteyev, after whom the State Museum of Art of Kazakhstan was renamed in 1984.
The Kazakh school of fine arts was fully formed by the 1940s and flourished in the 1950s. Local painters, graphic artists and sculptors, trained under the unified Soviet system of artist education, began active work, often using national motifs in their art. The painters O. Tansykbaev, J. Shardenov, K. Telzhanov, and S. Aitbaev, graphic artists E. Sidorkina and A. Duzelkhanov, and sculptors H. Nauryzbaeva and E. Sergebaeva are today counted among the key figures of Kazakhstani art.
Cuisine
In the national cuisine, livestock meat, like horse meat and beef can be cooked in a variety of ways and is usually served with a wide assortment of traditional bread products. Refreshments include black tea, often served with milk and dried fruits (such as dried apricots) and nuts. In southern provinces, people often prefer green tea. Traditional milk-derived drinks such as ayran, shubat and kymyz. A traditional Kazakh dinner involves a multitude of appetisers on the table, followed by a soup and one or two main courses such as pilaf and beshbarmak. They also drink their national beverage, which consists of fermented mare's milk.
Sport
Kazakhstan consistently performs in Olympic competitions. It is especially successful in boxing. This has brought some attention to the Central Asian nation and increased world awareness of its athletes. Dmitry Karpov and Olga Rypakova are among the most notable Kazakhstani athletes. Dmitry Karpov is a distinguished decathlete, taking bronze in both the 2004 Summer Olympics, and the 2003 World Championships in Athletics, 2003 and 2007 World Athletics Championships. Olga Rypakova is an athlete, specialising in triple jump (women's), taking silver in the 2011 World Championships in Athletics and Gold in the 2012 Summer Olympics.

Kazakhstan's city of
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
submitted bids twice for the Winter Olympics: in Almaty bid for the 2014 Winter Olympics, 2014 and again for the 2022 Winter Olympics.
Astana
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim (river), Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmo ...
and
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
hosted the 2011 Asian Winter Games.
Popular sports in Kazakhstan include football, basketball, ice hockey, bandy, and boxing.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Kazakhstan. The Football Federation of Kazakhstan is the sport's national governing body. The FFK organises the Kazakhstan national football team, men's, Kazakhstan women's national football team, women's, and futsal national teams.
Kazakhstan's most famous basketball player was Alzhan Zharmukhamedov, who played for PBC CSKA Moscow, CSKA Moscow and the Soviet Union's national basketball team in the 1960s and 1970s. Throughout his career, he won multiple titles and medals at some of the world's most prestigious basketball competitions, including the Basketball at the Summer Olympics, Summer Olympics, the Basketball World Cup, the EuroBasket (the European Basketball Championship), and the EuroLeague. In 1971 he earned the title Unified Sports Classification System of the USSR, Master of Sports of the USSR, International Class and a year later he was awarded the Order of the Badge of Honor. Kazakhstan's national basketball team was established in 1992, after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Since its foundation, it has been competitive at the continental level. Its greatest accomplishment was at the Basketball at the 2002 Asian Games – Men, 2002 Asian Games, where it defeated the Philippines men's national basketball team, Philippines in its last game to win the bronze medal. At the official Asian Basketball Championship, now called FIBA Asia Cup, the Kazakhs' best finish was 4th place in 2007.
The Kazakhstan national bandy team is among the best in the world, and has many times won the bronze medal at the Bandy World Championship, including the 2012 Bandy World Championship, 2012 edition when Kazakhstan hosted the tournament on home ice. In the 2011 Bandy World Championship, 2011 tournament, they were an extra-time in the semi-final from reaching the final for the first time. In 2012, they were even closer when they took it to a penalty shootout. The team won the first Bandy at the 2011 Asian Winter Games, bandy tournament at the Asian Winter Games. During the Soviet time, Dynamo Alma-Ata won the List of Russian bandy champions, Soviet Union national championships in 1977 and 1990 and the European Cup (bandy), European Cup in 1978. Bandy is developed in ten of the country's seventeen administrative divisions (eight of the fourteen regions and two of the three cities which are situated inside of but are not part of regions). Akzhaiyk from Oral, Kazakhstan, Oral, however, is the only professional club.

The Kazakhstan men's national ice hockey team, Kazakh national ice hockey team have competed in ice hockey in the 1998 and 2006 Winter Olympics, as well as in the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. The Kazakhstan Hockey Championship is held since 1992. Barys Astana is the main domestic Kazakhstani ice hockey professional team, and having played in the Kazakhstani national league until the 2008–09 season, when they were transferred to play in the Kontinental Hockey League. Meanwhile, the Kazzinc-Torpedo and play in the Supreme Hockey League since 1996 and the Saryarka Karagandy since 2012. Top Kazakhstani ice hockey players include Nik Antropov, Ivan Kulshov and Evgeni Nabokov.
Kazakhstan national amateur boxing athletes, Kazakh boxers are generally well known in the world. In the last three Olympic Games, their performance was assessed as one of the best and they had more medals than any country in the world, except Cuba and Russia (in all three games). In 1996 and 2004, three Kazakhstani boxers (Vassiliy Jirov in 1996, Bakhtiyar Artayev in 2004 and Serik Sapiyev in 2012) were recognised as the best boxers for their techniques with the Val Barker Trophy, awarded to the best boxer of the tournament. In boxing, Kazakhstan performed well in the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney. Two boxers, Bekzat Sattarkhanov and Yermakhan Ibraimov, earned gold medals. Another two boxers, Bulat Zhumadilov and Mukhtarkhan Dildabekov, earned silver medals. Oleg Maskaev, born in Taraz, Zhambyl, representing Russia, was the World Boxing Council, WBC Heavyweight Champion after knocking out Hasim Rahman on 12 August 2006. The reigning World Boxing Association, WBA, WBC, IBF and International Boxing Organization, IBO list of middleweight boxing champions, middleweight champion is Kazakh boxer Gennady Golovkin. Natascha Ragosina, representing Russia, but from Karaganda held seven versions of the women's super middleweight title, and two heavyweight titles during her boxing career. She holds the record as the longest-reigning WBA female super middleweight champion, and the longest-reigning WBC female super middleweight champion.
Film

Kazakhstan's film industry is run through the state-owned Kazakhfilm studios based in Almaty. The studio has produced award-winning movies such as ''Myn Bala'', ''Harmony Lessons'', and ''Shal''. Kazakhstan is the host of the International Astana Action Film Festival and the Eurasia International Film Festival held annually. Hollywood director Timur Bekmambetov is from Kazakhstan and has become active in bridging Hollywood to the Kazakhstan film industry.
Kazakhstan journalist Artur Platonov won Best Script for his documentary "Sold Souls" about Kazakhstan's contribution to the struggle against terrorism at the 2013 Cannes Corporate Media and TV Awards.
Serik Aprymov's ''Little Brother'' (''Bauyr'') won at the Central and Eastern Europe Film Festival goEast from the German Federal Foreign Office.
Media

Kazakhstan is ranked 161 out of 180 countries on the World Press Freedom Index, compiled by Reporters Without Borders. A mid-March 2002 court order, with the government as a plaintiff, stated that ''Respublika (Kazakh newspaper), Respublika'' were to stop printing for three months.
The order was evaded by printing under other titles, such as ''Not That Respublika''.
In early 2014, a court also issued a cease publication order to the small-circulation Assandi-Times newspaper, saying it was a part of the Respublika group. Human Rights Watch said: "this absurd case displays the lengths to which Kazakh authorities are willing to go to bully critical media into silence."
With support from the US Department of State's Bureau for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (DRL), the American Bar Association Rule of Law Initiative opened a media support centre in Almaty to bolster free expression and journalistic rights in Kazakhstan.
UNESCO World Heritage sites
Kazakhstan has three cultural and two natural sites on the UNESCO World Heritage list. The cultural sites are:
* Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi, Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yassaui, added in 2003
* Petroglyphs within the Archaeological Landscape of Tamgaly, added in 2004
* Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor, added in 2014
The natural sites are:
* Saryarka - Steppe and Lakes of Northern Kazakhstan, added in 2008
* Western Tien Shan, added in 2016.
Public holidays
See also
* Outline of Kazakhstan
* Index of Kazakhstan-related articles
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
*
* Cameron, Sarah. (2018) ''The Hungry Steppe: Famine, Violence, and the Making of Soviet Kazakhstan'' (Cornell University Press, 2018
online review
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Nahaylo, Bohdan and Victor Swoboda. ''Soviet Disunion: A History of the Nationalities problem in the USSR'' (1990
excerpt
*
*
*
*
* Rashid, Ahmed. ''The Resurgence of Central Asia: Islam or Nationalism?'' (2017)
*
*
* Smith, Graham, ed. ''The Nationalities Question in the Soviet Union'' (2nd ed. 1995)
*
External links
General
Caspian Pipeline Controversyfrom th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital ArchivesCountry Profilefrom BBC News.
Kazakhstan ''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Kazakhstaninformation from the United States Department of State
Portals to the Worldfrom the United States Library of Congress.
Kazakhstanat ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''.
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Internet EncyclopediaKazakhstan at 20 years of independence, The Economist, 17 December 2011"Blowing the lid off" – Unrest in Kazakhstan, The Economist, 20 December 2011The Region Initiative (TRI)*
*
*
fro
Kazakhstan Discovery* [http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=KZ Key Development Forecasts for Kazakhstan] from International Futures.
Government
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan
E-Government of the Republic of KazakhstanGovernment of Kazakhstan
Trade
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Kazakhstan
{{Coord, 48, N, 68, E, scale:20000000_source:GNS, display=title
Kazakhstan,
1991 establishments in Asia
1991 establishments in Europe
Central Asian countries
Countries in Asia
Countries in Europe
Eastern European countries
Eurasian Steppe
Landlocked countries
Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States
Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Member states of the Organization of Turkic States
Member states of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
Member States of the Eurasian Economic Union
Member states of the United Nations
Member States of the Collective Security Treaty Organization
Members of the International Organization of Turkic Culture
Republics
Russian-speaking countries and territories
States and territories established in 1991
Transcontinental countries
Turkic states
 The main
The main 
 Following the collapse of central government in
Following the collapse of central government in  The Eastern Front (World War II), Soviet-German War (1941–1945) led to an increase in industrialisation and mineral extraction in support of the war effort. At the time of Joseph Stalin's death in 1953, however, Kazakhstan still had an overwhelmingly agricultural economy. In 1953, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev initiated the Virgin Lands Campaign designed to turn the traditional pasturelands of Kazakhstan into a major grain-producing region for the Soviet Union. The Virgin Lands policy brought mixed results. However, along with later modernisations under Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev (in power 1964–1982), it accelerated the development of the agricultural sector, which remains the source of livelihood for a large percentage of Kazakhstan's population. Because of the decades of privation, war and resettlement, by 1959 the Kazakhs had become a minority in the country, making up 30 percent of the population. Ethnic Russians accounted for 43 percent.
In 1947, the USSR government, as part of its Soviet atomic bomb project, atomic bomb project, founded an Semipalatinsk Test Site, atomic bomb test site near the north-eastern town of
The Eastern Front (World War II), Soviet-German War (1941–1945) led to an increase in industrialisation and mineral extraction in support of the war effort. At the time of Joseph Stalin's death in 1953, however, Kazakhstan still had an overwhelmingly agricultural economy. In 1953, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev initiated the Virgin Lands Campaign designed to turn the traditional pasturelands of Kazakhstan into a major grain-producing region for the Soviet Union. The Virgin Lands policy brought mixed results. However, along with later modernisations under Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev (in power 1964–1982), it accelerated the development of the agricultural sector, which remains the source of livelihood for a large percentage of Kazakhstan's population. Because of the decades of privation, war and resettlement, by 1959 the Kazakhs had become a minority in the country, making up 30 percent of the population. Ethnic Russians accounted for 43 percent.
In 1947, the USSR government, as part of its Soviet atomic bomb project, atomic bomb project, founded an Semipalatinsk Test Site, atomic bomb test site near the north-eastern town of  On 25 October 1990, Kazakhstan declared its sovereignty on its territory as a republic within the Soviet Union. Following the August 1991 aborted 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, coup attempt in Moscow, Kazakhstan declared Kazakhstani Independence Day, independence on 16 December 1991, thus becoming the last Soviet republic to declare independence. Ten days later, the Soviet Union itself dissolution of the Soviet Union, ceased to exist.
Kazakhstan's communist-era leader, Nursultan Nazarbayev, became the country's first President. Nazarbayev ruled in an authoritarian manner. An emphasis was placed on converting the country's economy to a market economy while political reforms lagged behind economic advances. By 2006, Kazakhstan was generating 60 percent of the GDP of Central Asia, primarily through its oil industry.
In 1997, the government moved the capital to
On 25 October 1990, Kazakhstan declared its sovereignty on its territory as a republic within the Soviet Union. Following the August 1991 aborted 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, coup attempt in Moscow, Kazakhstan declared Kazakhstani Independence Day, independence on 16 December 1991, thus becoming the last Soviet republic to declare independence. Ten days later, the Soviet Union itself dissolution of the Soviet Union, ceased to exist.
Kazakhstan's communist-era leader, Nursultan Nazarbayev, became the country's first President. Nazarbayev ruled in an authoritarian manner. An emphasis was placed on converting the country's economy to a market economy while political reforms lagged behind economic advances. By 2006, Kazakhstan was generating 60 percent of the GDP of Central Asia, primarily through its oil industry.
In 1997, the government moved the capital to  As it extends across both sides of the Ural River, considered the dividing line separating Europe and Asia, Kazakhstan is one of only two Landlocked country, landlocked countries in the world that transcontinental countries, has territory in two continents (the other is Azerbaijan).
With an area of equivalent in size to Western EuropeKazakhstan is the ninth-largest country and largest landlocked country in the world. While it was part of the
As it extends across both sides of the Ural River, considered the dividing line separating Europe and Asia, Kazakhstan is one of only two Landlocked country, landlocked countries in the world that transcontinental countries, has territory in two continents (the other is Azerbaijan).
With an area of equivalent in size to Western EuropeKazakhstan is the ninth-largest country and largest landlocked country in the world. While it was part of the  It shares borders of with Russia, with
It shares borders of with Russia, with  Kazakhstan has an abundant supply of accessible mineral and fossil fuel resources. Development of petroleum, natural gas, and mineral extractions has attracted most of the over $40 billion in foreign investment in Kazakhstan since 1993 and accounts for some 57 percent of the nation's industrial output (or approximately 13 percent of gross domestic product). According to some estimates,Mineral Wealth
Kazakhstan has an abundant supply of accessible mineral and fossil fuel resources. Development of petroleum, natural gas, and mineral extractions has attracted most of the over $40 billion in foreign investment in Kazakhstan since 1993 and accounts for some 57 percent of the nation's industrial output (or approximately 13 percent of gross domestic product). According to some estimates,Mineral Wealth There are ten List of protected areas of Kazakhstan, nature reserves and ten List of national parks of Kazakhstan, national parks in Kazakhstan that provide safe haven for many rare and endangered plants and animals. Common plants are ''Astragalus'', ''Gagea'', ''Allium'', ''Carex'' and ''Oxytropis''; endangered plant species include native wild apple (''Malus sieversii''), wild grape (''Vitis vinifera'') and several wild tulip species (e.g., ''Tulipa greigii'') and rare onion species ''Allium karataviense'', also ''Iris willmottiana'' and ''Tulipa kaufmanniana''. Kazakhstan had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.23/10, ranking it 26th globally out of 172 countries.
Common mammals include the wolf, red fox, corsac fox, moose, argali (the largest species of sheep), Eurasian lynx, Pallas's cat, and snow leopards, several of which are protected.
Kazakhstan's Red Book of Protected Species lists 125 vertebrates including many birds and mammals, and 404 plants including fungi, algae and lichens.
There are ten List of protected areas of Kazakhstan, nature reserves and ten List of national parks of Kazakhstan, national parks in Kazakhstan that provide safe haven for many rare and endangered plants and animals. Common plants are ''Astragalus'', ''Gagea'', ''Allium'', ''Carex'' and ''Oxytropis''; endangered plant species include native wild apple (''Malus sieversii''), wild grape (''Vitis vinifera'') and several wild tulip species (e.g., ''Tulipa greigii'') and rare onion species ''Allium karataviense'', also ''Iris willmottiana'' and ''Tulipa kaufmanniana''. Kazakhstan had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.23/10, ranking it 26th globally out of 172 countries.
Common mammals include the wolf, red fox, corsac fox, moose, argali (the largest species of sheep), Eurasian lynx, Pallas's cat, and snow leopards, several of which are protected.
Kazakhstan's Red Book of Protected Species lists 125 vertebrates including many birds and mammals, and 404 plants including fungi, algae and lichens.
 Elections in Kazakhstan, Elections to the Majilis in September 2004, yielded a lower house dominated by the pro-government Nur-Otan, Otan Party, headed by President Nazarbayev. Two other parties considered sympathetic to the president, including the agrarian-industrial bloc AIST and the Asar Party, founded by President Nazarbayev's daughter, won most of the remaining seats. The opposition parties which were officially registered and competed in the elections won a single seat. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe was monitoring the election, which it said fell short of international standards.
Elections in Kazakhstan, Elections to the Majilis in September 2004, yielded a lower house dominated by the pro-government Nur-Otan, Otan Party, headed by President Nazarbayev. Two other parties considered sympathetic to the president, including the agrarian-industrial bloc AIST and the Asar Party, founded by President Nazarbayev's daughter, won most of the remaining seats. The opposition parties which were officially registered and competed in the elections won a single seat. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe was monitoring the election, which it said fell short of international standards.
 On 4 December 2005, Nursultan Nazarbayev was re-elected in an apparent landslide victory. The electoral commission announced that he had won over 90% of the vote. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) concluded the election did not meet international standards despite some improvements in the administration of the election.
On 17 August 2007, elections to the lower house of parliament were held and a coalition led by the ruling Nur-Otan party, which included the Asar Party, the Civil Party of Kazakhstan, and the Agrarian Party of Kazakhstan, Agrarian Party, won every seat with 88% of the vote. None of the opposition parties has reached the benchmark 7% level of the seats. Opposition parties made accusations of serious irregularities in the election.
On 4 December 2005, Nursultan Nazarbayev was re-elected in an apparent landslide victory. The electoral commission announced that he had won over 90% of the vote. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) concluded the election did not meet international standards despite some improvements in the administration of the election.
On 17 August 2007, elections to the lower house of parliament were held and a coalition led by the ruling Nur-Otan party, which included the Asar Party, the Civil Party of Kazakhstan, and the Agrarian Party of Kazakhstan, Agrarian Party, won every seat with 88% of the vote. None of the opposition parties has reached the benchmark 7% level of the seats. Opposition parties made accusations of serious irregularities in the election.
 Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Economic Cooperation Organization and the
Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Economic Cooperation Organization and the  On 6 March 2020, the Concept of the Foreign Policy of Kazakhstan for 2020–2030 was announced. The document outlines the following main points:
* An open, predictable and consistent foreign policy of the country, which is progressive in nature and maintains its endurance by continuing the course of the First President – the country at a new stage of development;
* Protection of human rights, development of humanitarian diplomacy and environmental protection;
* Promotion of the country's economic interests in the international arena, including the implementation of state policy to attract investment;
* Maintaining international peace and security;
* Development of regional and multilateral diplomacy, which primarily involves strengthening mutually beneficial ties with key partners – Russia, China, the United States, Central Asian states and the EU countries, as well as through multilateral structures – the United Nations, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, the Commonwealth of Independent States, and others.
On 6 March 2020, the Concept of the Foreign Policy of Kazakhstan for 2020–2030 was announced. The document outlines the following main points:
* An open, predictable and consistent foreign policy of the country, which is progressive in nature and maintains its endurance by continuing the course of the First President – the country at a new stage of development;
* Protection of human rights, development of humanitarian diplomacy and environmental protection;
* Promotion of the country's economic interests in the international arena, including the implementation of state policy to attract investment;
* Maintaining international peace and security;
* Development of regional and multilateral diplomacy, which primarily involves strengthening mutually beneficial ties with key partners – Russia, China, the United States, Central Asian states and the EU countries, as well as through multilateral structures – the United Nations, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, the Commonwealth of Independent States, and others.
 Kazakhstan's memberships of international organisations include:
*
Kazakhstan's memberships of international organisations include:
*  Most of Kazakhstan's military was inherited from the Soviet Armed Forces' Turkestan Military District. These units became the core of Kazakhstan's new military. It acquired all the units of the 40th Army (Soviet Union), 40th Army (the former 32nd Army) and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land-force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments, and a large amount of equipment that had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. Since the late 20th century, the Kazakhstan Army has focused on expanding the number of its armoured units. Since 1990, armoured units have expanded from 500 to 1,613 in 2005.
The Kazakh air force is composed mostly of Soviet-era planes, including 41 MiG-29s, 44 MiG-31s, 37 Su-24s and 60 Su-27s. A small naval force is maintained on the Caspian Sea.
Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq to assist the History of Iraq (2003–2011), US post-invasion mission in Iraq. During the second Iraq War, Kazakhstani troops dismantled 4 million mines and other explosives, helped provide medical care to more than 5,000 coalition members and civilians, and purified of water.
Kazakhstan's National Security Committee of the Republic of Kazakhstan, National Security Committee (UQK) was established on 13 June 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, Border Guard, several Commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau). The latter is considered the most important part of KNB. Its director is Nurtai Abykayev.
Since 2002, the joint tactical peacekeeping exercise "Steppe Eagle" has been hosted by the Kazakhstan government. "Steppe Eagle" focuses on building coalitions and gives participating nations the opportunity to work together. During the Steppe Eagle exercises, the KAZBAT peacekeeping battalion operates within a multinational force under a unified command within multidisciplinary peacekeeping operations, with NATO and the U.S. Military.
In December 2013, Kazakhstan announced it will send officers to support United Nations Peacekeeping forces in Haiti, Western Sahara, Ivory Coast and Liberia.
Most of Kazakhstan's military was inherited from the Soviet Armed Forces' Turkestan Military District. These units became the core of Kazakhstan's new military. It acquired all the units of the 40th Army (Soviet Union), 40th Army (the former 32nd Army) and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land-force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments, and a large amount of equipment that had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. Since the late 20th century, the Kazakhstan Army has focused on expanding the number of its armoured units. Since 1990, armoured units have expanded from 500 to 1,613 in 2005.
The Kazakh air force is composed mostly of Soviet-era planes, including 41 MiG-29s, 44 MiG-31s, 37 Su-24s and 60 Su-27s. A small naval force is maintained on the Caspian Sea.
Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq to assist the History of Iraq (2003–2011), US post-invasion mission in Iraq. During the second Iraq War, Kazakhstani troops dismantled 4 million mines and other explosives, helped provide medical care to more than 5,000 coalition members and civilians, and purified of water.
Kazakhstan's National Security Committee of the Republic of Kazakhstan, National Security Committee (UQK) was established on 13 June 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, Border Guard, several Commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau). The latter is considered the most important part of KNB. Its director is Nurtai Abykayev.
Since 2002, the joint tactical peacekeeping exercise "Steppe Eagle" has been hosted by the Kazakhstan government. "Steppe Eagle" focuses on building coalitions and gives participating nations the opportunity to work together. During the Steppe Eagle exercises, the KAZBAT peacekeeping battalion operates within a multinational force under a unified command within multidisciplinary peacekeeping operations, with NATO and the U.S. Military.
In December 2013, Kazakhstan announced it will send officers to support United Nations Peacekeeping forces in Haiti, Western Sahara, Ivory Coast and Liberia.


 Kazakhstan climbed to 41st on the 2018 Economic Freedom Index published by ''The Wall Street Journal'' and The Heritage Foundation.
Kazakhstan's economy grew at an average of 8 percent per year over the past decade on the back of hydrocarbon exports. Despite the lingering uncertainty of the global economy, Kazakhstan's economy has been stable. GDP growth in January–September 2013 was 5.7 percent, according to preliminary calculations of the Ministry Economy and Budget Planning.
From January to September 2014 Kazakhstan's GDP grew at 4 percent. According to the results from the first half of the year, the current account surplus is $6.6 billion, a figure two times higher than that of the first half of 2013. According to the Chairman of the National Bank of Kazakhstan, Kairat Kelimbetov, the increase was caused by a trade surplus of 17.4 per cent, or approximately US$22.6 billion. The overall inflation rate for 2014 is forecasted at 7.4 percent.
China is one of the main economic and trade partners of Kazakhstan. In 2013, China launched the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in which Kazakhstan functions as a transit hub.
Kazakhstan climbed to 41st on the 2018 Economic Freedom Index published by ''The Wall Street Journal'' and The Heritage Foundation.
Kazakhstan's economy grew at an average of 8 percent per year over the past decade on the back of hydrocarbon exports. Despite the lingering uncertainty of the global economy, Kazakhstan's economy has been stable. GDP growth in January–September 2013 was 5.7 percent, according to preliminary calculations of the Ministry Economy and Budget Planning.
From January to September 2014 Kazakhstan's GDP grew at 4 percent. According to the results from the first half of the year, the current account surplus is $6.6 billion, a figure two times higher than that of the first half of 2013. According to the Chairman of the National Bank of Kazakhstan, Kairat Kelimbetov, the increase was caused by a trade surplus of 17.4 per cent, or approximately US$22.6 billion. The overall inflation rate for 2014 is forecasted at 7.4 percent.
China is one of the main economic and trade partners of Kazakhstan. In 2013, China launched the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in which Kazakhstan functions as a transit hub.

 Railways provide 68 percent of all cargo and passenger traffic to over 57 percent of the country. There are in common carrier service, excluding industrial lines. of gauge, electrified, in 2012. Most cities are connected by railroad; high-speed trains go from
Railways provide 68 percent of all cargo and passenger traffic to over 57 percent of the country. There are in common carrier service, excluding industrial lines. of gauge, electrified, in 2012. Most cities are connected by railroad; high-speed trains go from  Kazakhstan launched the Green Economy Plan in 2013. It committed Kazakhstan to meet 50 percent of its energy needs from alternative and renewable sources by 2050. The green economy was projected to increase GDP by 3 percent and create some 500,000 jobs. The government set prices for energy produced from renewable sources. The price of 1 kilowatt-hour for energy produced by wind power plants was set at 22.68 tenge ($0.12), for 1 kilowatt-hour produced by small hydro-power plants 16.71 tenges ($0.09), and from biogas plants 32.23 tenges ($0.18).
Kazakhstan launched the Green Economy Plan in 2013. It committed Kazakhstan to meet 50 percent of its energy needs from alternative and renewable sources by 2050. The green economy was projected to increase GDP by 3 percent and create some 500,000 jobs. The government set prices for energy produced from renewable sources. The price of 1 kilowatt-hour for energy produced by wind power plants was set at 22.68 tenge ($0.12), for 1 kilowatt-hour produced by small hydro-power plants 16.71 tenges ($0.09), and from biogas plants 32.23 tenges ($0.18).
 The housing market of Kazakhstan grew after 2010. In 2013, the total housing area in Kazakhstan amounted to . Urban areas contained 62.5 per cent of the country's housing stock. The housing stock rose over the year to 32.7 million sq. ft., nearly an 11 percent increase. Between 2012 and 2013, the living area per Kazakh citizen rose from . The UN's recommended standard for housing stands at per person. Kazakhstan was projected to reach the UN standards by 2019 or 2020.
The housing market of Kazakhstan grew after 2010. In 2013, the total housing area in Kazakhstan amounted to . Urban areas contained 62.5 per cent of the country's housing stock. The housing stock rose over the year to 32.7 million sq. ft., nearly an 11 percent increase. Between 2012 and 2013, the living area per Kazakh citizen rose from . The UN's recommended standard for housing stands at per person. Kazakhstan was projected to reach the UN standards by 2019 or 2020.
 During subsequent five-year plans to 2050, new industries will be established in fields such as mobile, multi-media, nano- and space technologies, robotics, genetic engineering and alternative energy. Food processing enterprises will be developed with an eye to turning the country into a major regional exporter of beef, dairy and other agricultural products. Low-return, water-intensive crop varieties will be replaced with vegetable, oil and fodder products. As part of the shift to a "green economy" by 2030, 15% of acreage will be cultivated with water-saving technologies. Experimental agrarian and innovational clusters will be established and drought-resistant genetically modified crops developed.
The Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy fixes a target of devoting 3 percent of GDP to research and development by 2050 to allow for the development of new high-tech sectors.
The Digital Kazakhstan program was launched in 2018 to boost the country's economic growth through the implementation of digital technologies. Kazakhstan's digitization efforts generated 800 billion tenges (US$1.97 billion) in two years. The program helped create 120,000 jobs and attracted 32.8 billion tenges (US$80.7 million) of investment into the country.
Around 82 percent of all public services became automated as part of the Digital Kazakhstan program.
During subsequent five-year plans to 2050, new industries will be established in fields such as mobile, multi-media, nano- and space technologies, robotics, genetic engineering and alternative energy. Food processing enterprises will be developed with an eye to turning the country into a major regional exporter of beef, dairy and other agricultural products. Low-return, water-intensive crop varieties will be replaced with vegetable, oil and fodder products. As part of the shift to a "green economy" by 2030, 15% of acreage will be cultivated with water-saving technologies. Experimental agrarian and innovational clusters will be established and drought-resistant genetically modified crops developed.
The Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy fixes a target of devoting 3 percent of GDP to research and development by 2050 to allow for the development of new high-tech sectors.
The Digital Kazakhstan program was launched in 2018 to boost the country's economic growth through the implementation of digital technologies. Kazakhstan's digitization efforts generated 800 billion tenges (US$1.97 billion) in two years. The program helped create 120,000 jobs and attracted 32.8 billion tenges (US$80.7 million) of investment into the country.
Around 82 percent of all public services became automated as part of the Digital Kazakhstan program.

 Significant Russian immigration was also connected with the Virgin Lands Campaign and Soviet space program during the Nikita Khrushchev, Khrushchev era. In 1989, ethnic Russians were 37.8 percent of the population and Kazakhs held a majority in only 7 of the 20 regions of the country. Before 1991 there were about 1 million Germans of Kazakhstan, Germans in Kazakhstan, mostly descendants of the
Significant Russian immigration was also connected with the Virgin Lands Campaign and Soviet space program during the Nikita Khrushchev, Khrushchev era. In 1989, ethnic Russians were 37.8 percent of the population and Kazakhs held a majority in only 7 of the 20 regions of the country. Before 1991 there were about 1 million Germans of Kazakhstan, Germans in Kazakhstan, mostly descendants of the 
 According to the 2021 census, 69.3% of the population is Islam in Kazakhstan, Muslim; 17.2% is Christianity in Kazakhstan, Christian; 0.2% follows Religion in Kazakhstan, other religions (mostly Buddhism in Kazakhstan, Buddhist and History of the Jews in Kazakhstan, Jewish), and 13.3% are Irreligion, irreligious or chose not to answer. According to its Constitution, Kazakhstan is a secular state.
Religious freedoms are guaranteed by Article 39 of Kazakhstan's Constitution. Article 39 states: "Human rights and freedoms shall not be restricted in any way." Article 14 prohibits "discrimination on religious basis" and Article 19 ensures that everyone has the "right to determine and indicate or not to indicate his/her ethnic, party and religious affiliation." The Constitutional Council affirmed these rights in a 2009 declaration, which stated that a proposed law limiting the rights of certain individuals to practice their religion was declared unconstitutional.
Islam in Kazakhstan, Islam is the largest religion in Kazakhstan, followed by Eastern Orthodoxy in Kazakhstan, Eastern Orthodox Christianity. After decades of Religion in the Soviet Union, religious suppression by the Soviet Union, the coming of independence witnessed a surge in the expression of ethnic identity, partly through religion. The free practice of Religion, religious beliefs and the establishment of full freedom of religion led to an increase of religious activity. Hundreds of mosques, churches, and other religious structures were built in the span of a few years, with the number of religious associations rising from 670 in 1990 to 4,170 today.
Some figures show that non-denominational Muslims form the majority, while others indicate that most Muslims in the country are Sunni Islam, Sunnis following the Hanafi school. These include ethnic Kazakhs, who constitute about 70% of the population, as well as ethnic Uzbeks, Uighurs, and Tatars.Kazakhstan – International Religious Freedom Report 2008
According to the 2021 census, 69.3% of the population is Islam in Kazakhstan, Muslim; 17.2% is Christianity in Kazakhstan, Christian; 0.2% follows Religion in Kazakhstan, other religions (mostly Buddhism in Kazakhstan, Buddhist and History of the Jews in Kazakhstan, Jewish), and 13.3% are Irreligion, irreligious or chose not to answer. According to its Constitution, Kazakhstan is a secular state.
Religious freedoms are guaranteed by Article 39 of Kazakhstan's Constitution. Article 39 states: "Human rights and freedoms shall not be restricted in any way." Article 14 prohibits "discrimination on religious basis" and Article 19 ensures that everyone has the "right to determine and indicate or not to indicate his/her ethnic, party and religious affiliation." The Constitutional Council affirmed these rights in a 2009 declaration, which stated that a proposed law limiting the rights of certain individuals to practice their religion was declared unconstitutional.
Islam in Kazakhstan, Islam is the largest religion in Kazakhstan, followed by Eastern Orthodoxy in Kazakhstan, Eastern Orthodox Christianity. After decades of Religion in the Soviet Union, religious suppression by the Soviet Union, the coming of independence witnessed a surge in the expression of ethnic identity, partly through religion. The free practice of Religion, religious beliefs and the establishment of full freedom of religion led to an increase of religious activity. Hundreds of mosques, churches, and other religious structures were built in the span of a few years, with the number of religious associations rising from 670 in 1990 to 4,170 today.
Some figures show that non-denominational Muslims form the majority, while others indicate that most Muslims in the country are Sunni Islam, Sunnis following the Hanafi school. These include ethnic Kazakhs, who constitute about 70% of the population, as well as ethnic Uzbeks, Uighurs, and Tatars.Kazakhstan – International Religious Freedom Report 2008 Education is universal and mandatory through to the Secondary education, secondary level and the List of countries by literacy rate, adult literacy rate is 99.5%. On average, these statistics are equal to both women and men in Kazakhstan.
Education consists of three main phases: primary education (forms 1–4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and vocational education. Vocational Education usually lasts three or four years. (Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education.) These levels can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g., primary school, then secondary school). Recently, several secondary schools, specialised schools, magnet schools, Gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, Lyceum#Lyceums in today's education, lyceums and linguistic and technical gymnasiums have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and vocational schools.
At present, there are List of universities in Kazakhstan, universities, Academy, academies and institutes, College or university school of music, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. There are three main levels: basic higher education that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to the award of the Bachelor's degree; specialised higher education after which students are awarded the Specialist's Diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education which leads to the master's degree. Postgraduate education leads to the ''Kandidat Nauk'' ("Candidate of Sciences") and the Doctor of Sciences (PhD). With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed.
Over 2,500 students in Kazakhstan have applied for student loans totalling about $9 million. The largest number of student loans come from Almaty, Astana and Kyzylorda.
The training and skills development programs in Kazakhstan are also supported by international organisations. For example, on 30 March 2015, the World Banks' Group of Executive Directors approved a $100 million loan for the Skills and Job project in Kazakhstan. The project aims to provide training to unemployed, unproductively self-employed, and employees in need of training.
Education is universal and mandatory through to the Secondary education, secondary level and the List of countries by literacy rate, adult literacy rate is 99.5%. On average, these statistics are equal to both women and men in Kazakhstan.
Education consists of three main phases: primary education (forms 1–4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and vocational education. Vocational Education usually lasts three or four years. (Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education.) These levels can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g., primary school, then secondary school). Recently, several secondary schools, specialised schools, magnet schools, Gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, Lyceum#Lyceums in today's education, lyceums and linguistic and technical gymnasiums have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and vocational schools.
At present, there are List of universities in Kazakhstan, universities, Academy, academies and institutes, College or university school of music, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. There are three main levels: basic higher education that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to the award of the Bachelor's degree; specialised higher education after which students are awarded the Specialist's Diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education which leads to the master's degree. Postgraduate education leads to the ''Kandidat Nauk'' ("Candidate of Sciences") and the Doctor of Sciences (PhD). With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed.
Over 2,500 students in Kazakhstan have applied for student loans totalling about $9 million. The largest number of student loans come from Almaty, Astana and Kyzylorda.
The training and skills development programs in Kazakhstan are also supported by international organisations. For example, on 30 March 2015, the World Banks' Group of Executive Directors approved a $100 million loan for the Skills and Job project in Kazakhstan. The project aims to provide training to unemployed, unproductively self-employed, and employees in need of training.
 Kazakhstan is home to a large number of prominent contributors to literature, science and philosophy: Abay Qunanbayuli, Mukhtar Auezov, Gabit Musirepov, Kanysh Satpayev, Mukhtar Shakhanov, Saken Seyfullin, Jambyl Jabayev, among many others.
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry in Kazakhstan and it is joining the international tourism networking. In 2010, Kazakhstan joined The Region Initiative (TRI) which is a Tri-regional Umbrella of Tourism-related organisations. TRI is functioning as a link between three regions: South Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe. Armenia, Bangladesh, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkey, and Ukraine are now partners, and Kazakhstan is linked with other South Asian, Eastern European, and Central Asian countries in the tourism market.
Kazakhstan is home to a large number of prominent contributors to literature, science and philosophy: Abay Qunanbayuli, Mukhtar Auezov, Gabit Musirepov, Kanysh Satpayev, Mukhtar Shakhanov, Saken Seyfullin, Jambyl Jabayev, among many others.
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry in Kazakhstan and it is joining the international tourism networking. In 2010, Kazakhstan joined The Region Initiative (TRI) which is a Tri-regional Umbrella of Tourism-related organisations. TRI is functioning as a link between three regions: South Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe. Armenia, Bangladesh, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkey, and Ukraine are now partners, and Kazakhstan is linked with other South Asian, Eastern European, and Central Asian countries in the tourism market.
 According to Chinese written sources from the 6th–8th centuries CE, the Turkic tribes of Kazakhstan had an oral poetry tradition. These came from earlier periods and were primarily transmitted by bards: professional storytellers and musical performers. Traces of this tradition are shown on Old Turkic alphabet, Orkhon script stone carvings dated 5th–7th centuries CE that describe rule of Kultegin and Bilge, two early Turkic rulers ("kagans"). Amongst the Kazakhs, the bard was a primarily, though not exclusively, male profession. Since at least the 17th century, Kazakh bards could be divided into two main categories: the zhıraws (zhiraus, žyraus), who passed on the works of others, usually not creating and adding their own original work; and the aqyns (akyns), who improvised or created their own poems, stories or songs. There were several types of works, such as didactic ''termes'', elegiac ''tolgaws'', and epic (genre), epic ''zhırs''. Although the origins of such tales are often unknown, most of them were associated with bards of the recent or more distant past, who supposedly created them or passed them on, by the time most Kazakh poetry and prose was first written down in the second half of the 19th century. There are clear stylistic differences between works first created in the 19th century, and works dating from earlier periods but not documented before the 19th century, such as those attributed to such 16th- and 17th-century bards as Er Shoban and Dosmombet Zhıraw (also known as Dospambet Žyrau; he appeared to have been literate, and reportedly visited Constantinople), and even to such 15th-century bards as Shalkiz and Asan Qayghı.
Other notable bards include Kaztugan Žyrau, Žiembet Žyrau, Axtamberdy Žyrau, and Buxar Žyrau Kalkamanuly, who was an advisor to
According to Chinese written sources from the 6th–8th centuries CE, the Turkic tribes of Kazakhstan had an oral poetry tradition. These came from earlier periods and were primarily transmitted by bards: professional storytellers and musical performers. Traces of this tradition are shown on Old Turkic alphabet, Orkhon script stone carvings dated 5th–7th centuries CE that describe rule of Kultegin and Bilge, two early Turkic rulers ("kagans"). Amongst the Kazakhs, the bard was a primarily, though not exclusively, male profession. Since at least the 17th century, Kazakh bards could be divided into two main categories: the zhıraws (zhiraus, žyraus), who passed on the works of others, usually not creating and adding their own original work; and the aqyns (akyns), who improvised or created their own poems, stories or songs. There were several types of works, such as didactic ''termes'', elegiac ''tolgaws'', and epic (genre), epic ''zhırs''. Although the origins of such tales are often unknown, most of them were associated with bards of the recent or more distant past, who supposedly created them or passed them on, by the time most Kazakh poetry and prose was first written down in the second half of the 19th century. There are clear stylistic differences between works first created in the 19th century, and works dating from earlier periods but not documented before the 19th century, such as those attributed to such 16th- and 17th-century bards as Er Shoban and Dosmombet Zhıraw (also known as Dospambet Žyrau; he appeared to have been literate, and reportedly visited Constantinople), and even to such 15th-century bards as Shalkiz and Asan Qayghı.
Other notable bards include Kaztugan Žyrau, Žiembet Žyrau, Axtamberdy Žyrau, and Buxar Žyrau Kalkamanuly, who was an advisor to  The modern state of Kazakhstan is home to the Kazakh State Kurmangazy Orchestra of Folk Instruments, the Kazakh State Philharmonic Orchestra, the Kazakh National Opera and the Kazakh State Chamber Orchestra. The folk instrument orchestra was named after Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly, a famous composer and dombra player from the 19th century. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1931, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed.
The Foundation Asyl Mura is archiving and publishing historical recordings of great samples of Kazakh music both traditional and classical. The leading conservatoire is in Almaty, the Qurmanghazy Conservatoire. It competes with the national conservatoire in Astana, Kazakhstan's capital.
When referring to traditional Kazakh music, authentic folklore must be separated from "folklorism". The latter denotes music executed by academically trained performers who aim at preserving the traditional music for coming generations. As far as can be reconstructed, the music of Kazakhstan from the period before a strong Russian influence consists of instrumental music and vocal music. Instrumental music, with the pieces ("Küy") being performed by soloists. Text is often seen in the background (or "program") for the music, as a lot of Küy titles refer to stories. Vocal music, either as part of a ceremony such as a wedding (mainly performed by women), or as part of a feast. Here we might divide into subgenres: epic singing, containing not only historical facts, but as well the tribe's genealogy, love songs, and didactic verses; and as a special form the composition of two or more singers in public (Aitys), of dialogue character and usually unexpectedly frankly in content.
The modern state of Kazakhstan is home to the Kazakh State Kurmangazy Orchestra of Folk Instruments, the Kazakh State Philharmonic Orchestra, the Kazakh National Opera and the Kazakh State Chamber Orchestra. The folk instrument orchestra was named after Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly, a famous composer and dombra player from the 19th century. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1931, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed.
The Foundation Asyl Mura is archiving and publishing historical recordings of great samples of Kazakh music both traditional and classical. The leading conservatoire is in Almaty, the Qurmanghazy Conservatoire. It competes with the national conservatoire in Astana, Kazakhstan's capital.
When referring to traditional Kazakh music, authentic folklore must be separated from "folklorism". The latter denotes music executed by academically trained performers who aim at preserving the traditional music for coming generations. As far as can be reconstructed, the music of Kazakhstan from the period before a strong Russian influence consists of instrumental music and vocal music. Instrumental music, with the pieces ("Küy") being performed by soloists. Text is often seen in the background (or "program") for the music, as a lot of Küy titles refer to stories. Vocal music, either as part of a ceremony such as a wedding (mainly performed by women), or as part of a feast. Here we might divide into subgenres: epic singing, containing not only historical facts, but as well the tribe's genealogy, love songs, and didactic verses; and as a special form the composition of two or more singers in public (Aitys), of dialogue character and usually unexpectedly frankly in content.
 The Russian influence on the music life in Kazakhstan can be seen in two spheres: first, the introduction of musical academic institutions such as concert houses with opera stages, and conservatories, where European music was performed and taught, and second, by trying to incorporate Kazakh traditional music into these academic structures. Controlled first by the
The Russian influence on the music life in Kazakhstan can be seen in two spheres: first, the introduction of musical academic institutions such as concert houses with opera stages, and conservatories, where European music was performed and taught, and second, by trying to incorporate Kazakh traditional music into these academic structures. Controlled first by the  Kazakhstan's city of
Kazakhstan's city of  Kazakhstan's film industry is run through the state-owned Kazakhfilm studios based in Almaty. The studio has produced award-winning movies such as ''Myn Bala'', ''Harmony Lessons'', and ''Shal''. Kazakhstan is the host of the International Astana Action Film Festival and the Eurasia International Film Festival held annually. Hollywood director Timur Bekmambetov is from Kazakhstan and has become active in bridging Hollywood to the Kazakhstan film industry.
Kazakhstan journalist Artur Platonov won Best Script for his documentary "Sold Souls" about Kazakhstan's contribution to the struggle against terrorism at the 2013 Cannes Corporate Media and TV Awards.
Serik Aprymov's ''Little Brother'' (''Bauyr'') won at the Central and Eastern Europe Film Festival goEast from the German Federal Foreign Office.
Kazakhstan's film industry is run through the state-owned Kazakhfilm studios based in Almaty. The studio has produced award-winning movies such as ''Myn Bala'', ''Harmony Lessons'', and ''Shal''. Kazakhstan is the host of the International Astana Action Film Festival and the Eurasia International Film Festival held annually. Hollywood director Timur Bekmambetov is from Kazakhstan and has become active in bridging Hollywood to the Kazakhstan film industry.
Kazakhstan journalist Artur Platonov won Best Script for his documentary "Sold Souls" about Kazakhstan's contribution to the struggle against terrorism at the 2013 Cannes Corporate Media and TV Awards.
Serik Aprymov's ''Little Brother'' (''Bauyr'') won at the Central and Eastern Europe Film Festival goEast from the German Federal Foreign Office.
 Kazakhstan is ranked 161 out of 180 countries on the World Press Freedom Index, compiled by Reporters Without Borders. A mid-March 2002 court order, with the government as a plaintiff, stated that ''Respublika (Kazakh newspaper), Respublika'' were to stop printing for three months. The order was evaded by printing under other titles, such as ''Not That Respublika''. In early 2014, a court also issued a cease publication order to the small-circulation Assandi-Times newspaper, saying it was a part of the Respublika group. Human Rights Watch said: "this absurd case displays the lengths to which Kazakh authorities are willing to go to bully critical media into silence."
With support from the US Department of State's Bureau for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (DRL), the American Bar Association Rule of Law Initiative opened a media support centre in Almaty to bolster free expression and journalistic rights in Kazakhstan.
Kazakhstan is ranked 161 out of 180 countries on the World Press Freedom Index, compiled by Reporters Without Borders. A mid-March 2002 court order, with the government as a plaintiff, stated that ''Respublika (Kazakh newspaper), Respublika'' were to stop printing for three months. The order was evaded by printing under other titles, such as ''Not That Respublika''. In early 2014, a court also issued a cease publication order to the small-circulation Assandi-Times newspaper, saying it was a part of the Respublika group. Human Rights Watch said: "this absurd case displays the lengths to which Kazakh authorities are willing to go to bully critical media into silence."
With support from the US Department of State's Bureau for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (DRL), the American Bar Association Rule of Law Initiative opened a media support centre in Almaty to bolster free expression and journalistic rights in Kazakhstan.